
中国水稻科学 ›› 2023, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (2): 125-132.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2023.220413
王雨1,#, 孙全翌1,#, 杜海波1, 许志文1, 吴科霆1, 尹力1, 冯志明1,2, 胡珂鸣1,2, 陈宗祥1,2,*( ), 左示敏1,2,3,*(
), 左示敏1,2,3,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-04-24
修回日期:2022-09-03
出版日期:2023-03-10
发布日期:2023-03-10
通讯作者:
陈宗祥,左示敏
作者简介:第一联系人:#共同第一作者
基金资助:
WANG Yu1,#, SUN Quanyi1,#, DU Haibo1, XU Zhiwen1, WU Keting1, YIN Li1, FENG Zhiming1,2, HU Keming1,2, CHEN Zongxiang1,2,*( ), ZUO Shimin1,2,3,*(
), ZUO Shimin1,2,3,*( )
)
Received:2022-04-24
Revised:2022-09-03
Online:2023-03-10
Published:2023-03-10
Contact:
CHEN Zongxiang, ZUO Shimin
About author:First author contact:#These authors contributed equally to this work
摘要:
【目的】稻瘟病和纹枯病是水稻两大重要病害,严重影响稻米的产量和品质。培育抗病品种是降低其危害最经济有效的措施。【方法】本研究结合分子标记辅助选择技术,将广谱抗稻瘟病基因Pigm和抗纹枯病数量性状基因qSB-9TQ、qSB-11HJX导入优良食味粳稻品种南粳9108中,构建不同抗性基因/基因组合的株系,并评价这些株系的稻瘟病和纹枯病抗性,考查其主要农艺性状和品质性状。【结果】导入Pigm能显著提高南粳9108对苗瘟和穗颈瘟的抗性;分别导入qSB-9TQ、qSB-11HJX均能提高南粳9108的纹枯病抗性,且两个抗性基因聚合时呈现一定的抗性累加效应。其中,导入Pigm的株系穗长和每穗粒数显著增加,导入qSB-11HJX的株系千粒重显著增加,其他农艺及品质性状与南粳9108无明显差异。【结论】这些抗性基因导入/聚合能在不降低农艺及品质性状的同时,显著提高纹枯病和稻瘟病的抗性水平,为粳稻抗病育种提供新的种质资源。
王雨, 孙全翌, 杜海波, 许志文, 吴科霆, 尹力, 冯志明, 胡珂鸣, 陈宗祥, 左示敏. 利用抗稻瘟病基因Pigm和抗纹枯病数量性状基因qSB-9TQ、qSB-11HJX改良南粳9108的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(2): 125-132.
WANG Yu, SUN Quanyi, DU Haibo, XU Zhiwen, WU Keting, YIN Li, FENG Zhiming, HU Keming, CHEN Zongxiang, ZUO Shimin. Improvement of the Resistance of Nanjing 9108 to Blast and Sheath Blight by Pyramiding Resistance Gene Pigm and Quantitative Trait Genes qSB-9TQ and qSB-11HJX[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(2): 125-132.
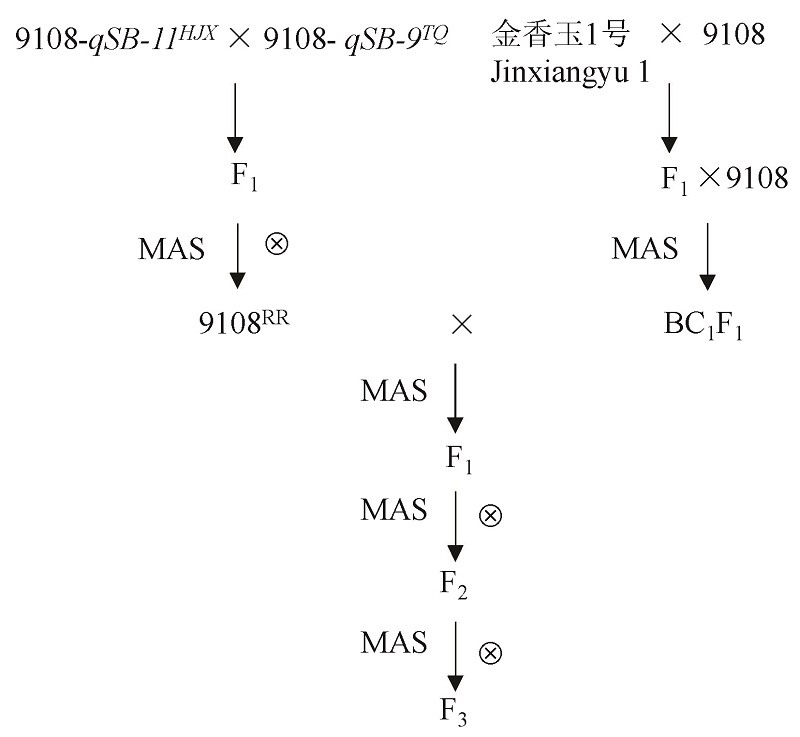
图1 聚合Pigm、qSB-9TQ和qSB-11HJX的材料创制 图中“9108”代表 “南粳9108”。
Fig. 1. Breeding of lines pyramiding Pigm, qSB-9TQ and qSB-11HJX. “9108” represents “Nanjing 9108”.
| 目标基因 Gene | 标记 Primer | 正向引物 Forward primer (5'-3') | 反向引物 Reverse primer (5'-3') |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pigm | M143104 | CCTTGTTCCTCCTGCTATC | ATCTCGCTGTTCAGTCTTG |
| qSB-9TQ | Y93.5 | CTGTTCTTCTCCTGCGTTCT | ATGTCCTCGTGCTTCTGC |
| Y90.2 | CGGGATTAAATACGAGACAT | TTTCTTAGGTCCCATTCTTC | |
| Y84.2 | AAAGGTTGCGAGGAGATTAGAGT | TAGGGGTTGGTTTCTGGTTGTAG | |
| qSB-11HJX | RM224 | ATCGATCGATCTTCACGAGG | TGCTATAAAAGGCATTCGGG |
| ZYJ28.23 | AGGGCACAGAGGGAACAAT | ACAGGGTCAGGCAGTCAGG |
表1 用于检测Pigm、qSB-9TQ和qSB-11HJX抗性基因的标记名称和序列信息
Table 1. Primer sequences of molecular markers detecting Pigm, qSB-9TQ and qSB-11HJX.
| 目标基因 Gene | 标记 Primer | 正向引物 Forward primer (5'-3') | 反向引物 Reverse primer (5'-3') |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pigm | M143104 | CCTTGTTCCTCCTGCTATC | ATCTCGCTGTTCAGTCTTG |
| qSB-9TQ | Y93.5 | CTGTTCTTCTCCTGCGTTCT | ATGTCCTCGTGCTTCTGC |
| Y90.2 | CGGGATTAAATACGAGACAT | TTTCTTAGGTCCCATTCTTC | |
| Y84.2 | AAAGGTTGCGAGGAGATTAGAGT | TAGGGGTTGGTTTCTGGTTGTAG | |
| qSB-11HJX | RM224 | ATCGATCGATCTTCACGAGG | TGCTATAAAAGGCATTCGGG |
| ZYJ28.23 | AGGGCACAGAGGGAACAAT | ACAGGGTCAGGCAGTCAGG |
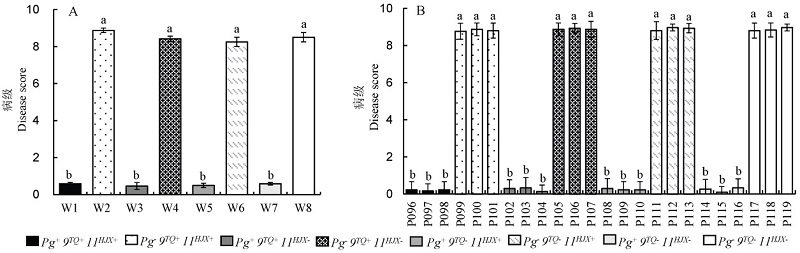
图2 不同基因型株系的穗颈瘟接种鉴定结果 A-8个株系,3次重复;B-24个株系,无重复;平均值±标准差,不同小写字母代表株系间差异达0.05显著水平(one-way ANOVA)。
Fig. 2. Panicle blast resistance evaluation of lines harboring different resistance genes. A, Disease identification of 8 lines(n=3). B, Disease identification of 24 lines(n=1). Data are shown as mean±SD. Bars superscripted by different lowercase letters are significantly different at 0.05 level (one-way ANOVA).
| 编号 No. | 基因型 Genotype | 菌株数 No. of strains | 抗谱 Resistance frequency/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总数Total | 抗Resistant | 感Susceptible | |||
| W1 | Pg+ 9TQ+ 11HJX+ | 23 | 23 | 0 | 100.0 |
| W2 | Pg− 9TQ+ 11HJX+ | 23 | 9 | 14 | 39.1 |
| W3 | Pg+ 9TQ+ 11HJX− | 23 | 22 | 1 | 95.6 |
| W4 | Pg− 9TQ+ 11HJX− | 23 | 11 | 12 | 47.8 |
| W5 | Pg+ 9TQ− 11HJX+ | 23 | 23 | 0 | 100.0 |
| W6 | Pg− 9TQ− 11HJX+ | 23 | 10 | 13 | 43.5 |
| W7 | Pg+ 9TQ− 11HJX− | 23 | 23 | 0 | 100.0 |
| W8 | Pg− 9TQ− 11HJX− | 23 | 7 | 16 | 30.4 |
表2 8种基因型株系的苗瘟接种鉴定抗谱
Table 2. Seedling blast resistance evaluation of eight lines with different genotypes.
| 编号 No. | 基因型 Genotype | 菌株数 No. of strains | 抗谱 Resistance frequency/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总数Total | 抗Resistant | 感Susceptible | |||
| W1 | Pg+ 9TQ+ 11HJX+ | 23 | 23 | 0 | 100.0 |
| W2 | Pg− 9TQ+ 11HJX+ | 23 | 9 | 14 | 39.1 |
| W3 | Pg+ 9TQ+ 11HJX− | 23 | 22 | 1 | 95.6 |
| W4 | Pg− 9TQ+ 11HJX− | 23 | 11 | 12 | 47.8 |
| W5 | Pg+ 9TQ− 11HJX+ | 23 | 23 | 0 | 100.0 |
| W6 | Pg− 9TQ− 11HJX+ | 23 | 10 | 13 | 43.5 |
| W7 | Pg+ 9TQ− 11HJX− | 23 | 23 | 0 | 100.0 |
| W8 | Pg− 9TQ− 11HJX− | 23 | 7 | 16 | 30.4 |
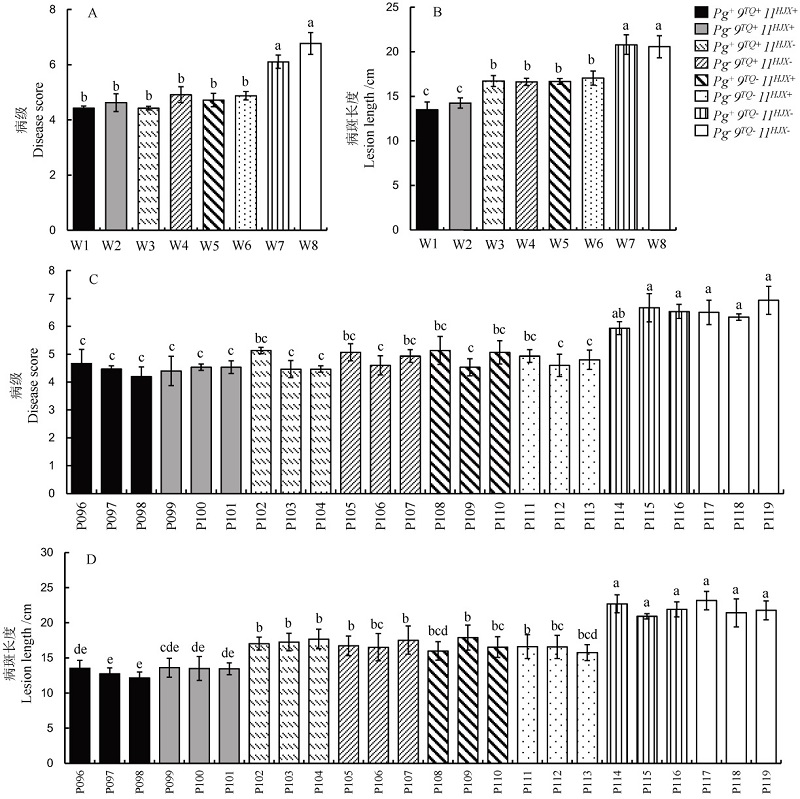
图3 不同基因型株系的纹枯病抗性鉴定结果 A, B―8个株系3重复大田成株期(A)和孕穗期温室(B)抗性鉴定结果;C, D―24个株系无重复大田成株期(C)和孕穗期温室(D)抗性鉴定结果;图中数据为平均值±标准差,不同小写字母代表株系间差异达0.05显著水平(one-way ANOVA)。
Fig. 3. Sheath blight resistance evaluation of lines harboring different resistance genes. A and B, Resistance evaluation of eight lines (n=3) against sheath blight in field at rice tillering stage(A) and in greenhouse at rice booting stage(B). C and D, Resistance evaluation of 24 lines (n=1) against sheath blight in field at rice tillering stage(C) and in green house at rice booting stage(D). Data are shown as mean±SD. Bars superscripted by different lowercase letters are significantly different at 0.05 level (one-way ANOVA).
| 编号 No. | 类型 Genotype | 生育期 | 株高 | 穗长 | 一次枝梗数 | 二次枝梗数 | 每穗粒数 Grain number | 结实率 | 千粒重 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heading date/d | Plant height / cm | Panicle length / cm | No. of primary rachis branches | No. of secondary rachis branches | Seed setting rate/% | 1000-grain weight/g | |||
| W1 | Pg+9TQ+11HJX+ | 82.2±1.0 | 116.7±2.2a | 21.12±0.06a | 16.4±1.4 | 45.9±9.4 | 149.34±3.95a | 88±4 | 27.57±0.21a |
| W2 | Pg−9TQ+11HJX+ | 82.7±0.8 | 108.5±4.5b | 21.28±0.25a | 16.8±1.3 | 42.1±10.4 | 151.69±6.42a | 87±3 | 26.34±0.16cd |
| W3 | Pg+9TQ+11HJX− | 81.3±1.5 | 110.0±3.1ab | 21.45±0.28a | 15.8±0.8 | 47.8±8.0 | 150.79±12.15a | 88±4 | 27.41±0.15ab |
| W4 | Pg−9TQ+11HJX− | 81.5±0.5 | 114.3±2.0ab | 20.39±0.20b | 15.8±1.8 | 43.9±7.9 | 134.86±8.07ab | 88±3 | 27.36±0.13ab |
| W5 | Pg+9TQ-11HJX+ | 81.7±1.0 | 110.4±2.2ab | 19.86±0.12b | 15.6±0.4 | 43.1±5.1 | 135.33±1.29ab | 89±1 | 26.73±0.26bc |
| W6 | Pg−9TQ−11HJX+ | 80.7±0.8 | 108.2±1.0b | 20.33±0.30b | 15.5±0.8 | 44.9±2.3 | 135.47±3.16ab | 90±3 | 27.91±0.52a |
| W7 | Pg+9TQ−11HJX− | 82.5±2.2 | 108.5±3.0b | 21.41±0.39a | 16.1±0.2 | 49.7±4.2 | 149.50±1.88a | 88±1 | 25.92±0.13d |
| W8 | Pg−9TQ−11HJX− | 82.8±0.3 | 109.3±2.6ab | 20.14±0.07b | 16.0±0.2 | 44.5±0.9 | 132.06±1.52b | 88±5 | 26.80±0.08bc |
表3 8种基因型株系的主要农艺性状比较
Table 3. Comparison of the main agronomic traits of eight lines harboring different resistance genes.
| 编号 No. | 类型 Genotype | 生育期 | 株高 | 穗长 | 一次枝梗数 | 二次枝梗数 | 每穗粒数 Grain number | 结实率 | 千粒重 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heading date/d | Plant height / cm | Panicle length / cm | No. of primary rachis branches | No. of secondary rachis branches | Seed setting rate/% | 1000-grain weight/g | |||
| W1 | Pg+9TQ+11HJX+ | 82.2±1.0 | 116.7±2.2a | 21.12±0.06a | 16.4±1.4 | 45.9±9.4 | 149.34±3.95a | 88±4 | 27.57±0.21a |
| W2 | Pg−9TQ+11HJX+ | 82.7±0.8 | 108.5±4.5b | 21.28±0.25a | 16.8±1.3 | 42.1±10.4 | 151.69±6.42a | 87±3 | 26.34±0.16cd |
| W3 | Pg+9TQ+11HJX− | 81.3±1.5 | 110.0±3.1ab | 21.45±0.28a | 15.8±0.8 | 47.8±8.0 | 150.79±12.15a | 88±4 | 27.41±0.15ab |
| W4 | Pg−9TQ+11HJX− | 81.5±0.5 | 114.3±2.0ab | 20.39±0.20b | 15.8±1.8 | 43.9±7.9 | 134.86±8.07ab | 88±3 | 27.36±0.13ab |
| W5 | Pg+9TQ-11HJX+ | 81.7±1.0 | 110.4±2.2ab | 19.86±0.12b | 15.6±0.4 | 43.1±5.1 | 135.33±1.29ab | 89±1 | 26.73±0.26bc |
| W6 | Pg−9TQ−11HJX+ | 80.7±0.8 | 108.2±1.0b | 20.33±0.30b | 15.5±0.8 | 44.9±2.3 | 135.47±3.16ab | 90±3 | 27.91±0.52a |
| W7 | Pg+9TQ−11HJX− | 82.5±2.2 | 108.5±3.0b | 21.41±0.39a | 16.1±0.2 | 49.7±4.2 | 149.50±1.88a | 88±1 | 25.92±0.13d |
| W8 | Pg−9TQ−11HJX− | 82.8±0.3 | 109.3±2.6ab | 20.14±0.07b | 16.0±0.2 | 44.5±0.9 | 132.06±1.52b | 88±5 | 26.80±0.08bc |
| 编号 No. | 类型 Genotype | 峰值黏度 Peak viscosity /cP | 热浆黏度 Hot paste viscosity /cP | 崩解值 Breakdown /cP | 终值黏度 Final viscosity /cP | 回复值 Setback /cP | 糊化温度 Gelatinization temperature /℃ | 胶稠度 Gel consistency /mm | 直链淀粉 含量Amylose /% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W1 | Pg+9TQ+11HJX+ | 2967.1±29.4 | 1401.3±75.2 | 1565.8±102.5 | 1931.6±20.6 | −1035.5±15.6 | 12.6±0.1 | 84.3±0.7 | 70.7±0.1 | |
| W2 | Pg−9TQ+11HJX+ | 2984.6±88.6 | 1362.7±107 | 1622.0±191.9 | 1902.0±80.2 | −1082.6±165.1 | 12.9±0.4 | 85.1±2.1 | 70.7±0.1 | |
| W3 | Pg+9TQ+11HJX− | 2978.8±44.7 | 1317.3±64.8 | 1661.5±66.9 | 1891.6±41.5 | −1087.1±66.1 | 13.0±0.1 | 83.5±0.8 | 70.6±0.1 | |
| W4 | Pg-9TQ+11HJX− | 3053.6±93.8 | 1356.7±83.5 | 1697.0±28.4 | 1959.5±52.2 | −1094.1±69.5 | 13.1±0.2 | 82.6±0.3 | 70.8±0.1 | |
| W5 | Pg+9TQ−11HJX+ | 2982.1±58.5 | 1448.3±40.7 | 1533.8±99.1 | 1951.3±20.5 | −1030.8±60.6 | 12.8±0.4 | 82.6±1.5 | 70.7±0.2 | |
| W6 | Pg−9TQ−11HJX+ | 3005.6±145.0 | 1500.3±2.8 | 1505.3±146.5 | 1976.5±128.6 | −1029.1±38.2 | 13.1±0.6 | 82.5±1.0 | 70.6±0.1 | |
| W7 | Pg+9TQ−11HJX− | 2943.1±97.2 | 1495.5±152 | 1447.6±236.6 | 1888.5±114.1 | −1054.6±33.1 | 13.3±0.1 | 83.3±1.1 | 70.7±0.1 | |
| W8 | Pg−9TQ−11HJX− | 2998.1±10.7 | 1499.5±63.3 | 1498.6±73.9 | 1952.6±8.3 | −1045.5±13.7 | 12.7±0.1 | 84.2±1.7 | 70.5±0.1 | |
表4 8种基因型株系的品质性状比较
Table 4. Comparison of the quality traits of eight lines harboring different resistance genes.
| 编号 No. | 类型 Genotype | 峰值黏度 Peak viscosity /cP | 热浆黏度 Hot paste viscosity /cP | 崩解值 Breakdown /cP | 终值黏度 Final viscosity /cP | 回复值 Setback /cP | 糊化温度 Gelatinization temperature /℃ | 胶稠度 Gel consistency /mm | 直链淀粉 含量Amylose /% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W1 | Pg+9TQ+11HJX+ | 2967.1±29.4 | 1401.3±75.2 | 1565.8±102.5 | 1931.6±20.6 | −1035.5±15.6 | 12.6±0.1 | 84.3±0.7 | 70.7±0.1 | |
| W2 | Pg−9TQ+11HJX+ | 2984.6±88.6 | 1362.7±107 | 1622.0±191.9 | 1902.0±80.2 | −1082.6±165.1 | 12.9±0.4 | 85.1±2.1 | 70.7±0.1 | |
| W3 | Pg+9TQ+11HJX− | 2978.8±44.7 | 1317.3±64.8 | 1661.5±66.9 | 1891.6±41.5 | −1087.1±66.1 | 13.0±0.1 | 83.5±0.8 | 70.6±0.1 | |
| W4 | Pg-9TQ+11HJX− | 3053.6±93.8 | 1356.7±83.5 | 1697.0±28.4 | 1959.5±52.2 | −1094.1±69.5 | 13.1±0.2 | 82.6±0.3 | 70.8±0.1 | |
| W5 | Pg+9TQ−11HJX+ | 2982.1±58.5 | 1448.3±40.7 | 1533.8±99.1 | 1951.3±20.5 | −1030.8±60.6 | 12.8±0.4 | 82.6±1.5 | 70.7±0.2 | |
| W6 | Pg−9TQ−11HJX+ | 3005.6±145.0 | 1500.3±2.8 | 1505.3±146.5 | 1976.5±128.6 | −1029.1±38.2 | 13.1±0.6 | 82.5±1.0 | 70.6±0.1 | |
| W7 | Pg+9TQ−11HJX− | 2943.1±97.2 | 1495.5±152 | 1447.6±236.6 | 1888.5±114.1 | −1054.6±33.1 | 13.3±0.1 | 83.3±1.1 | 70.7±0.1 | |
| W8 | Pg−9TQ−11HJX− | 2998.1±10.7 | 1499.5±63.3 | 1498.6±73.9 | 1952.6±8.3 | −1045.5±13.7 | 12.7±0.1 | 84.2±1.7 | 70.5±0.1 | |
| [1] |
Skamnioti P, Gurr S J. Against the grain: Safeguarding rice from rice blast disease[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2009, 27(3): 141-150.
PMID |
| [2] | 何峰, 张浩, 刘金灵, 王志龙, 王国梁. 水稻抗稻瘟病天然免疫机制及抗病育种新策略[J]. 遗传, 2014, 36(8): 756-765. |
| Heng F, Zhang H, Liu J L, Wang Z L, Wang G L. Recent advances in understanding the innate immune mechanisms and developing new disease resistance breeding strategies against the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae in rice[J]. Heraditas(Beijing), 2014, 36(8): 756-765. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | Zheng A P, Lin R M, Zhang D H, Qin P G, Xu L Z, Ai P, Ding L, Wang Y R, Chen Y, Liu Y, Sun Z G, Feng H T, Liang X X, Fu R T, Tang C Q, Li Q, Zhang J, Xie Z L, Wang L X, Liu H N, Li P. The evolution and pathogenic mechanisms of the rice sheath blight pathogen[J]. Nature Communications, 2013, 4(1424): 1-10. |
| [4] | Lee N F, Rush M C. Rice sheath blight: A major rice disease[J]. Plant Disease, 1983, 6(7): 829-832. |
| [5] | Wang B H, Daniel J, Ebbole W Z, Wang Z H. The arms race between Magnaporthe oryzae and rice: Diversity and interaction of Avr and R genes[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2017, 16(12): 2746-2760. |
| [6] | Chen S, Wang L, Que Z Q, Pan R Q. Genetic and physical mapping of pi37(t), a new gene conferring resistance to rice blast[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2005, 111(8): 1563-1570. |
| [7] |
Wang Z X, Yano M, Yamanouchi U, Iwamoto M, Monna L, Hayasaka H, Katayose Y, Sasaki T. The Pib gene for rice blast resistance belongs to the nucleotide binding and leucine-rich repeat class of plant disease resistance genes[J]. Plant Journal, 1999, 19(1): 55-64.
PMID |
| [8] |
Zhou B, Qu S, Liu G, Dolan M, Sakai H, Lu G D, Bellizzi M, Wang G L. The eight amino-acid differences within three leucine-rich repeats between Pi2 and Piz-t resistance proteins determine the resistance specificity to Magnaporthe grisea[J]. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 2006, 19(11): 1216-1228.
PMID |
| [9] |
Ashikawa I, Hayashi N, Yamane H, Kanamori H, Wu J Z, Matsumoto T, Ono K, Yano M. Two adjacent nucleotide-binding site-leucine-rich repeat class genes are required to confer Pikm-specific rice blast resistance[J]. Genetics, 2008, 180(4): 2267-2276.
PMID |
| [10] |
Deng Y, Zhai K, Xie Z, Deng Y W, Zhai K R, Xie Z, Yang D Y, Zhu X D, Liu J Z, Wang X, Qin P, Yang Y Z, Zhang G M, Li Q, Zhang J F, Wu S Q, Milazzo J, Mao B Z, He Z H. Epigenetic regulation of antagonistic receptors confers rice blast resistance with yield balance[J]. Science, 2017, 355(6328): 962-965.
PMID |
| [11] |
Bryan G T, Wu K S, Farrall L, Jia Y L, Hershey H, McAdams S, Faulk K, Donaldson G, Tarchini R, Valent B. A single amino acid difference distinguishes resistant and susceptible alleles of the rice blast resistance gene Pi-ta[J]. Plant Cell, 2000, 12(11): 2033-2045.
PMID |
| [12] | Rama Devi S J S, Singh K, Umakanth B, Vishalakshi B, Renu P, Sudhakar K V, Prasad M S, Viraktamath B C, Babu V R, Madhav M S. Development and identification of novel rice blast resistant sources and their characterization using molecular markers[J]. Rice Science, 2015, 22(6): 300-308. |
| [13] | 田红刚, 陈红旗, 胡江, 雷财林, 朱旭东, 钱前. 抗稻瘟病基因Pigm导入对寒地粳稻抗病性和产量性状的影响[J]. 沈阳农业大学学报, 2016, 47(5): 520-526. |
| Tian H G, Chen H Q, Hu J, Lei C L, Zhu X D, Qian Q. Effect of introgressed Pigm gene on rice blast resistance and yield traits of japonica rice in cold area[J]. Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University, 2016, 47(5): 520-526. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | 张礼霞, 王林友, 范宏环, 王建军. 利用Pigm基因改良粳稻保持系的稻瘟病抗性研究[J]. 核农学报, 2017, 31(3): 424-431. |
| Zhang L X, Wang L Y, Fan H H, Wang J J. Improvement of rice blast resistance of japonica rice maintainer lines using gene Pigm[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 31(3): 424-431. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 杨平, 邹国兴, 陈春莲, 黄永萍, 兰波, 熊运华, 尹建华. 利用分子标记辅助选择改良春恢350稻瘟病抗性[J]. 分子植物育种, 2015, 13(4): 741-747. |
| Yang P, Zou G X, Chen C L, Huang Y P, Lan B, Xiong Y H, Yin J H. Improvement of rice blast resistance of Chunhui 350 by using molecular-marker assisted selection[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2015, 13(4): 741-747. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 陈涛, 孙旭超, 张善磊, 梁文化, 周丽慧, 赵庆勇, 姚姝, 赵凌, 赵春芳, 朱镇, 张亚东, 王才林. 稻瘟病广谱抗性基因Pigm特异性分子标记的开发和应用[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(1): 28-36. |
| Chen T, Sun X C, Zhang S L, Liang W H, Zhou L H, Zhao Q Y, Yao S, Zhao L, Zhao C F, Zhu Z, Zhang Y D, Wang C L. Development and verification of specific molecular markers for Pigm gene associated with broad-spectrum resistance to rice blast[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2020, 34(1): 28-36. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | Zou J H, Pan X B, Chen Z X, Xu J Y, Lu J F, Zhai W X, Zhu L H. Mapping quantitative trait loci controlling sheath blight resistance in two rice cultivars[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2000, 101(4): 569-573. |
| [18] | Pinson S R M, Capdevielle F M, Oard J H. Blight resistance in rice using recombinant inbred lines[J]. Crop Science, 2005, 45(2): 503-510. |
| [19] |
Li Z, Pinson S R M, Marchetti M A, Stansel J W, Park W D. Characterization of quantitative trait loci (QTLs) in cultivated rice contributing to field resistance to sheath blight (Rhizoctonia solani)[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 1995, 91(2): 382-388.
PMID |
| [20] | 潘学彪, Rush M C. 美国的水稻纹枯病抗病遗传育种研究[J]. 江苏农学院学报, 1997, 18(1): 57-63. |
| Pan X B, Rush M C. Studies in the U.S. on genetics and breeding of resistance to rice sheath blight[J]. Journal of Jiangsu Agricultural College, 1997, 18(1): 57-63. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | 左示敏, 张亚芳, 陈宗祥, 陈夕军, 潘学彪. 水稻抗纹枯病遗传育种研究进展[J]. 中国科学:生命科学, 2013, 40(11): 1014-1023. |
| Zuo S M, Zhang Y F, Chen Z X, Chen X J, Pan X B. Current progress on genetics and breeding in resistance to rice sheath blight[J]. Science China: Life Sciences, 2010, 40(11): 1014-1023. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | 陈宗祥, 邹军煌, 徐敬友, 童蕴慧, 汤述翥, 王子斌, 蒋日民, 凌兵, 唐进, 潘学彪. 对水稻纹枯病抗源的初步研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2000, 14(1): 15-18. |
| Chen Z X, Zou J H, Xu J Y, Tong Y H, Tang S Z, Wang Z B, Jiang Y M, Ling B, Tang J, Pan X B. A preliminary study on resources of resistance to rice sheath blight[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2000, 14(1): 15-18. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 殷跃军, 左示敏, 王辉, 张亚芳, 陈宗祥, 马玉银, 顾世梁, 潘学彪. 抗水稻纹枯病qSB-9Tq基因效应及作用方式分析[J]. 作物学报, 2009, 35(2): 279-285. |
| Yin Y J, Zuo S M, Wang H, Zhang Y F, Chen Z X, Ma Y Y, Gu S L, Pan X B. Effect and action analysis of qSB-9Tq conferring resistance to rice sheath blight[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2009, 35(2): 279-285. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | Zhu Y J, Zuo S M, Chen Z X, Chen X G, Li G, Zhang Y F. Identification of two major rice sheath blight resistance QTLs, qSB1-1HJX74 and qSB11HJX74, in field trials using chromosome segment substitution lines[J]. Plant Disease, 2014, 98(8): 1112-1121. |
| [25] | 王才林, 张亚东, 朱镇, 姚姝, 赵庆勇, 陈涛, 周丽慧, 赵凌. 优良食味粳稻新品种南粳9108的选育与利用[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2013, 41(9): 86-88. |
| Wang C L, Zhang Y D, Zhu Z, Yao S, Zhao Q Y, Chen T, Zhou L H, Zhao L. Breeding and utilization of a new japonica rice variety Nanjing 9108 with good taste[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2013, 41(9): 86-88. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | 张亚东, 姚姝, 陈涛, 王军, 朱镇, 赵庆勇, 周丽慧, 赵凌, 赵春芳, 路凯, 梁文化, 王才林. 聚合Wx-mp、fgr和Pi-ta、Pi-b基因选育优质粳稻新品种[J]. 分子植物育种, 2021, https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1068.S.20210709.1328.025.html |
| Zhang Y D, Yao S, Chen T, Wang J, Zhu Z, Zhao Q Y, Zhou L H, Zhao L, Zhao C F, Lu K, Liang W H, Wang C L. Pyramiding Wx-mp, fgr and Pi-ta, Pi-b genes by marker-assisted selection in new japonica rice varieties with good quality[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2021. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1068.S.20210709.1328.025.html (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | 李明友, 王嘉楠, 王广达, 冯志明, 叶英豪, 姜伟, 左天, 张亚芳, 陈夕军, 潘学彪. 抗纹枯病数量性状基因qSB-11HJX及qSB-9TQ改良粳稻品种的抗性研究[J]. 扬州大学学报: 农业与生命科学版, 2019, 40(6): 1-7. |
| Li M Y, Wang J N, Wang G D, Feng Z M, Ye Y H, Jiang W, Zuo T, Zhang Y F, Chen X J, Pan X B. Improvement of japonica rice resistance to sheath blight disease by incorporating quantitative resistance genes qSB-11HJX and qSB-9TQ[J]. Journal of Yangzhou University: Agricultural and Life Science Edition, 2019, 40(6): 1-7. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | 贺闽, 尹俊杰, 冯志明, 朱孝波, 赵剑华, 左示敏, 陈学伟. 水稻稻瘟病和纹枯病抗性鉴定方法[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(5): 577-587. |
| He M, Yin J J, Feng Z M, Zhu X B, Zhao J H, Zuo S M, Chen X W. Identification methods of resistance to rice blast and sheath blight[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55(5): 577-587. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | 王小秋. 江苏粳稻抗稻瘟病基因应用与稻瘟菌多样性分析[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2020. |
| Wang X Q. Research on blast resistance genes utilized in japonica rice and analysis of blast isolates diversity in Jiangsu Province[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | 左示敏, 张亚芳, 殷跃军, 陈宗祥, 潘学彪. 田间水稻纹枯病抗性鉴定体系的确立与完善[J]. 扬州大学学报:农业与生命科学版, 2006, 27(4): 57-61. |
| Zuo S M, Zhang Y F, Yin Y J, Chen Z X, Pan X B. Establishment and improvement of inoculation technique and rating system in researching rice sheath blight resistance in field[J]. Journal of Yangzhou University: Agricultural and Life Science Edition, 2006, 27(4): 57-61. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | 朱大伟. 三种关键栽培措施对软米粳稻产量与品质的影响[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2018. |
| Zhu D W. Effect of three key cultivation measures on yield and quality of japonica soft rice[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [32] |
Liu Y, Chen L, Fu D, Lou Q J, Mei H W, Xiong L, Li M S, Xu X Y, Mei X H, Luo L J. Dissection of additive, epistatic effect and QTL × environment interaction of quantitative trait loci for sheath blight resistance in rice[J]. Hereditas, 2014, 151(2-3): 28-37.
PMID |
| [33] | Eizenga G C, Prasad B, Jackson A K, Jia M H. Identification of rice sheath blight and blast quantitative trait loci in two different O. sativa/O. nivara advanced backcross populations[J]. Molecular Breeding, 2013, 31(4): 889-907. |
| [34] | 陈宗祥, 冯志明, 王龙平, 冯凡, 张亚芳, 马玉银, 潘学彪, 左示敏. 水稻分蘖角基因TAC1的育种应用价值分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(6): 590-598. |
| Chen Z X, Feng Z M, Wang L P, Feng F, Zhang Y F, Ma Y Y, Pan X B, Zuo S M. Breeding potential of rice TAC1 gene for tiller angle[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2017, 31(6): 590-598. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [2] | 丁正权, 潘月云, 施扬, 黄海祥. 基于基因芯片的嘉禾系列长粒优质食味粳稻综合评价与比较[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 397-408. |
| [3] | 景秀, 周苗, 王晶, 王岩, 王旺, 王开, 郭保卫, 胡雅杰, 邢志鹏, 许轲, 张洪程. 穗分化末期-灌浆初期干旱胁迫对优质食味粳稻根系形态和叶片光合特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(1): 33-47. |
| [4] | 童琪, 王春燕, 阙亚伟, 肖宇, 王政逸. 稻瘟病菌热激蛋白(HSP)40编码基因MoMHF6的鉴定及功能研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(6): 563-576. |
| [5] | 冯爱卿, 汪聪颖, 苏菁, 封金奇, 陈凯玲, 林晓鹏, 陈炳, 梁美玲, 杨健源, 朱小源, 陈深. 水稻细菌性条斑病抗性新品系的创制及其农艺性状分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(6): 587-596. |
| [6] | 陈明亮, 熊文涛, 沈雨民, 熊焕金, 罗世友, 吴小燕, 胡兰香, 肖叶青. 广谱抗稻瘟病水稻保持系赣香B的抗性遗传解析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(5): 470-477. |
| [7] | 李刚, 高清松, 李伟, 张雯霞, 王健, 程保山, 王迪, 高浩, 徐卫军, 陈红旗, 纪剑辉. 定向敲除SD1基因提高水稻的抗倒性和稻瘟病抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(4): 359-367. |
| [8] | 黄亚茹, 徐鹏, 王乐乐, 贺一哲, 王辉, 柯健, 何海兵, 武立权, 尤翠翠. 外源海藻糖对粳稻品系W1844籽粒灌浆特性及产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(4): 379-391. |
| [9] | 姚姝, 赵春芳, 陈涛, 路凯, 周丽慧, 赵凌, 朱镇, 赵庆勇, 梁文化, 赫磊, 王才林, 张亚东. 低谷蛋白半糯型粳稻营养品质与蒸煮食味品质特征分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(2): 178-188. |
| [10] | 裴峰, 王广达, 高鹏, 冯志明, 胡珂鸣, 陈宗祥, 陈红旗, 崔傲, 左示敏. 敲除OsNramp5基因创制低镉优质粳稻新材料的应用评价[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(1): 16-28. |
| [11] | 陈涛, 赵庆勇, 朱镇, 赵凌, 姚姝, 周丽慧, 赵春芳, 张亚东, 王才林. 利用分子标记辅助选择培育优良食味、低谷蛋白香粳稻新品系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(1): 55-65. |
| [12] | 周永林, 申小磊, 周立帅, 林巧霞, 王朝露, 陈静, 冯慧捷, 张振文, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsLOX10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(4): 348-356. |
| [13] | 陈奕璇, 覃贵亮, 周晓欣, 黄军军, 蒙全, 吴俊辉, 闫晓静, 袁会珠. 不同植保机械喷施雾滴在水稻冠层沉积分布规律及对病虫害防效比较[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(2): 207-214. |
| [14] | 曹煜东, 肖湘谊, 叶乃忠, 丁晓雯, 易晓璇, 刘金灵, 肖应辉. 生长素调控因子OsGRF4协同调控水稻粒形和稻瘟病抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(6): 629-638. |
| [15] | 冯志明, 王广达, 赵剑华, 居冉, 李梦臣, 高鹏, 胡珂鸣, 陈宗祥, 左示敏. 水稻富含半胱氨酸类受体激酶家族基因对纹枯病菌和植物激素的响应特征分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(5): 439-448. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||