
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2021, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (3): 207-224.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2021.0514
• Reviews and Special Topics • Next Articles
Yubo WANG, Yue WANG, Xiong LIU, Wenbang TANG*( )
)
Received:2020-05-20
Revised:2021-03-03
Online:2021-05-10
Published:2021-05-10
Contact:
Wenbang TANG
通讯作者:
唐文帮
基金资助:Yubo WANG, Yue WANG, Xiong LIU, Wenbang TANG. Research Progress of Photoperiod Regulation in Rice Flowering[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2021, 35(3): 207-224.
王玉博, 王悦, 刘雄, 唐文帮. 水稻光周期调控开花的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(3): 207-224.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2021.0514
| 基因符号 Gene symbol | 基因登录号 Locus ID | 拟南芥同源基因 Ortholog gene of Arabidopsis | 功能 Description | 文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OsGI | Os01g0182600 | GI | 昼夜节律基因,Hd1的激活子,短日照条件下促进开花,长日照条件下抑制开花 | [29] |
| OsLFL1 | Os01g0713600 | - | 长日照条件下抑制开花,通过与Ehd1启动子RY顺式元件,抑制其表达 | [67] |
| OsMADS51 | Os01g0922800 | - | 短日照条件下促进开花,参与将OsGI信号传递至Ehd1 | [65] |
| LC2/OsVIL3 | Os02g0152500 | - | 水稻开花的正调控子,能通过光周期诱导的OsLF表观沉默促进水稻抽穗 | [71] |
| OsCOL4 | Os02g0610500 | - | 组成型开花抑制因子,通过Ehd1介导途径抑制开花 | [74] |
| DTH2/OsCOL9/OsCCT08 | Os02g0724000 | - | 编码一个CONSTANS类似蛋白,通过诱导成花素基因Hd3a和RFT1的表达而促进水稻抽穗,且独立于已知的Hd1和Ehd1的途径。 | [83] |
| Ehd4 | Os03g0112700 | - | 促进开花;编码一个CCH类锌指蛋白,通过Ehd1上调成花素基因,但不能直接与Ehd1启动子区域结合 | [107] |
| OsMADS50/OsSOC1/DTH3 | Os03g0122600 | SOC1/AGL20 | 长、短日照条件下,通过抑制开花抑制基因OsLFL1的表达,间接激活Ehd1的表达,促使早花 | [73] |
| OsDof12/OsCDF1 | Os03g0169600 | AtCDF | 长日照条件下促进开花,独立于Ehd1途径,调控Hd3a和OsMADS14表达调节抽穗 | [85] |
| OsphyB | Os03g0309200 | PHYB | 调节Hd1介导成花素Hd3a的表达和临界日长,抑制开花 | [54] |
| OsphyA | Os03g0719800 | PHYA | 光敏色素,短日照条件影响OsGI表达诱导开花,长日照条件下通过影响Ghd7抑制开花 | [54-55] |
| OsphyC | Os03g0752100 | PHYC | 抑制开花 | [54-55] |
| OsMADS14 | Os03g0752800 | AP1 | 短日照条件下,促进开花,成花素激活复合物(FAC)下游基因,参与水稻营养生长向生殖生长转变 | [100] |
| OsMADS34 | Os03g0753100 | SEP | 促进开花,PAP2和3个属于AP1/FUL类基因的MADS14、MADS15、MADS18相互协作,共同决定成花素信号下游花序分生组织特征的建成 | [101] |
| Hd6/CK2 | Os03g0762000 | CK2 | 编码酪蛋白激酶CK2 的α 亚基,长日照条件下Hd1的促进因子,对Hd1间接的翻译后修饰,抑制开花,短日照条件下不能延迟水稻抽穗 | [114] |
| Hd16/EL1/CKI | Os03g0793500 | - | 编码酪蛋白激酶CK1,长日照条件下,通过对Ghd7磷酸化作用抑制水稻开花,短日照条件下效应不明显 | [59] |
| SPIN1 | Os03g0815700 | - | 下调成花素基因Hd3a表达,抑制开花,短日照条件下通过Hd1介导抑制开花,长日照条件下独立于Hd1途径抑制开花 | [40, 42] |
| Hd17/OsELF3-1/OsELF3.1/ OsELF3/Ef7 | Os06g0142600 | ELF3 | 短日照条件下,Hd17通过激活Ehd1参与蓝光介导; 长日照条件下,抑制Ghd7,促进开花 | [59] |
| RFT1/FTL3 | Os06g0157500 | FT | 促进开花,长日照条件下成花素基因 | [77, 90] |
| Hd3a/FTL2 | Os06g0157700 | FT | 促进开花,短日照条件下成花素基因 | [87] |
| Hd1 | Os06g0275000 | CO | 编码一个包含395个氨基酸,含有锌指结构域,短日照条件下促进开花,长日照条件下抑制开花,OsGI-Hd1-Hd3a保守途径上重要的信号整合点 | [104, 108] |
| Se5 | Os06g0603000 | HY1 | 编码一个血红素加氧酶,参与光敏色素发色团生物合成,短日照条件下提前开花 | [53] |
| HAF1 | Os06g0645700 | - | 短日照条件下,对Hd1泛素化 | [35] |
| OsMADS15/DEP | Os07g0108900 | AP1 | 促进开花,14-3-3蛋白能够介导Hd3a与转录因子OsFD1互作,在APETALA1同源基因OsMADS15的启动子上,形成三重结构的成花素激活复合物(FAC),参与水稻营养生长向生殖生长转变 | [98] |
| Hd4/Ghd7 | Os07g0261200 | - | 长日照条件下,与Ghd7互作形成复合体,特异与Ehd1顺式调控区结合,抑制Ehd1表达 | [111, 113] |
| Ehd3 | Os08g0105000 | - | 促进开花;编码一个植物同源结构域的锌指蛋白,长日照条件下,既可通过抑制Ghd7的表达诱导抽穗,又可通过一个不依赖Ghd7的方式上调Ehd1表达,促进开花 | [60, 62] |
| Hd5/DTH8/Ghd8/OsHAP3H/ LHD1/EF8/CAR8/OsNF-YB11 | Os08g0174500 | Hap3b | 编码一个由297个氨基酸组成的多肽,长日照条件下,Ghd8通过调节Ehd1、RFT1和Hd3a 延迟水稻开花,但短日照条件下促进水稻开花 | [68] |
| 基因符号 Gene symbol | 基因登录号 Locus ID | 拟南芥同源基因 Ortholog gene of Arabidopsis | 功能 Description | 文献 Reference |
| OsTrx1/SDG723 | Os09g0134500 | ATX1 | OsTrx1的PHD基序能与组蛋白H3结合,SET结构域具有组蛋白H3甲基转移酶活性,通过调节染色质结构,调控水稻开花期 | [82] |
| OsCO3 | Os09g0240200 | - | 短日照条件下,负向调节FT类基因表达抑制开花,独立于Hd1和Ehd1介导的开花调控途径 | [83] |
| OsEMF2b | Os09g0306800 | EMF2 | 介导OsLFL1和OsMADS4的H3K27me3沉淀,作为水稻成花转变和花器管特征调控因子 | [67] |
| SDG724/IVP1 | Os09g0307800 | - | 调控MADS50和RFT1位点的H3K36me2/3甲基化水平促进开花 | [77] |
| Ehd2/OsID1/RID1Ghd10 | Os10g0419200 | ID1 | 编码一个具有锌指基序的转录因子,促进抽穗,控制开花转化和成花诱导的起始 | [63] |
| Hd14/Ehd1 | Os10g0463400 | - | 促进开花;编码一个B型反应调节子,是水稻中特有基因,长日照条件下开花调控信号重要整合点 | [45, 46] |
| OsMADS56 | Os10g0536100 | SOC/AGL20 | 长日照条件下,与OsMADS50形成复合物,通过正调控OsLFL1,间接抑制Ehd1表达,延迟抽穗 | [73] |
| RBS1 | Os11g0250000 | - | 长、短日照条件下,通过正调控SPIN1,延迟开花 | [40] |
| OsVIL2 | Os12g0533500 | - | LC2和OsVIL2是水稻开花的正调控子,它们能互作,长日照条件下,通过光周期诱导的OsLF表观沉默,间接激活Ehd1的表达,促进开花 | [71] |
| SPL11 | Os12g0570000 | AtSpl11 | 促进开花,通过负调控开花负调控因子SPIN1和RBS1,参与花期调控 | [39, 41] |
| OsMADS18 | Os07g0605200 | AP1 | 过表达OsMADS18能诱导早花 | [98] |
| OsMFT1 | Os06g0498800 | MFT | 延迟抽穗,过表达显著增加每穗颖花数和枝梗数 | [70] |
Table 1 Photoperiod regulated genes on flowering time in rice.
| 基因符号 Gene symbol | 基因登录号 Locus ID | 拟南芥同源基因 Ortholog gene of Arabidopsis | 功能 Description | 文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OsGI | Os01g0182600 | GI | 昼夜节律基因,Hd1的激活子,短日照条件下促进开花,长日照条件下抑制开花 | [29] |
| OsLFL1 | Os01g0713600 | - | 长日照条件下抑制开花,通过与Ehd1启动子RY顺式元件,抑制其表达 | [67] |
| OsMADS51 | Os01g0922800 | - | 短日照条件下促进开花,参与将OsGI信号传递至Ehd1 | [65] |
| LC2/OsVIL3 | Os02g0152500 | - | 水稻开花的正调控子,能通过光周期诱导的OsLF表观沉默促进水稻抽穗 | [71] |
| OsCOL4 | Os02g0610500 | - | 组成型开花抑制因子,通过Ehd1介导途径抑制开花 | [74] |
| DTH2/OsCOL9/OsCCT08 | Os02g0724000 | - | 编码一个CONSTANS类似蛋白,通过诱导成花素基因Hd3a和RFT1的表达而促进水稻抽穗,且独立于已知的Hd1和Ehd1的途径。 | [83] |
| Ehd4 | Os03g0112700 | - | 促进开花;编码一个CCH类锌指蛋白,通过Ehd1上调成花素基因,但不能直接与Ehd1启动子区域结合 | [107] |
| OsMADS50/OsSOC1/DTH3 | Os03g0122600 | SOC1/AGL20 | 长、短日照条件下,通过抑制开花抑制基因OsLFL1的表达,间接激活Ehd1的表达,促使早花 | [73] |
| OsDof12/OsCDF1 | Os03g0169600 | AtCDF | 长日照条件下促进开花,独立于Ehd1途径,调控Hd3a和OsMADS14表达调节抽穗 | [85] |
| OsphyB | Os03g0309200 | PHYB | 调节Hd1介导成花素Hd3a的表达和临界日长,抑制开花 | [54] |
| OsphyA | Os03g0719800 | PHYA | 光敏色素,短日照条件影响OsGI表达诱导开花,长日照条件下通过影响Ghd7抑制开花 | [54-55] |
| OsphyC | Os03g0752100 | PHYC | 抑制开花 | [54-55] |
| OsMADS14 | Os03g0752800 | AP1 | 短日照条件下,促进开花,成花素激活复合物(FAC)下游基因,参与水稻营养生长向生殖生长转变 | [100] |
| OsMADS34 | Os03g0753100 | SEP | 促进开花,PAP2和3个属于AP1/FUL类基因的MADS14、MADS15、MADS18相互协作,共同决定成花素信号下游花序分生组织特征的建成 | [101] |
| Hd6/CK2 | Os03g0762000 | CK2 | 编码酪蛋白激酶CK2 的α 亚基,长日照条件下Hd1的促进因子,对Hd1间接的翻译后修饰,抑制开花,短日照条件下不能延迟水稻抽穗 | [114] |
| Hd16/EL1/CKI | Os03g0793500 | - | 编码酪蛋白激酶CK1,长日照条件下,通过对Ghd7磷酸化作用抑制水稻开花,短日照条件下效应不明显 | [59] |
| SPIN1 | Os03g0815700 | - | 下调成花素基因Hd3a表达,抑制开花,短日照条件下通过Hd1介导抑制开花,长日照条件下独立于Hd1途径抑制开花 | [40, 42] |
| Hd17/OsELF3-1/OsELF3.1/ OsELF3/Ef7 | Os06g0142600 | ELF3 | 短日照条件下,Hd17通过激活Ehd1参与蓝光介导; 长日照条件下,抑制Ghd7,促进开花 | [59] |
| RFT1/FTL3 | Os06g0157500 | FT | 促进开花,长日照条件下成花素基因 | [77, 90] |
| Hd3a/FTL2 | Os06g0157700 | FT | 促进开花,短日照条件下成花素基因 | [87] |
| Hd1 | Os06g0275000 | CO | 编码一个包含395个氨基酸,含有锌指结构域,短日照条件下促进开花,长日照条件下抑制开花,OsGI-Hd1-Hd3a保守途径上重要的信号整合点 | [104, 108] |
| Se5 | Os06g0603000 | HY1 | 编码一个血红素加氧酶,参与光敏色素发色团生物合成,短日照条件下提前开花 | [53] |
| HAF1 | Os06g0645700 | - | 短日照条件下,对Hd1泛素化 | [35] |
| OsMADS15/DEP | Os07g0108900 | AP1 | 促进开花,14-3-3蛋白能够介导Hd3a与转录因子OsFD1互作,在APETALA1同源基因OsMADS15的启动子上,形成三重结构的成花素激活复合物(FAC),参与水稻营养生长向生殖生长转变 | [98] |
| Hd4/Ghd7 | Os07g0261200 | - | 长日照条件下,与Ghd7互作形成复合体,特异与Ehd1顺式调控区结合,抑制Ehd1表达 | [111, 113] |
| Ehd3 | Os08g0105000 | - | 促进开花;编码一个植物同源结构域的锌指蛋白,长日照条件下,既可通过抑制Ghd7的表达诱导抽穗,又可通过一个不依赖Ghd7的方式上调Ehd1表达,促进开花 | [60, 62] |
| Hd5/DTH8/Ghd8/OsHAP3H/ LHD1/EF8/CAR8/OsNF-YB11 | Os08g0174500 | Hap3b | 编码一个由297个氨基酸组成的多肽,长日照条件下,Ghd8通过调节Ehd1、RFT1和Hd3a 延迟水稻开花,但短日照条件下促进水稻开花 | [68] |
| 基因符号 Gene symbol | 基因登录号 Locus ID | 拟南芥同源基因 Ortholog gene of Arabidopsis | 功能 Description | 文献 Reference |
| OsTrx1/SDG723 | Os09g0134500 | ATX1 | OsTrx1的PHD基序能与组蛋白H3结合,SET结构域具有组蛋白H3甲基转移酶活性,通过调节染色质结构,调控水稻开花期 | [82] |
| OsCO3 | Os09g0240200 | - | 短日照条件下,负向调节FT类基因表达抑制开花,独立于Hd1和Ehd1介导的开花调控途径 | [83] |
| OsEMF2b | Os09g0306800 | EMF2 | 介导OsLFL1和OsMADS4的H3K27me3沉淀,作为水稻成花转变和花器管特征调控因子 | [67] |
| SDG724/IVP1 | Os09g0307800 | - | 调控MADS50和RFT1位点的H3K36me2/3甲基化水平促进开花 | [77] |
| Ehd2/OsID1/RID1Ghd10 | Os10g0419200 | ID1 | 编码一个具有锌指基序的转录因子,促进抽穗,控制开花转化和成花诱导的起始 | [63] |
| Hd14/Ehd1 | Os10g0463400 | - | 促进开花;编码一个B型反应调节子,是水稻中特有基因,长日照条件下开花调控信号重要整合点 | [45, 46] |
| OsMADS56 | Os10g0536100 | SOC/AGL20 | 长日照条件下,与OsMADS50形成复合物,通过正调控OsLFL1,间接抑制Ehd1表达,延迟抽穗 | [73] |
| RBS1 | Os11g0250000 | - | 长、短日照条件下,通过正调控SPIN1,延迟开花 | [40] |
| OsVIL2 | Os12g0533500 | - | LC2和OsVIL2是水稻开花的正调控子,它们能互作,长日照条件下,通过光周期诱导的OsLF表观沉默,间接激活Ehd1的表达,促进开花 | [71] |
| SPL11 | Os12g0570000 | AtSpl11 | 促进开花,通过负调控开花负调控因子SPIN1和RBS1,参与花期调控 | [39, 41] |
| OsMADS18 | Os07g0605200 | AP1 | 过表达OsMADS18能诱导早花 | [98] |
| OsMFT1 | Os06g0498800 | MFT | 延迟抽穗,过表达显著增加每穗颖花数和枝梗数 | [70] |
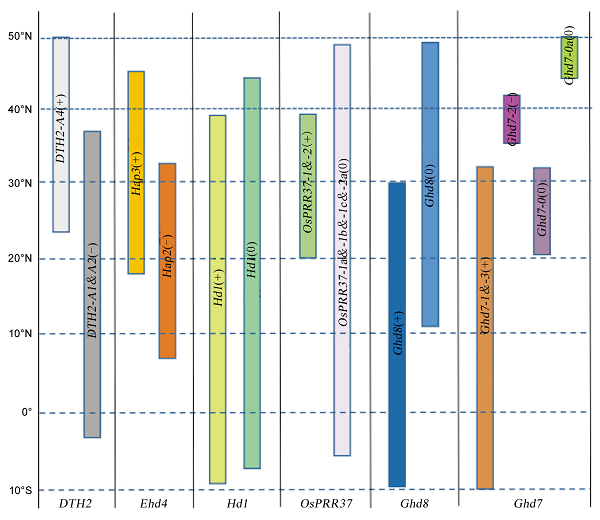
Fig. 3. Distribution of alleles influencing flowering of rice. The vertical axis refers to dimensions; The horizontal axis refers to genes; +, - and 0 alleles represent the alleles with the strong effect, weak effect and no effect, respectively.
| [1] | 徐铨, 奥本裕, 王晓雪. 水稻开花期调控分子机理研究进展[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2014, 15(1): 134-140. |
| Xu Q, Ao B Y, Wang X X.Research progress on regulatory molecular mechanisms of flowering time in rice[J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2014, 15(1): 134-140. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | Hayama R, Yokoi S, Tamaki S, Yano M, Shimamoto K.Adaptation of photoperiodic control pathways produces short-day flowering in rice[J]. Nature, 2003, 422(6933): 719-722. |
| [3] | 魏鑫, 曹立荣, 杨庆文, 曾汉来. 水稻抽穗期的光周期调控分子基础研究进展[J]. 生命科学研究, 2010, 14(5): 456-463. |
| Wei X, Cao L R, Yang Q W, Zeng H L.Research progress of photoperiodic response controlling heading in rice[J]. Life Science Research, 2010, 14(5): 456-463. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | Chaw S M, Chang C C, Chen H L, Li W H.Dating the monocot-dicot divergence and the origin of core eudicots using whole chloroplast genomes[J]. Journal of Molecular Evolution, 2004, 58(4): 424-441. |
| [5] | Xue W Y, Xing Y Z, Weng X Y, Zhao Y, Tang W J, Wang L, Zhou H J, Yu S B, Xu C G, Li X H, Zhang Q F.Natural variation in Ghd7 is an important regulator of heading date and yield potential in rice[J]. Nature Genetics, 2008, 40(6): 761-767. |
| [6] | Nakamichi N, Tudo T, Makita N, Kiba T, Kinoshita T, Sakakibara H.Flowering time control in rice by introducing Arabidopsis clock-associated PSEUDO- RESPONSE REGULATOR 5[J]. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 2020, 3(27): 970-979. |
| [7] | Zhang W F, Tan L B, Sun H Y, Zhao X H, Liu F X, Cai H W, Fu Y C, Sun X Y, Gu P, Zhu Z P, Sun C Q. Natural variations at TIG1 encoding a TCP transcription factor contribute to plant architecture domestication in rice[J]. Molecular Plant, 2019, 12(8): 1075-1089. |
| [8] | Chen E W, Huang X H, Tian Z X, Wing R A, Han B.The genomics of Oryza species provides insights into rice domestication and heterosis[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2019, 70: 639-665. |
| [9] | Liu Y, Yang J, Yang M.Pathways of flowering regulation in plants[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2015, 31(11): 1553-1566. |
| [10] | 彭凌涛. 控制拟南芥和水稻开花时间光周期途径的分子机制[J]. 植物生理学通讯, 2006, 42(6): 1021-1030. |
| Peng L T.Molecular mechanism of flowering time controlling photoperiod pathway in Arabidopsis and rice[J]. Plant Physiology Communications, 2006, 42(6): 1021-1030. (in Chinese) | |
| [11] | Sawa M, Nusinow D A, Kay S A, Imaizumi T.FKF1 and GIGANTEA complex formation is required for day-length measurement in Arabidopsis[J]. Science, 2007, 318(5848): 261-265. |
| [12] | Imaizumi T, Schultz T F, Harmon F G, Ho L A, Kay S A.FKF1 F-box protein mediates cyclic degradation of a repressor of CONSTANS in Arabidopsis[J]. Science, 2005, 309(5732): 293-297. |
| [13] | Niwa Y, Ito S, Nakamichi N, Mizoguchi N, Niinuma T, Yamashino K, Mizuno T.Genetic linkages of the circadian clock-associated genes, TOC1, CCA1 and LHY, in the photoperiodic control of flowering time in Arabidopsis thaliana[J]. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2007, 48(7): 925-937. |
| [14] | Chang G X, Yang W J, Zhang Q L, Huang J L, Yang Y P, Hu X Y.ABI5-BINDING PROTEIN2 coordinates CONSTANS to delay flowering by recruiting the transcriptional corepressor TPR2[J]. Plant Physiology, 2019, 179(2): 477-490. |
| [15] | Kozarewa I, Ibáñez C, Johansson M, Ogren E, Mozley D, Nylander E, Chono M, Moritz T, Eriksson M E.Alteration of PHYA expression change circadian rhythms and timing of bud set in Populus[J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 2010, 73(12): 143-156. |
| [16] | Liu L J, Zhang Y C, Li Q H, Sang Y, Mao J, Lian H L, Wang L, Yang H Q.COP1-mediated ubiquitination of CONSTANS is implicated in cryptochrome regulation of flowering in Arabidopsis[J]. The Plant Cell, 2008, 20(2): 292-306. |
| [17] | 骆倩. 拟南芥PIF3-LIKE1与phyB和COP1互作调控光形态建成的分子机制研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2014. |
| Luo Q.COP1 and phyB physically interact with PIL1 to regulate its stability and photomorphogenic development in Arabidopsis[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | Pittendrigh C S, Minis D H.The entrainment of circadian oscillations by light and their role as photoperiodic clocks[J]. The American Naturalist, 1964, 98(902): 261-294. |
| [19] | 陈福禄, 傅永福, 林辰涛. CO/FT调节元件与植物开花时间调节研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2009, 11(2): 17-22. |
| Chen F L, Fu Y F, Lin C T.Research progress on CO/FT regulon and its role in adjusting plant flowering[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2009, 11(2): 17-22. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | Yano M, Katayose Y, Ashikari M, Yamanouchi U, Monna L, Fuse T, Baba T, Yamamoto K, Umehara Y, Nagamura Y, Sasaki T.Hd1, a major photoperiod sensitivity quantitative trait locus in rice, is closely related to the Arabidopsis flowering time gene CONSTANS[J]. The Plant Cell, 2000, 12(12): 2473-2483. |
| [21] | Izawa T, Takahashi Y, Yano M.Comparative biology comes into bloom: Genomic and genetic comparison of flowering pathways in rice and Arabidopsis[J]. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2003, 6(2): 113-120. |
| [22] | Ogiso E, Takahashi Y, Sasaki T, Yano M, Izawa T.The role of casein kinaseⅡin flowering time regulation has diversified during evolution[J]. Plant Physiology, 2010, 152(2): 808-820. |
| [23] | Murakami M, Tago Y, Yamashino T, Mizuno T.Characterization of the rice circadian clock-associated pseudo-response regulators in Arabidopsis thaliana[J]. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 2007, 71(4): 70048-70052. |
| [24] | Kojima S, Takahashi Y, Kobayashi Y, Monna L, Sasaki T, Araki T, Yano M.Hd3a, a rice ortholog of the Arabidopsis FT gene, promotes transition to flowering downstream of Hd1 under short-day conditions[J]. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2002, 43(10): 1096-1105. |
| [25] | Ishikawa R, Aoki M, Kurotani K, Yokoi S, Shinomura T, Takano M, Shimamoto K.Phytochrome B regulates Heading date 1 (Hd1)-mediated expression of rice florigen Hd3a and critical day length in rice[J]. Molecular Genetics and Genomics, 2011, 285(6): 461-470. |
| [26] | Tsuji H, Taoka K, Shimamoto K.Florigen in rice: Complex gene network for florigen transcription, florigen activation complex, and multiple functions[J]. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2013, 16(2): 228-235. |
| [27] | Goretti D, Martignago D, Landini M, Brambilla V, Ariza J G, Gnesutta N, Galbiati F, Collani S, Takagi H, Terauchi R, Mantovani R, Fornara F.Transcriptional and post-transcriptional mechanisms limit heading date 1 (Hd1) function to adapt rice to high latitudes[J]. PLoS Genetics, 2017, 13(1): e1006530. |
| [28] | Nemoto Y, Nonoue Y, Yano M, Izawa T. Hd1, a CONSTANS ortholog in rice, functions as an Ehd1 repressor through interaction with monocot-specific CCT-domain protein Ghd7[J]. The Plant Journal, 2016, 86(3): 221-233. |
| [29] | Lee Y S, An G.OsGI controls flowering time by modulating rhythmic flowering time regulators preferentially under short day in rice[J]. Journal of Plant Biology, 2015, 58(2): 137-145. |
| [30] | Nguyen Q N, Lee Y S, Cho L H, Jeong H J, An G, Jung K H.Genome-wide identification and analysis of Catharanthus roseus RLK1-like kinases in rice[J]. Planta, 2015, 241(3): 603-613. |
| [31] | Wuriyanghan H, Zhang B, Cao W H, Ma B, Lei G, Liu Y F, Wei W, Wu H J, Chen L J, Chen H W, Cao Y R, He S J, Zhang W K, Wang X J, Chen S Y, Zhang J S.The ethylene receptor ETR2 delays floral transition and affects starch accumulation in rice[J]. The Plant Cell, 2009, 21(5): 1473-1494. |
| [32] | Koo B H, Yoo S C, Park J W, Kwon C T, Lee B D, An G, Zhang Z Y, Li Z C, Paek N C.Natural variation in OsPRR37 regulates heading date and contributes to rice cultivation at a wide range of latitudes[J]. Molecular Plant, 2013, 6(6): 1877-1888. |
| [33] | Li D J, Yang C H, Li X B, Gan Q, Zhao X F, Zhu L H.Functional characterization of rice OsDof12[J]. Planta, 2009, 229(6): 1159-1169. |
| [34] | Takahashi Y, Shomura A, Sasaki T, Yano M.Hd6, a rice quantitative trait locus involved in photoperiod sensitivity, encodes the α subunit of protein kinase CK2[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2001, 98(14): 7922-7927. |
| [35] | Yang Y, Fu D, Zhu C, He Y, Zhang H, Liu T, Wu C.The RING-finger ubiquitin ligase HAF1 mediates heading date 1 degradation during photoperiodic flowering in rice[J]. The Plant Cell, 2015, 27(9): 2455-2468. |
| [36] | Subudhi P K, De Leon T B, Tapia R, Chai C, Karan R, Ontoy J, Singh P K. Genetic interaction involving photoperiod-responsive Hd1 promotes early flowering under long-day conditions in rice[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 1-11. |
| [37] | Zhu C, Peng Q, Fu D, Zhuang D X, Yu Y M, Duan M, Xie W B, Cai Y H.The E3 ubiquitin ligase HAF1 modulates circadian accumulation of EARLY FLOWERING3 to control heading date in rice under long-day conditions[J]. The Plant Cell, 2018, 30(10): 2352-2367. |
| [38] | Yang Y, Peng Q, Chen G X, Li X H, Wu C Y.OsELF3 is involved in circadian clock regulation for promoting flowering under long-day conditions in rice[J]. Molecular Plant, 2013, 6(1): 202-215. |
| [39] | Vega-Sánchez M E, Zeng L R, Chen S B, Leung H, Wang G L. SPIN1, a K homology domain protein negatively regulated and ubiquitinated by the E3 ubiquitin ligase SPL11, is involved in flowering time control in rice[J]. The Plant Cell, 2008, 20(6): 1456-1469. |
| [40] | Cai Y, Vega-Sánchez M E, Park C H, Bellizzi M, Guo Z, Wang GL. RBS1, an RNA binding protein, interacts with SPIN1 and is involved in flowering time control in rice[J]. PloS ONE, 2014, 9(1): e87258. |
| [41] | Liu J, Park C H, He F, Nagano M, Wang M, Bellizzi M, Zhang K, Zeng X S, Liu W D, Ning Y, Kawano Y, Wang G L.The RhoGAP SPIN6 associates with SPL11 and OsRac1 and negatively regulates programmed cell death and innate immunity in rice[J]. PLoS Pathogens, 2015, 11(2): e1004629. |
| [42] | Yamashita H, Komeda Y.Control of flower development[J]. Plant Developmental Biology- Biotechnological Perspectives, 2010, 15(1): 195-208. |
| [43] | Vega-Sanchez M E. The E3 ubiquitin ligase SPL11 regulates both programmed cell death and flowering time in rice[D]. Ohio: The Ohio State University, 2008. |
| [44] | Shirsekar G S, Vega-sanchez M, Bordeos A, Baraoidan M, Swisshelm A, Fan J B, Park C H, Leung H, Wang G L. Identification and characterization of suppressor mutants of spl11-mediated cell death in rice[J]. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 2014, 27(6): 528-536. |
| [45] | Doi K, Izawa T, Fuse T, Yamanouchi U, Kubo T, Shimatani Z, Yano M, Yoshimura A.Ehd1, a B-type response regulator in rice, confers short-day promotion of flowering and controls FT-like gene expression independently of Hd1[J]. Genes & Development, 2004, 18(8): 926-936. |
| [46] | 宋远丽, 栾维江. 水稻开花的光温调控分子机理[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2012, 26(4): 383-392. |
| Song Y L, Luan W J.The regulatory pathways of rice flowering in different light and temperature conditions[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2012, 26(4): 383-392. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [47] | Lu L, Yan W, Xue W Y, Shao D, Xing Y Z.Evolution and association analysis of Ghd7 in rice[J]. PloS ONE, 2012, 7(5): e34021. |
| [48] | 崔志文, 夏烨, 孙小娟, 蔡志明. 温度和光周期对水稻抽穗期调控的交互作用[J]. 生命科学, 2012, 24(4): 316-320. |
| Cui Z W, Xia Y, Sun X J, Cai Z M.Interaction between temperature and photoperiod in regulation of flowering time in rice[J]. China Life Science, 2012, 24(4): 316-320. (in Chinese) | |
| [49] | Itoh H, Nonoue Y, Yano M, Izawa T.A pair of floral regulators sets critical day length for Hd3a florigen expression in rice[J]. Nature Genetics, 2010, 42(7): 635-638. |
| [50] | Xu Q, Ao B, Wang X X.Review of mechanism of rice flowering in response to photoperiod[J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2014, 15(1): 129-136. |
| [51] | Lee Y S, Yi J, An G.OsPhyA modulates rice flowering time mainly through OsGI under short days and Ghd7 under long days in the absence of phytochrome B[J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 2016, 91(4): 413-427. |
| [52] | Xu Q, Saito H, Hirose I, Katsura K, Yoshitake Y, Yokoo T, Tsukiyama T, Teraishi M, Tanisaka T, Okumoto Y.The effects of the photoperiod-insensitive alleles, se13, hd1 and ghd7, on yield components in rice[J]. Molecular Breeding, 2014, 33(4): 813-819. |
| [53] | 胡时开, 苏岩, 叶卫军, 郭龙彪. 水稻抽穗期遗传与分子调控机理研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2012, 26(3): 373-382. |
| Hu S K, Su Y, Ye W J, Guo L B.Advances in genetic analysis and molecular regulation mechanism of heading date in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2012, 26(3): 373-382. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [54] | Zheng T, Sun J, Zhou S, Chen S, Lu J, Cui S, Tian Y, Zhang H, Cai M, Zhu S, Wu M, Wang Y, Jiang L, Zhai H, Wang H, Wan J.Post-transcriptional regulation of Ghd7 protein stability by phytochrome and OsGI in photoperiodic control of flowering in rice[J]. New Phytologist, 2019, 224(1): 306-320. |
| [55] | Lee Y S, Yi J, Jung K H, An G.Comparison of rice flowering-time genes under paddy conditions[J]. Journal of Plant Biology, 2016, 59(3): 238-246. |
| [56] | Matsubara K, Hori K, Ogiso-Tanaka E, Yano M.Cloning of quantitative trait genes from rice reveals conservation and divergence of photoperiod flowering pathways in Arabidopsis and rice[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2014, 5(1): 193-200. |
| [57] | Giakountis A, Cremer F, Sim S, Reymond M, Schimitt J, Coupland G.Distinct patterns of genetic variation alter flowering responses of Arabidopsis accessions to different daylength[J]. Plant Physiology, 2010, 152(1): 177-191. |
| [58] | Hu Y, Li S, Xing Y.Lessons from natural variations: Artificially induced heading date variations for improvement of regional adaptation in rice[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2019, 132(2): 383-394. |
| [59] | Hori K, Ogiso-Tanaka E, Matsubara K, Yamanouchi U, Ebana K, Yano M.Hd16, a gene for casein kinase I, is involved in the control of rice flowering time by modulating the day-length response[J]. The Plant Journal, 2013, 76(1): 36-46. |
| [60] | Xiang C, Qu L J, Gao Y M, Shi Y Y.Flower development and photoperiodic control of flowering in rice[J]. Rice Science, 2013, 20(2): 79-87. |
| [61] | Matsubara K, Yamanouchi U, Nonoue Y, Sugimoto K, Wang Z X, Minobe Y, Yano M.Ehd3, encoding a plant homeodomain finger-containing protein, is a critical promoter of rice flowering[J]. The Plant Journal, 2011, 66(4): 603-612. |
| [62] | Zhao J M, Huang X, Ouyang X H, Chen W L, Du A P, Zhu S G, Deng X W, Li S G.OsELF3-1, an ortholog of Arabidopsis early flowering 3, regulates rice circadian rhythm and photoperiodic flowering[J]. PLoS ONE, 2012, 7(8): e43705. |
| [63] | Matsubara K, Yamanouchi U, Wang Z X, Minobe Y, Izawa T, Yano M.Ehd2, a rice ortholog of the maize INDETERMINATE1 gene, promotes flowering by up-regulating Ehd1[J]. Plant Physiology, 2008, 148(3): 1425-1435. |
| [64] | Gao H, Zheng X M, Fei G L, Chen J, Jin M N, Ren Y L, Wu W X, Zhou K N, Sheng P K, Zhou F, Jiang L, Wang J, Zhang X, Guo X P, Wang J L, Cheng Z J, Wu C Y, Wang H Y, Wan J M.Ehd4 encodes a novel and Oryza-genus-specific regulator of photoperiodic flowering in rice[J]. PLoS Genetics, 2013, 9(2): e1003281. |
| [65] | Sui P F, Shi J L, Gao X Y, Shen W H, Dong A W.H3K36 methylation is involved in promoting rice flowering[J]. Molecular Plant, 2013, 6(3): 975-977. |
| [66] | 孔德艳, 陈守俊, 周立国, 高欢, 罗利军, 刘灶长. 水稻开花光周期调控相关基因研究进展[J]. 遗传, 2016, 38(6): 532-542. |
| Kong D Y, Chen S J, Zhou L G, Gao H, Luo L J, Liu Z C.Research progress of photoperiod regulated genes on flowering time in rice[J]. Hereditas, 2016, 38(6): 532-542. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [67] | Xie S Y, Chen M, Pei R, Ouyang Y D, Yao J L,. OsEMF2b acts as a regulator of flowering transition and floral organ identity by mediating H3K27me3 deposition at OsLFL1 and OsMADS4 in rice[J]. Plant Molecular Biology Reporter, 2015, 33(1): 121-132. |
| [68] | Wu M J, Liu H Q, Lin Y, Chen J M, Fu Y P, Luo J M, Zhang Z J, Liang K J, Chen S B, Wang F.In-frame and frame-shift editing of the Ehd1 gene to develop japonica rice with prolonged basic vegetative growth periods[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2020, 11(4): 307-321. |
| [69] | Dai X D, Ding Y N, Tan L B, Fu Y C, Liu F X, Zhu Z F, Sun X Y, Sun X W, Gu P, Cai H W, Sun C Q. LHD1, an allele of DTH8/Ghd8, controls late heading date in common wild rice (Oryza rufipogon)[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2012, 54(10): 790-799. |
| [70] | Song S, Wang G F, Hu Y, Liu H Y, Bai X F, Qin R, Xing Y Z.OsMFT1 increases spikelets per panicle and delays heading date in rice by suppressing Ehd1, FZP and SEPALLATA-like genes[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2018, 69(18): 4283-4293. |
| [71] | Wang J, Hu J, Qian Q, Xue H W.LC2 and OsVIL2 promote rice flowering by photoperoid-induced epigenetic silencing of OsLF[J]. Molecular Plant, 2013, 6(2): 514-527. |
| [72] | Chen M, Xie S Y, Ouyang Y D, Yao J L.Rice PcG gene OsEMF2b controls seed dormancy and seedling growth by regulating the expression of OsVP1[J]. Plant Science, 2017, 260(7): 80-89. |
| [73] | Ryu C H, Lee S, Cho L H, Kim S L, Lee Y S, Choi S C, Jeong H J, Yi J, Park S J, Han C D, An G.OsMADS50 and OsMADS56 function antagonistically in regulating long day (LD)-dependent flowering in rice[J]. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2009, 32(10): 1412-1427. |
| [74] | Sheng P K, Wu F Q, Tan J J, Zhang H, Ma W W, Chen L P, Wang J C, Wang J, Zhu S S, Guo X P, Wang J L,. Zhang X, Cheng Z J, Bao Y Q, Wu C Y, Liu X M, Wan J M.A CONSTANS-like transcriptional activator, OsCOL13, functions as a negative regulator of flowering downstream of OsphyB and upstream of Ehd1 in rice[J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 2016, 92(2): 209-222. |
| [75] | Liu B, Wei G, Shi J L, Jin J, Shen T, Ni T, Shen W H, Yu Y, Dong A W.SET DOMAIN GROUP 708, a histone H3 lysine 36-specific methyltransferase, controls flowering time in rice (Oryza sativa)[J]. New Phytologist, 2016, 210(2): 577-588. |
| [76] | 何星辉, 王金彪, 阮颖, 黄勇. 水稻SDG736抑制拟南芥FLC表达调控开花时间[J]. 基因组学与应用生物学, 2020, 39(5): 2118-2126. |
| He X H, Wang J B, Yuan Y, Huang Y.SDG736 regulating flowering time by reducing expressing of FLC in Arabidopsis thaliana[J]. Genomics and Applied Biology, 2020, 39(5): 2118-2126. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [77] | Sun C H, Fang J, Zhao T L, Xu B, Zhang F T, Liu L C, Tang J Y, Zhang C F, Deng X J, Chen F, Qian Q, Cao X F, Chu C C.The histone methyltransferase SDG724 mediates H3K36me2/3 deposition at MADS50 and RFT1 and promotes flowering in rice[J]. The Plant Cell, 2012, 24(8): 3235-3247. |
| [78] | 隋鹏飞. 水稻组蛋白H3K36甲基转移酶SDG725调控植物生长发育的功能研究[D]. 上海: 复旦大学, 2013. |
| Sui P F.Functional study of rice H3K36 methyltransferase SDG725 in rice growth and development[D]. Shanghai: Fudan University, 2013. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [79] | Sang Y K, Zhu T, Sung Z R.Epigenetic regulation of gene programs by EMF1 and EMF2 in Arabidopsis[J]. Plant Physiology, 2010, 152(2): 516-528. |
| [80] | Sánchez R, Kim M Y, Calonje M, Moon Y H, Sung Z R.Temporal and spatial requirement of EMF1 activity for Arabidopsis vegetative and reproductive development[J]. Molecular Plant, 2009, 2(4): 643-653. |
| [81] | 蒋彬. 水稻OsEMF2b介导的花器官发育研究[D]. 雅安: 四川农业大学, 2013. |
| Jiang B.OsEM3b mediated floral organ development research in rice[D]. Ya’an: Sichuan Agricultural University, 2013. | |
| [82] | Jiang P F, Wang S L, Zheng H, Li H, Zhang F, Su Y H, Xu Z T, Lin H Y, Qian Q, Ding Y.SIP1 participates in regulation of flowering time in rice by recruiting OsTrx1 to Ehd1[J]. New Phytologist, 2018, 219(1): 422-435. |
| [83] | Sun C H, Chen D, Fang J, Wang P R, Deng X J, Chu C C.Understanding the genetic and epigenetic architecture in complex network of rice flowering pathways[J]. Protein & Cell, 2014, 5(12): 889-898. |
| [84] | 张林, 何祖华. 水稻重要农艺性状自然变异研究进展及其应用策略[J]. 科学通报, 2015, 60(12): 1066-1078. |
| Zhang L, He Z H.Understanding natural variations: The source of elite agronomic traits for rice breeding[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2015, 60(12): 1066-1078. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [85] | Wu Q, Li D Y, Li D J, Liu X, Zhao X F, Li X B, Li S G, Zhu L H.Overexpression of OsDof12 affects plant architecture in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2015, 6(8): 833-844. |
| [86] | Corbesier L, Vincent C, Jang S, Fornara F, Fan Q Z, Searle L, Giakountis A, Farrona S, Gissot L, Turnbull C, Coupland G.FT protein movement contributes to long-distance signaling in floral induction of Arabidopsis[J]. Science, 2007, 316(5827): 1030-1033. |
| [87] | 朱岩, 彭振英, 张斌, 毕玉平. PEBP家族基因在植物中功能的研究进展[J]. 山东农业科学, 2013, 45(2): 139-145. |
| Zhu Y, Peng Z Y, Zhang B, Bi Y P.Advances in function research of PEBP family genes in plants[J]. Shandong Agriculture Sciences, 2013, 45(2): 139-145. (in Chinese) | |
| [88] | Klintenäs M, Pin P A, Benlloch R, Ingvarsson P K, Nilsson O.Analysis of conifer FLOWERING LOCUS T/TERMINAL FLOWER1-like genes provides evidence for dramatic biochemical evolution in the angiosperm FT lineage[J]. New Phytologist, 2012, 196(4): 1260-1273. |
| [89] | Tamaki S, Tsuji H, Matsumoto A, Fujita A, Shimatani Z, Terada R, Sakamoto T, Kurata T, Shimamoto K.FT-like proteins induce transposon silencing in the shoot apex during floral induction in rice[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2015, 112(8): 901-910. |
| [90] | Brambilla V, Martignago D, Goretti D, Cerise M, Somssich M, De R M, Galbiati F, Shrestha R, Lazzaro F, Simon R, Fornara F.Antagonistic transcription factor complexes modulate the floral transition in rice[J]. The Plant Cell, 2017, 29(11): 2801-2816. |
| [91] | 孙昌辉, 邓晓建, 方军, 储成才. 高等植物开花诱导研究进展[J]. 遗传, 2007, 29(10): 1182-1190. |
| Sun C H, Deng X J, Fang J, Chu C C.An overview of flowering transition in higher plants[J]. Hereditas, 2007, 29(10): 1182-1190. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [92] | Yang X W, Lee W H, Sobott F.Structural basis for protein-protein interactions in the 14-3-3 protein family[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2006, 103(46): 17237-17242. |
| [93] | Jaspert N, Throm C, Oecking C.Arabidopsis 14-3-3 proteins: Fascinating and less fascinating aspects[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2011, 10(21): 1-8. |
| [94] | 丛楠, 程治军, 万建民. 控制花器官发育的ABCDE模型[J]. 中国农学通报, 2007, 123(7): 124-129. |
| Cong N, Cheng Z J, Wan J M.The ABCDE model of floral organ development[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2007, 123(7): 124-129. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [95] | Hempel F D, Weigel D, Mandel M A, Ditta G, Zambryski P C, Feldman L J, Yanofsky M F.Floral determination and expression of floral regulatory genes in Arabidopsis[J]. Development, 1997, 124(19): 3845-3853. |
| [96] | Kotoda N, Wada M.MdTFL1, a TFL1-like gene of apple, retards the transition from the vegetative to reproductive phase in transgenic Arabidopsis[J]. Plant Science, 2005, 168(1): 95-104. |
| [97] | 戚晓利, 卢孟柱. 拟南芥APETALA1基因在花发育中的网络调控及其生物学功能[J]. 中国农学通报, 2011, 27(8): 103-107. |
| Qi X L, Lu M Z.Regulation network and biological roles of APETALA1 of Arabidopsis Thaliana in flower development[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2011, 27(8): 103-107. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [98] | Yin X M, Liu X, Xu P Y, Dong T, Yang T, Ye T T, Feng Y Q, Wu Y.OsMADS18, a membrane-bound MADS-box transcription factor, modulates plant architecture and the abscisic acid response in rice[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2019, 70(15): 3895-3909. |
| [99] | Lu S J, He W, Wang Y, Wang H M, Yang R F, Zhang X B, Tu J M.Overexpression of a transcription factor OsMADS15 modifies plant architecture and flowering time in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Plant Molecular Biology Reporter, 2012, 30(6): 1461-1469. |
| [100] | Lu S J, Wang H M, Yang R F, Zhang X B, Tu J M.Screening of rice OsMADS15 interacting proteins by yeast two hybrid system[J]. Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology, 2013 (2): 127-136. |
| [101] | Zhang Y, Yu H P, Liu J, Wang W, Sun J, Gao Q, Zhang Y H, Ma D R, Wang J Y, Xu Z J, Chen W F.Loss of function of OsMADS34 leads to large sterile lemma and low grain yield in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Molecular Breeding, 2016, 36(11): 147-152. |
| [102] | Naranjo L, Talón M, Domingo C.Diversity of floral regulatory genes of japonica rice cultivated at northern latitudes[J]. BMC Genomics, 2014, 15(1): 1471-2164. |
| [103] | Komiya R, Ikegami A, Tamaki S, Yokoi S, Shimamoto K.Hd3a and RFT1 are essential for flowering in rice[J]. Development, 2008, 135(4): 767-774. |
| [104] | Takahashi Y, Teshima K M, Yokoi S, Innan H, Shimamoto K.Variations in Hd1 proteins, Hd3a promoters, and Ehd1 expression levels contribute to diversity of flowering time in cultivated rice[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2009, 106(11): 4555-4560. |
| [105] | Ogiso-Tanaka E, Matsubara K, Yamamoto S I, Nonoue Y, Wu J Z, Fujisawa H, Ishikubo H, Tanaka T, Ando T, Matsumoto T, Yano M.Natural variation of the RICE FLOWERING LOCUS T1 contributes to flowering time divergence in rice[J]. PloS ONE, 2013, 8(10): e75959. |
| [106] | Wu W X, Zheng X M, Lu G W, Zhong Z Z, Gao H, Chen L P, Wu C Y, Wang H J, Wang Q, Zhou K N, Wang J L, Wu F Q, Zhang X, Guo X P, Cheng Z J, Lei C L, Lin Q B, Jiang L, Wang H Y, Ge S, Wan J M.Association of functional nucleotide polymorphisms at DTH2 with the northward expansion of rice cultivation in Asia[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2013, 110(8): 2775-2780. |
| [107] | Matsubara K, Yano M.Genetic and molecular dissection of flowering time control in rice//Rice Genomics, Genetics and Breeding[M]. Singapore: Springer, 2018: 177-190. |
| [108] | Takahashi Y, Shimamoto K.Heading date 1 (Hd1), an ortholog of Arabidopsis CONSTANS, is a possible target of human selection during domestication to diversify flowering times of cultivated rice[J]. Genes & Genetic Systems, 2011, 86(3): 175-182. |
| [109] | Yang Q, Li Z, Li W Q, Ku L X, Wang C, Ye J R, Li K, Yang N, Li Y P, Zhong T, Li J S, Chen Y H, Yan J B, Yang X H, Xu M L.CACTA-like transposable element in ZmCCT attenuated photoperiod sensitivity and accelerated the postdomestication spread of maize[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2013, 110(42): 16969-16974. |
| [110] | Ebana K, Shibaya T, Wu J Z, Matsubara K, Kanamori H, Yamane H, Yamanouchi U, Mizubayashi T, Kono I, Shomura A, Ito S, Ando T, Hori K, Matsumoto T, Yano M.Uncovering of major genetic factors generating naturally occurring variation in heading date among Asian rice cultivars[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2011, 122(6): 1199-1210. |
| [111] | Liu C, Song G Y, Zhou Y H, Qu X F, Guo Z B, Liu Z W, Jiang D M, Yang D C.OsPRR37 and Ghd7 are the major genes for general combining ability of DTH, PH and SPP in rice[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5(1): 1-11. |
| [112] | Fujino K, Yamanouchi U, Yano M.Roles of the Hd5 gene controlling heading date for adaptation to the northern limits of rice cultivation[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2013, 126(3): 611-618. |
| [113] | Zhang J, Zhou X C, Yan W H, Zhang Z Y, Lu L, Han Z M, Zhao H, Liu H Y, Song P, Hu Y, Shen G J, He Q, Guo S B, Gao G Q, Wang G W, Xing Y Z.Combinations of the Ghd7, Ghd8 and Hd1 genes largely define the ecogeographical adaptation and yield potential of cultivated rice[J]. New Phytologist, 2015, 208(4): 1056-1066. |
| [114] | Kwon C T, Yoo S C, Koo B H, Cho S H, Park J W, Zhang Z J, Li J J, Li Z C, Paek N C.Natural variation in Early flowering1 contributes to early flowering in japonica rice under long days[J]. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2014, 37(1): 101-112. |
| [1] | GUO Zhan, ZHANG Yunbo. Research Progress in Physiological,Biochemical Responses of Rice to Drought Stress and Its Molecular Regulation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | WEI Huanhe, MA Weiyi, ZUO Boyuan, WANG Lulu, ZHU Wang, GENG Xiaoyu, ZHANG Xiang, MENG Tianyao, CHEN Yinglong, GAO Pinglei, XU Ke, HUO Zhongyang, DAI Qigen. Research Progress in the Effect of Salinity, Drought, and Their Combined Stresses on Rice Yield and Quality Formation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | XU Danjie, LIN Qiaoxia, LI Zhengkang, ZHUANG Xiaoqian, LING Yu, LAI Meiling, CHEN Xiaoting, LU Guodong. OsOPR10 Positively Regulates Rice Blast and Bacterial Blight Resistance [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | CHEN Mingliang, ZENG Xihua, SHEN Yumin, LUO Shiyou, HU Lanxiang, XIONG Wentao, XIONG Huanjin, WU Xiaoyan, XIAO Yeqing. Typing of Inter-subspecific Fertility Loci and Fertility Locus Pattern of indica-japonica Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 386-396. |
| [5] | DING Zhengquan, PAN Yueyun, SHI Yang, HUANG Haixiang. Comprehensive Evaluation and Comparative Analysis of Jiahe Series Long-Grain japonica Rice with High Eating Quality Based on Gene Chip Technology [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 397-408. |
| [6] | HOU Xiaoqin, WANG Ying, YU Bei, FU Weimeng, FENG Baohua, SHEN Yichao, XIE Hangjun, WANG Huanran, XU Yongqiang, WU Zhihai, WANG Jianjun, TAO Longxing, FU Guanfu. Mechanisms Behind the Role of Potassium Fulvic Acid in Enhancing Salt Tolerance in Rice Seedlings [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [7] | LÜ Zhou, YI Binghuai, CHEN Pingping, ZHOU Wenxin, TANG Wenbang, YI Zhenxie. Effects of Nitrogen Application Rate and Transplanting Density on Yield Formation of Small Seed Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| [8] | HU Jijie, HU Zhihua, ZHANG Junhua, CAO Xiaochuang, JIN Qianyu, ZHANG Zhiyuan, ZHU Lianfeng. Effects of Rhizosphere Saturated Dissolved Oxygen on Photosynthetic and Growth Characteristics of Rice at Tillering Stage [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [9] | WU Yue, LIANG Chengwei, ZHAO Chenfei, SUN Jian, MA Dianrong. Occurrence of Weedy Rice Disaster and Ecotype Evolution in Direct-Seeded Rice Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 447-455. |
| [10] | LIU Fuxiang, ZHEN Haoyang, PENG Huan, ZHENG Liuchun, PENG Deliang, WEN Yanhua. Investigation and Species Identification of Cyst Nematode Disease on Rice in Guangdong Province [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [11] | CHEN Haotian, QIN Yuan, ZHONG Xiaohan, LIN Chenyu, QIN Jinghang, YANG Jianchang, ZHANG Weiyang. Research Progress on the Relationship Between Rice Root, Soil Properties and Methane Emissions in Paddy Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [12] | MIAO Jun, RAN Jinhui, XU Mengbin, BO Liubing, WANG Ping, LIANG Guohua, ZHOU Yong. Overexpression of RGG2, a Heterotrimeric G Protein γ Subunit-Encoding Gene, Improves Drought Tolerance in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [13] | YIN Xiaoxiao, ZHANG Zhihan, YAN Xiulian, LIAO Rong, YANG Sijia, Beenish HASSAN, GUO Daiming, FAN Jing, ZHAO Zhixue, WANG Wenming. Signal Peptide Validation and Expression Analysis of Multiple Effectors from Ustilaginoidea virens [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [14] | ZHU Yujing, GUI Jinxin, GONG Chengyun, LUO Xinyang, SHI Jubin, ZHANG Haiqing, HE Jiwai. QTL Mapping for Tiller Angle in Rice by Genome-wide Association Analysis [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [15] | WEI Qianqian, WANG Yulei, KONG Haimin, XU Qingshan, YAN Yulian, PAN Lin, CHI Chunxin, KONG Yali, TIAN Wenhao, ZHU Lianfeng, CAO Xiaochuang, ZHANG Junhua, ZHU Chunqun. Mechanism of Hydrogen Sulfide, a Signaling Molecule Involved in Reducing the Inhibitory Effect of Aluminum Toxicity on Rice Growth Together with Sulfur Fertilizer [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||