
中国水稻科学 ›› 2024, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (2): 172-184.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2024.230902
郑广杰, 叶昌, 朱均林, 陶怡, 肖德顺, 徐亚楠, 褚光, 徐春梅, 王丹英( )
)
收稿日期:2023-09-04
修回日期:2024-01-05
出版日期:2024-03-10
发布日期:2024-03-14
通讯作者:
* email:wangdanying@caas.cn
基金资助:
ZHENG Guangjie, YE Chang, ZHU Junlin, TAO Yi, XIAO Deshun, XU Yanan, CHU Guang, XU Chunmei, WANG Danying( )
)
Received:2023-09-04
Revised:2024-01-05
Online:2024-03-10
Published:2024-03-14
Contact:
* email:wangdanying@caas.cn
摘要:
【目的】为了探明淹水逆境下水稻种子向胚芽供应葡萄糖能力的品种间差异及其与胚芽存活的关系,从而解析水稻芽苗期耐淹机理。【方法】以4个淹水耐性不同的品种为试验材料,设置长期淹水和湿润播种(对照)两个处理,分析种子和胚芽组织的非结构性碳水化合物含量,种子α-淀粉酶活性、胚芽抗氧化酶活性随时间的动态变化,及其与胚芽存活率的相关性。【结果】淹水胁迫下,淹水敏感材料中嘉8号(S1)和中嘉早17(S2)胚芽的葡萄糖含量、SOD、POD酶比蛋白活性在淹水72h后显著下降,表型上表现为胚芽生长停滞并出现死亡症状;而耐淹材料日本晴(T1)、耘两优玖48(T2)的胚芽中葡萄糖含量、SOD、POD的酶比蛋白活性在淹水96 h内保持稳定,胚芽持续伸长。对种子α-淀粉酶活性的分析表明,虽然短期淹水(0-48 h)能够增强所有4个材料的种子α-淀粉酶活性,但随淹水时间的延长(72-96h),仅耐淹的T1、T2保持α-淀粉酶高活性,其种子内的淀粉含量持续下降而葡萄糖含量不断增加,胚芽葡萄糖含量相对稳定;而淹水敏感材料S1、S2种子内的α-淀粉酶活性则分别在淹水72 h和48 h后下降,种子内淀粉含量相对稳定,但种子和胚芽的葡萄糖含量大幅度下降。相关分析表明,胚芽的存活率与胚芽和种子的葡萄糖含量、胚芽的过氧化物酶(POD)活性极显著正相关,但与种子淀粉含量极显著负相关。【结论】淹水胁迫下胚芽组织消耗大量的葡萄糖维持其生理代谢平衡,种子向胚芽供应葡萄糖的能力直接关系到其存活,种子α-淀粉酶活性变化对胚芽葡萄糖的供应有决定性作用,是种子在淹水条件下存活出苗的关键。
郑广杰, 叶昌, 朱均林, 陶怡, 肖德顺, 徐亚楠, 褚光, 徐春梅, 王丹英. 淹水胁迫下水稻种子和胚芽葡萄糖供应差异与胚芽存活的关系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 172-184.
ZHENG Guangjie, YE Chang, ZHU Junlin, TAO Yi, XIAO Deshun, XU Yanan, CHU Guang, XU Chunmei, WANG Danying. Relationship Between Embryo Survival and Glucose Supply of Rice Seed and Embryo Under Flooding Stress[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(2): 172-184.
| 材料 Material | 胚芽长度比值Germ length ratio(T/CK,%) | 胚芽干物质量比值Germ dry weight ratio(T/CK,%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HAS24 | HAS48 | HAS72 | HAS96 | HAS24 | HAS48 | HAS72 | HAS96 | ||
| T1 | 235.3±8.7 a | 169.8±2.7 b | 128.6±2.6 c | 112.0±4.1 d | 70.5±3.3 a | 67.9±2.3 a | 59.2±2.6 b | 50.7±1.6 c | |
| T2 | 230.8±8.6 a | 142.8±4.8 b | 97.9±3.5 c | 81.4±6.9 d | 66.9±4.8 a | 55.0±2.7 a | 44.7±1.0 b | 42.4±1.4 c | |
| S1 | 210.5±9.4 a | 177.1±7.9 b | 103.8±8.7 c | 71.2±4.4 d | 65.4±4.3 a | 59.4±4.0 b | 45.2±5.3 c | 35.2±1.1 c | |
| S2 | 163.3±11.6 a | 95.5±8.5 b | 62.0±3.0 c | 43.1±3.3 d | 50.3±4.8 a | 32.7±1.8 b | 20.4±0.6 c | 16.8±0.5 c | |
表1 淹水胁迫对不同水稻材料胚芽长度和干物质量的影响
Table 1. Effects of flooding stress on the embryo length and dry matter accumulation in different rice materials
| 材料 Material | 胚芽长度比值Germ length ratio(T/CK,%) | 胚芽干物质量比值Germ dry weight ratio(T/CK,%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HAS24 | HAS48 | HAS72 | HAS96 | HAS24 | HAS48 | HAS72 | HAS96 | ||
| T1 | 235.3±8.7 a | 169.8±2.7 b | 128.6±2.6 c | 112.0±4.1 d | 70.5±3.3 a | 67.9±2.3 a | 59.2±2.6 b | 50.7±1.6 c | |
| T2 | 230.8±8.6 a | 142.8±4.8 b | 97.9±3.5 c | 81.4±6.9 d | 66.9±4.8 a | 55.0±2.7 a | 44.7±1.0 b | 42.4±1.4 c | |
| S1 | 210.5±9.4 a | 177.1±7.9 b | 103.8±8.7 c | 71.2±4.4 d | 65.4±4.3 a | 59.4±4.0 b | 45.2±5.3 c | 35.2±1.1 c | |
| S2 | 163.3±11.6 a | 95.5±8.5 b | 62.0±3.0 c | 43.1±3.3 d | 50.3±4.8 a | 32.7±1.8 b | 20.4±0.6 c | 16.8±0.5 c | |
| 材料 Material | 存活率Survival rate(%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HAS24 | HAS48 | HAS72 | HAS96 | ||
| T1 | 100±0 a | 100±0 a | 100±0 a | 100±0 a | |
| T2 | 100±0 a | 100±0 a | 100±0 a | 100±0 a | |
| S1 | 100±0 a | 100±0 a | 93±2 b | 86±4 c | |
| S2 | 100±0 a | 99±1 a | 87±3 c | 78±6 d | |
表2 淹水胁迫对不同水稻材料胚芽存活的影响
Table 2. Effect of flooding on embryo survival of different rice materials
| 材料 Material | 存活率Survival rate(%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HAS24 | HAS48 | HAS72 | HAS96 | ||
| T1 | 100±0 a | 100±0 a | 100±0 a | 100±0 a | |
| T2 | 100±0 a | 100±0 a | 100±0 a | 100±0 a | |
| S1 | 100±0 a | 100±0 a | 93±2 b | 86±4 c | |
| S2 | 100±0 a | 99±1 a | 87±3 c | 78±6 d | |
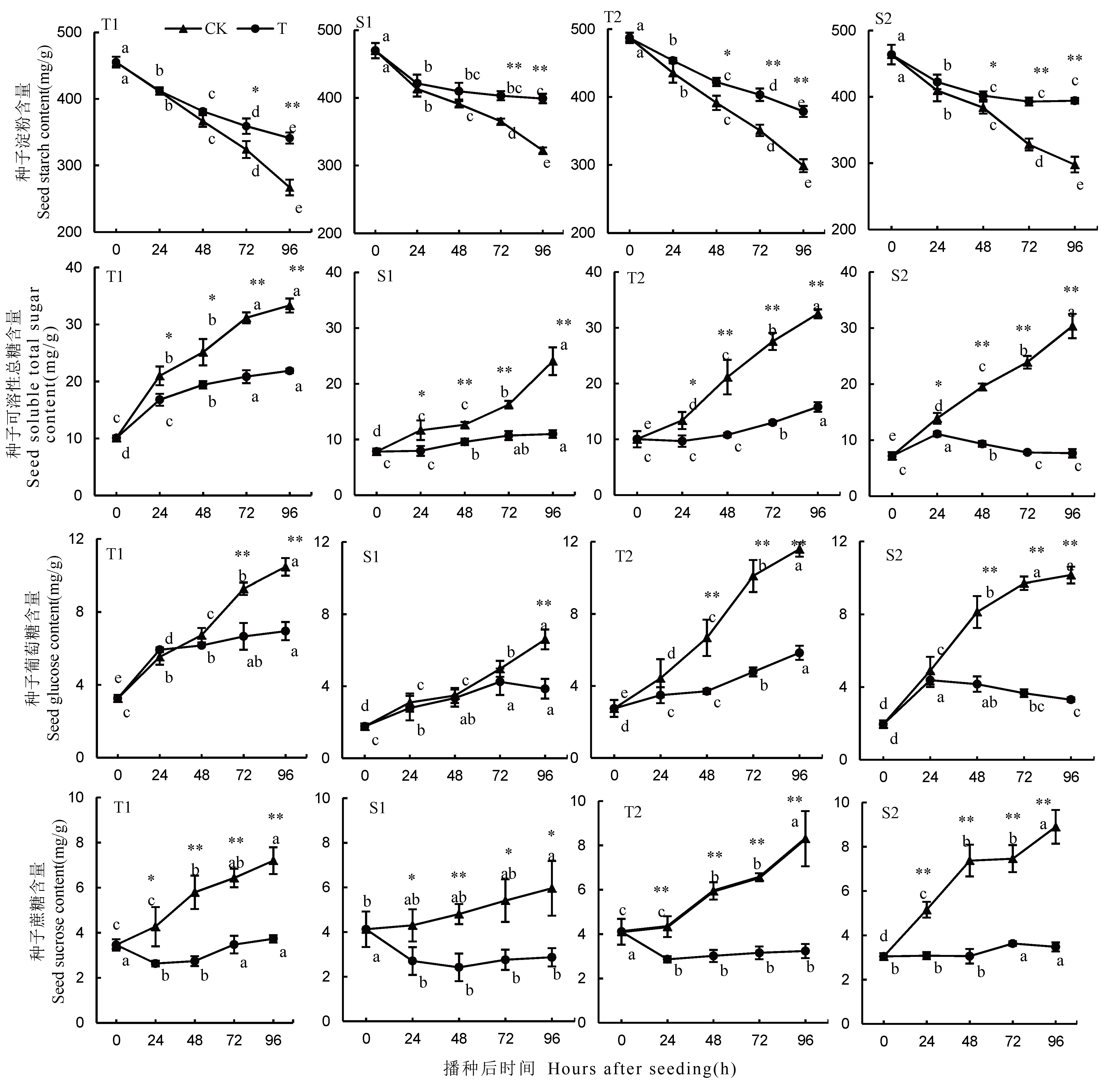
图2 不同处理下4份材料种子淀粉、可溶性总糖、葡萄糖和蔗糖的含量变化及差异 数值表示平均值±标准差(n=3),不同的小写字母表示同一品种、同一处理、不同处理时间的数据在0.05水平上存在显著性差异。*和**表示同一品种、同一时间、不同处理的数据在0.05和0.01水平上存在显著性差异。下同。
Fig. 2. Changes and differences in seed starch, total soluble sugar, glucose and sucrose contents of 4 rice materials under different treatments Data are means ± SD (n = 3). Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences at the 0.05 level for data from the same variety under the same treatment for different treatment time. * and ** indicate that data from the same variety under different treatments for the same treatment time are significantly different at the 0.05 and 0.01 levels. The same below.
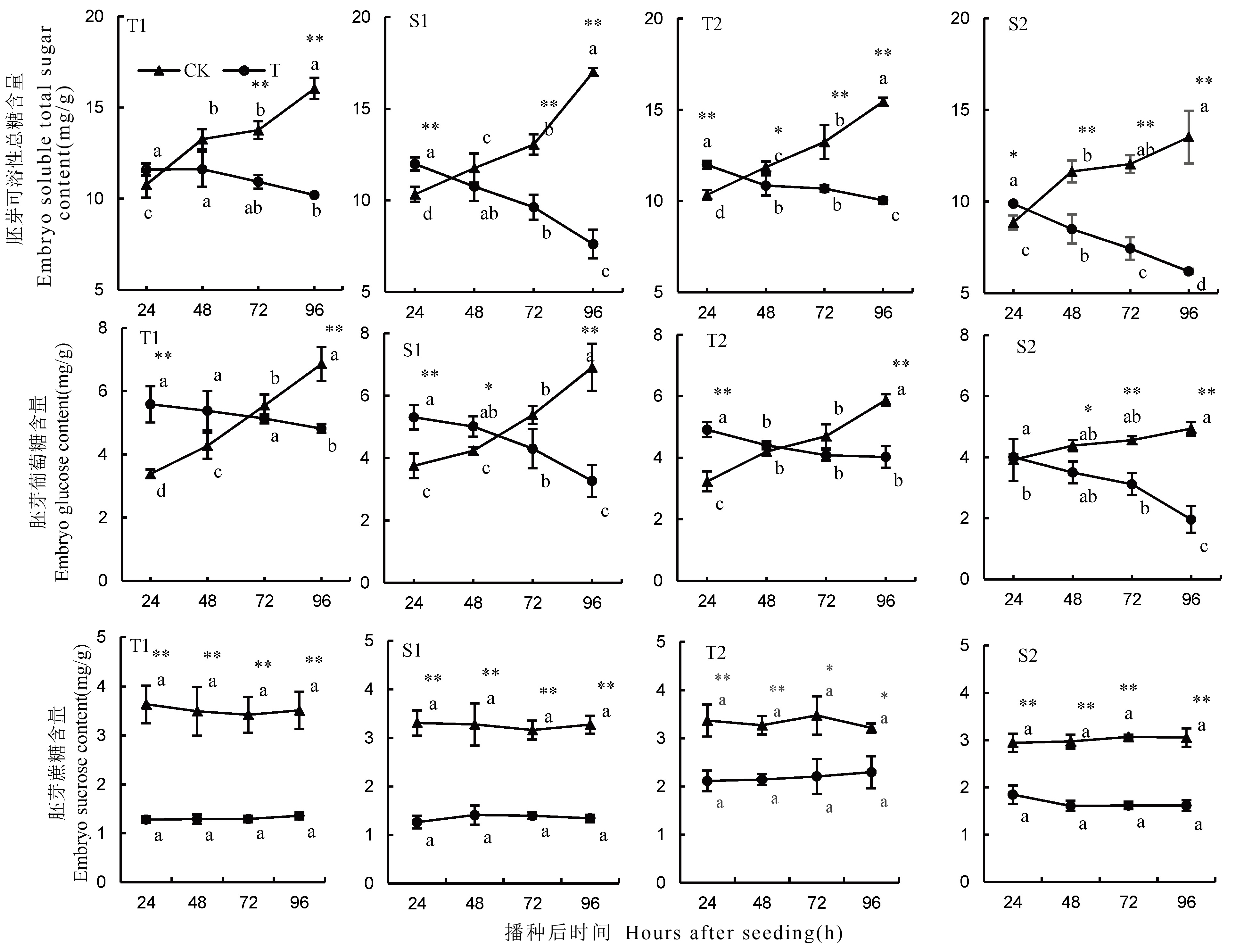
图3 不同处理下4份材料胚芽可溶性总糖、葡萄糖和蔗糖含量变化及差异
Fig. 3. Changes and differences in total soluble sugar, glucose and sucrose contents of germ of four rice materials under different treatments

图5 不同处理下4份材料胚芽可溶性蛋白含量和抗氧化酶比蛋白活性变化及差异
Fig. 5. Changes and differences in soluble protein content and specific protein activities of antioxidant enzymes in the germs of 4 rice materials under different treatments
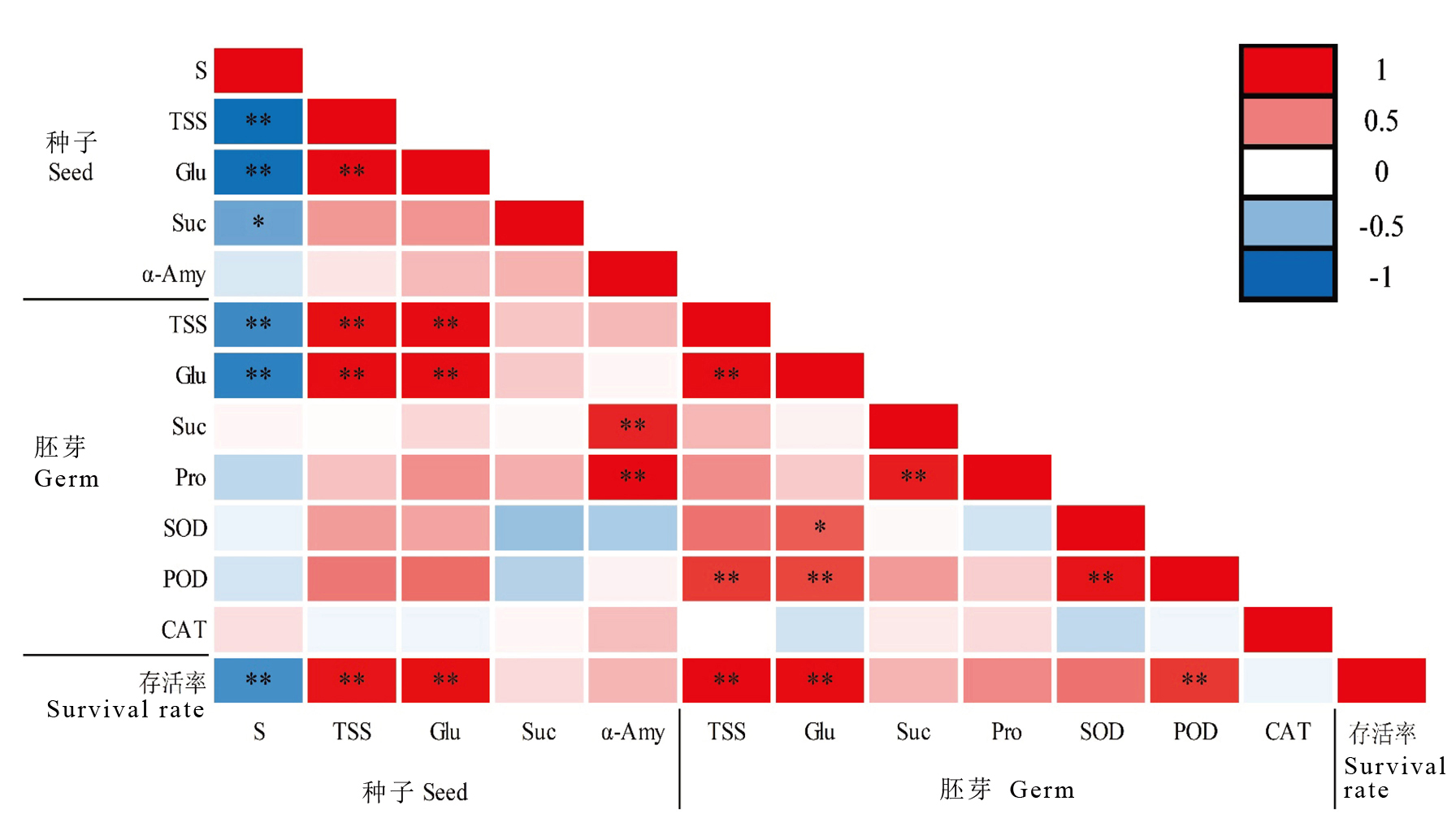
图6 淹水条件下4份材料存活率与生理指标间的相关性 S:淀粉含量;TSS:可溶性糖含量;Glu:葡萄糖含量;Suc:蔗糖含量;α-Amy:α-淀粉酶活性;Pro:可溶性蛋白质含量;SOD:超氧化物歧化酶活性;POD:过氧化物酶活性;CAT过氧化氢酶活性。*表示在0.05水平上存在显著性差异,**表示在0.01水平上存在显著差异。
Fig. 6. Correlation between survival and physiological indicators in 4 rice materials under flooding treatment S, Seed starch; TSS, Total soluble sugars; Glu, Glucose; Suc, Sucrose; α-Amy, α- amylase; Pro, Protein; SOD, Superoxide dismutase; POD, Peroxidase; CAT, Catalase. * indicate significant difference at the 0.05 level, ** indicate significant difference at the 0.01 level.
| [1] | 罗锡文, 王在满, 曾山, 臧英, 杨文武, 张明华. 水稻机械化直播技术研究进展[J]. 华南农业大学学报, 2019, 40(5): 1-13. |
| Luo X W, Wang Z M, Zeng S, Zang Y, Yang W W, Zhang M H. Recent advances in mechanized direct seeding technology for rice[J]. Journal of South China Agricultural University, 2019, 40(5): 1-13. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | 赵正洪, 戴力, 黄见良, 潘晓华, 游艾青, 赵全志, 陈光辉, 周政, 胡文彬, 纪龙. 长江中游稻区水稻产业发展现状、问题与建议[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(6): 553-564. |
| Zhao Z H, Dai L, Huang J L, Pan X H, You A Q, Zhao Q Z, Chen G H, Zhou Z, Hu W B, Ji L. Status, problems and solutions in rice industry development in the middle reaches of the Yangtze river[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2019, 33(6): 553-564. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 宋超. 水稻种子人工老化过程中抗氧化系统的变化[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2012. |
| Song C. Changes of detoxifying systems of rice seed after artificial aging[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 陈璋琦, 王蓓, 何雨, 黄婷婷, 王洋. 浙江省主栽水稻品种种子活力鉴定与评价[J]. 种子, 2019, 38(2): 7-11. |
| Chen Z Q, Wang B, He Y, Huang T T, Wang Y. Identification and evaluation of seed vigor of main cultured rice varieties in Zhejiang province[J]. Seed, 2019, 38(2): 7-11. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | Julia B S, Takeshi F, Daniel J G, Michael J H, Seung C L, Francesco L, Pierdomenico P, Laurentius A C J V, Joost T D. Making sense of low oxygen sensing[J]. Ternds in Plant Science, 2012, 17(3): 129-138. |
| [6] | 熊怀阳, 李阳生. 水稻的耐淹性状及其Sub1基因[J]. 遗传, 2010, 32(9): 886-892. |
| Xiong H Y, Li Y S. Submergence tolerance and Sub1 locus in rice[J]. Hereditas, 2010, 32(9): 886-892. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 熊怀阳, 阳菁, 安保光, 李阳生. 水稻适应淹水胁迫的分子机理及品种改良[J]. 武汉大学学报: 理学版, 2013, 59(1): 17-23. |
| Xiong H Y, Yang Q, An B G, Li Y S. Molecular mechanism of rice adaptation and improvement strategies to submergence tress[J]. Journal of Wuhan University: Natural Science Edition, 2013, 59(1): 17-23. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | 王忠,. 植物生理学. 2版[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2008. |
| Wang Z. Plant Physiology 2nd edn.[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Press, 2008. (in Chinese) | |
| [9] | Das A, Uchimiya H. Oxygen stress and adaptation of a semi-aquatic plant: Rice (Oryza sativa)[J]. Journal of Plant Research, 2002, 115: 315-320. |
| [10] | Yu S M, Lo S F, Ho T H D. Source-sink communication: regulated by hormone, nutrient, and stress cross-signaling[J]. Trends in Plant Science, 2015, 20(12): 844-857. |
| [11] | 盛毅迪. GABA对大麦及水稻糊粉细胞α-淀粉酶生成的诱导效应[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2015. |
| Sheng Y D. Induction of aleurone α-amylase production by GABA in seeds of barley and rice[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 王忠, 顾蕴洁, 李卫芳, 黄山, 李克武. 水稻糊粉层的形成及其在萌发过程中的变化[J]. 扬州大学学报: 自然科学版, 1998(1):19-24. |
| Wang Z, Gu Y J, Li W F, Huang S, Li K W. Formation of rice aleurone layer and its changes during germination[J]. Journal of Yangzhou University: Natural Science Edition, 1998(1): 19-24. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | Ismail A M, Ella E S, Vergara G V, Mackill D J. Mechanisms associated with tolerance to flooding during germination and early seedling growth in rice (Oryza sativa)[J]. Annals of Botany, 2009, 103(2): 197-209. |
| [14] | 张明方, 李志凌. 高等植物中与蔗糖代谢相关的酶[J]. 植物生理学通讯, 2002(3): 289-295. |
| Zhang M F, Li Z L. Sucrose-metabolizing enzymes in higher plants[J]. Plant Physiology Communications, 2002(3): 289-295. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 李孟珠. 水稻蔗糖转运蛋白(OsSUTs)参与蔗糖转运的功能分析[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2020. |
| Li M Z. Function analysis of sucrose transporters (OsSUTs) in sucrose transport in rice[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 柴静, 张会, 姚丽丽, 俞嘉宁. 蔗糖合酶在植物生长发育中的作用研究[J]. 生命科学, 2012, 24(1): 81-88. |
| Chai J, Zhang H, Yao L L, Yu J N. The function of sucrose synthase in plant growth and development[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Life Sciences, 2012, 24(1): 81-88. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | 何艺涛, 王广亚, 范春芬, 夏涛, 彭良才, 丰胜求. 植物蔗糖合酶研究进展[J]. 植物生理学报, 2020, 56(6): 1165-1176. |
| He Y T, Wang G Y, Fan C F, Xia T, Peng L C, Feng S Q. Research progress of sucrose synthase in plants[J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 2020, 56(6): 1165-1176. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | 郭月. 乙烯和赤霉素参与调节完全淹水诱导的水稻根表锰膜形成[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2014. |
| Guo Y. Involvement of ethylene and gibberellins in regulating the complete submergence-induced formation of manganese plaque on root surface in rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | Tatsuro H, Scofield G N, Tomio T. An expression analysis profile for the entire sucrose synthase gene family in rice[J]. Plant Science, 2008, 174: 534-543. |
| [20] | 王广亚. 水稻蔗糖合酶基因功能研究及甘蔗属植物生物质降解转化[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2016. |
| Wang G Y. Functional analysis of sucrose synthase genes in rice and biomass digestibility of genus saccharum[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | 刘聪, 董腊嫒, 林建中, 刘选明. 逆境胁迫下植物体内活性氧代谢及调控机理研究进展[J]. 生命科学研究, 2019, 23(3): 253-258. |
| Liu C, Dong L Y, Lin J Z, Liu X M. Research advances on regulation mechanism of reactive oxygen species metabolism under stresses[J]. Life Science Research, 2019, 23(3): 253-258. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | 赵晶晶, 詹万龙, 周浓. 非生物胁迫下植物体内活性氧和丙酮醛代谢的研究进展[J]. 南方农业学报, 2022, 53(8): 2099-2113. |
| Zhao J J, Zhan W L, Zhou N. Research progress on the metabolisms of reactive oxygen species and methylglyoxal in plants under abiotic stresses[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2022, 53(8): 2099-2113. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 陈东, 李强, 彭彦, 吴天昊, 张秀丽, 董家瑜, 毛毕刚, 赵炳然. 淹水胁迫下褪黑素浸种对水稻幼苗生长的影响[J]. 华北农学报, 2019, 34(3): 129-136. |
| Chen D, Li Q, Peng Y, Wu T H, Zhang X L, Dong J Y, Mao B G, Zhao B R. Effect of melatonin on rice seedling growth under submergence stress[J]. North China Journal of Agriculture, 2019, 34(3): 129-136. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | 侯名语. 水稻低温、低氧发芽力的QTL定位[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2003. |
| Hou M Y. The QTL mapping of low temperature germinability and anoxia germinability in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2003. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | Sen L T H, Ranamukhaarachchi S L, Zoebisch M A, Hasan M M, Meskuntavon W. Effects of early-inundation and water depth on weed competition and grain yield of rice in the Central Plains of Thailand[J]. Conference on International Agricultural Research for Development, 2002: 9-11. |
| [26] | 张志良, 瞿伟菁, 李小方. 植物生理学实验指导. 4版[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2009. |
| Zhang Z L, Qu W J, Li X F. Plant Physiology Lab Instruction. 4th edn[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2009. (in Chinese) | |
| [27] | 张彩霞. 高温影响水稻韧皮部同化物转运及代谢的作用机制及调控[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2018. |
| Zhang C X. The mechanism and regulation underlying the inhibition on the assimilates transport and metabolism in phloem of rice caused by heat stress[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | 王孝平, 邢树礼. 考马斯亮蓝法测定蛋白含量的研究[J]. 天津化工, 2009, 23(3): 40-42. |
| Wang X P, Xing S L. Determination of protein quantitation using the method of coomassie brilliant blue[J]. Tianjin Chemical Industry, 2009, 23(3): 40-42. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | Giannopolitis C N, Ries S K. Superoxide dismutases: I. Occurrence in higher plants[J]. Plant Physiology, 1977, 59(2): 309-314. |
| [30] | Maehly A C, Chance B. The assay of catalases and peroxidases[J]. Methods of Biochemical Analysis, 1954(1): 357-424. |
| [31] | Zhang C X, Fu G F, Yang X Q, Yang Y J, Zhao X, Chen T T, Zhang X F, Jin Q Y, Tao L X. Heat stress effects are stronger on spikelets than on flag leaves in rice due to differences in dissipation capacity[J]. Journal of Agronomy and Crop Science, 2016, 202 (5): 394-408. |
| [32] | Masuda Y, Kamisaka S, Hoson T. Growth behaviour of rice coleoptiles[J]. Journal of Plant Physiology, 1998, 52(2-3): 180-188. |
| [33] | Angaji S A, Septiningsih E M, Mackill D J, Ismail A M. QTLs associated with tolerance of flooding during germination in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Euphytica, 2010, 172(2): 159-168. |
| [34] | Simon A, Yuri S, Hironobu S, Kenji I. Genotypic variation in coleoptile or mesocotyl lengths of upland rice (Oryza sativa L.) and seedling emergence in deep sowing[J]. African Journal of Agricultural Research, 2012, 7(47): 6239-6248. |
| [35] | 钟昀, 陶诗顺, 马鹏, 余康宁. 淹水处理对萌发状态杂交稻种子出苗的影响[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2016, 44(1): 99-101. |
| Zhong Y, Tao S S, Ma P, Yu K N. Effect of flooding treatment on seedling emergence of hybrid rice in germinated state[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Science, 2016, 44(1): 99-101. (in Chinese) | |
| [36] | Ram P C, Singhe B B, Singh A K, Ram P, Singh P N, Singh H P, Boamfa I, Harren F, Santosa E, Jackson M B, Setter T L, Reuss J, Wade L J, Singh V P, Singh R K. Submergence tolerance in rainfed lowland rice: physiological basis and prospects for cultivar improvement through marker-aided breeding[J]. Field Crops Research, 2002, 76: 131-152. |
| [37] | Huang S, Greenway H, Colmer T D. Anoxia tolerance in rice seedlings: exogenous glucose improves growth of an anoxia-‘intolerant’, but not of a ‘tolerant’ genotype[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2003, 54(391): 2363-2373. |
| [38] | 潘澜, 薛立. 植物淹水胁迫的生理学机制研究进展[J]. 生态学杂志, 2012, 31(10): 2662-2672. |
| Pan L, Xue L. Plant physiological mechanisms in adapting to waterlogging stress[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2012, 31(10): 2662-2672. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [39] | Lee K W, Chen P W, Lu C A, Chen S, Ho T H D, Yu S M. Coordinated responses to oxygen and sugar deficiency allow rice seedlings to tolerate flooding[J]. Science Signaling, 2009, 2(91): 61. |
| [40] | Lu C A, Lin C C, Lee K W, Chen J L, Huang L F, Ho S L, Liu H J, Yu S M. The SnRK1A protein kinase plays a key role in sugar signaling during germination and seedling growth of rice[J]. The Plant Cell, 2007, 19(8): 2484-2499. |
| [41] | Yu S M, Lee H T, Lo S F, Hua T, Ho D. How does rice cope with too little oxygen during its early life?[J]. The New Phytologist, 2021, 229: 36-41. |
| [42] | Huang J R, Yamaguchi J, Akita S. Expression of the ar-Amylase Gene RAmy3D in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) under Aerobic, Hypoxic and Anoxic Conditions[J]. Plant Production Science, 2000, 3(3): 213-218. |
| [43] | 徐旭. 淹水胁迫下水稻胚芽鞘中激素代谢相关酶基因的表达及其RNAi载体的构建[D]. 武汉: 湖北大学, 2011. |
| Xu X. The expression and the vector construction for RNAi of the enzyme genes related with hormone metabolism about the coleoptiles under submerged stress[D]. Wuhan: Hubei University, 2011. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [44] | 杨婷. 膜脂过氧化对植物细胞的伤害[J]. 科技与创新, 2018, 104(8): 61-62. |
| Yang T. Injury to plant cells by membrane lipid peroxidation[J]. Science and Technology & Innovation, 2018, 104(8): 61-62. (in Chinese) | |
| [45] | Leonardo M, Pierdomenico P. Rice germination and seedling growth in the absence of oxygen[J]. Annals of Botany, 2009, 103(2): 181-196. |
| [46] | 龙国辉, 武鹏雨, 付嘉智, 鹿宏丽, 张锐. 过氧化物酶调控木质素合成研究进展[J]. 现代农业科技, 2021(23): 47-49+54. |
| Long G H, Wu P Y, Fu J Z, Lu H L, Zhang R. Research progress on regulation of peroxidase on lignin synthesis[J]. Modern agricultural science and technology, 2021(23): 47-49+54. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [47] | 林植芳, 刘楠. 活性氧调控植物生长发育的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2012, 47(1): 74-86. |
| Lin Z F, Liu N. Research progress in the control and regulation of plant growth and development by reactive oxygen species[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2012, 47(1): 74-86. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [48] | 梁艳荣, 胡晓红, 张颍力, 刘湘萍. 植物过氧化物酶生理功能研究进展[J]. 内蒙古农业大学学报: 自然科学版, 2003(2): 110-113. |
| Liang Y R, Hu X H, Zhang Y L, Liu X P. Progress on physiological function research of lant peroxidase[J]. Journal of Mongolia Agricultural University, 2003(2): 110-113. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [49] | 张静, 孙炳蕊, 毛兴学, 江立群, 吕树伟, 陈文丰, 范芝兰, 于航, 陈平丽, 刘清, 李晨. 水稻淹水萌发对低氧胁迫的适应及其机制研究进展[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2024, 25(1): 13-20. |
| Zhang J, Sun B R, Mao X X, Jiang L Q, Lu S W, Chen W F, Fan Z L, Yu H, Chen P L, Liu Q, Li C. Research progress on the adaptation and mechanism of rice submerged germination to hypoxia stress[J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2024, 25(1): 13-20. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [2] | 刘忠奇, 张海清, 贺记外, 桂金鑫. 成熟期水稻种子脱水速率全基因组关联分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 150-159. |
| [3] | 黄奇娜, 徐有祥, 林光号, 党洪阳, 郑振权, 张燕, 王晗, 邵国胜, 尹献远. 硅对镉胁迫下水稻苗期抗氧化酶系统及镉离子吸收和转运相关基因表达水平的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(5): 486-496. |
| [4] | 夏杨, 李传明, 刘琴, 韩光杰, 徐彬, 黄立鑫, 祁建杭, 陆玉荣, 徐健. 印度梨形孢对盐胁迫下水稻幼苗生长及抗氧化系统的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(5): 543-552. |
| [5] | 朱春权, 徐青山, 曹小闯, 朱练峰, 孔亚丽, 金千瑜, 张均华. 不同属性特征基质对早稻秧苗耐低温的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(5): 503-512. |
| [6] | 李路, 徐以华, 梁梦琦, 王玲, 刘连盟, 侯雨萱, 黎起秦, 黄世文. 水稻对穗枯病的抗病机理初步研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(5): 551-558. |
| [7] | 向妙莲1,付永琦1 ,何永明1 ,黄友明1,2,曾晓春1,2,*. 茉莉酸甲酯浸种对水稻幼苗白叶枯病抗性及抗氧化酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2014, 28(4): 419-426. |
| [8] | 罗楚平1,3刘永锋1陈志谊1,3,*王晓宇1方先文2陈忠明2刘邮洲1聂亚锋1张荣胜1. 水稻纹枯病菌6磷酸葡萄糖胺合成酶基因的克隆、测序及表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2012, 26(2): 137-143. |
| [9] | 孟杰,王人民, 万吉丽,付力成. 不同锌效率水稻基因型及其杂种一代幼苗生长和抗氧化酶活性对Zn2+活度的反应[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2010, 24(3): 289-296 . |
| [10] | 李钱峰 张桂云,于恒秀,辛世文,顾铭洪,刘巧泉,. 水稻异淀粉酶基因ISA1及其启动子的表达特性分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2009, 23(1): 12-12~18 . |
| [11] | 刘芳,郭晶晶,龚丽丽,许晓明. 5-氨基乙酰丙酸促进水稻耐低温光抑制与抗氧化酶活性有关[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2008, 22(4): 411-415 . |
| [12] | 文春描,徐正君,蔡平钟,向跃武,张志雄,刘俊,王闵霞,蒲志刚,张志勇. 拟南芥热激启动子(HSP18.2)在水稻中的启动效率探讨[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2008, 22(3): 323-326 . |
| [13] | 汪仁, 沈文飚, 江玲, 刘玲珑, 翟虎渠, 万建民 . 水稻种子脂氧合酶基因OsLOX1的原核表达、纯化及鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2008, 22(2): 118-124 . |
| [14] | 张光恒,曾大力,郭龙彪,刘慧娟,胡江,高振宇,华志华,钱前,. 葡萄糖焦磷酸酶基因与巨胚基因聚合创建营养功能稻[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2007, 21(6): 567-572 . |
| [15] | 曹云英, 赵华. 高温胁迫下油菜素内酯对水稻幼苗的保护作用[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2007, 21(5): 525-529 . |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||