
中国水稻科学 ›› 2023, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (2): 113-124.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2023.220314
• 研究报告 • 下一篇
廉院训1,2,#, 韦子芸1,2,#, 张强2, 李清2, 任德勇2, 胡江2, 朱丽2, 高振宇2, 张光恒2, 郭龙彪2, 曾大力2, 钱前2,*( ), 沈兰2,*(
), 沈兰2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-03-28
修回日期:2022-05-09
出版日期:2023-03-10
发布日期:2023-03-10
通讯作者:
钱前,沈兰
作者简介:第一联系人:#共同第一作者
基金资助:
LIAN Yuanxun1,2,#, WEI Ziyun1,2,#, ZHANG Qiang2, LI Qing2, REN Deyong2, HU Jiang2, ZHU Li2, GAO Zhenyu2, ZHANG Guangheng2, GUO Longbiao2, ZENG Dali2, QIAN Qian2,*( ), SHEN Lan2,*(
), SHEN Lan2,*( )
)
Received:2022-03-28
Revised:2022-05-09
Online:2023-03-10
Published:2023-03-10
Contact:
QIAN Qian, SHEN Lan
About author:First author contact:#These authors contributed equally to this work
摘要:
【目的】斑马叶突变体作为水稻叶色突变体的重要种质资源,是研究植物光合作用机制和高光效育种的理想材料,对于解析光合作用机理和提高水稻产量具有重要意义。【方法】用甲基磺酸乙酯(EMS)诱变粳稻品种春江06建立突变体库,从突变体库中筛选到1份苗期为斑马叶的突变体,该突变体被命名为zl7 (zebra leaf 7)。在常规大田种植条件下分别比较突变体与野生型在苗期、抽穗期和成熟期叶色表型和产量性状差异,通过透射电镜实验分析叶片叶绿体发育情况,利用图位克隆方法克隆候选基因,利用荧光定量PCR 方法分析参与叶绿素合成和叶绿体发育相关基因的表达水平。【结果】从苗期开始,突变体zl7表现出典型的斑马叶,叶绿素含量降低,直到抽穗期,斑马叶表型消失,叶片逐渐复绿,叶绿素含量无明显差异。光合速率测定和电镜观察结果显示,突变体zl7的光合速率、气孔导度下降,叶绿体发育异常。与野生型相比,突变体的株高、分蘖、穗长、一次枝梗、二次枝梗和每穗粒数均显著降低,而粒长、粒宽和千粒重均略有增加。荧光定量PCR结果表明突变体中参与叶绿素降解相关基因的表达量显著升高,而参与叶绿素合成和叶绿体发育相关基因的表达量显著降低。遗传分析表明,该突变体受一对隐性核基因调控。通过图位克隆将该基因定位在第7染色体,测序发现突变体的目标基因ZL7编码区发生单碱基替换,导致一个氨基酸由丝氨酸变为天冬酰胺。【结论】ZL7 (Zebra Leaf 7)突变导致叶绿体发育异常,水稻叶片出现斑马叶表型,该基因在叶绿素合成及叶绿体发育中起重要作用。
廉院训, 韦子芸, 张强, 李清, 任德勇, 胡江, 朱丽, 高振宇, 张光恒, 郭龙彪, 曾大力, 钱前, 沈兰. 水稻斑马叶突变体zl7的鉴定与基因的精细定位[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(2): 113-124.
LIAN Yuanxun, WEI Ziyun, ZHANG Qiang, LI Qing, REN Deyong, HU Jiang, ZHU Li, GAO Zhenyu, ZHANG Guangheng, GUO Longbiao, ZENG Dali, QIAN Qian, SHEN Lan. Identification and Gene Mapping of a Zebra Leaf Mutant zl7 in Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(2): 113-124.
| 标记 Marker | 正向引物序列 Forward primer sequence | 反向引物序列 Reverse primer sequence |
|---|---|---|
| M1 | GTCCATGCATCCATCTCTAG | ACGGAAGGAATACGTCTGTA |
| M2 | TGTGGACAACCTCAACTGAAAGC | CATAATCACCAACATCGGAGAAGC |
| M3 | TGTTGAGCTAGAAGAGAGGGG | TGAACACAAAAGGATGCGCT |
| M4 | CCAAGTCTTAAGCTACCCCT | CGCAGGGCTTAATAGAATAC |
| M5 | GATAGAGCGAGTGAGCAAAC | CCTACCAATTCAACTCCAAC |
| M6 | TGGATTGAGGATCAGGATAG | TCTGGAATTTTCCCTAATGA |
| M7 | GAAATCAGTCAGAAAGACCG | CCATCTTCTCACTGTGGAGT |
| M8 | GCCCTAATTGCTCCAGGTCT | AATTCTAGCAGTGTTCCATTGTG |
| M9 | TTCTTCCATGTAGCAAGCATT | CCTACTGCCTGCCAAATCTAT |
表1 基因定位所用引物及序列
Table 1. Primers and sequences used in gene mapping.
| 标记 Marker | 正向引物序列 Forward primer sequence | 反向引物序列 Reverse primer sequence |
|---|---|---|
| M1 | GTCCATGCATCCATCTCTAG | ACGGAAGGAATACGTCTGTA |
| M2 | TGTGGACAACCTCAACTGAAAGC | CATAATCACCAACATCGGAGAAGC |
| M3 | TGTTGAGCTAGAAGAGAGGGG | TGAACACAAAAGGATGCGCT |
| M4 | CCAAGTCTTAAGCTACCCCT | CGCAGGGCTTAATAGAATAC |
| M5 | GATAGAGCGAGTGAGCAAAC | CCTACCAATTCAACTCCAAC |
| M6 | TGGATTGAGGATCAGGATAG | TCTGGAATTTTCCCTAATGA |
| M7 | GAAATCAGTCAGAAAGACCG | CCATCTTCTCACTGTGGAGT |
| M8 | GCCCTAATTGCTCCAGGTCT | AATTCTAGCAGTGTTCCATTGTG |
| M9 | TTCTTCCATGTAGCAAGCATT | CCTACTGCCTGCCAAATCTAT |
| 基因 Gene | 基因登录号 Gene ID | 定量正向引物序列 Forward primer sequence | 定量反向引物序列 Reverse primer sequence | 功能 Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NYC1 | LOC_Os01g12710 | CATGCAACACCAACAAAAGG | GACCATTCCAGGAGAAGCAG | 叶绿素b还原酶基因 |
| NOL | LOC_Os03g45194 | CCACGAAAGGTATAGGATATG | TCAAGTCAGTCACCGCAGAT | 叶绿素b还原酶基因 |
| NYC3 | LOC_Os06g24730 | TCTATCTAGGTGCCAAAGGC | ATTCTGGCACCTGCTGTTTC | α/β折叠水解酶家族蛋白 |
| PAO | LOC_Os03g05310 | AAGCCTCCGATGTTACCGAA | CGAGGGTTTCCAGAATTTGA | 脱镁叶绿酸a加氧酶,叶绿体前体 |
| SGR | LOC_Os09g36200 | GCAATGTCGCCAAATGACG | GCTCACCACACTCATTCCCTAAAG | 镁离子去螯合酶 |
| RCCR1 | LOC_Os10g25020 | GGATCGACGATTGATTTCATG | GTCGAGGCGTTCAGAAAGAT | 红色叶绿素分解代谢还原酶 |
| RCCR2 | LOC_Os10g25040 | TGGCGAGGGACAGGAAGGT | GGATGTGGTGGCGAGAGAAAC | 红色叶绿素分解代谢还原酶 |
| LchP2 | LOC_Os09g17740 | GAAGAAGATCAAGAACGGCC | TTGCCGGGGACGAAGTTGGT | 捕光叶绿素a/b结合蛋白基因 |
| PsbA | LOC_Os12g19580 | AGAGACGCGAAAGTACAAGC | AAGTTGCGGTCAATAAGGTA | 光合反应中心蛋白 |
| RpoC2 | LOC_Os04g16830 | ATGCATCGCAGGTACACCAA | CCCTCGCGTAAATTGCTTTG | DNA定向RNA聚合酶亚单位β |
| Rps15 | LOC_Os12g10580 | AGATACGGAGACTTGCTTCA | GCTCCCTAATATCCAACTGACT | 核酮糖二磷酸羧化酶大链前体 |
| V1 | LOC_Os03g45400 | AGAATCAGCGCGAGAAGAGAACCT | TACACCAGCTTTGGAGGAGCTGAA | 质体蛋白 |
| V2 | LOC_Os03g20460 | AGCAGATCCGTGATTACATGGCGA | TGCCTCTTCACTCTCTGCAACCAA | 鸟苷酸激酶 |
| YGL8 | LOC_Os01g17170 | TGGATCTAACATGACACGCACCCA | ACTGTAACGGCATTCTTCTCCGGT | 镁原卟啉IX单酯环化酶的催化亚基 |
| CAO1 | LOC_Os10g41780 | TTGGCTCAGTTAATGAGGGCAGAATCC | GGATGCGCACGTTGAGCATCTTTGTGG | 叶绿素a加氧酶 |
| PORA | LOC_Os04g58200 | ATGGCTCTCCAAGTTCAG | TGGCTCACGCTAAGGAAC | NADPH:原叶绿素酸酯氧化还原酶A |
| PORB | LOC_Os10g35370 | CCGCAAGGAGGGAGCGGTG | CCCTCTTGGTGCTAAGGCCG | 原叶绿素酸酯氧化还原酶B |
| CHLH | LOC_Os03g20700 | GCACGGGAACTTGGCGTTTCATTA | ACATGTCCTGGAGCTGCTTCTCAT | 镁离子螯合酶H亚基 |
| CHLD | LOC_Os03g59640 | TAGCACAGCTGTCAGAGTGGGTTT | TTGCCAGCCACCTCAAGTATCTCA | 镁离子螯合酶D亚基 |
| CHLI | LOC_Os03g36540 | AGGGATGCTGAACTCAGGGTGAAA | AAGTAGGACTCACGGAACGCCTTT | 镁离子螯合酶I亚基 |
| DVR | LOC_Os03g22780 | AGCCCAGGTTCATCAAGGT | TGATCACCCTCTCGAAGAACT | 联乙烯还原酶基因 |
| OsCHLM | LOC_Os06g04150 | GCTTCATCTCCACGCAGTTCTACT | GCAATGACGAATCGAAGACGCACA | 镁原卟啉O-甲基转移酶 |
| YGL1 | LOC_Os05g28200 | CCAGCCACTGATGAAAGCAGCAAT | AGAGCGCTAATACACTCGCGAACA | 叶绿素合成酶 |
| OsHEMA1 | LOC_Os10g35840 | GATGCAATCACTGCTGGAAAGCGT | CCATCTTGCCAGCACCAATCAACA | 莽草酸/奎宁酸5-脱氢酶 |
| OsHEML | LOC_Os08g41990 | AGAACAAAGGGCAGATTGCTGCTG | TGTTTCGTCAAGTCACGGAGAGCA | 转氨酶 |
| OsHEMB | LOC_Os06g49110 | TGGCATTGTCAGGGAAGATGGAGT | CCAAAGCAGCACGTATTGCTCCAA | δ-氨基乙酰丙酸脱水酶,叶绿体前体 |
| GUN4 | LOC_Os11g16550 | AAGGGAAGGAGAGGCCAAAGTTCA | ACCATGACCAGCATCTCTGCATCA | 镁离子螯合酶H亚基结合蛋白 |
表2 qRT-PCR所用基因及引物序列
Table 2. Genes and primer sequences used in qRT-PCR.
| 基因 Gene | 基因登录号 Gene ID | 定量正向引物序列 Forward primer sequence | 定量反向引物序列 Reverse primer sequence | 功能 Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NYC1 | LOC_Os01g12710 | CATGCAACACCAACAAAAGG | GACCATTCCAGGAGAAGCAG | 叶绿素b还原酶基因 |
| NOL | LOC_Os03g45194 | CCACGAAAGGTATAGGATATG | TCAAGTCAGTCACCGCAGAT | 叶绿素b还原酶基因 |
| NYC3 | LOC_Os06g24730 | TCTATCTAGGTGCCAAAGGC | ATTCTGGCACCTGCTGTTTC | α/β折叠水解酶家族蛋白 |
| PAO | LOC_Os03g05310 | AAGCCTCCGATGTTACCGAA | CGAGGGTTTCCAGAATTTGA | 脱镁叶绿酸a加氧酶,叶绿体前体 |
| SGR | LOC_Os09g36200 | GCAATGTCGCCAAATGACG | GCTCACCACACTCATTCCCTAAAG | 镁离子去螯合酶 |
| RCCR1 | LOC_Os10g25020 | GGATCGACGATTGATTTCATG | GTCGAGGCGTTCAGAAAGAT | 红色叶绿素分解代谢还原酶 |
| RCCR2 | LOC_Os10g25040 | TGGCGAGGGACAGGAAGGT | GGATGTGGTGGCGAGAGAAAC | 红色叶绿素分解代谢还原酶 |
| LchP2 | LOC_Os09g17740 | GAAGAAGATCAAGAACGGCC | TTGCCGGGGACGAAGTTGGT | 捕光叶绿素a/b结合蛋白基因 |
| PsbA | LOC_Os12g19580 | AGAGACGCGAAAGTACAAGC | AAGTTGCGGTCAATAAGGTA | 光合反应中心蛋白 |
| RpoC2 | LOC_Os04g16830 | ATGCATCGCAGGTACACCAA | CCCTCGCGTAAATTGCTTTG | DNA定向RNA聚合酶亚单位β |
| Rps15 | LOC_Os12g10580 | AGATACGGAGACTTGCTTCA | GCTCCCTAATATCCAACTGACT | 核酮糖二磷酸羧化酶大链前体 |
| V1 | LOC_Os03g45400 | AGAATCAGCGCGAGAAGAGAACCT | TACACCAGCTTTGGAGGAGCTGAA | 质体蛋白 |
| V2 | LOC_Os03g20460 | AGCAGATCCGTGATTACATGGCGA | TGCCTCTTCACTCTCTGCAACCAA | 鸟苷酸激酶 |
| YGL8 | LOC_Os01g17170 | TGGATCTAACATGACACGCACCCA | ACTGTAACGGCATTCTTCTCCGGT | 镁原卟啉IX单酯环化酶的催化亚基 |
| CAO1 | LOC_Os10g41780 | TTGGCTCAGTTAATGAGGGCAGAATCC | GGATGCGCACGTTGAGCATCTTTGTGG | 叶绿素a加氧酶 |
| PORA | LOC_Os04g58200 | ATGGCTCTCCAAGTTCAG | TGGCTCACGCTAAGGAAC | NADPH:原叶绿素酸酯氧化还原酶A |
| PORB | LOC_Os10g35370 | CCGCAAGGAGGGAGCGGTG | CCCTCTTGGTGCTAAGGCCG | 原叶绿素酸酯氧化还原酶B |
| CHLH | LOC_Os03g20700 | GCACGGGAACTTGGCGTTTCATTA | ACATGTCCTGGAGCTGCTTCTCAT | 镁离子螯合酶H亚基 |
| CHLD | LOC_Os03g59640 | TAGCACAGCTGTCAGAGTGGGTTT | TTGCCAGCCACCTCAAGTATCTCA | 镁离子螯合酶D亚基 |
| CHLI | LOC_Os03g36540 | AGGGATGCTGAACTCAGGGTGAAA | AAGTAGGACTCACGGAACGCCTTT | 镁离子螯合酶I亚基 |
| DVR | LOC_Os03g22780 | AGCCCAGGTTCATCAAGGT | TGATCACCCTCTCGAAGAACT | 联乙烯还原酶基因 |
| OsCHLM | LOC_Os06g04150 | GCTTCATCTCCACGCAGTTCTACT | GCAATGACGAATCGAAGACGCACA | 镁原卟啉O-甲基转移酶 |
| YGL1 | LOC_Os05g28200 | CCAGCCACTGATGAAAGCAGCAAT | AGAGCGCTAATACACTCGCGAACA | 叶绿素合成酶 |
| OsHEMA1 | LOC_Os10g35840 | GATGCAATCACTGCTGGAAAGCGT | CCATCTTGCCAGCACCAATCAACA | 莽草酸/奎宁酸5-脱氢酶 |
| OsHEML | LOC_Os08g41990 | AGAACAAAGGGCAGATTGCTGCTG | TGTTTCGTCAAGTCACGGAGAGCA | 转氨酶 |
| OsHEMB | LOC_Os06g49110 | TGGCATTGTCAGGGAAGATGGAGT | CCAAAGCAGCACGTATTGCTCCAA | δ-氨基乙酰丙酸脱水酶,叶绿体前体 |
| GUN4 | LOC_Os11g16550 | AAGGGAAGGAGAGGCCAAAGTTCA | ACCATGACCAGCATCTCTGCATCA | 镁离子螯合酶H亚基结合蛋白 |
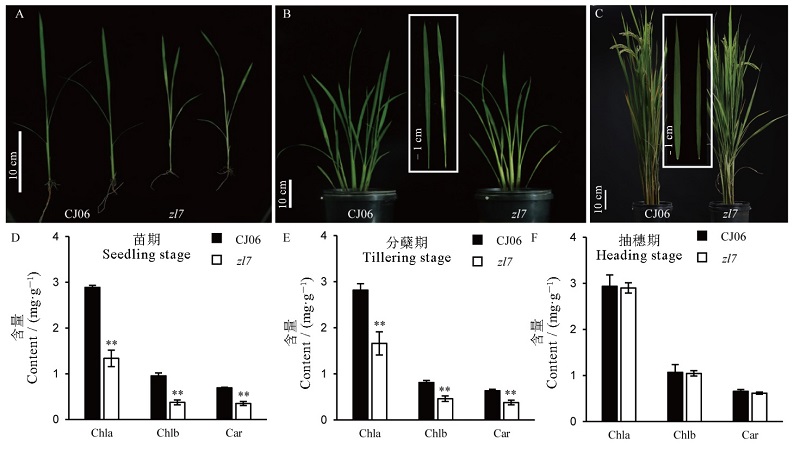
图1 野生型和突变体zl7不同生育期的表型 A,B,C分别为苗期、分蘖期和抽穗期野生型春江06和突变体zl7植株表型,B, C白框中为放大的叶片。D,E,F分别为苗期、分蘖期和抽穗期的叶绿素含量;Chla―叶绿素a,Chlb―叶绿素b,Car―类胡萝卜素;误差线表示3次生物学重复试验的标准差;*,**分别表示野生型与突变体在0.05和0.01水平下差异显著(t检验)。
Fig. 1. Phenotypes of wild type CJ06 and zl7 at different growth stages. A, B and C are the phenotypes of wild-type Chunjiang06 and zl7 plants at seedling stage, tillering stage, and heading stage. The white box in figure B and C are enlarged leaves. D, E and F are chlorophyll contents at seedling stage, tillering stage and heading stage, respectively; Chla, Chlorophyll a; Chlb, Chlorophyll b; Car, Carotenoid; Means±SD(n=3); *,** indicates that there is significant difference between the wild type and the mutant at the level of 0.05 and 0.01 (t-test).
| 农艺性状 Agronomic trait | 野生型 Wild type | 突变体 Mutant zl7 |
|---|---|---|
| 株高 Plant height/cm | 91.2±4.0 | 79.5±2.7** |
| 分蘖 Tillering number | 10.0±1.2 | 8.0±0.8* |
| 穗长 Panicle length/cm | 22.5±1.3 | 20.2±0.8* |
| 一次枝梗 Primary rachis branches | 17.0±0.5 | 14.0±1.1* |
| 二次枝梗 Secondary rachis branches | 28.0±1.9 | 23.0±1.6* |
| 每穗粒数 No. of grains per panicle | 152.0±6.0 | 126.0±4.7** |
| 结实率Seed setting rate/% | 93.4±0.0 | 93.7±0.0 |
| 千粒重 1000-grain weight/g | 23.2±0.6 | 24.9±0.4 |
| 粒长 Grain length/mm | 7.35±0.40 | 7.67±0.63 |
| 粒宽 Grain width/mm | 3.08±0.23 | 3.17±0.24 |
表3 野生型春江06与突变体zl7的主要农艺性状比较
Table 3. Comparison of main agronomic traits between wild type Chunjiang 06 and mutant zl7.
| 农艺性状 Agronomic trait | 野生型 Wild type | 突变体 Mutant zl7 |
|---|---|---|
| 株高 Plant height/cm | 91.2±4.0 | 79.5±2.7** |
| 分蘖 Tillering number | 10.0±1.2 | 8.0±0.8* |
| 穗长 Panicle length/cm | 22.5±1.3 | 20.2±0.8* |
| 一次枝梗 Primary rachis branches | 17.0±0.5 | 14.0±1.1* |
| 二次枝梗 Secondary rachis branches | 28.0±1.9 | 23.0±1.6* |
| 每穗粒数 No. of grains per panicle | 152.0±6.0 | 126.0±4.7** |
| 结实率Seed setting rate/% | 93.4±0.0 | 93.7±0.0 |
| 千粒重 1000-grain weight/g | 23.2±0.6 | 24.9±0.4 |
| 粒长 Grain length/mm | 7.35±0.40 | 7.67±0.63 |
| 粒宽 Grain width/mm | 3.08±0.23 | 3.17±0.24 |
| 材料 Material | 光合作用速率 Pn/ (μmol·m−2 s−1) | 气孔导度 Gs / (mol·m−2 s−1) | 胞间CO2浓度 Ci / (μmol·mol−1) | 蒸腾速率 Tr/ (mol·m−2 s−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 野生型WT | 26.41±0.34 | 0.06±0.01 | 442.34±24.64 | 2.94±0.08 |
| Mutant-g | 21.67±0.51 ** | 0.05±0.01 | 246.63±29.41** | 2.83±0.32 |
| Mutant-y | 13.21±0.47 ** | 0.04±0.01 | 133.69±7.49** | 2.34±0.17* |
表4 野生型CJ06和突变体zl7分蘖盛期光合参数
Table 4. Photosynthetic parameters of the wild type CJ06 and the mutant zl7 at peak tillering stage.
| 材料 Material | 光合作用速率 Pn/ (μmol·m−2 s−1) | 气孔导度 Gs / (mol·m−2 s−1) | 胞间CO2浓度 Ci / (μmol·mol−1) | 蒸腾速率 Tr/ (mol·m−2 s−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 野生型WT | 26.41±0.34 | 0.06±0.01 | 442.34±24.64 | 2.94±0.08 |
| Mutant-g | 21.67±0.51 ** | 0.05±0.01 | 246.63±29.41** | 2.83±0.32 |
| Mutant-y | 13.21±0.47 ** | 0.04±0.01 | 133.69±7.49** | 2.34±0.17* |
| 材料 Material | 光合作用速率 Pn/ (μmol·m−2·s−1) | 气孔导度 Gs / (mol·m−2·s−1) | 胞间CO2浓度 Ci / (μmol·mol−1) | 蒸腾速率 Tr/ (mol·m−2·s−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | 16.06±0.56 | 0.15±0.02 | 204.24±17.42 | 3.29±0.30 |
| Mutant-g | 18.34±0.64** | 0.28±0.02* | 278.66±9.48** | 4.79±0.26** |
| Mutant-y | 9.93±1.41** | 0.13±0.03 | 262.71±15.41** | 2.71±0.58 |
表5 野生型CJ06和突变体zl7抽穗期光合参数
Table 5. Photosynthetic parameters of wild type CJ06 and mutant zl7 at heading stage.
| 材料 Material | 光合作用速率 Pn/ (μmol·m−2·s−1) | 气孔导度 Gs / (mol·m−2·s−1) | 胞间CO2浓度 Ci / (μmol·mol−1) | 蒸腾速率 Tr/ (mol·m−2·s−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | 16.06±0.56 | 0.15±0.02 | 204.24±17.42 | 3.29±0.30 |
| Mutant-g | 18.34±0.64** | 0.28±0.02* | 278.66±9.48** | 4.79±0.26** |
| Mutant-y | 9.93±1.41** | 0.13±0.03 | 262.71±15.41** | 2.71±0.58 |
| 杂交组合 Hybrid combination | F1 | F2 | χ2 (3:1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 正常表型 Wild-type phenotype | 突变表型 zl7 phenotype | 正常表型 Wild-type phenotype | 突变表型 zl7 phenotype | ||
| zl7/93-11 | 13 | 0 | 2065 | 655 | 1.225 |
| 93-11/ zl7 | 8 | 0 | 822 | 271 | 0.025 |
表6 突变体zl7的遗传分析
Table 6. Genetic analysis of the mutant zl7.
| 杂交组合 Hybrid combination | F1 | F2 | χ2 (3:1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 正常表型 Wild-type phenotype | 突变表型 zl7 phenotype | 正常表型 Wild-type phenotype | 突变表型 zl7 phenotype | ||
| zl7/93-11 | 13 | 0 | 2065 | 655 | 1.225 |
| 93-11/ zl7 | 8 | 0 | 822 | 271 | 0.025 |
| 预测基因 Predictive gene | 基因功能注释 Gene function annotation |
|---|---|
| ORF1 | 转座子蛋白 |
| ORF2 | 表达蛋白 |
| ORF3 | ζ-胡萝卜素脱氢酶 |
| ORF4 | 表达蛋白 |
| ORF5 | 细胞色素b-c1复合亚单位7 |
| ORF6 | 表达蛋白 |
| ORF7 | 核苷酸结合蛋白 |
| ORF8 | 羧基末端肽酶 |
| ORF9 | 表达蛋白 |
| ORF10 | 肽酶,M24家族蛋白 |
| ORF11 | 细胞周期蛋白相关蛋白 |
| ORF12 | 表达蛋白 |
表7 开放阅读框基因注释
Table 7. Gene function annotation of ORFs.
| 预测基因 Predictive gene | 基因功能注释 Gene function annotation |
|---|---|
| ORF1 | 转座子蛋白 |
| ORF2 | 表达蛋白 |
| ORF3 | ζ-胡萝卜素脱氢酶 |
| ORF4 | 表达蛋白 |
| ORF5 | 细胞色素b-c1复合亚单位7 |
| ORF6 | 表达蛋白 |
| ORF7 | 核苷酸结合蛋白 |
| ORF8 | 羧基末端肽酶 |
| ORF9 | 表达蛋白 |
| ORF10 | 肽酶,M24家族蛋白 |
| ORF11 | 细胞周期蛋白相关蛋白 |
| ORF12 | 表达蛋白 |

图4 野生型春江06(CJ06)及其突变体zl7叶绿体发育相关基因的表达量分析 误差线表示3次生物学重复试验的标准差。*和**分别表示野生型春江 06(CJ06) 和突变体间差异达 0.05 和 0.01 显著水平(t 检验)。
Fig. 4. Expression analysis of chloroplast development related genes of the wild type Chunjiang 06(CJ06) and its mutant zl7. Mean±SD(n=3). *, ** indicates that there is significant difference between wild type(CJ06) and mutant at the level of 0.05 and 0.01 respectively (t-test)
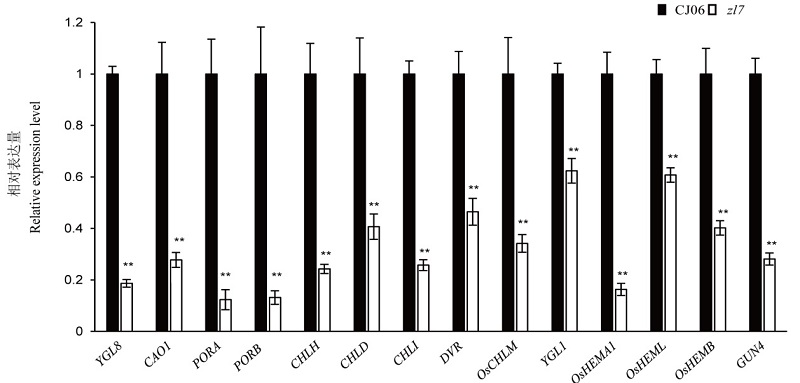
图5 野生型春江06(CJ06)及其突变体zl7叶绿素合成相关基因的表达量分析
Fig. 5. Expression analysis of chlorophyll synthesis related genes of the wild type Chunjiang 06(CJ06) and its mutant zl7.
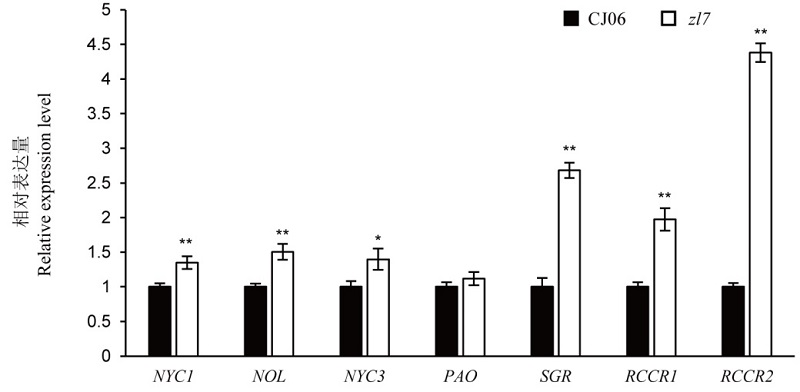
图6 野生型春江06(CJ06)及其突变体zl7叶绿素降解相关基因的表达量分析 误差线表示 3 次生物学重复试验的标准差。*和**分别表示野生型春江 06 和突变体间差异达 0.05 和 0.01 显著水平(t 检验)。
Fig. 6. Expression analysis of chlorophyll degradation related genes of the wild type Chunjiang 06(CJ06) and its mutant zl7. Mean±SD (n=3). *, ** indicate that there is significant difference between the wild type and the mutant at the level of 0.05 and 0.01 respectively (t-test).
| [1] |
Hao J, Wang D, Wu Y, Huang K, Duan P, Li N, Xu R, Zeng D, Dong G, Zhang B, Zhang L, Inze D, Qian Q, Li Y. The GW2-WG1-OsbZIP47 pathway controls grain size and weight in rice[J]. Molecular Plant, 2021, 14(8): 1266-1280.
PMID |
| [2] | Tian Z, Wang J W, Li J, Han B. Designing future crops: Challenges and strategies for sustainable agriculture[J]. Plant Journal, 2021, 105(5): 1165-1178. |
| [3] |
Fromme P, Melkozernov A, Jordan P, Krauss N. Structure and function of photosystem: I. Interaction with its soluble electron carriers and external antenna systems[J]. FEBS Letters, 2003, 555(1): 40-44.
PMID |
| [4] | Zhen X H, Xu J G, Shen W J, Zhang X J, Zhang Q J, Lu C G, Chen G X, Gao Z P. Photosynthetic characteristics of flag leaves in rice white stripe mutant 6001 during senescence process[J]. Rice Science, 2014, 21(6): 335-342. |
| [5] |
Yang Y, Xu J, Huang L, Leng Y, Dai L, Rao Y, Chen L, Wang Y, Tu Z, Hu J, Ren D, Zhang G, Zhu L, Guo L, Qian Q, Zeng D. PGL, encoding chlorophyllide a oxygenase 1, impacts leaf senescence and indirectly affects grain yield and quality in rice[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2016, 67(5): 1297-1310.
PMID |
| [6] | Cao W, Zhang H, Zhou Y, Zhao J, Lu S, Wang X, Chen X, Yuan L, Guan H, Wang G, Shen W, De Vleesschauwer D, Li Z, Shi X, Gu J, Guo M, Feng Z, Chen Z, Zhang Y, Pan X, Liu W, Liang G, Yan C, Hu K, Liu Q, Zuo S. Suppressing chlorophyll degradation by silencing OsNYC3 improves rice resistance to Rhizoctonia solani, the causal agent of sheath blight[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2022, 20(2): 335-349. |
| [7] | Yoo S C, Cho S H, Sugimoto H, Li J, Kusumi K, Koh H J, Iba K, Paek N C. Rice virescent3 and stripe1encoding the large and small subunits of ribonucleotide reductase are required for chloroplast biogenesis during early leaf development[J]. Plant Physiology, 2009, 150(1): 388-401. |
| [8] | Zhu X, Ze M, Yin J, Chen M, Wang M, Zhang X, Deng R, Li Y, Liao H, Wang L, Tu B, Song L, He M, Li S, Wang W M, Chen X, Wang J, Li W. A phosphofructokinase B-type carbohydrate kinase family protein, PFKB1, is essential for chloroplast development at early seedling stage in rice[J]. Plant Science, 2020, 290: 110295. |
| [9] | 杨颜榕, 黄纤纤, 赵亚男, 汤佳玉, 刘喜. 水稻叶色基因克隆与分子机制研究进展[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2020, 21(4): 794-803. |
| Yang Y R, Huang X X, Zhao Y N, Tang J Y, Liu X. Advances on gene isolation and molecular mechanism of rice leaf color genes[J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2020, 21(4): 794-803. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | Kusumi K, Sakata C, Nakamura T, Kawasaki S, Yoshimura AIba K. A plastid protein NUS1 is essential for build-up of the genetic system for early chloroplast development under cold stress conditions[J]. Plant Journal, 2011, 68(6):1039-1050. |
| [11] |
Wang P, Gao J, Wan C, Zhang F, Xu Z, Huang X, Sun X, Deng X. Divinyl chlorophyll(ide) a can be converted to monovinyl chlorophyll(ide) a by a divinyl reductase in rice[J]. Plant Physiology, 2010, 153(3): 994-1003.
PMID |
| [12] | Yang Y L, Xu J, Rao Y C, Zeng Y J, Liu H J, Zheng T T, Zhang G H, Hu J, Guo L B, Qian Q, Zeng D L, Shi Q H. Cloning and functional analysis of pale-green leaf (PGL10) in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Plant Growth Regulation, 2016, 78(1): 69-77. |
| [13] |
Tang J, Zhang W, Wen K, Chen G, Sun J, Tian Y, Tang W, Yu J, An H, Wu T, Kong F, Terzaghi W, Wang C, Wan J. OsPPR6, a pentatricopeptide repeat protein involved in editing and splicing chloroplast RNA, is required for chloroplast biogenesis in rice[J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 2017, 95(4-5): 345-357.
PMID |
| [14] |
Shin D, Lee S, Kim T H, Lee J H, Park J, Lee J, Lee J Y, Cho L H, Choi J Y, Lee W, Park J H, Lee D W, Ito H, Kim D H, Tanaka A, Cho J H, Song Y C, Hwang D, Purugganan M D, Jeon J S, An G, Nam H G. Natural variations at the Stay-Green gene promoter control lifespan and yield in rice cultivars[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 2819. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-16573-2.
PMID |
| [15] | Liu Z, Wang Z, Gu H, You J, Hu M, Zhang Y, Zhu Z, Wang Y, Liu S, Chen L, Liu X, Tian Y, Zhou S, Jiang L, Liu L, Wan J. Identification and phenotypic characterization of ZEBRA LEAF16 encoding a beta-hydroxyacyl-ACP dehydratase in rice[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2018, 9: 782. |
| [16] | Feng P, Shi J, Zhang T, Zhong Y, Zhang L, Yu G, Zhang T, Zhu X, Xing Y, Yin W, Sang X, Ling Y, Zhang C, Yang Z, He G, Wang N. Zebra leaf 15, a receptor-like protein kinase involved in moderate low temperature signaling pathway in rice[J]. Rice (N Y), 2019, 12(1): 83. |
| [17] | Li J, Pandeya D, Nath K, Zulfugarov I S, Yoo S C, Zhang H, Yoo J H, Cho S H, Koh H J, Kim D S, Seo H S, Kang B C, Lee C H, Paek N C. ZEBRA-NECROSIS, a thylakoid-bound protein, is critical for the photoprotection of developing chloroplasts during early leaf development[J]. Plant Journal, 2010, 62(4): 713-725. |
| [18] |
Livak K J, Schmittgen T D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method[J]. Methods, 2001, 25(4): 402-408.
PMID |
| [19] |
Sugimoto H, Kusumi K, Noguchi K, Yano M, Yoshimura A, Iba K. The rice nuclear gene, VIRESCENT 2, is essential for chloroplast development and encodes a novel type of guanylate kinase targeted to plastids and mitochondria[J]. Plant Journal, 2007, 52(3): 512-527.
PMID |
| [20] | Sakuraba Y, Rahman M L, Cho S H, Kim Y S, Koh H J, Yoo S C, Paek N C. The rice faded green leaf locus encodes protochlorophyllide oxidoreductase B and is essential for chlorophyll synthesis under high light conditions[J]. Plant Journal, 2013, 74(1): 122-133. |
| [21] | Jiang H, Li M, Liang N, Yan H, Wei Y, Xu X, Liu J, Xu Z, Chen F, Wu G. Molecular cloning and function analysis of the stay green gene in rice[J]. Plant Journal, 2007, 52(2): 197-209. |
| [22] | Shin D, Lee S, Kim T H, Lee J H, Park J, Lee J, Lee J Y, Cho L H, Choi J Y, Lee W, Park J H, Lee D W, Ito H, Kim D H, Tanaka A, Cho J H, Song Y C, Hwang D, Purugganan M D, Jeon J S, An G, Nam H G. Natural variations at the Stay-Green gene promoter control lifespan and yield in rice cultivars[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 2819. |
| [23] | 方希林, 王悦, 朱敏敏, 邓跃军, 张晶李恩宇. 水稻叶色突变基因的遗传研究进展[J]. 北方水稻, 2016, 46(6): 4-8. |
| Fang X L, Wang Y, Zhu M M, Deng Y J, Zhang J, Li E Y. Research progress of rice leaf color mutation genetic analysis[J]. North Rice, 2016, 46(6): 4-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] |
Beale S I. Green genes gleaned[J]. Trends in Plant Science, 2005, 10(7): 309-312.
PMID |
| [25] | 李佳佳, 于旭东, 蔡泽坪, 吴繁花, 罗佳佳, 郑李婷, 楚文清. 高等植物叶绿素生物合成研究进展[J]. 分子植物育种, 2019, 17(18): 6013-6019. |
| Li J J, Yu X D, Cai Z P, Wu F H, Luo J J, Zheng L T, Chu W Q. An overview of chlorophyll biosynthesis in higher plants[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2019, 17(18): 6013-6019. | |
| [26] | 赵绍路, 刘凯, 宛柏杰, 朱静雯, 刘艳艳, 唐红生, 严国红, 孙明法. 水稻叶色突变研究进展[J]. 大麦与谷类科学, 2018, 35(6): 1-6. |
| Zhao S L, Liu K, Wan B J, Zhu J W, Liu Y Y, Tang H S, Yan G H, Sun M F. Advances in research on rice leaf color mutants[J]. Barley and Cereal Sciences, 2018, 35(6): 1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] |
Cazzonelli C I, Pogson B J. Source to sink: regulation of carotenoid biosynthesis in plants[J]. Trends in Plant Science, 2010, 15(5): 266-274.
PMID |
| [28] | 陆晨飞, 刘钰婷. 类胡萝卜素代谢调控与植物颜色变异[J]. 北方园艺, 2016, 16: 193-199. |
| Lu C F, Liu Y T. Plant color mutants and the regulation of carotenoids metabolism[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2016, 16: 193-199. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | Kusumi K, Komori H, Satoh H, Iba K. Characterization of a zebra mutant of rice with increased susceptibility to light stress[J]. Plant Cell Physiology, 2000, 41(2): 158-164. |
| [30] | Sakuraba Y. Light-mediated regulation of leaf senescence[J]. International Journal of Molecular Medicine, 2021, 22(7). |
| [31] | 张天雨, 周春雷, 刘喜, 孙爱伶, 曹鹏辉, Nguyen T, 田云录, 翟虎渠, 江玲. 一个水稻温敏黄化突变体的表型分析和基因定位[J]. 作物学报, 2017, 43(10): 1426-1433. |
| Zhang T Y, Zhou C L, Liu X, Sun A L, Cao P H, Nguyen T, Tian Y L, Zhai H Q, Jiang L. Phenotypes and gene mapping of a thermo-sensitive yellow leaf mutant of rice[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2017, 43(10): 1426-1433. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [32] | 王威, 张联合, 李华, 张志华, 胡斌, 储成才. 水稻营养吸收和转运的分子机制研究进展[J]. 中国科学: 生命科学, 2015, 45(6):569-590. |
| Wang W, Zhang L H, Li H, Zhang Z H, Hu B, Chu C C. Recent progress in molecular dissection of nutrient uptake and transport in rice[J]. Scientia Sinica: Vitae, 2015, 45(6): 569-590. | |
| [33] | Long J R, Ma G H, Wan Y Z, Song C F, Sun J, Qin R J. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer level on chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics in flag leaf of super hybrid rice at late growth stage[J]. Rice Science, 2013, 20(3): 220-228. |
| [34] |
Carol P, Stevenson D, Bisanz C, Breitenbach J, Sandmann G, Mache R, Coupland G, Kuntz M. Mutations in the Arabidopsis gene IMMUTANS cause a variegated phenotype by inactivating a chloroplast terminal oxidase associated with phytoene desaturation[J]. Plant Cell, 1999, 11(1): 57-68.
PMID |
| [35] |
Chen M, Choi Y, Voytas D F, Rodermel S. Mutations in the Arabidopsis VAR2 locus cause leaf variegation due to the loss of a chloroplast FtsH protease[J]. Plant Journal, 2000, 22(4): 303-313.
PMID |
| [36] |
Naested H, Holm A, Jenkins T, Nielsen H B, Harris C A, Beale M H, Andersen M, Mant A, Scheller H, Camara B, Mattsson O, Mundy J. Arabidopsis VARIEGATED 3 encodes a chloroplast-targeted, zinc-finger protein required for chloroplast and palisade cell development[J]. Journal of Cell Science, 2004, 117(Pt 20): 4807-4818.
PMID |
| [37] |
Wang Y, Shang L, Yu H, Zeng L, Hu J, Ni S, Rao Y, Li S, Chu J, Meng X, Wang L, Hu P, Yan J, Kang S, Qu M, Lin H, Wang T, Wang Q, Hu X, Chen H, Wang B, Gao Z, Guo L, Zeng D, Zhu X, Xiong G, Li J, Qian Q. A strigolactone biosynthesis gene contributed to the green revolution in rice[J]. Molecular Plant, 2020, 13(6): 923-932.
PMID |
| [38] | Zou J, Zhang S, Zhang W, Li G, Chen Z, Zhai W, Zhao X, Pan X, Xie Q, Zhu L. The rice HIGH-TILLERING DWARF1 encoding an ortholog of Arabidopsis MAX3 is required for negative regulation of the outgrowth of axillary buds[J]. Plant Journal, 2006, 48(5): 687-698. |
| [39] |
Wang Y, Wang C, Zheng M, Lyu J, Xu Y, Li X, Niu M, Long W, Wang D, Wang H, Terzaghi W, Wang Y, Wan J. WHITE PANICLE1, a val-tRNA synthetase regulating chloroplast ribosome biogenesis in rice, is essential for early chloroplast development[J]. Plant Physiology, 2016, 170(4): 2110-2123.
PMID |
| [40] | Wang Z W, Lü J, Xie S Z, Zhang Y, Qiu Z N, Chen P, Cui Y T, Niu Y F, Hu S K, Jiang H Z, Ge S Z, Trinh H, Lei K R, Bai W Q, Zhang Y, Guo L B, Ren D Y. OsSLA4 encodes a pentatricopeptide repeat protein essential for early chloroplast development and seedling growth in rice[J]. Plant Growth Regulation, 2018, 84(2): 249-260. |
| [41] | Ma X, Ma J, Zhai H, Xin P, Chu J, Qiao Y, Han L. CHR729 is a CHD3 protein that controls seedling development in rice[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(9): e0138934. |
| [42] | Bang W Y, Chen J, Jeong I S, Kim S W, Kim C W, Jung H S, Lee K H, Kweon H S, Yoko I, Shiina T, Bahk J D. Functional characterization of ObgC in ribosome biogenesis during chloroplast development[J]. Plant Journal, 2012, 71(1): 122-134. |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [6] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [7] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [8] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [9] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [10] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [11] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [12] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [13] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| [14] | 许用强, 姜宁, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 水稻开花期高温热害响应机理及其调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 111-126. |
| [15] | 吕海涛, 李建忠, 鲁艳辉, 徐红星, 郑许松, 吕仲贤. 稻田福寿螺的发生、危害及其防控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 127-139. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||