
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2024, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (1): 57-71.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2024.230209
• Research Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
YONG Mingling1,2, YE Miao1,2, ZHANG Yu1,2, TAO Yu1,2, NI Chuan1,2, KANG Yuying1,2, ZHANG Zujian1,2,*( )
)
Received:2023-02-28
Revised:2023-03-17
Online:2024-01-10
Published:2024-01-16
Contact:
* email:
雍明玲1,2, 叶苗1,2, 张雨1,2, 陶钰1,2, 倪川1,2, 康钰莹1,2, 张祖建1,2,*( )
)
通讯作者:
* email: 基金资助:YONG Mingling, YE Miao, ZHANG Yu, TAO Yu, NI Chuan, KANG Yuying, ZHANG Zujian. Rice Starch Structure and Physicochemical Properties of Good Taste japonica Rice Varieties and Their Regulations by Nitrogen[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(1): 57-71.
雍明玲, 叶苗, 张雨, 陶钰, 倪川, 康钰莹, 张祖建. 不同食味水稻品种稻米淀粉结构与理化特性及其对氮素响应的差异[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(1): 57-71.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2024.230209
| 处理 | 品种 | 外观 | 硬度 | 黏度 | 平衡度 | 食味值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment | Cultivar | Appearance | Hardness | Viscosity | Balance degree | Taste value |
| N1 | 金香玉1号 Jinxiangyu 1 | 8.0±0.1 a | 5.8±0.1 c | 8.3±0.2 a | 8.2±0.1 a | 80±1.0 a |
| 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 6.8±0.2 b | 6.4±0.1 b | 7.5±0.3 b | 7.4±0.2 b | 75±1.5 b | |
| 武密粳 Wumijing | 4.8±0.2 c | 7.1±0.2 a | 5.1±0.1 c | 4.8±0.2 c | 61±1.0 c | |
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | 4.3±0.3 c | 7.3±0.3 a | 4.5±0.4 c | 4.4±0.2 d | 56±2.5 d | |
| N2 | 金香玉1号 Jinxiangyu 1 | 7.7±0.1 a | 6.1±0.2 c | 7.9±0.1 a | 7.7±0.1 a | 77±0.6 a |
| 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 6.7±0.2 b | 6.6±0.2 b | 6.8±0.2 b | 6.6±0.1 b | 72±1.0 b | |
| 武密粳 Wumijing | 4.1±0.2 c | 7.5±0.2 a | 4.1±0.2 c | 4.1±0.1 c | 57±2.3 c | |
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | 3.7±0.2 d | 7.8±0.2 a | 3.9±0.1 c | 3.9±0.1 c | 53±1.5 d | |
| N3 | 金香玉1号 Jinxiangyu 1 | 6.7±0.3 a | 6.2±0.1 b | 7.2±0.2 a | 7.3±0.2 a | 74±1.2 a |
| 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 6.3±0.1 b | 6.9±0.2 b | 6.7±0.2 a | 6.5±0.2 b | 69±1.0 b | |
| 武密粳 Wumijing | 3.6±0.1 c | 7.9±0.4 a | 3.6±0.3 b | 3.5±0.2 c | 53±2.1 c | |
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | 2.7±0.4 d | 8.2±0.1 a | 3.3±0.2 b | 2.9±0.2 d | 48±1.5 d | |
| 方差分析 Analysis of variance | 氮素水平Nitrogen level (N) | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| 品种 Cultivar (C) | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | |
| 氮素水平×品种 N×C | ** | ns | ns | ** | ns |
Table 1. Taste traits of the tested rice varieties at different nitrogen levels.
| 处理 | 品种 | 外观 | 硬度 | 黏度 | 平衡度 | 食味值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment | Cultivar | Appearance | Hardness | Viscosity | Balance degree | Taste value |
| N1 | 金香玉1号 Jinxiangyu 1 | 8.0±0.1 a | 5.8±0.1 c | 8.3±0.2 a | 8.2±0.1 a | 80±1.0 a |
| 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 6.8±0.2 b | 6.4±0.1 b | 7.5±0.3 b | 7.4±0.2 b | 75±1.5 b | |
| 武密粳 Wumijing | 4.8±0.2 c | 7.1±0.2 a | 5.1±0.1 c | 4.8±0.2 c | 61±1.0 c | |
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | 4.3±0.3 c | 7.3±0.3 a | 4.5±0.4 c | 4.4±0.2 d | 56±2.5 d | |
| N2 | 金香玉1号 Jinxiangyu 1 | 7.7±0.1 a | 6.1±0.2 c | 7.9±0.1 a | 7.7±0.1 a | 77±0.6 a |
| 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 6.7±0.2 b | 6.6±0.2 b | 6.8±0.2 b | 6.6±0.1 b | 72±1.0 b | |
| 武密粳 Wumijing | 4.1±0.2 c | 7.5±0.2 a | 4.1±0.2 c | 4.1±0.1 c | 57±2.3 c | |
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | 3.7±0.2 d | 7.8±0.2 a | 3.9±0.1 c | 3.9±0.1 c | 53±1.5 d | |
| N3 | 金香玉1号 Jinxiangyu 1 | 6.7±0.3 a | 6.2±0.1 b | 7.2±0.2 a | 7.3±0.2 a | 74±1.2 a |
| 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 6.3±0.1 b | 6.9±0.2 b | 6.7±0.2 a | 6.5±0.2 b | 69±1.0 b | |
| 武密粳 Wumijing | 3.6±0.1 c | 7.9±0.4 a | 3.6±0.3 b | 3.5±0.2 c | 53±2.1 c | |
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | 2.7±0.4 d | 8.2±0.1 a | 3.3±0.2 b | 2.9±0.2 d | 48±1.5 d | |
| 方差分析 Analysis of variance | 氮素水平Nitrogen level (N) | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| 品种 Cultivar (C) | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | |
| 氮素水平×品种 N×C | ** | ns | ns | ** | ns |
| 处理 Treatment | 品种 Cultivar | 直链淀粉含量 Amylose content/% | 胶稠度 Gel consistency/mm | 蛋白质含量 Protein content/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1 | 金香玉1号 Jinxiangyu 1 | 11.64±0.67 c | 82±1.0 a | 6.32±0.19 b |
| 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 14.93±0.31 b | 81±1.7 a | 6.49±0.17 b | |
| 武密粳 Wumijing | 18.18±0.14 a | 84±1.2 a | 7.22±0.57 a | |
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | 18.63±0.31 a | 78±1.5 b | 7.51±0.51 a | |
| N2 | 金香玉1号 Jinxiangyu 1 | 11.05±0.16 d | 81±0.6 a | 7.04±0.08 c |
| 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 14.56±0.45 c | 79±1.0 ab | 7.25±0.12 c | |
| 武密粳 Wumijing | 17.92±0.11 b | 81±3.8 a | 7.57±0.09 b | |
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | 18.51±0.08 a | 76±1.2 b | 7.81±0.11 a | |
| N3 | 金香玉1号 Jinxiangyu 1 | 10.64±0.75 c | 78±1.5 ab | 7.53±0.22 b |
| 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 14.06±0.86 b | 77±1.5 ab | 7.75±0.21 b | |
| 武密粳 Wumijing | 17.47±0.54 a | 79±3.6 a | 8.34±0.27 a | |
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | 18.05±0.43 a | 75±0.6 b | 8.49±0.18 a | |
| 方差分析 Analysis of variance | 氮素水平Nitrogen level (N) | ** | ** | ** |
| 品种 Cultivar (C) | ** | ** | ** | |
| 氮素水平×品种 N×C | ns | ns | ns |
Table 2. Cooking quality of the tested rice varieties at different nitrogen levels.
| 处理 Treatment | 品种 Cultivar | 直链淀粉含量 Amylose content/% | 胶稠度 Gel consistency/mm | 蛋白质含量 Protein content/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1 | 金香玉1号 Jinxiangyu 1 | 11.64±0.67 c | 82±1.0 a | 6.32±0.19 b |
| 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 14.93±0.31 b | 81±1.7 a | 6.49±0.17 b | |
| 武密粳 Wumijing | 18.18±0.14 a | 84±1.2 a | 7.22±0.57 a | |
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | 18.63±0.31 a | 78±1.5 b | 7.51±0.51 a | |
| N2 | 金香玉1号 Jinxiangyu 1 | 11.05±0.16 d | 81±0.6 a | 7.04±0.08 c |
| 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 14.56±0.45 c | 79±1.0 ab | 7.25±0.12 c | |
| 武密粳 Wumijing | 17.92±0.11 b | 81±3.8 a | 7.57±0.09 b | |
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | 18.51±0.08 a | 76±1.2 b | 7.81±0.11 a | |
| N3 | 金香玉1号 Jinxiangyu 1 | 10.64±0.75 c | 78±1.5 ab | 7.53±0.22 b |
| 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 14.06±0.86 b | 77±1.5 ab | 7.75±0.21 b | |
| 武密粳 Wumijing | 17.47±0.54 a | 79±3.6 a | 8.34±0.27 a | |
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | 18.05±0.43 a | 75±0.6 b | 8.49±0.18 a | |
| 方差分析 Analysis of variance | 氮素水平Nitrogen level (N) | ** | ** | ** |
| 品种 Cultivar (C) | ** | ** | ** | |
| 氮素水平×品种 N×C | ns | ns | ns |
| 处理 | 品种 | 最高黏度 | 热浆黏度 | 崩解值 | 最终黏度 | 消减值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment | Cultivar | Peak viscosity/cP | Hot viscosity/cP | Breakdown/cP | Final viscosity/cP | Setback/cP |
| N1 | 金香玉1号 Jinxiangyu 1 | 3447±77 a | 1848±104 a | 1598±128 a | 2792±60 b | −655±27 c |
| 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 3322±110 a | 2017±260 a | 1305±169 b | 3009±94 a | −313±19 b | |
| 武密粳 Wumijing | 3018±96 b | 2163±89 a | 855±8 c | 2863±81 ab | −155±17 a | |
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | 2934±105 b | 2097±97 a | 837±12 c | 2811±120 ab | −123±34 a | |
| N2 | 金香玉1号 Jinxiangyu 1 | 3436±110 a | 1864±104 c | 1572±44 a | 2791±114 b | −645±25 d |
| 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 3266±21 b | 2106±34 a | 1160±14 b | 2977±26 a | −289±13 c | |
| 武密粳 Wumijing | 2812±61 c | 2011±46 ab | 801±16 c | 2726±41 bc | −86±24 b | |
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | 2686±78 d | 1938±50 bc | 749±28 d | 2654±64 c | −32±16 a | |
| N3 | 金香玉1号 Jinxiangyu 1 | 3305±178 a | 1973±445 a | 1333±268 a | 2744±139 ab | −562±47 c |
| 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 3142±73 a | 2029±54 a | 1113±45 a | 2906±49 a | −235±25 b | |
| 武密粳 Wumijing | 2688±59 b | 1919±48 a | 769±11 b | 2629±65 b | −59±7 a | |
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | 2612±106 b | 1909±114 a | 703±11 b | 2595±102 b | −17±8 a | |
| 方差分析 Analysis of variance | 氮素水平Nitrogen level (N) | ** | ns | ** | ** | ** |
| 品种 Cultivar (C) | ** | ns | ** | ** | ** | |
| 氮素水平×品种 N×C | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns |
Table 3. RVA spectral characteristic values of starch in the tested rice varieties at different nitrogen levels.
| 处理 | 品种 | 最高黏度 | 热浆黏度 | 崩解值 | 最终黏度 | 消减值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment | Cultivar | Peak viscosity/cP | Hot viscosity/cP | Breakdown/cP | Final viscosity/cP | Setback/cP |
| N1 | 金香玉1号 Jinxiangyu 1 | 3447±77 a | 1848±104 a | 1598±128 a | 2792±60 b | −655±27 c |
| 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 3322±110 a | 2017±260 a | 1305±169 b | 3009±94 a | −313±19 b | |
| 武密粳 Wumijing | 3018±96 b | 2163±89 a | 855±8 c | 2863±81 ab | −155±17 a | |
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | 2934±105 b | 2097±97 a | 837±12 c | 2811±120 ab | −123±34 a | |
| N2 | 金香玉1号 Jinxiangyu 1 | 3436±110 a | 1864±104 c | 1572±44 a | 2791±114 b | −645±25 d |
| 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 3266±21 b | 2106±34 a | 1160±14 b | 2977±26 a | −289±13 c | |
| 武密粳 Wumijing | 2812±61 c | 2011±46 ab | 801±16 c | 2726±41 bc | −86±24 b | |
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | 2686±78 d | 1938±50 bc | 749±28 d | 2654±64 c | −32±16 a | |
| N3 | 金香玉1号 Jinxiangyu 1 | 3305±178 a | 1973±445 a | 1333±268 a | 2744±139 ab | −562±47 c |
| 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 3142±73 a | 2029±54 a | 1113±45 a | 2906±49 a | −235±25 b | |
| 武密粳 Wumijing | 2688±59 b | 1919±48 a | 769±11 b | 2629±65 b | −59±7 a | |
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | 2612±106 b | 1909±114 a | 703±11 b | 2595±102 b | −17±8 a | |
| 方差分析 Analysis of variance | 氮素水平Nitrogen level (N) | ** | ns | ** | ** | ** |
| 品种 Cultivar (C) | ** | ns | ** | ** | ** | |
| 氮素水平×品种 N×C | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| 处理 Treatment | 品种 Cultivar | 起始温度 Onset temperature/℃ | 峰值温度 Peak temperature/℃ | 终止温度 Conclusion temperature/℃ | 糊化焓 Enthalpy of gelatinization /(J·g−1) | 回升焓 Enthalpy of recovery /(J·g−1) | 回升度 Recovery ratio/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1 | 金香玉1号 Jinxiangyu 1 | 64.3±0.1 b | 70.1±0.1 c | 76.5±0.6 c | 7.93±0.12 d | 1.55±0.14 b | 19.51±0.02 b |
| 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 65.0±0.1 a | 70.8±0.2 b | 76.9±0.4 bc | 8.34±0.23 c | 2.04±0.16 b | 24.48±0.02 b | |
| 武密粳 Wumijing | 64.4±0.6 b | 70.3±0.1 c | 77.5±0.2 b | 8.67±0.23 b | 2.69±0.36 a | 31.02±0.04 a | |
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | 65.3±0.2 a | 72.0±0.1 a | 78.8±0.5 a | 9.21±0.27 a | 2.95±0.37 a | 31.96±0.03 a | |
| N2 | 金香玉1号 Jinxiangyu 1 | 64.1±0.1 c | 70.1±0.1 d | 75.9±0.4 c | 8.37±0.19 b | 1.92±0.29 b | 22.92±0.03 c |
| 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 65.1±0.2 b | 70.6±0.2 c | 77.3±0.2 b | 8.56±0.36 b | 2.17±0.29 b | 25.50±0.04 bc | |
| 武密粳 Wumijing | 64.3±0.2 c | 71.1±0.2 b | 77.3±0.6 b | 9.26±0.27 a | 2.89±0.10 a | 31.20±0.02 ab | |
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | 65.9±0.3 a | 72.2±0.2 a | 78.8±0.4 a | 9.53±0.35 a | 3.20±0.14 a | 33.58±0.02 a | |
| N3 | 金香玉1号 Jinxiangyu 1 | 64.2±0.2 c | 70.3±0.2 d | 76.5±0.4 b | 8.63±0.22 d | 2.01±0.27 b | 23.27±0.03 b |
| 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 65.1±0.1 b | 71.0±0.1 c | 77.2±0.4 b | 9.02±0.49 c | 2.25±0.41 b | 24.83±0.03 b | |
| 武密粳 Wumijing | 64.9±0.3 b | 71.7±0.3 b | 77.1±0.7 b | 9.60±0.20 b | 3.14±0.35 a | 32.71±0.03 a | |
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | 65.9±0.1 a | 73.3±0.2 a | 79.0±0.2 a | 10.01±0.17 a | 3.37±0.33 a | 33.67±0.04 a | |
| 方差分析Analysis of variance | 氮素水平N level (N) | * | ** | ns | ** | * | ns |
| 品种 Cultivar (C) | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | |
| 氮素水平×品种 N×C | ns | ** | ns | ns | ns | ns |
Table 4. Thermodynamic characteristic values of starch in the tested rice varieties at different nitrogen levels.
| 处理 Treatment | 品种 Cultivar | 起始温度 Onset temperature/℃ | 峰值温度 Peak temperature/℃ | 终止温度 Conclusion temperature/℃ | 糊化焓 Enthalpy of gelatinization /(J·g−1) | 回升焓 Enthalpy of recovery /(J·g−1) | 回升度 Recovery ratio/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1 | 金香玉1号 Jinxiangyu 1 | 64.3±0.1 b | 70.1±0.1 c | 76.5±0.6 c | 7.93±0.12 d | 1.55±0.14 b | 19.51±0.02 b |
| 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 65.0±0.1 a | 70.8±0.2 b | 76.9±0.4 bc | 8.34±0.23 c | 2.04±0.16 b | 24.48±0.02 b | |
| 武密粳 Wumijing | 64.4±0.6 b | 70.3±0.1 c | 77.5±0.2 b | 8.67±0.23 b | 2.69±0.36 a | 31.02±0.04 a | |
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | 65.3±0.2 a | 72.0±0.1 a | 78.8±0.5 a | 9.21±0.27 a | 2.95±0.37 a | 31.96±0.03 a | |
| N2 | 金香玉1号 Jinxiangyu 1 | 64.1±0.1 c | 70.1±0.1 d | 75.9±0.4 c | 8.37±0.19 b | 1.92±0.29 b | 22.92±0.03 c |
| 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 65.1±0.2 b | 70.6±0.2 c | 77.3±0.2 b | 8.56±0.36 b | 2.17±0.29 b | 25.50±0.04 bc | |
| 武密粳 Wumijing | 64.3±0.2 c | 71.1±0.2 b | 77.3±0.6 b | 9.26±0.27 a | 2.89±0.10 a | 31.20±0.02 ab | |
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | 65.9±0.3 a | 72.2±0.2 a | 78.8±0.4 a | 9.53±0.35 a | 3.20±0.14 a | 33.58±0.02 a | |
| N3 | 金香玉1号 Jinxiangyu 1 | 64.2±0.2 c | 70.3±0.2 d | 76.5±0.4 b | 8.63±0.22 d | 2.01±0.27 b | 23.27±0.03 b |
| 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 65.1±0.1 b | 71.0±0.1 c | 77.2±0.4 b | 9.02±0.49 c | 2.25±0.41 b | 24.83±0.03 b | |
| 武密粳 Wumijing | 64.9±0.3 b | 71.7±0.3 b | 77.1±0.7 b | 9.60±0.20 b | 3.14±0.35 a | 32.71±0.03 a | |
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | 65.9±0.1 a | 73.3±0.2 a | 79.0±0.2 a | 10.01±0.17 a | 3.37±0.33 a | 33.67±0.04 a | |
| 方差分析Analysis of variance | 氮素水平N level (N) | * | ** | ns | ** | * | ns |
| 品种 Cultivar (C) | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | |
| 氮素水平×品种 N×C | ns | ** | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| 处理 | 品种 | 相对结晶度 |
|---|---|---|
| Treatment | Cultivar | Relative crystallinity/% |
| N1 | 金香玉1号 Jinxiangyu 1 | 29.08±0.15 a |
| 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 28.13±0.16 a | |
| 武密粳 Wumijing | 26.43±0.09 b | |
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | 24.67±0.87 c | |
| N2 | 金香玉1号 Jinxiangyu 1 | 29.98±1.02 a |
| 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 28.40±0.13 ab | |
| 武密粳 Wumijing | 26.88±0.53 bc | |
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | 25.45±0.04 c | |
| N3 | 金香玉1号 Jinxiangyu 1 | 30.43±0.56 a |
| 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 28.66±0.11 b | |
| 武密粳 Wumijing | 27.00±1.14 bc | |
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | 25.74±0.09 c | |
| 方差分析 Analysis of variance | 氮素水平Nitrogen level (N) | * |
| 品种 Cultivar (C) | ** | |
| 氮素水平×品种 N×C | ns |
Table 5. Relative crystallinity of starch in the tested rice varieties at different nitrogen levels.
| 处理 | 品种 | 相对结晶度 |
|---|---|---|
| Treatment | Cultivar | Relative crystallinity/% |
| N1 | 金香玉1号 Jinxiangyu 1 | 29.08±0.15 a |
| 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 28.13±0.16 a | |
| 武密粳 Wumijing | 26.43±0.09 b | |
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | 24.67±0.87 c | |
| N2 | 金香玉1号 Jinxiangyu 1 | 29.98±1.02 a |
| 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 28.40±0.13 ab | |
| 武密粳 Wumijing | 26.88±0.53 bc | |
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | 25.45±0.04 c | |
| N3 | 金香玉1号 Jinxiangyu 1 | 30.43±0.56 a |
| 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 28.66±0.11 b | |
| 武密粳 Wumijing | 27.00±1.14 bc | |
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | 25.74±0.09 c | |
| 方差分析 Analysis of variance | 氮素水平Nitrogen level (N) | * |
| 品种 Cultivar (C) | ** | |
| 氮素水平×品种 N×C | ns |
| 处理 Treatment | 品种 Cultivar | 溶解度 Solubility/% | 膨胀势 Swelling power/(g·g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| N1 | 金香玉1号 Jinxiangyu 1 | 13.46±0.37 a | 15.10±0.37 a |
| 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 12.40±0.81 b | 13.87±0.44 b | |
| 武密粳 Wumijing | 10.48±0.15 c | 11.95±0.53 c | |
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | 9.58±0.30 c | 11.01±0.58 c | |
| N2 | 金香玉1号 Jinxiangyu 1 | 12.47±0.89 a | 14.34±0.39 a |
| 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 11.48±0.34 a | 13.16±0.32 b | |
| 武密粳 Wumijing | 9.66±0.47 b | 11.35±0.24 c | |
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | 8.81±0.13 b | 10.35±0.31 d | |
| N3 | 金香玉1号 Jinxiangyu 1 | 11.96±0.52 a | 13.47±0.63 a |
| 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 11.04±0.35 b | 12.75±0.23 a | |
| 武密粳 Wumijing | 8.68±0.33 c | 10.28±0.60 b | |
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | 7.87±0.32 c | 9.77±0.31 b | |
| 方差分析 Analysis of variance | 氮素水平Nitrogen level (N) | ** | ** |
| 品种 Cultivar (C) | ** | ** | |
| 氮素水平×品种 N×C | ns | ns |
Table 6. Solubility and swelling potential of starch in the tested rice varieties at different nitrogen levels.
| 处理 Treatment | 品种 Cultivar | 溶解度 Solubility/% | 膨胀势 Swelling power/(g·g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| N1 | 金香玉1号 Jinxiangyu 1 | 13.46±0.37 a | 15.10±0.37 a |
| 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 12.40±0.81 b | 13.87±0.44 b | |
| 武密粳 Wumijing | 10.48±0.15 c | 11.95±0.53 c | |
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | 9.58±0.30 c | 11.01±0.58 c | |
| N2 | 金香玉1号 Jinxiangyu 1 | 12.47±0.89 a | 14.34±0.39 a |
| 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 11.48±0.34 a | 13.16±0.32 b | |
| 武密粳 Wumijing | 9.66±0.47 b | 11.35±0.24 c | |
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | 8.81±0.13 b | 10.35±0.31 d | |
| N3 | 金香玉1号 Jinxiangyu 1 | 11.96±0.52 a | 13.47±0.63 a |
| 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 11.04±0.35 b | 12.75±0.23 a | |
| 武密粳 Wumijing | 8.68±0.33 c | 10.28±0.60 b | |
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | 7.87±0.32 c | 9.77±0.31 b | |
| 方差分析 Analysis of variance | 氮素水平Nitrogen level (N) | ** | ** |
| 品种 Cultivar (C) | ** | ** | |
| 氮素水平×品种 N×C | ns | ns |
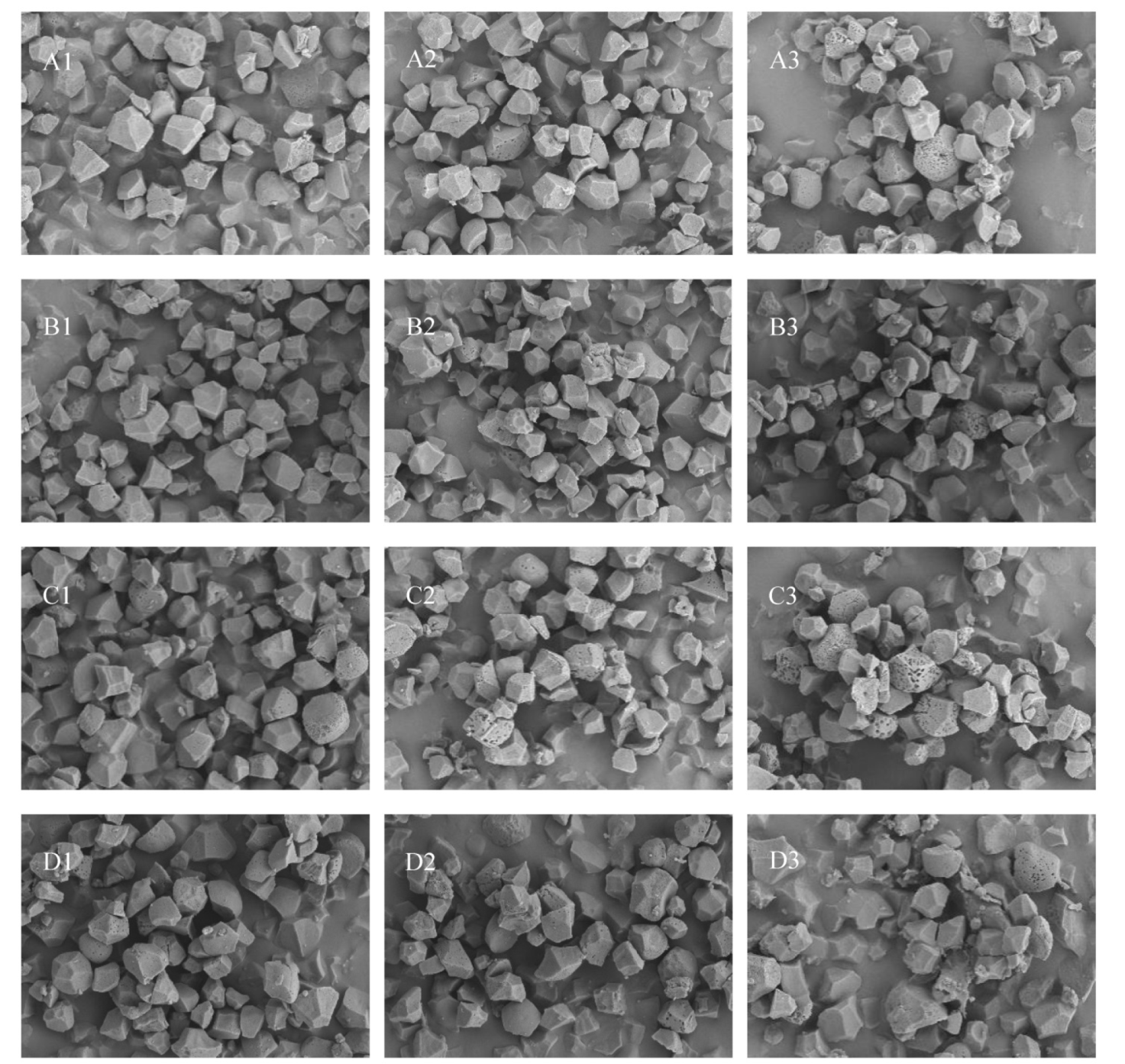
Fig. 2. Electron microscopic photographs of rice starch granules at different nitrogen levels. A-D respectively represent Jinxiangyu 1, Wuyujing 3, Wumijing and Huaidao 5; 1-3 respectively represent N1, N2 and N3.
| 处理 Treatment | 品种 Cultivar | A链含量 A chain content /% | B1链含量 B1 chain content /% | B2链含量 B2 chain content /% | B3链含量 B3 chain content /% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1 | 金香玉1号 Jinxiangyu 1 | 26.51±0.15 a | 43.08±0.38 a | 8.51±0.50 c | 11.13±0.05 d |
| 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 25.35±0.67 b | 42.56±0.19 a | 9.83±0.07 b | 13.24±0.07 c | |
| 武密粳 Wumijing | 24.48±0.14 c | 41.44±0.07 b | 10.10±0.07 ab | 14.09±0.11 b | |
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | 21.56±0.42 d | 37.42±0.47 c | 10.30±0.13 a | 14.61±0.11 a | |
| N2 | 金香玉1号 Jinxiangyu 1 | 25.66±0.42 a | 42.74±0.11 a | 9.16±0.04 c | 11.77±0.55 c |
| 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 24.41±0.63 b | 42.03±0.23 a | 9.89±0.06 b | 13.49±0.02 b | |
| 武密粳 Wumijing | 23.39±0.14 c | 40.87±0.54 b | 10.31±0.08 a | 14.37±0.06 a | |
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | 20.47±0.22 d | 36.63±0.12 c | 10.39±0.05 a | 14.66±0.03 a | |
| N3 | 金香玉1号 Jinxiangyu 1 | 25.24±0.50 a | 42.51±0.08 a | 9.36±0.12 c | 12.96±0.42 d |
| 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 24.15±0.74 b | 41.46±0.11 ab | 10.03±0.05 b | 13.80±0.22 c | |
| 武密粳 Wumijing | 23.19±0.02 c | 40.32±0.43 b | 10.38±0.02 a | 14.43±0.12 b | |
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | 20.35±0.13 d | 34.70±1.44 c | 10.47±0.04 a | 15.07±0.41 a | |
| 方差分析 Analysis of variance | 氮素水平Nitrogen level (N) | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| 品种 Cultivar (C) | ** | ** | ** | ** | |
| 氮素水平×品种 N×C | ns | ns | ns | * |
Table 7. Distribution ratio of amylopectin chain length of the tested rice varieties at different nitrogen levels.
| 处理 Treatment | 品种 Cultivar | A链含量 A chain content /% | B1链含量 B1 chain content /% | B2链含量 B2 chain content /% | B3链含量 B3 chain content /% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1 | 金香玉1号 Jinxiangyu 1 | 26.51±0.15 a | 43.08±0.38 a | 8.51±0.50 c | 11.13±0.05 d |
| 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 25.35±0.67 b | 42.56±0.19 a | 9.83±0.07 b | 13.24±0.07 c | |
| 武密粳 Wumijing | 24.48±0.14 c | 41.44±0.07 b | 10.10±0.07 ab | 14.09±0.11 b | |
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | 21.56±0.42 d | 37.42±0.47 c | 10.30±0.13 a | 14.61±0.11 a | |
| N2 | 金香玉1号 Jinxiangyu 1 | 25.66±0.42 a | 42.74±0.11 a | 9.16±0.04 c | 11.77±0.55 c |
| 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 24.41±0.63 b | 42.03±0.23 a | 9.89±0.06 b | 13.49±0.02 b | |
| 武密粳 Wumijing | 23.39±0.14 c | 40.87±0.54 b | 10.31±0.08 a | 14.37±0.06 a | |
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | 20.47±0.22 d | 36.63±0.12 c | 10.39±0.05 a | 14.66±0.03 a | |
| N3 | 金香玉1号 Jinxiangyu 1 | 25.24±0.50 a | 42.51±0.08 a | 9.36±0.12 c | 12.96±0.42 d |
| 武育粳3号 Wuyujing 3 | 24.15±0.74 b | 41.46±0.11 ab | 10.03±0.05 b | 13.80±0.22 c | |
| 武密粳 Wumijing | 23.19±0.02 c | 40.32±0.43 b | 10.38±0.02 a | 14.43±0.12 b | |
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | 20.35±0.13 d | 34.70±1.44 c | 10.47±0.04 a | 15.07±0.41 a | |
| 方差分析 Analysis of variance | 氮素水平Nitrogen level (N) | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| 品种 Cultivar (C) | ** | ** | ** | ** | |
| 氮素水平×品种 N×C | ns | ns | ns | * |
| 指标 Index | 食味值 Taste value |
|---|---|
| 直链淀粉含量 Amylose content | −0.866** |
| 胶稠度 Gel consistency | 0.588* |
| 蛋白质含量 Protein content | −0.861** |
| 崩解值 Breakdown | 0.965** |
| 消减值 Setback | −0.949** |
| 相对结晶度 Relative crystallinity | 0.818** |
| 回升度 Recovery ratio | −0.832** |
| 溶解度 Solubility | 0.984** |
| 膨胀势 Swelling power | 0.983** |
| A链含量 A chain content | 0.918** |
| B3链含量 B3 chain content | −0.956** |
Table 8. Correlation analysis between eating quality of rice and physicochemical properties of starch.
| 指标 Index | 食味值 Taste value |
|---|---|
| 直链淀粉含量 Amylose content | −0.866** |
| 胶稠度 Gel consistency | 0.588* |
| 蛋白质含量 Protein content | −0.861** |
| 崩解值 Breakdown | 0.965** |
| 消减值 Setback | −0.949** |
| 相对结晶度 Relative crystallinity | 0.818** |
| 回升度 Recovery ratio | −0.832** |
| 溶解度 Solubility | 0.984** |
| 膨胀势 Swelling power | 0.983** |
| A链含量 A chain content | 0.918** |
| B3链含量 B3 chain content | −0.956** |
| [1] | 张洪程, 胡雅杰, 杨建昌, 戴其根, 霍中洋, 许轲, 魏海燕, 高辉, 郭保卫, 邢志鹏, 胡群. 中国特色水稻栽培学发展与展望[J]. 中国农业科学, 2021, 54(7): 1301-1321. |
| Zhang H C, Hu Y J, Yang J C, Dai Q G, Huo Z Y, Xu K, Wei H Y, Gao H, Guo B W, Xing Z P, Hu Q. Development and prospect of rice cultivation in China[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2021, 54(7): 1301-1321. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | 蒋天昊, 任晓佳, 仇景涛, 顾雪怡, 张祖建. 晚播晚栽机插水稻稻米品质的变化特征[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2021, 49(12): 67-71. |
| Jiang T H, Ren X J, Qiu J T, Gu X Y, Zhang Z J. Variation characteristics of rice quality of late sowing and late planting machine-transplanted rice[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 49(12): 67-71. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | Maclean J L, Dawe D C, Hardy B, Hettel G P. Rice Almanac: Source Book for the Most Important Economic Activity on Earth[M]. Manila, the Philippines: International Rice Research Institute, 2002. |
| [4] | Hasjim J, Li E P, Dhital S. Milling of rice grains: Effects of starch/flour structures on gelatinization and pasting properties[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2013, 92(1): 682-690. |
| [5] | Tester R F, Karkalas J, Qi X. Starch—composition, fine structure and architecture[J]. Journal of Cereal Science, 2004, 39(2): 151-165. |
| [6] | Patindol J A, Siebenmorgen T J, Wang Y J. Impact of environmental factors on rice starch structure: A review[J]. Starch‐Stärke, 2015, 67(1-2): 42-54 |
| [7] | 明东风, 马均, 马文波, 许凤英, 孙晓辉, 田彦华. 稻米直链淀粉及其含量研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2003, 19(1): 68-71. |
| Ming D F, Ma J, Ma W B, Xu F Y, Sun X H, Tian Y H. A review of rice amylose and its content[J]. Chinese Agriculture Science Bulletin, 2003, 19(1): 68-71. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | Buleon A, Colonna P, Planchot V, Ball S. Starch granules: Structure and biosynthesis[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 1998, 23(2): 85-112. |
| [9] | 张艳霞. 稻米直链淀粉含量与淀粉理化特性及品质的关系[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2007. |
| Zhang Y X. Relationship between rice quality, physicochemical property of starch and amylose content[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agriculture University, 2007. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | Zhang C Q, Zhou L H, Zhu Z B, Lu H W, Zhou X Z, Qian Y T, Li Q F, Lu Y, Gu M H, Liu Q Q. Characterization of grain quality and starch fine structure of two japonica rice (Oryza sativa) cultivars with good sensory properties at different temperatures during the filling stage[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2016, 64(20): 4048-4057. |
| [11] | 施利利, 张欣, 丁得亮, 王松文, 崔晶. 稻米理化特性与食味品质的相关性研究[J]. 种子, 2010 (11): 82-84. |
| Shi L L, Zhang X, Ding D L, Wang S W, Cui J. Study on the correlation of rice physicochemical properties and palatability quality[J]. Seed, 2010(11): 82-84. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 金丽晨, 耿志明, 李金州, 王澎, 陈菲, 刘蔼民. 稻米淀粉组成及分子结构与食味品质的关系[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2011, 27(1): 13-18. |
| Jin L L, Gen Z M, Lin J Z, Wang P, Chen F, Liu E M. Correlation between components and molecule structure of rice starch and eating quality[J]. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2011, 27(1): 13-18. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | 蔡一霞, 刘春香, 王维, 张洪熙, 张祖建, 杨静, 唐汉忠. 灌浆期表观直链淀粉含量相似品种稻米胶稠度和 RVA 谱的动态差异[J]. 中国农业科学, 2011, 44(12): 2439-2445. |
| Cai Y X, Liu C X, Wang W, Zhang H X, Zhang Z J, Yang J, Tang H Z. Dynamic differences of the RVA profile and gel consistency in two rice varieties with similar apparent amylose content during grain filling[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2011, 44(12): 2439-2445. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | 周天阳. 栽培措施对超级稻产量和品质的影响[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2020. |
| Zhou T Y. Effects of cultivation treatments on yield and quality of supe rice[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 侯丹平. 不同栽培措施对稻田土壤理化特性和米质的影响[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2019. |
| Hou D P. Effect of different cultivation patterns on physicochemical properties of soil and rice quality[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 朱大伟. 三种关键栽培措施对软米粳稻产量与品质的影响[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2018. |
| Zhu D W. Effects of three key cultivation measures on yield and quality of soft rice japonica[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | 彭少兵, 黄见良, 钟旭华, 杨建昌, 王光火, 邹应斌, 张福锁, 朱庆森,Buresh R, Witt C. 提高中国稻田氮肥利用率的研究策略[J]. 中国农业科学, 2002, 35: 1095-1103. |
| Peng S B, Huang J L, Zhong X H, Yang J C, Wang G H, Zou Y B, Zhang F S, Zhu Q S, Buresh R, Witt C. Research strategy in improving fertilizer-nitrogen use efficiency of irrigated rice in China[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2002, 35: 1095-1103. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | Huang L Y, Sun F, Yuan S, Peng S B, Wang F. Different mechanisms underlying the yield advantage of ordinary hybrid and super hybrid rice over inbred rice under low and moderate N input conditions[J]. Field Crops Research, 2018, 216: 150-157. |
| [19] | 吴家青, 熊若愚, 解嘉鑫, 蒋海燕, 谭雪明, 潘晓华, 曾勇军, 石庆华, 曾研华. 稻米食味品质形成及其响应氮素调控作用的研究进展[J]. 中国稻米, 2021, 27(2): 28-37. |
| Wu J Q, Xiong R Y, Jie J X, Jiang H Y, Tan X M, Pan X H, Zeng Y J, Shi Q H, Zeng Y H. Research advances on rice eating grain quality formation and its response to nitrogen application[J]. China Rice, 2021, 27(2): 28-37. (in Chinese) | |
| [20] | 韩春雷, 侯守贵, 刘宪平, 魏树和, 邹积斌. 栽培技术对稻米品质的作用及其数量关系研究[J]. 辽宁农业科学, 1997(1): 18-21. |
| Han C L, Hou S G, Liu X P, Wei S H, Zou J B. Study on the effect of cultivation techniques on the rice quality and its quantitative relationship[J]. Liaoning Agricultural Science, 1997(1): 18-21. (in Chinese) | |
| [21] | 孙艳丽, 沈鹏, 金正勋, 金学泳, 马红. 氮素营养对稻米理化特性及淀粉谱特性的影响[J]. 东北农业大学学报, 2002(2): 134-138. |
| Sun Y L, Shen P, Jin Z X, Jin X Y, Ma H. Effects of nitrogenous nutrition on the physicochemical properties and amylogram properties of rice grain[J]. Journal of Northeast Agricultural University, 2002(2): 134-138. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | 金正勋, 同拉嘎, 李丹, 李明月, 潘冬, 张玉磊, 王海微, 韩云飞, 张忠臣. 灌浆成熟期氮素营养对水稻增产及淀粉品质的影响[J]. 东北农业大学学报, 2017, 48(4): 1-6. |
| Jin Z X, Tong L G, Li D, Li M Y, Pan D, Zhang Y L, Wang H W, Han Y F, Zhang Z C. Effect of grain-filling nitrogen on yield increasing and starch quality in rice[J]. Journal of Northeast Agricultural University, 2017, 48(4): 1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | Gu J F, Chen J, Chen L, Wang Z Q, Zhang H, Yang J C. Grain quality changes and responses to nitrogen fertilizer of japonica rice cultivars released in the Yangtze River Basin from the 1950s to 2000s[J]. The Crop Journal, 2015, 3(4): 285-297. |
| [24] | 申勇. 不同粳稻品种稻米品质对施氮量的响应差异及其原因分析[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2021. |
| Shen Y. Difference in response of grain quality to nitrogen application rates among japonica rice varieties and its causes[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | Cai J W, Cai C H, Man J M, Yang Y, Zhang F M, Wei C X. Crystalline and structural properties of acid-modified lotus rhizome C-type starch[J]. Carbohydr Polym, 2014, 102: 799-807. |
| [26] | 沈泓, 姚栋萍, 吴俊, 罗秋红, 吴志鹏, 雷东阳, 邓启云, 柏斌. 灌浆期不同时段高温对稻米淀粉理化特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(4): 377-387. |
| Shen H, Yao D P, Wu J, Luo Q H, Wu Z P, Lei D Y, Den Q Y, Bai B. Effects of high temperature at different times during grain filling stage on rice starch physicochemical properties[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2022, 36(4): 377-387. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | Syahariza Z A, Li E, Hasjim J. Extraction and dissolution of starch from rice and sorghum grains for accurate structural analysis[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2010, 82(1): 14-20. |
| [28] | Wu A C, Li E P, Gilbert R G. Exploring extraction/ dissolution procedures for analysis of starch chain-length distributions[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2014, 114: 36-42. |
| [29] | 徐斌, 满建民, 韦存虚. 粉末X射线衍射图谱计算植物淀粉结晶度方法的探讨[J]. 植物学报, 2012, 47 (3): 278-285. |
| Xu B, Man J M, Wei C X. Methods for determining relative crystallinity of plant starch X-ray powder diffraction spectra[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2012, 47(3): 278-285. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | 薛薇. 江苏省粳米品质分析及其淀粉性质的研究[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2021. |
| Xue W. Study on quality analysis and starch properties of Japonica rice in Jiangsu Province[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | 卢毅, 路兴花, 张青峰, 余建国, 肖雄雄, 庞林江, 成纪予. 稻米直链淀粉与米饭物性及食味品质的关联特征研究[J]. 食品科技, 2018, 43(10): 219-223. |
| Lu Y, Lu X H, Zhang Q F, Yu J G, Xiao X X, Pang L J, Cheng J Y. Correlation of rice amylose with physical properties and taste quality of rice[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2018, 43(10): 219-223. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [32] | 张小明, 石春海, 富田桂. 稻米淀粉特性与食味间的相关性分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2002(2): 60-64. |
| Zhang X M, Shi C H, Fu C G. Correlation analysis between starch characteristics and taste quality in japonica rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2002(2): 60-64. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [33] | 杨标, 雍明玲, 赵步洪, 陈前, 叶苗, 张祖建. 氮肥减施对粳稻稻米淀粉结构与食味品质的效应[J]. 扬州大学学报: 农业与生命科学版, 2022, 43(5): 37-46. |
| Yang B, Yong M L, Zhao B H, Chen Q, Ye M, Zhang Z J. Effects of reducing nitrogen fertilization on the starch structure and the eating quality of japonica rice grain[J]. Journal of Yangzhou University: Agricultural and Life Science Edition, 2022, 43(5): 37-46. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [34] | 周慧颖, 彭小松, 欧阳林娟, 朱昌兰, 陈小荣, 傅军如, 边建民, 胡丽芳, 贺浩华, 贺晓鹏. 支链淀粉结构对稻米淀粉糊化特性的影响[J]. 中国粮油学报, 2018, 33(8): 25-30. |
| Zhou H Y, Peng X S, Ouyang L J, Zhu C L, Chen X R, Fu J R, Bian J M, Hu L F, He H H, He X P. Effects of amylopectin structure on gelatinization characteristics of rice starch[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association, 2018, 33(8): 25-30. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [35] | 李丁鲁, 张建明, 王慧, 李茂柏, 朴钟泽. 长江下游地区部分优质粳稻品种与越光稻米支链淀粉结构特征及品质性状比较[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2010(4): 379-384. |
| Li D L, Zhang J M, Wang H, Li M B, Piao Z Z. Differences in amylopectin structure and grain quality of rice between some high-quality japonica cultivars from the lower Yangtze River region, China and Koshihikari from Niigata, Japan[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2010(4): 379-384. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [36] | 隋炯明, 李欣, 严松, 严长杰, 张蓉, 汤述翥, 陆驹飞, 陈宗祥, 顾铭洪. 稻米淀粉 RVA 谱特征与品质性状相关性研究[J]. 中国农业科学, 2005, 38(4): 657-663. |
| Sui J M, Lin X, Yan S, Yan C J, Zhang R, Tang S Z, Lu J F, Chen Z X, Gu M H. Studies on the rice RVA profile characteristics and its correlation with the quality[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2005, 38(4): 657-663. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [37] | 蔡金文. 普通水稻淀粉结构和功能特性研究[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2015. |
| Cai J W. Structural and functional properties of normal rice starches[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [38] | 张艳霞, 丁艳锋, 李刚华, 王强盛, 黄丕生, 王绍华. 直链淀粉含量不同的稻米淀粉结构, 糊化特性研究[J]. 作物学报, 2007, 33(7): 1201-1205. |
| Zhang Y X, Ding Y F, Li G H, Wang Q S, Huang B S, Wang S H. Starch structure and paste property of rice with different amylose content[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2007, 33(7): 1201-1205. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [39] | 赵春芳, 岳红亮, 黄双杰, 周丽慧, 赵凌, 张亚东, 陈涛, 朱镇, 赵庆勇, 姚姝, 梁文化, 路凯, 王才林. 南粳系列水稻品种的食味品质与稻米理化特性[J]. 中国农业科学, 2019, 52(5): 909-920. |
| Zhao C F, Yue H L, Huang S J, Zhou L H, Zhao L, Zhang Y D, Chen T, Zhu Z, Zhao Q Y, Yao S, Liang W H, Lu K, Wang C L. Eating quality and physicochemical properties in Nanjing rice varieties[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2019, 52(5): 909-920. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [40] | Bhat F M, Riar C S. Effect of amylose, particle size & morphology on the functionality of starches of traditional rice cultivars[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2016, 92: 637-644. |
| [41] | 王艳, 崔晶, 王小波, 赵梅, 朱长娟, 施利利, 张欣. 施肥对中日水稻品系土壤养分及食味品质的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2010, 18(2): 286-289. |
| Wang Y, Cui J, Wang X B, Zhao M, Zhu C J, Shi L L, Zhang X. Effect of fertilization method on soil available nutrients and taste of Japanese and Chinese rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2010, 18(2): 286-289. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [42] | 张艳霞, 丁艳锋, 王强盛, 李刚华, 李福春, 王绍华. 氮素穗肥对不同品种稻米品质性状的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2007(6): 1080-1085. |
| Zhang Y X, Ding Y F, Wang Q S, Li G H, Li F C, Wang S H. Effect of panicle nitrogen fertilizer on quality properties of different rice varieties[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2007(6): 1080-1085. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [43] | 孙文星, 田伟, 肖峰, 高叶敏, 敖和军. 施用粒肥对水稻产量和氮素吸收利用的影响[J]. 湖北农业科学, 2022, 61(13): 31-36. |
| Sun W X, Tian W, Xiao F, Gao Y M, Ao H J. Effects of grain fertilizer application on rice yield and nitrogen uptake and utilization[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 61(13): 31-36. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [44] | 石吕, 张新月, 孙惠艳, 曹先梅, 刘建, 张祖建. 不同类型水稻品种稻米蛋白质含量与蒸煮食味品质的关系及后期氮肥的效应[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(6): 541-552. |
| Shi L, Zhang X Y, Sun H Y, Cao X M, Liu J, Zhang Z J. Relationship of grain protein content with cooking and eating quality as affected by nitrogen fertilizer at late growth stage for different types of rice varieties[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2019, 33(6): 541-552. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [45] | 戴湘桂, 赵一童, 宋肖肖, 黎江川, 冯艺章, 韦有访, 刘丕庆. 粒肥施用对籽粒蛋白质含量组分及米质性状的影响[J/OL]. 分子植物育种, 2022: 1-22[2023-03-13]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1068.S.20220829.1738.004.html |
| Dai X G, Zhao Y T, Song X X, Li J C, Feng Y Z, WeiY F, Liu B Q. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer application on protein content and rice(Oryza sativa. L) grain quality[J/OL]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2022: 1-22 [2023-03-13]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1068.S.20220829.1738.004.html. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [46] | 刘文哲. 开放式增温条件下氮素粒肥对水稻籽粒灌浆及品质的影响[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2019. |
| Liu W Z. Effects of nitrogen granule fertilizer on rice grain filling and quality under open warming conditions[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agriculture University, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [47] | 窦志. 灌浆期开放式增温对水稻籽粒灌浆和品质的影响及氮素粒肥的调控效应[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2017. |
| Dou Z. Effects of free-air warming during grain filling stage on rice grain filling and quality and the regulation effects of nitrogen spikelet fertilizer[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agriculture University, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [48] | 朱大伟, 李敏, 郭保卫, 张洪程. 氮肥水平对优质粳稻蒸煮食味品质与质构特性的影响[J]. 贵州农业科学, 2018, 46(3): 62-66. |
| Zhu D W, Li M, Guo B W, Zhang H C. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer application level on eating and textural characteristics of high quality Japonica rice[J]. Guizhou Agricultura Sciences, 2018, 46(3): 62-66. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [49] | 朱安. 穗粒肥用量对优质食味水稻品种产量和品质的影响[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2021. |
| Zhu A. Effects of panicle and grain nitrogen fertilizer rates on yield and grain quality of rice with good taste quality[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [50] | 陆丹丹, 雍明玲, 陶钰, 叶苗, 张祖建. 优良食味水稻品种籽粒蛋白质积累特征及其对氮素水平的响应[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(5): 520-530. |
| Lu D D, Yong M L, Tao Y, Ye M, Zhang Z J. Characteristics of grain protein accumulation and its response to nitrogen level in good taste rice varieties[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2022, 36(5): 520-530. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [51] | 孙涛, 同拉嘎, 赵书宇, 王海微, 韩云飞, 张忠臣, 金正勋. 氮肥对水稻胚乳淀粉品质、相关酶活性及基因表达量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(5): 475-484. |
| Sun T, Tong L G, Zhao S Y, Wang H W, Han Y F, Zhang Z C, Jin Z X. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer application on starch quality, activities and gene expression levels of related enzymes in rice endosperm[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2018, 32(5): 475-484. | |
| [52] | 王才林. 江苏省优良食味粳稻品种培育的发展与启示[J]. 中国稻米, 2022, 28(5): 82-91. |
| Wang C L. Development and enlightenment of Japonica rice breeding with good eating quality in Jiangsu Province[J]. China Rice, 2022, 28(5): 82-91. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [53] | Zhang C Q, Yang Y, Chen S J, Liu X J, Zhu J H, Zhou L H, Lu Y, Li Q F, Fan X L, Tang S Z, Gu M H, Liu Q Q. A rare Waxy allele coordinately improves rice eating and cooking quality and grain transparency[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2021, 63(5): 889-901. |
| [54] | 赵凌, 朱镇, 陈涛, 赵庆勇, 赵春芳, 张亚东, 王才林. 水稻优良品种南粳46及其衍生品种特性分析[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2023, 24(3): 648-660. |
| Zhao L, Zhu Z, Chen T, Zhao Q Y, Zhao C F, Zhang Y D, Wang C L. Analysis on characteristics of rice core germplasm Nanjing 46 with good eating quality and its derived varieties[J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2023, 24(3): 648-660. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] |
WANG Yichen, ZHU Benshun, ZHOU Lei, ZHU Jun, YANG Zhongnan.
Sterility Mechanism of Photoperiod/Thermo-sensitive Genic Male Sterile Lines and Development and Prospects of Two-line Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(5): 463-474. |
| [2] |
XU Yongqiang XU Jun, FENG Baohua, XIAO Jingjing, WANG Danying, ZENG Yuxiang, FU Guanfu.
Research Progress of Pollen Tube Growth in Pistil of Rice and Its Response to Abiotic stress [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(5): 495-506. |
| [3] |
HE Yong, LIU Yaowei, XIONG Xiang, ZHU Danchen, WANG Aiqun, MA Lana, WANG Tingbao, ZHANG Jian, LI Jianxiong, TIAN Zhihong.
Creation of Rice Grain Size Mutants by Editing OsOFP30 via CRISPR/Cas9 System [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(5): 507-515. |
| [4] |
LÜ Yang, LIU Congcong, YANG Longbo, CAO Xinglan, WANG Yueying, TONG Yi, Mohamed Hazman, QIAN Qian, SHANG Lianguang, GUO Longbiao.
Identification of Candidate Genes for Rice Nitrogen Use Efficiency by Genome-wide Association Analysis [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(5): 516-524. |
| [5] |
YANG Hao, HUANG Yanyan, WANG Jian, YI Chunlin, SHI Jun, TAN Chutian, REN Wenrui, WANG Wenming.
Development and Application of Specific Molecular Markers for Eight Rice Blast Resistance Genes in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(5): 525-534. |
| [6] |
TANG Weijie, CHEN Haiyuan, ZHANG Suobing, TANG Jun, LIN Jing, FANG Xianwen, ZHANG Shunan, XIAO Ning, WU Yunyu, LI Aihong, ZHANG Yunhui.
Analysis of Nitrogen-response Related Loci in japonica Rice Varieties from Jiangsu Province [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(5): 535-543. |
| [7] |
JIANG Peng, ZHANG Lin, ZHOU Xingbing, GUO Xiaoyi, ZHU Yongchuan, LIU Mao, GUO Chanchun, XIONG Hong, XU Fuxian.
Yield Formation Characteristics of Ratooning Hybrid Rice Under Simplified Cultivation Practices in Winter Paddy Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(5): 544-554. |
| [8] |
YANG Mingyu, CHEN Zhicheng, PAN Meiqing, ZHANG Bianhong, PAN Ruixin, YOU Lindong, CHEN Xiaoyan, TANG Lina, HUANG Jinwen.
Effects of Nitrogen Reduction Combined with Biochar Application on Stem and Sheath Assimilate Translocation and Yield Formation in Rice Under Tobacco-rice Rotation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(5): 555-566. |
| [9] |
XIONG Jiahuan, ZHANG Yikai, XIANG Jing, CHEN Huizhe, XU Yicheng, WANG Yaliang, WANG Zhigang, YAO Jian, ZHANG Yuping .
Effect of Biochar-based Fertilizer Application on Rice Yield and Nitrogen Utilization in Film- mulched PaddyFields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(5): 567-576. |
| [10] | GUO Zhan, ZHANG Yunbo. Research Progress in Physiological,Biochemical Responses of Rice to Drought Stress and Its Molecular Regulation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [11] | WEI Huanhe, MA Weiyi, ZUO Boyuan, WANG Lulu, ZHU Wang, GENG Xiaoyu, ZHANG Xiang, MENG Tianyao, CHEN Yinglong, GAO Pinglei, XU Ke, HUO Zhongyang, DAI Qigen. Research Progress in the Effect of Salinity, Drought, and Their Combined Stresses on Rice Yield and Quality Formation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [12] | XU Danjie, LIN Qiaoxia, LI Zhengkang, ZHUANG Xiaoqian, LING Yu, LAI Meiling, CHEN Xiaoting, LU Guodong. OsOPR10 Positively Regulates Rice Blast and Bacterial Blight Resistance [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [13] | CHEN Mingliang, ZENG Xihua, SHEN Yumin, LUO Shiyou, HU Lanxiang, XIONG Wentao, XIONG Huanjin, WU Xiaoyan, XIAO Yeqing. Typing of Inter-subspecific Fertility Loci and Fertility Locus Pattern of indica-japonica Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 386-396. |
| [14] | DING Zhengquan, PAN Yueyun, SHI Yang, HUANG Haixiang. Comprehensive Evaluation and Comparative Analysis of Jiahe Series Long-Grain japonica Rice with High Eating Quality Based on Gene Chip Technology [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 397-408. |
| [15] | HOU Xiaoqin, WANG Ying, YU Bei, FU Weimeng, FENG Baohua, SHEN Yichao, XIE Hangjun, WANG Huanran, XU Yongqiang, WU Zhihai, WANG Jianjun, TAO Longxing, FU Guanfu. Mechanisms Behind the Role of Potassium Fulvic Acid in Enhancing Salt Tolerance in Rice Seedlings [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||