
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2022, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (3): 269-277.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2022.210309
• Research Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
CHEN Yun1,2, LIU Kun1, LI Tingting1, LI Siyu1, LI Guoming2, ZHANG Weiyang1, ZHANG Hao1, GU Junfei1, LIU Lijun1,*( ), YANG Jianchang1
), YANG Jianchang1
Received:2021-03-19
Revised:2021-06-01
Online:2022-05-10
Published:2022-05-11
Contact:
LIU Lijun
陈云1,2, 刘昆1, 李婷婷1, 李思宇1, 李国明2, 张伟杨1, 张耗1, 顾骏飞1, 刘立军1,*( ), 杨建昌1
), 杨建昌1
通讯作者:
刘立军
基金资助:CHEN Yun, LIU Kun, LI Tingting, LI Siyu, LI Guoming, ZHANG Weiyang, ZHANG Hao, GU Junfei, LIU Lijun, YANG Jianchang. Effects of Alternate Wetting and Moderate Soil Drying Irrigation on Root Traits, Grain Yield and Soil Properties in Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(3): 269-277.
陈云, 刘昆, 李婷婷, 李思宇, 李国明, 张伟杨, 张耗, 顾骏飞, 刘立军, 杨建昌. 结实期干湿交替灌溉对水稻根系、产量和土壤的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(3): 269-277.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2022.210309
| 来源 Source of variation | 自由度 df | 产量 Grain yield | 根系干质量 Root dry weight | 根系氧化力 Root oxidation activity | 土壤硝态氮含量 Soil nitrate nitrogen content | 土壤脲酶活性 Soil urease activity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年份 Year (Y) | 1 | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| 处理 Treatment (T) | 1 | 5.2* | 4.9* | 54.4** | 14.8** | 9.8** |
| 年份×处理 Y×T | 1 | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS |
Table 1. Analysis of variance of F-values of grain yield and main root and soil traits.
| 来源 Source of variation | 自由度 df | 产量 Grain yield | 根系干质量 Root dry weight | 根系氧化力 Root oxidation activity | 土壤硝态氮含量 Soil nitrate nitrogen content | 土壤脲酶活性 Soil urease activity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年份 Year (Y) | 1 | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| 处理 Treatment (T) | 1 | 5.2* | 4.9* | 54.4** | 14.8** | 9.8** |
| 年份×处理 Y×T | 1 | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| 品种 Cultivar | 处理 Treatment | 总颖花量 Total spikelets per pot | 结实率 Seed-setting rate/% | 千粒重 1000-grain weight/g | 产量 Grain yield/(g·pot-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 扬稻6号YD6 | CI | 3450.9 a | 89.1 b | 29.5 b | 90.8 b |
| WMD | 3541.3 a | 92.2 a | 30.1 a | 98.2 a | |
| 南粳9108 NJ9108 | CI | 4189.4 a | 87.3 b | 24.1 a | 88.0 b |
| WMD | 4228.8 a | 90.9 a | 24.6 a | 94.6 a | |
| 扬两优6号YLY6 | CI | 4018.2 a | 87.4 b | 28.7 a | 100.8 b |
| WMD | 4156.6 a | 90.7 a | 29.2 a | 110.0 a | |
| 常优5号CY5 | CI | 4326.8 a | 86.3 b | 24.8 a | 92.4 b |
| WMD | 4416.7 a | 89.6 a | 25.3 a | 100.0 a | |
| 甬优2640 YY2640 | CI | 5468.3 a | 80.9 b | 23.4 b | 103.4 b |
| WMD | 5534.4 a | 84.5 a | 24.1 a | 112.4 a |
Table 2. Effect of WMD during the grain filling stage on rice yield and its components.
| 品种 Cultivar | 处理 Treatment | 总颖花量 Total spikelets per pot | 结实率 Seed-setting rate/% | 千粒重 1000-grain weight/g | 产量 Grain yield/(g·pot-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 扬稻6号YD6 | CI | 3450.9 a | 89.1 b | 29.5 b | 90.8 b |
| WMD | 3541.3 a | 92.2 a | 30.1 a | 98.2 a | |
| 南粳9108 NJ9108 | CI | 4189.4 a | 87.3 b | 24.1 a | 88.0 b |
| WMD | 4228.8 a | 90.9 a | 24.6 a | 94.6 a | |
| 扬两优6号YLY6 | CI | 4018.2 a | 87.4 b | 28.7 a | 100.8 b |
| WMD | 4156.6 a | 90.7 a | 29.2 a | 110.0 a | |
| 常优5号CY5 | CI | 4326.8 a | 86.3 b | 24.8 a | 92.4 b |
| WMD | 4416.7 a | 89.6 a | 25.3 a | 100.0 a | |
| 甬优2640 YY2640 | CI | 5468.3 a | 80.9 b | 23.4 b | 103.4 b |
| WMD | 5534.4 a | 84.5 a | 24.1 a | 112.4 a |
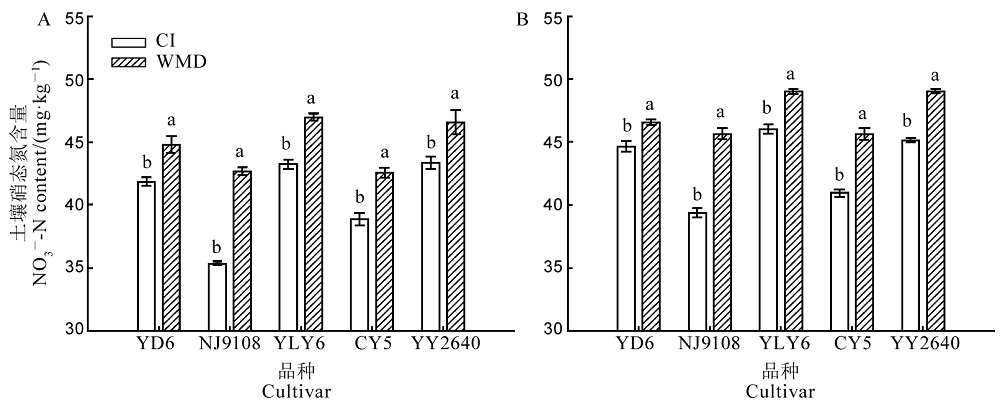
Fig. 1. Nitrate nitrogen contents in rice rhizosphere (A) and non-rhizosphere (B) soils after rewatering in WMD during the grain filling stage. YD6, Yangdao 6; NJ9108, Nanjing 9108; YLY6, Yangliangyou 6; CY5, Changyou 5; YY2640, Yongyou 2640. CI, Continuously flooded irrigation; WMD, Alternate wetting and moderate soil drying irrigation. For a variety, different lowercase letters above the column indicate statistical significance at the P = 0.05 level.
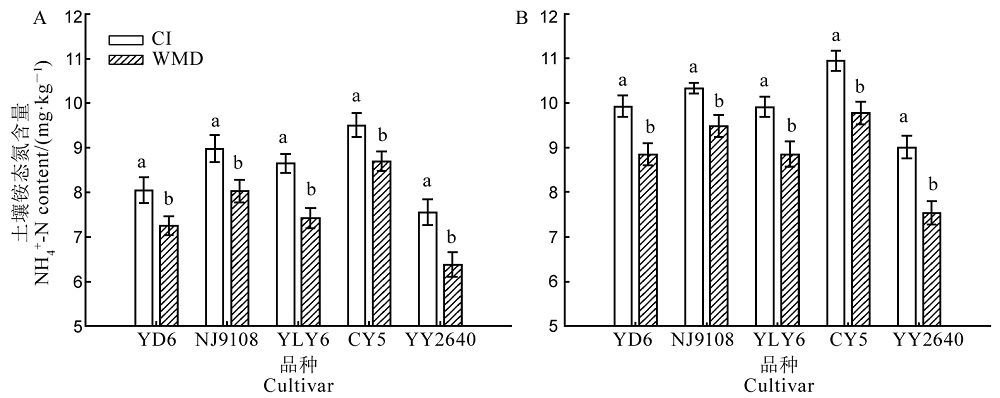
Fig. 2. Ammonium nitrogen contents in rice rhizosphere (A) and non-rhizosphere (B) soils after rewatering in WMD during the grain filling stage. YD6, Yangdao 6; NJ9108, Nanjing 9108; YLY6, Yangliangyou 6; CY5, Changyou 5; YY2640, Yongyou 2640. CI, Continuously flooded irrigation; WMD, Alternate wetting and moderate soil drying irrigation. For a variety, different letters above the column indicate statistical significance at the P = 0.05 level.
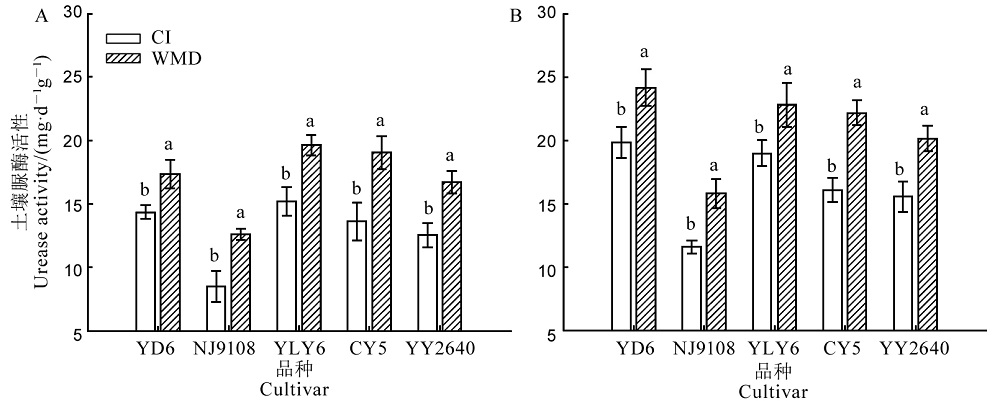
Fig. 3. Urease activities in rice rhizosphere (A) and non-rhizosphere (B) soils after rewatering in WMD during the grain filling stage. YD 6, Yangdao 6; NJ 9108, Nanjing 9108; YLY 6, Yangliangyou 6; CY 5, Changyou 5; YY2640, Yongyou 2640. CI, Continuously flooded irrigation; WMD, Alternate wetting and moderate soil drying irrigation. For variety, different lowercase letters above the column indicate statistical significance at the P = 0.05 level.
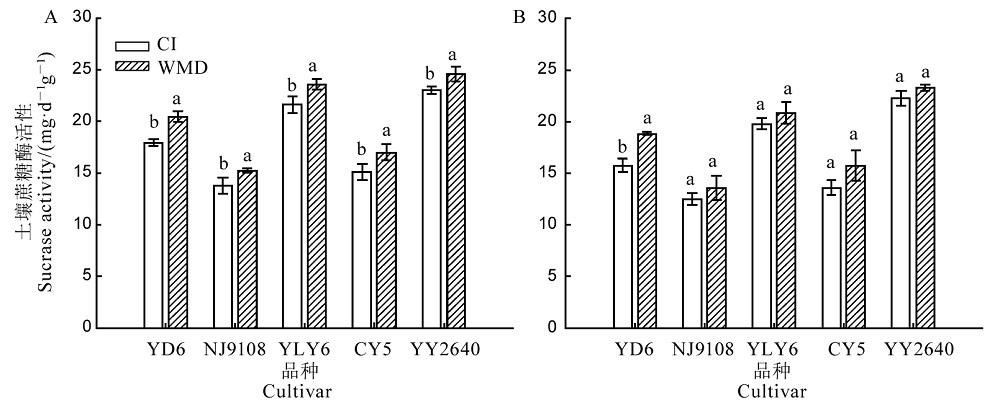
Fig. 4. Sucrase activities in rice rhizosphere (A) and non-rhizosphere (B) soils after rewatering in WMD during the grain filling stage. YD 6, Yangdao 6; NJ 9108, Nanjing 9108; YLY 6, Yangliangyou 6; CY 5, Changyou 5; YY2640, Yongyou 2640. CI, Continuously flooded irrigation; WMD, Alternate wetting and moderate soil drying irrigation. For variety, different lowercase letters above the column indicate statistical significance at 0.05 level.
| 品种 Cultivar | 处理 Treatment | 根干质量 Root dry weight /(g·pot-1) | 根冠比 Root-shoot ratio | 根数 Root number /(×100·pot-1) | 根长 Root length /(m·pot-1) | 根表面积 Root surface /(cm2·pot-1) | 根系直径 Root diameter /mm | 根体积 Root volume /(cm3·pot-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 扬稻6号 | CI | 25.5 b | 0.23 a | 20.0 b | 876.9 b | 9 267.7 b | 0.51 a | 125.5 a |
| YD6 | WMD | 29.8 a | 0.24 a | 23.6 a | 960.1 a | 10 623.8 a | 0.52 a | 137.3 a |
| 南粳9108 | CI | 22.3 b | 0.23 a | 21.3 b | 624.5 b | 10 134.7 b | 0.57 a | 98.8 b |
| NJ9108 | WMD | 25.9 a | 0.24 a | 24.0 a | 661.6 a | 10 797.6 a | 0.58 a | 110.3 a |
| 扬两优6号 | CI | 30.4 b | 0.22 a | 23.6 b | 767.3 b | 9 993.9 b | 0.61 a | 121.3 b |
| YLY6 | WMD | 36.3 a | 0.23 a | 26.6 a | 812.5 a | 10 784.1 a | 0.61 a | 133.6 a |
| 常优5号 | CI | 25.1 a | 0.18 a | 21.7 b | 766.9 b | 10 675.1 b | 0.49 a | 112.3 b |
| CY5 | WMD | 26.4 a | 0.18 a | 23.9 a | 809.4 a | 11 580.0 a | 0.48 a | 122.2 a |
| 甬优2640 | CI | 24.0 b | 0.24 a | 17.6 b | 883.5 b | 11 546.6 a | 0.48 a | 102.2 b |
| YY2640 | WMD | 27.6 a | 0.25 a | 18.6 a | 984.2 a | 12 600.9 a | 0.47 a | 114.6 a |
Table 3. Morphological characteristics of rice roots after rewatering in WMD during the grain filling stage.
| 品种 Cultivar | 处理 Treatment | 根干质量 Root dry weight /(g·pot-1) | 根冠比 Root-shoot ratio | 根数 Root number /(×100·pot-1) | 根长 Root length /(m·pot-1) | 根表面积 Root surface /(cm2·pot-1) | 根系直径 Root diameter /mm | 根体积 Root volume /(cm3·pot-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 扬稻6号 | CI | 25.5 b | 0.23 a | 20.0 b | 876.9 b | 9 267.7 b | 0.51 a | 125.5 a |
| YD6 | WMD | 29.8 a | 0.24 a | 23.6 a | 960.1 a | 10 623.8 a | 0.52 a | 137.3 a |
| 南粳9108 | CI | 22.3 b | 0.23 a | 21.3 b | 624.5 b | 10 134.7 b | 0.57 a | 98.8 b |
| NJ9108 | WMD | 25.9 a | 0.24 a | 24.0 a | 661.6 a | 10 797.6 a | 0.58 a | 110.3 a |
| 扬两优6号 | CI | 30.4 b | 0.22 a | 23.6 b | 767.3 b | 9 993.9 b | 0.61 a | 121.3 b |
| YLY6 | WMD | 36.3 a | 0.23 a | 26.6 a | 812.5 a | 10 784.1 a | 0.61 a | 133.6 a |
| 常优5号 | CI | 25.1 a | 0.18 a | 21.7 b | 766.9 b | 10 675.1 b | 0.49 a | 112.3 b |
| CY5 | WMD | 26.4 a | 0.18 a | 23.9 a | 809.4 a | 11 580.0 a | 0.48 a | 122.2 a |
| 甬优2640 | CI | 24.0 b | 0.24 a | 17.6 b | 883.5 b | 11 546.6 a | 0.48 a | 102.2 b |
| YY2640 | WMD | 27.6 a | 0.25 a | 18.6 a | 984.2 a | 12 600.9 a | 0.47 a | 114.6 a |
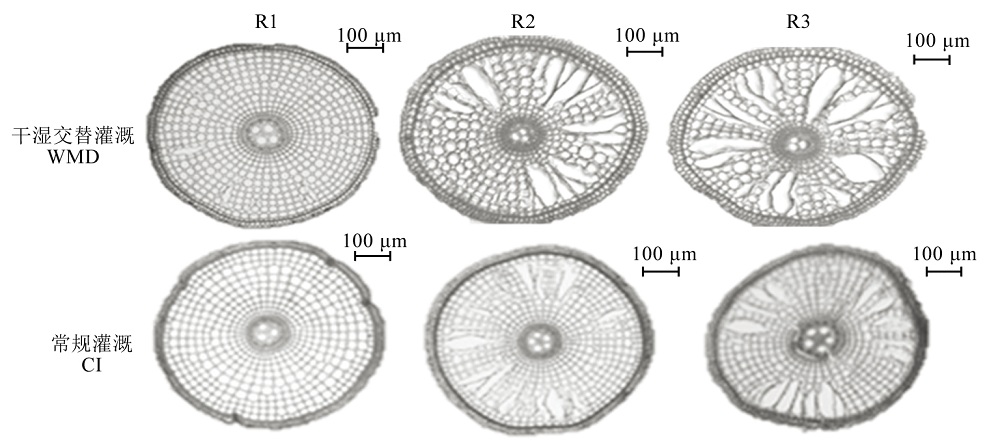
Fig. 5. Microstructure of root aerenchyma after rewatering in WMD during the grain filling stage (Yangdao 6). CI, Continuously flooded irrigation; WMD, Alternate wetting and moderate soil drying irrigation. R1, 1 cm from root tip; R2, 2 cm from root tip; R3, 3 cm from root tip.
| 品种 Cultivar | 部位 Site | 处理 Treatment | 横截面积(S1) Cross-section area(S1) /(×104 μm2) | 通气组织面积(S2) Aerenchyma area(S2) /(×104 μm2) | 面积比(S2/S1) Area ratio(S2/S1) /% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 扬稻6号 | R1 | CI | 50.9 a | 0.0 a | 0.0 a |
| YD6 | WMD | 62.0 a | 0.0 a | 0.0 a | |
| R2 | CI | 64.6 a | 9.4 a | 14.6 a | |
| WMD | 53.2 a | 8.7 a | 16.4 a | ||
| R3 | CI | 54.3 b | 10 b | 18.4 b | |
| WMD | 74.7 a | 16.1 a | 21.6 a | ||
| 南粳9108 | R1 | CI | 78.8 a | 0.0 a | 0.0 a |
| NJ9108 | WMD | 73.6 a | 0.0 a | 0.0 a | |
| R2 | CI | 95.5 a | 12.9 a | 13.5 b | |
| WMD | 90.2 a | 13.5 a | 15.0 a | ||
| R3 | CI | 86.2 a | 14.5 b | 16.8 b | |
| WMD | 83.8 a | 17.5 a | 20.9 a | ||
| 扬两优6号 | R1 | CI | 61.5 a | 0.0 a | 0.0 a |
| YLY6 | WMD | 60.6 a | 0.0 a | 0.0 a | |
| R2 | CI | 57.9 a | 8.9 b | 15.4 b | |
| WMD | 63.1 a | 10.9 a | 17.3 a | ||
| R3 | CI | 69.5 a | 12.5 a | 18.0 b | |
| WMD | 64.3 a | 12.3 a | 19.1 a | ||
| 常优5号 | R1 | CI | 84.5 a | 0.0 a | 0.0 a |
| CY5 | WMD | 75.6 a | 0.0 a | 0.0 a | |
| R2 | CI | 91.7 a | 12.2 a | 13.3 b | |
| WMD | 77.7 b | 12.9 a | 16.6 a | ||
| R3 | CI | 80.2 a | 15.2 b | 19.0 b | |
| WMD | 84.9 a | 20.3 a | 23.9 a | ||
| 甬优2640 | R1 | CI | 70.7 a | 0.0 a | 0.0 a |
| YY 2640 | WMD | 62.3 a | 0.0 a | 0.0 a | |
| R2 | CI | 75.6 a | 10.9 a | 14.4 b | |
| WMD | 71.1 a | 12.0 a | 16.9 a | ||
| R3 | CI | 71.0 a | 14.1 b | 19.9 b | |
| WMD | 66.8 a | 17.3 a | 25.9 a |
Table 4. Aerenchyma in rice root system after rewatering in WMD during the grain filling stage.
| 品种 Cultivar | 部位 Site | 处理 Treatment | 横截面积(S1) Cross-section area(S1) /(×104 μm2) | 通气组织面积(S2) Aerenchyma area(S2) /(×104 μm2) | 面积比(S2/S1) Area ratio(S2/S1) /% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 扬稻6号 | R1 | CI | 50.9 a | 0.0 a | 0.0 a |
| YD6 | WMD | 62.0 a | 0.0 a | 0.0 a | |
| R2 | CI | 64.6 a | 9.4 a | 14.6 a | |
| WMD | 53.2 a | 8.7 a | 16.4 a | ||
| R3 | CI | 54.3 b | 10 b | 18.4 b | |
| WMD | 74.7 a | 16.1 a | 21.6 a | ||
| 南粳9108 | R1 | CI | 78.8 a | 0.0 a | 0.0 a |
| NJ9108 | WMD | 73.6 a | 0.0 a | 0.0 a | |
| R2 | CI | 95.5 a | 12.9 a | 13.5 b | |
| WMD | 90.2 a | 13.5 a | 15.0 a | ||
| R3 | CI | 86.2 a | 14.5 b | 16.8 b | |
| WMD | 83.8 a | 17.5 a | 20.9 a | ||
| 扬两优6号 | R1 | CI | 61.5 a | 0.0 a | 0.0 a |
| YLY6 | WMD | 60.6 a | 0.0 a | 0.0 a | |
| R2 | CI | 57.9 a | 8.9 b | 15.4 b | |
| WMD | 63.1 a | 10.9 a | 17.3 a | ||
| R3 | CI | 69.5 a | 12.5 a | 18.0 b | |
| WMD | 64.3 a | 12.3 a | 19.1 a | ||
| 常优5号 | R1 | CI | 84.5 a | 0.0 a | 0.0 a |
| CY5 | WMD | 75.6 a | 0.0 a | 0.0 a | |
| R2 | CI | 91.7 a | 12.2 a | 13.3 b | |
| WMD | 77.7 b | 12.9 a | 16.6 a | ||
| R3 | CI | 80.2 a | 15.2 b | 19.0 b | |
| WMD | 84.9 a | 20.3 a | 23.9 a | ||
| 甬优2640 | R1 | CI | 70.7 a | 0.0 a | 0.0 a |
| YY 2640 | WMD | 62.3 a | 0.0 a | 0.0 a | |
| R2 | CI | 75.6 a | 10.9 a | 14.4 b | |
| WMD | 71.1 a | 12.0 a | 16.9 a | ||
| R3 | CI | 71.0 a | 14.1 b | 19.9 b | |
| WMD | 66.8 a | 17.3 a | 25.9 a |
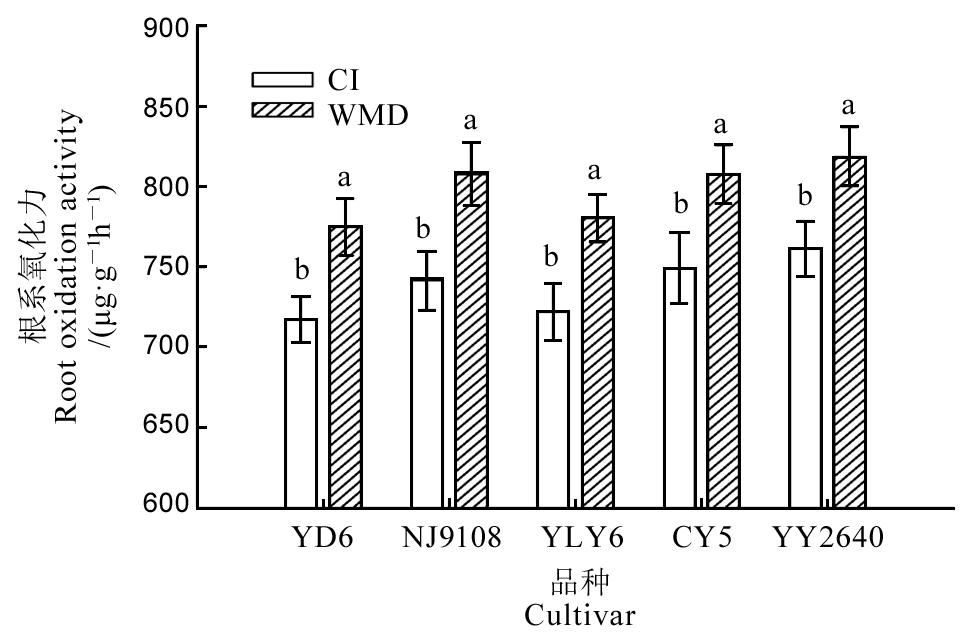
Fig. 6. Root oxidation activity after rewatering in WMD during the grain filling stage. YD6, Yangdao 6; NJ9108, Nanjing 9108; YLY6, Yangliangyou 6; CY5, Changyou 5; YY2640, Yongyou 2640. CI, Continuously flooded irrigation; WMD, Alternate wetting and moderate soil drying irrigation. For a variety, different letters above the column indicate statistical significance at the P = 0.05 level.
| [1] | Peng S, Tang Q, Zou Y. Current status and challenges of rice production in China[J]. Plant Production Science, 2009, 12(1): 3-8. |
| [2] | Ma G H, Yuan L P. Hybrid rice achievements, development and prospect in China[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2015, 14(2): 197-205. |
| [3] | Chu G, Chen T, Chen S, Xu C, Wang D, Zhang X. Agronomic performance of drought-resistance rice cultivars grown under alternate wetting and drying irrigation management in southeast China[J]. Crop Journal, 2018, 6(5): 482-494. |
| [4] | Zhang Z, Xue Y, Wang Z, Yang J, Zhang J. The relationship of grain filling with abscisic acid and ethylene under non-flooded mulching cultivation[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science, 2009, 147(4): 423-436. |
| [5] | Wang Z, Zhang W, Beebout S S, Zhang H, Liu L, Yang J, Zhang J. Grain yield, water and nitrogen use efficiencies of rice as influenced by irrigation regimes and their interaction with nitrogen rates[J]. Field Crops Research, 2016, 193: 54-69. |
| [6] | 褚光, 展明飞, 朱宽宇, 王志琴, 杨建昌. 干湿交替灌溉对水稻产量与水分利用效率的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2016, 42(7): 1026-1036. |
| Chu G, Zhan M F, Zhu K Y, Wang Z Q, Yang J C. Effects of alternate wetting and drying irrigation on yield and water use efficiency of rice[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2016, 42(7): 1026-1036. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 李婷婷, 冯钰枫, 朱安, 黄健, 汪浩, 李思宇, 刘昆, 彭如梦, 张宏路, 刘立军. 主要节水灌溉方式对水稻根系形态生理的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(4): 293-302. |
| Li T T, Feng Y F, Zhu A, Huang J, Wang H, Li S Y, Liu K, Peng R M, Zhang H L, Liu L J. Effects of main water-saving irrigation methods on morphological and physiological traits of rice roots[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2019, 33(4): 293-302. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | Ye Y, Liang X, Chen Y, Liu J, Gu J, Guo R, Li L. Alternate wetting and drying irrigation and controlled-release nitrogen fertilizer in late-season rice. Effects on dry matter accumulation, yield, water and nitrogen use[J]. Field Crops Research, 2013, 144: 212-224. |
| [9] | Lampayan R, Rejesus R, Singleton G, Bouman B. Adoption and economics of alternate wetting and drying water management for irrigated lowland rice[J]. Field Crops Research, 2015, 170: 95-108. |
| [10] | Zhou Q, Ju C, Wang Z, Zhang H, Liu L, Yang J, Zhang J. Grain yield and water use efficiency of super rice under soil water deficit and alternate wetting and drying irrigation[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2017, 16(5): 1028-1043. |
| [11] | 杨建昌. 水稻根系形态生理与产量、品质形成及养分吸收利用的关系[J]. 中国农业科学, 2011, 44(1): 36-46. |
| Yang J C. Relationships of rice root morphology and physiology with the formation of grain yield and quality and the utrient absorption and utilization[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2011, 44(1): 36-46. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | Liu K, Li T, Chen Y, Huang J, Qiu Y, Li S, Wang H, Zhu A, Zhuo X, Yu F, Zhang H, Gu J, Liu L, Yang J. Effects of root morphology and physiology on the formation and regulation of large panicles in rice[J]. Field Crops Research, 2020, 258: 1-12. |
| [13] | Sun L, Liu Q, Xue Y, Xu C, Peng C, Yuan X, Shi J. Dynamic influence of S fertilizer on Cu bioavailability in rice (Oryza sativa L.) rhizosphere soil during the whole life cycle of rice plants[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 19: 198-210. |
| [14] | M. Valé, Nguyen C, Dambrine E, Dupouey J L. Microbial activity in the rhizosphere soil of six herbaceous species cultivated in a greenhouse is correlated with shoot biomass and root C concentrations[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2005, 37(12): 2329-2333. |
| [15] | Xu H, Qu Q, Chen Y, Liu G, Xue S. Responses of soil enzyme activity and soil organic carbon stability over time after cropland abandonment in different vegetation zones of the Loess Plateau of China[J]. Catena, 2021, 196: 1-13. |
| [16] | Xu G W, Lu D K, Wang H Z, Li Y. Morphological and physiological traits of rice roots and their relationships to yield and nitrogen utilization as influenced by irrigation regime and nitrogen rate[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2018, 203: 385-394. |
| [17] | Edwards J, Johnson C, Santos-MedellÃn C, Lurie E, Podishetty N K, Bhatnagar S, Eisen J A, Sundaresan V, Jeffery L D. Structure, variation, and assembly of the root-associated microbiomes of rice[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2015, 112(8): 911-920. |
| [18] | 桂娟, 陈小云, 刘满强, 庄喜平, 孙震, 胡锋. 节水与减氮措施对稻田土壤微生物和微动物群落的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2016, 27(1): 107-116. |
| Gui J, Chen X Y, Liu M Q, Zhuang X P, Sun Z, Hu Feng. Influences of water-saved and nitrogen-reduced practice on soil microbial and microfauna assemblage in paddy field[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2016, 27(1): 107-116. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | 巩闪闪, 刘晓静, 张志勇, 马新明, 孔玉华. 不同施氮措施对冬小麦农田土壤酶活性和氮转化的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2020, 29(11): 2215-2222. |
| Gong S S, Liu X J, Zhang Z Y, Ma X M, Kong Y H. Effect of different nitrogen application measures on soil enzyme activities and nitrogen turnover in winter wheat cropland[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2020, 29(11): 2215-2222. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | Carrijo D R, Lundy M E, Linquist B A. Rice yields and water use under alternate wetting and drying irrigation: a meta-analysis[J]. Field Crops Research, 2017, 203: 173-180. |
| [21] | Yang J, Zhou Q, Zhang J. Moderate wetting and drying increases rice yield and reduces water use, grain arsenic level, and methane emission[J]. Crop Journal, 2017, 5(2): 151-158. |
| [22] | Chen Y, Li S, Zhang Y, Li T, Ge H, Xia S, Gu J, Zhang H, Lü B, Wu X, Wang Z, Yang J, Zhang J, Liu L. Rice root morphological and physiological traits interaction with rhizosphere soil and its effect on methane emissions in paddy fields[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2019, 129: 191-200. |
| [23] | Ramasamy S, Berge H, Purushothaman S. Yield formation in rice in response to drainage and nitrogen application[J]. Field Crops Research, 1997, 51(1-2): 65-82. |
| [24] | 曹慧, 孙辉, 杨浩, 孙波, 赵其国. 土壤酶活性及其对土壤质量的指示研究进展[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 2003(1): 105-109. |
| Cao H, Sun H, Yang H, Sun B, Zhao Q G. A review sil enzyme activity and its indication for soil quality[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 2003(1): 105-109. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | 陈文博, 王旭东, 石思博, 季诗域, 叶正钱, 任泽涛, 刘璋. 长期菌渣化肥配施对稻田土壤酶活性的影响及交互效应[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2021, 38(1): 21-30. |
| Chen W B, Wang X D, Shi S B, Ji S Y, Ye Z Q, Ren Z T, Liu Z. Effects of long-term combined application of fungus residue and chemical fertilizer on soil enzyme activities in paddy field[J]. Journal of Zhejiang A & F University, 2021, 38(1): 21-30. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | 刘艳, 孙文涛, 宫亮, 蔡广兴. 水分调控对水稻根际土壤及产量的影响[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 2014, 33(2): 98-100. |
| Liu Y, Sun W T, Gong L, Cai G X. Effects of water regulation on rhizosphere soils and yield of rice[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2014, 33(2): 98-100. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | Huang S, Pant H K, Lu J. Effects of water regimes on nitrous oxide emission from soils[J]. Ecological Engineering, 2007, 31(1): 9-15. |
| [28] | Sepaskhah A R, Tafteh A. Yield and nitrogen leaching in rapeseed field under different nitrogen rates and water saving irrigation[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2012, 112: 55-62. |
| [29] | 张亚丽, 董园园, 沈其荣, 段英华. 不同水稻品种对铵态氮和硝态氮吸收特性的研究[J]. 土壤学报, 2004(6): 918-923. |
| Zhang Y L, Dong Y Y, Shen Q R, Duan Y H. Characteristics of NH4+ and NO3- uptake by rices of different genotypes[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2004(6): 918-923. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | 段英华, 张亚丽, 沈其荣. 水稻根际的硝化作用与水稻的硝态氮营养[J]. 土壤学报, 2004, 41(5): 803-809. |
| Duan Y H, Zhang Y L, Shen Q R. Nitrification in rice rhizosphere and the nitrate nutrition of rice[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2004, 41(5): 803-809. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | Saetre P, Stark J M. Microbial dynamics and carbon and nitrogen cycling following re-wetting of soils beneath two semi-arid plant species[J]. Oecologia, 2005, 142: 247-260. |
| [1] | GUO Zhan, ZHANG Yunbo. Research Progress in Physiological,Biochemical Responses of Rice to Drought Stress and Its Molecular Regulation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | WEI Huanhe, MA Weiyi, ZUO Boyuan, WANG Lulu, ZHU Wang, GENG Xiaoyu, ZHANG Xiang, MENG Tianyao, CHEN Yinglong, GAO Pinglei, XU Ke, HUO Zhongyang, DAI Qigen. Research Progress in the Effect of Salinity, Drought, and Their Combined Stresses on Rice Yield and Quality Formation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | XU Danjie, LIN Qiaoxia, LI Zhengkang, ZHUANG Xiaoqian, LING Yu, LAI Meiling, CHEN Xiaoting, LU Guodong. OsOPR10 Positively Regulates Rice Blast and Bacterial Blight Resistance [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | CHEN Mingliang, ZENG Xihua, SHEN Yumin, LUO Shiyou, HU Lanxiang, XIONG Wentao, XIONG Huanjin, WU Xiaoyan, XIAO Yeqing. Typing of Inter-subspecific Fertility Loci and Fertility Locus Pattern of indica-japonica Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 386-396. |
| [5] | DING Zhengquan, PAN Yueyun, SHI Yang, HUANG Haixiang. Comprehensive Evaluation and Comparative Analysis of Jiahe Series Long-Grain japonica Rice with High Eating Quality Based on Gene Chip Technology [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 397-408. |
| [6] | HOU Xiaoqin, WANG Ying, YU Bei, FU Weimeng, FENG Baohua, SHEN Yichao, XIE Hangjun, WANG Huanran, XU Yongqiang, WU Zhihai, WANG Jianjun, TAO Longxing, FU Guanfu. Mechanisms Behind the Role of Potassium Fulvic Acid in Enhancing Salt Tolerance in Rice Seedlings [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [7] | LÜ Zhou, YI Binghuai, CHEN Pingping, ZHOU Wenxin, TANG Wenbang, YI Zhenxie. Effects of Nitrogen Application Rate and Transplanting Density on Yield Formation of Small Seed Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| [8] | HU Jijie, HU Zhihua, ZHANG Junhua, CAO Xiaochuang, JIN Qianyu, ZHANG Zhiyuan, ZHU Lianfeng. Effects of Rhizosphere Saturated Dissolved Oxygen on Photosynthetic and Growth Characteristics of Rice at Tillering Stage [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [9] | WU Yue, LIANG Chengwei, ZHAO Chenfei, SUN Jian, MA Dianrong. Occurrence of Weedy Rice Disaster and Ecotype Evolution in Direct-Seeded Rice Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 447-455. |
| [10] | LIU Fuxiang, ZHEN Haoyang, PENG Huan, ZHENG Liuchun, PENG Deliang, WEN Yanhua. Investigation and Species Identification of Cyst Nematode Disease on Rice in Guangdong Province [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [11] | CHEN Haotian, QIN Yuan, ZHONG Xiaohan, LIN Chenyu, QIN Jinghang, YANG Jianchang, ZHANG Weiyang. Research Progress on the Relationship Between Rice Root, Soil Properties and Methane Emissions in Paddy Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [12] | MIAO Jun, RAN Jinhui, XU Mengbin, BO Liubing, WANG Ping, LIANG Guohua, ZHOU Yong. Overexpression of RGG2, a Heterotrimeric G Protein γ Subunit-Encoding Gene, Improves Drought Tolerance in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [13] | YIN Xiaoxiao, ZHANG Zhihan, YAN Xiulian, LIAO Rong, YANG Sijia, Beenish HASSAN, GUO Daiming, FAN Jing, ZHAO Zhixue, WANG Wenming. Signal Peptide Validation and Expression Analysis of Multiple Effectors from Ustilaginoidea virens [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [14] | ZHU Yujing, GUI Jinxin, GONG Chengyun, LUO Xinyang, SHI Jubin, ZHANG Haiqing, HE Jiwai. QTL Mapping for Tiller Angle in Rice by Genome-wide Association Analysis [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [15] | ZHAO Yiting, XIE Keran, GAO Ti, CUI Kehui. Effects of Drought Priming During Tillering Stage on Panicle Development and Yield Formation Under High Temperature During Panicle Initiation Stage in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 277-289. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||