
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2023, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (1): 16-28.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2023.220503
• Research Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
PEI Feng1, WANG Guangda1, GAO Peng1, FENG Zhiming1,2, HU Keming1,2, CHEN Zongxiang1,2, CHEN Hongqi3, CUI Ao4, ZUO Shimin1,2,5( )
)
Received:2022-05-06
Revised:2022-07-31
Online:2023-01-10
Published:2023-01-10
Contact:
ZUO Shimin
裴峰1, 王广达1, 高鹏1, 冯志明1,2, 胡珂鸣1,2, 陈宗祥1,2, 陈红旗3, 崔傲4, 左示敏1,2,5( )
)
通讯作者:
左示敏
基金资助:PEI Feng, WANG Guangda, GAO Peng, FENG Zhiming, HU Keming, CHEN Zongxiang, CHEN Hongqi, CUI Ao, ZUO Shimin. Evaluation of New japonica Rice Lines with Low Cadmium Accumulation and Good Quality Generated by Knocking Out OsNramp5[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(1): 16-28.
裴峰, 王广达, 高鹏, 冯志明, 胡珂鸣, 陈宗祥, 陈红旗, 崔傲, 左示敏. 敲除OsNramp5基因创制低镉优质粳稻新材料的应用评价[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(1): 16-28.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2023.220503
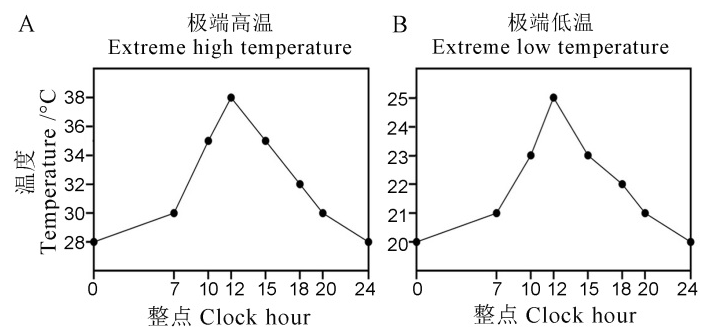
Fig. 1. Temperature curves for extreme temperature conditions. A, Diurnal temperature curve of extreme high temperature; B, Diurnal temperature curve of extreme low temperature.
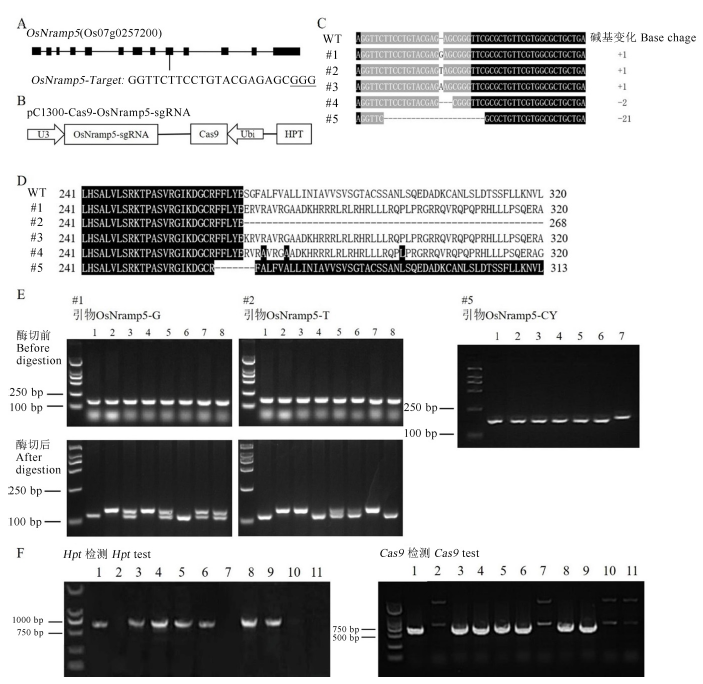
Fig. 2. Construction and genotyping of OsNramp5 knockout lines. Note: (A) Position of the target sequence in OsNramp5; (B) Construction of the vector of pC1300-Cas9-OsNramp5-sgRNA;(C) Comparative analysis of gene sequences between T0 generation plants and wild type. Black shadows represent the same sequences, gray shadows represent the target sequence, ‘+’ Insertion, ‘-’ Deletion, ‘WT’ Wild type;(D) Comparative analysis of amino acids between T0 generation plants and wild type. The numbers to the left and right of the sequence indicate the position of the amino acid sequence in the protein. The black shadows represent the same sequences as the wild type, ‘-’ Deletion, ‘WT’ Wild type ;(E) Development of molecular markers specific to three different variants lines. Different mutant lines and their specific markers were marked at the top of the figure. CAPS markers were developed for mutant lines #1 and #2, and in their electrophoretic picture, the lane 1 represents homozygous mutant that was confirmed by sequencing. The lane 2 indicates the wild type and remaining lanes 3~8 represent different individual plants from T2 population. InDel marker was developed for genotyping mutant lines #5, and the lane 7 and the remaining lanes indicate wild type and different individual T2 plants, respectively. DL 2000 was used as the molecular marker (Same as below). (F) Detection of transgenic components for some homozygous mutant plant lines. Lanes 1 and 2 are positive and negative controls, respectively. Lanes 3~11 represent different homozygous mutant plant lines, and among them, lanes 7, 10 and 11 correspond to nramp5ko-1, -2 and -3 respectively.
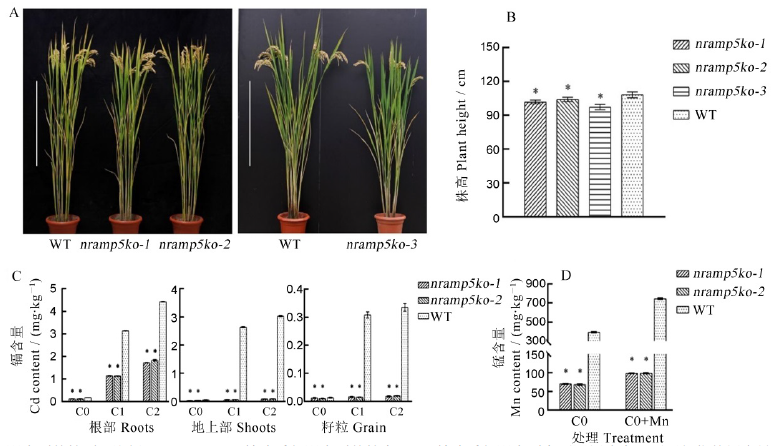
Fig. 3. Whole plant and analysis of cadmium and manganese contents in OsNramp5 knockout lines. A,Whole plant of the wild type and homozygous mutant lines. Scale = 50 cm. B, Plant height of knockout lines and wild type. C, Cadmium content in different parts of knockout lines and wild type under different cadmium concentrations. ‘C0’,control; ‘C1’, 1.2 mg/kg cadmium; ‘C2’, 2.0 mg/kg cadmium; D, Manganese content in shoots of knockout lines and wild type under different treatments. ‘C0’, control; ‘C0+Mn’, spraying manganese fertilizer treatment. Data are shown as means ± SD(n=3). * represent a significant difference from WT (P<0.05) (t-test).
| 分蘖肥处理 Tillering fertilizer level | 株系 Line | 有效穗 Effective panicle | 每穗粒数 Grains per panicle | 结实率 Seed setting rate/ % | 千粒重 1000-grain weight / g | 理论产量Theoretical yield/(kg·hm−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 低肥 Low (37.5 kg/hm2) | nramp5ko-1 | 9.6±1.1 b | 125.4±3.9 e | 96.12±0.96 a | 24.36±0.15 bc | 8541.75 |
| nramp5ko-2 | 9.9±2.1 ab | 123.2±3.3 e | 96.59±0.98 a | 24.47±0.47 abc | 8735.70 | |
| WT | 7.8±1.1 c | 156.0±4.9 b | 95.71±0.95 a | 24.82±0.05 a | 8759.25 | |
| 正常 Normal (112.5 kg/hm2) | nramp5ko-1 | 9.9±1.1 ab | 138.4±1.9 cd | 91.27±1.43 c | 24.42±0.03 abc | 9254.10 |
| nramp5ko-2 | 9.6±1.9 b | 141.4±2.1 cd | 92.69±1.73 bc | 24.41±0.07 abc | 9306.90 | |
| WT | 9.9±1.6 ab | 163.8±4.2 a | 95.44±0.77 a | 24.73±0.04 ab | 11 598.15 | |
| 高肥 High (187.5 kg/hm2) | nramp5ko-1 | 11.2±1.0 a | 137.0±1.7 d | 92.15±2.60 bc | 23.02±0.08 d | 9863.40 |
| nramp5ko-2 | 11.1±1.8 ab | 141.8±2.3 c | 91.33±3.39 c | 23.19±0.03 d | 10 101.75 | |
| WT | 10.8±1.6 ab | 165.2±3.2 a | 93.52±1.23 b | 24.23±0.09 c | 12 251.25 |
Table 1. Comparison of theoretical yield and its components between OsNramp5 knockout lines and control at different tillering fertilizer levels.
| 分蘖肥处理 Tillering fertilizer level | 株系 Line | 有效穗 Effective panicle | 每穗粒数 Grains per panicle | 结实率 Seed setting rate/ % | 千粒重 1000-grain weight / g | 理论产量Theoretical yield/(kg·hm−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 低肥 Low (37.5 kg/hm2) | nramp5ko-1 | 9.6±1.1 b | 125.4±3.9 e | 96.12±0.96 a | 24.36±0.15 bc | 8541.75 |
| nramp5ko-2 | 9.9±2.1 ab | 123.2±3.3 e | 96.59±0.98 a | 24.47±0.47 abc | 8735.70 | |
| WT | 7.8±1.1 c | 156.0±4.9 b | 95.71±0.95 a | 24.82±0.05 a | 8759.25 | |
| 正常 Normal (112.5 kg/hm2) | nramp5ko-1 | 9.9±1.1 ab | 138.4±1.9 cd | 91.27±1.43 c | 24.42±0.03 abc | 9254.10 |
| nramp5ko-2 | 9.6±1.9 b | 141.4±2.1 cd | 92.69±1.73 bc | 24.41±0.07 abc | 9306.90 | |
| WT | 9.9±1.6 ab | 163.8±4.2 a | 95.44±0.77 a | 24.73±0.04 ab | 11 598.15 | |
| 高肥 High (187.5 kg/hm2) | nramp5ko-1 | 11.2±1.0 a | 137.0±1.7 d | 92.15±2.60 bc | 23.02±0.08 d | 9863.40 |
| nramp5ko-2 | 11.1±1.8 ab | 141.8±2.3 c | 91.33±3.39 c | 23.19±0.03 d | 10 101.75 | |
| WT | 10.8±1.6 ab | 165.2±3.2 a | 93.52±1.23 b | 24.23±0.09 c | 12 251.25 |
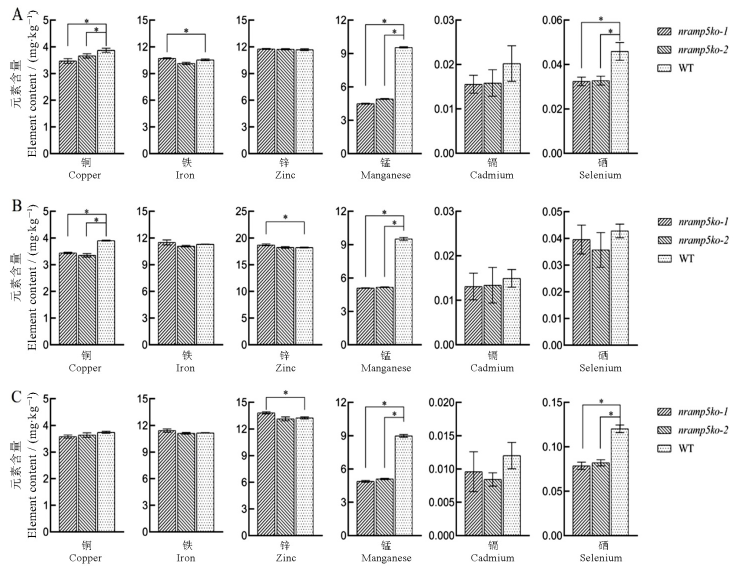
Fig. 4. Element contents in grains of OsNramp5 knockout lines and wild type under three fertilization treatments. A, B and C were contents of copper, iron, zinc, manganese, cadmium and selenium in grains under normal fertilization, zinc fertilization and selenium fertilization respectively. Data are shown as means ± SD(n=3). * represents significant differences between lines(P<0.05) (t-test).
| 施肥方式Fertilization treatment | 株系 Line | 糙米率 Brown rice rate /% | 精米率 Milled rice rate /% | 整精米率 Head milled rice rate /% | 垩白粒率 Chalky rice rate/% | 垩白度 Chalkiness /% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 正常 Conventional | nramp5ko-1 | 84.89±0.17 b | 72.20±0.50 b | 67.29±0.70 b | 6.6±0.2 f | 2.0±0.1 d |
| nramp5ko-2 | 85.12±0.27 ab | 73.44±1.97 ab | 67.31±1.59 b | 7.7±0.2 e | 1.9±0.1 d | |
| WT | 84.91±0.23 ab | 73.86±0.83 a | 69.49±0.74 ab | 8.7±0.1 c | 2.3±0.1 c | |
| 锌肥 +Zn | nramp5ko-1 | 84.91±0.29 ab | 71.95±0.39 b | 67.63±1.58 b | 9.4±0.3 b | 2.7±0.2 b |
| nramp5ko-2 | 84.95±0.08 ab | 72.92±0.86 ab | 67.61±1.15 b | 8.2±0.1 d | 2.5±0.1 bc | |
| WT | 84.82±0.26 b | 73.38±1.00 ab | 69.85±1.99 a | 11.8±0.2 a | 3.4±0.2 a | |
| 硒肥 +Se | nramp5ko-1 | 85.24±0.15 a | 73.10±1.69 ab | 67.72±1.17 b | 4.3±0.1 h | 1.1±0.1 e |
| nramp5ko-2 | 85.22±0.18 a | 72.53±0.26 ab | 67.66±2.85 b | 4.6±0.1 h | 1.2±0.1 e | |
| WT | 84.94±0.27 ab | 73.30±0.68 ab | 70.08±0.42 a | 5.5±0.2 g | 1.4±0.1 e |
Table 2. Comparison of rice processing and quality related indexes of OsNramp5-ko knockout lines under different fertilization treatments.
| 施肥方式Fertilization treatment | 株系 Line | 糙米率 Brown rice rate /% | 精米率 Milled rice rate /% | 整精米率 Head milled rice rate /% | 垩白粒率 Chalky rice rate/% | 垩白度 Chalkiness /% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 正常 Conventional | nramp5ko-1 | 84.89±0.17 b | 72.20±0.50 b | 67.29±0.70 b | 6.6±0.2 f | 2.0±0.1 d |
| nramp5ko-2 | 85.12±0.27 ab | 73.44±1.97 ab | 67.31±1.59 b | 7.7±0.2 e | 1.9±0.1 d | |
| WT | 84.91±0.23 ab | 73.86±0.83 a | 69.49±0.74 ab | 8.7±0.1 c | 2.3±0.1 c | |
| 锌肥 +Zn | nramp5ko-1 | 84.91±0.29 ab | 71.95±0.39 b | 67.63±1.58 b | 9.4±0.3 b | 2.7±0.2 b |
| nramp5ko-2 | 84.95±0.08 ab | 72.92±0.86 ab | 67.61±1.15 b | 8.2±0.1 d | 2.5±0.1 bc | |
| WT | 84.82±0.26 b | 73.38±1.00 ab | 69.85±1.99 a | 11.8±0.2 a | 3.4±0.2 a | |
| 硒肥 +Se | nramp5ko-1 | 85.24±0.15 a | 73.10±1.69 ab | 67.72±1.17 b | 4.3±0.1 h | 1.1±0.1 e |
| nramp5ko-2 | 85.22±0.18 a | 72.53±0.26 ab | 67.66±2.85 b | 4.6±0.1 h | 1.2±0.1 e | |
| WT | 84.94±0.27 ab | 73.30±0.68 ab | 70.08±0.42 a | 5.5±0.2 g | 1.4±0.1 e |
| 施肥方式 Fertilization treatment | 株系 Line | 蛋白质含量 Protein content / % | 直链淀粉含量 Amylose content/% | 胶稠度 Gel consistency /mm | 硬度Hardness | 黏度viscosity | 平衡度Balance | 食味值 Taste value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 正常 Conventional | nramp5ko-1 | 7.55±0.02 a | 9.35±0.00 d | 75.5±0.5 a | 6.1±0.1 a | 7.3±0.1 d | 7.3±0.1 e | 74.6±0.9 de |
| nramp5ko-2 | 7.24±0.01 b | 9.87±0.00 c | 75.5±0.5 a | 5.8±0.0 c | 7.9±0.3 abc | 7.9±0.2 bcd | 77.9±1.4 bcd | |
| WT | 6.82±0.01 c | 10.20±0.04 b | 77.5±0.5 a | 5.6±0.0 d | 8.4±0.1 a | 8.4±0.1 a | 81.4±0.8 a | |
| 锌肥 +Zn | nramp5ko-1 | 7.30±0.00 b | 10.38±0.00 ab | 77.5±0.5 a | 5.9±0.1 bc | 8.2±0.2 ab | 8.2±0.3 ab | 79.8±1.9 ab |
| nramp5ko-2 | 7.47±0.02 a | 10.60±0.08 a | 77.0±1.0 a | 5.9±0.1 bc | 8.1±0.2 ab | 8.0±0.1 abc | 78.5±1.0 abc | |
| WT | 6.89±0.04 c | 10.72±0.18 a | 78.5±0.5 a | 5.8±0.1 c | 7.7±0.3 bcd | 7.8±0.2 bcde | 77.3±1.7 bcde | |
| 硒肥 +Se | nramp5ko-1 | 7.22±0.04 b | 10.42±0.11 ab | 69.0±1.0 b | 6.0±0.2 ab | 7.4±0.5 cd | 7.4±0.5 de | 75.2±3.0 de |
| nramp5ko-2 | 7.27±0.04 b | 10.53±0.15 ab | 69.5±1.5 b | 6.1±0.0 a | 7.4±0.2 cd | 7.3±0.1 e | 74.4±0.7 e | |
| WT | 7.25±0.02 b | 10.42±0.04 ab | 69.0±1.0 b | 5.9±0.0 bc | 7.5±0.1 cd | 7.5±0.0 cde | 75.8±0.2 cde |
Table 3. Comparison of OsNramp5-ko knockout lines in rice nutritional quality and food quality indexes under different fertilization treatments.
| 施肥方式 Fertilization treatment | 株系 Line | 蛋白质含量 Protein content / % | 直链淀粉含量 Amylose content/% | 胶稠度 Gel consistency /mm | 硬度Hardness | 黏度viscosity | 平衡度Balance | 食味值 Taste value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 正常 Conventional | nramp5ko-1 | 7.55±0.02 a | 9.35±0.00 d | 75.5±0.5 a | 6.1±0.1 a | 7.3±0.1 d | 7.3±0.1 e | 74.6±0.9 de |
| nramp5ko-2 | 7.24±0.01 b | 9.87±0.00 c | 75.5±0.5 a | 5.8±0.0 c | 7.9±0.3 abc | 7.9±0.2 bcd | 77.9±1.4 bcd | |
| WT | 6.82±0.01 c | 10.20±0.04 b | 77.5±0.5 a | 5.6±0.0 d | 8.4±0.1 a | 8.4±0.1 a | 81.4±0.8 a | |
| 锌肥 +Zn | nramp5ko-1 | 7.30±0.00 b | 10.38±0.00 ab | 77.5±0.5 a | 5.9±0.1 bc | 8.2±0.2 ab | 8.2±0.3 ab | 79.8±1.9 ab |
| nramp5ko-2 | 7.47±0.02 a | 10.60±0.08 a | 77.0±1.0 a | 5.9±0.1 bc | 8.1±0.2 ab | 8.0±0.1 abc | 78.5±1.0 abc | |
| WT | 6.89±0.04 c | 10.72±0.18 a | 78.5±0.5 a | 5.8±0.1 c | 7.7±0.3 bcd | 7.8±0.2 bcde | 77.3±1.7 bcde | |
| 硒肥 +Se | nramp5ko-1 | 7.22±0.04 b | 10.42±0.11 ab | 69.0±1.0 b | 6.0±0.2 ab | 7.4±0.5 cd | 7.4±0.5 de | 75.2±3.0 de |
| nramp5ko-2 | 7.27±0.04 b | 10.53±0.15 ab | 69.5±1.5 b | 6.1±0.0 a | 7.4±0.2 cd | 7.3±0.1 e | 74.4±0.7 e | |
| WT | 7.25±0.02 b | 10.42±0.04 ab | 69.0±1.0 b | 5.9±0.0 bc | 7.5±0.1 cd | 7.5±0.0 cde | 75.8±0.2 cde |
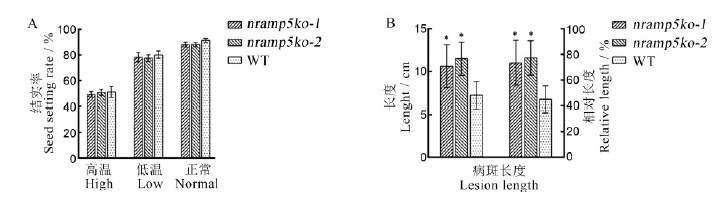
Fig 6. Stress resistance difference between OsNramp5 knockout lines and wild-type under extreme high and low temperature and rice sheath blight inoculation. A, Seed setting rate of knockout lines and wild type under extreme high and low temperature stress; B, Incidence of rice sheath blight of knockout lines and wild type after inoculation in vitro. Data are shown as means ± SD(n=3). * represents a significant difference from WT(P<0.05) (t-test).
| [1] | 陈璐, 刘黎瑶, 丛方地. 我国粮食安全的挑战性问题分析及应对策略探讨[J]. 粮油与饲料科技, 2021(6): 1-5. |
| Chen L, Liu L Y, Cong F D. Analysis on the challenging problems of China’s food security and discussion on the countermeasures[J]. Grain Oil and Feed Technology, 2021(6): 1-5. (in Chinese) | |
| [2] | 徐春春, 纪龙, 陈中督, 方福平. 2020年我国水稻产业形势分析及2021年展望[J]. 中国稻米, 2021, 27(2): 1-4. |
| Xu C C, Ji L, Chen Z D, Fang F P. Analysis of China’s rice industry in 2020 and the outlook for 2021[J]. China Rice, 2021, 27(2): 1-4. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 陈印军, 方琳娜, 杨俊彦. 我国农田土壤污染状况及防治对策[J]. 中国农业资源与区划, 2014, 35(4): 1-5. |
| Chen Y J, Fang L N, Yang J Y. The cropland pollution in China: Status and countermeaures[J]. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning, 2014, 35(4): 1-5. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 周启星, 宋玉芳. 污染土壤修复原理与方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2004. |
| Zhou Q X, Song Y F. Principles and Methods of Contaminated Soil Remediation[M]. Beijing: China Science Press, 2004. (in Chinese) | |
| [5] | 宋伟, 陈百明, 刘琳. 中国耕地土壤重金属污染概况[J]. 水土保持研究, 2013, 20(2): 293-298. |
| Song W, Chen B M, Liu L. Soil heavey meatal pollution of cultivated land in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning, 2013, 20(2): 293-298. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 蔡美芳, 李开明, 谢丹平, 吴仁人. 我国耕地土壤重金属污染现状与防治对策研究[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2014, 37(S2): 223-230. |
| Cai M F, Li K M, Xie D P, Wu R R. The status and protection strategy of farmland soils polluted by heavy metals[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 37(S2): 223-230. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | Bertin G, Averbeck D. Cadmium: Cellular effects, modifications of biomolecules, modulation of DNA repair and genotoxic consequences[J]. Biochimie, 2006, 88(11): 1549-1559. |
| [8] | Nawrot T, Plusquin M, Hogervorst J, Roels H A, Staessen J A. Environmental exposure to cadmium and risk of cancer: A prospective population-based study[J]. Lancet Oncology, 2006, 7(2): 119-126. |
| [9] | Kumar S, Sharma A. Cadmium toxicity: Effects on human reproduction and fertility[J]. Reviews on Environmental Health, 2019, 34(4): 327-338. |
| [10] | Genchi G, Sinicropi M S, Lauria G, Carocci A, Catalano A. The effects of cadmium toxicity[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2020, 17(11): 3782. |
| [11] | Codex Alimentarius Commission, Joint FAO. Codex Alimentarius Commission: Procedural Manual[M]. Codex Alimentarius, 2007. |
| [12] | 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会, 国家食品药品监督管理总局.食品安全国家标准食品中污染物限量:GB 2762-2017[Z]. 2017: 24. |
| State Health and Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China, State Food and Drug Administration.National Food Safety Standard Limit of Pollutants in Food:GB 2762-2017[Z]. 2017: 24. (in Chinese) | |
| [13] | Colangelo E P, Guerinot M L. Put the metal to the petal: metal uptake and transport throughout plants[J]. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2006, 9(3): 322-330. |
| [14] | Xia J, Yamaji N, Kasai T, Jian F M. Plasma membrane-localized transporter for aluminum in rice[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2010, 107(43): 18381-18385. |
| [15] | Nevo Y, Nelson N. The NRAMP family of metal-ion transporters[J]. Molecular Cell Research, 2006, 1763(7): 609-620. |
| [16] | Akimasa S, Naoki Y, Kengo Y, Feng M J. Nramp5 is a major transporter responsible for manganese and cadmium uptake in rice[J]. The Plant Cell, 2012, 24(5): 2155-2167. |
| [17] | Ishimaru Y, Takahashi R, Bashir K, Shimo H, Nishizawa N K. Characterizing the role of rice NRAMP5 in manganese, iron and cadmium transport[J]. Scientific Reports, 2012, 2(6071): 286. |
| [18] | Ishimaru Y, Bashir K, Nakanishi H, Nishizawa N K. OsNRAMP5, a major player for constitutive iron and manganese uptake in rice[J]. Plant Signaling & Behavior, 2012, 7(7): 763-766. |
| [19] | Ishikawa S, Ishimaru Y, Igura M, Kuramata M, Abe T, Senoura T, Hase Y, Arao T, Nishizawa N K, Nakanishi H. Ion-beam irradiation, gene identification, and marker-assisted breeding in the development of low-cadmium rice[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2012, 109(47): 19166-19171. |
| [20] | Ryuichi T, Yasuhiro I, Hugo S, Khurram B, Takeshi S, Kazuhiko S, Kazuko O, Nobuo S, Naoki K, Satomi I. From laboratory to field: OsNRAMP5-knockdown rice is a promising candidate for Cd phytoremediation in paddy fields[J]. PloS ONE, 2014, 9(6): e98816. |
| [21] | Wang T K, Li Y X, Fu Y F. Mutation at different sites of metal transporter gene OsNramp5 affects Cd accumulation and related agronomic traits in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2019, 10: 1081-1092. |
| [22] | Tang L, Mao B G, Li Y K, Lv Q M, Zhang L P, Chen C Y, He H J, Wang W P, Zeng X F, Shao Y, Pan Y L, Hu Y Y, Peng Y, Li H Q, Xia S T, Zhao B R. Knockout of OsNramp5 using the CRISPR/Cas9 system produces low Cd-accumulating indica rice without compromising yield[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 14438. |
| [23] | 吕爱清, 罗天相, 刘沐生. 隐性饥饿的研究现状与应对策略[J]. 中国食物与营养, 2017, 23(6): 5-8. |
| Lü A Q, Luo T X, Liu M S. Research advancements and coping strategies on hidden hunger[J]. Food and Nutrition in China, 2017, 23(6): 5-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | Guilbert J J. The world health report 2002: Reducing risks, promoting healthy life[J]. Education for Health, 2003, 16(2): 230. |
| [25] | 中国营养学会. 中国居民膳食营养素参考摄入量[J]. 营养学报, 2001, 23(3): 193-196. |
| Chinese Nutrition Society. Chinese Dietary Reference Intakes, DRIs[J]. Acta Nutrimenta Sinica, 2001, 23(3): 193-196. (in Chinese) | |
| [26] | 梅忠, 王治学, 梅沙, 蒋宙蕾, 梅淑芳, 舒小丽, 吴殿星. 高锌水稻研究进展[J]. 核农学报, 2016, 30(8): 1515-1523. |
| Mei Z, Wang Z X, Mei S, Jiang Z L, Mei S F, Shu X L, Wu D X. Study on rice high in zinc content[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 30(8): 1515-1523. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | Gao J, Liu Y, Huang Y, Lin Z Q, Bañuelos G S, Lam M H W, Yin X. Daily selenium intake in a moderate selenium deficiency area of Suzhou, China[J]. Food Chemistry, 2011, 126(3): 1088-1093. |
| [28] | Rayman M P. Food-chain selenium and human health: Emphasis on intake[J]. British Journal of Nutrition, 2008, 100(2): 254-268. |
| [29] | 李海蓉, 杨林生, 谭见安, 王五一, 侯少范, 李永华, 虞江萍, 韦炳干. 我国地理环境硒缺乏与健康研究进展[J]. 生物技术进展, 2017, 7(5): 381-386. |
| Li H R, Yang L R, Tan J A, Wang W Y, Hou S F, Li Y H, Yu J P, Wei B G. Progress on selenium deficiency in geographical environment and its health impacts in China[J]. Current Biotechnology, 2017, 7(5): 381-386. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | 向敏, 黄鹤春. 功能性稻米研究进展[J]. 湖北农业科学, 2016, 55(12): 2997-3000. |
| Xiang M, Huang H C. Progress of functional rice research[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 55(12): 2997-3000. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | 胡时开, 胡培松. 功能稻米研究现状与展望[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(4): 311-325. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| Hu S K, Hu P S. Research progress and prospect of functional rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2021, 35(4): 311-325. | |
| [32] | 张云慧, 杜平, 秦晓鹏. 不同浓度锌处理下水稻幼苗对镉的累积效应[J]. 环境科学研究, 2020, 33(3): 761-768. |
| Zhang Y H, Du P, Qin X P. Accumulation of cadmium in rice seedlings after treatment with different concentrations of zinc[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2020, 33(3): 761-768. (in Chinese) | |
| [33] | 李小秀, 吕启明, 袁定阳. OsNramp5基因变异影响水稻重要农艺性状的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(6): 562-571. |
| Li X X, Lü Q M, Yuan D Y. Research progress on the effects of OsNramp5 mutation on important agronomic traits in rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2022, 36(6): 562-571. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [34] | 梁欢婷, 何冰, 顾明华, 王学礼, 吕梦婷, 韦燕燕. 施硒对镉污染稻米中镉,硒含量的影响及其膳食风险评估[J]. 食品工业, 2021, 42(3): 331-335. |
| Liang H T, He B, Gu M H, Wang X L, Lü M T, Wei Y Y. Foliar selenium application on the concentrations of selenium and cadmium in rice grain and health risk assessment[J]. The Food Industry, 2021, 42(3): 331-335. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [35] | 刘永贤, 潘丽萍, 黄雁飞, 农梦玲, 鹿士杨, 赵于莹, 梁潘霞, 熊柳梅, 李科冰, 兰秀. 外源喷施硒与硅对水稻籽粒镉累积的影响[J]. 西南农业学报, 2017, 30(7): 1588-1592. |
| Liu Y X, Pan L P, Huang Y F, Nong M L, Lu S Y, Zhao Y Y, Liang P X, Xiong L M, Li K B, Lan X. Effects of selenium or silicon foliar fertilizer on cadmium accumulation in rice[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 30(7): 1588-1592. (in Chinese with English abstract)1 | |
| [36] | Huang QQ, Liu YY,Qin X,Zhao LJ,Liang XF,Xu YM. Selenite mitigates cadmium-induced oxidative stress and affects Cd uptake in rice seedlings under different water management systems[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 168: 486-494. |
| [37] | 王才林, 张亚东, 陈涛, 朱镇, 赵庆勇, 姚姝, 赵凌, 赵春芳, 周丽慧, 魏晓东, 路凯, 梁文化. 姊妹系间杂交快速培育优良食味半糯粳稻新品种的育种效果[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35 (5): 455-465. |
| Wang C L, Zhang Y D, Chen T, Zhu Z, Zhao Q Y, Yao S, Zhao L, Zhao C F, Zhou L H, Wei X D, Lu K, Liao W H. Rapid breeding of new semi-glutinous japonica rice varieties with good eating quality by crossing between sister lines[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2021, 35 (5): 455-465. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [38] | 王才林, 张亚东, 陈涛, 朱镇, 赵庆勇, 赵春芳, 姚姝, 周丽慧, 赵凌, 魏晓东, 路凯, 梁文化. 地点和播期对半糯粳稻食味品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35 (4): 373-382. |
| Wang C L, Zhang Y D, Chen T, Zhu Z, Zhao Q Y, Zhao C F, Yao S, Zhou L H, Zhao L, Wei X D, Lu K, Liao W H. Effect of location and sowing date on eating quality of semi-waxy japonica rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2021, 35(4): 373-382. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [39] | Miao J, Guo D S, Zhang J Z, Huang Q P, Qin G J, Zhang X, Wan J M, Gu H Y, Qu L J. Targeted mutagenesis in rice using CRISPR-Cas system[J]. Cell Research, 2013, 23(10): 1233-1236. |
| [40] | 王广达, 高鹏, 杨文艳, 崔傲, 赵剑华, 冯志明, 曹文磊, 陈宗祥, 左示敏. 金粳818抗咪唑啉酮类除草剂基因的功能标记开发与应用[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(4): 316-324. |
| Wang G D, Gao P, Yang W Y, Cui A, Zhao J H, Feng Z M, Cao W L, Chen Z X, Zuo S M. Development and utilization of functional markers for imidazolinone herbicides resistance gene in japonica rice variety Jinjing 818[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2020, 34(4): 316-324. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [41] | 贺闽, 尹俊杰, 冯志明, 朱孝波, 赵剑华, 左示敏, 陈学伟. 水稻稻瘟病和纹枯病抗性鉴定方法[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(5): 577-587. |
| He M, Yin J J, Feng Z M, Zhu X B, Zhao J H, Zuo S M, Chen X W. Methods for evaluation of rice resistance to blast and sheath blight diseases[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55(5): 577-587. (in Chinese) | |
| [42] | 董家瑜, 吴天昊, 孙远涛, 何含杰, 李曜魁, 彭彦, 冀中英, 孟前程, 赵炳然, 唐丽. 不同锰浓度环境下OsNRAMP5突变对水稻耐热性和主要经济性状的影响[J]. 杂交水稻, 2021, 36(2): 79-88. |
| Dong J Y, Wu T H, Sun Y T, He H J, Li Y K, Peng Y, Ji Z Y, Meng Q C, Zhao B R, Tang L. Effects of OsNRAMP5 mutation on heat tolerance and main economic traits of rice under the conditions of different manganese concentration[J]. Hybrid Rice, 2021, 36(2): 79-88. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [43] | 龙起樟, 黄永兰, 唐秀英, 王会民, 芦明, 袁林峰, 万建林. 利用CRISPR/Cas9敲除OsNramp5基因创制低镉籼稻[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(5): 407-420. |
| Long Q Z, Huang Y L, Tang X Y, Wang H M, Lu M, Yuan L F, Wan J L. Creation of low-Cd-accumulating indica rice by disruption of OsNramp5 gene via CRISPR/Cas9[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2019, 33(5): 407-420. | |
| [44] | Gashu D, Nalivata P C, Amede T, Ander E L, Bailey E H, Botoman L, Chagumaira C, Gameda S, Haefele S M, Hailu K, Joy E J M, Kalimbira A A, Kumssa D B, Lark R M, Ligowe I S, Towett E K, Walsh M G, Wilson L, Young S D, Broadley M R. The nutritional quality of cereals varies geospatially in Ethiopia and Malawi[J]. Nature, 2021, 594: 71-76. |
| [1] |
HE Yong, LIU Yaowei, XIONG Xiang, ZHU Danchen, WANG Aiqun, MA Lana, WANG Tingbao, ZHANG Jian, LI Jianxiong, TIAN Zhihong.
Creation of Rice Grain Size Mutants by Editing OsOFP30 via CRISPR/Cas9 System [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(5): 507-515. |
| [2] |
JIANG Peng, ZHANG Lin, ZHOU Xingbing, GUO Xiaoyi, ZHU Yongchuan, LIU Mao, GUO Chanchun, XIONG Hong, XU Fuxian.
Yield Formation Characteristics of Ratooning Hybrid Rice Under Simplified Cultivation Practices in Winter Paddy Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(5): 544-554. |
| [3] | WEI Huanhe, MA Weiyi, ZUO Boyuan, WANG Lulu, ZHU Wang, GENG Xiaoyu, ZHANG Xiang, MENG Tianyao, CHEN Yinglong, GAO Pinglei, XU Ke, HUO Zhongyang, DAI Qigen. Research Progress in the Effect of Salinity, Drought, and Their Combined Stresses on Rice Yield and Quality Formation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [4] | ZHAO Yiting, XIE Keran, GAO Ti, CUI Kehui. Effects of Drought Priming During Tillering Stage on Panicle Development and Yield Formation Under High Temperature During Panicle Initiation Stage in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 277-289. |
| [5] | LIANG Chuyan, WU Mingming, HUANG Fengming, ZHAI Rongrong, YE Jing, ZHU Guofu, YU Faming, ZHANG Xiaoming, YE Shenghai. Prospects for the Application of Gene Editing and Genomic Selection in Rice Breeding [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(1): 1-12. |
| [6] | JING Xiu, ZHOU Miao, WANG Jing, WANG Yan, WANG Wang, WANG Kai, GUO Baowei, HU Yajie, XING Zhipeng, XU Ke, ZHANG Hongcheng. Effect of Drought Stress on Root Morphology and Leaf Photosynthetic Characteristics of Good Taste japonica Rice from Late Stage of Panicle Differentiation to Early Stage of Grain Filling [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(1): 33-47. |
| [7] | ZHU Wang, ZHANG Xiang, GENG Xiaoyu, ZHANG Zhe, CHEN Yinglong, WEI Huanhe, DAI Qigen, XU Ke, ZHU Guanglong, ZHOU Guisheng, MENG Tianyao. Morphological and Physiological Characteristics of Rice Roots Under Combined Salinity-Drought Stress and Their Relationships with Yield Formation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(6): 617-627. |
| [8] | LI Gang, GAO Qingsong, LI Wei, ZHANG Wenxia, WANG Jian, CHEN Baoshan, WANG Di, GAO Hao, XU Weijun, CHEN Hongqi, JI Jianhui. Directed Knockout of SD1 Gene Improves Lodging Resistance and Blast Resistance of Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(4): 359-367. |
| [9] | HUANG Yaru, XU Peng, WANG Lele, HE Yizhe, WANG Hui, KE Jian, HE Haibing, WU Liquan, YOU Cuicui. Effects of Exogenous Trehalose on Grain Filling Characteristics and Yield Formation of japonica Rice Cultivar W1844 [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(4): 379-391. |
| [10] | WANG Yu, SUN Quanyi, DU Haibo, XU Zhiwen, WU Keting, YIN Li, FENG Zhiming, HU Keming, CHEN Zongxiang, ZUO Shimin. Improvement of the Resistance of Nanjing 9108 to Blast and Sheath Blight by Pyramiding Resistance Gene Pigm and Quantitative Trait Genes qSB-9TQ and qSB-11HJX [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(2): 125-132. |
| [11] | CHEN Tao, ZHAO Qingyong, ZHU Zhen, ZHAO Ling, YAO Shu, ZHOU Lihui, ZHAO Chunfang, ZHANG Yadong, WANG Cailin. Development of New Low Glutelin Content japonica Rice Lines with Good Eating Quality and Fragrance by Molecular Marker-Assisted Selection [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(1): 55-65. |
| [12] | YANG Taotao, ZOU Jixiang, WU Longmei, BAO Xiaozhe, JIANG Yu, ZHANG Nan, ZHANG Bin. Effect of Free Air Temperature Increase on Grain Quality of Double-cropping Rice in South China [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(1): 66-77. |
| [13] | WANG Yingheng, CHEN Lijuan, CUI Lili, ZHAN Shengwei, SONG Yu, CHEN Shian, XIE Zhenxing, JIANG Zhaowei, WU Fangxi, ZHUO Chuanying, CAI Qiuhua, XIE Huaan, ZHANG Jianfu. Effects of Nitrogen Rate on Photosynthesis, Yield and Grain Quality of Superior Quality Rice “Fuxiangzhan” [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(1): 89-101. |
| [14] | REN Weichen, CHANG Qingxia, ZHANG Yajun, ZHU Kuanyu, WANG Zhiqin, YANG Jianchang. Characteristics and Physiological Mechanism of Carbon and Nitrogen Accumulation and Translocation of japonica Rice Varieties Differing in Nitrogen Use Efficiency [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(6): 586-600. |
| [15] | YIN Liying, ZHANG Yuanye, LI Rongtian, HE Mingliang, WANG Fangquan, XU Yang, LIU Xinxin, PAN Tingting, TIAN Xiaojie, BU Qingyun, LI Xiufeng. Improvement of Herbicide Resistance in Rice by Using CRISPR/Cas9 System [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(5): 459-466. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||