
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2016, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (3): 223-231.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2016.5177
• Orginal Article • Next Articles
Xin LIU, Heng ZHANG, Hu-fei KAN, Li-shuai ZHOU, Hao HUANG, Lin-lin SONG, Huan-chen ZHAI, Jun ZHANG, Guo-dong LU*( )
)
Received:2015-11-30
Revised:2016-03-16
Online:2016-05-10
Published:2016-05-10
Contact:
Guo-dong LU
刘鑫, 张恒, 阚虎飞, 周立帅, 黄昊, 宋林林, 翟焕趁, 张君, 鲁国东*( )
)
通讯作者:
鲁国东
基金资助:CLC Number:
Xin LIU, Heng ZHANG, Hu-fei KAN, Li-shuai ZHOU, Hao HUANG, Lin-lin SONG, Huan-chen ZHAI, Jun ZHANG, Guo-dong LU. Bioinformatic and Expression Analysis of Rice Ubiquitin-conjugating Enzyme Gene Family[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2016, 30(3): 223-231.
刘鑫, 张恒, 阚虎飞, 周立帅, 黄昊, 宋林林, 翟焕趁, 张君, 鲁国东. 水稻泛素结合酶基因家族的生物信息学与表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2016, 30(3): 223-231.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2016.5177
| 基因 Gene | 表达诱导因素 Expression inducing factors | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 稻瘟病菌侵染 Blast fungus infection | 盐胁迫 Salinity stress | 脱落酸 Abscisic acid | 赤霉素 Gibberellin | 细胞分裂素 Cytokinin | 寡聚糖几丁质 Chitin oligosaccharide | |
| OsUBC1 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC2 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC3 | + | + | n | n | + | n |
| OsUBC4 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC5 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC6 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC7 | + | + | n | n | + | n |
| OsUBC8 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC9 | n | n | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC10 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC11 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC12 | + | + | n | n | + | n |
| OsUBC13 | + | + | n | n | + | n |
| OsUBC14 | n | n | + | + | n | + |
| OsUBC15 | n | n | n | n | n | n |
| OsUBC16 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC17 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC18 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC19 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC20 | N | N | N | N | N | N |
| OsUBC21 | N | N | N | N | N | N |
| OsUBC22 | N | N | N | N | N | N |
| OsUBC23 | N | N | N | N | N | N |
| OsUBC24 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC25 | N | N | N | N | N | N |
| OsUBC26 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC27 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC28 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC29 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC30 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC31 | + | + | n | n | + | n |
| OsUBC32 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC33 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC34 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC35 | N | N | N | N | N | N |
| OsUBC36 | N | N | N | N | N | N |
| OsUBC37 | + | + | n | n | + | + |
| OsUBC38 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC39 | N | N | N | N | N | N |
| OsUBC40 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC41 | + | + | n | n | + | N |
| OsUBC42 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC43 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC44 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC45 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC46 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC47 | + | + | n | n | + | N |
| OsUBC48 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
Table 1 Expression pattern of rice UBC gene family in silico.
| 基因 Gene | 表达诱导因素 Expression inducing factors | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 稻瘟病菌侵染 Blast fungus infection | 盐胁迫 Salinity stress | 脱落酸 Abscisic acid | 赤霉素 Gibberellin | 细胞分裂素 Cytokinin | 寡聚糖几丁质 Chitin oligosaccharide | |
| OsUBC1 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC2 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC3 | + | + | n | n | + | n |
| OsUBC4 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC5 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC6 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC7 | + | + | n | n | + | n |
| OsUBC8 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC9 | n | n | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC10 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC11 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC12 | + | + | n | n | + | n |
| OsUBC13 | + | + | n | n | + | n |
| OsUBC14 | n | n | + | + | n | + |
| OsUBC15 | n | n | n | n | n | n |
| OsUBC16 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC17 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC18 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC19 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC20 | N | N | N | N | N | N |
| OsUBC21 | N | N | N | N | N | N |
| OsUBC22 | N | N | N | N | N | N |
| OsUBC23 | N | N | N | N | N | N |
| OsUBC24 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC25 | N | N | N | N | N | N |
| OsUBC26 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC27 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC28 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC29 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC30 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC31 | + | + | n | n | + | n |
| OsUBC32 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC33 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC34 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC35 | N | N | N | N | N | N |
| OsUBC36 | N | N | N | N | N | N |
| OsUBC37 | + | + | n | n | + | + |
| OsUBC38 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC39 | N | N | N | N | N | N |
| OsUBC40 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC41 | + | + | n | n | + | N |
| OsUBC42 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC43 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC44 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC45 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC46 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| OsUBC47 | + | + | n | n | + | N |
| OsUBC48 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
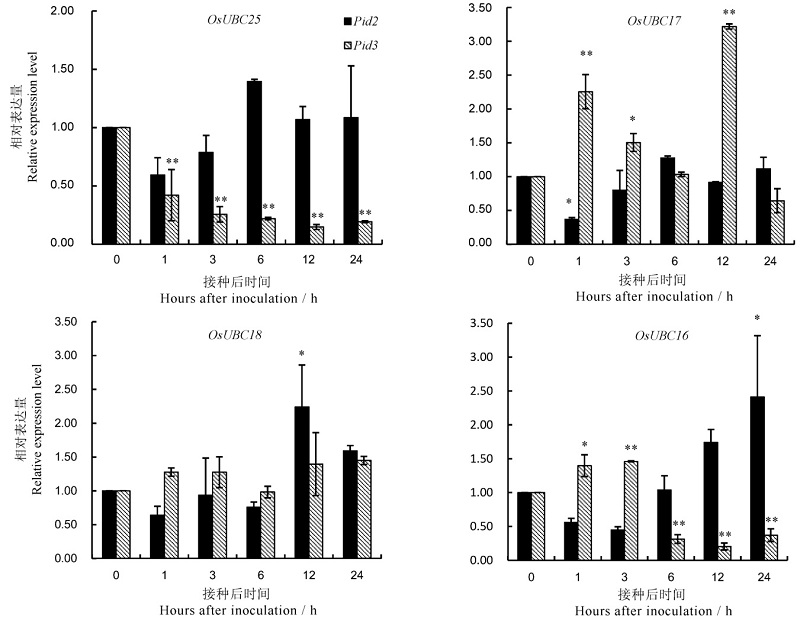
Fig. 5. Expression level of rice ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme genes after Magnaporthe oryzae inoculation. *,** indicate significantly or extremely significantly upregulated expression levels,respectively.
| [1] | Hershko A.The ubiquitin system for protein degradation and some of its roles in the control of the cell division cycle.Cell Death Differ, 2005, 12: 1191-1197. |
| [2] | Dielen A, Badaoui S, Candresse T, et al.The ubiquitin/26S proteasome system in plant-pathogen interactions: A never-ending hide-and-seek game.Mol Plant Pathol, 2010, 11(2): 293-308. |
| [3] | Zeng L R, Miguel E V, Zhu T, et al.Ubiquitination-mediated protein degradation and modification: An emerging theme in plant-microbe interactions.Cell Res, 2006, 16: 423-426. |
| [4] | Stone S L.The role of ubiquitin and the 26S proteasome in plant abiotic stress signaling.Front Plant Sci, 2014, 5. |
| [5] | Marino D, Peeters N, Rivas S.Ubiquitination during plant immune signaling.Plant Physiol, 2012, 160(1): 15-27. |
| [6] | Smalle J, Vierstra R D.The ubiquitin 26S proteasome proteolytic pathway.Annu Rev Plant Biol, 2004, 55: 555-590. |
| [7] | Madden L V, Wheelis M.The threat of plant pathogens as weapons against U.S. crops.Annu Rev Phytopathol, 2003, 41(4): 155-176. |
| [8] | Zeng L R, Qu S H, Bordeos A, et al.Spotted leaf11, a negative regulator of plant cell death and defense, encodes a U-Box/Armadillo repeat protein endowed with E3 ubiquitin ligase activity.Plant Cell, 2004, 16: 2795-2808. |
| [9] | Park C, Chen S B, Shirsekar G, et al.The Magnaporthe oryzae effector AvrPiz-t targets the RING E3 ubiquitin ligase APIP6 to suppress pathogen-associated molecular pattern-triggered immunity in rice.Plant Cell, 2012, 24: 4748-4762. |
| [10] | 蒋春苗, 黄兴奇, 付坚, 等.疣粒野生稻泛素结合酶基因的全长cDNA序列克隆与分析. 作物学报,2012,38(5): 808-813. |
| Jiang C M, Huang X Q, Fu J, et al.Cloning and analysis on full-Length cDNA sequence of ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme gene from Oryza meyeriana Baill.Acta Agron Sin, 2012, 38(5): 808-813. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 胡婷丽, 李魏, 刘雄伦, 等. 泛素化在植物抗病中的作用. 微生物学通报, 2014, 41(6): 1175-1179. |
| Hu T L, Li W, Liu X L, et al.The role of ubiquitination in plant disease resistance.Microbiol China, 2014, 41(6): 1175-1179. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 杨玖霞, 张浩, 王志龙, 等. E3泛素连接酶调控植物抗病分子机理研究进展. 植物保护,2015,41(4): 1-8. |
| Yang J X, Zhang H, Wang Z L, et al.Recent progresses in the regulation mechanism of E3 ligases in plant disease resistance.Plant Protect, 2015, 41(4): 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | 林艺娟. OsRBCS和OsUBC2在水稻抗病防御中的作用机制. 福州:福建农林大学,2014. |
| Lin Y J.The mechanism of OsRBCs and OsUBC2 in rice disease resistance. Fuzhou: Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, 2014.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | Hansol B, Woo T K.Classification and interaction modes of 40 rice E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes with 17 rice ARM-U-box E3 ubiquitin ligases.Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2014, 444: 575-580. |
| [15] | E Z G, Zhang Y P, Li T T, et al. Characterization of the ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme gene family in rice and evaluation of expression profiles under abiotic stresses and hormone treatments.PLoS ONE, 2015, 10(4). |
| [16] | Xu L, Ménard R, Berr A, et al.The E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes, AtUBC1 and AtUBC2, play redundant roles and are involved in activation of FLC expression and repression of flowering in Arabidopsis thaliana.Plant J, 2009, 57(2): 279-288. |
| [17] | Cui F, Liu L J, Zhao Q Z, et al.Arabidopsis ubiquitin conjugase UBC32 is an ERAD component that functions in brassinosteroid-mediated salt stress tolerance.Plant Cell, 2012, 24(1): 233-244. |
| [18] | Chung E, Cho C W, So H A, et al.Overexpression of VrUBC1, a mung bean E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme, enhances osmotic stress tolerance in Arabidopsis.PLoS ONE, 2013, 8(6). |
| [19] | Wan X R, Mo A Q, Liu S, et al.Constitutive expression of a peanut ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme gene in Arabidopsis confers improved water-stress tolerance through regulation of stress-responsive gene expression.J Biosci Bioengin, 2011, 111(4): 478-484. |
| [20] | Zhou G A, Chang R Z, Qiu L J.Overexpression of soybean ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme gene GmUBC2 confers enhanced drought and salt tolerance through modulating abiotic stress-responsive gene expression in Arabidopsis.Plant Mol Biol, 2010, 72(4-5): 357-367. |
| [21] | Jeon E H, Pak J H, Kim M J, et al.Ectopic expression of ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme gene from wild rice, OgUBC1, confers resistance against UV-B radiation and Botrytis infection in Arabidopsis thaliana.Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2012, 427(2): 309-314. |
| [22] | Kawahara Y, Bastide M D L, Hamilton J P, et al. Improvement of the Oryza sativa Nipponbare reference genome using next generation sequence and optical map data.Rice, 2013, 6: 4. |
| [23] | Finn R D, Bateman A, Clements J, et al. The Pfam protein families database. Nucl Acids Res, 2014, Database Issue 42: D222-D230. |
| [24] | Higo K, Ugawa Y, Iwamoto M,et al.Plant cis-acting regulatory DNA elements (PLACE) database.Nucl Acids Res, 1999, 27: 297-300. |
| [25] | Prestridge D S.SIGNAL SCAN: A computer program that scans DNA sequences for eukaryotic transcriptional elements.Computer Appl Biosci, 1991, 7: 203-206. |
| [26] | de Hoon M J L, Imoto S, Nolan J, et al. Open source clustering software.Bioinformatics, 2004, 20(9): 1453-1454. |
| [27] | Mortazavi A, Williams B A, Mccue, et al. Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq.Nat Methods, 2008, 5(7): 621-628. |
| [28] | van Demark A P, Hofmann R M, Tsui C, et al. Molecular insights into polyubiquitin chain assembly: Crystal structure of the Mms2/Ubc13 heterodimer.Cell, 2001, 105(6): 711-720. |
| [29] | Andersen P L, Zhou H, Pastushok L, et al.Distinct regulation of Ubc13 functions by the two ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme variants Mms2 and Uev1A.J Cell Biol, 2005, 170(5): 745-755. |
| [30] | Ye Y, Rape M.Building ubiquitin chains: E2 enzymes at work.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2009, 10(11): 755-764. |
| [1] | GUO Zhan, ZHANG Yunbo. Research Progress in Physiological,Biochemical Responses of Rice to Drought Stress and Its Molecular Regulation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | WEI Huanhe, MA Weiyi, ZUO Boyuan, WANG Lulu, ZHU Wang, GENG Xiaoyu, ZHANG Xiang, MENG Tianyao, CHEN Yinglong, GAO Pinglei, XU Ke, HUO Zhongyang, DAI Qigen. Research Progress in the Effect of Salinity, Drought, and Their Combined Stresses on Rice Yield and Quality Formation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | XU Danjie, LIN Qiaoxia, LI Zhengkang, ZHUANG Xiaoqian, LING Yu, LAI Meiling, CHEN Xiaoting, LU Guodong. OsOPR10 Positively Regulates Rice Blast and Bacterial Blight Resistance [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | CHEN Mingliang, ZENG Xihua, SHEN Yumin, LUO Shiyou, HU Lanxiang, XIONG Wentao, XIONG Huanjin, WU Xiaoyan, XIAO Yeqing. Typing of Inter-subspecific Fertility Loci and Fertility Locus Pattern of indica-japonica Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 386-396. |
| [5] | DING Zhengquan, PAN Yueyun, SHI Yang, HUANG Haixiang. Comprehensive Evaluation and Comparative Analysis of Jiahe Series Long-Grain japonica Rice with High Eating Quality Based on Gene Chip Technology [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 397-408. |
| [6] | HOU Xiaoqin, WANG Ying, YU Bei, FU Weimeng, FENG Baohua, SHEN Yichao, XIE Hangjun, WANG Huanran, XU Yongqiang, WU Zhihai, WANG Jianjun, TAO Longxing, FU Guanfu. Mechanisms Behind the Role of Potassium Fulvic Acid in Enhancing Salt Tolerance in Rice Seedlings [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [7] | LÜ Zhou, YI Binghuai, CHEN Pingping, ZHOU Wenxin, TANG Wenbang, YI Zhenxie. Effects of Nitrogen Application Rate and Transplanting Density on Yield Formation of Small Seed Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| [8] | HU Jijie, HU Zhihua, ZHANG Junhua, CAO Xiaochuang, JIN Qianyu, ZHANG Zhiyuan, ZHU Lianfeng. Effects of Rhizosphere Saturated Dissolved Oxygen on Photosynthetic and Growth Characteristics of Rice at Tillering Stage [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [9] | WU Yue, LIANG Chengwei, ZHAO Chenfei, SUN Jian, MA Dianrong. Occurrence of Weedy Rice Disaster and Ecotype Evolution in Direct-Seeded Rice Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 447-455. |
| [10] | LIU Fuxiang, ZHEN Haoyang, PENG Huan, ZHENG Liuchun, PENG Deliang, WEN Yanhua. Investigation and Species Identification of Cyst Nematode Disease on Rice in Guangdong Province [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [11] | CHEN Haotian, QIN Yuan, ZHONG Xiaohan, LIN Chenyu, QIN Jinghang, YANG Jianchang, ZHANG Weiyang. Research Progress on the Relationship Between Rice Root, Soil Properties and Methane Emissions in Paddy Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [12] | MIAO Jun, RAN Jinhui, XU Mengbin, BO Liubing, WANG Ping, LIANG Guohua, ZHOU Yong. Overexpression of RGG2, a Heterotrimeric G Protein γ Subunit-Encoding Gene, Improves Drought Tolerance in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [13] | YIN Xiaoxiao, ZHANG Zhihan, YAN Xiulian, LIAO Rong, YANG Sijia, Beenish HASSAN, GUO Daiming, FAN Jing, ZHAO Zhixue, WANG Wenming. Signal Peptide Validation and Expression Analysis of Multiple Effectors from Ustilaginoidea virens [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [14] | ZHU Yujing, GUI Jinxin, GONG Chengyun, LUO Xinyang, SHI Jubin, ZHANG Haiqing, HE Jiwai. QTL Mapping for Tiller Angle in Rice by Genome-wide Association Analysis [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [15] | WEI Qianqian, WANG Yulei, KONG Haimin, XU Qingshan, YAN Yulian, PAN Lin, CHI Chunxin, KONG Yali, TIAN Wenhao, ZHU Lianfeng, CAO Xiaochuang, ZHANG Junhua, ZHU Chunqun. Mechanism of Hydrogen Sulfide, a Signaling Molecule Involved in Reducing the Inhibitory Effect of Aluminum Toxicity on Rice Growth Together with Sulfur Fertilizer [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||