
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2022, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (4): 428-438.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2022.211008
• Research Papers • Previous Articles
WANG Mengjie,#, WU Junnan,#, LIU Yaobin, XU Chunchun, FENG Jinfei, LI Fengbo, FANG Fuping( )
)
Received:2021-10-25
Revised:2022-04-06
Online:2022-07-10
Published:2022-07-12
Contact:
FANG Fuping
王梦杰,#, 吴俊男,#, 刘耀斌, 徐春春, 冯金飞, 李凤博, 方福平( )
)
通讯作者:
方福平
基金资助:WANG Mengjie, WU Junnan, LIU Yaobin, XU Chunchun, FENG Jinfei, LI Fengbo, FANG Fuping. Effect of Feed Protein Contents on Gaseous Nitrogen Emissions, Growth Performance of Catfish and Nitrogen Utilization in Rice-yellow Catfish Co-culture Model[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(4): 428-438.
王梦杰, 吴俊男, 刘耀斌, 徐春春, 冯金飞, 李凤博, 方福平. 饲料蛋白含量对稻-黄颡鱼共作模式气态氮排放、黄颡鱼生长和氮利用率的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(4): 428-438.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2022.211008
| 原料成分 Raw material | 配方目标含量 Formula target content | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 45% | 40% | 35% | 30% | 25% | |
| 豆粕Soybean meal/g | 24.00 | 25.00 | 22.00 | 18.00 | 24.00 |
| 鱼粉Fish meal/g | 49.00 | 39.00 | 31.00 | 24.00 | 12.00 |
| 小麦粉Wheat flour/g | 9.00 | 14.00 | 17.00 | 27.00 | 38.00 |
| 麦麸 Wheat bran/g | 10.00 | 14.00 | 21.00 | 22.00 | 17.00 |
| 微晶纤维素Microcrystallie cellulose/g | 1.50 | 1.50 | 1.50 | 1.50 | 1.50 |
| 菜籽油 Rapeseed oil/g | 1.00 | 1.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 |
| 卵磷脂Lecthin/g | 4.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 |
| 抗氧化剂Antioxidants/g | 1.50 | 1.50 | 1.50 | 1.50 | 1.50 |
| 总计Total/g | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| 粗蛋白含量Crude protein content/% | 45.16 | 39.38 | 34.15 | 31.52 | 26.73 |
| 粗脂肪含量Crude fat content/% | 9.75 | 9.66 | 9.75 | 9.75 | 8.79 |
| 总能量Total energy/(kJ·g−1) | 22.37 | 20.51 | 19.12 | 18.17 | 15.80 |
Table 1. Feed formula and raw material ratio (dry weight).
| 原料成分 Raw material | 配方目标含量 Formula target content | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 45% | 40% | 35% | 30% | 25% | |
| 豆粕Soybean meal/g | 24.00 | 25.00 | 22.00 | 18.00 | 24.00 |
| 鱼粉Fish meal/g | 49.00 | 39.00 | 31.00 | 24.00 | 12.00 |
| 小麦粉Wheat flour/g | 9.00 | 14.00 | 17.00 | 27.00 | 38.00 |
| 麦麸 Wheat bran/g | 10.00 | 14.00 | 21.00 | 22.00 | 17.00 |
| 微晶纤维素Microcrystallie cellulose/g | 1.50 | 1.50 | 1.50 | 1.50 | 1.50 |
| 菜籽油 Rapeseed oil/g | 1.00 | 1.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 |
| 卵磷脂Lecthin/g | 4.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 |
| 抗氧化剂Antioxidants/g | 1.50 | 1.50 | 1.50 | 1.50 | 1.50 |
| 总计Total/g | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| 粗蛋白含量Crude protein content/% | 45.16 | 39.38 | 34.15 | 31.52 | 26.73 |
| 粗脂肪含量Crude fat content/% | 9.75 | 9.66 | 9.75 | 9.75 | 8.79 |
| 总能量Total energy/(kJ·g−1) | 22.37 | 20.51 | 19.12 | 18.17 | 15.80 |
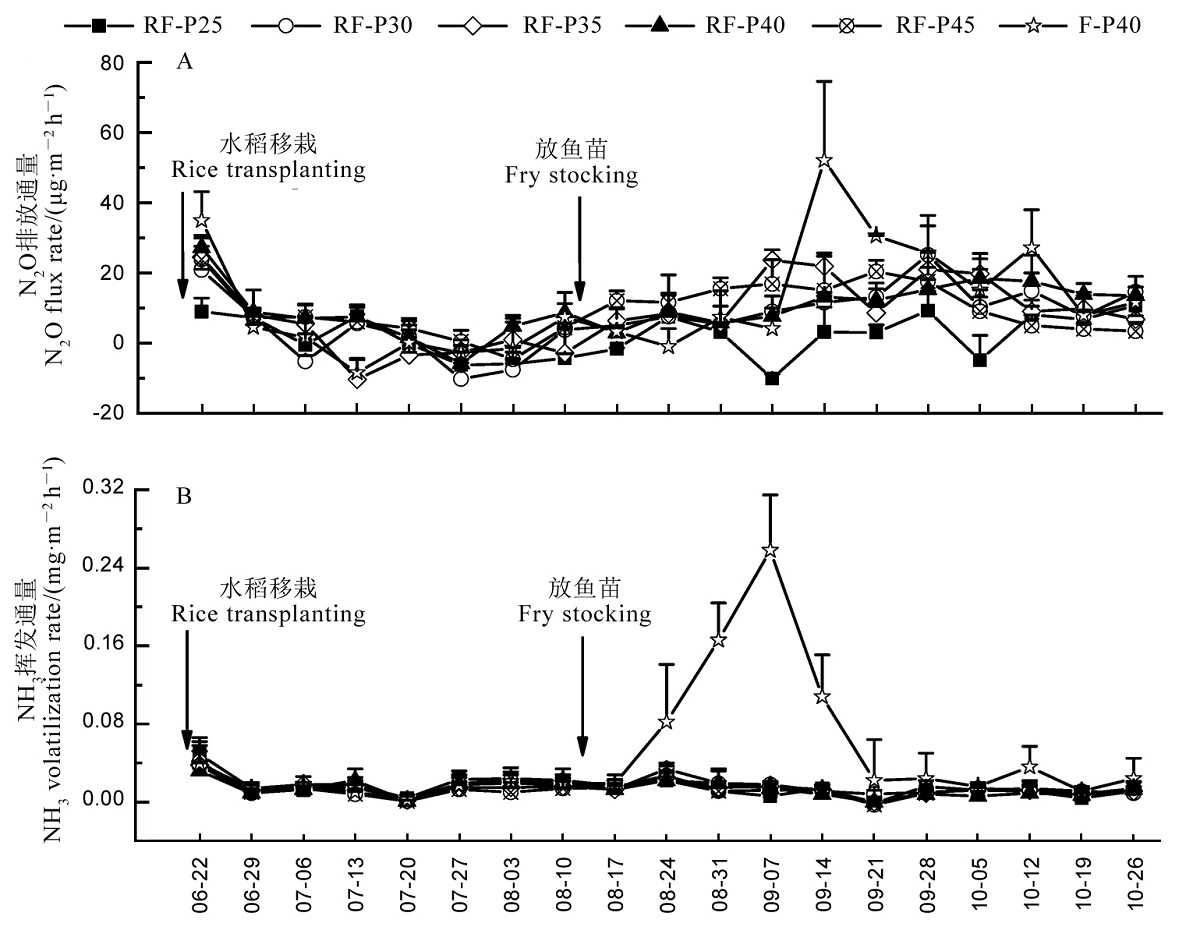
Fig. 1. Dynamics of N2O (A) and NH3 (B) flux rates under different treatments during the experimental periods. RF, Rice-yellow catfish co-culture treatment; F, Yellow catfish monoculture treatment; P25, Protein content in the feed is 25%; P30, Protein content in the feed is 30%; P35, Protein content in the feed is 35%; P40, Protein content in the feed is 40%; P45, Protein content in the feed is 45%.
| 处理 Treatment | TN /(mg∙L−1) | NH4+-N /(mg∙L−1) | NO3−-N /(mg∙L−1) | NO2−-N /(mg∙L−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RF-P25 | 4.31±0.22 e | 0.58±0.07 c | 1.91±0.15 e | 0.17±0.02 c |
| RF-P30 | 5.67±0.15 d | 2.04±0.51 b | 2.36±0.17 d | 0.21±0.03 c |
| RF-P35 | 6.08±0.48 cd | 2.53±0.56 b | 2.72±0.08 c | 0.28±0.03 b |
| RF-P40 | 6.61±0.1 c | 2.64±0.26 b | 3.27±0.09 b | 0.30±0.02 b |
| RF-P45 | 7.24±0.33 b | 2.87±0.22 b | 3.47±0.12 b | 0.31±0.02 b |
| F-P40 | 11.26±0.54 a | 5.95±1.16 a | 3.68±0.03 a | 0.56±0.07 a |
| F值F value | 142.09** | 27.70** | 106.15** | 49.72** |
Table 2. Average concentrations of total and inorganic nitrogen in water of each treatment.
| 处理 Treatment | TN /(mg∙L−1) | NH4+-N /(mg∙L−1) | NO3−-N /(mg∙L−1) | NO2−-N /(mg∙L−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RF-P25 | 4.31±0.22 e | 0.58±0.07 c | 1.91±0.15 e | 0.17±0.02 c |
| RF-P30 | 5.67±0.15 d | 2.04±0.51 b | 2.36±0.17 d | 0.21±0.03 c |
| RF-P35 | 6.08±0.48 cd | 2.53±0.56 b | 2.72±0.08 c | 0.28±0.03 b |
| RF-P40 | 6.61±0.1 c | 2.64±0.26 b | 3.27±0.09 b | 0.30±0.02 b |
| RF-P45 | 7.24±0.33 b | 2.87±0.22 b | 3.47±0.12 b | 0.31±0.02 b |
| F-P40 | 11.26±0.54 a | 5.95±1.16 a | 3.68±0.03 a | 0.56±0.07 a |
| F值F value | 142.09** | 27.70** | 106.15** | 49.72** |
| 处理 Treatment | TN /(g∙kg−1) | NH4+-N /(mg∙kg−1) | NO3−-N /(mg∙kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| RF-P25 | 1.30±0.01 c | 25.69±0.81 c | 4.42±0.32 a |
| RF-P30 | 1.32±0.01 bc | 27.27±1.75 bc | 4.12±0.17 ab |
| RF-P35 | 1.30±0.01 c | 29.22±0.76 b | 4.00±0.09 b |
| RF-P40 | 1.31±0.02 bc | 29.18±0.64 b | 4.39±0.04 a |
| RF-P45 | 1.35±0.01 a | 28.66±1.14 b | 4.41±0.18 a |
| F-P40 | 1.33±0.01 ab | 45.27±0.87 a | 3.40±0.10 c |
| F值F value | 7.00** | 137.156** | 15.334** |
Table 3. Average contents of total nitrogen, ammonia nitrogen and nitrate nitrogen in soil.
| 处理 Treatment | TN /(g∙kg−1) | NH4+-N /(mg∙kg−1) | NO3−-N /(mg∙kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| RF-P25 | 1.30±0.01 c | 25.69±0.81 c | 4.42±0.32 a |
| RF-P30 | 1.32±0.01 bc | 27.27±1.75 bc | 4.12±0.17 ab |
| RF-P35 | 1.30±0.01 c | 29.22±0.76 b | 4.00±0.09 b |
| RF-P40 | 1.31±0.02 bc | 29.18±0.64 b | 4.39±0.04 a |
| RF-P45 | 1.35±0.01 a | 28.66±1.14 b | 4.41±0.18 a |
| F-P40 | 1.33±0.01 ab | 45.27±0.87 a | 3.40±0.10 c |
| F值F value | 7.00** | 137.156** | 15.334** |
| 环境参数 Environmental parameter | N2O排放通量 N2O flux | NH3挥发通量NH3 flux | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 稻-黄颡鱼共作RF | 黄颡鱼单养F | 稻-黄颡鱼共作RF | 黄颡鱼单养F | |||
| 水体环境 Water environment | NH4+ | 0.450 | 0.666** | −0.329 | 0.458** | |
| NO3− | 0.593** | 0.513** | −0.357 | −0.178 | ||
| NO2− | 0.370 | 0.722** | 0.163 | 0.040 | ||
| TOC | 0.675** | 0.559** | −0.230 | 0.430** | ||
| DO | −0.534* | −0.213 | −0.267 | −0.286* | ||
| pH | −0.589** | −0.593** | 0.226 | −0.076 | ||
| 底泥环境 Mud environment | NH4+ | 0.049 | 0.389 | 0.168 | 0.363 | |
| NO3− | −0.036 | 0.129 | −0.153 | 0.247 | ||
| pH | −0.096 | −0.513 | 0.283 | −0.572* | ||
Table 4. Correlation analysis of N2O and NH3 flux rates and the parameters of water and bottom soil (n=18).
| 环境参数 Environmental parameter | N2O排放通量 N2O flux | NH3挥发通量NH3 flux | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 稻-黄颡鱼共作RF | 黄颡鱼单养F | 稻-黄颡鱼共作RF | 黄颡鱼单养F | |||
| 水体环境 Water environment | NH4+ | 0.450 | 0.666** | −0.329 | 0.458** | |
| NO3− | 0.593** | 0.513** | −0.357 | −0.178 | ||
| NO2− | 0.370 | 0.722** | 0.163 | 0.040 | ||
| TOC | 0.675** | 0.559** | −0.230 | 0.430** | ||
| DO | −0.534* | −0.213 | −0.267 | −0.286* | ||
| pH | −0.589** | −0.593** | 0.226 | −0.076 | ||
| 底泥环境 Mud environment | NH4+ | 0.049 | 0.389 | 0.168 | 0.363 | |
| NO3− | −0.036 | 0.129 | −0.153 | 0.247 | ||
| pH | −0.096 | −0.513 | 0.283 | −0.572* | ||
| 处理 Treatment | 产量 Yield | 生长性能 Growth performance | 饲料转化 Feed conversion | 粗蛋白沉积 Crude protein deposition | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HW /(g·m−2) | SR /% | SGR /(%·d−1) | FCR /(kg·kg−1) | FU /% | CPR /% | PG /g | ||||
| RF-P25 | 554.7±28.6 a | 94.4±0.6 a | 0.73±0.03 d | 4.3±0.2 bc | 15.0±2.3 a | 15.0±0.4 c | 1.3±0.2 c | |||
| RF-P30 | 563.2±13.9 a | 95.6±1.4 a | 0.84±0.02 c | 4.1±0.6 ab | 12.4±1.2 b | 15.4±0.6 bc | 1.4±0.1 c | |||
| RF-P35 | 569.1±8.6 a | 93.4±0.9 a | 0.92±0.02 b | 4.6±0.5 a | 10.6±1.3 bc | 16.4±0.7 a | 1.5±0.0 bc | |||
| RF-P40 | 571.5±31.8 a | 96.9±0.6 a | 0.97±0.01 a | 3.2±0.0 c | 9.3±0.9 c | 16.2±0.5 a | 1.8±0.1 a | |||
| RF-P45 | 570.8±27.6 a | 93.3±2.6 a | 0.98±0.01 a | 2.6±0.3 c | 9.2±1.3 c | 16.4±0.4 a | 1.8±0.2 ab | |||
| F-P40 | 559.4±18.8 a | 92.8±2.8 a | 0.98±0.02 a | 2.9±0.8 c | 9.2±0.7 c | 15.3±0.4 c | 1.5±0.0 c | |||
| F值F value | 1.181 | 1.080 | 103.375** | 9.079** | 9.912** | 4.203* | 5.855** | |||
Table 5. Growth performance and feed utilization of yellow catfish fed with different protein content feeds.
| 处理 Treatment | 产量 Yield | 生长性能 Growth performance | 饲料转化 Feed conversion | 粗蛋白沉积 Crude protein deposition | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HW /(g·m−2) | SR /% | SGR /(%·d−1) | FCR /(kg·kg−1) | FU /% | CPR /% | PG /g | ||||
| RF-P25 | 554.7±28.6 a | 94.4±0.6 a | 0.73±0.03 d | 4.3±0.2 bc | 15.0±2.3 a | 15.0±0.4 c | 1.3±0.2 c | |||
| RF-P30 | 563.2±13.9 a | 95.6±1.4 a | 0.84±0.02 c | 4.1±0.6 ab | 12.4±1.2 b | 15.4±0.6 bc | 1.4±0.1 c | |||
| RF-P35 | 569.1±8.6 a | 93.4±0.9 a | 0.92±0.02 b | 4.6±0.5 a | 10.6±1.3 bc | 16.4±0.7 a | 1.5±0.0 bc | |||
| RF-P40 | 571.5±31.8 a | 96.9±0.6 a | 0.97±0.01 a | 3.2±0.0 c | 9.3±0.9 c | 16.2±0.5 a | 1.8±0.1 a | |||
| RF-P45 | 570.8±27.6 a | 93.3±2.6 a | 0.98±0.01 a | 2.6±0.3 c | 9.2±1.3 c | 16.4±0.4 a | 1.8±0.2 ab | |||
| F-P40 | 559.4±18.8 a | 92.8±2.8 a | 0.98±0.02 a | 2.9±0.8 c | 9.2±0.7 c | 15.3±0.4 c | 1.5±0.0 c | |||
| F值F value | 1.181 | 1.080 | 103.375** | 9.079** | 9.912** | 4.203* | 5.855** | |||
| 处理 Treatment | 每桶氮输入 N input per pot/g | 每桶氮收获 N harvest per pot/g | 氮利用率 N utilization/% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 进水 Water flow(N) | 饲料氮 Feed N | 鱼苗 Fry fish | 水稻 Rice | 鱼吸收 Fish harvest | 稻吸收 Rice harvest | |||
| RF-P25 | 14.89 | 86.10 | 17.71 | 0.25 | 12.89 ab | 17.37 a | 24.39 a | |
| RF-P30 | 14.35 | 98.64 | 18.11 | 0.24 | 11.65 b | 14.49 b | 20.38 b | |
| RF-P35 | 14.30 | 111.87 | 18.25 | 0.26 | 11.86 b | 16.86 a | 19.69 bc | |
| RF-P40 | 14.30 | 124.05 | 17.72 | 0.24 | 13.33 a | 17.40 a | 19.66 bc | |
| RF-P45 | 14.54 | 140.96 | 18.02 | 0.23 | 14.39 a | 16.89 a | 17.99 c | |
| F-P40 | 14.77 | 124.05 | 17.93 | 0.25 | 11.37 b | / | 7.24 d | |
Table 6. Nitrogen budget in different treatments.
| 处理 Treatment | 每桶氮输入 N input per pot/g | 每桶氮收获 N harvest per pot/g | 氮利用率 N utilization/% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 进水 Water flow(N) | 饲料氮 Feed N | 鱼苗 Fry fish | 水稻 Rice | 鱼吸收 Fish harvest | 稻吸收 Rice harvest | |||
| RF-P25 | 14.89 | 86.10 | 17.71 | 0.25 | 12.89 ab | 17.37 a | 24.39 a | |
| RF-P30 | 14.35 | 98.64 | 18.11 | 0.24 | 11.65 b | 14.49 b | 20.38 b | |
| RF-P35 | 14.30 | 111.87 | 18.25 | 0.26 | 11.86 b | 16.86 a | 19.69 bc | |
| RF-P40 | 14.30 | 124.05 | 17.72 | 0.24 | 13.33 a | 17.40 a | 19.66 bc | |
| RF-P45 | 14.54 | 140.96 | 18.02 | 0.23 | 14.39 a | 16.89 a | 17.99 c | |
| F-P40 | 14.77 | 124.05 | 17.93 | 0.25 | 11.37 b | / | 7.24 d | |
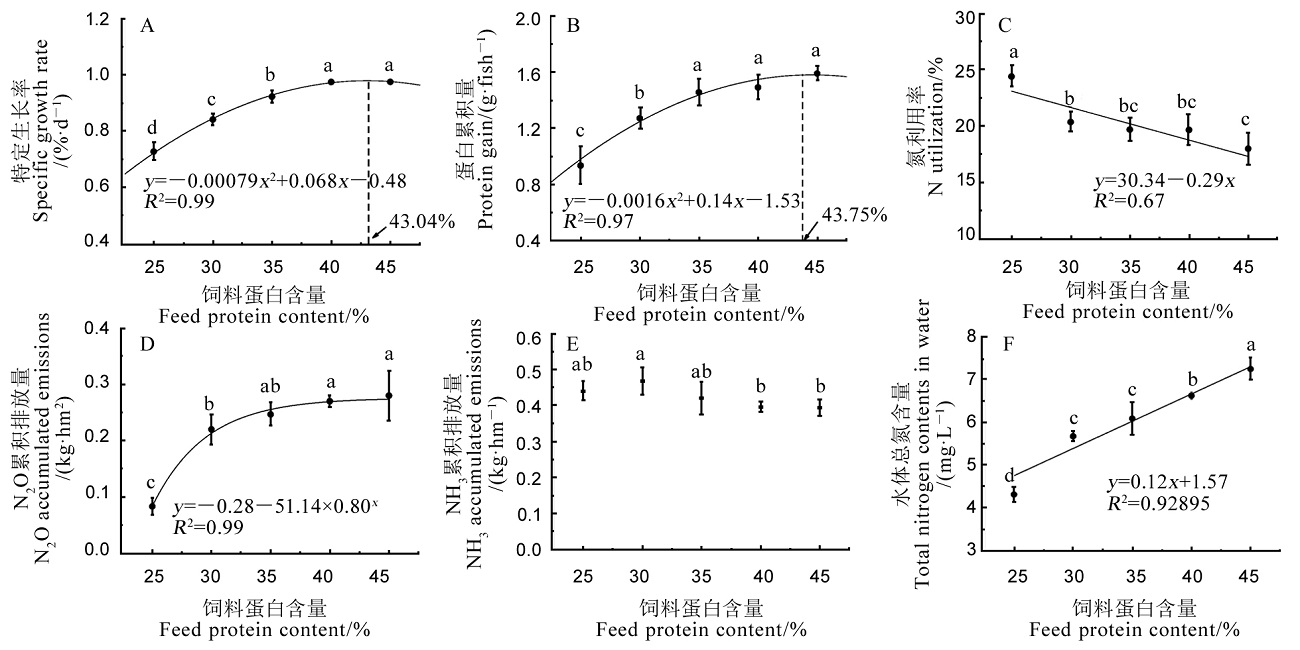
Fig. 4. Fitting analysis of different dietary protein contents and specific growth rate(SGR), protein gain(PG), N utilization, N2O cumulative emission, NH3 cumulative emission and total nitrogen contents in water.
| [1] | 于秀娟, 徐乐俊, 吴反修. 中国渔业统计年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2020: 15-46. |
| Yu X J, Xu L J, Wu F X. China Fishery Statisticai Yearbook[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2020: 15-46. (in Chinese) | |
| [2] | Crab R, Avnimelech Y, Defoirdt T, Bossier P, Verstraete W. Nitrogen removal techniques in aquaculture for a sustainable production[J]. Aquaculture, 2007, 270(1-4): 1-14. |
| [3] | Yuan J, Xiang J, Liu D, Kang H, He T, Kim S, Ding W. Rapid growth in greenhouse gas emissions from the adoption of industrial-scale aquaculture[J]. Nature Climate Change, 2019, 9: 318-322. |
| [4] | 张卫建, 严圣吉, 张俊, 江瑜, 邓艾兴. 国家粮食安全与农业双碳目标的双赢策略[J]. 中国农业科学, 2021, 54(18): 3892-3902. |
| Zhang W J, Yan S J, Zhang J, Jiang Y, Deng A X. Win-Win strategy for national food security and agricultural double-carbon goals[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2021, 54(18): 3892-3902. (in Chinese) | |
| [5] | 李成芳, 曹凑贵, 汪金平, 潘盛刚, 叶成, 叶威. 稻鸭稻鱼共作生态系统中稻田田面水的N素动态变化及淋溶损失[J]. 环境科学学报, 2008, 28(10): 2125-2132. |
| Li C F, Cao C G, Wang J P, Pan S G, Ye C, Ye W. Dynamic variations and losses of N in floodwater of paddy fields in integrated rice-duck and rich-fish ecosystems[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2008, 28 (10): 2125-2132. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | Hu Z, Lee J W, Chandran K, Kim S, Khanal S K. Nitrous oxide (N2O) emission from aquaculture: A review[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2012, 46(12): 6470-6480. |
| [7] | Wei Z, Xia L, Yan X. Vertical distribution of denitrification end-products in paddy soils[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 576(15): 462-471. |
| [8] | 丁维新, 袁俊吉, 刘德燕, 陈增明. 淡水养殖系统温室气体CH4和N2O排放量研究进展[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2020, 39(4): 749-761. |
| Ding W X, Yuan J J, Liu D Y, Chen Z M. CH4 and N2O emissions from freshwater aquaculture[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2020, 39(4): 749-761. (in Chinese) | |
| [9] | Silva-Carrillo Y, Hernández C, Hardy R W, B González-Rodríguez, Castillo-Vargasmachuca S. The effect of substituting fish meal with soybean meal on growth, feed efficiency, body composition and blood chemistry in juvenile spotted rose snapper Lutjanus guttatus (Steindachner, 1869)[J]. Aquaculture, 2012, (364-365): 180-185. |
| [10] | 韩庆, 罗玉双, 夏维福, 王文斌. 不同饲料蛋白源对黄颡鱼生长的影响[J]. 上海海洋大学学报, 2002, 11(3): 259-263. |
| Han Q, Luo Y S, Xia W F, Wang W B. Effects of different protein levels and animal protein percentage on Pelteobagrus fulvidraco[J]. Journal of Shanghai Fisheries University, 2002, 11(3): 259-263. (in Chinese) | |
| [11] | NRC. Nutrient Requirements of Fish and Shrimp[M]. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press, 2011: 221-228, 253-268. |
| [12] | 李香兰, 徐华, 蔡祖聪. 水分管理影响稻田氧化亚氮排放研究进展[J]. 土壤, 2009, 41(1): 1-7. |
| Li X L, Xu H, Cai Z C. Effect of water management on nitrous oxide emission from rice paddy field: A review[J]. Soil, 2009, 41(1): 1-7. (in Chinese) | |
| [13] | 王朝辉, 刘学军, 巨晓棠, 张福锁. 田间土壤氨挥发的原位测定——通气法[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2002, 8(2): 205-209. |
| Wang Z H, Liu X J, Ju X T, Zhang F S. Field in situ determination of ammonia volatilization from soil: Venting method[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2002, 8(2): 205-209. (in Chinese) | |
| [14] | Li F, Feng J, Zhou X, Xu C, Jijakli M H, Zhang W, Fang F. Impact of rice-fish/shrimp co-culture on the N2O emission and NH3volatilization in intensive aquaculture ponds[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 655(3): 284-291. |
| [15] | 杨园园, 高志岭, 王雪君. 有机,无机氮肥施用对苜蓿产量,土壤硝态氮和温室气体排放的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2016, 27(3): 822-828. |
| Yang Y Y, Gao Z L, Wang X J. Impacts of organic and inorganic fertilizations on alfalfa yield,soil nitrate and greenhouse gas emissions[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2016, 27(3): 822-828. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 李成芳, 曹凑贵, 汪金平, 展茗, 袁伟玲, 高超, 潘圣刚. 稻鸭稻鱼共作生态系统N素平衡的研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2008(4): 1326-1334. |
| Li C F, Cao C G, Wang J P, Zhan M, Yuan W L, Gao C, Pan S G. Studies on nitrogen cycling in integrated rice- duck, rice-fish ecosystems[J]. Journal of Agro- Environment Science, 2008(4): 1326-1334. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | Yang P, Tan L S, Huang J F, He Q H, Tong C. Diurnal variations of CH4 and N2O fluxes from the drained aquaculture pond in the Minjiang River Estuary during early winter[J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(1): 300-309. |
| [18] | Sun G, Sun M, Du L S, Zhang L S, Zhang Z, Wang Z C, Zhang G B, Nie S A, Xu H Q, Wang H. Ecological rice-cropping systems mitigate global warming: A meta-analysis[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 789: 147-155. |
| [19] | 刘国锋, 徐跑, 吴霆, 徐增洪, 徐刚春. 中国水产养殖环境氮磷污染现状及未来发展思路[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2018, 34(1): 225-233. |
| Liu G F, Xu P, Wu T, Xu Z H, Xu G C. Present condition of aquaculture nitrogen and phosphorus environmental pollution and future development strategy[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Journal, 2018, 34(1): 225-233. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | Shuang W, Hu Z, Tao H, Jie C, Kai Y, Zou J. Annual methane and nitrous oxide emissions from rice paddies and inland fish aquaculture wetlands in southeast China[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2018, 175: 135-144. |
| [21] | Bouldin D R, Johnson R L, Burda C, Kao C W. Losses of inorganic nitrogen from aquatic systems[J]. Journal of Environmental Quality, 1974, 3(2): 107-114. |
| [22] | Lian Z, Ouyang W, Liu H, Zhang D, Liu L. Ammonia volatilization modeling optimization for rice watersheds under climatic differences[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 765(1): 44-71. |
| [23] | 王昂, 马旭洲, 于永清, 徐静, 吕为群. 北方稻蟹共作系统氨挥发损失的研究[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2018, 30(4): 622-631. |
| Wang A, Ma X Z, Yu Y Q, Xu J, Lü W Q. Ammonia volatilization from rice-crab culture systems in northern China[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2018, 30(4): 622-631. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | Collins S A, Øverland Margareth, Skrede A, Drew M D. Effect of plant protein sources on growth rate in salmonids: Meta-analysis of dietary inclusion of soybean, pea and canola/rapeseed meals and protein concentrates[J]. Aquaculture, 2013(400-401): 85-100. |
| [25] | 李晨晨, 黄文文, 金敏, 朱婷婷, 罗嘉翔, 马红娜, 袁野, 周歧存. 大豆浓缩蛋白替代鱼粉对黄颡鱼生长,饲料利用,消化酶和抗氧化酶活性的影响[J]. 动物营养学报, 2018, 30(1): 375-386. |
| Li C C, Huang W W, Jin M, Zhu T T, Luo J X, Ma H N, Yuan Y, Zhou Q C. Effects of fish meal replacement with soybean protein concentrate on growth performance,feed utilization and digestive enzyme and antioxidant enzyme activities of yellow catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco)[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2018, 30(1): 375-386. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | He J, Feng P, Lv C, Lv M, Wang R. Effect of a fish-rice co-culture system on the growth performance and muscle quality of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus)[J]. Aquaculture Reports, 2020, 17: 1-13. |
| [27] | Zhang J, Zhao N, Zaki S, Li Y, Ma J, Lou Y. Effects of dietary lipid and protein levels on growth and physiological metabolism of Pelteobagrus fulvidraco larvae under recirculating aquaculture system (RAS)[J]. Aquaculture, 2018, 495: 458-464. |
| [28] | Cai Z, Qian X, Xie S. Optimal dietary protein concentrations for largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) of different sizes (10-500g). Aquaculture International, 2020, 28(2): 831-840. |
| [29] | Garling D L, Wilson R P. Optimum dietary protein to energy ratio for channel catfish fingerlings, Ictalurus punctatus[J]. Journal of Nutrition, 1976, 106(9): 1368-1375. |
| [30] | Giri S K, Sahoo B N, Paul S N, Sahu A K. Effect of dietary protein levels on growth, feed utilization and carcass composition of endangered bagrid catfish Horabagrus brachysoma (Gunther 1864) fingerlings[J]. Aquaculture Nutrition, 2011, 17(3): 332-337. |
| [31] | Lee S M, Park C S, Bang I C. Dietary protein requirement of young Japanese flounder Paralichthys olivaceus fed isocaloric diets[J]. Fisheries Science, 2010, 68(1): 158-164. |
| [32] | 陈曦飞, 许洁, 艾春香. 黄颡鱼的营养需求研究与配合饲料研发[J]. 饲料工业, 2011, 32(10): 48-51. |
| Chen X F, Xu J, Ai C X. Research on nutrient requirement of yellow catfish and research and development of compound feed[J]. Feed Industry, 2011, 32(10): 48-51. (in Chinese) |
| [1] | XIAO Lequan, LI Lei, DAI Weimin, QIANG Sheng, SONG Xiaoling. Seedling Growth Characteristics of Hybrids Between Transgenic Rice with cry2A*/bar Genes and Weedy Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(4): 347-358. |
| [2] | LIN Dan, JIANG Min, MIAO Bo, GUO Meng, SHI Chunlin. Research on Simulation Model of High Temperature Stress on Rice and Its Application in Fujian Province [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(3): 307-320. |
| [3] | WANG Xuandong, YU Junjie, GAO Runjie, LAN Heting, JIANG Yingzi, QI Wenjie, SONG Zhen, JIANG Donghua. Streptomyces zaomyceticus Sz-11, a Potential Biocontrol Agent with the Functions of Preventing Plant Diseases and Promoting Plant Growth [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(2): 200-212. |
| [4] | MA Jingjing, PAN Yanyan, YANG Sunyuyue, WANG Jiaqi, JIANG Donghua. Control Effect of St-79 (Streptomyces thioluteus) on Rice Bacterial Blight and Its Growth-promoting Effect [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(6): 623-638. |
| [5] | WANG Yang, ZHANG Rui, LIU Yonghao, LI Rongkai, GE Jianfei, DENG Shiwen, ZHANG Xubin, CHEN Yinglong, WEI Huanhe, DAI Qigen. Rice Response to Salt Stress and Research Progress in Salt Tolerance Mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(2): 105-117. |
| [6] | XU Qingshan, HUANG Jing, SUN Aijun, HONG Xiaozhi, ZHU Lianfeng, CAO Xiaochuang, KONG Yali, JIN Qianyu, ZHU Chunquan, ZHANG Junhua. Effects of Low Temperature on the Growth and Development of Rice Plants and the Advance of Regulation Pathways: A Review [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(2): 118-130. |
| [7] | Mengjia WANG, Min YIN, Guang CHU, Yuanhui LIU, Chunmei XU, Xiufu ZHANG, Danying WANG, Song CHENG. Ecological Differences in Yield, Growth Period and the Utilization of Temperature and Light Resources of Double-cropping Late japonica Rice in the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2021, 35(5): 475-486. |
| [8] | Yuxiang LI, Hairong LIN, Qian LIANG, Guodong WANG. Effects of Dopamine Priming on Seed Germination and Seedling Growth of Rice Under Salt Stress [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2021, 35(5): 487-494. |
| [9] | Yali ZHENG, Linchuang YU, Xiaoxiao AN, Xinle CHENG, Lijun REN, Zilong SU, Xiaoya ZHENG, Tao LAN. Identification of a Knockout Mutant of OsWOX3B Gene in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2021, 35(2): 112-120. |
| [10] | Chunmei XU, Lilun YUAN, Song CHEN, Guang CHU, Weifa YE, Yuhua DING, Danying WANG, Xiufu ZHANG. Difference in Growth Characteristics, Utilization of Temperature and Illumination of Double- Cropping High Quality Late Rice in Different Ecological Regions of the Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2020, 34(5): 457-469. |
| [11] | Guohui HU, Shunqi SONG, Jing XIANG, Defeng ZHU, Huizhe CHEN, Yikai ZHANG, Yaliang WANG, Yicheng XU, Zihao YI, Junke WANG, Yuping ZHANG. Effect of Biodegradable Film Mulching on Growth and Quality of Mechanically Transplanted Rice (Oryza sativa L.) [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2020, 34(2): 159-170. |
| [12] | Qiang XU, Xiaopeng MA, Tingbo LÜ, Dongwang WANG, Meng BAI, Zelin WANG, Jingran NIU. Effects of Different Soil Texture on Root Growth and Distribution of Rice Seedlings Under Drip Irrigation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2019, 33(3): 249-256. |
| [13] | Hui DENG, Zhiguo E, Baixiao NIU, Lei WANG, Chen CHEN. Influence of DNA Methylation Inhibitor 5-Aza-2′-deoxycytidine on DNA Methylation and Seedling Development of Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2019, 33(2): 108-117. |
| [14] | Zhenxing XIE, Junian ZHANG, Qi LIN, Feng LIU, Chuzhang ZHANG, Fangmei ZHUO, Zhaowei JIANG, Chuanying ZHUO. Effect of Plant Growth Regulators on Rice Lodging Resistance and Grain Production of Main-crop and Ratooning Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2019, 33(2): 158-166. |
| [15] | Bing FENG, Yafei SUN, Hao AI, Xiuli LIU, Jing YANG, Lu LIU, Feiyan GAO, Guohua XU, Shubin SUN. Overexpression of Sucrose Transporter OsSUT1 Affects Rice Morphology and Physiology [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2018, 32(6): 549-556. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||