
中国水稻科学 ›› 2024, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (6): 672-684.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2024.240110
刘俊峰1,2, 牟静怡2, 赵红艳2, 郭诗梦2, 李漪濛2, 梁超2, 周婵婵2,*( ), 王术2,*(
), 王术2,*( ), 黄元财2
), 黄元财2
收稿日期:2024-01-24
修回日期:2024-05-09
出版日期:2024-11-10
发布日期:2024-11-15
通讯作者:
*email: swang123@syau.edu.cn;zhouchan@syau.edu.cn
基金资助:
LIU Junfeng1,2, MOU Jingyi2, ZHAO Hongyan2, GUO Shimeng2, LI Yimeng2, LIANG Chao2, ZHOU Chanchan2,*( ), WANG Shu2,*(
), WANG Shu2,*( ), HUANG Yuancai2
), HUANG Yuancai2
Received:2024-01-24
Revised:2024-05-09
Online:2024-11-10
Published:2024-11-15
Contact:
*email: swang123@syau.edu.cn;zhouchan@syau.edu.cn
摘要:
【目的】研究施氮方式与行距配置对不同穗型粳稻产量和氮素利用率的影响,明确其最佳组合,为辽宁水稻高产高效栽培提供理论依据。【方法】以沈稻9号(穗粒兼顾型)、沈稻505(穗数型)和沈稻527(穗重型)为材料于2019年和2020年在沈阳市进行田间试验,设置N0(不施氮肥)、N1(农户方式)、N2(底氮减施)、N3(底氮减施后移)4种施氮方式和R1(常规行距30 cm)、R2(缩行增密25 cm)、R3(宽窄行40 cm+20 cm) 3种行距配置,分析其对不同穗型粳稻产量及氮素利用率的影响。【结果】施氮方式与行距配置对不同穗型粳稻产量和氮素利用率有极显著影响和互作效应。N3可以通过提高单位面积颖花数、结实率、千粒重、干物质积累量、氮素积累量、氮肥偏生产力、氮肥农学利用率和氮肥回收利用率来增加沈稻9号、沈稻505的产量和氮素利用率,但沈稻527却在N1实现高产,在N2实现高效目标。对于行距配置的响应,3个品种表现大致相同,产量、单位面积颖花数、干物质积累量、氮素积累量、氮肥偏生产力、氮肥农学利用率和氮肥回收利用率均在R2达到最高。施氮方式与行距配置互作显示,沈稻9号和沈稻505在N3R2产量最高,与N1R1相比,分别增加了18.53%和14.27%的产量,18.38%和22.47%的干物质积累量,37.22%和29.15%的氮素积累量,39.30%和34.25%的氮肥偏生产力,52.59 %和26.73%的氮肥农学利用率,27.65%和17.70%的氮肥回收利用率,降低了15.75%和8.16%的土壤氮依存率。沈稻527产量则在N1R1、N1R2和N2R2处理下较高且差异不显著,但比较3个组合的干物质积累量、氮素积累量以及氮素利用率,N2R2表现优异。【结论】在本试验条件下,沈稻9号、沈稻505的最适组合为底氮减施后移和行距25 cm,沈稻527为底氮减施和行距25 cm,此时3个品种高产且氮肥利用率也较高。
刘俊峰, 牟静怡, 赵红艳, 郭诗梦, 李漪濛, 梁超, 周婵婵, 王术, 黄元财. 施氮方式与行距配置对不同穗型粳稻品种产量和氮素利用率的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(6): 672-684.
LIU Junfeng, MOU Jingyi, ZHAO Hongyan, GUO Shimeng, LI Yimeng, LIANG Chao, ZHOU Chanchan, WANG Shu, HUANG Yuancai. Effects of Nitrogen Application Practice and Row Spacing on Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency in japonica Rice With Different Panicle Types[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(6): 672-684.
| 年份 Year | pH值 pH value | 有机质含量 Organic matter content(g/kg) | 全氮 Total N (g/kg) | 全磷 Total P (g/kg) | 全钾 Total K (g/kg) | 速效氮 Available N (mg/kg) | 速效磷 Available P (mg/kg) | 速效钾 Available K (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 7.28 | 18.47 | 1.24 | 0.96 | 15.88 | 107.67 | 14.34 | 86.59 |
| 2020 | 7.22 | 17.96 | 1.28 | 1.03 | 14.16 | 112.31 | 13.49 | 98.20 |
表1 2019和2020水稻移栽前0-20 cm土壤理化性状
Table 1. Physical and chemical properties of 0-20 cm soil before rice transplanting in 2019 and 2020
| 年份 Year | pH值 pH value | 有机质含量 Organic matter content(g/kg) | 全氮 Total N (g/kg) | 全磷 Total P (g/kg) | 全钾 Total K (g/kg) | 速效氮 Available N (mg/kg) | 速效磷 Available P (mg/kg) | 速效钾 Available K (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 7.28 | 18.47 | 1.24 | 0.96 | 15.88 | 107.67 | 14.34 | 86.59 |
| 2020 | 7.22 | 17.96 | 1.28 | 1.03 | 14.16 | 112.31 | 13.49 | 98.20 |
| 施氮方式 N application pattern | 合计 Total | 基肥 Basal fertilizer | 分蘖肥 Fertilizer for tillering | 拔节肥 Fertilizer for panicle initiation | 孕穗肥 Fertilizer for panicle differentiation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 不施氮肥Zero nitrogen(N0) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 农户方式Farmer’s practice(N1) | 235 | 155 | 30 | 50 | 0 |
| 底氮减施Reduced basal nitrogen application(N2) | 200 | 120 | 30 | 50 | 0 |
| 底氮减施后移Reduced and delayed basal nitrogen(N3) | 200 | 80 | 30 | 50 | 40 |
表2 氮肥运筹方案
Table 2. Experimental design of nitrogen application management kg/hm2
| 施氮方式 N application pattern | 合计 Total | 基肥 Basal fertilizer | 分蘖肥 Fertilizer for tillering | 拔节肥 Fertilizer for panicle initiation | 孕穗肥 Fertilizer for panicle differentiation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 不施氮肥Zero nitrogen(N0) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 农户方式Farmer’s practice(N1) | 235 | 155 | 30 | 50 | 0 |
| 底氮减施Reduced basal nitrogen application(N2) | 200 | 120 | 30 | 50 | 0 |
| 底氮减施后移Reduced and delayed basal nitrogen(N3) | 200 | 80 | 30 | 50 | 40 |
| 变异来源 Source of variation | 单位面积穗数 Panicles per unit area | 每穗颖花数 Spikelets per panicle | 单位面积 颖花数 Spikelets per unit area | 结实率 Seed- setting rate | 千粒重 1000- grain weight | 产量 Grain yield | 干物质 积累量 Dry matter accumulation | 氮素积累量 N accumulation | 氮肥偏生产力 PFPN | 氮肥农学利用率 AEN | 氮肥回收利用率 REN | 土壤氮依存率 CRSN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年份Year(Y) | ** | ** | ** | ns | ns | ** | ** | ns | ** | ns | ns | ns |
| 品种Cultivar(C) | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ns | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| 施氮方式Nitrogen fertilization pattern(N) | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| 行距配置 Row spacing(R) | ** | ** | ** | ** | ns | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| Y×C | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| Y×N | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| Y×R | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| C×N | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | * | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| C×R | ** | ** | ** | ** | ns | ** | ** | ns | ** | ns | ** | ** |
| N×R | ** | ** | ** | ** | ns | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| Y×C×N | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| Y×C×R | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| Y×N×R | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| C×N×R | ** | ** | ** | ** | ns | ** | ns | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| Y×C×N×R | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns |
表3 两年所有测试指标的方差分析
Table 3. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) for all indicators tested in 2019 and 2020
| 变异来源 Source of variation | 单位面积穗数 Panicles per unit area | 每穗颖花数 Spikelets per panicle | 单位面积 颖花数 Spikelets per unit area | 结实率 Seed- setting rate | 千粒重 1000- grain weight | 产量 Grain yield | 干物质 积累量 Dry matter accumulation | 氮素积累量 N accumulation | 氮肥偏生产力 PFPN | 氮肥农学利用率 AEN | 氮肥回收利用率 REN | 土壤氮依存率 CRSN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年份Year(Y) | ** | ** | ** | ns | ns | ** | ** | ns | ** | ns | ns | ns |
| 品种Cultivar(C) | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ns | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| 施氮方式Nitrogen fertilization pattern(N) | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| 行距配置 Row spacing(R) | ** | ** | ** | ** | ns | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| Y×C | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| Y×N | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| Y×R | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| C×N | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | * | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| C×R | ** | ** | ** | ** | ns | ** | ** | ns | ** | ns | ** | ** |
| N×R | ** | ** | ** | ** | ns | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| Y×C×N | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| Y×C×R | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| Y×N×R | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| C×N×R | ** | ** | ** | ** | ns | ** | ns | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| Y×C×N×R | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| 品种 Cultivar | 处理 Treatment | 单位面积穗数 Panicles per unit area(×104/hm2) | 每穗颖花数 Spikelets per panicle | 单位面积颖花数 Spikelets per unit area (×107/hm2) | 结实率 Seed-setting rate (%) | 千粒重 1000-grain weight (g) | 产量 Grain yield (t/hm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 沈稻9号 | N0 | 220.54±10.56 d | 115.62±3.04 d | 25.48±0.85 d | 91.42±1.20 a | 24.10±0.19 a | 5.11±0.32 c |
| Shendao 9 | N1 | 365.91±38.92 a | 120.32±6.96 c | 43.80±2.27 c | 83.86±1.39 c | 23.37±0.35 b | 8.47±0.18 b |
| N2 | 356.38±25.96 b | 130.41±2.86 b | 46.42±2.52 b | 85.08±2.34 c | 23.44±0.55 b | 8.56±0.42 b | |
| N3 | 345.57±27.83 c | 140.48±5.71 a | 48.42±2.26 a | 87.95±2.26 b | 23.73±0.42 ab | 8.97±0.72 a | |
| 沈稻 505 | N0 | 257.41±24.93 d | 98.42±2.66 d | 25.35±2.75 c | 85.47±1.14 a | 25.96±0.39 a | 4.36±0.43 d |
| Shendao 505 | N1 | 484.09±32.11 a | 111.65±3.30 c | 54.04±3.72 a | 69.97±3.35 c | 24.23±0.62 c | 8.77±0.23 b |
| N2 | 428.41±37.15 b | 116.10±7.69 b | 49.84±6.27 b | 72.11±4.01 b | 24.97±0.22 b | 8.41±0.82 c | |
| N3 | 410.26±21.69 c | 128.56±3.74 a | 52.75±3.28 a | 73.03±3.49 b | 25.18±0.25 b | 9.01±0.61 a | |
| 沈稻 527 | N0 | 153.00±16.81 d | 157.86±10.77 d | 24.00±1.32 c | 95.92±0.87 a | 28.23±0.43 a | 5.09±0.41 d |
| Shendao 527 | N1 | 237.94±18.99 a | 172.07±10.35 c | 40.48±1.32 a | 86.04±2.40 d | 25.53±0.62 b | 8.52±0.26 a |
| N2 | 224.47±14.98 b | 182.81±8.13 b | 40.94±1.55 a | 90.10±1.97 c | 24.98±1.18 b | 8.20±0.48 b | |
| N3 | 198.83±23.40 c | 191.36±12.95 a | 37.80±2.42 b | 92.07±1.50 b | 25.56±0.46 b | 7.76±0.59 c |
表4 施氮方式对水稻产量及其构成因素的影响
Table 4. Effects of N application pattern on rice yield and its components
| 品种 Cultivar | 处理 Treatment | 单位面积穗数 Panicles per unit area(×104/hm2) | 每穗颖花数 Spikelets per panicle | 单位面积颖花数 Spikelets per unit area (×107/hm2) | 结实率 Seed-setting rate (%) | 千粒重 1000-grain weight (g) | 产量 Grain yield (t/hm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 沈稻9号 | N0 | 220.54±10.56 d | 115.62±3.04 d | 25.48±0.85 d | 91.42±1.20 a | 24.10±0.19 a | 5.11±0.32 c |
| Shendao 9 | N1 | 365.91±38.92 a | 120.32±6.96 c | 43.80±2.27 c | 83.86±1.39 c | 23.37±0.35 b | 8.47±0.18 b |
| N2 | 356.38±25.96 b | 130.41±2.86 b | 46.42±2.52 b | 85.08±2.34 c | 23.44±0.55 b | 8.56±0.42 b | |
| N3 | 345.57±27.83 c | 140.48±5.71 a | 48.42±2.26 a | 87.95±2.26 b | 23.73±0.42 ab | 8.97±0.72 a | |
| 沈稻 505 | N0 | 257.41±24.93 d | 98.42±2.66 d | 25.35±2.75 c | 85.47±1.14 a | 25.96±0.39 a | 4.36±0.43 d |
| Shendao 505 | N1 | 484.09±32.11 a | 111.65±3.30 c | 54.04±3.72 a | 69.97±3.35 c | 24.23±0.62 c | 8.77±0.23 b |
| N2 | 428.41±37.15 b | 116.10±7.69 b | 49.84±6.27 b | 72.11±4.01 b | 24.97±0.22 b | 8.41±0.82 c | |
| N3 | 410.26±21.69 c | 128.56±3.74 a | 52.75±3.28 a | 73.03±3.49 b | 25.18±0.25 b | 9.01±0.61 a | |
| 沈稻 527 | N0 | 153.00±16.81 d | 157.86±10.77 d | 24.00±1.32 c | 95.92±0.87 a | 28.23±0.43 a | 5.09±0.41 d |
| Shendao 527 | N1 | 237.94±18.99 a | 172.07±10.35 c | 40.48±1.32 a | 86.04±2.40 d | 25.53±0.62 b | 8.52±0.26 a |
| N2 | 224.47±14.98 b | 182.81±8.13 b | 40.94±1.55 a | 90.10±1.97 c | 24.98±1.18 b | 8.20±0.48 b | |
| N3 | 198.83±23.40 c | 191.36±12.95 a | 37.80±2.42 b | 92.07±1.50 b | 25.56±0.46 b | 7.76±0.59 c |
| 品种 Cultivar | 处理 Treatment | 单位面积穗数 Panicles per unit area(×104/hm2) | 每穗颖花数 Spikelets per panicle | 单位面积颖花数 Spikelets per unit area (×107/hm2) | 结实率 Seed-setting rate (%) | 千粒重 1000-grain weight (g) | 产量 Grain yield (t/hm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 沈稻9号 | R1 | 312.48±60.60 b | 127.79±10.53 b | 40.30±9.71 b | 86.44±3.45 b | 23.48±0.62 b | 7.40±1.51 c |
| Shendao 9 | R2 | 355.03±74.22 a | 121.41±10.05 c | 43.35±10.40 a | 86.36±3.89 b | 23.67±0.38 ab | 8.23±1.76 a |
| R3 | 298.79±50.99 c | 130.92±10.43 a | 39.42±8.57 c | 88.43±2.81 a | 23.84±0.36 a | 7.71±1.64 b | |
| 沈稻 505 | R1 | 369.62±88.76 c | 109.53±11.36 c | 41.02±11.88 c | 75.17±6.24 b | 25.03±0.68 b | 7.12±1.94 c |
| Shendao 505 | R2 | 426.11±99.27 a | 113.53±11.70 b | 49.00±13.66 a | 71.91±7.77 c | 24.89±0.93 b | 8.22±2.05 a |
| R3 | 389.39±78.16 b | 117.98±11.88 a | 46.47±11.75 b | 78.36±5.29 a | 25.34±0.52 a | 7.57±2.04 b | |
| 沈稻 527 | R1 | 202.02±34.19 b | 174.79±11.74 b | 35.46±6.93 b | 90.63±5.03 b | 26.08±1.77 a | 7.54±1.36 b |
| Shendao 527 | R2 | 223.57±34.72 a | 165.00±14.10 c | 37.16±7.57 a | 91.86±3.52 a | 25.99±1.39 a | 7.76±1.45 a |
| R3 | 185.08±35.75 c | 188.29±14.49 a | 35.02±7.71 b | 90.60±3.46 b | 26.16±1.32 a | 6.88±1.48 c |
表5 行距配置对水稻产量及其构成因素的影响
Table 5. Effects of row spacing on yield and its components
| 品种 Cultivar | 处理 Treatment | 单位面积穗数 Panicles per unit area(×104/hm2) | 每穗颖花数 Spikelets per panicle | 单位面积颖花数 Spikelets per unit area (×107/hm2) | 结实率 Seed-setting rate (%) | 千粒重 1000-grain weight (g) | 产量 Grain yield (t/hm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 沈稻9号 | R1 | 312.48±60.60 b | 127.79±10.53 b | 40.30±9.71 b | 86.44±3.45 b | 23.48±0.62 b | 7.40±1.51 c |
| Shendao 9 | R2 | 355.03±74.22 a | 121.41±10.05 c | 43.35±10.40 a | 86.36±3.89 b | 23.67±0.38 ab | 8.23±1.76 a |
| R3 | 298.79±50.99 c | 130.92±10.43 a | 39.42±8.57 c | 88.43±2.81 a | 23.84±0.36 a | 7.71±1.64 b | |
| 沈稻 505 | R1 | 369.62±88.76 c | 109.53±11.36 c | 41.02±11.88 c | 75.17±6.24 b | 25.03±0.68 b | 7.12±1.94 c |
| Shendao 505 | R2 | 426.11±99.27 a | 113.53±11.70 b | 49.00±13.66 a | 71.91±7.77 c | 24.89±0.93 b | 8.22±2.05 a |
| R3 | 389.39±78.16 b | 117.98±11.88 a | 46.47±11.75 b | 78.36±5.29 a | 25.34±0.52 a | 7.57±2.04 b | |
| 沈稻 527 | R1 | 202.02±34.19 b | 174.79±11.74 b | 35.46±6.93 b | 90.63±5.03 b | 26.08±1.77 a | 7.54±1.36 b |
| Shendao 527 | R2 | 223.57±34.72 a | 165.00±14.10 c | 37.16±7.57 a | 91.86±3.52 a | 25.99±1.39 a | 7.76±1.45 a |
| R3 | 185.08±35.75 c | 188.29±14.49 a | 35.02±7.71 b | 90.60±3.46 b | 26.16±1.32 a | 6.88±1.48 c |
| 品种 Cultivar | 处理 Treatment | 单位面积穗数 Panicles per unit area(×104/hm2) | 每穗颖花数 Spikelets per panicle | 单位面积颖花数 Spikelets per unit area (×107/hm2) | 结实率 Seed-setting rate (%) | 千粒重 1000-grain weight(g) | 产量 Grain yield (t/hm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 沈稻9号 | N0R1 | 212.43±3.07 i | 115.87±2.83 fg | 24.61±0.40 h | 91.43±1.37 a | 24.13±0.28 a | 4.90±0.29 g |
| Shendao 9 | N0R2 | 234.14±3.52 h | 112.58±1.35 gh | 26.36±0.61 g | 91.08±0.91 ab | 24.05±0.18 a | 5.43±0.27 f |
| N0R3 | 215.04±1.66 i | 118.42±1.14 ef | 25.47±0.28 gh | 91.74±1.66 a | 24.12±0.15 a | 5.01±0.16 g | |
| N1R1 | 351.69±7.48 d | 121.81±3.14 e | 42.84±1.58 ef | 83.71±0.81 ef | 23.15±0.53 bc | 8.31±0.23 de | |
| N1R2 | 415.95±3.32 a | 111.95±1.57 h | 46.56±0.56 c | 82.80±1.15 f | 23.40±0.13 abc | 8.58±0.06 cd | |
| N1R3 | 330.09±2.61 f | 127.20±1.46 d | 41.98±0.27 f | 85.06±1.36 def | 23.55±0.26 abc | 8.53±0.11 cd | |
| N2R1 | 345.17±3.01 e | 131.70±2.30 c | 45.46±0.81 cd | 84.97±1.95 def | 23.00±0.62 c | 8.12±0.11 e | |
| N2R2 | 390.25±2.21 b | 127.16±1.68 d | 49.62±0.54 ab | 82.84±0.70 f | 23.57±0.58 abc | 9.07±0.07 b | |
| N2R3 | 333.73±1.50 f | 132.37±0.73 c | 44.17±0.19 de | 87.43±1.33 cd | 23.77±0.10 ab | 8.49±0.09 cd | |
| N3R1 | 340.63±2.71 e | 141.80±1.71 b | 48.30±0.87 b | 85.65±2.53 de | 23.62±0.46 abc | 8.25±0.13 de | |
| N3R2 | 379.79±1.25 c | 133.96±3.39 c | 50.87±1.13 a | 88.71±1.09 bc | 23.65±0.28 abc | 9.85±0.34 a | |
| N3R3 | 316.29±3.01 g | 145.67±3.03 a | 46.08±1.07 c | 89.49±0.66 abc | 23.92±0.58 a | 8.81±0.06 bc | |
| 沈稻 505 | N0R1 | 231.82±0.00 f | 96.02±1.52 g | 22.26±0.35 g | 85.17±1.09 ab | 25.87±0.45 a | 4.01±0.11 h |
| Shendao 505 | N0R2 | 272.22±20.30 e | 97.73±1.19 fg | 26.59±1.67 f | 84.49±0.18 b | 26.00±0.48 a | 4.86±0.05 g |
| N0R3 | 268.18±24.24 e | 101.50±0.98 f | 27.21±2.34 f | 86.75±0.04 a | 26.00±0.40 a | 4.21±0.36 h | |
| N1R1 | 462.64±2.96 b | 108.91±0.88 e | 50.39±0.65 d | 70.77±1.11 ef | 24.15±0.15 c | 8.55±0.18 de | |
| N1R2 | 525.25±14.00 a | 110.71±1.53 e | 58.16±2.18 a | 65.90±1.39 h | 23.62±0.08 d | 8.92±0.18 c | |
| N1R3 | 464.38±10.30 b | 115.32±2.74 d | 53.56±2.08 bc | 73.23±0.29 d | 24.92±0.50 b | 8.83±0.19 cd | |
| N2R1 | 390.37±15.63 d | 107.14±3.09 e | 41.79±0.52 e | 71.85±2.09 de | 24.92±0.10 b | 7.46±0.13 f | |
| N2R2 | 470.61±0.00 b | 117.47±0.85 d | 55.28±0.40 abc | 67.91±1.66 gh | 24.83±0.25 b | 9.32±0.12 b | |
| N2R3 | 424.24±20.20 c | 123.69±4.10 c | 52.45±2.26 cd | 76.59±0.63 c | 25.17±0.18 b | 8.46±0.22 e | |
| N3R1 | 393.64±10.10 d | 126.05±2.24 bc | 49.63±1.97 d | 72.90±1.95 de | 25.17±0.13 b | 8.48±0.21 e | |
| N3R2 | 436.36±14.24 c | 128.23±3.90 ab | 55.96±2.77 ab | 69.33±1.33 fg | 25.10±0.38 b | 9.77±0.21 a | |
| N3R3 | 400.77±2.48 d | 131.41±3.71 a | 52.66±1.18 cd | 76.86±0.62 c | 25.28±0.25 b | 8.78±0.17 cde | |
| 沈稻527 | N0R1 | 154.88±11.66 e | 158.47±1.75 f | 24.53±1.61 d | 95.79±0.73 a | 28.52±0.28 a | 5.33±0.09 f |
| Shendao 527 | N0R2 | 169.70±4.24 d | 145.46±4.40 g | 24.67±0.26 d | 96.38±1.37 a | 28.03±0.32 a | 5.36±0.12 f |
| N0R3 | 134.41±5.89 f | 169.66±1.19 e | 22.81±1.03 d | 95.60±0.33 a | 28.13±0.60 a | 4.58±0.27 g | |
| N1R1 | 242.42±0.00 a | 171.03±2.11 e | 41.46±0.51 ab | 83.30±1.32 f | 25.53±0.19 bc | 8.60±0.25 abc | |
| N1R2 | 255.89±11.66 a | 161.06±3.64 f | 41.19±1.04 ab | 87.20±0.40 e | 25.62±0.79 bc | 8.66±0.04 a | |
| N1R3 | 215.49±6.01 b | 184.13±3.05 cd | 39.68±1.58 b | 87.61±2.03 e | 25.45±0.93 bc | 8.31±0.31 c | |
| N2R1 | 215.49±11.66 b | 183.29±3.20 cd | 39.47±1.58 b | 90.02±1.07 cd | 24.38±1.80 c | 8.35±0.12 bc | |
| N2R2 | 242.42±0.00 a | 173.60±3.15 e | 42.08±0.76 a | 92.02±1.62 bc | 24.70±0.66 bc | 8.64±0.16 ab | |
| N2R3 | 215.49±6.01 b | 191.55±1.37 b | 41.28±1.10 ab | 88.25±1.01 de | 25.85±0.35 b | 7.60±0.08 d | |
| N3R1 | 195.29±5.84 c | 186.38±3.15 c | 36.39±0.70 c | 93.42±1.73 b | 25.88±0.29 b | 7.87±0.05 d | |
| N3R2 | 226.26±3.32 b | 179.88±3.35 d | 40.69±0.25 ab | 91.85±0.33 bc | 25.60±0.58 bc | 8.38±0.02 abc | |
| N3R3 | 174.95±11.9 d | 207.81±2.90 a | 36.33±2.01 c | 90.95±1.07 c | 25.20±0.28 bc | 7.03±0.03 e |
表6 施氮方式与行距配置互作对水稻产量及产量构成因素的影响
Table 6. Effects of N application pattern and row spacing on rice yield and its components
| 品种 Cultivar | 处理 Treatment | 单位面积穗数 Panicles per unit area(×104/hm2) | 每穗颖花数 Spikelets per panicle | 单位面积颖花数 Spikelets per unit area (×107/hm2) | 结实率 Seed-setting rate (%) | 千粒重 1000-grain weight(g) | 产量 Grain yield (t/hm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 沈稻9号 | N0R1 | 212.43±3.07 i | 115.87±2.83 fg | 24.61±0.40 h | 91.43±1.37 a | 24.13±0.28 a | 4.90±0.29 g |
| Shendao 9 | N0R2 | 234.14±3.52 h | 112.58±1.35 gh | 26.36±0.61 g | 91.08±0.91 ab | 24.05±0.18 a | 5.43±0.27 f |
| N0R3 | 215.04±1.66 i | 118.42±1.14 ef | 25.47±0.28 gh | 91.74±1.66 a | 24.12±0.15 a | 5.01±0.16 g | |
| N1R1 | 351.69±7.48 d | 121.81±3.14 e | 42.84±1.58 ef | 83.71±0.81 ef | 23.15±0.53 bc | 8.31±0.23 de | |
| N1R2 | 415.95±3.32 a | 111.95±1.57 h | 46.56±0.56 c | 82.80±1.15 f | 23.40±0.13 abc | 8.58±0.06 cd | |
| N1R3 | 330.09±2.61 f | 127.20±1.46 d | 41.98±0.27 f | 85.06±1.36 def | 23.55±0.26 abc | 8.53±0.11 cd | |
| N2R1 | 345.17±3.01 e | 131.70±2.30 c | 45.46±0.81 cd | 84.97±1.95 def | 23.00±0.62 c | 8.12±0.11 e | |
| N2R2 | 390.25±2.21 b | 127.16±1.68 d | 49.62±0.54 ab | 82.84±0.70 f | 23.57±0.58 abc | 9.07±0.07 b | |
| N2R3 | 333.73±1.50 f | 132.37±0.73 c | 44.17±0.19 de | 87.43±1.33 cd | 23.77±0.10 ab | 8.49±0.09 cd | |
| N3R1 | 340.63±2.71 e | 141.80±1.71 b | 48.30±0.87 b | 85.65±2.53 de | 23.62±0.46 abc | 8.25±0.13 de | |
| N3R2 | 379.79±1.25 c | 133.96±3.39 c | 50.87±1.13 a | 88.71±1.09 bc | 23.65±0.28 abc | 9.85±0.34 a | |
| N3R3 | 316.29±3.01 g | 145.67±3.03 a | 46.08±1.07 c | 89.49±0.66 abc | 23.92±0.58 a | 8.81±0.06 bc | |
| 沈稻 505 | N0R1 | 231.82±0.00 f | 96.02±1.52 g | 22.26±0.35 g | 85.17±1.09 ab | 25.87±0.45 a | 4.01±0.11 h |
| Shendao 505 | N0R2 | 272.22±20.30 e | 97.73±1.19 fg | 26.59±1.67 f | 84.49±0.18 b | 26.00±0.48 a | 4.86±0.05 g |
| N0R3 | 268.18±24.24 e | 101.50±0.98 f | 27.21±2.34 f | 86.75±0.04 a | 26.00±0.40 a | 4.21±0.36 h | |
| N1R1 | 462.64±2.96 b | 108.91±0.88 e | 50.39±0.65 d | 70.77±1.11 ef | 24.15±0.15 c | 8.55±0.18 de | |
| N1R2 | 525.25±14.00 a | 110.71±1.53 e | 58.16±2.18 a | 65.90±1.39 h | 23.62±0.08 d | 8.92±0.18 c | |
| N1R3 | 464.38±10.30 b | 115.32±2.74 d | 53.56±2.08 bc | 73.23±0.29 d | 24.92±0.50 b | 8.83±0.19 cd | |
| N2R1 | 390.37±15.63 d | 107.14±3.09 e | 41.79±0.52 e | 71.85±2.09 de | 24.92±0.10 b | 7.46±0.13 f | |
| N2R2 | 470.61±0.00 b | 117.47±0.85 d | 55.28±0.40 abc | 67.91±1.66 gh | 24.83±0.25 b | 9.32±0.12 b | |
| N2R3 | 424.24±20.20 c | 123.69±4.10 c | 52.45±2.26 cd | 76.59±0.63 c | 25.17±0.18 b | 8.46±0.22 e | |
| N3R1 | 393.64±10.10 d | 126.05±2.24 bc | 49.63±1.97 d | 72.90±1.95 de | 25.17±0.13 b | 8.48±0.21 e | |
| N3R2 | 436.36±14.24 c | 128.23±3.90 ab | 55.96±2.77 ab | 69.33±1.33 fg | 25.10±0.38 b | 9.77±0.21 a | |
| N3R3 | 400.77±2.48 d | 131.41±3.71 a | 52.66±1.18 cd | 76.86±0.62 c | 25.28±0.25 b | 8.78±0.17 cde | |
| 沈稻527 | N0R1 | 154.88±11.66 e | 158.47±1.75 f | 24.53±1.61 d | 95.79±0.73 a | 28.52±0.28 a | 5.33±0.09 f |
| Shendao 527 | N0R2 | 169.70±4.24 d | 145.46±4.40 g | 24.67±0.26 d | 96.38±1.37 a | 28.03±0.32 a | 5.36±0.12 f |
| N0R3 | 134.41±5.89 f | 169.66±1.19 e | 22.81±1.03 d | 95.60±0.33 a | 28.13±0.60 a | 4.58±0.27 g | |
| N1R1 | 242.42±0.00 a | 171.03±2.11 e | 41.46±0.51 ab | 83.30±1.32 f | 25.53±0.19 bc | 8.60±0.25 abc | |
| N1R2 | 255.89±11.66 a | 161.06±3.64 f | 41.19±1.04 ab | 87.20±0.40 e | 25.62±0.79 bc | 8.66±0.04 a | |
| N1R3 | 215.49±6.01 b | 184.13±3.05 cd | 39.68±1.58 b | 87.61±2.03 e | 25.45±0.93 bc | 8.31±0.31 c | |
| N2R1 | 215.49±11.66 b | 183.29±3.20 cd | 39.47±1.58 b | 90.02±1.07 cd | 24.38±1.80 c | 8.35±0.12 bc | |
| N2R2 | 242.42±0.00 a | 173.60±3.15 e | 42.08±0.76 a | 92.02±1.62 bc | 24.70±0.66 bc | 8.64±0.16 ab | |
| N2R3 | 215.49±6.01 b | 191.55±1.37 b | 41.28±1.10 ab | 88.25±1.01 de | 25.85±0.35 b | 7.60±0.08 d | |
| N3R1 | 195.29±5.84 c | 186.38±3.15 c | 36.39±0.70 c | 93.42±1.73 b | 25.88±0.29 b | 7.87±0.05 d | |
| N3R2 | 226.26±3.32 b | 179.88±3.35 d | 40.69±0.25 ab | 91.85±0.33 bc | 25.60±0.58 bc | 8.38±0.02 abc | |
| N3R3 | 174.95±11.9 d | 207.81±2.90 a | 36.33±2.01 c | 90.95±1.07 c | 25.20±0.28 bc | 7.03±0.03 e |
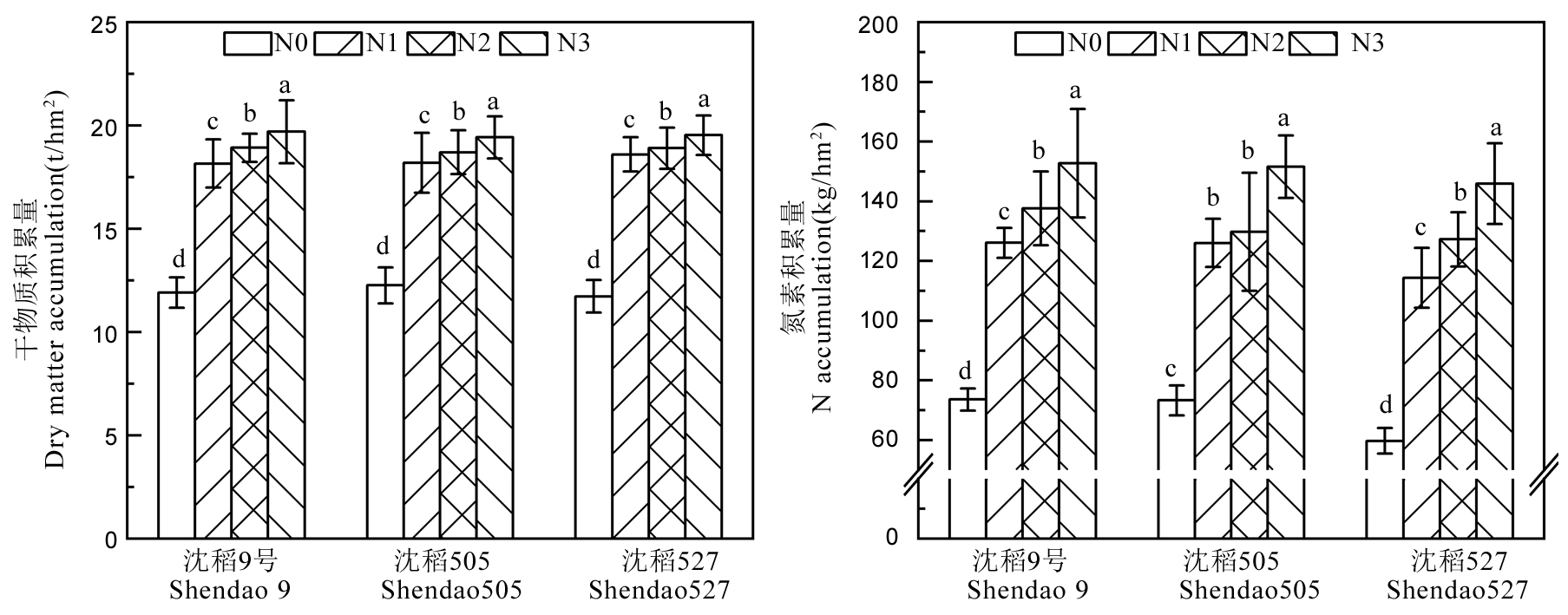
图1 施氮方式对水稻干物质积累量与氮素积累量的影响 图中数据为平均值±标准差(n=3);柱上不同字母表示处理间在0.05水平上差异显著(Duncan新复极差法)。下同。
Fig. 1. Effects of N application pattern on rice dry matter accumulation and N accumulation Values are mean ± SD(n=3); Different letters above the bars indicate significant difference among treatments at the 0.05 level (Duncan's new multiple range test). The same below.
| 品种 Cultivar | 处理 Treatment | 氮肥偏生产力 PFPN (kg/kg) | 氮肥农学利用率 AEN (kg/kg) | 氮肥回收利用率 REN(%) | 土壤氮依存率 CRSN(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 沈稻9号 | N1 | 36.05±0.77 c | 14.29±0.92 c | 22.32±1.99 c | 58.44±2.82 a |
| Shendao 9 | N2 | 42.80±2.10 b | 17.24±1.16 b | 31.97±6.04 b | 53.87±4.99 b |
| N3 | 44.83±3.62 a | 19.27±2.41 a | 39.56±9.08 a | 48.74±5.65 c | |
| 沈稻505 | N1 | 37.30±0.98 c | 18.75±1.29 c | 22.44±1.84 c | 58.17±1.93 a |
| Shendao 505 | N2 | 42.07±4.08 b | 20.26±2.32 b | 28.21±8.10 b | 57.18±5.36 a |
| N3 | 45.05±3.04 a | 23.25±1.19 a | 39.15±3.97 a | 48.43±2.74 b | |
| 沈稻527 | N1 | 36.27±1.09 c | 14.61±1.07 b | 23.23±2.70 c | 52.36±1.99 a |
| Shendao 527 | N2 | 41.00±2.39 a | 15.54±0.86 a | 33.75±2.99 b | 47.00±2.02 b |
| N3 | 38.81±2.95 b | 13.35±1.50 c | 43.05±5.55 a | 41.12±2.90 c |
表7 施氮方式对水稻氮素利用率的影响
Table 7. Effects of N application pattern on rice N use efficiency
| 品种 Cultivar | 处理 Treatment | 氮肥偏生产力 PFPN (kg/kg) | 氮肥农学利用率 AEN (kg/kg) | 氮肥回收利用率 REN(%) | 土壤氮依存率 CRSN(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 沈稻9号 | N1 | 36.05±0.77 c | 14.29±0.92 c | 22.32±1.99 c | 58.44±2.82 a |
| Shendao 9 | N2 | 42.80±2.10 b | 17.24±1.16 b | 31.97±6.04 b | 53.87±4.99 b |
| N3 | 44.83±3.62 a | 19.27±2.41 a | 39.56±9.08 a | 48.74±5.65 c | |
| 沈稻505 | N1 | 37.30±0.98 c | 18.75±1.29 c | 22.44±1.84 c | 58.17±1.93 a |
| Shendao 505 | N2 | 42.07±4.08 b | 20.26±2.32 b | 28.21±8.10 b | 57.18±5.36 a |
| N3 | 45.05±3.04 a | 23.25±1.19 a | 39.15±3.97 a | 48.43±2.74 b | |
| 沈稻527 | N1 | 36.27±1.09 c | 14.61±1.07 b | 23.23±2.70 c | 52.36±1.99 a |
| Shendao 527 | N2 | 41.00±2.39 a | 15.54±0.86 a | 33.75±2.99 b | 47.00±2.02 b |
| N3 | 38.81±2.95 b | 13.35±1.50 c | 43.05±5.55 a | 41.12±2.90 c |
| 品种 Cultivar | 处理 Treatment | 氮肥偏生产力 PFPN (kg/kg) | 氮肥农学利用率 AEN (kg/kg) | 氮肥回收利用率 REN(%) | 土壤氮依存率 CRSN(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 沈稻9号 | R1 | 39.07±2.88 c | 15.76±1.24 c | 30.63±6.48 b | 53.61±3.75 b |
| Shendao 9 | R2 | 43.68±5.71 a | 17.89±3.84 a | 37.51±12.06 a | 49.15±6.39 c |
| R3 | 40.94±3.55 b | 17.14±1.77 b | 25.71±4.95 c | 58.29±3.97 a | |
| 沈稻505 | R1 | 38.69±2.89 c | 19.66±2.24 b | 28.46±8.98 b | 54.44±6.52 ab |
| Shendao 505 | R2 | 44.46±5.03 a | 21.34±3.26 a | 33.44±9.21 a | 52.73±4.87 b |
| R3 | 41.27±2.97 b | 21.26±1.61 a | 27.89±7.77 b | 56.61±5.46 a | |
| 沈稻527 | R1 | 39.24±2.32 b | 13.90±1.14 b | 32.20±7.42 a | 47.06±4.03a |
| Shendao 527 | R2 | 40.65±2.95 a | 15.18±1.09 a | 35.22±9.85 a | 47.42±4.97a |
| R3 | 36.19±1.54 c | 14.42±1.85 b | 32.60±10.49 a | 46.01±6.74a |
表8 行距配置对水稻氮素利用率的影响
Table 8. Effects of row spacing on rice N use efficiency
| 品种 Cultivar | 处理 Treatment | 氮肥偏生产力 PFPN (kg/kg) | 氮肥农学利用率 AEN (kg/kg) | 氮肥回收利用率 REN(%) | 土壤氮依存率 CRSN(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 沈稻9号 | R1 | 39.07±2.88 c | 15.76±1.24 c | 30.63±6.48 b | 53.61±3.75 b |
| Shendao 9 | R2 | 43.68±5.71 a | 17.89±3.84 a | 37.51±12.06 a | 49.15±6.39 c |
| R3 | 40.94±3.55 b | 17.14±1.77 b | 25.71±4.95 c | 58.29±3.97 a | |
| 沈稻505 | R1 | 38.69±2.89 c | 19.66±2.24 b | 28.46±8.98 b | 54.44±6.52 ab |
| Shendao 505 | R2 | 44.46±5.03 a | 21.34±3.26 a | 33.44±9.21 a | 52.73±4.87 b |
| R3 | 41.27±2.97 b | 21.26±1.61 a | 27.89±7.77 b | 56.61±5.46 a | |
| 沈稻527 | R1 | 39.24±2.32 b | 13.90±1.14 b | 32.20±7.42 a | 47.06±4.03a |
| Shendao 527 | R2 | 40.65±2.95 a | 15.18±1.09 a | 35.22±9.85 a | 47.42±4.97a |
| R3 | 36.19±1.54 c | 14.42±1.85 b | 32.60±10.49 a | 46.01±6.74a |
| 品种 Cultivar | 处理 Treatment | 氮肥偏生产力 PFPN (kg/kg) | 氮肥农学利用率 AEN (kg/kg) | 氮肥回收利用率 REN(%) | 土壤氮依存率 CRSN(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 沈稻9 | N1R1 | 35.34±0.97 f | 14.47±0.73 gh | 22.64±1.41 e | 57.92±1.18 abc |
| Shendao 9 | N1R2 | 36.50±0.27 f | 13.40±0.87 h | 23.89±1.26 e | 56.50±0.47 bcd |
| N1R3 | 36.31±0.46 f | 15.00±0.23 fg | 20.43±1.76 e | 60.90±3.88 a | |
| N2R1 | 40.61±0.55 e | 16.09±0.94 ef | 32.26±2.11 cd | 53.17±0.48 de | |
| N2R2 | 45.33±0.36 b | 18.19±0.99 bc | 38.34±3.21 b | 48.78±1.45 f | |
| N2R3 | 42.47±0.46 d | 17.44±0.36 cd | 25.29±1.81 e | 59.65±2.73 ab | |
| N3R1 | 41.25±0.64 de | 16.73±0.84 de | 36.99±1.09 bc | 49.73±1.95 ef | |
| N3R2 | 49.23±1.68 a | 22.08±0.73 a | 50.29±6.73 a | 42.17±2.62 g | |
| N3R3 | 44.03±0.30 c | 18.99±0.52 b | 31.40±0.91 d | 54.33±1.99 cd | |
| 沈稻505 | N1R1 | 36.38±0.75 e | 19.34±0.29 d | 21.55±1.38 b | 57.68±3.05 a |
| Shendao 505 | N1R2 | 37.95±0.76 e | 17.25±0.53 e | 24.10±2.19 b | 57.40±1.08 a |
| N1R3 | 37.58±0.82 e | 19.66±1.09 d | 21.67±0.80 b | 59.44±0.86 a | |
| N2R1 | 37.31±0.63 e | 17.28±0.12 e | 23.74±3.08 b | 59.36±1.34 a | |
| N2R2 | 46.59±0.61 b | 22.27±0.34 bc | 36.96±8.95 a | 51.26±5.48 b | |
| N2R3 | 42.30±1.08 d | 21.24±0.76 c | 23.92±0.81 b | 60.92±1.58 a | |
| N3R1 | 42.39±1.07 d | 22.36±0.56 bc | 40.10±1.76 a | 46.27±2.64 c | |
| N3R2 | 48.84±1.07 a | 24.51±0.81 a | 39.25±7.35 a | 49.52±3.51 bc | |
| N3R3 | 43.92±0.86 c | 22.87±0.93 b | 38.08±1.70 a | 49.49±0.49 bc | |
| 沈稻527 | N1R1 | 36.61±1.08 e | 13.91±0.85 c | 24.82±1.32 d | 50.30±0.86 bc |
| Shendao 527 | N1R2 | 36.84±0.15 e | 14.03±0.40 c | 24.66±1.67 d | 52.80±0.72 ab |
| N1R3 | 35.38±1.30 f | 15.89±0.23 ab | 20.21±2.06 d | 53.99±1.98 a | |
| N2R1 | 41.77±0.62 b | 15.10±0.18 bc | 31.71±4.20 c | 48.32±2.80 cd | |
| N2R2 | 43.22±0.82 a | 16.42±0.23 a | 35.99±0.97 bc | 47.35±0.69 cd | |
| N2R3 | 38.02±0.42 d | 15.12±1.08 bc | 33.54±1.81 bc | 45.34±1.01 de | |
| N3R1 | 39.35±0.25 c | 12.68±0.20 d | 40.07±5.11 ab | 42.55±2.76 e | |
| N3R2 | 41.90±0.10 b | 15.10±0.52 bc | 45.02±8.49 a | 42.12±3.49 e | |
| N3R3 | 35.17±0.14 f | 12.27±1.27 d | 44.05±2.05 a | 38.70±0.62 f |
表9 施氮方式与行距配置对水稻氮素利用率的影响
Table 9. Effects of N application pattern and row spacing on rice N use efficiency
| 品种 Cultivar | 处理 Treatment | 氮肥偏生产力 PFPN (kg/kg) | 氮肥农学利用率 AEN (kg/kg) | 氮肥回收利用率 REN(%) | 土壤氮依存率 CRSN(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 沈稻9 | N1R1 | 35.34±0.97 f | 14.47±0.73 gh | 22.64±1.41 e | 57.92±1.18 abc |
| Shendao 9 | N1R2 | 36.50±0.27 f | 13.40±0.87 h | 23.89±1.26 e | 56.50±0.47 bcd |
| N1R3 | 36.31±0.46 f | 15.00±0.23 fg | 20.43±1.76 e | 60.90±3.88 a | |
| N2R1 | 40.61±0.55 e | 16.09±0.94 ef | 32.26±2.11 cd | 53.17±0.48 de | |
| N2R2 | 45.33±0.36 b | 18.19±0.99 bc | 38.34±3.21 b | 48.78±1.45 f | |
| N2R3 | 42.47±0.46 d | 17.44±0.36 cd | 25.29±1.81 e | 59.65±2.73 ab | |
| N3R1 | 41.25±0.64 de | 16.73±0.84 de | 36.99±1.09 bc | 49.73±1.95 ef | |
| N3R2 | 49.23±1.68 a | 22.08±0.73 a | 50.29±6.73 a | 42.17±2.62 g | |
| N3R3 | 44.03±0.30 c | 18.99±0.52 b | 31.40±0.91 d | 54.33±1.99 cd | |
| 沈稻505 | N1R1 | 36.38±0.75 e | 19.34±0.29 d | 21.55±1.38 b | 57.68±3.05 a |
| Shendao 505 | N1R2 | 37.95±0.76 e | 17.25±0.53 e | 24.10±2.19 b | 57.40±1.08 a |
| N1R3 | 37.58±0.82 e | 19.66±1.09 d | 21.67±0.80 b | 59.44±0.86 a | |
| N2R1 | 37.31±0.63 e | 17.28±0.12 e | 23.74±3.08 b | 59.36±1.34 a | |
| N2R2 | 46.59±0.61 b | 22.27±0.34 bc | 36.96±8.95 a | 51.26±5.48 b | |
| N2R3 | 42.30±1.08 d | 21.24±0.76 c | 23.92±0.81 b | 60.92±1.58 a | |
| N3R1 | 42.39±1.07 d | 22.36±0.56 bc | 40.10±1.76 a | 46.27±2.64 c | |
| N3R2 | 48.84±1.07 a | 24.51±0.81 a | 39.25±7.35 a | 49.52±3.51 bc | |
| N3R3 | 43.92±0.86 c | 22.87±0.93 b | 38.08±1.70 a | 49.49±0.49 bc | |
| 沈稻527 | N1R1 | 36.61±1.08 e | 13.91±0.85 c | 24.82±1.32 d | 50.30±0.86 bc |
| Shendao 527 | N1R2 | 36.84±0.15 e | 14.03±0.40 c | 24.66±1.67 d | 52.80±0.72 ab |
| N1R3 | 35.38±1.30 f | 15.89±0.23 ab | 20.21±2.06 d | 53.99±1.98 a | |
| N2R1 | 41.77±0.62 b | 15.10±0.18 bc | 31.71±4.20 c | 48.32±2.80 cd | |
| N2R2 | 43.22±0.82 a | 16.42±0.23 a | 35.99±0.97 bc | 47.35±0.69 cd | |
| N2R3 | 38.02±0.42 d | 15.12±1.08 bc | 33.54±1.81 bc | 45.34±1.01 de | |
| N3R1 | 39.35±0.25 c | 12.68±0.20 d | 40.07±5.11 ab | 42.55±2.76 e | |
| N3R2 | 41.90±0.10 b | 15.10±0.52 bc | 45.02±8.49 a | 42.12±3.49 e | |
| N3R3 | 35.17±0.14 f | 12.27±1.27 d | 44.05±2.05 a | 38.70±0.62 f |
| [1] | FAO. FAO Statistical Yearbook 2021: World Food and Agriculture[M]. Rome: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, 2021. |
| [2] | Hameed F, Xu J Z, Rahim S F, Wei Q, Rehman K A, Liao Q. Optimizing nitrogen options for improving nitrogen use efficiency of rice under different water regimes[J]. Agronomy, 2019, 9(1): 39. |
| [3] | Cai S Y, Zhao X, Pittelkow C M, Fan M S, Zhang X, Yan X Y. Optimal nitrogen rate strategy for sustainable rice production in China[J]. Nature, 2023(615): 73-79. |
| [4] | 程前, 李广浩, 陆卫平, 陆大雷. 增密减氮提高夏玉米产量和氮素利用效率[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2020, 26(6): 1035-1046. |
| Cheng Q, Li G H, Lu W P, Lu D L. Increasing planting density and decreasing nitrogen rate increase yield and nitrogen use efficiency of summer maize[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2020, 26(6): 1035-1046. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | 彭少兵, 黄见良, 钟旭华, 杨建昌, 王光火, 邹应斌, 张福锁, 朱庆森, Buresh R, Witt C. 提高中国稻田氮肥利用率的研究策略[J]. 中国农业科学, 2002, 35(9): 1095-1103. |
| Peng S B, Huang J L, Zhong X H, Yang J C, Wang G H, Zou Y B, Zhang F S, Zhu Q S, Buresh R, Witt C. Research strategy in improving fertilizer-nitrogen use efficiency of irrigated rice in China[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2002, 35(9): 1095-1103. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 徐冉, 陈松, 徐春梅, 刘元辉, 章秀福, 王丹英, 褚光. 施氮量对籼粳杂交稻甬优1540产量和氮肥利用效率的影响及其机制[J]. 作物学报, 2023, 49(6): 1630-1642. |
| Xu R, Chen S, Xu C M, Liu Y H, Zhang X F, Wang D Y, Chu G. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer rates on grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency of japonica-indica hybrid rice cultivar Yongyou 1540 and its physiological bases[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2023, 49(6): 1630-1642. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 王艳, 易军, 高继平, 张丽娜, 杨继芬, 赵艳泽, 辛威, 甄晓溪, 张文忠. 不同叶龄蘖、穗氮肥组合对粳稻产量及氮素利用的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2020, 46(1): 102-116. |
| Wang Y, Yi J, Gao J P, Zhang L N, Yang J F, Zhao Y Z, Xin W, Zhen X X, Zhang W Z. Effects of precision leaf age fertilization on yield and nitrogen utilization of japonica rice[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2020, 46(1): 102-116. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | 易秉怀, 袁帅, 苏雨婷, 覃诗棋, 陈平平, 易镇邪. 氮肥运筹对湘南双季稻氮素吸收转运与利用及产量的影响[J]. 杂交水稻, 2023, 38(1): 112-121. |
| Yi B H, Yuan S, Su Y T, Qin S Q, Chen P P, Yi Z X. Effects of nitrogen management on uptake, transport and utilization of nitrogen and yield of double-cropping rice in Southern Hunan[J]. Hybrid Rice, 2023, 38(1): 112-121. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 张洪程, 吴桂成, 吴文革, 戴其根, 霍中洋, 许轲, 高辉, 魏海燕, 黄幸福, 龚金龙. 水稻“精苗稳前、控蘖优中、大穗强后”超高产定量化栽培模式[J]. 中国农业科学, 2010, 43(13): 2645-2660. |
| Zhang H C, Wu G C, Wu W G, Dai Q G, Huo Z Y, Xu K, Gao H, Wei H Y, Huang X F, Gong J L. The SOI model of quantitative cultivation of super-high yielding rice[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2010, 43(13): 2645-2660. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | 凌启鸿, 张洪程, 戴其根, 丁艳锋, 凌励, 苏祖芳, 徐茂, 阙金华, 王绍华. 水稻精确定量施氮研究[J]. 中国农业科学, 2005, (12): 2457-2467. |
| Ling Q H, Zhang H C, Dai Q G, Ding Y F, Ling L, Su Z F, Xu M, Que J H, Wang S H. Study on precise and quantitative n application in rice[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2005, (12): 2457-2467. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | Peng S B, Buresh R J, Huang J L, Yang J C, Zou Y B, Zhong X H, Wang G H, Zhang F S. Strategies for overcoming low agronomic nitrogen use efficiency in irrigated rice systems in China[J]. Field Crops Research, 2006, 96: 37-47. |
| [12] | 朱德峰, 张玉屏, 陈惠哲, 向镜, 张义凯. 中国水稻高产栽培技术创新与实践[J]. 中国农业科学, 2015, 48(17): 3404-3414. |
| Zhu D F, Zhang Y P, Chen H Z, Xiang J, Zhang Y K. Innovation and practice of high-yield rice cultivation technology in China[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2015, 48(17): 3404-3414. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | Hou W F, Khan M R, Zhang J L, Lu J W, Ren T, Cong R H, Li X K. Nitrogen rate and plant density interaction enhances radiation interception, yield and nitrogen use efficiency of mechanically transplanted rice[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 2019, 269: 183-192. |
| [14] | 赵海新, 杨丽敏, 陈书强, 姜树坤, 黄晓群, 单莉莉, 潘国君. 行距对两个不同类型水稻品种冠层结构与产量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2011, 25(5): 488-494. |
| Zhao H X, Yang L M, Chen S Q, Jiang S Q, Huang X Q, Shan L L, Pan G J. Effects of row-spacing on canopy structure and yield in different type rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2011, 25(5): 488-494. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 汤亮, 朱相成, 曹梦莹, 曹卫星, 朱艳. 水稻冠层光截获、光能利用与产量的关系[J]. 应用生态学报, 2012, 23(5): 1269-1276. |
| Tang L, Zhu X C, Cao M Y, Cao W X, Zhu Y. Relationships of rice canopy PAR interception and light use efficiency to grain yield.[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2012, 23(5): 1269-1276. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 董立强, 杨铁鑫, 李睿, 商文奇, 马亮, 李跃东, 隋国民. 株行距配置对超高产田水稻产量及根系形态生理特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37 (4): 392-404. |
| Dong L Q, Yang T X, Li R, Shang W Q, Ma L, Li Y D, Sui G M. Effect of plant-row spacing on rice yield and root morphological and physiological characteristics in super high yield field[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2023, 37(4): 392-404. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | 尹彩侠, 刘志全, 孔丽丽, 李前, 张磊, 侯云鹏, 郝彩环. 减氮增密提高寒地水稻产量与氮素吸收利用[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2022, 39(6): 1124-1132. |
| Yin C X, Liu Z Q, Kong L L, Li Q, Zhang L, Hou Y P, Hao C X. Reducing nitrogen and increasing rice transplanting density in a cold region of China can improve rice yield, nitrogen absorption, and nitrogen utilization[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2022, 39(6): 1124-1132. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | 刘红江, 张辉, 盛婧, 张岳芳, 郭智, 郑建初, 陈留根. 基肥侧位深施条件下穗肥减量对水稻氮素利用率的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2021, 40(5): 1366-1374. |
| Liu H J, Zhang H, Sheng J, Zhang Y F, Guo Z, Zheng J C, Chen L G. Effects of panicle fertilizer reduction on nitrogen use efficiency of rice under side deep application of basal fertilizer[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2021, 40(5): 1366-1374. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | Guo X H, Lan Y C, Xu L Q, Yin D W, Li H Y, Qian Y D, Zheng G P, Lv Y D. Effects of nitrogen application rate and hill density on rice yield and nitrogen utilization in sodic saline-alkaline paddy fields[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2021, 20(2): 540-553. |
| [20] | 王术, 王铁良. 水稻安全生产技术指南[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2012. |
| Wang S, Wang T L. Technical guide for safe production of rice[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2012. (in Chinese) | |
| [21] | 刘俊峰, 李漪濛, 梁超, 周婵婵, 王术, 贾宝艳, 黄元财, 王岩, 王韵. 施氮方式与行距配置对水稻冠层结构及产量的影响[J]. 华北农学报, 2022, 37(1): 77-85. |
| Liu J F, Li Y M, Li C, Zhou C C, Wang S, Jia B Y, Huang Y C, Wang Y, Wang Y. Effect of nitrogen application pattern and row spacing on canopy structure and yield of rice[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2022, 37(1): 77-85. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | 范立慧, 徐珊珊, 侯朋福, 薛利红, 李刚华, 丁艳锋, 杨林章. 不同地力下基蘖肥运筹比例对水稻产量及氮肥吸收利用的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2016, 49(10): 1872-1884. |
| Fan L H, Xu S S, Hou P F, Xue L H, Li G H, Ding Y F, Yang L Z. Effect of different ratios of basal to tiller nitrogen on rice yield and nitrogen utilization under different soil fertility[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2016, 49(10): 1872-1884. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 付景, 尹海庆, 王亚, 杨文博, 张珍, 白涛, 王越涛, 王付华, 王生轩. 不同追氮模式对河南沿黄稻区粳稻根系生长和产量的影响[J]. 作物杂志, 2021, (2): 77-86. |
| Fu J, Yin H Q, Wang Y, Yang W B, Zhang Z, Bai T, Wang Y T, Wang F H, Wang S X. Effects of nitrogen topdressing models on root growth and grain yield of japonica rice in the region along Yellow River of Henan Province[J]. Crops, 2021, (2): 77-86. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | 黄恒, 姜恒鑫, 刘光明, 袁嘉琦, 汪源, 赵灿, 王维领, 霍中洋, 许轲, 戴其根, 张洪程, 李德剑, 刘国林. 侧深施氮对水稻产量及氮素吸收利用的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2021, 47(11): 2232-2249. |
| Huang H, Jiang H X, Liu G M, Yuan J Q, Wang Y, Zhao C, Wang W L, Huo Z Y, Xu K, Dai Q G, Zhang H C, Li D J, Liu G L. Effects of side deep placement of nitrogen on rice yield and nitrogen use efficiency[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2021, 47(11): 2232-2249. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | 郭九信, 孔亚丽, 谢凯柳, 李东海, 冯绪猛, 凌宁, 王敏, 郭世伟. 养分管理对直播稻产量和氮肥利用率的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2016, 42(7): 1016-1025. |
| Guo J X, Kong Y L, Xie K L, Li D H, Feng X M, Ling N, Wang M, Guo S W. Effects of nutrient management on yield and nitrogen use efficiency of direct seeding rice[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2016, 42(7): 1016-1025. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | 朱从桦, 孙永健, 杨志远, 贾现文, 徐徽, 马均. 晒田强度和穗期氮素运筹对不同氮效率水稻根系、叶片生长及产量的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2017, 31(6): 196-203+256. |
| Zhu C H, Sun Y J, Yang Z Y, Jia X W, Xu W, Ma J. Effect of paddy field drainage and panicle nitrogen fertilizer management on rice root system, leaf growth and yield with different nitrogen efficiency[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2017, 31(6): 196-203+256. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | 夏琼梅, 胡家权, 董林波, 钱文娟, 李贵勇, 龙瑞平, 朱海平, 杨从党. 水稻前控后促施氮技术增产机理研究[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2022, (5): 18-26. |
| Xia Q M, Hu J Q, Dong L B, Qian W J, Li G Y, Yong R P, Zhu H P, Yang C D. Mechanism of reduced amount with late application of nitrogen on increasing yield of japonica rice[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2022, (5): 18-26. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | 李小朋, 王术, 黄元财, 贾宝艳, 王岩, 曾群云. 株行距配置对齐穗期粳稻冠层结构及产量的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2015, 26 (11): 3329-3336. |
| Li X P, Wang S, Huang Y C, Jia B Y, Wang Y, Zeng Q Y. Effects of spacing on the yields and canopy structure of japonica rice at full heading stage[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2015, 26 (11): 3329-3336. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | 衣政伟, 王晓兵. 长江下游地区不同水稻品种两种行距下的生长发育和产量及品质特征[J]. 安徽农业大学学报, 2022, 49(1): 20-26. |
| Yi Z W, Wang X B. The characteristics of growth, yield and quality of different rice varieties under two kinds of row spacings in the lower reaches of the Yangtze River[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural University, 2022, 49(1): 20-26. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | 杨海超, 夏可, 陈杰, 苗淑杰, 乔云发. 行株距配置对水稻冠层光合特性及产量的影响[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2023, 51(21): 93-98. |
| Yang H C, Xia K, Chen J, Miao S J, Qiao Y F. Impacts of spaces in and between rows on canopy photosynthetic characteristics and yield of rice[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 51(21): 93-98. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | 李思平, 曾路生, 吴立鹏, 张玉晓, 解军蕊, 丁效东. 氮肥水平与栽植密度对植稻土壤养分含量变化与氮肥利用效率的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(1): 69-79. |
| Li S P, Zeng L S, Wu L P, Zhang Y X, Xie J R, Ding S D. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer level and planting density on changes in soil nutrient contents and nitrogen use efficiency in rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2020, 34(1): 69-79. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [32] | 周江明, 赵琳, 董越勇, 徐进, 边武英, 毛杨仓, 章秀福. 氮肥和栽植密度对水稻产量及氮肥利用率的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2010, 16(2): 274-281. |
| Zhou J M, Zhao L, Dong Y Y, Xu J, Bian W Y, Mao Y C, Zhang X F. Nitrogen and transplanting density interactions on the rice yield and N use rate[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2010, 16(2): 274-281. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [33] | 辽宁省统计局, 国际统计局辽宁调查总队. 辽宁省2023年国民经济和社会发展统计公报[R/OL]. https://tjj.ln.gov.cn/uiFramework/js/pdfjs/web/viewer.html?file=/tjj/attachDir/2024/03/2024032815431143514.pdf(2024-03-28). |
| [34] | 杨振玉. 北方杂交粳稻育种研究[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社, 1999. |
| Yang Z Y. Research on Northern hybrid japonica rice breeding[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, 1999. (in Chinese) | |
| [35] | 杨守仁, 张龙步, 王进民. 水稻理想株形育种的理论和方法初论[J]. 中国农业科学, 1984(3): 6-13. |
| Yang S R, Zhang L B, Wang J M. The theory and method of ideal plant morphology in rice breeding[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 1984(3): 6-13. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [36] | 杨守仁, 张龙步, 陈温福, 徐正进, 王进民. 水稻超高产育种的理论和方法[J]. 中国水稻科学, 1996(2): 115-120. |
| Yang S R, Zhang L B, Chen W F, Xu Z J, Wang J M. Theories and methods of rice breeding for maximun yield[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 1996(2): 115-120. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [37] | 马兴全, 侯守贵, 陈盈, 于广星. 辽宁省水稻栽培技术发展与展望[J]. 中国稻米, 2014, 20(1): 36-40. |
| Ma X Q, Huo S G, Chen Y, Yu G X. Development and prospects of rice cultivation techniques in Liaoning Province[J]. China Rice, 2014, 20(1): 36-40. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 冯向前, 王爱冬, 洪卫源, 李子秋, 覃金华, 詹丽钏, 陈里鹏, 张运波, 王丹英, 陈松. 基于低空无人机遥感的水稻产量估测方法研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(6): 604-616. |
| [2] | 曹玉东, 吴朋浩, 戴志刚, 王贵兵, 何帅, 巩细民, 李小坤. 侧深施肥对水稻产量、养分吸收及经济效益的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(6): 695-708. |
| [3] | 姚姝, 陈涛, 赵春芳, 周丽慧, 赵凌, 梁文化, 赫磊, 路凯, 朱镇, 赵庆勇, 管菊, 王才林, 张亚东. 江淮稻区不同类型粳稻品种外观及蒸煮食味品质特征比较[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(6): 709-718. |
| [4] | 蒋鹏, 张林, 周兴兵, 郭晓艺, 朱永川, 刘茂, 郭长春, 熊洪, 徐富贤. 冬水田轻简化栽培杂交稻蓄留再生稻产量形成特点[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 544-554. |
| [5] | 熊家欢, 张义凯, 向镜, 陈惠哲, 徐一成, 王亚梁, 王志刚, 姚坚, 张玉屏. 覆膜稻田施用炭基肥对水稻产量及氮素利用的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 567-576. |
| [6] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [7] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [8] | 丁正权, 潘月云, 施扬, 黄海祥. 基于基因芯片的嘉禾系列长粒优质食味粳稻综合评价与比较[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 397-408. |
| [9] | 吕宙, 易秉怀, 陈平平, 周文新, 唐文帮, 易镇邪. 施氮量与移栽密度对小粒型杂交水稻产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| [10] | 赵艺婷, 谢可冉, 高逖, 崔克辉. 水稻分蘖期干旱锻炼对幼穗分化期高温下穗发育和产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 277-289. |
| [11] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [12] | 彭显龙, 董强, 张辰, 李鹏飞, 李博琳, 刘智蕾, 于彩莲. 不同土壤条件下秸秆还田量对土壤还原性物质及水稻生长的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 198-210. |
| [13] | 景秀, 周苗, 王晶, 王岩, 王旺, 王开, 郭保卫, 胡雅杰, 邢志鹏, 许轲, 张洪程. 穗分化末期-灌浆初期干旱胁迫对优质食味粳稻根系形态和叶片光合特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(1): 33-47. |
| [14] | 朱旺, 张翔, 耿孝宇, 张哲, 陈英龙, 韦还和, 戴其根, 许轲, 朱广龙, 周桂生, 孟天瑶. 盐-旱复合胁迫下水稻根系的形态和生理特征及其与产量形成的关系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(6): 617-627. |
| [15] | 邹宇傲, 吴启侠, 周乾顺, 朱建强, 晏军. 孕穗期杂交中稻对淹涝胁迫的响应[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(6): 642-656. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||