
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2021, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (3): 303-310.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2021.0717
• Research Papers • Previous Articles
Shufang LIU1,2,#, Liying DONG1,2,#, Xundong LI1,2, Wumin ZHOU1,3, Qinzhong YANG1,2,*( )
)
Received:2020-07-24
Revised:2020-11-24
Online:2021-05-10
Published:2021-05-10
Contact:
Qinzhong YANG
About author:#These authors contributed equally to this work;
刘树芳1,2,#, 董丽英1,2,#, 李迅东1,2, 周伍民1,3, 杨勤忠1,2,*( )
)
通讯作者:
杨勤忠
作者简介:#共同第一作者;
基金资助:Shufang LIU, Liying DONG, Xundong LI, Wumin ZHOU, Qinzhong YANG. Different Reactions of Rice Monogenic Line IRBL9-W Harboring Pi9 Gene to Magnaporthe oryzae Containing AvrPi9 During Seedling and Adult-plant Stages[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2021, 35(3): 303-310.
刘树芳, 董丽英, 李迅东, 周伍民, 杨勤忠. 持有Pi9基因的水稻单基因系IRBL9-W对稻瘟病菌苗期和成株期抗性差异[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(3): 303-310.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2021.0717
| 单基因系 Monogenic line | 抗性基因 R gene | 稻瘟病菌株 Magnaporthe oryzae strains | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YX2-2-1 | YX2-3-2 | YX2-5-1 | YX2-6-1 | YX2-10-1 | YX2-14-1 | YX2-7-1 | YX2-15-1 | Y363 | ||
| IRBLA-A | Pia | R | R | R | R | R | R | S | S | S |
| IRBLI-F5 | Pii | R | S | R | S | S | R | S | S | S |
| IRBLKS-F5 | Piks | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| KRBLK KA | Pik | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| KRBLKP-K60 | Pikp | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R |
| KRBLKH-K3 | Pikh | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | S | R |
| IRBLZ5-CA | Pi2 | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| IRBLZ FU | Piz | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| IRBLZT-T | Pizt | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R |
| IRBLTA-K1 | Pita | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| IRBLB-B | Pib | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| IRBLT-K59 | Pit | R | R | R | R | R | R | S | S | S |
| IRBLSH-B | Pish | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R |
| IRBL1-CL | Pi1 | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | S | S |
| IRBL3-CP4 | Pi3 | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| IRBL5-M | Pi5 | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R |
| IRBL7-M | Pi7 | S | S | S | S | R | S | S | S | R |
| IRBL12-M | Pi12 | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R |
| IRBL19-A | Pi19 | S | S | S | S | R | S | S | S | S |
| IRBLKM-TS | Pikm | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | S | S |
| IRBL20-IR24 | Pi20 | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R |
| IRBLTA2-PI | Pita2 | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | S | R |
| IRBL11-ZH | Pi11 | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| IRBL9-W | Pi9 | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R |
| LTH | - | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
Table 1 Pathotyping of Magnaporthe oryzae strains on monogenic lines.
| 单基因系 Monogenic line | 抗性基因 R gene | 稻瘟病菌株 Magnaporthe oryzae strains | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YX2-2-1 | YX2-3-2 | YX2-5-1 | YX2-6-1 | YX2-10-1 | YX2-14-1 | YX2-7-1 | YX2-15-1 | Y363 | ||
| IRBLA-A | Pia | R | R | R | R | R | R | S | S | S |
| IRBLI-F5 | Pii | R | S | R | S | S | R | S | S | S |
| IRBLKS-F5 | Piks | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| KRBLK KA | Pik | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| KRBLKP-K60 | Pikp | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R |
| KRBLKH-K3 | Pikh | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | S | R |
| IRBLZ5-CA | Pi2 | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| IRBLZ FU | Piz | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| IRBLZT-T | Pizt | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R |
| IRBLTA-K1 | Pita | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| IRBLB-B | Pib | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| IRBLT-K59 | Pit | R | R | R | R | R | R | S | S | S |
| IRBLSH-B | Pish | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R |
| IRBL1-CL | Pi1 | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | S | S |
| IRBL3-CP4 | Pi3 | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| IRBL5-M | Pi5 | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R |
| IRBL7-M | Pi7 | S | S | S | S | R | S | S | S | R |
| IRBL12-M | Pi12 | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R |
| IRBL19-A | Pi19 | S | S | S | S | R | S | S | S | S |
| IRBLKM-TS | Pikm | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | S | S |
| IRBL20-IR24 | Pi20 | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R |
| IRBLTA2-PI | Pita2 | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | S | R |
| IRBL11-ZH | Pi11 | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| IRBL9-W | Pi9 | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R |
| LTH | - | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
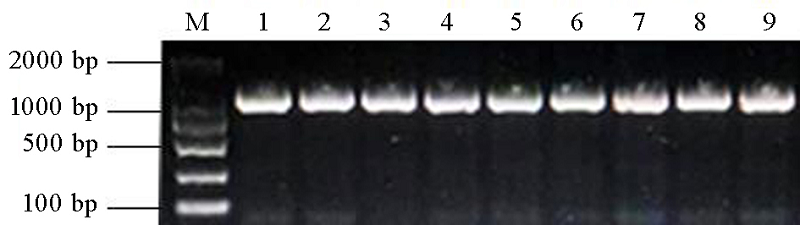
Fig. 2. Amplification of AvrPi9 from different M. oryzae strains. M, DNA molecular marker; DL2000; Lane 1 to Lane 9 refer to YX2-2-1, YX2-3-2, YX2-5-1, YX2-6-1, YX2-10-1, YX2-14-1, YX2-7-1, YX2-15-1 and Y363, respectively.
| 稻瘟病菌株 M. oryzae strain | 发病级别 Disease scores | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 9 | |
| YX2-7-1 | 0a | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 13 |
| YX2-15-1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 13 |
| Y363 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 14 |
| 空白对照CKb | 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Table 2 Investigating results of panicle blast of IRBL9-W inoculated with three M. oryzae strains at late-booting stage.
| 稻瘟病菌株 M. oryzae strain | 发病级别 Disease scores | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 9 | |
| YX2-7-1 | 0a | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 13 |
| YX2-15-1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 13 |
| Y363 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 14 |
| 空白对照CKb | 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |

Fig. 1. Symptoms of monogenic line IRBL9-W inoculated with M. oryzae fungus at late-booting stage and seedling stage. A–C, Symptoms of monogenic line IRBL9-W inoculated with M. oryze strains YX2-7-1, YX2-15-1 and Y363 at late booting stage, respectively. D–F: Symptoms of monogenic line IRBL9-W (left) and Lijiangxintuanheigu (right) inoculated with M. oryzae strains YX2-7-1, YX2-15-1 and Y363 at seedling stage, respectively.
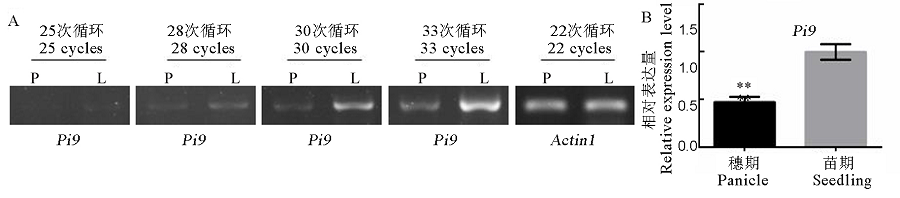
Fig. 3. Expression level of Pi9 gene. A, Expression analysis of Pi9 gene by semi-quantitative RT-PCR method. The cDNA prepared from panicles (P) of adult plants and seedling leaves (L) of IRBL9-W carrying Pi9 gene was used as template for PCR amplification, with Actin 1 as reference gene; B, Comparative analysis of relative expression level of Pi9 gene in panicle and seedling leaves of IRBL9-W by real-time quantitative RT-PCR.
| [1] | Couch B C, Kohn L M.A multilocus gene genealogy concordant with host preference indicates segregation of a new species, Magnaporthe oryzae, from M. grisea[J]. Mycologia, 2002, 94(4): 683-693. |
| [2] | Wilson R A, Talbot N J.Under pressure: Investigating the biology of plant infection by Magnaporthe oryzae[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2009, 7: 185-195. |
| [3] | Savary S, Willocquet L, Pethybridge S J, Esker P, McRoberts N, Nelson A. The global burden of pathogens and pests on major food crops[J]. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 2019, 3(3): 430-439. |
| [4] | Sesma A, Osbourn A E.The rice leaf blast pathogen undergoes developmental processes typical of root-infecting fungi.Nature, 2004, 431(7008): 582-586. |
| [5] | Skamnioti P, Gurr S J.Against the grain: Safeguarding rice from rice blast disease[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2008, 27(3): 141-150. |
| [6] | Dean R, van Kan J A L, Pretorius Z A, Hammond-kosack K E, Pietro A D, Spanu P D, Rudd J J, Dickman M, Kahmann R, Ellis J, Foster G D. The top 10 fungal pathogens in molecular plant pathology[J]. Molecular Plant Pathology, 2012, 13(4): 414-430. |
| [7] | Puri K D, Shreshta S M, Chhetri G B K, Joshi K D. Leaf and neck blast resistance reaction in tropical rice lines under greenhouse condition[J]. Euphytica, 2009, 165(3): 523-532. |
| [8] | Flor H H.Current status of the gene-for-gene concept[J]. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 1971, 9(1): 275-296. |
| [9] | Silué D, Notteghem J L, Tharreau D.Evidence of a gene-for-gene relationship in the Oryza sativa- Magnaporthe grisea pathosystem[J]. Phytopathology, 1992, 82: 577-580. |
| [10] | Jia Y, McAdams S A, Bryan G T, Hershey H P, Valent B. Direct interaction of resistance gene and avirulence gene products confers rice blast resistance[J]. The EMBO Journal, 2000, 19: 4004-4014. PMID: 10921881. |
| [11] | Ebbole D J.Magnaporthe as a model for understanding host-pathogen interactions[J]. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 2007, 45(1): 437-456. |
| [12] | Kalia S, Rathour R.Current status on mapping of genes for resistance to leaf and neck-blast disease in rice[J]. 3 Biotech, 2019, 9: 209. |
| [13] | Zhuang J Y, Ma W B, Wu J L, Chai R Y, Lu J, Fan Y Y, Jin M Z, Leung H, Zheng K L.Mapping of leaf and neck blast resistance genes with resistance gene analog, RAPD and RFLP in rice[J]. Euphytica , 2002, 128: 363-370. |
| [14] | Ma J, Lei C, Xu X, Hao K, Wang J, Cheng Z, Wan J.Pi64, encoding a novel CC-NBS-LRR protein, confers resistance to leaf and neck blast in rice[J]. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 2015, 28(5): 558-568. |
| [15] | Fujii K, Hayano-Saito Y, Saito K, Sugiura N, Hayashi N, Tsuji T, Izawa T, Iwasaki M.Identification of a RFLP marker tightly linked to the panicle blast resistance gene, Pb1, in rice[J]. Breeding Science, 2000, 50: 183-188. |
| [16] | Chen J, Shi Y F, Liu W Z, Chai R Y, Fu Y P, Zhuang J Y, Wu J L.A Pid3 allele from rice cultivar Gumei 2 confers resistance to Magnaporthe oryzae[J]. Journal of Genetics and Genomics, 2011, 38: 209-216. |
| [17] | Hayashi N, Inoue H, Kato T, Funao T, Shirota M, Shimizu T, Kanamori H, Yamane H, Hayano-Saito Y, Matsumoto T, Yano M, Takatsuji H.Durable panicle blast-resistance gene Pb1 encodes an atypical CC-NBS-LRR protein and was generated by acquiring a promoter through local genome duplication[J]. The Plant Journal, 2010, 64(3): 498-510. |
| [18] | Fang N, Wei X, Shen L, Yu Y, Li M, Yin C, He W, Guan C, Chen H, Zhang H, Bao Y.Fine mapping of a panicle blast resistance gene Pb-bd1 in japonica landrace Bodao and its application in rice breeding[J]. Rice, 2019, 12(1): 18. |
| [19] | Wang R, Fang N, Guan C, He W, Bao Y, Zhang H.Characterization and fine mapping of a blast resistant gene Pi-jnw1 from the japonica rice landrace Jiangnanwan[J]. PLOS ONE,2016, 11(12): e0169417. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0169417. |
| [20] | Qu S, Liu G, Zhou B, Bellizzi M, Zeng L, Dai L, Han B, Wang G L.The broad-spectrum blast resistance gene Pi9 encodes a nucleotide-binding site-leucine-rich repeat protein and is a member of a multigene family in rice[J]. Genetics, 2006, 172(3): 1901-1914. |
| [21] | Liu G, Lu G, Zeng L, Wang G L.Two broad-spectrum blast resistance genes, Pi9(t) and Pi2(t), are physically linked on rice chromosome 6[J]. Molecular Genetic and Genomics, 2002, 267(4): 472-480. |
| [22] | 雷财林, 张国民, 程治军, 马军滔, 王久林, 辛爱华, 陈平, 肖家雷, 张欣, 刘迎雪, 郭秀平, 王洁, 翟虎渠, 万建民. 黑龙江省稻瘟病菌生理小种毒力基因分析与抗病育种策略[J]. 作物学报, 2011, 37(1): 18-27. |
| Lei C L, Zhang G M, Cheng Z J, Ma J T, Wang J L, Xin A H, Chen P, Xiao J L, Zhang X, Liu Y X, Guo X P, Wang J, Zhai H Q, Wan J M.Pathogenic races and virulence gene structure of Magnaporthe oryzae population and rice breeding strategy for blast resistance in Heilongjiang Province[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2011, 37(1): 18-27. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 董丽英, 王群, 刘树芳, 郑凤萍, 李迅东, 杨勤忠. 云南省稻瘟病菌群体对稻瘟病抗性单基因系的致病性分析[J]. 西南农业学报, 2012, 25(2): 467-473. |
| Dong L, Wang Q, Liu S, Zheng F, Li X, Yang Q.Pathogenicity analysis of Magnaporthe oryzae populations of Yunnan on monogenic lines for resistance to rice blast[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2012, 25(2): 467-473. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | 汪文娟, 苏菁, 杨健源, 韦小燕, 陈凯玲, 陈珍, 陈深, 朱小源. 源于广8A 杂交稻组合的稻瘟病菌无毒基因型分析[J]. 中国农业科学, 2018, 51(24): 4633-4646. |
| Wang W J, Su Q, Yang J Y, Wei X Y, Chen K L, Chen Z, Chen S, Zhu X Y.Analysis of Magnaporthe oryzae avirulent genes in the infected hybrid rice combinations derived from a sterile line of Guang 8A[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2018, 51(24): 4633-4646. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | Wang J C, Jia Y, Wen J W, Liu W P, Liu X M, Li L, Jiang Z Y, Zhang J H, Guo X L, Ren J P.Identification of rice blast resistance genes using international monogenic differentials[J]. Crop Protection, 2013, 45: 109-116. |
| [26] | 刘水芳, 杨秀荣, 孙淑琴, 刘春艳, 王勇, 张春祥, 顾红艳. 水稻品种抗稻瘟病鉴定技术[J]. 天津农业科学, 2007, 13(4): 55-58. |
| Liu S, Yang X, Sun S, Liu C, Wang Y, Zhang C, Gu H.Identification technique of rice resistance to Magnaporthe grisea[J]. Tianjin Agricultural Sciences, 2007, 13(4): 55-58. (in Chinese) | |
| [27] | Wu J, Kou Y J, Bao J D, Li Y, Tang M Z, Zhu X L, Ponaya A, Xiao G, Li J B, Li C Y, Song M Y, Cumagun C J R, Deng Q Y, Lu G D, Jeon J S, Naqvi N, Zhou B. Comparative genomics identifies the Magnaporthe oryzae avirulence effector Avr-Pi9 that triggers Pi9-mediated blast resistance in rice[J]. New Phytologist, 2015, 206(4): 1463-1475. |
| [28] | Wu Y Y, Yu L, Pan C H, Dai Z Y, Li Y H, Xiao N, Zhang X X, Ji H J, Huang N S, Zhao B H, Zhou C H, Liu G Q, Liu X J, Pan X B, Liang C Z, Li A H.Development of near-isogenic lines with different alleles of Piz locus and analysis of their breeding effect under Yangdao 6 background[J]. Molecular Breeding, 2016, 36: 12. |
| [29] | Wu Y Y, Chen Y, Pan C H, Xiao N, Yu L, Li Y H, Zhang X X, Pan X B, Chen X J, Dai Z Y, Li A H.Development and evaluation of near-isogenic lines with different blast resistance alleles at the Piz locus in japonica rice from the lower region of the Yangtze River, China[J]. Plant Disease, 2017, 101: 1283-1291. |
| [30] | Collard B C Y, Mackill D J. Marker-assisted selection: An approach for precision plant breeding in the twenty-first century.Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London: Series B, 2008, 363: 557-572. |
| [31] | 倪大虎, 易成新, 李莉, 汪秀峰, 王文相, 杨剑波. 利用分子标记辅助选择聚合水稻基因Xa21和Pi9(t)[J]. 分子植物育种, 2005, 3(3): 329-334. |
| Ni D H, Yi C X, Li L, Wang X F, Wang W X, Yang J B.Pyramiding Xa21 and Pi9(t) in rice by marker-assisted selection[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2005, 3(3): 329-334. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [32] | 殷得所, 夏明元, 李进波, 万丙良, 査中萍, 杜雪树, 戚华雄. 抗稻瘟病基因Pi9的STS连锁标记开发及在分子标记辅助育种中的应用[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2011, 25(1): 25-30. |
| Yin D S, Xia M Y, Li J B, Wan B L, Zha Z P, Du X S, Qi H X.Development of STS marker linked to rice blast resistance gene Pi9 in marker-assisted selection breeding[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2011, 25(1): 25-30. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [33] | 陈建民, 付志英, 权宝权, 田大刚, 李刚, 王锋. 分子标记辅助培育双抗稻瘟病和白叶枯病杂交稻恢复系[J]. 分子植物育种, 2009, 7(3): 465-470. |
| Chen J M, Fu Z Y, Quan B Q, Tian D G, Li G, Wang F.Breeding hybrid rice restoring line with double resistance to rice blast and bacterial blight by marker-assisted selection[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2009, 7(3): 465-470. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | HOU Xiaoqin, WANG Ying, YU Bei, FU Weimeng, FENG Baohua, SHEN Yichao, XIE Hangjun, WANG Huanran, XU Yongqiang, WU Zhihai, WANG Jianjun, TAO Longxing, FU Guanfu. Mechanisms Behind the Role of Potassium Fulvic Acid in Enhancing Salt Tolerance in Rice Seedlings [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [2] | SUN Zhiguang, DAI Huimin, CHEN Tingmu, LI Jingfang, CHI Ming, ZHOU Zhenling, LIU Yan, LIU Jinbo, XU Bo, XING Yungao, YANG Bo, LI Jian, LU Baiguan, FANG Zhaowei, WANG Baoxiang, XU Dayong. Phenotypic Identification and Gene Mapping of a Lesion Mimic Mutant lmm7 in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(4): 357-366. |
| [3] | LIANG Cheng, XIANG Xunchao, ZHANG Ouling, YOU Hui, XU Liang, CHEN Yongjun. Analyses on Agronomic Traits and Genetic Characteristics of Two New Plant-architecture Lines in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(2): 171-180. |
| [4] | Yujun ZHU, Ziwei ZUO, Zhenhua ZHANG, Yeyang FAN. A New Approach for Fine-mapping and Map-based Cloning of Minor-Effect QTL in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2021, 35(4): 407-414. |
| [5] | Yali ZHENG, Linchuang YU, Xiaoxiao AN, Xinle CHENG, Lijun REN, Zilong SU, Xiaoya ZHENG, Tao LAN. Identification of a Knockout Mutant of OsWOX3B Gene in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2021, 35(2): 112-120. |
| [6] | Yiwei KANG, Yuyu CHEN, Yingxin ZHANG. Research Progress and Breeding Prospects of Grain Size Associated Genes in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2020, 34(6): 479-490. |
| [7] | Feng MENG, Yaling ZHANG, Xuehui JIN. Detection and Analysis of Magnaporthe oryzae Avirulent Gene AVR-Pita and Its Homologous Genes in Heilongjiang Province [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2020, 34(2): 143-149. |
| [8] | Yanhua CHEN, Yaliang WANG, Defeng ZHU, Qinghua SHI, Huizhe CHEN, Jing XIANG, Yikai ZHANG, Yuping ZHANG. Mechanism of Exogenous Brassinolide in Alleviating High Temperature Injury at Panicle Initiation Stage in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2019, 33(5): 457-466. |
| [9] | Jingfang LI, Yunlu TIAN, Xi LIU, Shijia LIU, Liangming CHEN, Ling JIANG, Wenwei ZHANG, Dayong XU, Yihua WANG, Jianmin WAN. The Guanylate Kinase OsGK1 is Essential for Seed Development in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2018, 32(5): 415-426. |
| [10] | Xi LIU, Changling MOU, Chunlei ZHOU, Zhijun CHENG, Ling JIANG, Jianmin WAN. Research Progress on Cloning and Regulation Mechanism of Rice Grain Shape Genes [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2018, 32(1): 1-11. |
| [11] | Yan LU, Xiaomin ZHANG, Yan QI, Changquan ZHANG, Yuping LING, Qiaoquan LIU. Scanning Electron Microscopic Analysis of Grain Cross-section from Rice with Different Transparency [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2018, 1(1): 189-199. |
| [12] | Xiangyang FENG, Zhen ZHANG, Rongyao CHAI, Haiping QIU, Jiaoyu WANG, Xueqin MAO, Yanli WANG, Guochang SUN. Functional Analysis of MoMET3 in Growth, Development and Pathogenicity of Magnaporthe oryzae [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2017, 31(5): 542-550. |
| [13] | Minghai ZHU, Lei PI, Canwei SHU, Erxun ZHOU. AFLP Analyses of Genetic Diversity and Population Genetic Structure of Magnaporthe oryzae from South China Crop Breeding Area [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2017, 31(3): 320-326. |
| [14] | Hongchun RUAN, Niuniu SHI, Yixin DU, Lin GAN, Xiujuan YANG, Yuli DAI, Furu CHEN. Analysis on Resistance of Pi Genes to Predominant Races of Mangnaporthe oryzae in Fujian Province, China [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2017, 31(1): 105-110. |
| [15] | Zhuo-kan GU, Ling LI, Jiao-yu WANG, Rong-yao CHAI, Yan-li WANG, Zhen ZHANG, Xue-qin MAO, Hai-ping QIU, Guo-chang SUN. Observation of Sexual Structure of Magnaporthe oryzae via Calcofluor White and Nile Red Staining [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2016, 30(6): 668-672. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||