
中国水稻科学 ›› 2024, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (1): 13-24.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2024.230602
侯本福1,2,3, 杨传铭1,2,3, 张喜娟2,5, 杨贤莉2,5, 王立志2,5, 王嘉宇4, 李红宇1,*( ), 姜树坤2,3,5,*(
), 姜树坤2,3,5,*( )
)
收稿日期:2023-05-13
修回日期:2023-07-14
出版日期:2024-01-10
发布日期:2024-01-16
通讯作者:
* email: 基金资助:
HOU Benfu1,2,3, YANG Chuanming1,2,3, ZHANG Xijuan2,5, YANG Xianli2,5, WANG Lizhi2,5, WANG Jiayu4, LI Hongyu1,*( ), JIANG Shukun2,3,5,*(
), JIANG Shukun2,3,5,*( )
)
Received:2023-05-13
Revised:2023-07-14
Online:2024-01-10
Published:2024-01-16
Contact:
* email: 摘要:
【目的】粒形是决定稻米产量、品质和商品价值的重要数量性状之一。本研究旨在利用水稻重组自交系群体鉴定控制粒形的QTL,为水稻粒形基因的挖掘和长粒形粳稻育种应用奠定基础。【方法】以短圆粒形的粳型超级稻品种龙稻5号(LD5)为母本和细长粒形的早熟籼稻品种中优早8号(ZYZ8)为父本构建包含176个家系的重组自交系群体测定粒长、粒宽、长宽比和粒厚等粒形性状,分析粒形性状间的关系并进行QTL定位和比较分析。【结果】利用区间作图法共检测到8个粒形QTL,分布在3、5、6、7和11号染色体上,表型贡献率范围为4.69%~18.89%,LOD值范围为2.52~8.74。这8个QTL包括3个粒长QTL qGL3、qGL7和qGL11,2个粒宽QTL qGW3和qGW5,2个粒厚QTL qGT3和qGT6,1个长宽比QTL qLWR3。其中,qGL3、qGL7、qGW3、qGW5和qLWR3可以在3个年份稳定检测到。利用多环境联合分析共检测到14个粒形QTL,包括qGL2、qGL3、qGL7和qGL11共4个粒长QTL;qGW3和qGW5共2个粒宽QTL;qGT3、qGT5和qGT6共3个粒厚QTL;qLWR3a、qLWR3b、qLWR5、qLWR7和qLWR11共5个长宽比QTL,分布在2、3、5、6、7和11号染色体上,表型贡献率范围为2.28%~15.78%,LOD值范围为4.20~20.90。与已克隆的粒形基因进行染色体位置比较发现,qGL3/qLWR3区间包含已克隆的GL3.1;qGW5区间包含已克隆的GW5;qLWR3b/qGT3区间包含已克隆的TGW3。【结论】利用区间作图法和多环境联合分析的方法从龙稻5号和中优早8号的重组自交系群体中共鉴定了14个粒形QTL,其中8个QTL是两种方法重复检测到的。这些QTL定位区间内包含已克隆的GL3.1、TGW3和GW5等粒形基因。
侯本福, 杨传铭, 张喜娟, 杨贤莉, 王立志, 王嘉宇, 李红宇, 姜树坤. 利用龙稻5号/中优早8号RIL群体定位粒形QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(1): 13-24.
HOU Benfu, YANG Chuanming, ZHANG Xijuan, YANG Xianli, WANG Lizhi, WANG Jiayu, LI Hongyu, JIANG Shukun. Mapping of Grain Shape QTLs Using RIL Population from Longdao 5/Zhongyouzao 8[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(1): 13-24.
| 年份Year | 性状 Trait | 亲本 Parents | 群体 Population | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 龙稻5号 Longdao 5 | 中优早8号 Zhongyouzao 8 | 平均值 Mean | 群体区间 Range | 偏度 Skewness | 峰度 Kurtosis | |||
| 2020 | 粒长 Grain length /mm | 6.81±0.33 | 8.98±0.38** | 8.18±0.62 | 6.43~9.65 | 0.11 | −0.45 | |
| 粒宽 Grain width /mm | 3.43±0.21 | 3.24±0.13** | 3.30±0.25 | 2.65~3.94 | 0.05 | −0.26 | ||
| 粒厚 Grain thickness/mm | 2.13±0.07 | 1.96±0.18* | 1.98±0.15 | 1.53~2.33 | −0.07 | 0.16 | ||
| 长宽比 Length to width ratio | 1.99±0.14 | 2.78±0.16** | 2.50±0.26 | 1.91~3.38 | 0.48 | 0.33 | ||
| 2021 | 粒长 Grain length /mm | 6.53±0.30 | 8.67±0.30** | 7.73±0.59 | 6.24~9.30 | 0.08 | −0.31 | |
| 粒宽 Grain width/mm | 3.50±0.10 | 3.20±0.13** | 3.28±0.26 | 2.68~3.89 | 0.02 | −0.48 | ||
| 粒厚 Grain thickness | 2.10±0.04 | 1.93±0.22* | 1.96±0.14 | 1.54~2.36 | −0.11 | 0.03 | ||
| 长宽比 Length to width ratio | 1.86±0.08 | 2.72±0.13** | 2.37±0.24 | 1.80~3.41 | 0.56 | 1.27 | ||
| 2022 | 粒长 Grain length/mm | 6.86±0.27 | 9.04±0.24** | 8.08±0.64 | 6.35~9.67 | 0.09 | −0.53 | |
| 粒宽 Grain width /mm | 3.48±0.15 | 3.22±0.17** | 3.29±0.24 | 2.71~3.88 | 0.00 | −0.53 | ||
| 粒厚 Grain thickness /mm | 2.08±0.08 | 1.92±0.06** | 1.95±0.14 | 1.60~2.29 | −0.01 | −0.25 | ||
| 长宽比 Length to width ratio | 1.98±0.12 | 2.82±0.15** | 2.48±0.26 | 1.87~3.48 | 0.53 | 0.94 | ||
表1 亲本及RIL群体粒形相关数据表型分析
Table 1. Phenotypic analysis of grain shape related traits of parents and RIL population.
| 年份Year | 性状 Trait | 亲本 Parents | 群体 Population | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 龙稻5号 Longdao 5 | 中优早8号 Zhongyouzao 8 | 平均值 Mean | 群体区间 Range | 偏度 Skewness | 峰度 Kurtosis | |||
| 2020 | 粒长 Grain length /mm | 6.81±0.33 | 8.98±0.38** | 8.18±0.62 | 6.43~9.65 | 0.11 | −0.45 | |
| 粒宽 Grain width /mm | 3.43±0.21 | 3.24±0.13** | 3.30±0.25 | 2.65~3.94 | 0.05 | −0.26 | ||
| 粒厚 Grain thickness/mm | 2.13±0.07 | 1.96±0.18* | 1.98±0.15 | 1.53~2.33 | −0.07 | 0.16 | ||
| 长宽比 Length to width ratio | 1.99±0.14 | 2.78±0.16** | 2.50±0.26 | 1.91~3.38 | 0.48 | 0.33 | ||
| 2021 | 粒长 Grain length /mm | 6.53±0.30 | 8.67±0.30** | 7.73±0.59 | 6.24~9.30 | 0.08 | −0.31 | |
| 粒宽 Grain width/mm | 3.50±0.10 | 3.20±0.13** | 3.28±0.26 | 2.68~3.89 | 0.02 | −0.48 | ||
| 粒厚 Grain thickness | 2.10±0.04 | 1.93±0.22* | 1.96±0.14 | 1.54~2.36 | −0.11 | 0.03 | ||
| 长宽比 Length to width ratio | 1.86±0.08 | 2.72±0.13** | 2.37±0.24 | 1.80~3.41 | 0.56 | 1.27 | ||
| 2022 | 粒长 Grain length/mm | 6.86±0.27 | 9.04±0.24** | 8.08±0.64 | 6.35~9.67 | 0.09 | −0.53 | |
| 粒宽 Grain width /mm | 3.48±0.15 | 3.22±0.17** | 3.29±0.24 | 2.71~3.88 | 0.00 | −0.53 | ||
| 粒厚 Grain thickness /mm | 2.08±0.08 | 1.92±0.06** | 1.95±0.14 | 1.60~2.29 | −0.01 | −0.25 | ||
| 长宽比 Length to width ratio | 1.98±0.12 | 2.82±0.15** | 2.48±0.26 | 1.87~3.48 | 0.53 | 0.94 | ||
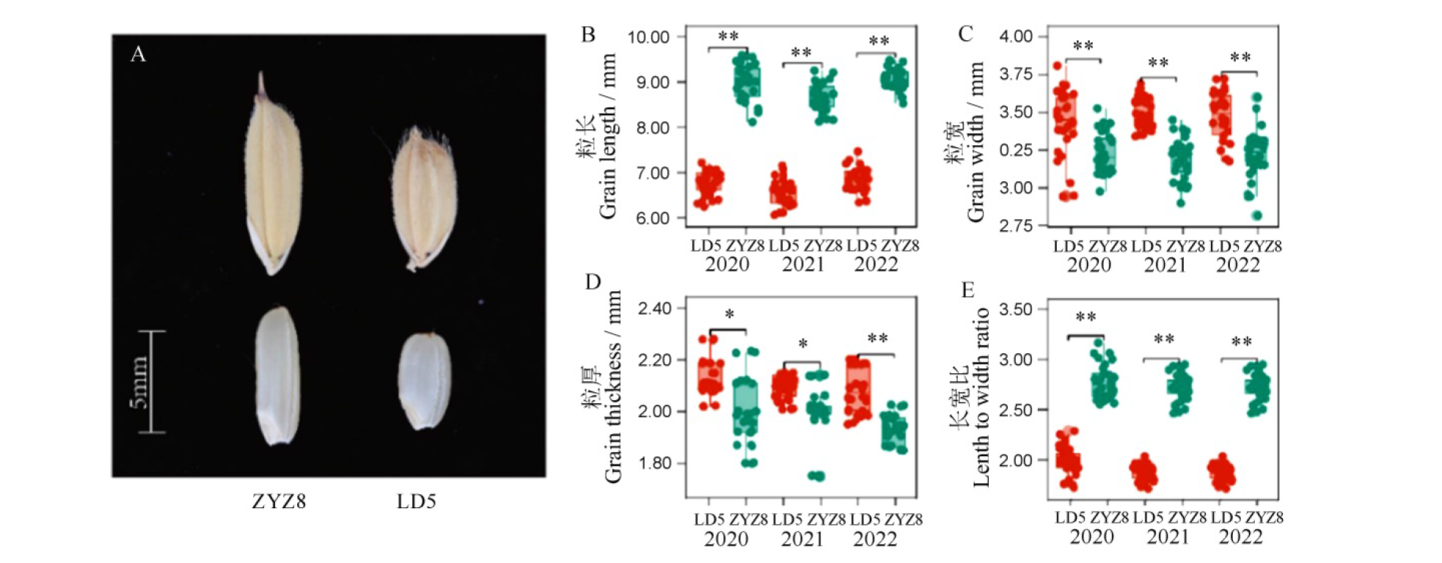
图2 亲本粒形比较 LD5—龙稻5号,ZYZ8—中优早8号。*和**分别表示双亲间差异达 0.05 和 0.01 的显著水平。
Fig. 2. Comparison of grain shape traits between two parents. LD5, Longdao 5; ZYZ8, Zhongyouzao 8. * and ** represent significant difference between two parents at the 0.05 and 0.01 levels, respectively.
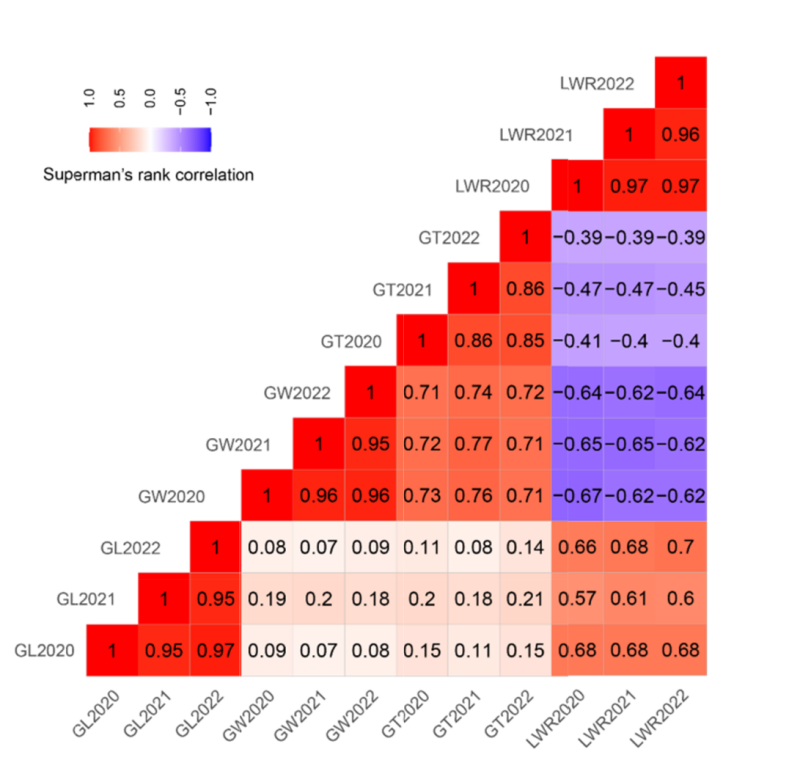
图5 RIL群体粒形性状间相关性分析 GL—粒长;GW—粒宽;GT—粒厚;LWR—长宽比。
Fig. 5. Correlation of grain shape traits in RIL population. GL, Grain length; GW, Grain width; GT, Grain thickness; LWR, Grain length-width ratio.
| QTL | Chr. | 标记区间 Marker interval | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 增效等位 基因来源 Positive allele | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOD | 表型 贡献率Var./% | 加性 效应Add. | LOD | 表型 贡献率Var./% | 加性 效应 Add. | LOD | 表型 贡献率Var./% | 加性 效应 Add. | |||||||||
| qGL3 | 3 | R3M30−RM3513 | 8.05 | 18.52 | 0.28 | 7.69 | 16.52 | 0.28 | 8.74 | 18.89 | 0.31 | ZYZ8 | |||||
| qGL7 | 7 | RM3404−RM11 | 2.90 | 5.37 | 0.16 | 3.33 | 5.73 | 0.16 | 2.90 | 5.30 | 0.16 | ZYZ8 | |||||
| qGL11 | 11 | RM1124−STS11.1 | 2.52 | 4.69 | 0.14 | ZYZ8 | |||||||||||
| qGW3 | 3 | STS3.10−RM3684 | 4.46 | 9.53 | −0.09 | 4.44 | 9.13 | −0.09 | 4.03 | 8.54 | −0.08 | LD5 | |||||
| qGW5 | 5 | R5M13−RM3476 | 3.20 | 7.48 | −0.08 | 3.94 | 9.22 | −0.09 | 3.21 | 7.8 | −0.08 | LD5 | |||||
| qGT3 | 3 | RM503−RM700 | 3.21 | 8.05 | −0.05 | 3.70 | 9.34 | −0.04 | 2.76 | 6.36 | −0.04 | LD5 | |||||
| qGT6 | 6 | RM3827−RM1340 | 2.53 | 6.09 | 0.04 | ZYZ8 | |||||||||||
| qLWR3a | 3 | R3M30−RM3513 | 5.34 | 12.46 | 0.10 | 5.76 | 13.33 | 0.10 | 6.10 | 14.33 | 0.11 | ZYZ8 | |||||
表2 水稻RIL群体粒形性状的BIP-QTL定位结果
Table 2. BIP-QTL mapping of grain shape traits in rice RIL population.
| QTL | Chr. | 标记区间 Marker interval | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 增效等位 基因来源 Positive allele | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOD | 表型 贡献率Var./% | 加性 效应Add. | LOD | 表型 贡献率Var./% | 加性 效应 Add. | LOD | 表型 贡献率Var./% | 加性 效应 Add. | |||||||||
| qGL3 | 3 | R3M30−RM3513 | 8.05 | 18.52 | 0.28 | 7.69 | 16.52 | 0.28 | 8.74 | 18.89 | 0.31 | ZYZ8 | |||||
| qGL7 | 7 | RM3404−RM11 | 2.90 | 5.37 | 0.16 | 3.33 | 5.73 | 0.16 | 2.90 | 5.30 | 0.16 | ZYZ8 | |||||
| qGL11 | 11 | RM1124−STS11.1 | 2.52 | 4.69 | 0.14 | ZYZ8 | |||||||||||
| qGW3 | 3 | STS3.10−RM3684 | 4.46 | 9.53 | −0.09 | 4.44 | 9.13 | −0.09 | 4.03 | 8.54 | −0.08 | LD5 | |||||
| qGW5 | 5 | R5M13−RM3476 | 3.20 | 7.48 | −0.08 | 3.94 | 9.22 | −0.09 | 3.21 | 7.8 | −0.08 | LD5 | |||||
| qGT3 | 3 | RM503−RM700 | 3.21 | 8.05 | −0.05 | 3.70 | 9.34 | −0.04 | 2.76 | 6.36 | −0.04 | LD5 | |||||
| qGT6 | 6 | RM3827−RM1340 | 2.53 | 6.09 | 0.04 | ZYZ8 | |||||||||||
| qLWR3a | 3 | R3M30−RM3513 | 5.34 | 12.46 | 0.10 | 5.76 | 13.33 | 0.10 | 6.10 | 14.33 | 0.11 | ZYZ8 | |||||
| 数量性状基因 | 染色体 | 标记区间 | LOD值 | 表型贡献率 | 加性效应 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QTL | Chr. | Marker interval | LOD value | Var./% | Add. |
| qGL2 | 2 | RM6933―ID2 | 4.20 | 3.14 | 0.12 |
| qGL3 | 3 | R3M30―RM3513 | 20.90 | 15.78 | 0.26 |
| qGL7 | 7 | RM3404―RM11 | 8.26 | 5.02 | 0.15 |
| qGL11 | 11 | RM1124―STS11.1 | 8.51 | 5.85 | 0.16 |
| qGW3 | 3 | STS3.10―RM3684 | 6.20 | 4.55 | ―0.06 |
| qGW5 | 5 | STS5.2―RM3476 | 10.85 | 9.43 | ―0.08 |
| qGT3 | 3 | RM503―RM7000 | 6.83 | 5.26 | ―0.34 |
| qGT5 | 5 | R5M13―RM3476 | 4.84 | 4.37 | ―0.31 |
| qGT6 | 6 | RM3827―RM1340 | 5.07 | 3.85 | 0.29 |
| qLWR3a | 3 | R3M30―RM3513 | 16.61 | 8.71 | 0.10 |
| qLWR3b | 3 | STS3.10―RM3684 | 14.77 | 9.96 | 0.11 |
| qLWR5 | 5 | STS5.2―RM3476 | 4.64 | 2.01 | 0.05 |
| qLWR7 | 7 | RM3404―RM11 | 6.97 | 3.40 | 0.06 |
| qLWR11 | 11 | RM1124―STS11.1 | 4.99 | 2.28 | 0.05 |
表3 水稻RIL群体粒形性状的MET-QTL定位结果
Table 3. MET-QTL mapping of grain shape traits in rice RIL population.
| 数量性状基因 | 染色体 | 标记区间 | LOD值 | 表型贡献率 | 加性效应 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QTL | Chr. | Marker interval | LOD value | Var./% | Add. |
| qGL2 | 2 | RM6933―ID2 | 4.20 | 3.14 | 0.12 |
| qGL3 | 3 | R3M30―RM3513 | 20.90 | 15.78 | 0.26 |
| qGL7 | 7 | RM3404―RM11 | 8.26 | 5.02 | 0.15 |
| qGL11 | 11 | RM1124―STS11.1 | 8.51 | 5.85 | 0.16 |
| qGW3 | 3 | STS3.10―RM3684 | 6.20 | 4.55 | ―0.06 |
| qGW5 | 5 | STS5.2―RM3476 | 10.85 | 9.43 | ―0.08 |
| qGT3 | 3 | RM503―RM7000 | 6.83 | 5.26 | ―0.34 |
| qGT5 | 5 | R5M13―RM3476 | 4.84 | 4.37 | ―0.31 |
| qGT6 | 6 | RM3827―RM1340 | 5.07 | 3.85 | 0.29 |
| qLWR3a | 3 | R3M30―RM3513 | 16.61 | 8.71 | 0.10 |
| qLWR3b | 3 | STS3.10―RM3684 | 14.77 | 9.96 | 0.11 |
| qLWR5 | 5 | STS5.2―RM3476 | 4.64 | 2.01 | 0.05 |
| qLWR7 | 7 | RM3404―RM11 | 6.97 | 3.40 | 0.06 |
| qLWR11 | 11 | RM1124―STS11.1 | 4.99 | 2.28 | 0.05 |
| [1] | 陈燕红, 胡标林, 张帆涛. 稻米品质遗传分析研究现状[J]. 中国稻米, 2023, 29(1): 44-54. |
| Cheng Y H, Hu B L, Zhang F T. Research status of genetic analysis of rice quality[J]. China Rice, 2023, 29(1): 44-54. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | 李苗苗, 李儒香, 秦鱼河, 余金琎, 徐光益, 向思茜, 杨正林, 桑贤春, 凌英华, 何光华, 赵芳明. 基于水稻矮秆长粒CSSL-Z688的QTL鉴定及SSSLs培育[J]. 西南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2023, 45(1): 33-44. |
| Li M M, Li R X, Qin Y H, Yu J J, Xu G Y, Xiang S Q, Yang Z L, Sang X C, Ling Y H, He G H, Zhao F M. Identification of QTL based on a dwarf and long-large grain rice CSSL-Z688 and development of SSSLs[J]. Journal of Southwest University: Natural Science Edition, 2023, 45(1): 33-44. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 李金吉, 张银霞, 赵娜, 田蕾, 杨淑琴, 李培富. 水稻粒形与千粒质量的QTL分析[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报: 自然科学版, 2021, 49(2): 54-60. |
| Li J J, Zhang Y X, Zhao N, Tian L, Yang S Q, Li P F. QTL analysis of rice grain shape and thousand-grain weight[J]. Journal of Northwest A & F University: Natural Science Edition, 2021, 49(2): 54-60. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 郑跃滨, 李智, 赵海燕, 朱光枫, 廖芷依, 竺正航, 王兰. 水稻粒长QTL定位与主效基因的遗传分析[J]. 西北植物学报, 2020, 40(4): 598-604. |
| Zheng Y B, Li Z, Zhao H Y, Zhu G F, Liao Z Y, Zhu Z H, Wang L. Mapping quantitative trait loci associated with grain length and genetic analysis of major quantitative loci in rice[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2020, 40(4): 598-604. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | Zhou Y, Hou J, Li P B, Yang H Y, Xia D, Zhou H, Alam M, Gao G J, Zhang Q L, He Y Q. Genetic dissection and validation of QTLs for grain shape and weight in rice and fine mapping of qGL1.3, a major QTL for grain length and weight[J]. Molecular Breeding, 2019, 39(12): 1-11. |
| [6] | 向思茜, 李儒香, 徐光益, 邓岢莉, 余金琎, 李苗苗, 杨正林, 凌英华, 桑贤春, 何光华, 赵芳明. 基于水稻长大粒染色体片段代换系Z66的粒形QTL的鉴定及其聚合分析[J]. 作物学报, 2023, 49(3): 731-743. |
| Xiang S Q, Li R X, Xu Gu Y, Deng K L, Yu J J, Li M M, Yang Z L, Ling Y H, Sang X C, He G H, Zhao F M. Identification and pyramid analysis of QTLs for grain size based on rice long-large-grain chromosome segment substitution line Z66[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2023, 49(3): 731-743. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 梁文化, 陈涛, 姚姝, 赵凌, 朱镇, 赵庆勇, 周丽慧, 赵春芳, 路凯, 赫磊, 王才林, 张亚东. 基于高密度遗传图谱定位水稻籽粒长宽比QTL[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2021, 49(23): 47-52. |
| Liang W H, Chen T, Yao Z, Zhao L, Zhu Z, Zhao Q Y, Zhou L H, Zhao C F, Lu K, Hao L, Wang C L, Zhang Y D. QTL mapping for grain length-width ratio based on high-density genetic map in rice[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 49(23): 47-52. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | 周梦玉, 宋昕蔚, 徐静, 付雪, 李婷, 朱雨晨, 肖幸运, 毛一剑, 曾大力, 胡江, 朱丽, 任德勇, 高振宇, 郭龙彪, 钱前, 吴明国, 林建荣, 张光恒. 籼稻C84和粳稻春江16B重组自交系遗传图谱构建及籽粒性状QTL定位与验证[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(3): 207-218. |
| Zhou M Y, Song X W, Xu J, Fu X, Li T, Zhu Y H, Xiao X Y, Mao Y J, Zeng D L, Hu J, Zhu L, Ren D Y, Gao Z Y, Guo L B, Qian Q, Wu M G, Lin J R, Zhang G H. Construction of genetic map and mapping and verification of grain traits QTLs using recombinant inbred lines derived from a cross between indica C84 and japonica CJI6B[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2018, 32(3): 207-218. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 宋博文, 王朝欢, 赵哲, 陈淳, 黄明, 陈伟雄, 梁克勤, 肖武名. 基于高密度遗传图谱对水稻粒形QTL定位及分析[J]. 作物学报, 2022, 48(11): 2813-2829. |
| Song B W, Wang C H, Zhao Z, Chen C, Huang M, Chen W X, Liang K Q, Xiao W M. Mapping and analysis of QTLs for grain size in rice based on high density genetic map[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2022, 48(11): 2813-2829. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | 姚晓云, 陈春莲, 熊运华, 黄永萍, 彭志勤, 刘进, 尹建华. 水稻加工和外观品质性状QTL鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37 (5): 507-517. |
| Yao X Y, Chen C L, Xiong Y H, Huang Y P, Peng Z Q, Liu J, Yin J H. Identification of QTL for milling and appearance quality traits in rice(Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2023, 37(5): 507-517. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | Fan C C, Xing Y Z, Mao H L, Lu T T, Han B, Xu C G, Li X H, Zhang Q. GS3, a major OTL for grain length and weight and minor OTL for grain width and thickness in rice encodes a putative transmembrane protein[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2006, 112(6): 1164-1171. |
| [12] | Wang Y X, Xiong G S, Hu J, Jiang L, Yu H, Xu J, Fang Y X, Zeng L J, Xu E B, Xu J, Ye W J, Meng X B, Liu R F, Chen H Q, Jing Y H, Wang Y H, Zhu X D, Li J Y, Qian Q. Copy number variation at the GL7 locus contributes to grain size diversity in rice[J]. Nature Genetics, 2015, 47(8): 944-948. |
| [13] | Wu W G, Liu X Y, Wang M H, Meyer R S, Zhu Z F. A single-nucleotide polymorphism causes smaller grain size and loss of seed shattering during African rice domestication[J]. Nature Plants, 2017, 3: 17064. |
| [14] | Xia D, Zhou N, Liu R J, Dan W H, Li P B, Wu B. GL3.3, a novel QTL encoding a GSK3/SHAGGY-like kinase, epistatically interacts with GS3 to Produce extra-long grains in rice[J]. Molecular Plant, 2018, 11(5): 754-756. |
| [15] | Hu Z J, Lu S J, Wang M J, He H H, Sun L, Wang H R, Lin X H, Jiang L, Sun J L, Xin X Y, Kong W, Chu C C, Xue H W, Yang J S, Lou X J, Liu J X. A novel QTL qTGW3 encodes the GSK3/SHAGGY-like kinase OsGSK5/OsSK41 that interacts with OsARF4 to negatively regulate grain size and weight in rice[J]. Molecular Plant, 2018, 11(5): 736-749. |
| [16] | Si L Z, Chen J Y, Huang X H, Gong H, Lou Q Q, Zhou T Y, Lu T T, Zhu J J, Shangguan Y Y, Chen E W, Gong C X, Zhao Q, Jing Y F, Zhao Y, Li Y, Cui L L, Fan D L, Lu Y Q, Weng Q J, Wang Y C, Zhan Q L, Liu K Y, Wei X H, Han B. OsSPL13 controls grain size in cultivated rice[J]. Nature Genetics, 2016, 48: 447-456. |
| [17] | Zhan P L, Ma S P, Xiao Z L, Li F P, Wei X, Lin S J, Wang X L, Ji Z, Fu Y, Pan J H, Zhou M, Liu Y, Chang Z Y, Li L, Bu S H, Liu Z P, Zhu H T, Liu G F, Zhang G Q, Wang S K. Natural variations in grain length 10(GL10) regulate rice grain size[J]. Journal of Genetics and Genomics, 2022, 49(5): 405-413. |
| [18] | Zhao D S, Li Q F, Zhang C Q, Zhang C, Yang Q Q, Pan L X, Ren X Y, Lu J, Gu M H, Liu Q Q. GS9 acts as a transcriptional activator to regulate rice grain shape and appearance quality[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 1240. |
| [19] | Qi P, Lin Y S, Song X J, Shen J B, Huang W, Shan J X, Zhu M Z, Jiang L W, Gao J P, Lin H X. The novel quantitative trait locus GL3.1 controls rice grain size and yield by regulating Cyclin-T1;3[J]. Cell Research, 2012, 22(12): 1666-1680. |
| [20] | Song X J, Huang W, Shi M, Zhu M Z, Lin H X. A QTL for rice grain width and weight encodes a previously unknown RING-type E3 ubiquitin ligase[J]. Nature Genetics, 2007, 39: 623-630. |
| [21] | Duan P G, Xu J S, Zeng D L, Zhang B L, Geng M F, Zhang G Z, Huang K, Huang L J, Xu R, Ge S, Qian Q, Li Y H. Natural variation in the promoter of GSE5 contributes to grain size diversity in rice[J]. Molecular Plant, 2017, 10(5): 685-694. |
| [22] | Wan X Y, Weng J F, Zhai H Q, Wang J K, Lei C L, Liu X L, Guo T, Jiang L, Su N, Wan J M. Quantitative trait loci (QTL) analysis for rice grain width and fine mapping of an identified QTL allele gw-5 in a recombination hotspot region on chromosome 5[J]. Genetics, 2008, 179(4): 2239-2252. |
| [23] | Shomura A, Izawa T, Ebana K, Takeshi E, Hiromi K, Saeko K, Masahiro Y. Deletion in a gene associated with grain size increased yields during rice domestication[J]. Nature Genetics, 2008, 40(8): 1023-1028. |
| [24] | Li Y B, Fan C C, Xing Y Z, Jiang Y H, Luo L J, Sun L, Shao D, Xu C J, Li X H, Xiao J H, He Y Q, Zhang Q F. Natural variation in GS5 plays an important role in regulating grain size and yield in rice[J]. Nature Genetics, 2011, 43(12): 1266-1269. |
| [25] | Wang S K, Wu K, Yuan Q B, Liu Z B, Lin X Y, Zeng R Z, Zhu H T, Dong G J, Qian Q, Zhang G Q, Fu X D. Control of grain size, shape and quality by OsSPL16 in rice[J]. Nature Genetics, 2012, 44(8): 950-954. |
| [26] | Liu D P, Zhao H, Xiao Y H, Zhang G X, Cao S Y, Yin W C, Qian Y W, Yin Y H, Zhang J S, Chen S Y, Chu C C. A cryptic inhibitor of cytokinin phosphorelay controls rice grain size[J]. Molecular Plant, 2022, 15(2): 293-307. |
| [27] | Liu D P, Yu Z K, Zhang G X, Yin W C, Li L L, Niu M, Meng W J, Zhang X X, Dong N N, Liu J H, Yang Y Z, Wang S M, Chu C C, Tong H N. Diversification of plant agronomic traits by genome editing of brassinosteroid signaling family genes in rice[J]. Plant Physiology, 2021, 187(4): 2563-2576. |
| [28] | Zhang X J, Wang J F, Huang J, Lan H X, Wang C L, Yin C F, Wu Y Y, Tang H J, Qian Q, Li J Y, Zhang H S. Rare allele of OsPPKL1 associated with grain length causes extra-large grain and a significant yield increase in rice[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2012, 109(52): 21534-21539. |
| [29] | 胡慧, 高若愚, 李志新, 徐俊英, 杨隆维, 田雨, 邱先进, 徐建龙. 利用双向导入系定位再生稻外观品质的QTL[J]. 核农学报, 2023, 37(2): 262-273. |
| Hu H, Gao R Y, Li Z X, Xu J Y, Yang L W, Tian Y, Qiu X J, Xu J L. QTL identification of appearance quality of ratoon rice using two sets of reciprocal introgression lines[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 37(2): 262-273. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | Tanabata T, Shibaya T, Hori K, Ebana K, Yano M. SmartGrain: High-throughput phenotyping software for measuring seed shape through image analysis[J]. Plant Physiology, 2012, 160(4): 1871-1880. |
| [31] | Murray M G, Thompson W F. Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 1980, 8(19): 4321-4325. |
| [32] | 刘进, 姚晓云, 刘丹, 余丽琴, 李慧, 王棋, 王嘉宇, 黎毛毛. 不同生态环境下水稻穗部性状QTL鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(2): 124-134. |
| Liu J, Yao X Y, Liu D, Xu L Q, Li H, Wang Q, Wang J Y, Li M M. Identification of QTL for panicle traits under multiple environments in rice(Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2019, 33(2): 124-134. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [33] | McCouch S R. Gene nomenclature system for rice[J]. Rice, 2008, 1(1): 72-84. |
| [34] | 丁膺宾, 张莉珍, 许睿, 王艳艳, 郑晓明, 张丽芳, 程云连, 吴凡, 杨庆文, 乔卫华, 兰进好. 基于染色体片段置换系的野生稻粒长QTL——qGL12的精细定位[J]. 中国农业科学, 2018, 51(18): 3435-3444. |
| Ding Y B, Zhang L Z, Xu R, Wang Y Y, Zheng X M, Zhang L F, Cheng Y L, Wu F, Yang Q W, Qiao W H, Lan J H. Fine mapping of grain length associated QTL, qGL12 in wild rice using a chromosome segment substitution line[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2018, 51(18): 3435-3444. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [35] | 张波, 裴瑞琴, 杨维丰, 朱海涛, 刘桂富, 张桂权, 王少奎. 利用单片段代换系鉴定巴西陆稻IAPAR9中的粒形基因[J]. 作物学报, 2021, 47(8): 1472-1480. |
| Zhang B, Pei R Q, Yang W F, Zhu H T, Liu G F, Zhang G Q, Wang S K. Mapping and identification QTLs controlling grain size in rice (Oryza sativa L.) by using single segment substitution lines derived from IAPAR9[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2021, 47(8): 1472-1480. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [36] | Ponce K, Zhang Y, Guo L B, Leng Y J, Ye G Y. Genome-wide association study of grain size traits in indica rice multiparent advanced generation intercross (MAGIC) population[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2020, 11(24): 395. |
| [37] | 张亚东, 梁文化, 赫磊, 赵春芳, 朱镇, 陈涛, 赵庆勇, 赵凌, 姚姝, 周丽慧, 路凯, 王才林. 水稻RIL群体高密度遗传图谱构建及粒形QTL定位[J]. 中国农业科学, 2021, 54(24): 5163-5176. |
| Zhang Y D, Liang W H, He L, Zhao C F, Zhu Z, Chen T, Zhao Q Y, Zhao L, Yao S, Zhou L H, Lu K, Wang C L. Construction of high-density genetic map and QTL analysis of grain shape in rice RIL population[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2021, 54(24): 5163-5176. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [38] | 黄涛, 王燕宁, 钟奇, 程琴, 杨朦朦, 王鹏, 吴光亮, 黄诗颖, 李才敬, 余剑峰, 贺浩华, 边建民. 利用染色体片段置换系群体定位和分析水稻粒重和粒形QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(2): 159-170. |
| Huang T, Wang Y N, Zhong Q, Cheng Q, Yang M M, Wang P, Wu G L, Huang S Y, Li C J, Yu J F, He H H, Bian J M. Mapping and analysis of QTLs for rice grain weight and grain shape using chromosome segment substitution line population. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2022, 36(2): 159-170. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [39] | Chan A N, Wang L L, Zhu Y J, Fan Y Y, Zhuang J Y, Zhang Z H. Identification through fine mapping and verification using CRISPR/Cas9-targeted mutagenesis for a minor QTL controlling grain weight in rice[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2021, 134(1): 327-337. |
| [40] | Ying J Z, Ma M, Bai C, Huang X, Liu J L, Fan Y Y, Song X J. TGW3, a major QTL that negatively modulates grain length and weight in rice[J]. Molecular Plant, 2018, 11(5): 750-753. |
| [41] | Ma M, Shen S Y, Bai C, Wang W Q, Feng X H, Ying J Z, Song X J. Control of grain size in rice by TGW3 phosphorylation of OsIAA10 through potentiation of OsIAA10-OsARF4-mediated auxin signaling[J]. Cell Reports, 2023, 42(3): 112187. |
| [42] | Xia D, Zhou H, Liu R J, Dan W H, Li P B, Wu B, Chen J X, Wang L Q, Gao G J, Zhang Q L, He Y Q. GL3.3,a novel QTL encoding a GSK3/SHAGGY-like kinase, epistatically interacts with GS3 to produce extra-long grains in rice[J]. Molecular Plant, 2018, 11(5): 754-756. |
| [43] | Tian P, Liu J F, Mou C L, Shi C L, Zhang H, Zhao Z C, Lin Q B, Wang J, Wang J L, Zhang X, Guo X Z, Cheng Z J, Zhu S S, Ren Y L, Lei C L, Wang H Y, Wan J M. GW5-like, a homolog of GW5, negatively regulates grain width, weight and salt resistance in rice[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2019, 61(11): 1171-1185. |
| [44] | Li N, Xu R, Li Y H. Molecular networks of seed size control in plants[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2019, 70: 435-463. |
| [45] | 刘进, 姚晓云, 王棋, 李慧, 王嘉宇, 黎毛毛. 不同生态环境下籽粒大小相关性状QTL定位[J]. 华北农学报, 2018, 33(2): 133-138. |
| Liu J, Yao X Y, Wang Q, Li H, Wang J Y, Li M M. QTL mapping of seed size traits under different environment in rice[J]. Acta Agriculture Boerali-Sinica, 2018, 33(2): 133-138. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 汪邑晨, 朱本顺, 周磊, 朱骏, 杨仲南. 光/温敏核不育系的不育机理及两系杂交稻的发展与展望 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 463-474. |
| [2] | 许用强, 徐军, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 王丹英, 曾宇翔, 符冠富. 水稻花粉管生长及其对非生物逆境胁迫的响应机理研究进展 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 495-506. |
| [3] | 何勇, 刘耀威, 熊翔, 祝丹晨, 王爱群, 马拉娜, 王廷宝, 张健, 李建雄, 田志宏. 利用CRISPR/Cas9技术编辑OsOFP30基因创制水稻粒型突变体 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 507-515. |
| [4] | 吕阳, 刘聪聪, 杨龙波, 曹兴岚, 王月影, 童毅, Mohamed Hazman, 钱前, 商连光, 郭龙彪. 全基因组关联分析(GWAS)鉴定水稻氮素利用效率候选基因 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 516-524. |
| [5] | 杨好, 黄衍焱, 王剑, 易春霖, 石军, 谭楮湉, 任文芮, 王文明. 水稻中八个稻瘟病抗性基因特异分子标记的开发及应用 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 525-534. |
| [6] | 杨铭榆, 陈志诚, 潘美清, 张汴泓, 潘睿欣, 尤林东, 陈晓艳, 唐莉娜, 黄锦文. 烟-稻轮作下减氮配施生物炭对水稻茎鞘同化物转运和产量 形成的影响 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 555-566. |
| [7] | 熊家欢, 张义凯, 向镜, 陈惠哲, 徐一成, 王亚梁, 王志刚, 姚坚, 张玉屏. 覆膜稻田施用炭基肥对水稻产量及氮素利用的影响 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 567-576. |
| [8] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [9] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [10] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [11] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [12] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [13] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [14] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [15] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||