
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2018, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (5): 445-452.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2018.7152
• 研究论文 • Previous Articles Next Articles
Honggen ZHANG, Chongyuan ZHONG, Hua SI, Qiaoquan LIU, Minghong GU, Shuzhu TANG*( )
)
Received:2017-12-24
Revised:2018-03-01
Online:2018-09-10
Published:2018-09-10
Contact:
Shuzhu TANG
张宏根, 仲崇元, 司华, 刘巧泉, 顾铭洪, 汤述翥*( )
)
通讯作者:
汤述翥
基金资助:CLC Number:
Honggen ZHANG, Chongyuan ZHONG, Hua SI, Qiaoquan LIU, Minghong GU, Shuzhu TANG. Improving the Ability of C418 to Restore the Fertility of the Honglian-type Cytoplasmic Male Sterility japonica Lines via Molecular Marker-assisted Selection[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2018, 32(5): 445-452.
张宏根, 仲崇元, 司华, 刘巧泉, 顾铭洪, 汤述翥. 分子标记辅助选择改良C418对红莲型粳稻不育系的恢复力[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(5): 445-452.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2018.7152
| 基因 Gene | 标记 Marker | 正向序列 Forward primer(5′→3′) | 反向序列 Reverse primer(5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rf6 | RM407 | GACTACGAGACGAGTGATTTGAACC | GCGTGGGAAATGACTAGGAGTAGG |
| Rf1 | STS10-16 | CAGCAATCGGATCGCCTC | ATCTTTCCGTGATGGGAGGTA |
Table 1 Primers anchoring Rf6 and Rf1.
| 基因 Gene | 标记 Marker | 正向序列 Forward primer(5′→3′) | 反向序列 Reverse primer(5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rf6 | RM407 | GACTACGAGACGAGTGATTTGAACC | GCGTGGGAAATGACTAGGAGTAGG |
| Rf1 | STS10-16 | CAGCAATCGGATCGCCTC | ATCTTTCCGTGATGGGAGGTA |

Fig. 2. Molecular detection of 52605A/C418 F2 individuals using STS10-16. P1 and P2 are 52605A and C418, respectively, and others are individuals from 52605A/C418 F2 population.
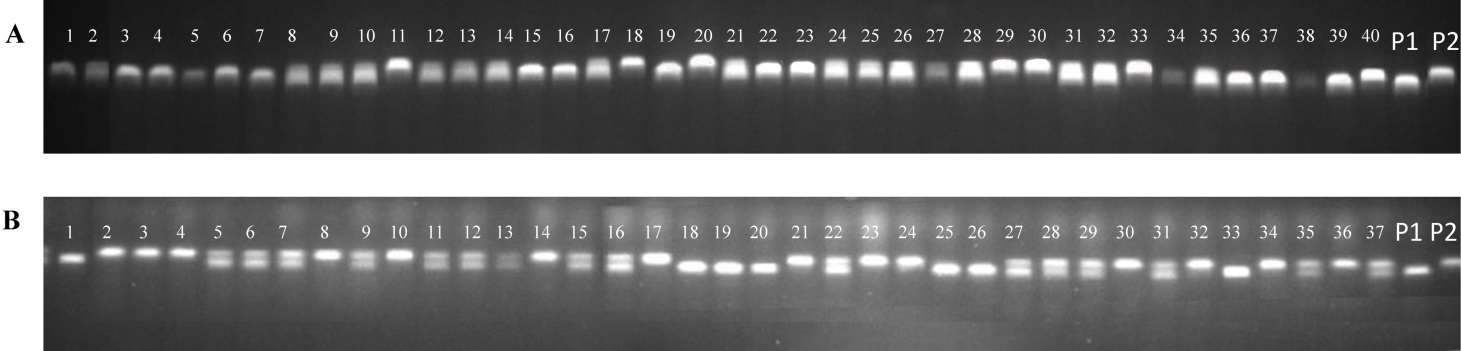
Fig. 3. Molecular detection of C418//C418/R1093 BC2F2 individuals. A, PCR amplification products using primer RM407; B, PCR amplification products using primer STS10-16. P1 and P2 are C418 and R1093, respectively, and others are individuals from C418//C418/R1093 BC2F2 population.
| 世代 Generation | 植株数 Number of measured plants | 基因型 Genotype | 频率 Frequency/ % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rf6Rf6 | Rf6rf6 | rf6rf6 | |||
| BC1F1 | 160 | 0 | 75 | 85 | 46.9 |
| BC2F1 | 100 | 0 | 47 | 53 | 47.0 |
| BC2F2 | 120 | 29 | 54 | 37 | 24.2 |
| BC3F1 | 19 | 0 | 9 | 10 | 47.3 |
| BC4F1 | 298 | 0 | 124 | 174 | 41.6 |
| BC4F2 | 1000 | 243 | 461 | 296 | 24.3 |
Table 2 Distribution of individuals of different genotypes at Rf6 locus in BCnF1 and BCnF2 populations.
| 世代 Generation | 植株数 Number of measured plants | 基因型 Genotype | 频率 Frequency/ % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rf6Rf6 | Rf6rf6 | rf6rf6 | |||
| BC1F1 | 160 | 0 | 75 | 85 | 46.9 |
| BC2F1 | 100 | 0 | 47 | 53 | 47.0 |
| BC2F2 | 120 | 29 | 54 | 37 | 24.2 |
| BC3F1 | 19 | 0 | 9 | 10 | 47.3 |
| BC4F1 | 298 | 0 | 124 | 174 | 41.6 |
| BC4F2 | 1000 | 243 | 461 | 296 | 24.3 |
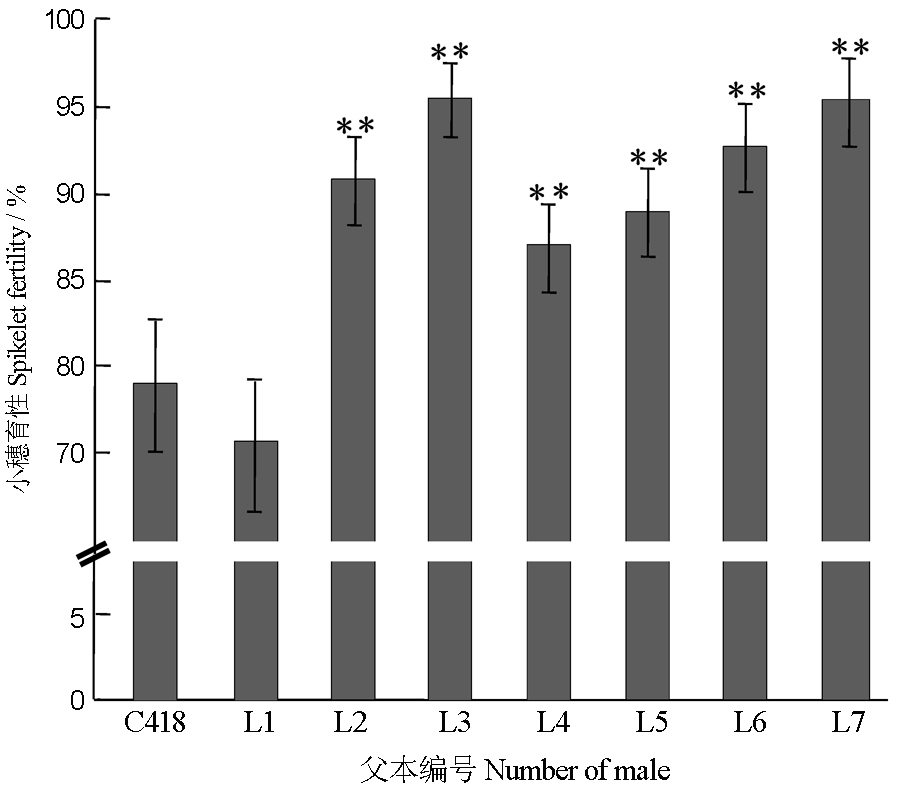
Fig. 4. Spikelet fertility of the testcrossing F1 plants from the crosses between HL-Liuqianxin A and the improved lines, HL-Liuqianxin A and C418, respectively(2015). All values are listed as mean±SD; ** mean significantly different on spikelet fertility between F1s from the improved lines and C418 at 0.01 level. The genotypes of C418 and L1 are Rf1Rf1rf6rf6, and the genotypes of L2-L7 are Rf1Rf1Rf6Rf6.
| 株系号 Line | 基因型 Genotype | BT型六千辛A BT-type Liuqianxin A | HL型六千辛A HL-type Liuqianxin A |
|---|---|---|---|
| SL1 | Rf1Rf1Rf6Rf6 | 91.03±4.98 | 95.09±1.69** |
| SL2 | Rf1Rf1Rf6Rf6 | 91.65±3.06 | 90.87±1.90** |
| SL3 | Rf1Rf1Rf6Rf6 | 92.84±3.72 | 92.25±3.42** |
| SL4 | Rf1Rf1Rf6Rf6 | 94.62±3.13 | 94.14±2.53** |
| SL5 | Rf1Rf1Rf6Rf6 | 95.82±1.75 | 91.49±3.91** |
| SL6 | Rf1Rf1Rf6Rf6 | 92.96±2.00 | 93.00±1.06** |
| SL7 | Rf1Rf1Rf6Rf6 | 97.13±2.02 | 85.89±7.25** |
| SL8 | Rf1Rf1Rf6Rf6 | 94.13±3.51 | 94.30±2.74** |
| SL9 | Rf1Rf1Rf6Rf6 | 94.18±2.25 | 95.02±2.83** |
| SL10 | Rf1Rf1Rf6Rf6 | 93.60±2.28 | 83.75±8.52** |
| C418 | Rf1Rf1rf6rf6 | 91.88±3.02 | 74.49±5.06 |
Table 3 Spikelet fertility of the testcrossing F1s from BT- and HL-type Liuqianxin A, respectively(2016). %
| 株系号 Line | 基因型 Genotype | BT型六千辛A BT-type Liuqianxin A | HL型六千辛A HL-type Liuqianxin A |
|---|---|---|---|
| SL1 | Rf1Rf1Rf6Rf6 | 91.03±4.98 | 95.09±1.69** |
| SL2 | Rf1Rf1Rf6Rf6 | 91.65±3.06 | 90.87±1.90** |
| SL3 | Rf1Rf1Rf6Rf6 | 92.84±3.72 | 92.25±3.42** |
| SL4 | Rf1Rf1Rf6Rf6 | 94.62±3.13 | 94.14±2.53** |
| SL5 | Rf1Rf1Rf6Rf6 | 95.82±1.75 | 91.49±3.91** |
| SL6 | Rf1Rf1Rf6Rf6 | 92.96±2.00 | 93.00±1.06** |
| SL7 | Rf1Rf1Rf6Rf6 | 97.13±2.02 | 85.89±7.25** |
| SL8 | Rf1Rf1Rf6Rf6 | 94.13±3.51 | 94.30±2.74** |
| SL9 | Rf1Rf1Rf6Rf6 | 94.18±2.25 | 95.02±2.83** |
| SL10 | Rf1Rf1Rf6Rf6 | 93.60±2.28 | 83.75±8.52** |
| C418 | Rf1Rf1rf6rf6 | 91.88±3.02 | 74.49±5.06 |
| 株系 Line | 世代 Generation | 播始历期 DTH/d | 株高 PH/cm | 茎粗 CT/mm | 单株穗数 PNP | 穗长 CPL/cm | 主茎穗颖花数SNC | 一次枝梗数 PBN | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C418 | 81 | 113.3±4.4 | 6.92±0.65 | 5.2±1.0 | 31.0±2.2 | 346.4±47.6 | 13.1±1.3 | ||
| G1 | BC3F4 | 81 | 110.0±3.7 | 7.08±0.44 | 5.8±1.0 | 31.3±1.5 | 368.7±50.1 | 14.1±1.6 | |
| G2 | BC3F4 | 87 | 117.4±2.9 | 7.22±0.66 | 5.6±1.1 | 32.6±1.1 | 294.8±27.3 | 12.4±0.9 | |
| G3 | BC4F3 | 84 | 114.7±3.5 | 7.01±0.51 | 5.2±0.9 | 30.1±2.4 | 343.0±37.9 | 12.8±1.2 | |
| G4 | BC4F3 | 87 | 112.4±5.3 | 7.36±0.47 | 5.6±0.8 | 31.6±2.1 | 357.2±40.7 | 13.4±1.2 | |
| G5 | BC4F3 | 87 | 110.6±3.4 | 6.86±0.39 | 6.5±0.7 | 32.3±1.6 | 305.4±30.6 | 12.9±1.5 | |
| G6 | BC4F3 | 85 | 113.6±3.4 | 7.42±0.32 | 5.7±0.8 | 32.9±2.3 | 389.2±48.4 | 12.9±1.1 | |
| 株系 Line | 剑叶基角 AFL/° | 倒3叶长 TLL/cm | 倒2叶长 SLL/cm | 剑叶长 FLL/cm | 穗叶差 DPFL/cm | 穗颈粗 PND/mm | 穗弯曲度 PCD/° | ||
| C418 | 7.7±3.9 | 52.5±4.9 | 53.7±4.0 | 37.7±7.2 | –2.6±6.8 | 2.77±0.18 | 58.40±13.95 | ||
| G1 | 9.6±4.7 | 55.7±3.2 | 58.3±4.8 | 42.5±6.5 | –7.2±5.9 | 2.92±0.20 | 74.75±18.90 | ||
| G2 | 10.0±4.1 | 60.4±5.2 | 62.8±4.5 | 46.6±5.3* | –9.0±4.5 | 2.80±0.30 | 88.30±20.41 | ||
| G3 | 10.5±3.8 | 57.6±3.1 | 56.8±5.9 | 40.8±6.4 | –5.2±5.6 | 2.84±0.26 | 71.33±14.21 | ||
| G4 | 11.1±7.2 | 56.3±4.5 | 56.8±4.8 | 40.6±6.7 | –6.1±7.1 | 2.80±0.26 | 82.42±17.76 | ||
| G5 | 7.8±5.3 | 54.6±2.9 | 54.2±4.8 | 43.0±4.3 | –4.8±4.4 | 2.84±0.22 | 67.22±14.67 | ||
| G6 | 10.1±5.7 | 55.1±3.2 | 59.7±5.1 | 42.8±6.7 | –5.7±6.6 | 3.08±0.23 | 71.08±14.01 | ||
Table 4 Agronomic traits of the improved lines and C418(2016).
| 株系 Line | 世代 Generation | 播始历期 DTH/d | 株高 PH/cm | 茎粗 CT/mm | 单株穗数 PNP | 穗长 CPL/cm | 主茎穗颖花数SNC | 一次枝梗数 PBN | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C418 | 81 | 113.3±4.4 | 6.92±0.65 | 5.2±1.0 | 31.0±2.2 | 346.4±47.6 | 13.1±1.3 | ||
| G1 | BC3F4 | 81 | 110.0±3.7 | 7.08±0.44 | 5.8±1.0 | 31.3±1.5 | 368.7±50.1 | 14.1±1.6 | |
| G2 | BC3F4 | 87 | 117.4±2.9 | 7.22±0.66 | 5.6±1.1 | 32.6±1.1 | 294.8±27.3 | 12.4±0.9 | |
| G3 | BC4F3 | 84 | 114.7±3.5 | 7.01±0.51 | 5.2±0.9 | 30.1±2.4 | 343.0±37.9 | 12.8±1.2 | |
| G4 | BC4F3 | 87 | 112.4±5.3 | 7.36±0.47 | 5.6±0.8 | 31.6±2.1 | 357.2±40.7 | 13.4±1.2 | |
| G5 | BC4F3 | 87 | 110.6±3.4 | 6.86±0.39 | 6.5±0.7 | 32.3±1.6 | 305.4±30.6 | 12.9±1.5 | |
| G6 | BC4F3 | 85 | 113.6±3.4 | 7.42±0.32 | 5.7±0.8 | 32.9±2.3 | 389.2±48.4 | 12.9±1.1 | |
| 株系 Line | 剑叶基角 AFL/° | 倒3叶长 TLL/cm | 倒2叶长 SLL/cm | 剑叶长 FLL/cm | 穗叶差 DPFL/cm | 穗颈粗 PND/mm | 穗弯曲度 PCD/° | ||
| C418 | 7.7±3.9 | 52.5±4.9 | 53.7±4.0 | 37.7±7.2 | –2.6±6.8 | 2.77±0.18 | 58.40±13.95 | ||
| G1 | 9.6±4.7 | 55.7±3.2 | 58.3±4.8 | 42.5±6.5 | –7.2±5.9 | 2.92±0.20 | 74.75±18.90 | ||
| G2 | 10.0±4.1 | 60.4±5.2 | 62.8±4.5 | 46.6±5.3* | –9.0±4.5 | 2.80±0.30 | 88.30±20.41 | ||
| G3 | 10.5±3.8 | 57.6±3.1 | 56.8±5.9 | 40.8±6.4 | –5.2±5.6 | 2.84±0.26 | 71.33±14.21 | ||
| G4 | 11.1±7.2 | 56.3±4.5 | 56.8±4.8 | 40.6±6.7 | –6.1±7.1 | 2.80±0.26 | 82.42±17.76 | ||
| G5 | 7.8±5.3 | 54.6±2.9 | 54.2±4.8 | 43.0±4.3 | –4.8±4.4 | 2.84±0.22 | 67.22±14.67 | ||
| G6 | 10.1±5.7 | 55.1±3.2 | 59.7±5.1 | 42.8±6.7 | –5.7±6.6 | 3.08±0.23 | 71.08±14.01 | ||
| [1] | 邓华凤, 何强, 舒服, 张武汉, 杨飞, 荆彦辉, 东丽, 谢辉. 中国杂交粳稻研究现状与对策. 杂交水稻, 2006, 21(1): 1-6. |
| Deng H F, He Q, Shu F, Zhang W H, Yang F, Jing Y H, Dong L, Xie H.Status and technical strategy on development of japonica hybrid rice in China. Hybrid Rice, 2006, 21(1): 1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | Fujimura T, Akagi H, Oka M, Nakamura A, Sawada R.Establishment of a rice protoplast culture and application of an asymmetric protoplast fusion technique to hybrid rice breeding. J Food Sci, 2010, 13(3): 243-247. |
| [3] | 曾千春, 周开达, 朱祯, 罗琼. 中国水稻杂种优势利用现状. 中国水稻科学, 2000, 14(4): 243-246. |
| Zeng Q C, Zhou K D, Zhu Z, Luo Q.Current status in the use of hybrid rice heterosis in China.Chin J Rice Sci, 2000, 14(4): 243-246. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 汤述翥, 张宏根, 梁国华, 严长杰, 刘巧泉, 顾铭洪. 三系杂交粳稻发展缓慢的原因及对策. 杂交水稻, 2008, 23(1): 1-5. |
| Tang S Z, Zhang H G, Liang G H, Yan C J, Liu Q Q, Gu M H.Reasons and counter measures of slow development on three-line japonica hybrid rice. Hybrid Rice, 2008, 23(1): 1-5. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | 汤述翥, 孙叶, 张宏根, 顾燕娟, 陆驹飞, 田舜, 余波, 顾铭洪. 同核异质粳稻不育系特性比较. 中国水稻科学2005, 19(6): 521-526. |
| Tang S Z, Sun Y, Zhang H G, Gu Y J, Lu J F, Tian S, Yu B, Gu M H.Comparison on the characteristics of the isonuclear alloplasmic CMS lines in japonica rice. Chin J Rice Sci, 2005, 19(6): 521-526. (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [6] | 汤述翥, 张宏根, 朱正斌, 刘超, 李鹏, 梁国华, 严长杰, 刘巧泉, 于恒秀, 顾铭洪. 红莲型不育细胞质在杂交粳稻育种中的应用. 中国水稻科学, 2010, 24(2): 116-124. |
| Tang S Z, Zhang H G, Zhu Z B, Liu C, Li P, Liang G H, Yan C J, Liu Q Q, Yu H X, Gu M H.Application of HL type male sterile cytoplasm in japonica hybrid rice breeding. Chin J Rice Sci, 2010, 24(2): 116-124. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 汤述翥, 张宏根, 朱正斌, 刘巧泉, 梁国华, 严长杰, 刘超, 李鹏, 顾铭洪. 红莲型不育细胞质应用于粳稻杂种优势的思考与初探. 西南农业学报, 2009, 22(4): 1158-1164. |
| Tang S Z, Zhang H G, Zhu Z B, Liu Q Q, Liang G H, Yan C J, Liu C, Li P, Gu M H.Toward to apply HL-type male sterile cytoplasm for japonica heterosis utilization: Consideration and practice. Southwest China J Agric Sci, 2009, 22(4): 1158-1164. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | 朱正斌, 张宏根, 刘超, 李鹏, 裔传灯, 汤述翥, 顾铭洪. 四种细胞质六千辛A粳稻不育系育种利用特性的比较研究. 作物学报, 2010, 36(1): 1-8. |
| Zhu Z B, Zhang H G, Liu C, Li P, Yi C D, Tang S Z, Gu M H.Comparative study on breeding utilization characteristics of the isonuclear alloplasmic japonica CMS lines Liuqianxin A with four different cytoplasm sources. Acta Agron Sin, 2010, 36(1): 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | Wang Z, Zou Y, Li X, Zhang Q, Chen L, Wu H, Su D, Chen Y, Guo J, Luo D, Long Y, Zhong Y, Liu Y.Cytoplasmic male sterility of rice with Boro II cytoplasm is caused by a cytotoxic peptide and is restored by two related PPR motif genes via distinct modes of mRNA silencing.Plant Cell, 2006, 18(3): 676-687. |
| [10] | Akagi H, Nakamura A, Yokozeki-Misono Y, Inagaki A, Takahashi H, Mori K, Fujimura T.Positional cloning of the rice Rf-1 gene, a restorer of BT-type cytoplasmic male sterility that encodes a mitochondria-targeting PPR protein. Theor Appl Genet, 2004, 108(8): 1449-1457. |
| [11] | Huang Q, He Y, Jing R, Zhu R, Zhu Y.Mapping of the nuclear fertility restorer gene for HL cytoplasmic male sterility in rice using microsatellite markers.Chin Sci Bull, 2000, 45(5): 430-432. |
| [12] | Huang J, Hu J, Xu X, Li S, Yi P, Yang D, Ren F, Liu X, Zhu Y.Fine mapping of the nuclear fertility restorer gene for HL cytoplasmic male sterility in rice.Bot Bull Acad Sin, 2003, 44(4): 285-289. |
| [13] | Hu J, Wang K, Huang W, Liu G, Gao Y, Wang J, Huang Q, Ji Y, Qin X, Wan L, Zhu R, Li S, Yang D, Zhu Y. The rice pentatricopeptide repeat protein RF5 restores fertility in Hong-Lian cytoplasmic male-sterile lines via a complex with the glycine-rich protein GRP162. Plant Cell, 2012, 24(1): 109-122. |
| [14] | Huang W, Hu J, Yu C, Huang Q, Wan L, Wang L, Qin X, Ji Y, Zhu R, Li S, Zhu Y.Two non-allelic nuclear genes restore fertility in a gametophytic pattern and enhance abiotic stress tolerance in the hybrid rice plant. Theor Appl Genet, 2012, 124(5): 799-807. |
| [15] | Huang W, Yu C, Hu J, Wang L, Dan Z, Zhou W, He C, Zeng Y, Yao G, Qi J, Zhang Z, Zhu R, Chen X, Zhu Y.Pentatricopeptide-repeat family protein RF6 functions with hexokinase 6 to rescue rice cytoplasmic male sterility.Proc Natl Acad Sci, 2015, 112(48): 14984-14989. |
| [16] | Zhang H, Che J, Ge Y, Pei Y, Zhang L, Liu Q, Tang S, Gu M.Ability of Rf5 and Rf6 to restore fertility of Chinsurah Boro II-type cytoplasmic male sterile Oryza sativa(ssp. japonica) lines. Rice, 2017, 10(1): 2. |
| [17] | Rogers S O, Bendich A J.Extraction of DNA from milligram amounts of fresh, herbarium and mummified plant tissues. Plant Mol Biol, 1985, 5: 69-76. |
| [18] | Zhang H, Zhang L, Si H, Ge Y, Liang G, Gu M, Tang S.Rf5 is able to partially restore fertility to Honglian-type cytoplasmic male sterile japonica rice(Oryza sativa ) lines. Mol Breeding, 2016, 36(7): 102. |
| [19] | 杨振玉, 陈秋柏, 陈荣芳, 苏正基, 贾宝清, 佟景兴, 王健群. 水稻粳型恢复系C57的选育. 作物学报, 1981, 7(3): 153-156. |
| Yang Z Y, Chen Q B, Chen R F, Su Z J, Jia B Q, Tong J X, Wang J Q.The breeding of japonica rice restorer C57. Acta Agron Sin, 1981, 7(3): 153-156. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | 杨振玉, 张宗旭, 魏耀林, 赵迎春, 高勇. 粳型特异亲和恢复系C418的选育及其特性. 杂交水稻, 1998(3): 33-34. |
| Yang Z Y, Zhang Z X, Wei Y L, Zhao Y C, Gao Y.Breeding and characteristics ofjaponica type wide compatibility line C418. Hybrid Rice, 1998(3): 33-34. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | 赵迎春, 杨振玉, 魏耀林, 张忠旭. 从C418的育成再论北方杂交粳稻的发展形势. 杂交水稻, 2000(5): 5-6. |
| Zhao Y C, Yang Z Y, Wei Y L, Zhang Z X.A second discussion on development of northernjaponica hybrid rice from the successful breeding of restorer C418. Hybrid Rice, 2000(5): 5-6. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | DING Zhengquan, PAN Yueyun, SHI Yang, HUANG Haixiang. Comprehensive Evaluation and Comparative Analysis of Jiahe Series Long-Grain japonica Rice with High Eating Quality Based on Gene Chip Technology [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 397-408. |
| [2] | JING Xiu, ZHOU Miao, WANG Jing, WANG Yan, WANG Wang, WANG Kai, GUO Baowei, HU Yajie, XING Zhipeng, XU Ke, ZHANG Hongcheng. Effect of Drought Stress on Root Morphology and Leaf Photosynthetic Characteristics of Good Taste japonica Rice from Late Stage of Panicle Differentiation to Early Stage of Grain Filling [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(1): 33-47. |
| [3] | FENG Aiqing, WANG Congying, SU Jing, FENG Jinqi, CHEN Kailing, LIN Xiaopeng, CHEN Bing, LIANG Meiling, YANG Jianyuan, ZHU Xiaoyuan, CHEN Shen. Development and Agronomic Traits Analysis of New Rice Resistance Lines to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(6): 587-596. |
| [4] | HUANG Yaru, XU Peng, WANG Lele, HE Yizhe, WANG Hui, KE Jian, HE Haibing, WU Liquan, YOU Cuicui. Effects of Exogenous Trehalose on Grain Filling Characteristics and Yield Formation of japonica Rice Cultivar W1844 [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(4): 379-391. |
| [5] | WANG Yu, SUN Quanyi, DU Haibo, XU Zhiwen, WU Keting, YIN Li, FENG Zhiming, HU Keming, CHEN Zongxiang, ZUO Shimin. Improvement of the Resistance of Nanjing 9108 to Blast and Sheath Blight by Pyramiding Resistance Gene Pigm and Quantitative Trait Genes qSB-9TQ and qSB-11HJX [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(2): 125-132. |
| [6] | PEI Feng, WANG Guangda, GAO Peng, FENG Zhiming, HU Keming, CHEN Zongxiang, CHEN Hongqi, CUI Ao, ZUO Shimin. Evaluation of New japonica Rice Lines with Low Cadmium Accumulation and Good Quality Generated by Knocking Out OsNramp5 [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(1): 16-28. |
| [7] | WANG Shiguang, LU Zhanhua, LIU Wei, LU Dongbai, WANG Xiaofei, FANG Zhiqiang, WU Haoxiang, HE Xiuying. Generating Guangdong Simiao Rice Germplasms by Applying CRISPR/Cas9 Gene Editing and Marker-assisted Selection Technology [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(1): 29-36. |
| [8] | CHEN Tao, ZHAO Qingyong, ZHU Zhen, ZHAO Ling, YAO Shu, ZHOU Lihui, ZHAO Chunfang, ZHANG Yadong, WANG Cailin. Development of New Low Glutelin Content japonica Rice Lines with Good Eating Quality and Fragrance by Molecular Marker-Assisted Selection [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(1): 55-65. |
| [9] | ZHANG Xiaoxiang, SHAO Shimei, ZHAO Buhong, ZHANG Hao, JI Hongjuan, XIAO Ning, PAN Cunhong, LI Yuhong, WU Yunyu, CAI Yue, LIU Jianju, JI Chunming, ZHANG Xiuqin, LIU Guangqing, ZHOU Changhai, HUANG Niansheng, LI Aihong. Effects of Nitrogen Reduction Model on Yield and Nitrogen Absorption and Utilization of Late-maturing Mid-japonica Rice with Different Panicle Types [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(3): 278-294. |
| [10] | Cailin WANG, Yadong ZHANG, Tao CHEN, Zhen ZHU, Qingyong ZHAO, Shu YAO, Ling ZHAO, Chunfang ZHAO, Lihui ZHOU, Xiaodong Wei, Kai LU, Wenhua LIANG. Rapid Breeding of New Semi-glutinous japonica Rice Varieties with Good Eating Quality by Crossing Between Sister Lines [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2021, 35(5): 455-465. |
| [11] | Mengjia WANG, Min YIN, Guang CHU, Yuanhui LIU, Chunmei XU, Xiufu ZHANG, Danying WANG, Song CHENG. Ecological Differences in Yield, Growth Period and the Utilization of Temperature and Light Resources of Double-cropping Late japonica Rice in the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2021, 35(5): 475-486. |
| [12] | Cailin WANG, Yadong ZHANG, Tao CHEN, Zhen ZHU, Qingyong ZHAO, Chunfang ZHAO, Shu YAO, Lihui ZHOU, Ling ZHAO, Xiaodong Wei, Kai LU, Wenhua LIANG. Effect of Location and Sowing Date on Eating Quality of Semi-waxy japonica Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2021, 35(4): 373-382. |
| [13] | Qing ZHANG, Yajie HU, Baowei GUO, Hongcheng ZHANG, Xiaojie XU, Yufeng XU, Banghui ZHU, Jiefen XU, Zhongyi NIU, Rongwen TU. Study on the Characteristics of Soft japonica Rice Varieties with Good Taste and High Yield in Taihu Lake Area [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2021, 35(3): 279-290. |
| [14] | Kai LU, Tao CHEN, Shu YAO, Wenhua LIANG, Xiaodong WEI, Yadong ZHANG, Cailin WANG. Functional Analysis on Four Receptor-like Protein Kinases Under Salt Stress in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2021, 35(2): 103-111. |
| [15] | Feng WANG, Yilong LIAO, Wuge LIU, Diling LIU, Xueqing ZENG, Youqiang FU, Manshan ZHU, Jinhua LI, Chongyun FU, Xiaozhi MA, Xing HUO. Evaluation of Dynamic Plant Type and Radiation Use Efficiency of indica Hybrid Rice Restorer Lines [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2021, 35(2): 141-154. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||