
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2022, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (1): 43-54.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2022.210112
• Research Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHENG Xiaolong1,2, ZHOU Jingqing3, TENG Ying4, ZHANG Linping2, SHAO Yafang2, HU Peisong1,2, WEI Xiangjin2,*( )
)
Received:2021-01-12
Revised:2021-04-28
Online:2022-01-10
Published:2022-01-10
Contact:
WEI Xiangjin
郑小龙1,2, 周菁清3, 滕颖4, 章林平2, 邵雅芳2, 胡培松1,2, 魏祥进2,*( )
)
通讯作者:
魏祥进
基金资助:ZHENG Xiaolong, ZHOU Jingqing, TENG Ying, ZHANG Linping, SHAO Yafang, HU Peisong, WEI Xiangjin. Difference in Yield-related Traits of Grains in Various Parts of Panicle in japonica Rice and Its Correlation with Endogenous Hormones[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(1): 43-54.
郑小龙, 周菁清, 滕颖, 章林平, 邵雅芳, 胡培松, 魏祥进. 粳稻穗部不同部位籽粒产量相关性状差异及其与内源激素的相关性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(1): 43-54.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2022.210112
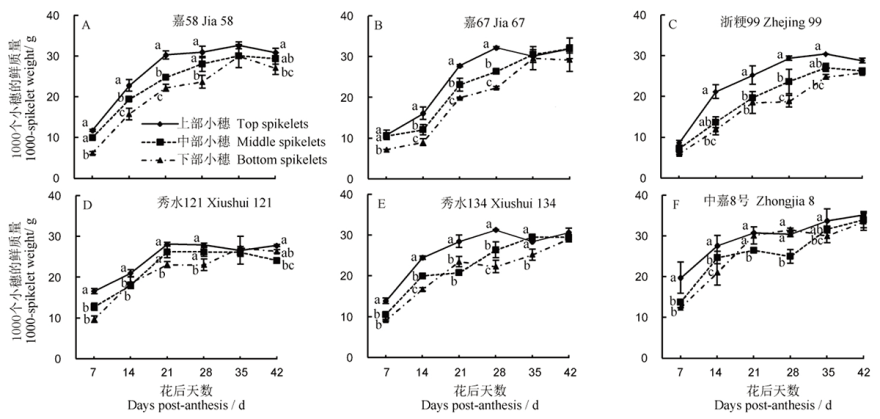
Fig. 2. Dynamic changes of fresh grain weight in different parts of panicle. The same lowercase letters in the same period indicate that the differences among grains in different parts are not significant(P<0.05)。
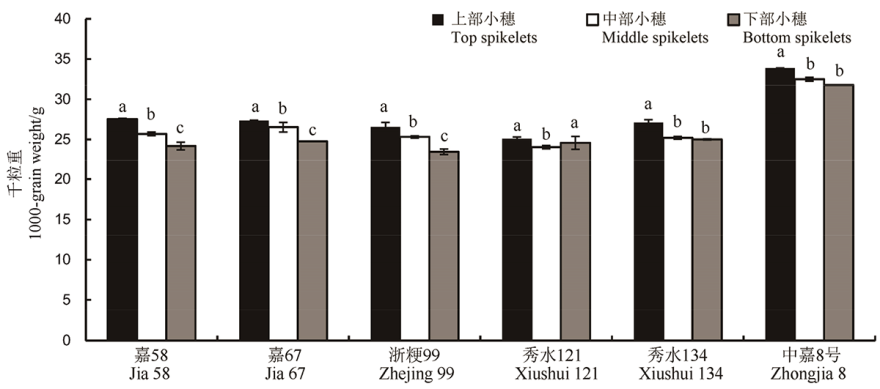
Fig. 3. Difference in 1000-grain weight in different parts. The same lowercase letters indicate that the differences among grains in different parts are not significant(P<0.05). The same below.
| 品种 Variety | 千粒重 1000-grain weight | 整精米率 Head rice rate | 长宽比 Length-width ratio | 胶稠度 Gel consistency | 碱消值 Alkali value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 嘉58 Jia 58 | 6.50 | 4.90 | 1.77 | 3.81 | 2.57 | |
| 嘉67 Jia 67 | 5.07 | 1.44 | 2.05 | 1.49 | 1.86 | |
| 浙粳99 Zhejing 99 | 6.23 | 2.08 | 1.65 | 5.84 | 1.23 | |
| 秀水121 Xiushui 121 | 2.12 | 9.44 | 0.16 | 2.26 | 1.86 | |
| 秀水134 Xiushui 134 | 4.46 | 6.10 | 0.00 | 15.04 | 1.23 | |
| 中嘉8号 Zhongjia 8 | 3.26 | 1.07 | 1.09 | 12.67 | 0.70 | |
| 所有品种 All varieties | 11.26 | 47.79 | 17.40 | 6.35 | 1.22 | |
Table 1 Variation coefficients of grain quality traits as affected by rice grain position. %
| 品种 Variety | 千粒重 1000-grain weight | 整精米率 Head rice rate | 长宽比 Length-width ratio | 胶稠度 Gel consistency | 碱消值 Alkali value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 嘉58 Jia 58 | 6.50 | 4.90 | 1.77 | 3.81 | 2.57 | |
| 嘉67 Jia 67 | 5.07 | 1.44 | 2.05 | 1.49 | 1.86 | |
| 浙粳99 Zhejing 99 | 6.23 | 2.08 | 1.65 | 5.84 | 1.23 | |
| 秀水121 Xiushui 121 | 2.12 | 9.44 | 0.16 | 2.26 | 1.86 | |
| 秀水134 Xiushui 134 | 4.46 | 6.10 | 0.00 | 15.04 | 1.23 | |
| 中嘉8号 Zhongjia 8 | 3.26 | 1.07 | 1.09 | 12.67 | 0.70 | |
| 所有品种 All varieties | 11.26 | 47.79 | 17.40 | 6.35 | 1.22 | |
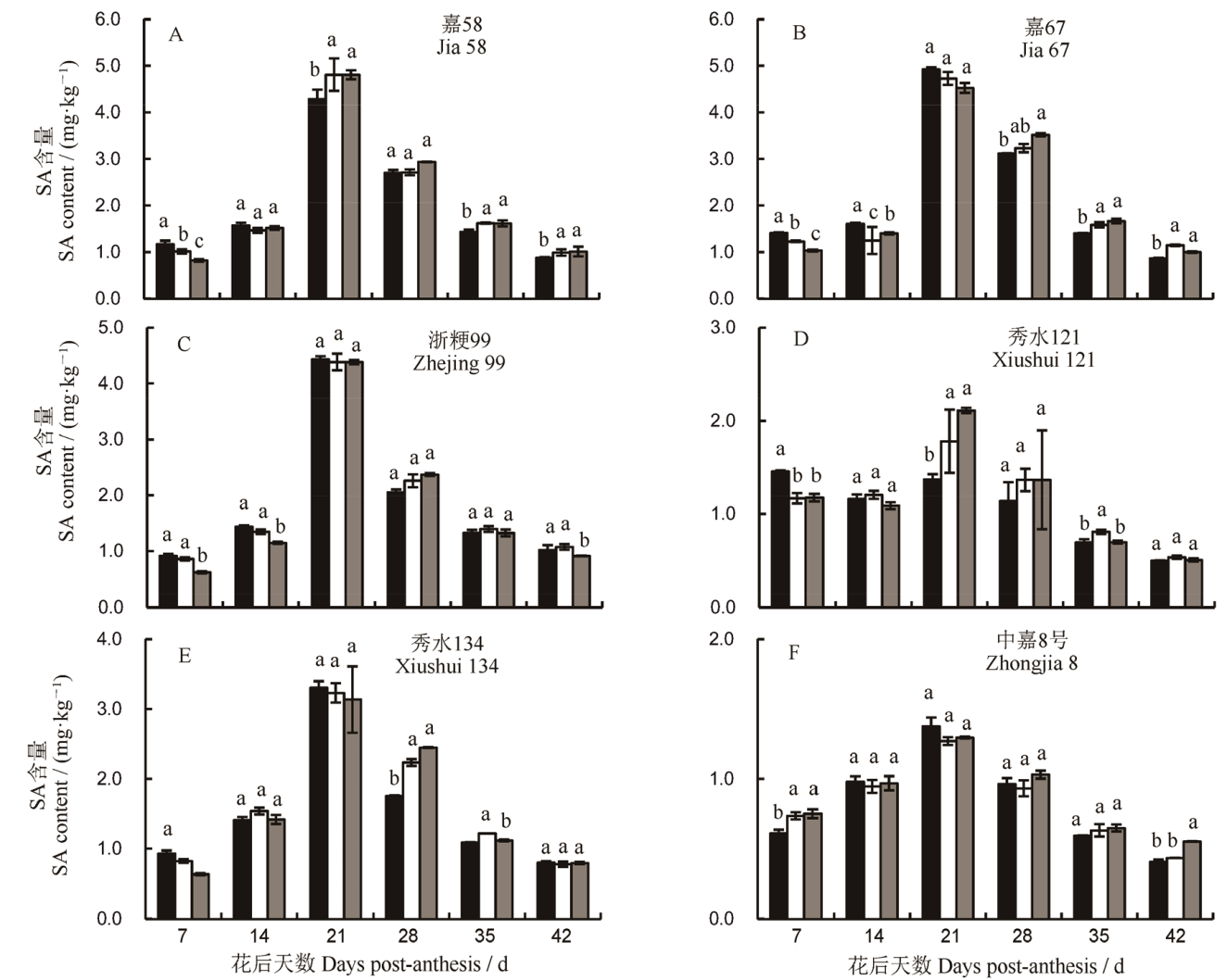
Fig. 6. Dynamic changes and differences of SA content in grains of different parts. The same lowercase letters in the same period indicate that the differences among grains in different parts are not significant at 0.05 level.
| 品种Variety | 花后天数Days post-anthesis / d | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | 14 | 21 | 28 | 35 | 42 | |||
| 嘉58 Jia 58 | 17.53 | 3.63 | 6.47 | 4.67 | 6.90 | 7.63 | ||
| 嘉67 Jia 67 | 15.21 | 12.80 | 4.18 | 6.24 | 8.78 | 14.07 | ||
| 浙粳99 Zhejing 99 | 19.20 | 11.10 | 0.59 | 7.17 | 3.01 | 8.28 | ||
| 秀水121 Xiushui 121 | 13.02 | 5.12 | 21.14 | 10.15 | 8.85 | 3.54 | ||
| 秀水134 Xiushui 134 | 18.98 | 5.06 | 2.64 | 16.49 | 6.02 | 1.47 | ||
| 中嘉8号 Zhongjia 8 | 10.89 | 1.81 | 4.18 | 5.12 | 4.59 | 16.66 | ||
| 所有品种 All varieties | 24.80 | 16.15 | 45.11 | 41.26 | 34.88 | 31.22 | ||
Table 2 Variation coefficients of SA content between grain positions and between varieties. %
| 品种Variety | 花后天数Days post-anthesis / d | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | 14 | 21 | 28 | 35 | 42 | |||
| 嘉58 Jia 58 | 17.53 | 3.63 | 6.47 | 4.67 | 6.90 | 7.63 | ||
| 嘉67 Jia 67 | 15.21 | 12.80 | 4.18 | 6.24 | 8.78 | 14.07 | ||
| 浙粳99 Zhejing 99 | 19.20 | 11.10 | 0.59 | 7.17 | 3.01 | 8.28 | ||
| 秀水121 Xiushui 121 | 13.02 | 5.12 | 21.14 | 10.15 | 8.85 | 3.54 | ||
| 秀水134 Xiushui 134 | 18.98 | 5.06 | 2.64 | 16.49 | 6.02 | 1.47 | ||
| 中嘉8号 Zhongjia 8 | 10.89 | 1.81 | 4.18 | 5.12 | 4.59 | 16.66 | ||
| 所有品种 All varieties | 24.80 | 16.15 | 45.11 | 41.26 | 34.88 | 31.22 | ||
| 品种-籽粒部位 Variety-grain position | 花后天数Days post-anthesis / d | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | 14 | 21 | 28 | 35 | 42 | |
| J58-TS | 12.85±1.83 a | 6.85±3.27 b | 44.15±1.34 a | 24.55±1.48 bc | 26.22±6.21 a | 35.86±2.29 a |
| J58-MS | 9.11±3.12 a | 9.93±5.06 a | 30.85±4.31 b | 28.35±3.18 ab | 25.31±1.59 a | 37.74±1.56 a |
| J58-BS | 15.44±6.65 a | 13.74±4.69 a | 27.00±21.21 b | 34.10±0.71 a | 23.09±0.62 a | 42.54±1.85 a |
| 变异系数 CV/% | 25.51 | 33.92 | 26.47 | 16.58 | 6.48 | 8.89 |
| J67-TS | 21.90±11.73 a | 9.54±3.62 a | 41.50±3.11 a | 29.90±3.11 a | 24.57±0.61 a | 34.19±0.93 b |
| J67-MS | 24.81±6.26 a | 2.80±4.11 b | 42.40±1.56 a | 27.70±0.99 a | 22.59±0.95 a | 43.82±1.67 a |
| J67-BS | 22.61±13.73 a | 11.24±3.47 a | 42.55±5.73 a | 32.25±2.47 a | 26.24±0.37 a | 26.42±2.09 b |
| 变异系数 CV/% | 6.55 | 56.78 | 1.35 | 7.60 | 7.47 | 25.03 |
| Z99-TS | 7.21±1.63 b | 4.49±1.88 a | 23.70±1.27 a | 23.00±2.69 a | 18.63±2.08 a | 32.66±5.04 a |
| Z99-MS | 16.25±6.17 a | 7.02±5.20 a | 26.70±4.67 a | 24.15±2.33 a | 19.04±2.35 a | 33.96±7.44 a |
| Z99-BS | 20.16±1.37 a | 3.75±3.17 a | 32.15±0.35 a | 25.55±3.89 a | 21.28±0.71 a | 34.51±1.57 a |
| 变异系数 CV/% | 45.66 | 33.76 | 15.57 | 5.27 | 7.27 | 2.82 |
| X121-TS | 13.82±3.11 a | 2.51±0.93 a | 20.85±0.21 a | 26.70±0.71 a | 24.85±0.71 a | 25.45±3.88 a |
| X121-MS | 10.41±5.90 a | 6.14±2.51 a | 15.28±8.80 a | 25.60±4.24 a | 21.86±0.42 a | 31.12±1.99 a |
| X121-BS | 10.00±3.87 a | 1.82±1.34 a | 23.65±1.34 a | 23.80±3.68 a | 25.74±1.12 a | 31.86±5.52 a |
| 变异系数 CV/% | 18.37 | 66.52 | 21.40 | 5.77 | 8.41 | 11.90 |
| X134-TS | 6.55±4.72 a | 3.89±0.36 a | 28.05±2.76 a | 24.30±0.71 a | 21.92±0.29 a | 29.23±0.95 a |
| X134-MS | 7.42±2.84 a | 9.92±3.69 a | 19.80±2.40 a | 23.75±1.77 a | 22.88±2.23 a | 29.27±1.74 a |
| X134-BS | 4.80±1.75 a | 9.87±3.15 a | 25.00±4.95 a | 25.10±3.25 a | 20.60±3.90 a | 33.11±3.17 a |
| 变异系数 CV/% | 21.33 | 43.97 | 17.18 | 2.78 | 5.24 | 7.29 |
| Z8-TS | 9.19±1.25 a | 7.49±1.51 a | 27.15±0.64 a | 39.60±2.55 a | 21.43±3.52 b | 30.99±4.23 a |
| Z8-MS | 13.41±6.66 a | 7.11±6.00 a | 26.85±2.33 a | 30.35±2.62 b | 28.40±5.15 a | 35.02±2.01 a |
| Z8-BS | 8.14±3.82 a | 8.43±1.71 a | 27.90±2.83 a | 23.70±1.70 c | 30.57±2.63 a | 36.47±2.35 a |
| 变异系数 CV/% | 27.22 | 8.84 | 1.98 | 25.58 | 17.81 | 8.31 |
Table 3 Differences of ABA content of grains in various positions. µg/kg
| 品种-籽粒部位 Variety-grain position | 花后天数Days post-anthesis / d | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | 14 | 21 | 28 | 35 | 42 | |
| J58-TS | 12.85±1.83 a | 6.85±3.27 b | 44.15±1.34 a | 24.55±1.48 bc | 26.22±6.21 a | 35.86±2.29 a |
| J58-MS | 9.11±3.12 a | 9.93±5.06 a | 30.85±4.31 b | 28.35±3.18 ab | 25.31±1.59 a | 37.74±1.56 a |
| J58-BS | 15.44±6.65 a | 13.74±4.69 a | 27.00±21.21 b | 34.10±0.71 a | 23.09±0.62 a | 42.54±1.85 a |
| 变异系数 CV/% | 25.51 | 33.92 | 26.47 | 16.58 | 6.48 | 8.89 |
| J67-TS | 21.90±11.73 a | 9.54±3.62 a | 41.50±3.11 a | 29.90±3.11 a | 24.57±0.61 a | 34.19±0.93 b |
| J67-MS | 24.81±6.26 a | 2.80±4.11 b | 42.40±1.56 a | 27.70±0.99 a | 22.59±0.95 a | 43.82±1.67 a |
| J67-BS | 22.61±13.73 a | 11.24±3.47 a | 42.55±5.73 a | 32.25±2.47 a | 26.24±0.37 a | 26.42±2.09 b |
| 变异系数 CV/% | 6.55 | 56.78 | 1.35 | 7.60 | 7.47 | 25.03 |
| Z99-TS | 7.21±1.63 b | 4.49±1.88 a | 23.70±1.27 a | 23.00±2.69 a | 18.63±2.08 a | 32.66±5.04 a |
| Z99-MS | 16.25±6.17 a | 7.02±5.20 a | 26.70±4.67 a | 24.15±2.33 a | 19.04±2.35 a | 33.96±7.44 a |
| Z99-BS | 20.16±1.37 a | 3.75±3.17 a | 32.15±0.35 a | 25.55±3.89 a | 21.28±0.71 a | 34.51±1.57 a |
| 变异系数 CV/% | 45.66 | 33.76 | 15.57 | 5.27 | 7.27 | 2.82 |
| X121-TS | 13.82±3.11 a | 2.51±0.93 a | 20.85±0.21 a | 26.70±0.71 a | 24.85±0.71 a | 25.45±3.88 a |
| X121-MS | 10.41±5.90 a | 6.14±2.51 a | 15.28±8.80 a | 25.60±4.24 a | 21.86±0.42 a | 31.12±1.99 a |
| X121-BS | 10.00±3.87 a | 1.82±1.34 a | 23.65±1.34 a | 23.80±3.68 a | 25.74±1.12 a | 31.86±5.52 a |
| 变异系数 CV/% | 18.37 | 66.52 | 21.40 | 5.77 | 8.41 | 11.90 |
| X134-TS | 6.55±4.72 a | 3.89±0.36 a | 28.05±2.76 a | 24.30±0.71 a | 21.92±0.29 a | 29.23±0.95 a |
| X134-MS | 7.42±2.84 a | 9.92±3.69 a | 19.80±2.40 a | 23.75±1.77 a | 22.88±2.23 a | 29.27±1.74 a |
| X134-BS | 4.80±1.75 a | 9.87±3.15 a | 25.00±4.95 a | 25.10±3.25 a | 20.60±3.90 a | 33.11±3.17 a |
| 变异系数 CV/% | 21.33 | 43.97 | 17.18 | 2.78 | 5.24 | 7.29 |
| Z8-TS | 9.19±1.25 a | 7.49±1.51 a | 27.15±0.64 a | 39.60±2.55 a | 21.43±3.52 b | 30.99±4.23 a |
| Z8-MS | 13.41±6.66 a | 7.11±6.00 a | 26.85±2.33 a | 30.35±2.62 b | 28.40±5.15 a | 35.02±2.01 a |
| Z8-BS | 8.14±3.82 a | 8.43±1.71 a | 27.90±2.83 a | 23.70±1.70 c | 30.57±2.63 a | 36.47±2.35 a |
| 变异系数 CV/% | 27.22 | 8.84 | 1.98 | 25.58 | 17.81 | 8.31 |
| 品种 Variety | 花后天数 Days post-anthesis / d | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | 14 | 21 | 28 | 35 | 42 | ||
| 嘉58 Jia 58 | 31.73 | 7.79 | 19.43 | 9.92 | 15.21 | 6.28 | |
| 嘉67 Jia 67 | 59.71 | 53.37 | 14.78 | 3.42 | 30.56 | 23.74 | |
| 浙粳99 Zhejing 99 | 33.88 | 25.12 | 25.92 | 14.68 | 16.49 | 5.30 | |
| 秀水121 Xiushui 121 | 81.04 | 4.11 | 20.35 | 0.16 | 1.95 | 6.24 | |
| 秀水134 Xiushui 134 | 57.47 | 3.98 | 4.25 | 19.88 | 12.24 | 3.62 | |
| 中嘉8号 Zhongjia 8 | 50.59 | 1.26 | 4.31 | 71.06 | 6.50 | 5.33 | |
| 所有品种 All varieties | 66.27 | 16.46 | 9.89 | 18.58 | 19.89 | 11.92 | |
Table 4 Variation coefficients of IAA between rice grain positions and between varieties. %
| 品种 Variety | 花后天数 Days post-anthesis / d | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | 14 | 21 | 28 | 35 | 42 | ||
| 嘉58 Jia 58 | 31.73 | 7.79 | 19.43 | 9.92 | 15.21 | 6.28 | |
| 嘉67 Jia 67 | 59.71 | 53.37 | 14.78 | 3.42 | 30.56 | 23.74 | |
| 浙粳99 Zhejing 99 | 33.88 | 25.12 | 25.92 | 14.68 | 16.49 | 5.30 | |
| 秀水121 Xiushui 121 | 81.04 | 4.11 | 20.35 | 0.16 | 1.95 | 6.24 | |
| 秀水134 Xiushui 134 | 57.47 | 3.98 | 4.25 | 19.88 | 12.24 | 3.62 | |
| 中嘉8号 Zhongjia 8 | 50.59 | 1.26 | 4.31 | 71.06 | 6.50 | 5.33 | |
| 所有品种 All varieties | 66.27 | 16.46 | 9.89 | 18.58 | 19.89 | 11.92 | |
| 性状 Trait | 脱落酸含量 ABA | 吲哚乙酸含量 IAA | 千粒重 1000-grain weight | 长宽比 Length-width ratio | 整精米率 Head rice rate | 胶稠度 Gel consistency | 碱消值 Alkali value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 水杨酸含量SA content | 0.54* | 0.59** | -0.53* | -0.66** | 0.95** | 0.04 | -0.04 | |
| 脱落酸含量ABA content | 0.62** | 0.15 | 0.12 | 0.31 | -0.16 | -0.27 | ||
| 吲哚乙酸含量IAA content | -0.26 | -0.28 | 0.48* | 0.08 | 0.02 | |||
| 千粒重1000-grain weight | 0.89** | -0.68** | -0.36 | -0.32 | ||||
| 长宽比Length-width ratio | -0.80** | -0.39 | -0.04 | |||||
| 整精米率Head rice rate | 0.20 | 0.02 | ||||||
| 胶稠度Gel consistency | 0.02 | |||||||
Table 5 Correlation of endogenous hormone, yield and quality.
| 性状 Trait | 脱落酸含量 ABA | 吲哚乙酸含量 IAA | 千粒重 1000-grain weight | 长宽比 Length-width ratio | 整精米率 Head rice rate | 胶稠度 Gel consistency | 碱消值 Alkali value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 水杨酸含量SA content | 0.54* | 0.59** | -0.53* | -0.66** | 0.95** | 0.04 | -0.04 | |
| 脱落酸含量ABA content | 0.62** | 0.15 | 0.12 | 0.31 | -0.16 | -0.27 | ||
| 吲哚乙酸含量IAA content | -0.26 | -0.28 | 0.48* | 0.08 | 0.02 | |||
| 千粒重1000-grain weight | 0.89** | -0.68** | -0.36 | -0.32 | ||||
| 长宽比Length-width ratio | -0.80** | -0.39 | -0.04 | |||||
| 整精米率Head rice rate | 0.20 | 0.02 | ||||||
| 胶稠度Gel consistency | 0.02 | |||||||
| [1] | 王慧, 方玉, 黄艳玲, 冯冲, 杨力, 周桂香, 张从合. 稻米主要食味品质基因型与环境互作分析及其相关性研究[J]. 中国稻米, 2020,26(2):23-26. |
| Wang H, Fang Y, Huang Y L, Feng C, Yang L, Zhou G X, Zhang C H. Analysis of the genotype and environment interactions as well as the correlation research of main taste quality in rice[J]. China Rice, 2020,26(2):23-26. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | Lin Z M, Zhang X H, Wang Z X, Jiang Y T, Liu Z H, Alexander D, Li G H, Wang S H, Ding Y F. Metabolomic analysis of pathways related to rice grain chalkiness by a notched-belly mutant with high occurrence of white-belly grains[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2017,17:39. |
| [3] | 贾小丽, 叶江华, 苗利国, 林红梅, 林文雄. 水稻籽粒灌浆速率的发育遗传机制研究[J]. 热带作物学报, 2012,33(2):622-626. |
| Jia X L, Ye J H, Miao L G, Lin H M, Lin W X. Developmental genetic mechanism research on grain- filling rate in rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2012,33(2):622-626. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 朱庆森, 曹显祖, 骆亦其. 水稻籽粒灌浆的生长分析[J]. 作物学报, 1988,14(3):182-192. |
| Zhu Q S, Cao X Z, Luo Y Q. Growth analysis of grain filling in rice[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 1988,14(3):182-192. (in Chinese) | |
| [5] | 户少武, 张欣, 景立权, 赖上坤, 王云霞, 朱建国, 王余龙, 杨连新. 高浓度CO2对稻穗不同位置籽粒结实和米质性状的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2019,30(11):3725-3734. |
| Hu S W, Zhang X, Jing L Q, Lai S K, Wang Y X, Zhu J G, Wang Y L, Yang L X. Effects of elevated CO2 concentration on grain filling capacity and quality of rice grains located at different positions on a panicle[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2019,30(11):3725-3734. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | Kusano H, Arisu Y, Nakajima J, Yaeshima M, Shimada H. Implications of the gene for F1-ATPase β subunit (AtpB) for the grain quality of rice matured in a high-temperature environment[J]. Plant Biotechnology, 2016,33(3):169-175 |
| [7] | 杨建昌, 刘立军, 王志琴, 郎有忠, 朱庆森. 稻穗颖花开花时间对胚乳发育的影响及其生理机制[J]. 中国农业科学, 1999,32(3):44-51. |
| Yang J C, Liu L J, Wang Z Q, Lang Y Z, Zhu Q S. Effect of flowering time of spikelet on endosperm development and its physiological mechanism[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 1999,32(3):44-51. (in Chinese) | |
| [8] | 陈新红, 韩正光, 张安存, 叶玉秀, 周青, 吕宏飞. 不同施氮量与种植密度对水稻穗上不同部位结实特性的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2014,26(6):1578-1582. |
| Chen X H, Han Z G, Zhang A C, Ye Y X, Zhou Q, Lv H F. Analysis on rice grain filling characteristics in different spikelet positions under different nitrogen rates and planting densities[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2014,26(6):1578-1582. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 袁莉民, 展明飞, 章星传, 王志琴, 杨建昌. 水稻穗上不同粒位籽粒胚乳结构及其结实期灌溉方式对它的调控作用[J]. 作物学报, 2018,44(2):245-259. |
| Yuan L M, Zhan M F, Zhang X C, Wang Z Q, Yang J C. Endosperm structure of grains at different positions of rice panicle and regulation effect of irrigation regimes on it during grain filling[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2018,44(2):245-259. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | Wobus U, Weber H. Seed maturation: Genetic programmers and control signals[J]. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 1999,2(1):33-38. |
| [11] | Yang J C, Peng S B, Visperas R M, Sanico A L, Zhu Q S, Gu S L. Grain filling pattern and cytokinein content in the grains and roots of rice plants[J]. Plant Growth Regulation, 2000,30(3):261-270. |
| [12] | 冯志威. 灌浆期喷施植物生长调节剂对谷子产量及生理特性的影响[D]. 太原: 山西农业大学, 2017. |
| Feng Z W. Effects of plant growth regulator on yield and physiological mechanism of foxtail millet in filling stage[D]. Taiyuan: Shanxi Agricultural University, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | 杨建昌, 王志琴, 朱庆森, 苏宝林. ABA与GA对水稻籽粒灌浆的调控[J]. 作物学报, 1999,25(3):341-348. |
| Yang J C, Wang Z Q, Zhu Q S, Shu B L. Regulation of ABA and GA to the grain filling of rice[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 1999,25(3):341-348. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | 张浩, 罗时石, 龚荐, 葛才林, 马飞. 吲哚乙酸对水稻花后剑叶光合产物输配作用的示踪动力学研究[J]. 江苏农学院学报, 1996(1):31-36. |
| Zhang H, Luo S S, Gong J, Ge C L, Ma F. Study on the isotope kinetics of the photosynthetic of flag leaf of post floral rice and IAA affection on it[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 1996(1):31-36. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 赵丹, 纪鹏, 何晓蕾, 景艳丽, 张涛, 王洪义. SA对盐胁迫下草本植物种子萌发及幼苗生理特性影响的研究进展[J]. 黑龙江八一农垦大学学报, 2020,32(3):7-12. |
| Zhao D, Ji P, He X L, Jing Y L, Zhang T, Wang H Y. Research progress of effect of SA on seed germination and seedling physiological characteristics of herbaceous plants under salt stress[J]. Journal of Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University, 2020,32(3):7-12. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 任菲, 张荣佳, 陈强, 白艳波, 黄菲, 李雪梅. ABA和SA对于提高植物抗旱及抗盐性的研究进展[J]. 生物技术通报, 2012(3):17-21. |
| Ren F, Zhang R J, Chen Q, Bai Y B, Huang F, Li X M. Progress in ABA and SA improving plant drought resistance and salt resistance[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2012(3):17-21. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | 曹转勤. 水稻几个突变体的籽粒灌浆特征及其与内源激素的关系[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2014. |
| Cao Z Q. Grain filling characteristics and their relations with endogenous hormones in several rice mutants[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | 王嘉宇, 徐正进, 张世春, 陈温福. 水稻穗不同部位籽粒品质性状差异的比较[J]. 华北农学报, 2008,23(1):96-100. |
| Wang J Y, Xu Z J, Zhang S C, Chen W F. Comparison in quality traits at different parts within a rice panicle[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2008,23(1):96-100. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | 董明辉, 桑大志, 王朋, 王学明, 杨建昌. 不同施氮水平下水稻穗上不同部位籽粒的蒸煮与营养品质变化[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2006(4):389-395. |
| Dong M H, Shang D Z, Wang P, Wang X M, Yang C J. Changes in cooking and nutritional qualities of grains at different positions within a rice panicle under different nitrogen levels[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2006(4):389-395. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | 蔡一霞, 刘春香, 王维, 张洪熙, 张祖建, 杨静, 唐汉忠. 灌浆期表观直链淀粉含量相似品种稻米胶稠度和RVA谱的动态差异[J]. 中国农业科学, 2011,44(12):2439-2445. |
| Cai Y X, Liu C X, Wang W, Zhang H X, Zhang Z J, Yang J, Tang H Z. Dynamic differences of the RVA profile and gel consistency in two rice varieties with similar apparent amylose content during grain filling[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2011,44(12):2439-2445. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | 丛琳. 辽宁不同时期水稻品种产量与品质特性研究[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学, 2018. |
| Cong L. study on the yield and quality characteristics of rice varieties in Liaoning at different stage[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Agricultural University, 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | 张蕊, 高志明, 吕俊, 王三根. 外源水杨酸对水稻幼苗耐寒性的影响[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2012,40(6):62-65. |
| Zhang R, Gao Z M, Lv J, Wang S G. Effect of exogenous salicylic acid on cold tolerance of rice seedling[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2012,40(6):62-65. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 王俊斌, 王海凤, 刘海学. 水杨酸促进盐胁迫条件下水稻种子萌发的机理研究[J]. 华北农学报, 2012,27(4):223-227. |
| Wang J B, Wang H F, Liu H X. Study on mechanism of salicylic acid on the promotion of rice seeds germination under salt stress[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2012,27(4):223-227. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | Feng B H, Zhang C X, Chen T T, Zhang X F, Tao L X, Fu G F. Salicylic acid reverses pollen abortion of rice caused by heat stress[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2018,18(1):1-16 |
| [25] | 符冠富, 张彩霞, 杨雪芹, 杨永杰, 陈婷婷, 赵霞, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 章秀福, 陶龙兴, 金千瑜. 水杨酸减轻高温抑制水稻颖花分化的作用机理研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2015,29(6):637-647. |
| Fu G F, Zhang C X, Yang X Q, Yang Y J, Chen T T, Zhao X, Fu W M, Feng B H, Zhang X F, Tao L X, Jin Q Y. Action mechanism by which SA alleviates high temperature-induced inhibition to spikelet differentiation[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2015,29(6):637-647. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | Mohammed A R, Tarpley L. Effects of night temperature, spikelet position and salicylic acid on yield and yield‐related parameters of rice plants[J]. Journal of Agronomy and Crop Science, 2011,197(1):40-49 |
| [27] | 周万海, 师尚礼, 寇江涛. 外源水杨酸对苜蓿幼苗盐胁迫的缓解效应[J]. 草业学报, 2012,21(3):171-176. |
| Zhou W H, Shi S L, Kou J T. Exogenous salicylic acid on alleviating salt stress in alfalfa seedlings[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2012,21(3):171-176. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | 王宝增, 张一名, 张江丽. 水杨酸对盐胁迫下沙打旺幼苗生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2016,25(8):74-80. |
| Wang B Z, Zhang Y M, Zhang J L, Bi S Q, Kong H. Effects of salicylic acid on growth of Astragalus adsurgens seedlings under salt stress[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2016,25(8):74-80. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | Wang Y F, Hou Y X, Qiu J H, Wang H M, Wang S, Tang L Q, Tong X H, Zhang J. Abscisic acid promotes jasmonic acid biosynjournal via a 'SAPK10-bZIP72-AOC' pathway to synergistically inhibit seed germination in rice[J]. The New Phytologist, 2020,228(4):1-47 |
| [30] | 俞乐, 高彬, 李烨林, 谭伟健, 刘拥海. 外源ABA对GalLDH超表达转基因水稻种子萌发和生理指标的影响[J]. 种子, 2019,38(12):13-19 |
| Yu L, Gao B, Li Y L, Tang W J, Liu Y H. Effects of exogenous ABA on seeds germination and physiological indicators of GalLDH-overexpressing rice[J]. Seed, 2019,38(12):13-19. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | Lee B T, Martin P, Bangerth F. Phytohormone levels in the florets of a single wheat spikelet during preanjournal development relationships to grain set[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 1988,39(204):933-937. |
| [32] | 张上隆, 陈昆松, 叶庆富, 陈大明, 刘春荣. 柑桔授粉处理和单性结实子房(幼果)内源IAA、ABA和ZT含量的变化[J]. 园艺学报, 1994,21(2):117-123. |
| Zhang S L, Chen K S, Ye Q F. Changes of endogenous IAA, ABA and ZT in pollinated, non-pollinated and parthenocarpic ovary (fruitlet) of citrus[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 1994,21(2):117-123. (in Chinese) | |
| [33] | Kato T, Sakurai N, Kuraishi S. The changes of endogenous abscisic acid in developing grains of two rice cultivars with different grain size[J]. Crop Science Society of Japan, 1993,62(3):456-461. |
| [34] | 范晓荣, 沈其荣. ABA、IAA对旱作水稻叶片气孔的调节作用[J]. 中国农业科学, 2003,36(12):1450-1455. |
| Fang X R, Shen Q R. Effects of ABA and IAA on the behavior of stomata of rice crop cultivated in aerobic soil condition[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2003,36(12):1450-1455. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [35] | 段娜, 贾玉奎, 徐军, 陈海玲, 孙鹏. 植物内源激素研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2015,31(2):159-165. |
| Duan N, Jia Y K, Xu J, Chen H L, Sun P. Research progress on plant endogenous hormones[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2015,31(2):159-165. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [36] | 沙汉景, 胡文成, 贾琰, 王新鹏, 田雪飞, 于美芳, 赵宏伟. 外源水杨酸、脯氨酸和γ-氨基丁酸对盐胁迫下水稻产量的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2017,43(11):1677-1688. |
| Sha H J, Hu W C, Jia Y, Wang X P, Tian X F, Yu M F. Effect of exogenous salicylic acid, proline, and γ-aminobutyric acid on yield of rice under salt stress[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2017,43(11):1677-1688. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [37] | 杨军, 蔡哲, 刘丹, 胡犁月, 曲文波, 张崇华, 王尚明, 田俊. 高温下喷施水杨酸和磷酸二氢钾对中稻生理特征和产量的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2019,30(12):4202-4210. |
| Yang J, Cai Z, Liu D, Hu L Y, Qu W B, Zhang C H, Wang S M, Tian J. Effects of spraying salicylic acid and potassium dihydrogen phosphate on physiological characteristics and grain yield of single-season rice under high temperature condition[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2019,30(12):4202-4210. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [38] | 段俊, 田长恩, 梁承邺, 黄毓文, 刘鸿先. 水稻结实过程中穗不同部位谷粒中内源激素的动态变化[J]. 植物学报, 1999(1):3-5. |
| Duan J, Tian C E, Liang C Y, Huang Y W, Liu H X. Dynamic changes of endogenous hormones in grains in different parts of the panicle during rice setting[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 1999(1):3-5. (in Chinese) | |
| [39] | 萧浪涛, 王若仲, 丁君辉, 严钦泉. 内源激素与亚种间杂交稻籽粒灌浆的关系[J]. 湖南农业大学学报: 自然科学版, 2002,28(4):269-273. |
| Xiao L T, Wang R Z, Ding J H. Relationship between endogenous hormones and grain filling of inter- subspecies hybrid rice[J]. Journal of Hunan Agricultural University: Natural Sciences, 2002,28(4):269-273. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [40] | 陶龙兴, 王熹, 黄效林. 内源IAA 对杂交稻强、弱势粒灌浆增重的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2003,17(2):56-62. |
| Tao L X, Wang X, Huang X L. Effects of endogenous IAA on grain filling of hybrid rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2003,17(2):56-62. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | YAO Shu, ZHAO Chunfang, CHEN Tao, LU Kai, ZHOU Lihui, ZHAO Ling, ZHU Zhen, ZHAO Qingyong, LIANG Wenhua, HE Lei, WANG Cailin, ZHANG Yadong. Nutritional Quality and Cooking and Eating Quality Characteristics of Low Glutelin Semi-glutinous japonica Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(2): 178-188. |
| [2] | TANG Ruodi, CHEN Chao. Effects of Outsourcing Services on Elderly Farmers Participation in Rice Production [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(6): 647-655. |
| [3] | CAO Yuexuan, YAN Huijing, WANG Kejian, LIU Chaolei. Rapid Identification of Rice Clonal Seeds Generated by Synthetic Apomixis at Seedling Stage [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(6): 656-662. |
| [4] | Zhidong WANG, Yibo CHEN, Rong GONG, Shaochuan ZHOU, Chongrong WANG, Hong LI, Daoqiang HUANG, Degui ZHOU, Lei ZHAO, Yangyang PAN, Yiqiang YANG, LIXiaofang. Correlation Between SPAD Value of Flag Leaf and Rice Quality of High Quality indica Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2021, 35(1): 89-97. |
| [5] | Yuping ZHANG, Junke WANG, Yaliang WANG, Yanhua CHEN, Dengfeng ZHU, Huizhe CHEN, Jing XIANG, Yikai ZHANG, Xiaojun LIU, Yan ZHU, Weixing CAO. Response ofRice Starch Synthesis to Night Temperature Changes [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2020, 34(6): 525-538. |
| [6] | Xiao-ping YUAN, Cai-hong WANG, Hong-zhong DENG, Qun XU, Yue FENG, Han-yong YU, Yi-ping WANG, Xing-hua WEI. Minimum of SSR Markers for Analyzing Genetic Variation of Oryza sativa L. [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2015, 29(6): 578-586. |
| [7] | Li-nan ZHU, Hai-ying LIU, Lu-lu SUN, Tao SUN, Xue-dong GUO, Fang-xu ZHU, Zhong-chen ZHANG, Zheng-xun JIN. Analysis of Expression Characteristics of Isoamylase and the Correlation with Starch Content During Grain Filling in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2015, 29(5): 528-534. |
| [8] | ZHANG Honggen#, QIAN Kai#, SUN Yibiao, PEI Yan, FENG Zhiqiang, LIU Xiaoyu, TANG Shuzhu*, LIANG Guohua, GU Minghong. Identifying the Genetic Basis of Spikelet Fertility Differences Between BTtype ThreeLine japonica Hybrids [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2014, 28(4): 377-383. |
| [9] | DING Mingliang1,2,#, SU Zhenxi2,#, ZOU Qian2, ZHU Zhenhua2, YUAN Pingrong2, CHEN Yumin2, LIU Weihua2, LU Shugang1, DAI Luyuan2,*. Relationship Between Lodging Resistance and Either Agronomic Traits or Parents′ Lodging Resistance in Plateau japonica Rice [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2012, 26(3): 325-330. |
| [10] | ZHAO Feng1, 2, ZHANG Weijian1, ZHANG Xiufu2,*, WANG Danying2, XU Chunmei2 . Effects of OxygenIncreasing Patterns in Paddy Fields on Rice GrainFilling [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2011, 25(6): 605-612. |
| [11] | ZHANG Jian-fu ,ZHU Yong-sheng,CAI Qiu-hua,ZHUO Chuan-ying,ZHANG Shang-shou,ZHENG Rong-he ,XIE Hua-an . Analysis on Correlationship of Net Photosynthetic Rate with Yield and Its Components of Ratooning Rice [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2011, 25(1): 103-106 . |
| [12] | WEI Hai-yan,ZHANG Hong-cheng*,DAI Qi-gen,MA Qun,LI Jie,ZHANG Qing,HUO Zhong-yang,XU Ke. Effect of Nitrogen Level on Iron Content in Milled Rice and Its Genotypic Difference [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2010, 24(1): 55-61 . |
| [13] | ZHANG Tao,#,NI Xian-lin,#,JIANG Kai-feng,YANG Qian-hua,YANG Li,WAN Xian-qi,CAO Ying-jiang,ZHENG Jia-kui, . Correlation Between Genetic Distance Based on Molecular Markers of Functional Genes and Heterosis in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2009, 23(6): 567-572 . |
| [14] | HAO Xian-bin,MA Xiu-fang,HU Pei-song,ZHANG Zhong-xu,SUI Guo-min ,HUA Ze-tian. Relationship Between Plant Type and Rice Quality of japonica Hybrid Rice in Northern China [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2009, 23(4): 398-404 . |
| [15] |
LI Gang,DENG Qiming,LI Shuangcheng,WANG Shiquan,LI Ping.
Correlation Analysis Between RVA Profile Characteristics and Quality in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2009, 23(1): 99-99~102 . |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||