
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2022, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (2): 105-117.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2022.210609
• Reviews and Special Topics • Next Articles
WANG Yang, ZHANG Rui, LIU Yonghao, LI Rongkai, GE Jianfei, DENG Shiwen, ZHANG Xubin, CHEN Yinglong, WEI Huanhe, DAI Qigen*( )
)
Received:2021-06-28
Revised:2021-08-13
Online:2022-03-10
Published:2022-03-11
Contact:
DAI Qigen
王洋, 张瑞, 刘永昊, 李荣凯, 葛建飞, 邓仕文, 张徐彬, 陈英龙, 韦还和, 戴其根*( )
)
通讯作者:
戴其根
基金资助:WANG Yang, ZHANG Rui, LIU Yonghao, LI Rongkai, GE Jianfei, DENG Shiwen, ZHANG Xubin, CHEN Yinglong, WEI Huanhe, DAI Qigen. Rice Response to Salt Stress and Research Progress in Salt Tolerance Mechanism[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(2): 105-117.
王洋, 张瑞, 刘永昊, 李荣凯, 葛建飞, 邓仕文, 张徐彬, 陈英龙, 韦还和, 戴其根. 水稻对盐胁迫的响应及耐盐机理研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(2): 105-117.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2022.210609
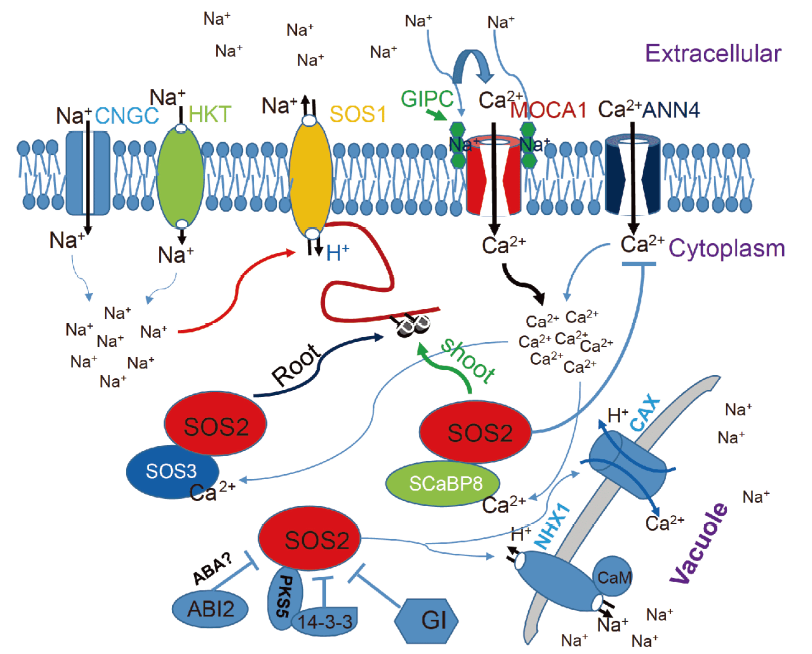
Fig. 1. Na+ transporters and their uptake, efflux and compartmentation of Na+[45]. In the case of high salt stress, Na+-GIPC activates the Na+ sensing mechanism of the Ca2+ osmotic channel MOCA1. Ca2+ rises to activate the SOS signaling system, and SOS3 combined with Ca2+ interacts with SOS2 and activates SOS2. The SOS3-SOS2 complex is recruited to the plasma membrane, where SOS2 phosphorylates SOS1. After phosphorylation, the activity of the Na+/H+ antiporter SOS1 is enhanced to promote Na+ efflux. ABI2, 14-3-3 and GI negatively regulate the activity of SOS2, but Ca2+-mediated 14-3-3 binding to PKS5 can release SOS2.
| 激素类型 Hormone type | 主要生理效应 Main physiological effect | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|
| 脱落酸 Abscisic acid | 气孔关闭、离子平衡、诱导盐胁迫基因表达 Stomatal closure, ion balance, induction of salt stress gene expression | [ |
| 赤霉素 Gibberellin | 提高发芽率、缓解花期延迟 Improve germination rate, alleviate flowering delay | [ |
| 水杨酸 Salicylic acid | 渗透调节剂、维持离子稳态、去除活性氧 Osmotic regulator, maintain ion homeostasis, remove reactive oxygen species | [ |
| 茉莉酸 Jasmonic acid | 缓解叶片衰老、根系伸长、去除活性氧 Alleviate leaf senescence, root elongation, remove reactive oxygen species | [ |
| 乙烯 Ethylene | 改善光合作用、维持离子稳态、介导应激信号 Improve photosynthesis, maintain ion homeostasis, mediate stress signaling | [ |
Table 1 Regulatory effects of plant hormones on rice under salt stress.
| 激素类型 Hormone type | 主要生理效应 Main physiological effect | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|
| 脱落酸 Abscisic acid | 气孔关闭、离子平衡、诱导盐胁迫基因表达 Stomatal closure, ion balance, induction of salt stress gene expression | [ |
| 赤霉素 Gibberellin | 提高发芽率、缓解花期延迟 Improve germination rate, alleviate flowering delay | [ |
| 水杨酸 Salicylic acid | 渗透调节剂、维持离子稳态、去除活性氧 Osmotic regulator, maintain ion homeostasis, remove reactive oxygen species | [ |
| 茉莉酸 Jasmonic acid | 缓解叶片衰老、根系伸长、去除活性氧 Alleviate leaf senescence, root elongation, remove reactive oxygen species | [ |
| 乙烯 Ethylene | 改善光合作用、维持离子稳态、介导应激信号 Improve photosynthesis, maintain ion homeostasis, mediate stress signaling | [ |
| [1] | 杨玉坤, 耿计彪, 于起庆, 王嘉, 于文勇, 赵薇. 盐碱地土壤利用与改良研究进展[J]. 农业与技术, 2019,39(24):108-111. |
| Yang Y K, Geng J B, Wang J, Yu W Y, Zhao W. Research progress of soil utilization and amelioration in saline-alkali land[J]. Agriculture and Technology, 2019,39(24):108-111. (in Chinese) | |
| [2] | 魏征, 屠乃美, 易镇邪. 盐碱地对水稻的胁迫效应及其改良与高效利用的研究进展[J]. 湖南生态科学学报, 2019,6(4):45-52. |
| Wei Z, Tu N M, Yi Z X. Research progress on stress effect of saline-alkali soil on rice and its improvement and efficient utilization[J]. Journal of Hunan Ecological Science, 2019,6(4):45-52. | |
| [3] | 梁银培, 孙健, 索艺宁, 刘化龙, 王敬国, 郑洪亮, 孙晓雪, 邹德堂. 水稻耐盐性和耐碱性相关性状的QTL定位及环境互作分析[J]. 中国农业科学, 2017,50(10):1747-1762. |
| Liang Y P, Sun J, Suo Y N, LIU H L, Wang J G, Zhang H L, Sun X X, Zou D T. QTL Mapping and QTL × environment interaction analysis of salt and alkali tolerance-related traits in rice(Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2017,50(10):1747-1762. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 张瑞珍, 邵玺文, 童淑媛, 汪恒武, 齐春燕, 孙长占. 盐碱胁迫对水稻源库与产量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2006(1):116-118. |
| Zhang R Z, Shao X W, Wang H W, Qi C Y, Sun C Z. Effect of saline-alkali stress on source-sink and yield of rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2006(1):116-118. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | 刘奕媺, 于洋, 方军. 盐碱胁迫及植物耐盐碱分子机制研究[J]. 土壤与作物, 2018,7(2):201-211. |
| Liu Y M, Yu Y, Fang J. Saline-alkali stress and molecular mechanism of saline-alkali tolerance in plants[J]. Soil and Crop, 2018,7(2):201-211. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 杨建昌. 水稻根系形态生理与产量、品质形成及养分吸收利用的关系[J]. 中国农业科学, 2011,44(1):36-46. |
| Yang J C. Relationships of rice root morphology and physiology with the formation of grain yield and quality and the nutrient absorption and utilization[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2011,44(1):36-46. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 翟荣荣, 叶胜海, 朱国富, 陆艳婷, 叶靖, 张小明. 纤维素合成相关基因调控水稻根系发育机制的研究进展[J]. 分子植物育种, 2019,17(20):6691-6695. |
| Zhai R R, Ye S H, Zhu G F, Lu Y T, Ye J, Zhang X M. Research progress on the regulation of rice root development by genes related to cellulose synjournal[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2019,17(20):6691-6695. | |
| [8] | Munns R, Tester M. Mechanisms of salinity tolerance[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2008,59(1):651-681. |
| [9] | 强晓晶. 小盐芥ThPIP1基因的水稻遗传转化及耐盐机理研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2015: 50-55. |
| Qiang X J. Thellungiella halophila ThPIP1 gene transferring rice and mechanism of salt stress tolerance[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2015: 50-55. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | 祁栋灵, 郭桂珍, 李明哲, 曹桂兰, 张俊国, 周庆阳, 张三元, 徐锡哲, 韩龙植. 水稻耐盐碱性生理和遗传研究进展[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2007(4):486-493. |
| Qi D L, Guo G Z, Li M Z, Cao G L, Zhang J G, Zhou Q Y, Zhang S Y, Xu X Z, Han L Z. Progress of physiology and genetic research on saline-alkaline tolerance in rice[J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2007(4):486-493. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 徐芬芬, 彦有娟, 韦蓉香. NaCl和Na2CO3胁迫对水稻根系生长的影响[J]. 杂交水稻, 2020,35(3):76-77. |
| Xu F F, Yan Y J, Wei R X. Effects of NaCl and Na2CO3 stress on growth of rice root[J]. Hybrid Rice, 2020,35(3):76-77. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 谷娇娇, 胡博文, 贾琰, 沙汉景, 李经纬, 马超, 赵宏伟. 盐胁迫对水稻根系相关性状及产量的影响[J]. 作物杂志, 2019(4):176-182. |
| Gu J J, Hu B W, Jia Y, Sha H J, Li J Y, Ma C, Zhao H W. Effects of salt stress on root related traits and yield of rice[J]. Crops, 2019(4):176-182. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | 单文忠, 宋虎彪, 李新永. 水稻遭受盐碱危害的生育表现和防治对策[J]. 北方水稻, 2006(1):44-46. |
| Shan W Z, Song H B, Li X Y. Generational manifestation and prophylactico-therapeutic measures on the condition of salinization damage[J]. North Rice, 2006(1):44-46. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | 梁正伟, 杨福, 王志春. 盐碱胁迫对水稻主要生育性状的影响[J]. 生态环境, 2004,13(1):43-46. |
| Liang Z W, Yang F, Wang Z C. Effect of the main growth characteristics of rice under saline-alkali stress[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2004,13(1):43-46. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | Khan M A, Abdullah Z. Salinity sodicity induced changes in reproductive physiology of rice (Oryza stativa) under dense soil conditions[J]. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2003,49(2):145-147 |
| [16] | 张瑞珍. 盐碱胁迫对水稻生理及产量的影响[D]. 长春: 吉林农业大学, 2003: 4-48. |
| Zhang R Z. Effect of salinity and alkalinity stress on physiology and grain yield in rice[D]. Changchun: Jilin Agricultural University, 2003: 4-48. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | 杨文钰, 屠乃美. 作物栽培学各论: 南方本[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2011: 21-40. |
| Yang W Y, Tu N M. Monograph on Crop Cultivation: Southern ed. [M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2011: 21-40. (in Chinese) | |
| [18] | 周政, 李宏, 孙勇, 黄道强, 朱苓华, 卢德城, 李康活, 徐建龙, 周少川, 黎志康. 高产、抗旱和耐盐选择对水稻产量相关性状的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2010,36(10):1725-1735. |
| Zhou Z, Li H, Sun Y, HuangG D Q, Zhu L H, Lu D C, Li K H, XU J L, Zhou S C, Li Z K. Effect of selection for high yield, drought and salinity tolerances on yield-related traits in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2010,36(10):1725-1735. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | 荆培培, 崔敏, 秦涛. 土培条件下不同盐分梯度对水稻产量及其生理特性的影响[J]. 中国稻米, 2017,23(4):26-23. |
| Jing P P, Cui M, Qin T. Effects of different saline stress on yield and physiological properties of rice in soil culture[J]. China Rice, 2017,23(4):26-23. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | 韦还和, 葛佳琳, 张徐彬, 孟天瑶, 陆钰, 李心月, 陶源, 丁恩浩, 陈英龙, 戴其根. 盐胁迫下粳稻品种南粳9108分蘖特性及其与群体生产力的关系[J]. 作物学报, 2020,46(8):1238-1247. |
| Wei H H, Ge J L, Zhang X B, Meng T Y, Lu Y, Li X Y, Tao Y, Ding E H, Chen Y L, Dai Q G. Tillering characteristics and its relationships with population productivity of japonica rice Nanjing 9108 under salinity stress[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2020,46(8):1238-1247. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | 李洪亮. 盐胁迫对水稻生育时期和农艺性状的影响[J]. 黑龙江农业科学, 2010(11):18-20. |
| Li H L. Effect of salt stress on maturity and agronomic characters of rice[J]. Heilongjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2010(11):18-20. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | Aisha S, Ansari R F. Rice Cultivation in Saline Soil[M]. Dordrect, the Netherland: Kluwer Academic Publishers, 2002: 38-56. |
| [23] | 杨福, 梁正伟, 王志春. 苏打盐碱胁迫对水稻品种长白9号穗部性状及产量构成的影响[J]. 华北农学报, 2010,25(S2):59-61. |
| Yang F, Liang Z W, Wang Z C. Effect of soda saline-sodic stress on the panicle traits and yield components of rice variety Changbai 9[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2010,25(S2):59-61. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | 李红宇, 潘世驹, 钱永德, 马艳, 司洋, 高尚, 郑桂萍, 姜玉伟, 周健. 混合盐碱胁迫对寒地水稻产量和品质的影响[J]. 南方农业学报, 2015,46(12):2100-2105. |
| Li H Y, Pan S J, Qian Y D, Ma Y, Si Y, Gao S, Zheng G P, Jiang Y W, Zhou J. Effects of saline-alkali stress on yield and quality of rice in cold region[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2015,46(12):2100-2105. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | 胡博文. 盐胁迫对水稻碳代谢及产量形成的影响[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学, 2019: 37-39. |
| Hu B W. Effects of salt stress on carbon metabolism and yield formation in rice[D]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2019: 37-39. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | 周根友, 翟彩娇, 邓先亮, 张蛟, 张振良, 戴其根, 崔士友. 盐逆境对水稻产量、光合特性及品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018,32(2):146-154. |
| Zhou G Y, Zhai C J, Deng X L, Zhang J, Zhang Z L, Dai Q G, Cui S Y. Performance of yield, photosynjournal and grain quality of japonica rice cultivars under salinity stress in micro-plots[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2018,32(2):146-154. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | 肖丹丹, 李军, 邓先亮, 卫平洋, 唐健, 韦还和, 陈英龙, 戴其根. 不同品种稻米品质形成对盐胁迫的响应[J]. 核农学报, 2020,34(8):1840-1847. |
| Xiao D D, Li J, Deng X L, Wei P Y, Tang J, Wei H H, Chen Y L, Dai Q G. Response of quality formation of different rice varieties to salt stress[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2020,34(8):1840-1847. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | Surekha R P, Mishra B, Gupta S R. Effects of soil salinity and alkalinity on grain quality of tolerant, semi-tolerant and sensitive rice genotypes[J]. Rice Science, 2013,20(4):284-291. |
| [29] | 马凌霄, 张素红, 孙杰. 高盐浓度筛选对水稻产量和品质的影响[J]. 北方水稻, 2017,47(6):13-17. |
| Ma L X, Zhang S H, Sun J. Effect of high salt concentration on rice yield and quality[J]. North Rice, 2017,47(6):13-17. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | 李天真. 稻米碾米品质及相关因素影响的研究进展[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2005(3):161-168. |
| Li T Z. Research progress on rice milling quality and related factors[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences, 2005(3):161-168. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | 余为仆. 秸秆还田条件下盐胁迫对水稻产量与品质形成的影响[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2014: 35-38. |
| Yu W P. Effect of salt stress associated with straw returning on yield and quality of rice[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2014: 35-38. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [32] | 赫臣, 郑桂萍, 李红宇, 吕艳东, 殷大伟, 姜玉伟, 赵海成, 陈立强, 牛同旭, 韩笑. 苏打盐碱土对水稻品质的影响[J]. 黑龙江农业科学, 2018(1):37-40. |
| He C, Zhang G P, Li H Y, Lv Y D, Yin D W, Jiang Y W, Zhao H C, Chen L Q, Niu T X, Han X. Effects of soda saline-alkali soil on rice quality[J]. Heilongjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2018(1):37-40. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [33] | 罗成科, 肖国举, 张峰举, 李茜. 不同浓度复合盐胁迫对水稻产量和品质的影响[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2017,31(1):137-141. |
| Luo C K, Xiao G J, Zhang F J, Li Q. Effects of different salt stresses on rice yield and quality[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2017,31(1):137-141. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [34] | Zhu J K. Regulation of ion homeostasis under salt stress[J]. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2003,6(5):441-445. |
| [35] | Liu N, Ni Z, Zhang H. The gene encoding subunit a of the vacuolar H +-ATPase from cotton plays an important role in conferring tolerance to water deficit [J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2018,6(9):758. |
| [36] | Takahashi R, Nishio T, Ichizen N, Takano T. Cloning and functional analysis of the K + transporter, PhaHAK2, from salt-sensitive and salt-tolerant reed plants [J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2007,29(3):501-506. |
| [37] | 杨晓慧, 蒋卫杰, 魏眠, 余宏军. 植物对盐胁迫的反应及其抗盐机理研究进展[J]. 山东农业大学学报: 自然科学版, 2006,37(2):302-305. |
| Yang X H, Jiang W J, Wei M, Yu H J. Review on plant response and resistance mechanism to salt stress[J]. Journal of Shandong Agricultural University: Natural Science Edition, 2006,37(2):302-305. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [38] | 瞿礼嘉, 顾红雅, 胡萍. 现代生物技术导论[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 1998: 68-93. |
| Qu L J, Gu H Y, Hu P. Introduction to Modern Biotechnology[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 1998: 68-93. (in Chinese) | |
| [39] | 张晓婷, 王雪松, 贾文飞, 徐振彪, 王颖, 吴林. 植物在盐处理下的研究进展[J]. 北方园艺, 2021,10(6):137-143. |
| Zhang X T, Wang X S, Jia W F, Xu Z B, Wang Y, Wu L. Research progress of plants under salt treatment[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2021,10(6):137-143. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [40] | Nieves-Cordones M, Miler A J, Alemán F, Martinez V, Rubio F. A putative role for the plasma membrane potential in the control of the expression of the gene encoding the tomato high-affinity potassium transporter HAK5[J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 2008,68(6):521. |
| [41] | Cai J, Chen L, Qu H Y, Lian J, Liu W, Hu Y B, Xu G H. Alteration of nutrient allocation and transporter genes expression in rice under N, P, K and Mg deficiencies[J]. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 2012,34(3):939-946. |
| [42] | 蒋薇, 靳容, 刘明, 赵鹏, 陈晓光, 张爱君, 唐忠厚. 低钾胁迫下植物生理响应机制及相关基因功能研究进展[J]. 江苏师范大学学报: 自然科学版, 2020,38(3):62-66. |
| Jiang W, Jin R, Liu M, Zhao P, Chen X G, Zhang A J, Tang Z H. Advances in plant physiological response mechanisms and related gene functions under low potassium stress[J]. Journal of Jiangsu Normal University: Natural Science Edition, 2020,38(3):62-66. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [43] | 张振兴. 钙提高西瓜植株耐盐性的生理机制及其对果实品质的影响[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2011: 1-15. |
| Zhang Z X. The physiological mechanism of improvement in watermelon salt tolerance by calcium and its effects on fruit quality[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2011: 1-15. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [44] | 杨春武. 虎尾草和水稻抗碱机制研究[D]. 长春: 东北师范大学, 2010: 131-136. |
| Yang C W. Mechanisms of alkali tolerance in Chloris virgata and rice (Oryza sativa)[D]. Changchun: Northeast Normal University, 2010: 131-136. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [45] | Gong Z Z, Xiong L M, Shi H Z, Yang S H, Luis R, H E, Xu G H, Chao D Y, Li J R, Wang P Y, Qin F, Li J G, Ding Y L, Shi Y T, Wang Y, Yang Y Q, Guo Y, Zhu J K. Plant abiotic stress response and nutrient use efficiency[J]. Science China: Life Science, 2020,63:635-674. |
| [46] | 王鑫月. 盐胁迫和铝胁迫对水稻膜脂组分和含量的影响[D]. 咸阳: 中国科学院大学, 2016. |
| Wang X Y. Effect of salt stress and aluminum stress on the composition and content of membrane lipids in rice[D]. Xianyang: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [47] | 刘晓龙, 徐晨, 季平, 李前, 杨洪涛, 武志海, 王洪君. 盐胁迫下水稻叶绿素荧光特性与离子积累的相关性分析[J]. 分子植物育种, 2021,19(3):972-982. |
| Liu X L, Xu C, Ji P, Li Q, Yang H T, Wu Z H, Wang H J. Correlation analysis of chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics of leaves and ions accumulation in rice under salt stress[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2021,19(3):972-982. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [48] | 张瑞坤, 李卓成, 祝德玉, 荣子国, 王建林. 盐胁迫下不同耐盐性水稻品种苗期光合特性的响应规律[J]. 青岛农业大学学报: 自然科学版, 2020,37(4):250-257. |
| Zhang R K, Li C Z, Zhu D Y, Rong Z G, Wang J L. Effects of salt stress on photosynthetic characteristics of different salt-tolerant rice varieties at the seedling stage[J]. Journal of Qingdao Agricultural University: Natural Science, 2020,37(4):250-257. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [49] | 王旭明, 赵夏夏, 周鸿凯, 陈景阳, 莫俊杰, 谢平, 叶昌辉. NaCl胁迫对不同耐盐性水稻某些生理特性和光合特性的影响[J]. 热带作物学报, 2019,40(5):882-890. |
| Wang X M, Zhao X X, Zhou H K, Chen J Y, Mo J J, Xie P, Ye C H. Effects of NaCl stress on some physiological and biochemical indices and photosynthetic physiology characteristics of rice cultivars with different salt[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2019,40(5):882-890. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [50] | Farquhar G D, Sharkey T D. Stomatal conductance and photosynjournal[J]. Annual Review of Plant Physiology, 1982,33(1):317-345. |
| [51] | 孙骏威. 水稻根系、光合和抗氧化酶对干旱胁迫的反应[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2004. |
| Sun J W. The response of root, photosynthesis and antioxidant enzyme to drought stress[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2004. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [52] | 王旭明, 赵夏夏, 陈景阳, 许江环, 周柏霖, 王盼盼, 莫素, 莫俊杰, 谢平, 周鸿凯. 盐胁迫下海水稻抗逆生理响应分析[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2019,27(5):747-756. |
| Wang X M, Zhao X X, Chen J Y, Xu J H, Zhou B L, Wang P P, Mo S, Mo J J, Xie P, Zhou H K. Physiological adversity resistance of sea rice to salinity stress[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2019,27(5):747-756. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [53] | 胡燕. 雷琼耐盐水稻种质的筛选及其耐盐性的生理机制研究[D]. 湛江: 广东海洋大学, 2020: 23-28. |
| Hu Y. Screening of salt tolerant rice landraces in Leiqiong area of south China and study on its physiological mechanism of salt tolerance[D]. Zhanjiang: Guangdong Ocean University, 2020: 23-28. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [54] | McSteen P, Zhao Y. Plant hormones and signaling: Common theme sand new developments[J]. Cell, 2008,14(4):467-473. |
| [55] | Debeaujon I, Koornneef M. Gibberellin requirement for Arabidopsis seed germination is determined both by testa characteristics and embryonic abscisic acid[J]. Plant Physiology, 2000,122(2):415-424. |
| [56] | 姚曼红, 刘琳, 曾幼玲. 五大类传统植物激素对植物响应盐胁迫的调控[J]. 生物技术通报, 2011(11):1-5. |
| Yao M H, Liu L, Zeng Y L. Several kinds of phytohormone in plants responses to salt-stress[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2011(11):1-5. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [57] | 汤日圣, 童红玉, 唐现洪, 钟雨, 余永柱. 脱落酸提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的效果[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2012,28(4):910-911. |
| Tang R S, Tong H Y, Tang X H, Zhong Y, Yu Y Z. Salt tolerance in rice seedlings improved by ABA[J]. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2012,28(4):910-911. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [58] | 张振华, 刘强, 宋海星, 荣湘民, Ismail A M. 水稻生长、根系生理特性和ABA含量的基因型差异与耐盐性的关系[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2011,17(5):1035-1043. |
| Zhang Z H, Liu Q, Song H X, Rong X M, Abdelbagi M. Ismail. Responses of different rice genotypes to salt stress and its relation to plant growth, root physiological characteristics and ABA content[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2011,17(5):1035-1043. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [59] | 刘莉. 盐胁迫下植物激素对水稻种子萌发及幼苗根系生长的调控机理研究[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2018: 82-89. |
| Liu L. The regulation and mechanism of phytohormone on rice seed germination and seedling root growth under salinity[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2018: 82-89. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [60] | Shen B, Allen W B, Zheng P Z, Li C J, Glassman K, Ranch J, Nubel D, Traczynski M C. Expression of ZmLEC1 and ZmWRI1 increases seed oil production in maize[J]. Plant Physiology, 2010,153(3):980-987. |
| [61] | Yuriko O, Kazuko Y S, Kazuo S, Lam S P T. ABA control of plant macro element membrane transport systems in response to waterdeficit and high salinity[J]. New Phytologist, 2014,202:35-49. |
| [62] | Huang G T, Ma S L, Bai L P, Zhang L, Ma H, Jia P, Liu J, Zhong M, Guo Z F. Signal transduction during cold, salt, and drought stresses in plants[J]. Molecular Biology Reports, 2012,39(2):969-987. |
| [63] | 温福平. 盐胁迫与赤霉素(GA3)处理下水稻幼苗的蛋白质组学分析[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2009. |
| Wen F P. Proteomics analysis of rice seedlings during salt and gibberellin(GA3) treatment[D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2009. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [64] | Achard P, Cheng H, Grauwe L D, Decat J, Schoutteten H, Moritz T, Van Der Straeten D, Peng J R, Harberd N P. Integration of plant responses to environmentally activated phytohormonal signals[J]. Science, 2006,311:91-94. |
| [65] | Misra N, Saxena P. Effect of salicylic acid on proline metabolism in lentil grown under salinity stress[J]. Plant Science, 2009,177:181-189. |
| [66] | Tufail A, Arfan M, Gurmani A R, Khan A, Bano A. Salicylic acid induced salinity tolerance in maize (Zea mays)[J]. Pakistan Journal of Botany, 2013,45(S1):75-82. |
| [67] | Lee S, Kim S G, Park C M. Salicylic acid promotes seed germination under high salinity by modulating antioxidant activity in Arabidopsis[J]. New Phytologist, 2010,188(2):626-637. |
| [68] | Kurotani K, Hayashi K, Hatanaka S, Toda Y, Ogawa D, Ichikawa H, Ishimaru Y, Tashita R, Suzuki T, Ueda M, Hattorl T, Takeda S. Elevated levels of CYP94 family gene expression alleviate the jasmonate response and enhance salt tolerance in rice[J]. Plant Cell Physiology. 2015,56(4):779-789. |
| [69] | Valenzuela C E, Acevedo-Acevedo O, Miranda G S, Vergara-Barros P, Holuigue L, Figueroa C R, Figueroa P M. Salt stress response triggers activation of the jasmonate signaling pathway leading to inhibition of cell elongation in Arabidopsis primary root[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2016,67(14):4209-4220. |
| [70] | Yang L, Zu Y G, Tang Z H. Ethylene improves Arabidopsis salt tolerance mainly via retaining K + in shoots and roots rather than decreasing tissue Na + content [J]. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2013,86:60-69. |
| [71] | Amjad M, Akhtar J, Anwarulhaq M, Yang A Z, Akhtar S S, Jacobsen S E. Integrating role of ethylene and ABA in tomato plants adaptation to salt stress[J]. Scientia Horticulturae, 2014,172:109-116. |
| [72] | Zhou H L, Cao W H, Cao Y R, Liu J, Hao Y J, Zhang J S, Chen S Y. Roles of ethylene receptor NTHK1 domains in plant growth, stress response and protein phosphorylation[J]. FEBS Letters, 2006,580(5):1239-1250. |
| [73] | Wang R, Cheng Y H, Ke X J, Zhang X F, Zhang H S, Huang J. Comparative analysis of salt responsive gene regulatory networks in rice and Arabidopsis[J]. Computational Biology and Chemistry, 2020,85:107188. |
| [74] | Dubouzet J G, Sakuma Y, Ito Y, Kasuga M, Dubouzet E G, Miura S, Seki M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi S K. OsDREB genes in rice, Oryza sativa L., encode transcription activators that function in drought-, high-salt- and cold-responsive gene expression[J]. The Plant Journal, 2003,33(4):751-763. |
| [75] | Zhou J, Ju P, Zhang F, Zhang C K, Bai B, Li Y P, Wang H F, Chen F, Xie X Z. OsSRK1, an atypical S-receptor-like kinase positively regulates leaf width and salt tolerance in rice[J]. Rice Science, 2020,27(2):133-142. |
| [76] | Cheng Y W, Qi Y C, Zhu Q, Chen X, Wang N, Zhao X, Chen H Y, Cui X J, Xu L L, Zhang W. New changes in the plasma-membrane-associated proteome of rice roots under salt stress[J]. Proteomics, 2010,9(11):3100-3114. |
| [77] | Malakshah S N, Rezaei M H, Heidari M, Salekdeh G H. Proteomics reveals new salt responsive proteins associated with rice plasma membrane[J]. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 2007,71(9):2144-2154. |
| [78] | 张婷婷, 杨美英, 王春红, 孙合美, 齐春艳, 侯立刚, 武志海. 盐碱胁迫下不同水稻品种渗透调节物质及相关基因的变化[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报: 自然科学版, 2016,44(4):39-47. |
| Zhang T T, Yang M Y, Wang C H, Sun H M, Qi C Y, Hou L G, Wu Z H. Changes in osmolytes and related genes of different rice varieties under saline-alkali stress[J]. Journal of Northwest A & F University: Natural Science Edition, 2016,44(4):39-47. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [79] | Song X J, Huang W, Shi M, Zhu M Z, Lin H X. A QTL for rice grain width and weight encodes a previously unknown ring-type E3 ubiquitin ligase[J]. Nature Genetics, 2007,39(5):623-630. |
| [80] | Ren Z H, Gao J P, Li L G, Cai X L, Huang W, Chao D Y, Zhu M Z, Wang Z Y, Luan S, Lin H X. A rice quantitative trait locus for salt tolerance encodes a sodium transporter[J]. Nature Genetics, 2005,37(10):1141-1146. |
| [81] | 鄂志国, 张丽靖. 水稻盐胁迫应答的分子机制[J]. 杂交水稻, 2010,25(2):1-5. |
| E Z G, Zhang L J. Molecular mechanism of rice responses to salt stress[J]. Hybrid Rice, 2010,25(2):1-5. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [82] | Chen Y, Zhou X, Chang S, Chu Z, Wang H, Han S, Wang Y. Calcium-dependent protein kinase 21 phosphorylates 14-3-3 proteins in response to ABA signaling and salt stress in rice[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 2017,493(4):1450-1456. |
| [83] | Guan Q J, Ma H Y, Wang Z J, Wang Z Y, Bu Q Y, Liu S K. A rice LSD1-like-type ZFP gene OsLOL5 enhances saline-alkaline tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana, yeast and rice[J]. BMC Genomics, 2016,17:142. |
| [84] | Huang X Y, Chao D Y, Gao J P, Zhu M Z, Shi M, Lin H X. A previously unknown zinc finger protein, DST, regulates drought and salt tolerance in rice via stomatal aperture control[J]. Genes & Development, 2009,23(15):1805-1817. |
| [85] | 王诗宇, 毛艇, 张丽丽, 李鑫, 刘研, 赵一洲, 倪善君, 钟顺成, 王柏秋, 张战. 水稻耐盐育种研究进展[J]. 北方水稻, 2021,51(4):48-51. |
| Wang S Y, Mao T, Zhang L L, Li X, Liu Y, Zhao Y Z, Ni S J, Zhong S C, Wang B Q, Zhang Z. Advances in salt tolerance breeding of rice[J]. North Rice, 2021,51(4):48-51. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [86] | 许雷. 辽盐系列水稻新品种效益显著[J]. 农业科技通讯, 1995(1):9-10. |
| Xu L. The new rice varieties of Liaoyan series have remarkable benefits[J]. Bulletin of Agricultural Science and Technology, 1995(1):9-10. (in Chinese) | |
| [87] | 孙明法, 严国红, 王爱民, 朱国永, 唐红生, 何冲霄, 任仲玲, 刘凯, 张桂云, 施伟, 赵绍路, 孙一标, 朱静雯, 宛柏杰, 姚立生. 水稻耐盐育种研究进展[J]. 大麦与谷类科学, 2017,34(4):1-9. |
| Sun M F, Yan G H, Wang A M, Zhu G Y, Tang H S, He C X, Ren Z L, Liu K, Zhang G Y, Shi W, Zhao S L, Sun Y B, Zhu J W, Wan B J, Yao L S. Research progress on the breeding of salt-tolerant rice varieties[J]. Barley and Cereal Sciences, 2017,34(4):1-9. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [88] | 赵记伍, 雷传松, 刘永权, 张露, 成云峰, 王晓玲. 海稻86萌发期耐盐碱性特征初探[J]. 中国稻米, 2018,24(3):87-92. |
| Zhao J W, Lei C S, Liu Y Q, Zhang L, Cheng Y F, Wang X L. Primary exploration on saline-alkali tolerance of Haidao 86 in germination period[J]. China Rice, 2018,24(3):87-92. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [89] | 郑崇珂, 窦玉慧, 解丽霞, 谢先芝. 水稻耐盐相关基因的研究进展[J]. 分子植物育种, 2017,15(11):4411-4422. |
| Zhang C K, Dou Y H, Xie L X, Xie X Z. Research progress on the genes related to salt tolerance in rice[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2017,15(11):4411-4422. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [90] | Kaewneramit T, Buaboocha T, Sangchai P, Wutipraditkul N. OsCaM1-1 overexpression in the transgenic rice mitigated salt-induced oxidative damage[J]. Biologia Plantarum, 2019,63(1):335-342. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [91] | 高继平, 林鸿宣. 水稻耐盐机理研究的重要进展——耐盐数量性状基因SKC1的研究[J]. 生命科学, 2005,17(6):563-565. |
| Gao J P, Lin H X. Studies on the salt tolerance quantitative trait gene SKC1 in rice[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Life Science, 2005,17(6):563-565. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [92] | 才晓溪, 沈阳, 胡冰霜, 王研, 陈悦, 孙明哲, 贾博为, 孙晓丽. 野生大豆类受体蛋白激酶基因GsCBRLK超量表达提高水稻耐盐碱性[J]. 植物生理学报, 2020,56(12):2683-2694. |
| Cai X X, Shen , Hu B S, Wang Y, Chen Y, Sun M Z, Jia B W, Sun X L. Overexpression of a Glycine soja receptor-like protein kinase gene GsCBRLK in rice increases salt-alkaline tolerance[J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 2020,56(12):2683-2694. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [93] | 毛庆莲, 王胜. 国内盐碱地治理趋势探究浅析[J]. 湖北农业科学, 2020,59(S1):302-306. |
| Mao Q L, Wang S. Brief analysis on the trend of improve saline alkali soil in China[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2020,59(S1):302-306. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [94] | 高海东. 陕北地区盐碱地土地开发工程实践研究[J]. 中国资源综合利用, 2019,37(3):86-89. |
| Gao H D. The empirical study of the project of management of saline-alkali land[J]. China Resources Comprehensive Utilization, 2019,37(3):86-89. (in Chinese) | |
| [95] | 梅映学, 魏玮, 张诗婉, 张韫璐, 王金缘, 王茜, 苏昕, 马莲菊. 干旱锻炼对盐胁迫下水稻幼苗根系抗氧化酶活性的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2016,28(8):1304-1308. |
| Mei Y X, Wei W, Zhang S W, Zhang Y L, Wang J Y, Wang Q, Su X, Ma L J. Effect of PEG pretreatment on antioxidant enzymes activity under salt stress in root of rice seedling[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2016,28(8):1304-1308. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [96] | 朱海, 杨劲松, 姚荣江, 高珊, 曹逸凡, 孙运朋. 有机无机肥配施对滨海盐渍农田土壤盐分及作物氮素利用的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2019,27(3):441-450. |
| Zhu H, Yang J S, Yao R J, Gao S, Cao Y F, Sun Y P. Effects of partial substitution of organic nitrogen for inorganic nitrogen in fertilization on salinity and nitrogen utilization in salinized coastal soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2019,27(3):441-450. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [97] | 侯立刚, 齐春艳, 马巍, 付珍玉, 刘亮, 刘晓亮, 付胜, 郭希明, 隋朋举. 苏打盐碱地水稻“一抢三替”栽培技术研究[J]. 北方水稻, 2016,46(4):9-13. |
| Hou L G, Qi C Y, Ma W, Fu Z Y, Liu L, Liu X L, Fu S, Guo X M, Sui P J. Research on one increase and three replacement ways of cultivation technology in soda alkali-saline rice[J]. North Rice, 2016,46(4):9-13. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [98] | 任永泉, 孙久红. 滨海盐碱地水稻高产栽培关键技术[J]. 北方水稻, 2010,40(1):38-40. |
| Ren Y Q, Sun J H. Key techniques of high-yield rice cultivation in coastal saline-alkali land[J]. North Rice, 2010,40(1):38-40. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [99] | 王才林, 张亚东, 赵凌, 路凯, 朱镇, 陈涛, 赵庆勇, 姚姝, 周丽慧, 赵春芳, 梁文化, 孙明法, 严国红. 耐盐碱水稻研究现状、问题与建议[J]. 中国稻米, 2019,25(1):1-6. |
| Wang C L, Zhang Y D, Zhao L, Lu K, Zhu Z, Chen T, Zhao Q Y, Yao S, Zhou L H, Zhao C F, Liang W H, Sun M F, Yan G H. Research status, problems and suggestions on salt-alkali tolerant rice[J]. China Rice, 2019,25(1):1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [100] | 刘铎, 白爽, 李平, 宁东峰, 杨庆山, 梁志杰, 郭魏, 齐学斌. 硅调控植物耐盐碱机制研究进展[J]. 麦类作物学报, 2019,39(12):1507-1513. |
| Liu D, Bai S, Li P, Ning D F, Yang C S, Liang Z J, Guo W, Qi X B. A Review on the mechanism of silicon regulating plant tolerent to saline-alkaline stresses[J]. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2019,39(12):1507-1513. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [101] | 朱晓军, 杨劲松, 梁永超, 娄运生, 杨晓英. 盐胁迫下钙对水稻幼苗光合作用及相关生理特性的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2004,37(10):1497-1503. |
| Zhu X J, Yang J S, Liang Y C, Lou Y S, Yang X Y. Effects of exogenous calcium on photosynjournal and its related physiological characteristics of rice seedlings under salt stress[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2004,37(10):1497-1503. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [102] | 温福平, 张檀, 张朝晖, 潘映红. 赤霉素对盐胁迫抑制水稻种子萌发的缓解作用的蛋白质组分析[J]. 作物学报, 2009,35(3):483-489. |
| Wen F P, Zhang T, Zhang Z H, Pan Y H. Proteome analysis of relieving effect of gibberellin on the inhibition of rice seed germination by salt stress[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2009,35(3):483-489. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [103] | 张丽丽, 倪善君, 张战, 赵一洲, 李鑫, 毛艇, 刘研, 刘福才. 外源赤霉素对盐胁迫下水稻种子萌发及幼苗生长的缓释效应[J]. 中国稻米, 2018,24(2):42-46. |
| Zhang L L, Ni S J, Zhang Z, Zhao Y Z, Li X, Mao T, Liu Y, Liu F C. Sustained release effects of exogenous GA3 on germination and growth of rice seedling under salt stress[J]. China Rice, 2018,24(2):42-46. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [104] | 安辉, 盛伟, 于玉凤, 张露倩, 曾红丽, 陈光辉. 外源2, 4-表油菜素内酯对盐胁迫下对水稻幼苗生理特性的影响[J]. 分子植物育种, 2021,19(8):2740-2746. |
| An H, Sheng W, Yu Y F, Zhang L Q, Zeng H L, Cheng G H. Effects of exogenous 2,4-epibrassinolide on physiological characteristics of rice seedlings under salt stress[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2021,19(8):2740-2746. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [105] | 陈影影, 符跃鑫, 张振克, 张凌华, 徐华夏. 中国滨海盐碱土治理相关专利技术评述[J]. 中国农学通报, 2014,30(11):279-285. |
| Chen Y Y, Fu Y X, Zhang Z K, Zhang L H, Xu H X. Review of the Chinese patents on coastal saline-alkali soil improvement[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2014,30(11):279-285. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | GUO Zhan, ZHANG Yunbo. Research Progress in Physiological,Biochemical Responses of Rice to Drought Stress and Its Molecular Regulation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | WEI Huanhe, MA Weiyi, ZUO Boyuan, WANG Lulu, ZHU Wang, GENG Xiaoyu, ZHANG Xiang, MENG Tianyao, CHEN Yinglong, GAO Pinglei, XU Ke, HUO Zhongyang, DAI Qigen. Research Progress in the Effect of Salinity, Drought, and Their Combined Stresses on Rice Yield and Quality Formation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | XU Danjie, LIN Qiaoxia, LI Zhengkang, ZHUANG Xiaoqian, LING Yu, LAI Meiling, CHEN Xiaoting, LU Guodong. OsOPR10 Positively Regulates Rice Blast and Bacterial Blight Resistance [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | CHEN Mingliang, ZENG Xihua, SHEN Yumin, LUO Shiyou, HU Lanxiang, XIONG Wentao, XIONG Huanjin, WU Xiaoyan, XIAO Yeqing. Typing of Inter-subspecific Fertility Loci and Fertility Locus Pattern of indica-japonica Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 386-396. |
| [5] | DING Zhengquan, PAN Yueyun, SHI Yang, HUANG Haixiang. Comprehensive Evaluation and Comparative Analysis of Jiahe Series Long-Grain japonica Rice with High Eating Quality Based on Gene Chip Technology [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 397-408. |
| [6] | HOU Xiaoqin, WANG Ying, YU Bei, FU Weimeng, FENG Baohua, SHEN Yichao, XIE Hangjun, WANG Huanran, XU Yongqiang, WU Zhihai, WANG Jianjun, TAO Longxing, FU Guanfu. Mechanisms Behind the Role of Potassium Fulvic Acid in Enhancing Salt Tolerance in Rice Seedlings [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [7] | LÜ Zhou, YI Binghuai, CHEN Pingping, ZHOU Wenxin, TANG Wenbang, YI Zhenxie. Effects of Nitrogen Application Rate and Transplanting Density on Yield Formation of Small Seed Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| [8] | HU Jijie, HU Zhihua, ZHANG Junhua, CAO Xiaochuang, JIN Qianyu, ZHANG Zhiyuan, ZHU Lianfeng. Effects of Rhizosphere Saturated Dissolved Oxygen on Photosynthetic and Growth Characteristics of Rice at Tillering Stage [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [9] | WU Yue, LIANG Chengwei, ZHAO Chenfei, SUN Jian, MA Dianrong. Occurrence of Weedy Rice Disaster and Ecotype Evolution in Direct-Seeded Rice Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 447-455. |
| [10] | LIU Fuxiang, ZHEN Haoyang, PENG Huan, ZHENG Liuchun, PENG Deliang, WEN Yanhua. Investigation and Species Identification of Cyst Nematode Disease on Rice in Guangdong Province [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [11] | CHEN Haotian, QIN Yuan, ZHONG Xiaohan, LIN Chenyu, QIN Jinghang, YANG Jianchang, ZHANG Weiyang. Research Progress on the Relationship Between Rice Root, Soil Properties and Methane Emissions in Paddy Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [12] | MIAO Jun, RAN Jinhui, XU Mengbin, BO Liubing, WANG Ping, LIANG Guohua, ZHOU Yong. Overexpression of RGG2, a Heterotrimeric G Protein γ Subunit-Encoding Gene, Improves Drought Tolerance in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [13] | YIN Xiaoxiao, ZHANG Zhihan, YAN Xiulian, LIAO Rong, YANG Sijia, Beenish HASSAN, GUO Daiming, FAN Jing, ZHAO Zhixue, WANG Wenming. Signal Peptide Validation and Expression Analysis of Multiple Effectors from Ustilaginoidea virens [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [14] | ZHU Yujing, GUI Jinxin, GONG Chengyun, LUO Xinyang, SHI Jubin, ZHANG Haiqing, HE Jiwai. QTL Mapping for Tiller Angle in Rice by Genome-wide Association Analysis [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [15] | WEI Qianqian, WANG Yulei, KONG Haimin, XU Qingshan, YAN Yulian, PAN Lin, CHI Chunxin, KONG Yali, TIAN Wenhao, ZHU Lianfeng, CAO Xiaochuang, ZHANG Junhua, ZHU Chunqun. Mechanism of Hydrogen Sulfide, a Signaling Molecule Involved in Reducing the Inhibitory Effect of Aluminum Toxicity on Rice Growth Together with Sulfur Fertilizer [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||