
中国水稻科学 ›› 2023, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (4): 415-426.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2023.220901
黄锦文1,2, 李日坤1,2, 陈志诚3, 张汴泓1,2, 雷涵1,2, 潘睿欣1,2, 杨铭榆1,2, 潘美清1,2, 唐莉娜3( )
)
收稿日期:2022-09-01
修回日期:2022-10-09
出版日期:2023-07-10
发布日期:2023-07-17
通讯作者:
*email: 704142780@qq.com
基金资助:
HUANG Jinwen1,2, LI Rikun1,2, CHEN Zhicheng3, ZHANG Bianhong1,2, LEI Han1,2, PAN Ruixin1,2, YANG Mingyu1,2, PAN Meiqing1,2, TANG Lina3( )
)
Received:2022-09-01
Revised:2022-10-09
Online:2023-07-10
Published:2023-07-17
Contact:
*email: 704142780@qq.com
摘要:
【目的】 探讨不同稻草还田技术措施对土壤特性的影响及根际微生物修复和改良土壤的内在机制,探索适合福建烟-稻轮作区的稻草高效还田技术,以期为烟-稻轮作区作物优质高效栽培提供依据。【方法】 以烤烟“云烟87”和晚稻“甬优1540”为材料,通过不同的稻草还田配施技术处理,进行了2年的田间定位试验,分析比较了烟-稻轮作系统耕层土壤养分、根际微生物和作物产量的变化规律以及根际微生物与土壤环境因子间的内在关系。【结果】 产量分析表明,连续2年稻草还田后,各处理产量均比对照显著增加,其中配施石灰和尿素的T2处理最显著,其烟草和水稻产量分别比对照提高25.67%、11.49%;其次是配施腐秆灵和尿素的T3处理,纯稻草T1还田处理效果最差;T1处理第1年稻草还田后烟草产量与对照差异不显著,第2年烟草和水稻产量分别比对照提高3.77%和5.90%。耕层土壤养分特性分析表明,经连续2年的稻草还田处理后,耕层土壤养分与有机碳含量均显著增加,其中T2处理效果最好,其次是T3处理。T2处理碱解氮、有效磷、速效钾、有机碳和可溶性有机碳含量分别比对照提高了7.09%、5.97%、3.01%、11.32%和5.47%。根际微生物群落分析表明,与对照相比,T2、T3处理下碳源代谢相关的HSB_OF53-F07、自毒物质降解有关的节杆菌属(Arthrobacter)和纤维素分解有关的假散囊菌属(Pseudeurotium)丰度均显著上升,而与发病相关的腐质霉属(Humicola)和青霉菌属(Penicillium)相对丰度则显著下降。相关分析表明,根际有益菌丰度与土壤养分因子多为正相关,而致病菌的丰度则与土壤养分因子负相关。【结论】 稻草还田配施石灰或腐秆灵和适量速效氮肥,有利于提高耕层养分含量,促进固氮等有益微生物生长,抑制病原菌,为烟-稻轮作提供良好的土壤环境,进而提高作物产量。
黄锦文, 李日坤, 陈志诚, 张汴泓, 雷涵, 潘睿欣, 杨铭榆, 潘美清, 唐莉娜. 不同稻草还田技术对烟-稻轮作系统土壤养分、有机碳及微生物多样性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(4): 415-426.
HUANG Jinwen, LI Rikun, CHEN Zhicheng, ZHANG Bianhong, LEI Han, PAN Ruixin, YANG Mingyu, PAN Meiqing, TANG Lina. Effects of Straw Returning Techniques on Soil Nutrients, Organic Carbon and Microbial Diversity in Tobacco-rice Rotation System[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(4): 415-426.
| 年份 Year | 处理 Treatment | 产量 Yield /(kg·hm−2) | 产值 Output value /(Yuan·hm−2) | 均价 Average price /(Yuan·kg−1) | 上中等烟比例 Ratio of superior-medium tobacco/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | T0 | 1828.51±32.35 c | 33318.60±968.35 c | 18.27±1.10 a | 82.93±1.99 b |
| T1 | 1841.55±38.32 c | 35175.30±1224.20 c | 19.10±0.07 a | 83.72±1.63 b | |
| T2 | 2291.11±119.23 a | 43335.90±991.05 a | 18.87±0.68 a | 85.47±0.93 a | |
| T3 | 1997.55±17.25 b | 39183.45±766.40 b | 19.63±0.52 a | 87.11±3.21 a | |
| 2021 | T0 | 1940.55±37.81 d | 34148.55±598.60 d | 17.60±0.07 c | 78.66±2.50 c |
| T1 | 2013.75±27.45 c | 37922.25±609.15 c | 18.83±0.11 b | 82.70±0.33 b | |
| T2 | 2438.75±18.00 a | 46702.06±959.30 a | 19.15±0.16 ab | 87.10±0.65 a | |
| T3 | 2124.61±53.41 b | 42710.85±744.60 b | 20.11±0.29 a | 88.84±0.82 a | |
| F值 F value | 年份 Year (Y) | ** | ** | NS | NS |
| 处理 Treatment (T) | ** | ** | ** | ** | |
| Y×T | NS | NS | NS | NS |
表1 烟-稻轮作系统中烤烟经济性状的变化
Table 1. Economic indexes of flue-cured tobacco in tobacco-rice rotation system.
| 年份 Year | 处理 Treatment | 产量 Yield /(kg·hm−2) | 产值 Output value /(Yuan·hm−2) | 均价 Average price /(Yuan·kg−1) | 上中等烟比例 Ratio of superior-medium tobacco/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | T0 | 1828.51±32.35 c | 33318.60±968.35 c | 18.27±1.10 a | 82.93±1.99 b |
| T1 | 1841.55±38.32 c | 35175.30±1224.20 c | 19.10±0.07 a | 83.72±1.63 b | |
| T2 | 2291.11±119.23 a | 43335.90±991.05 a | 18.87±0.68 a | 85.47±0.93 a | |
| T3 | 1997.55±17.25 b | 39183.45±766.40 b | 19.63±0.52 a | 87.11±3.21 a | |
| 2021 | T0 | 1940.55±37.81 d | 34148.55±598.60 d | 17.60±0.07 c | 78.66±2.50 c |
| T1 | 2013.75±27.45 c | 37922.25±609.15 c | 18.83±0.11 b | 82.70±0.33 b | |
| T2 | 2438.75±18.00 a | 46702.06±959.30 a | 19.15±0.16 ab | 87.10±0.65 a | |
| T3 | 2124.61±53.41 b | 42710.85±744.60 b | 20.11±0.29 a | 88.84±0.82 a | |
| F值 F value | 年份 Year (Y) | ** | ** | NS | NS |
| 处理 Treatment (T) | ** | ** | ** | ** | |
| Y×T | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| 年份 Year | 处理 Treatment | 有效穗数 Effective panicles /(×104·hm−2) | 穗粒数 No. of grains per panicle | 千粒重 1000-grain weight/g | 结实率 Seed setting rate/% | 理论产量 Theoretical Yield /(kg·hm−2) | 实际产量 Actual yield /(kg·hm−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | T0 | 210.17±2.08 b | 214.53±3.21 b | 22.88±1.29 a | 81.83±1.10 a | 8441.65±113.15 d | 8542.65±333.95 d |
| T1 | 208.50±2.65 b | 217.17±1.84 b | 23.82±0.79 a | 81.11±1.59 a | 9127.69±161.13 c | 8879.81±128.01 c | |
| T2 | 221.83±1.26 a | 230.81±2.77 a | 22.75±0.46 a | 81.06±1.57 a | 9441.98±183.21 a | 9338.41±122.44 a | |
| T3 | 220.50±2.92 a | 226.97±2.14 a | 22.81±0.28 a | 81.02±1.37 a | 9248.99±213.17 b | 9210.74±89.29 b | |
| 2021 | T0 | 207.84±2.36 c | 215.08±5.70 c | 22.91±0.57 a | 83.10±0.07 a | 8510.50±133.01 d | 8607.59±147.42 c |
| T1 | 217.68±2.74 b | 226.62±3.20 b | 23.21±0.34 a | 81.00±0.06 a | 9274.21±161.71 c | 9115.67±250.01 b | |
| T2 | 224.94±1.41 a | 231.08±1.96 a | 22.73±0.15 a | 82.10±0.10 a | 9699.91±203.11 a | 9597.45±108.01 a | |
| T3 | 222.84±2.36 a | 229.12±3.17 a | 22.63±0.13 a | 81.91±0.06 a | 9468.31±173.26 b | 9502.85±62.07 a | |
| F值 F value | Y | * | * | NS | NS | * | * |
| T | ** | ** | NS | NS | ** | ** | |
| Y×T | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS |
表2 烟-稻轮作系统中水稻产量及其构成因素的变化
Table 2. Grain yield and its components of rice in tobacco-rice rotation system.
| 年份 Year | 处理 Treatment | 有效穗数 Effective panicles /(×104·hm−2) | 穗粒数 No. of grains per panicle | 千粒重 1000-grain weight/g | 结实率 Seed setting rate/% | 理论产量 Theoretical Yield /(kg·hm−2) | 实际产量 Actual yield /(kg·hm−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | T0 | 210.17±2.08 b | 214.53±3.21 b | 22.88±1.29 a | 81.83±1.10 a | 8441.65±113.15 d | 8542.65±333.95 d |
| T1 | 208.50±2.65 b | 217.17±1.84 b | 23.82±0.79 a | 81.11±1.59 a | 9127.69±161.13 c | 8879.81±128.01 c | |
| T2 | 221.83±1.26 a | 230.81±2.77 a | 22.75±0.46 a | 81.06±1.57 a | 9441.98±183.21 a | 9338.41±122.44 a | |
| T3 | 220.50±2.92 a | 226.97±2.14 a | 22.81±0.28 a | 81.02±1.37 a | 9248.99±213.17 b | 9210.74±89.29 b | |
| 2021 | T0 | 207.84±2.36 c | 215.08±5.70 c | 22.91±0.57 a | 83.10±0.07 a | 8510.50±133.01 d | 8607.59±147.42 c |
| T1 | 217.68±2.74 b | 226.62±3.20 b | 23.21±0.34 a | 81.00±0.06 a | 9274.21±161.71 c | 9115.67±250.01 b | |
| T2 | 224.94±1.41 a | 231.08±1.96 a | 22.73±0.15 a | 82.10±0.10 a | 9699.91±203.11 a | 9597.45±108.01 a | |
| T3 | 222.84±2.36 a | 229.12±3.17 a | 22.63±0.13 a | 81.91±0.06 a | 9468.31±173.26 b | 9502.85±62.07 a | |
| F值 F value | Y | * | * | NS | NS | * | * |
| T | ** | ** | NS | NS | ** | ** | |
| Y×T | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| 处理 Treatment | 碱解氮 Alkali-hydrolyzed nitrogen /(mg·kg−1) | 有效磷 Available phosphorus /(mg·kg−1) | 速效钾 Available potassium /(mg·kg−1) | 土壤有机碳 Soil organic carbon /(g·kg−1) | 可溶性有机碳 Dissolved organic carbon /(mg·kg−1) | DOC有效率 DOC-SOC ratio /% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T0 | 89.33±8.50 c | 49.77±0.92 c | 191.20±5.42 b | 16.61±1.24 c | 67.43±3.65 c | 0.41±0.03 a |
| T1 | 93.00±4.08 b | 51.60±0.68 b | 194.00±12.54 a | 17.38±0.48 b | 69.67±1.95 b | 0.40±0.02 b |
| T2 | 95.66±10.37 a | 52.74±0.71 a | 196.96±7.64 a | 18.49±0.21 a | 71.12±2.10 a | 0.38±0.01 c |
| T3 | 95.33±8.37 a | 51.67±1.62 b | 196.89±10.46 a | 18.35±0.20 a | 69.55±3.30 b | 0.38±0.01 c |
表3 耕层土壤养分、有机碳、可溶性有机碳含量及其有效率变化(2021年)
Table 3. Changes of soil nutrient, SOC, DOC content and its effective rates in the topsoil(2021).
| 处理 Treatment | 碱解氮 Alkali-hydrolyzed nitrogen /(mg·kg−1) | 有效磷 Available phosphorus /(mg·kg−1) | 速效钾 Available potassium /(mg·kg−1) | 土壤有机碳 Soil organic carbon /(g·kg−1) | 可溶性有机碳 Dissolved organic carbon /(mg·kg−1) | DOC有效率 DOC-SOC ratio /% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T0 | 89.33±8.50 c | 49.77±0.92 c | 191.20±5.42 b | 16.61±1.24 c | 67.43±3.65 c | 0.41±0.03 a |
| T1 | 93.00±4.08 b | 51.60±0.68 b | 194.00±12.54 a | 17.38±0.48 b | 69.67±1.95 b | 0.40±0.02 b |
| T2 | 95.66±10.37 a | 52.74±0.71 a | 196.96±7.64 a | 18.49±0.21 a | 71.12±2.10 a | 0.38±0.01 c |
| T3 | 95.33±8.37 a | 51.67±1.62 b | 196.89±10.46 a | 18.35±0.20 a | 69.55±3.30 b | 0.38±0.01 c |
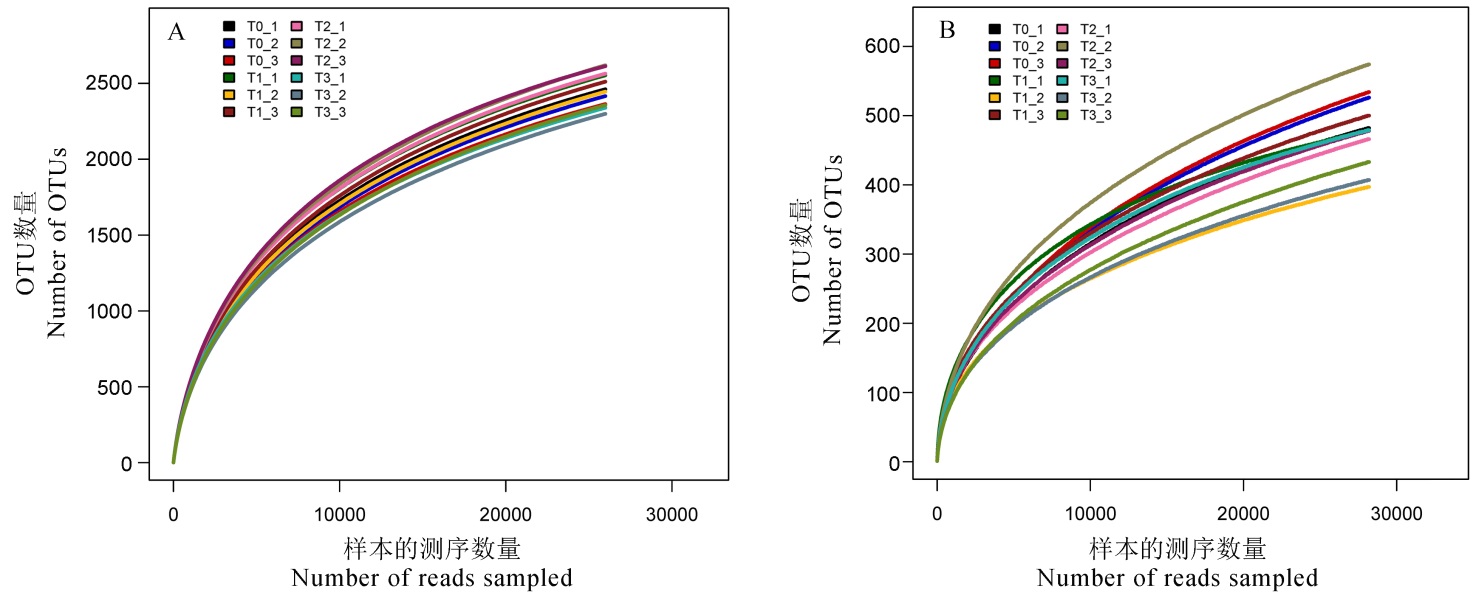
图1 烤烟旺长期根际土壤微生物稀释曲线 A―细菌稀释曲线;B―真菌稀释曲线。
Fig. 1. Microbial dilution curves of tobacco rhizosphere soil microorganisms during tobacco boom period. A and B represent bacterial and fungal dilution curves, respectively.
| 微生物 Microorganism | 处理 Treatment | 丰富度指数 Chao1 | 测序深度指数 Coverage/% | 多样性指数 Observed species | 香农指数 Shannon index | 辛普森指数 Simpson index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 细菌 Bacteria | T0 | 3173.82 b | 96.97 a | 2413.07 c | 9.26 b | 0.99 a |
| T1 | 3285.73 a | 96.95 a | 2502.87 b | 9.37 b | 0.99 a | |
| T2 | 3312.47 a | 95.87 a | 2598.57 a | 9.58 a | 1.00 a | |
| T3 | 3127.81 b | 95.66 a | 2330.93 d | 9.13 c | 0.99 a | |
| 真菌 Fungi | T0 | 747.19 a | 96.92 a | 513.99 a | 3.94 bc | 0.79 c |
| T1 | 642.35 a | 96.91 a | 458.31 a | 4.66 a | 0.89 a | |
| T2 | 726.45 a | 96.77 a | 505.97 a | 4.32 ab | 0.84 b | |
| T3 | 642.91 a | 95.96 a | 439.67 a | 3.78 c | 0.79 c |
表4 烤烟旺长期根际土壤细菌和真菌的α-多样性指数
Table 4. Diversity index of bacterial and fungi community in rhizosphere soil during tobacco booming period.
| 微生物 Microorganism | 处理 Treatment | 丰富度指数 Chao1 | 测序深度指数 Coverage/% | 多样性指数 Observed species | 香农指数 Shannon index | 辛普森指数 Simpson index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 细菌 Bacteria | T0 | 3173.82 b | 96.97 a | 2413.07 c | 9.26 b | 0.99 a |
| T1 | 3285.73 a | 96.95 a | 2502.87 b | 9.37 b | 0.99 a | |
| T2 | 3312.47 a | 95.87 a | 2598.57 a | 9.58 a | 1.00 a | |
| T3 | 3127.81 b | 95.66 a | 2330.93 d | 9.13 c | 0.99 a | |
| 真菌 Fungi | T0 | 747.19 a | 96.92 a | 513.99 a | 3.94 bc | 0.79 c |
| T1 | 642.35 a | 96.91 a | 458.31 a | 4.66 a | 0.89 a | |
| T2 | 726.45 a | 96.77 a | 505.97 a | 4.32 ab | 0.84 b | |
| T3 | 642.91 a | 95.96 a | 439.67 a | 3.78 c | 0.79 c |
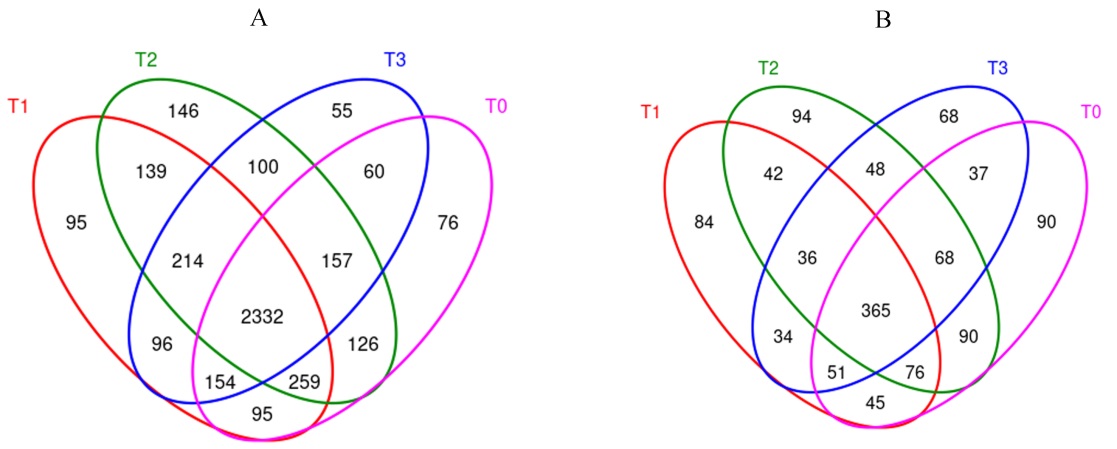
图2 根际土壤微生物OTU维恩图 A―细菌维恩图; B―真菌维恩图。
Fig. 2. Venn Graph of microbial OTU in rhizosphere soil. A and B represent bacteria and fungi Venn Graph, respectively.
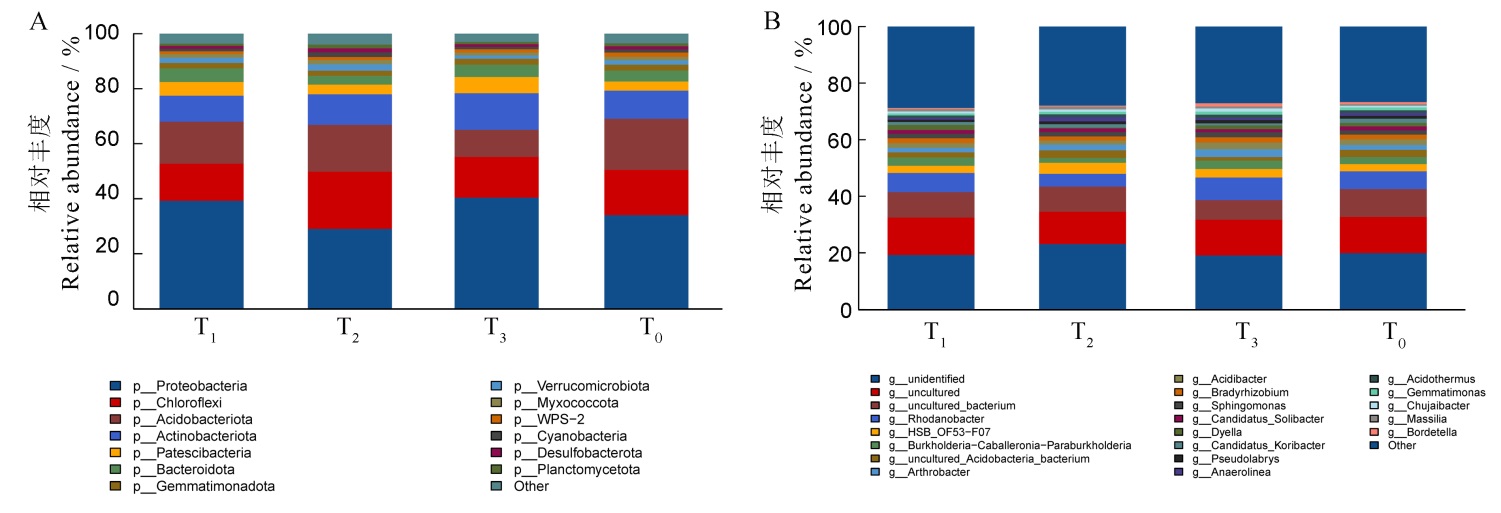
图4 烤烟旺长期根际土壤主要细菌相对丰度变化 A―门水平;B―属水平。
Fig. 4. Changes in the relative abundance of main bacteria in the rhizosphere soil during tobacco booming period. A, Phylum level; B, Genus level.
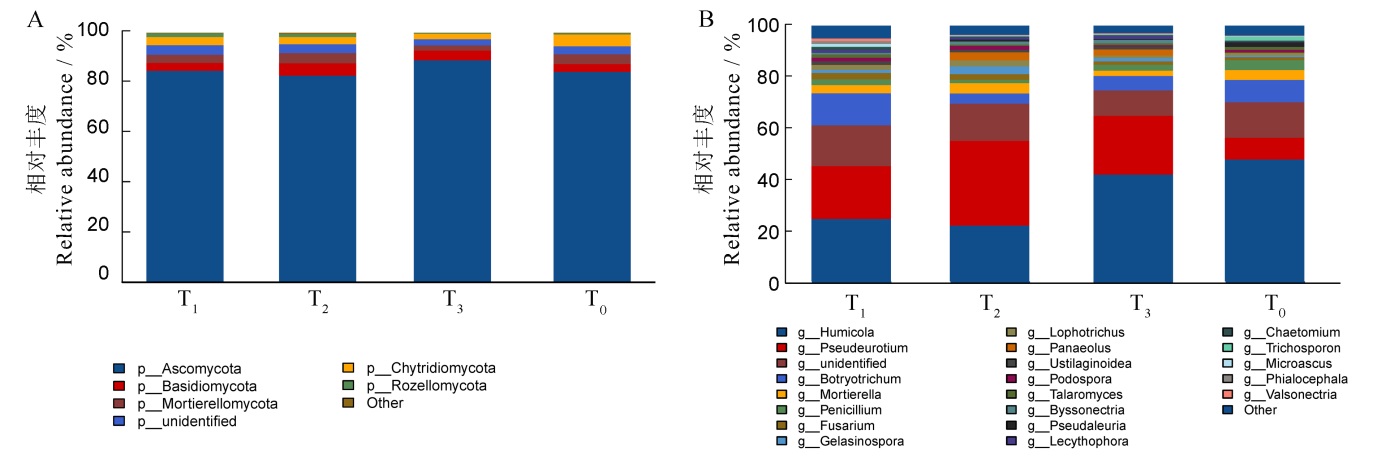
图5 烤烟旺长期根际土壤主要真菌相对丰度变化 A―门水平;B―属水平。
Fig. 5. Changes in the relative abundance of main fungi in the rhizosphere soil during tobacco booming period. A, Phylum level; B, Genus level.
| 微生物 Microorganism | 编号 No. | 相对丰度Relative abundance | 属名 Genus name | 功能 Function | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T0 | T1 | T2 | T3 | ||||
| 细菌 Bacteria | OTU_1051 | 6.29±1.09 b | 6.77±0.70 ab | 4.50±0.25 c | 7.99±0.73 a | Rhodanobacter | 反硝化作用[ |
| OTU_2436 | 2.49±0.75 b | 2.50±0.50 b | 3.71±0.35 a | 3.22±0.43 a | HSB_OF53-F07 | 碳源代谢[ | |
| OTU_253 | 2.53±0.42 a | 2.98±0.43 a | 1.67±0.35 b | 2.99±0.50 a | Burkholderia | 固氮、解磷[ | |
| OTU_2046 | 1.77±0.11 c | 1.58±0.20 d | 1.99±0.15 b | 2.72±0.17 a | Arthrobacter | 降解自毒物质 [ | |
| OTU_258 | 1.98±0.44 ab | 1.64±0.31 b | 1.41±0.08 b | 2.45±0.19 a | Acidibacter | 未知 | |
| OTU_2944 | 1.68±0.28 a | 1.71±0.39 a | 1.53±0.12 a | 1.79±0.15 a | Bradyrhizobium | 固氮[ | |
| OTU_3260 | 1.46±0.21 a | 1.52±0.23 a | 1.63±0.21 a | 1.83±0.31 a | Sphingomonas | 分解复杂有机物[ | |
| OTU_3317 | 1.04±0.11 b | 1.32±0.26 a | 1.30±0.12 a | 1.44±0.37 a | Candidatus_Solibacter | 分解有机质[ | |
| 真菌 Fungi | OTU_1056 | 47.75±0.33 a | 24.62±3.32 c | 22.00±4.79 c | 41.90±2.71 b | Humicola | 引起腐烂、疾病[ |
| OTU_3 | 8.49±1.90 c | 20.64±3.33 b | 33.07±5.50 a | 22.94±1.13 b | Pseudeurotium | 纤维素分解[ | |
| OTU_565 | 9.68±0.22 a | 12.50±4.52 a | 3.99±0.63 b | 5.64±0.85 b | Botryotrichum | 未知 | |
| OTU_572 | 3.88±0.09 a | 3.21±1.34 ab | 4.02±0.51 a | 2.03±0.17 b | Mortierella | 未知 | |
| OTU_1066 | 3.89±0.18 a | 2.36±0.21 b | 1.34±0.30 c | 2.27±0.39 b | Penicillium | 病害相关[ | |
| OTU_918 | 1.11±0.24 b | 2.44±0.52 a | 2.17±0.19 a | 1.26±0.12 b | Fusarium | 纤维素分解[ | |
表5 根际土壤优势细菌、真菌菌属功能分析
Table 5. Function analysis of dominant bacteria and fungi in the rhizosphere soil (at genus level).
| 微生物 Microorganism | 编号 No. | 相对丰度Relative abundance | 属名 Genus name | 功能 Function | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T0 | T1 | T2 | T3 | ||||
| 细菌 Bacteria | OTU_1051 | 6.29±1.09 b | 6.77±0.70 ab | 4.50±0.25 c | 7.99±0.73 a | Rhodanobacter | 反硝化作用[ |
| OTU_2436 | 2.49±0.75 b | 2.50±0.50 b | 3.71±0.35 a | 3.22±0.43 a | HSB_OF53-F07 | 碳源代谢[ | |
| OTU_253 | 2.53±0.42 a | 2.98±0.43 a | 1.67±0.35 b | 2.99±0.50 a | Burkholderia | 固氮、解磷[ | |
| OTU_2046 | 1.77±0.11 c | 1.58±0.20 d | 1.99±0.15 b | 2.72±0.17 a | Arthrobacter | 降解自毒物质 [ | |
| OTU_258 | 1.98±0.44 ab | 1.64±0.31 b | 1.41±0.08 b | 2.45±0.19 a | Acidibacter | 未知 | |
| OTU_2944 | 1.68±0.28 a | 1.71±0.39 a | 1.53±0.12 a | 1.79±0.15 a | Bradyrhizobium | 固氮[ | |
| OTU_3260 | 1.46±0.21 a | 1.52±0.23 a | 1.63±0.21 a | 1.83±0.31 a | Sphingomonas | 分解复杂有机物[ | |
| OTU_3317 | 1.04±0.11 b | 1.32±0.26 a | 1.30±0.12 a | 1.44±0.37 a | Candidatus_Solibacter | 分解有机质[ | |
| 真菌 Fungi | OTU_1056 | 47.75±0.33 a | 24.62±3.32 c | 22.00±4.79 c | 41.90±2.71 b | Humicola | 引起腐烂、疾病[ |
| OTU_3 | 8.49±1.90 c | 20.64±3.33 b | 33.07±5.50 a | 22.94±1.13 b | Pseudeurotium | 纤维素分解[ | |
| OTU_565 | 9.68±0.22 a | 12.50±4.52 a | 3.99±0.63 b | 5.64±0.85 b | Botryotrichum | 未知 | |
| OTU_572 | 3.88±0.09 a | 3.21±1.34 ab | 4.02±0.51 a | 2.03±0.17 b | Mortierella | 未知 | |
| OTU_1066 | 3.89±0.18 a | 2.36±0.21 b | 1.34±0.30 c | 2.27±0.39 b | Penicillium | 病害相关[ | |
| OTU_918 | 1.11±0.24 b | 2.44±0.52 a | 2.17±0.19 a | 1.26±0.12 b | Fusarium | 纤维素分解[ | |
| 微生物 Microbe | 属名 Genus name | 碱解氮 Alkali-hydrolyzed nitrogen | 有效磷 Available phosphorus | 速效钾 Available potassium | 有机碳 Soil organic carbon | 可溶性有机碳Dissolved organic carbon |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 细菌 | Rhodanobacter | 0.081 | −0.233 | 0.248 | −0.017 | 0.116 |
| Bacteria | HSB-OF53-F07 | 0.540 | 0.790** | 0.466 | 0.531 | −0.328 |
| Burkholderia | −0.135 | −0.228 | 0.093 | −0.072 | 0.3010 | |
| Arthrobacter | 0.856** | 0.493 | 0.718** | 0.458 | −0.216 | |
| Acidibacter | 0.296 | −0.015 | 0.252 | 0.012 | −0.090 | |
| Bradyrhizobium | −0.098 | −0.158 | 0.127 | 0.016 | 0.244 | |
| Sphingomonas | 0.346 | 0.533 | 0.357 | 0.153 | −0.302 | |
| Canidatus-solibacter | −0.604* | −0.133 | −0.403 | −0.280 | 0.014 | |
| 真菌 | Humicola | −0.078 | −0.394 | −0.092 | −0.455 | 0.040 |
| Fungi | Pseudeurotium | 0.658* | 0.700* | 0.479 | 0.774** | −0.257 |
| Botryotrichum | −0.702* | −0.545 | −0.501 | −0.529 | 0.188 | |
| Mortierella | −0.293 | −0.278 | −0.544 | −0.069 | 0.069 | |
| Penicillium | −0.477 | −0.664* | −0.431 | −0.678* | 0.329 | |
| Fusarium | 0.835** | 0.825** | 0.823** | 0.699* | −0.070 |
表6 根际优势微生物(属水平)与耕层土壤养分、有机碳的相关性
Table 6. Correlation of rhizosphere dominant microorganisms (genus level) with soil nutrients and organic carbon in topsoil.
| 微生物 Microbe | 属名 Genus name | 碱解氮 Alkali-hydrolyzed nitrogen | 有效磷 Available phosphorus | 速效钾 Available potassium | 有机碳 Soil organic carbon | 可溶性有机碳Dissolved organic carbon |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 细菌 | Rhodanobacter | 0.081 | −0.233 | 0.248 | −0.017 | 0.116 |
| Bacteria | HSB-OF53-F07 | 0.540 | 0.790** | 0.466 | 0.531 | −0.328 |
| Burkholderia | −0.135 | −0.228 | 0.093 | −0.072 | 0.3010 | |
| Arthrobacter | 0.856** | 0.493 | 0.718** | 0.458 | −0.216 | |
| Acidibacter | 0.296 | −0.015 | 0.252 | 0.012 | −0.090 | |
| Bradyrhizobium | −0.098 | −0.158 | 0.127 | 0.016 | 0.244 | |
| Sphingomonas | 0.346 | 0.533 | 0.357 | 0.153 | −0.302 | |
| Canidatus-solibacter | −0.604* | −0.133 | −0.403 | −0.280 | 0.014 | |
| 真菌 | Humicola | −0.078 | −0.394 | −0.092 | −0.455 | 0.040 |
| Fungi | Pseudeurotium | 0.658* | 0.700* | 0.479 | 0.774** | −0.257 |
| Botryotrichum | −0.702* | −0.545 | −0.501 | −0.529 | 0.188 | |
| Mortierella | −0.293 | −0.278 | −0.544 | −0.069 | 0.069 | |
| Penicillium | −0.477 | −0.664* | −0.431 | −0.678* | 0.329 | |
| Fusarium | 0.835** | 0.825** | 0.823** | 0.699* | −0.070 |
| [1] | 熊云明, 黄国勤, 王淑彬, 刘隆旺. 稻田轮作对土壤理化性状和作物产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2004(4): 42-45. |
| Xiong Y M, Huang G Q, Wang S B, Liu L W. Effect of crop rotation in paddy field on soil physical and chemical characteristics and crop yield[J]. Review of China Agriculture Science and Technology, 2004(4): 42-45. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | 向鹏华, 单雪华, 黄银章, 郭维, 龙世平. 烟-稻复种连作年限对土壤理化性状及烟叶产量与品质的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2016(5): 105-109. |
| Xiang P H, Shan X H, Huang Y Z, Guo W, Long S P. Effects of tobacco-rice continuous cropping years on soil physicochemical properties and tobacco yield and quality[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2016 (5): 105-109. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 周文新, 陈冬林, 卜毓坚, 屠乃美. 稻草还田对土壤微生物群落功能多样性的影响[J]. 环境科学学报, 2008(2): 326-330. |
| Zhou W X, Chen D L, Bu Y J, Tu N M. Effects of rice-straw returning to the field on the metabolic diversity of soil microbial communities[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2008(2): 326-330. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | Yan S Y, Song J M, Fan J S, Yan C, Dong S K, Ma C M, Gong Z P. Changes in soil organic carbon fractions and microbial community under rice straw return in Northeast China[J]. Global Ecology and Conservation, 2020, 22, e00962: 1-12. |
| [5] | 倪国荣, 涂国全, 魏赛金, 吴建富, 潘晓华. 稻草还田配施催腐菌剂对晚稻根际土壤微生物与酶活性及产量的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2012, 31(1): 149-154. |
| Ni G R, Tu G Q, Wei S J, Wu J F, Shi Q H. Effects of straw-returning using agent on microbe and enzyme activity in rhizosphere soils and yield of late rice[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2012, 31(1): 149-154. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 黄平娜, 秦道珠, 龙怀玉, 张认连, 雷秋良, 杨全柳. 稻草还田对烟田速效养分变化及烟叶产量品质的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2008, 24(12): 294-297. |
| Huang P N, Qin D Z, Long H Y, Zhang R L, Lei Q L, Yang Q L. Straw also available nutrient-changes in the tobacco fields and tobacco yield and quality[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2008, 24(12): 294-297. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 陆文龙, 赵标, 五毛毛. 施用不同方式处理的秸秆对土壤磷形态分布的影响[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2018, 46(2): 232-234. |
| Lu W L, Zhao B, Wu M M. Effects of different treatments of straw on soil phosphorus speciation distribution[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 46(2): 232-234. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | 易镇邪, 符呈祥, 褚百凤, 付红, 陈冬林, 周文新, 屠乃美. 快腐剂处理还田早稻秸秆对晚季土壤化学与生物学特性的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2012, 28(27): 94-98. |
| Yi Z X, Fu C X, Chu B F, Fu H, Chen D L, Zhou W X, Tu N M. Effect of treating returned early rice straw by decomposition accelerant on soil chemical and biological characteristics in late season[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2012, 28(27): 94-98. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 吴海勇, 李明德, 刘琼峰, 吴小丹. 稻草不同途径还田对土壤结构及有机质特征的影响[J]. 土壤通报, 2012, 43(4):836-841. |
| Wu H Y, Li M D, Liu Q F, Wu X D. Effects of different modes of straw returning on soil structure and character of soil organic matter[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2012, 43(4): 836-841. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | 李明德, 肖汉乾, 汤海涛, 张一扬, 汤睿, 靳志丽, 张淑贞, 张四伟. 稻草还田对烟田土壤性状和烟草产量及品质的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2006(6): 41-44. |
| Li M D, Xiao H Q, Tang H T, Zhang Y Y, Tang R, Jin Z L, Zhang S Z, Zhang S W. Effect of incorporation straw into field on soil properties and tobacco yield and quality[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2006(6): 41-44. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | Zhao S C, He P, Qiu S J, Jia L L, Liu M C, Jin J Y, Johnston A M. Long-term effects of potassium fertilization and straw return on soil potassium levels and crop yields in north-central China[J]. Field Crops Research, 2014, 169: 116-122. |
| [12] | 廖萍, 刘磊, 何宇轩, 唐刚, 张俊, 曾勇军, 吴自明, 黄山. 施石灰和秸秆还田对双季稻产量和氮素吸收的互作效应[J]. 作物学报, 2020, 46(1): 84-92. |
| Liao P, Liu L, He Y X, Tang G, Zhang J, Zeng Y J, Wu Z M, Huang S. Interactive effects of liming and straw incorporation on yield and nitrogen uptake in a double rice cropping system[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2020, 46(1): 84-92. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | 王雪仁, 张瀛, 张珊珊, 林建麒. 不同方式稻草还田对烤烟产质量的影响[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2017, 45(27): 41-44. |
| Wang X R, Zhang Y, Zhang S S, Lin J L. Effects of different ways of straw returning to soil on yield and quality of flue-cured tobacco[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 45(27): 41-44. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | 黄平娜, 秦道珠, 龙怀玉, 刘淑军, 黄晶. 连续3年稻草还田对烤烟产量品质及后茬晚稻产量影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2010, 26(11): 194-199. |
| Huang P N, Qin D Z, Long H Y, Liu S J, Huang J. Effects of rice straw for three consecutive years to the yields and qualities of flue-cured tobacco and stalk return field late rice[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2010, 26(11): 194-199. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 刘王锁, 李海泉, 何毅, 黄业芸, 邱开阳, 谢应忠. 根际微生物对植物与土壤交互调控的研究进展[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2021(5): 318-327. |
| Liu W S, Li H Q, He Y, Huang Y Y, Qiu K Y, Xie Y Z. Research progress on the interaction regulation of plant and soil by rhizosphere microbiome[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2021(5): 318-327. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2010. |
| Bao S D. Soil and Agricultural Chemistry Analysis[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2010. (in Chinese) | |
| [17] | 占新华, 周立祥. 土壤溶液和水体中水溶性有机碳的比色测定[J]. 中国环境科学, 2002(5):433-437. |
| Zhan X H, Zhou L X. Colorimetric determination of dissolved organic carbon in soil solution and water environment[J]. China Environmental Science, 2002(5):433-437. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | 周吉祥, 张贺, 杨静, 李桂花, 张建峰. 连续施用土壤改良剂对沙质潮土肥力及活性有机碳组分的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2020, 53(16): 3307-3318. |
| Zhou J X, Zhang H, Yang J, Li G H, Zhang J F. Effects of continuous application of soil amendments on fluvo-aquic soil fertility and active organic carbon components[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2020, 53(16): 3307-3318. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | Li H, Yang S, Semenov M V, Yao F, Ye J, Bu R C, Ma R A, Lin J J, Kurganova I, Wang X G, Deng Y, Kravchenko I, Jiang Y, Kuzyakov Y. Temperature sensitivity of SOM decomposition is linked with a K-selected microbial community[J]. Global Change Biology, 2021, 27(12): 1-17. doi: 10.1111/gcb.15593. |
| [20] | Wang Y, Sheng H F, He Y, Wu J Y, Jiang Y X, Tam N F, Zhou H W. Comparison of the levels of bacterial diversity in freshwater, intertidal wetland, and marine sediments by using millions of illumina tags[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2012, 78(23): 8264-8271. |
| [21] | Yang S D, Xiao J, Liang T, He W Z, Tan H W. Response of soil biological properties and bacterial diversity to different levels of nitrogen application in sugarcane fields[J]. AMB Express, 2021, 11(1): 172 |
| [22] | 李敏, 王桂莲, 马璐, 张琇. 节杆菌降解阿魏酸的效能[J]. 微生物学通报, 2021, 48(5): 1550-1559. |
| Li M, Wang G L, Ma L, Zhang X. Degradation of ferulic acid by Arthrobacter sp.[J]. Microbiology China, 2021, 48(5): 1550-1559. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 黎妍妍, 冯吉, 王林, 付裕,、 李锡宏. 万寿菊-烟草轮作调理植烟土壤细菌群落结构的作用[J]. 中国烟草科学, 2021, 42(1): 14-19. |
| Li Y Y, Feng J, Wang L, Fu Y, Li X H. Effects of marigold-tobacco rotation on bacterial community in tobacco rhizosphere soil[J]. Chinese Tobacco Science, 2021, 42(1): 14-19. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | 杨金燕, 姜于兰, 杨亚曦, 曾琛, 王肸芃. 腐质霉属真菌分类的研究进展[J]. 贵州农业科学, 2015, 43(8): 126-130. |
| Yang J Y, Jiang Y L, Yang Y X, Zeng C, Wang X P. Advances in taxonomy of Humicola genera[J]. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 43(8): 126-130. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | 戴蓬博, 张荣, 孙广宇. 中国苹果病害病原菌物名录[J]. 菌物学报, 2021, 40(4): 936-964. |
| Dai P B, Zhang R, Sun G Y. A checklist of pathogenic fungi on apple in China[J]. Mycosystema, 40(4): 936-964. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | Doveri F, Sarrocco S, Vannacci G. Studies on three rare coprophilous plectomycetes from Italy[J]. Mycotaxon, 2013, 124: 279-300. |
| [27] | Heuvel R N V D, Biezen E V D, Jetten M S M, Hefting M M, Kartal B. Denitrification at pH 4 by a soil-derived Rhodanobacter-dominated community[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 2010, 12(12): 3264-3271. |
| [28] | 张珂飞, 钟永嘉, 孙丽莉, 廖红. 植物有益伯克霍尔德氏菌的研究进展及其在农业中的应用[J]. 微生物学报, 2021, 61(8): 2205-2218. |
| Zhang K F, Zhong Y J, Sun L L, Liao H. Plant-associated beneficial Burkholderia[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2021, 61(8): 2205-2218. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | 张科, 李臻, 郑瑶, 麻红星, 刘梦含, 丁慧杰, 王瑜, 刘丽, 夏西超. 河南叶县岩盐可培养中度嗜盐菌的多样性[J]. 微生物学通报, 2020, 47(12): 3987-3997. |
| Zhang K, Li Z, Zheng Y, Ma H X, Liu M H, Ding H J, Wang Y, Liu L, Xia X C. Biodiversity of culturable moderate halophilic bacteria of rock salt in Yexian county, Henan Province[J]. Microbiology China, 2020, 47(12): 3987-3997. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | Schlesinger W H. Evidence from chrono sequence studies for a low carbon-storage potential of soils[J]. Nature, 1990, 348(6298): 232-234. |
| [31] | 赵惠丽, 董金琎, 师江澜, 徐苗, 田霄鸿. 秸秆还田模式对小麦-玉米轮作体系土壤有机碳固存的影响[J]. 土壤学报, 2021, 58(1): 213-224. |
| Zhao H L, Dong J J, Shi J L, Shi J L, Xu M, Tian X H. Effect of straw returning mode on soil organic carbon sequestration[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2021, 58(1): 213-224. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [32] | 王保君, 王伟, 胡乃娟, 顾泽海, 陈兵林, 张政文, 徐蒋来, 朱利群. 麦秸还田下水氮管理对稻田土壤养分、酶活性及碳库的短期影响[J]. 核农学报, 2016, 30(5): 957-964. |
| Wang B J, Wang W, Hu N J, Gu Z H, Chen B L, Zhang Z W, Xu J L, Zhu L Q. Short-term effect of different water and nitrogen managements on paddy soil nutrient, enzyme activity and carbon pool under wheat straw-returning fields[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 30(5): 957-964. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [33] | Jandl R, Sollins P. Water-extractable soil carbon in relation to the belowground carbon cycle[J]. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 1997, 25: 196-201. |
| [34] | Chantigny M H. Dissolved and water-extractable organic matter in soils: A review on the influence of land use and management practices[J]. Geoderma, 2003, 113: 357-380. |
| [35] | Chen H L, Zhou J M, Xiao B H. Characterization of dissolved organic matter derived from rice straw at different stages of decay[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2010, 10(5): 915-922. |
| [36] | Kalbitz K, Solinger S, Park J H, Michalzik B, Matzner E. Controls on the dynamics of dissolved organic matter in soils: A review[J]. Soil Science, 2000, 165(4): 277-304. |
| [37] | Garcia J, Kao-Kniffin J. Microbial group dynamics in plant rhizospheres and their implications on nutrient cycling[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2023, 14: 1186322. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.01516. |
| [38] | Li X Z, Rui J P, Xiong J B, Li J B, He Z L, Zhou J Z, Yannarell A C, Mackie R I. Functional potential of soil microbial communities in the maize rhizosphere[J]. PLoS ONE, 2014, 9(11): e112609. |
| [39] | 吴晋元, 职晓阳, 李岩, 关统伟, 唐蜀昆, 徐丽华, 李文均. 云南江城和黑井盐矿沉积物未培养放线菌多样性比较[J]. 微生物学报, 2008(10): 1550-1555. |
| Wu J Y, Zhi X Y, Li Y, Guan T W, Tang S K, Xu L H, Li W J. Comparison of actinobacterial diversity in Jiangcheng and Heijing saline mines in Yunnan by using culture-independent approach[J]. Microbiology, 2008(10): 1550-1555. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [40] | Carniel F C, Fortuna L, Zanelli D, Tretiach M. Graphene environmental biodegradation: Wood degrading and saprotrophic fungi oxidize few-layer graphene[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021: 125553. |
| [1] | 吴玉红, 李艳华, 王吕, 秦宇航, 李杉杉, 郝兴顺, 张庆路, 崔月贞, 肖飞. 陕南稻区紫云英稻草联合还田配施减量氮肥协同提升水稻产量与稻米品质[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(6): 628-641. |
| [2] | 陈云, 刘昆, 李婷婷, 李思宇, 李国明, 张伟杨, 张耗, 顾骏飞, 刘立军, 杨建昌. 结实期干湿交替灌溉对水稻根系、产量和土壤的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(3): 269-277. |
| [3] | 唐先干, 谢金水, 徐昌旭, 刘佳, 袁福生, 刘光荣, 李祖章. 红壤性稻田紫云英与化肥减施对早稻品质与养分吸收的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(5): 466-474. |
| [4] | 黄锦文, 吴珈谊, 陈鸿飞, 张志兴, 方长旬, 邵彩虹, 林伟伟, 翁佩莹, 林文雄. 头季稻氮肥运筹对再生稻根际机能及产量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(4): 383-395. |
| [5] | 李思平, 曾路生, 吴立鹏, 张玉晓, 解军蕊, 丁效东. 氮肥水平与栽植密度对植稻土壤养分含量变化与氮肥利用效率的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(1): 69-79. |
| [6] | 王彦荣,岩石真嗣 ,三木孝昭 ,华泽田, 张三元, 代贵金,. 自然农法条件下稻田有益微生物菌群多年施用累积效果[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2006, 20(4): 443-446 . |
| [7] | 姜丽娜, 符建荣, 范浩定. 水网平原稻田土壤养分空间变异特性研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2005, 19(2): 153-159 . |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||