
中国水稻科学 ›› 2023, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (1): 89-101.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2023.220606
王颖姮1,2, 陈丽娟3, 崔丽丽1,2, 詹生威3, 宋煜1,2, 陈世安4, 解振兴1,2, 姜照伟1,2, 吴方喜1,2, 卓传营3, 蔡秋华1,2, 谢华安1,2, 张建福1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-06-14
修回日期:2022-10-15
出版日期:2023-01-10
发布日期:2023-01-11
通讯作者:
张建福
基金资助:
WANG Yingheng1,2, CHEN Lijuan3, CUI Lili1,2, ZHAN Shengwei3, SONG Yu1,2, CHEN Shian4, XIE Zhenxing1,2, JIANG Zhaowei1,2, WU Fangxi1,2, ZHUO Chuanying3, CAI Qiuhua1,2, XIE Huaan1,2, ZHANG Jianfu1,2,*( )
)
Received:2022-06-14
Revised:2022-10-15
Online:2023-01-10
Published:2023-01-11
Contact:
ZHANG Jianfu
摘要: 目的 烟稻轮作生产模式可以有效改善土壤生态,促进农业增效、农民增收。氮肥是影响水稻生长发育的关键因素,为明确优质稻“福香占”在福建烟后稻区的最佳氮肥施用量,充分发挥其优质、高产特性。方法 本研究设置CK(0)、N1(51.75)、N2(103.5)、N3(155.25)、N4(207 kg/ hm2) 5个氮肥(以纯氮计)水平,在大田环境下,分析“福香占”光合特性、田间产量及其构成因素、稻米品质、香味等方面的变化。结果 随施氮量增加,“福香占”生育期逐渐延长,叶片SPAD值、净光合速率、叶绿体大小、叶片中蔗糖和淀粉含量均上升,N3或者N4达到最高。两年穗总粒数和田间产量均是N2最高,结实率、千粒重随施氮量增加而降低。稻米加工品质N2处理表现最好,外观品质和食味品质受氮肥水平影响不显著。蛋白质含量随氮肥量升高而增加,峰值黏度、热浆黏度、最终黏度、崩解值均随氮肥量增加而降低,消减值升高。N2处理糙米香味物质2-乙酰-1-吡咯啉(2-AP)的含量最高。结论 氮肥处理促进了“福香占”的光合作用,但过量氮肥使得植株贪青迟熟,结实率和产量下降。施氮量为103.5 kg/hm2 (N2)时,“福香占”高产和优质协调,香味物质积累多。本研究为“福香占”进一步在福建烟后稻区推广应用及优质稻产业高质量发展奠定了基础。
王颖姮, 陈丽娟, 崔丽丽, 詹生威, 宋煜, 陈世安, 解振兴, 姜照伟, 吴方喜, 卓传营, 蔡秋华, 谢华安, 张建福. 施氮量对优质稻“福香占”光合特性、产量及品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(1): 89-101.
WANG Yingheng, CHEN Lijuan, CUI Lili, ZHAN Shengwei, SONG Yu, CHEN Shian, XIE Zhenxing, JIANG Zhaowei, WU Fangxi, ZHUO Chuanying, CAI Qiuhua, XIE Huaan, ZHANG Jianfu. Effects of Nitrogen Rate on Photosynthesis, Yield and Grain Quality of Superior Quality Rice “Fuxiangzhan”[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(1): 89-101.
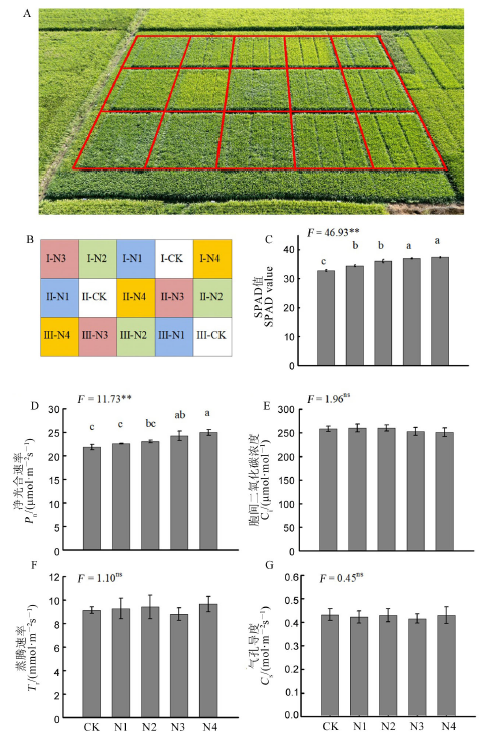
图2 福香占不同施氮处理下齐穗期田间表现及光合特性(2021) A-福香占齐穗期田间表现,5个氮肥处理,3个生物学重复;B-田间试验布局,I、II、III分别代表三个生物学重复,CK、N1、N2、N3、N4分别代表不同氮肥处理;C-SPAD值;D-净光合速率(Pn);E-胞间二氧化碳浓度(Ci);F-蒸腾速率(Tr);G-气孔导度(Cs)。平均值标准差(n = 4),多重比较,不同字母代表差异显著,P<0.05,ns表示差异不显著.
Fig. 2. Field performance and photosynthetic parameters of Fuxiangzhan during heading at different N rates(2021). A, Field performance of Fuxiangzhan at full heading date, including five treatments and three biological repeats; B, Field experiment design. I, II, III indicate three biological repeats. CK, N1, N2, N3, N4 indicate N-rates; C, SPAD value; D, Net photosynthesis rates (Pn); E, Internal CO2 concentration (Ci); F, Transpiration rates (Tr); G, Stomatal conductance (Cs). The data are means ± SD of four measurements. Different letters on the top of columns indicate significant difference at P< 0.05 according to LSD multiple range test, and ns indicates no significant difference.
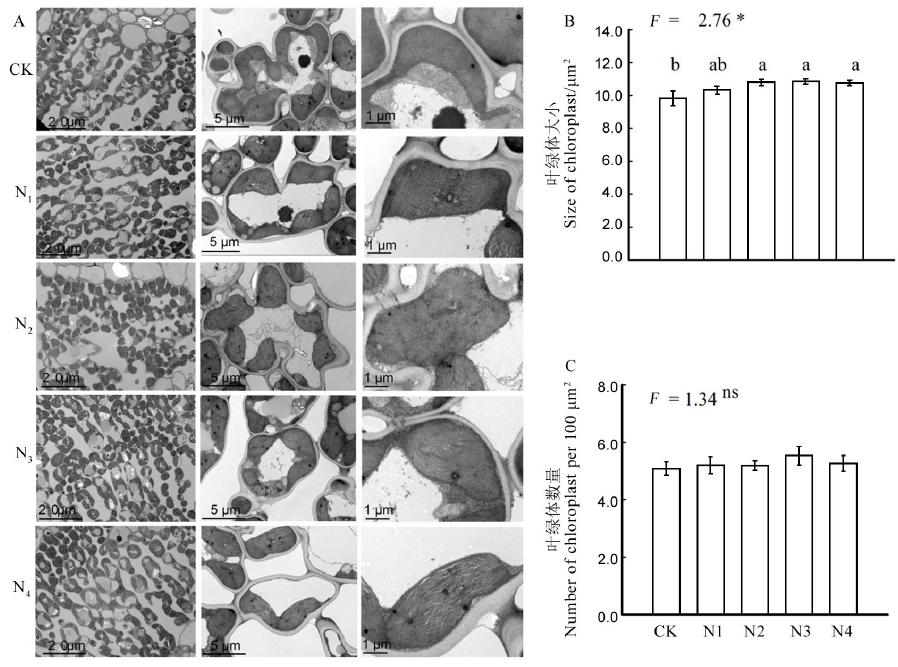
图3 齐穗期不同氮肥处理下“福香占”剑叶的超微结构 A-“福香占”不同施氮处理叶片透射电镜超微结构。CK、N1、N2、N3、N4分别代表不同氮肥处理;B-叶绿体大小;C-100 μm2叶绿体数量。平均值±标准差(n > 200), 不同字母代表差异显著,LSD多重比较,P<0.05,ns表示差异不显著.
Fig. 3. Ultrastructure of Fuxiangzhan leaves under different N-rates at full heading stage. A, Transmission electron micrographs of leaves of Fuxiangzhan under different N rates. CK, N1, N2, N3, N4 indicate N-rates; B, Size of chloroplasts; C, Numbers of chloroplasts per 100 μm2. Data are mean ± SD of more than 200 cells. Different letters on the top of columns indicate significant difference at P < 0.05 according to LSD multiple range test, and ns indicates no significant difference.
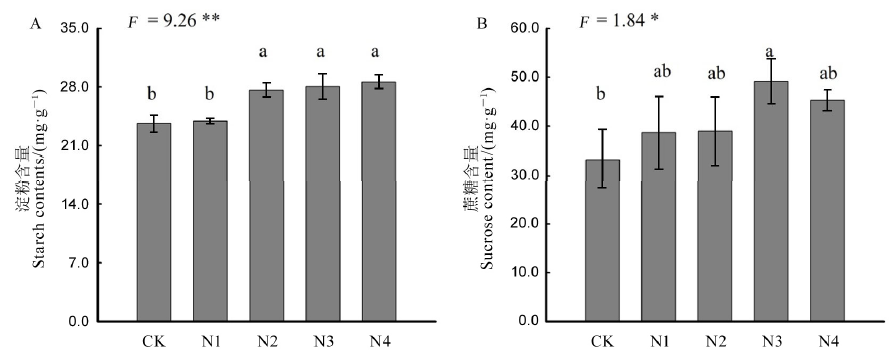
图4 不同氮肥处理“福香占”叶片中蔗糖和淀粉含量 A-淀粉含量;B-蔗糖含量。标准差为± SD(n = 3)。不同字母代表差异显著,LSD多重比较,P<0.05。
Fig. 4. Sucrose and starch contents of flag leaf under various N rates in Fuxiangzhan. A, Starch contents; B, Sucrose content. The data are means ± SD of three biological replicates. Different letters on the top of columns indicate significant difference at P < 0.05 according to LSD multiple range test.
| 年份 | 施氮处理 | 移栽期 | 始穗期 | 齐穗期 | 成熟期 | 生育期 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | N rate | Transplanting date | First heading date | Full heading date | Maturity date | Growth duration/d |
| 2020 | CK | 07-15 | 08-30 | 09-05 | 10-30 | 133 |
| N1 | 07-15 | 09-03 | 09-11 | 11-04 | 138 | |
| N2 | 07-15 | 09-04 | 09-13 | 11-07 | 141 | |
| N3 | 07-15 | 09-05 | 09-16 | 11-10 | 144 | |
| N4 | 07-15 | 09-07 | 09-20 | 11-13 | 146 | |
| 2021 | CK | 07-11 | 09-03 | 09-09 | 10-28 | 133 |
| N1 | 07-11 | 09-08 | 09-15 | 11-03 | 139 | |
| N2 | 07-11 | 09-10 | 09-18 | 11-08 | 144 | |
| N3 | 07-11 | 09-13 | 09-22 | 11-14 | 150 | |
| N4 | 07-11 | 09-15 | 09-25 | 11-18 | 154 |
表1 不同施氮量下“福香占”主要生育时期与生育期
Table 1. Growth duration of Fuxiangzhan under different N rates.
| 年份 | 施氮处理 | 移栽期 | 始穗期 | 齐穗期 | 成熟期 | 生育期 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | N rate | Transplanting date | First heading date | Full heading date | Maturity date | Growth duration/d |
| 2020 | CK | 07-15 | 08-30 | 09-05 | 10-30 | 133 |
| N1 | 07-15 | 09-03 | 09-11 | 11-04 | 138 | |
| N2 | 07-15 | 09-04 | 09-13 | 11-07 | 141 | |
| N3 | 07-15 | 09-05 | 09-16 | 11-10 | 144 | |
| N4 | 07-15 | 09-07 | 09-20 | 11-13 | 146 | |
| 2021 | CK | 07-11 | 09-03 | 09-09 | 10-28 | 133 |
| N1 | 07-11 | 09-08 | 09-15 | 11-03 | 139 | |
| N2 | 07-11 | 09-10 | 09-18 | 11-08 | 144 | |
| N3 | 07-11 | 09-13 | 09-22 | 11-14 | 150 | |
| N4 | 07-11 | 09-15 | 09-25 | 11-18 | 154 |
| 年份 Year | 施氮量N-rates | 有效穗数 Effective panicle (No.×104/hm2) | 每穗总粒数 Grain No. per panicle | 结实率 Seed setting rate/% | 千粒重 1000-grain weight/g | 产量 Yield/(kg·hm−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | CK | 212.74 ± 3.67 b | 131.16 ± 2.49 a | 91.46 ± 0.28 a | 25.35 ± 0.17 a | 5792.50 ± 67.67 b |
| N1 | 232.90 ± 13.44 ab | 137.20 ± 12.40 a | 88.77 ± 1.25 ab | 24.41 ± 0.09 b | 6130.50 ± 237.00 ab | |
| N2 | 232.49 ± 12.17 ab | 147.53 ± 8.24 a | 86.18 ± 1.42 b | 23.49 ± 0.12 c | 6194.00 ± 137.67 a | |
| N3 | 234.24 ± 6.67 ab | 140.16 ± 5.76 a | 76.28 ± 1.38 c | 23.53 ± 0.26 c | 5270.50 ± 89.33 c | |
| N4 | 237.16 ± 1.44 a | 146.57 ± 5.11 a | 67.96 ± 1.17 d | 23.65 ± 0.29 c | 5001.50 ± 169.67 c | |
| 2021 | CK | 212.17 ± 3.13 d | 173.47 ± 9.27 cd | 69.56 ± 2.19 a | 25.42 ± 0.16 a | 5857.50 ± 50.40 c |
| N1 | 229.75 ± 1.80 c | 185.73 ± 2.31 bc | 67.62 ± 1.95 ab | 24.45 ± 0.08 b | 6396.00 ± 48.28 b | |
| N2 | 244.17 ± 4.56 b | 202.00 ± 6.62 a | 64.06 ± 1.32 b | 23.54 ± 0.13 c | 6741.00 ± 52.54 a | |
| N3 | 255.84 ± 2.27 a | 169.33 ± 12.38 d | 55.49 ± 3.62 c | 23.66 ± 0.23 c | 5116.50 ± 60.22 d | |
| N4 | 259.67 ± 5.51 a | 190.97 ± 8.34 ab | 43.73 ± 1.54 d | 23.80 ± 0.17 c | 4651.50 ± 57.76 e | |
| 方差分析ANOVA | ||||||
| 施氮量N-rates (N) | 14.96** | 5.76** | 172.57** | 125.53** | 234.38** | |
| 年份Year (Y) | 9.97** | 155.67** | 1009.98** | 1.86 | 3.37 | |
| 施氮量×年份N × Y | 2.66 | 1.43 | 0.74 | 0.11 | 14.87** | |
表2 施氮量对“福香占”产量及构成的影响
Table 2. Effects of N rates on yield and its components of Fuxiangzhan.
| 年份 Year | 施氮量N-rates | 有效穗数 Effective panicle (No.×104/hm2) | 每穗总粒数 Grain No. per panicle | 结实率 Seed setting rate/% | 千粒重 1000-grain weight/g | 产量 Yield/(kg·hm−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | CK | 212.74 ± 3.67 b | 131.16 ± 2.49 a | 91.46 ± 0.28 a | 25.35 ± 0.17 a | 5792.50 ± 67.67 b |
| N1 | 232.90 ± 13.44 ab | 137.20 ± 12.40 a | 88.77 ± 1.25 ab | 24.41 ± 0.09 b | 6130.50 ± 237.00 ab | |
| N2 | 232.49 ± 12.17 ab | 147.53 ± 8.24 a | 86.18 ± 1.42 b | 23.49 ± 0.12 c | 6194.00 ± 137.67 a | |
| N3 | 234.24 ± 6.67 ab | 140.16 ± 5.76 a | 76.28 ± 1.38 c | 23.53 ± 0.26 c | 5270.50 ± 89.33 c | |
| N4 | 237.16 ± 1.44 a | 146.57 ± 5.11 a | 67.96 ± 1.17 d | 23.65 ± 0.29 c | 5001.50 ± 169.67 c | |
| 2021 | CK | 212.17 ± 3.13 d | 173.47 ± 9.27 cd | 69.56 ± 2.19 a | 25.42 ± 0.16 a | 5857.50 ± 50.40 c |
| N1 | 229.75 ± 1.80 c | 185.73 ± 2.31 bc | 67.62 ± 1.95 ab | 24.45 ± 0.08 b | 6396.00 ± 48.28 b | |
| N2 | 244.17 ± 4.56 b | 202.00 ± 6.62 a | 64.06 ± 1.32 b | 23.54 ± 0.13 c | 6741.00 ± 52.54 a | |
| N3 | 255.84 ± 2.27 a | 169.33 ± 12.38 d | 55.49 ± 3.62 c | 23.66 ± 0.23 c | 5116.50 ± 60.22 d | |
| N4 | 259.67 ± 5.51 a | 190.97 ± 8.34 ab | 43.73 ± 1.54 d | 23.80 ± 0.17 c | 4651.50 ± 57.76 e | |
| 方差分析ANOVA | ||||||
| 施氮量N-rates (N) | 14.96** | 5.76** | 172.57** | 125.53** | 234.38** | |
| 年份Year (Y) | 9.97** | 155.67** | 1009.98** | 1.86 | 3.37 | |
| 施氮量×年份N × Y | 2.66 | 1.43 | 0.74 | 0.11 | 14.87** | |
| 年份 Year | 施氮量 N-rates | 糙米率 Brown rice rate/% | 精米率 Milled rice rate/% | 整精米率 Head milled rice rate/% | 垩白粒率 Chalkiness grain rate/% | 垩白度 Chalkiness degree/% | 直链淀粉含量 Amylose content/% | 胶稠度 Gel consistency /mm | 蛋白质含量 Protein content /% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | CK | 80.27 ± 0.11 b | 70.60 ± 0.13 c | 45.73 ± 0.29 d | 6.67 ± 0.44 ab | 0.83 ± 0.13 bc | 19.98 ± 0.36 a | 65.00 ± 10.00 a | 7.77 ± 0.26 b |
| N1 | 81.37 ± 0.09 a | 73.57 ± 0.11 a | 49.10 ± 0.80 c | 6.67 ± 1.56 ab | 0.76 ± 0.32 bc | 20.21 ± 0.17 a | 68.33 ± 7.78 a | 8.12 ± 0.02 ab | |
| N2 | 81.50 ± 0.20 a | 73.63 ± 0.29 a | 57.67 ± 1.02 a | 6.67 ± 1.11 ab | 1.26 ± 0.31 a | 20.39 ± 0.35 a | 65.50 ± 5.33 a | 8.32 ± 0.23 ab | |
| N3 | 80.50 ± 0.07 b | 71.97 ± 0.09 b | 53.83 ± 0.31 b | 8.00 ± 0.67 a | 1.07 ± 0.19 ab | 20.22 ± 0.27 a | 73.50 ± 7.00 a | 8.38 ± 0.07 ab | |
| N4 | 80.47 ± 0.11 b | 72.03 ± 0.31 b | 54.37 ± 0.78 b | 5.00 ± 0.67 b | 0.51 ± 0.11 c | 19.93 ± 0.16 a | 71.67 ± 2.22 a | 8.50 ± 0.53 a | |
| 2021 | CK | 79.57 ± 0.51 b | 66.90 ± 0.20 c | 43.71 ± 0.65 b | 5.72 ± 1.30 a | 1.08 ± 0.16 a | 16.03 ± 0.51 a | 83.00 ± 2.00 a | 6.44 ± 0.17 d |
| N1 | 81.17 ± 0.11 a | 69.83 ± 0.16 a | 46.62 ± 0.42 a | 5.42 ± 1.36 a | 1.10 ± 0.36 a | 15.80 ± 0.40 a | 81.00 ± 2.00 a | 7.01 ± 0.24 c | |
| N2 | 81.40 ± 0.07 a | 69.97 ± 0.38 a | 47.70 ± 1.33 a | 4.36 ± 0.56 a | 0.88 ± 0.15 a | 16.17 ± 0.10 a | 78.33 ± 1.56 a | 7.58 ± 0.23 b | |
| N3 | 81.27 ± 0.11 a | 68.30 ± 0.20 b | 37.08 ± 0.53 c | 3.46 ± 0.39 a | 0.71 ± 0.06 a | 16.37 ± 0.18 a | 83.67 ± 3.56 a | 8.47 ± 0.17 a | |
| N4 | 81.57 ± 0.04 a | 68.67 ± 0.22 b | 33.29 ± 1.68 d | 3.43 ± 0.78 a | 0.71 ± 0.07 a | 16.13 ± 0.11 a | 79.67 ± 0.44 a | 8.43 ± 0.16 a | |
| 方差分析ANOVA | |||||||||
| 施氮量 N- rates (N) | 30.46** | 97.30** | 44.44** | 2.69 | 2.87 | 0.89 | 0.92 | 21.36** | |
| 年份Year (Y) | 3.23 | 1009.48** | 480.69** | 24.21** | 0.02 | 809.05** | 29.17** | 31.82** | |
| 施氮量×年份 N × Y | 11.75** | 0.34 | 62.93** | 2.27 | 3.01* | 0.68 | 0.54 | 6.19** | |
表3 施氮量对“福香占”品质和营养的影响
Table 3. Effects of N rates on rice quality and nutrition for Fuxiangzhan.
| 年份 Year | 施氮量 N-rates | 糙米率 Brown rice rate/% | 精米率 Milled rice rate/% | 整精米率 Head milled rice rate/% | 垩白粒率 Chalkiness grain rate/% | 垩白度 Chalkiness degree/% | 直链淀粉含量 Amylose content/% | 胶稠度 Gel consistency /mm | 蛋白质含量 Protein content /% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | CK | 80.27 ± 0.11 b | 70.60 ± 0.13 c | 45.73 ± 0.29 d | 6.67 ± 0.44 ab | 0.83 ± 0.13 bc | 19.98 ± 0.36 a | 65.00 ± 10.00 a | 7.77 ± 0.26 b |
| N1 | 81.37 ± 0.09 a | 73.57 ± 0.11 a | 49.10 ± 0.80 c | 6.67 ± 1.56 ab | 0.76 ± 0.32 bc | 20.21 ± 0.17 a | 68.33 ± 7.78 a | 8.12 ± 0.02 ab | |
| N2 | 81.50 ± 0.20 a | 73.63 ± 0.29 a | 57.67 ± 1.02 a | 6.67 ± 1.11 ab | 1.26 ± 0.31 a | 20.39 ± 0.35 a | 65.50 ± 5.33 a | 8.32 ± 0.23 ab | |
| N3 | 80.50 ± 0.07 b | 71.97 ± 0.09 b | 53.83 ± 0.31 b | 8.00 ± 0.67 a | 1.07 ± 0.19 ab | 20.22 ± 0.27 a | 73.50 ± 7.00 a | 8.38 ± 0.07 ab | |
| N4 | 80.47 ± 0.11 b | 72.03 ± 0.31 b | 54.37 ± 0.78 b | 5.00 ± 0.67 b | 0.51 ± 0.11 c | 19.93 ± 0.16 a | 71.67 ± 2.22 a | 8.50 ± 0.53 a | |
| 2021 | CK | 79.57 ± 0.51 b | 66.90 ± 0.20 c | 43.71 ± 0.65 b | 5.72 ± 1.30 a | 1.08 ± 0.16 a | 16.03 ± 0.51 a | 83.00 ± 2.00 a | 6.44 ± 0.17 d |
| N1 | 81.17 ± 0.11 a | 69.83 ± 0.16 a | 46.62 ± 0.42 a | 5.42 ± 1.36 a | 1.10 ± 0.36 a | 15.80 ± 0.40 a | 81.00 ± 2.00 a | 7.01 ± 0.24 c | |
| N2 | 81.40 ± 0.07 a | 69.97 ± 0.38 a | 47.70 ± 1.33 a | 4.36 ± 0.56 a | 0.88 ± 0.15 a | 16.17 ± 0.10 a | 78.33 ± 1.56 a | 7.58 ± 0.23 b | |
| N3 | 81.27 ± 0.11 a | 68.30 ± 0.20 b | 37.08 ± 0.53 c | 3.46 ± 0.39 a | 0.71 ± 0.06 a | 16.37 ± 0.18 a | 83.67 ± 3.56 a | 8.47 ± 0.17 a | |
| N4 | 81.57 ± 0.04 a | 68.67 ± 0.22 b | 33.29 ± 1.68 d | 3.43 ± 0.78 a | 0.71 ± 0.07 a | 16.13 ± 0.11 a | 79.67 ± 0.44 a | 8.43 ± 0.16 a | |
| 方差分析ANOVA | |||||||||
| 施氮量 N- rates (N) | 30.46** | 97.30** | 44.44** | 2.69 | 2.87 | 0.89 | 0.92 | 21.36** | |
| 年份Year (Y) | 3.23 | 1009.48** | 480.69** | 24.21** | 0.02 | 809.05** | 29.17** | 31.82** | |
| 施氮量×年份 N × Y | 11.75** | 0.34 | 62.93** | 2.27 | 3.01* | 0.68 | 0.54 | 6.19** | |
| 施氮量 N rates | 峰值黏度 Peak viscosity (PKV) | 热浆黏度 Hot viscosity (HPV) | 最终黏度 Final viscosity (CPV) | 崩解值 Breakdown viscosity (BDV) | 消减值 Setback viscosity (SBV) | 回复值 Cosistency viscosity (CSV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 3332.33±53.78 a | 1767.00±60.67 a | 2921.33±39.56 a | 1565.33±36.22 a | −411.00±50.00 a | 1154.33±24.22 a |
| N1 | 3167.00±125.33 a | 1663.33±50.44 a | 2814.33±62.89 a | 1503.67±121.11 a | −352.67±148.44 a | 1151.00±27.33 a |
| N2 | 3185.67±41.78 a | 1657.33±37.78 a | 2820.67±40.44 a | 1528.33±36.89 a | −365.00±74.67 a | 1163.33±37.78 a |
| N3 | 2971.67±220.44 a | 1594.67±169.11 a | 2761.33±152.22 a | 1377.00±51.33 a | −210.33±68.22 a | 1166.67±16.89 a |
| N4 | 2972.33±204.22 a | 1609.67±117.78 a | 2774.00±98.00 a | 1362.67±86.44 a | −198.33±106.22 a | 1164.33±20.22 a |
| 方差分析 ANOVA | ||||||
| 施氮量N rate | 3.06 | 1.42 | 1.20 | 2.47 | 1.88 | 0.14 |
表4 施氮量对“福香占”RVA谱的影响
Table 4. Effects of N rates on RVA for Fuxiangzhan. cP
| 施氮量 N rates | 峰值黏度 Peak viscosity (PKV) | 热浆黏度 Hot viscosity (HPV) | 最终黏度 Final viscosity (CPV) | 崩解值 Breakdown viscosity (BDV) | 消减值 Setback viscosity (SBV) | 回复值 Cosistency viscosity (CSV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 3332.33±53.78 a | 1767.00±60.67 a | 2921.33±39.56 a | 1565.33±36.22 a | −411.00±50.00 a | 1154.33±24.22 a |
| N1 | 3167.00±125.33 a | 1663.33±50.44 a | 2814.33±62.89 a | 1503.67±121.11 a | −352.67±148.44 a | 1151.00±27.33 a |
| N2 | 3185.67±41.78 a | 1657.33±37.78 a | 2820.67±40.44 a | 1528.33±36.89 a | −365.00±74.67 a | 1163.33±37.78 a |
| N3 | 2971.67±220.44 a | 1594.67±169.11 a | 2761.33±152.22 a | 1377.00±51.33 a | −210.33±68.22 a | 1166.67±16.89 a |
| N4 | 2972.33±204.22 a | 1609.67±117.78 a | 2774.00±98.00 a | 1362.67±86.44 a | −198.33±106.22 a | 1164.33±20.22 a |
| 方差分析 ANOVA | ||||||
| 施氮量N rate | 3.06 | 1.42 | 1.20 | 2.47 | 1.88 | 0.14 |
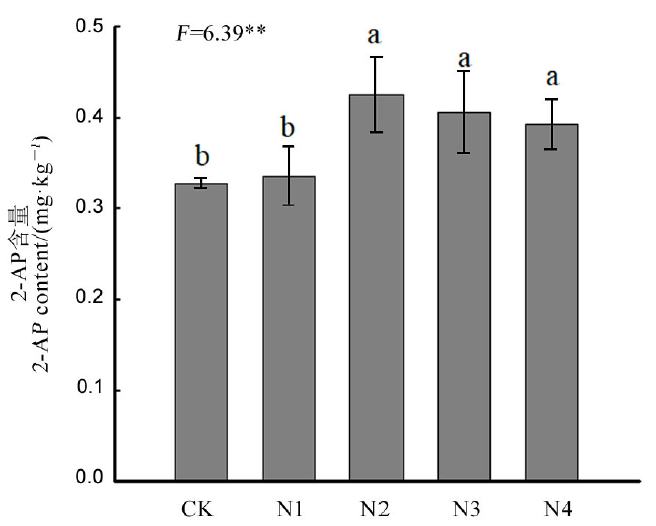
图5 不同氮肥处理对“福香占”糙米2-AP含量的影响 平均值±标准差(n=3)。不同字母代表差异显著,LSD多重比较,P<0.05。
Fig. 5. Effects of N-rates on 2-AP content of brown rice of Fuxiangzhan. The data are means ± SD of three biological replications. Different letters on the top of columns indicate significant difference at P < 0.05 according to LSD multiple range test.
| [1] | 徐春春, 纪龙, 陈中督, 方福平. 2021年我国水稻产业形势分析及2022年展望[J]. 中国稻米, 2022, 28(2): 16-19. |
| Xu C C, Ji L, Chen Z D, Fang F P. Analysis of China’s rice industry in 2021 and the outlook for 2022[J]. China Rice, 2022, 28(2):16-19. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | 赵正洪, 戴力, 黄见良, 潘晓华, 游艾青, 赵全志, 陈光辉, 周政, 胡文彬, 纪龙. 长江中游稻区水稻产业发展现状、问题与建议[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(6): 553-564. |
| Zhao Z H, Dai L, Huang J L, Pan X H, You A Q, Zhao Q Z, Chen G H, Zhou Z, Hu W B, Ji L. Status, Problems and Solutions in Rice Industry Development in the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2019, 33(6): 553-564. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 王伟妮, 鲁剑巍, 何予卿, 李小坤, 李慧. 氮、 磷、钾肥对水稻产量、品质及养分吸收利用的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2011, 25(6): 645-653. |
| Wang W N, Lu J W, He Y Q, Li X K, Li H,. Effectsof N, P, K Fertilizer applicationon grain yield, quality, nutrient uptakeand utilization of rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2011, 25(6): 645-653. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | Sun J L, Ye M, Peng S B, Li Y. Nitrogen can improve the rapid response of photosynthesis to changing irradiance in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6(10): 31305. |
| [5] | Cao X C, Zhong C, Sajid H, Zhu L F, Zhang J H, Wu L H, Jin Q Y. Effects of watering regime and nitrogen application rate on the photosynthetic parameters, physiological characteristics, and agronomic traits of rice[J]. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 2017, 39(6): 135. |
| [6] | Wang W N, Lu J W, Ren T, Li X K, Su W, Lu M X. Evaluating regional mean optimal nitrogen rates in combination with indigenous nitrogen supply for rice production[J]. Field Crops Research, 2012, 137 (20): 37-48. |
| [7] | 陶进, 钱希旸, 剧成欣, 刘立军, 张耗, 顾骏飞, 王志琴, 杨建昌. 不同年代中籼水稻品种的米质及其对氮肥的响应[J]. 作物学报, 2016, 42(9): 1352-1362. |
| Tao J, Qian X Y, Ju C X, Liu L J, Zhang H, Gu J F, Wang Z Q, Yang J C. Grain Quality and Its Response to nitrogen fertilizer in mid-season indica rice varieties planted in different decades from 1950s to 2010s[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2016, 42(9): 1352-1362. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | 陈莹莹, 胡星星, 陈京都, 杨雄, 马群, 陈乔, 葛梦婕, 戴其根. 氮肥水平对江苏早熟晚粳稻食味品质的影响及其品种间差异[J]. 作物学报, 2012, 38(11): 2086-2092. |
| Chen Y Y, Hu X X, Chen J D, Yang X, Ma Q, Chen Q, Ge M J, Dai Q G. Effect of nitrogen fertilizer application on eating quality of early-maturing late japonica rice in Jiangsu and its difference among varieties[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2012, 38(11): 2086-2092. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 蒋鹏, 熊洪, 张林, 周兴兵, 朱永川, 刘茂, 郭晓艺, 徐富贤. 施氮量和氮肥运筹模式对糯稻产量及品质的影响[J]. 作物研究, 2015, 29(6): 595-598. |
| Jiang P, Xiong H, Zhang L, Zhou X B, Zhu Y C, Liu M, Guo X Y, Xu F X. Effect of nitrogen rates and nitrogen application regimes on grain yield and rice quality of glutinous rice[J]. Crop Research. 2015, 29(6): 595-598. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | 唐健, 唐闯, 郭保卫, 张诚信, 张振振, 王科, 张洪程, 陈恒, 孙明珠. 氮肥施用量对机插优质晚稻产量和稻米品质的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2020, 46(1): 117-130. |
| Tang J, Tang C, Guo B W, Zhang C X, Zhang Z Z, Wang K, Zhang H C, Chen H, Sun M Z. Effect of nitrogen application on yield and rice quality of mechanical transplanting high quality late rice[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2020, 46(1): 117-130. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | Chu G, Chen S, Xu C M, Wang D Y, Zhang X F. Agronomic and physiological performance of indica/japonica hybrid rice cultivar under low nitrogen conditions[J]. Field Crops Research, 2019, 243(1): 107625. |
| [12] | Zhu K Y, Zhou Q, Shen Y, Yan J Q, Xu Y J, Wang Z Q, Yang J C. Agronomic and physiological performance of an indica-japonica rice variety with a high yield and high nitrogen use efficiency[J]. Crop Science, 2020, 60(3): 1556-1568. |
| [13] | Tirol-Padre A, Ladha J K, Singh U, Laureles E, Punzalan G, Akita S. Grain yield performance of rice genotypes at suboptimal levels of soil N as affected by N uptake and utilization efficiency[J]. Field Crops Research, 1996, 46(1-3): 127-143. |
| [14] | Dong G C, Wang Y L, Zhou J, Zhang B, Zhang C S, Zhang Y F, Yang L X, Huang J Y. Characteristics of nitrogen distribution and translocation in conventional indica rice varieties with different nitrogen use efficiency for grain output[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2009, 35(1): 149-155. |
| [15] | 董桂春, 陈琛, 袁秋梅, 羊彬, 朱正康, 曹文雅, 仲军, 周娟, 罗刚, 王熠, 黄建晔, 王余龙. 氮肥处理对氮素高效吸收水稻根系性状及氮肥利用率的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2016, 36(3): 642-651. |
| Dong G C, Chen C, Yuan Q M, Yang B, Zhu Z K, Cao W Y, Zhong J, Zhou J, Luo G, Wang Y, Huang J Y, Wang Y L. Effect of nitrogen fertilizer treatments on root traits and nitrogen use efficiency in indica rice varieties with high nitrogen absorption efficiency[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2016, 36(3): 642-651. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] |
Peng J F, Feng Y H, Wang X K, Li J, Xu G L, Phonenasay S, Luo Q X, Han Z L, Lu W. Effects of nitrogen application rate on the photosynthetic pigment, leaf fluorescence characteristics, and yield of indica hybrid rice and their interrelations[J]. Scientific Reports, 2021, 11(1): 7485.
PMID |
| [17] | Ray D, Sheshshayee M S, Mukhopadhyay K, Bindumadhave H. High nitrogen use efficiency in rice genotypes is associated with higher net photosynthetic rate at lower rubisco content[J]. Biologia Plantarum, 2003, 46(3): 251-256. |
| [18] | 中华人民共和国农业行业标准. NY/T83-2017. 米质测定方法[S]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2017. |
| Agricultural Industry Standard of the People's Republic of China. NY/T 83-2017. Rice Mass Determination method[S]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2017. (in Chinese) | |
| [19] | 邵高能, 谢黎虹, 焦桂爱, 魏祥进, 圣忠华, 唐绍清, 胡培松. 利用CRISPR/CAS9技术编辑水稻香味基因Badh2[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(2): 216-222. |
| Shao G N, Xie L H, Jiao G A, Wei X J, Sheng Z H, Tang S Q, Hu P S. CRISPR/CAS9-mediated editing of the fragrant gene Badh2 in rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2017, 31(2): 216-222. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | Kumar P A, Parry M A J, Mitchell R A C, Ahmad A, Abrol Y P,. Photosynthesis and nitrogen-use efficiency// Foyer C H, Noctor G. Photosynthetic nitrogen assimilation and associated carbon and respiratory metabolism. Place Published: Springer Netherlands, 2002: 23-34. |
| [21] | Xu G W, Lu D K, Wang H Z, Li Y J. Morphological and physiological traits of rice roots and their relationships to yield and nitrogen utilization as influenced by irrigation regime and nitrogen rate[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2018, 203(30): 385-394. |
| [22] | Sun Y J, Ma J, Sun Y Y, Xu H, Yang Z Y, Liu S J, Jia X W, Zheng H Z. The effects of different water and nitrogen managements on yield and nitrogen use efficiency in hybrid rice of China[J]. Field Crops Research, 2012, 127(27): 85-98. |
| [23] | Huang M, Lei T, Cao F B, Chen J N, Shan S L, Zou Y B. Grain yield responses to nitrogen rate in two elite double-cropped inbred rice cultivars released 41 years apart[J]. Field Crops Research, 2020, 259(15): 107970. |
| [24] | 袁锐, 周群, 王志琴, 张耗, 顾骏飞, 刘立军, 张伟杨, 杨建昌. 籼粳杂交稻甬优2640氮素吸收利用特点[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(1): 77-86. |
| Yuan R, Zhou Q, Wang Z Q, Zhang H, Gu J F, Liu L J, Zhang W Y, Yang J C. Characteristics of nitrogen absorption and utilization of an indica-japonica hybrid rice, Yongyou 2640[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2022, 36(1): 77-86. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | 谢黎虹, 叶定池, 胡培松, 陈能, 唐绍清, 罗炬, 焦桂爱. 氮肥用量和施肥方式对水稻“甬优6号”产量和品质的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2011, 17(4): 789-794. |
| Xie L H, Ye D C, Hu P S, Chen N, Tang S Q, Luo J, Jiao G A. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer application rate and management strategy on grain yield and quality of rice variety “Yongyou 6”[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2011, 17(4): 789-794. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | 高辉, 马群, 李国业, 杨雄, 李雪侨, 殷春渊, 李敏, 张庆, 张洪程, 戴其根, 魏海燕. 氮肥水平对不同生育类型粳稻稻米蒸煮食味品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2010, 43(21): 4543-4552. |
| Gao H, Ma Q, Li G Y, Yang X, Li X Q, Yin C Y, Li M, Zhang Q, Zhang H C, Dai Q G, Wei H Y. Effect of nitrogen application rate on cooking and eating qualities of different growth-development types of japonica rice[J]. Scientia Agriculture Sinica, 2010, 43(21): 4543-4552. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | 张庆, 郭保卫, 胡雅杰, 张洪程, 徐玉峰, 徐晓杰, 朱邦辉, 徐洁芬, 钮中一, 凃荣文. 不同氮肥水平下优质高产软米粳稻的产量与品质差异[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(6): 606-616. |
| Zhang Q, Guo B W, Hu Y J, Zhang H C, Xu Y F, Xu X J, Zhu B H, Xu J F, Niu Z Y, Tu R W. Differences in yield and rice quality of soft japonica rice with high quality and high yield under different nitrogen levels[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2021, 35(6): 606-616. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | Bao J S, Shen S Q, Sun M, Corke H. Analysis of genotypic diversity in the starch physicochemical properties of nonwaxy rice: apparent amylose content, pasting viscosity and gel texture[J]. Starch-Stärke, 2006, 58(6): 259-267. |
| [29] | Bryant R J, Yeater K M, McClung A M. Effect of nitrogen rate and the environment on physicochemical properties of selected high-amylose rice cultivars[J]. Cereal Chemistry, 2015, 92(6): 604-610. |
| [30] | 中华人民共和国农业行业标准.NY/T593-2021. 食用稻品种品质[S]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2021. |
| Agricultural Industry Standard of the People's Republic of China. NY/T 593-2021. Quality of Edible Rice Varieties[S]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2021. (in chinese) | |
| [31] |
Bradbury L M T, Fitzgerald T L, Henry R J, Jin Q S, Waters D L E. The gene for fragrance in rice[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2005, 3(3): 363-370.
PMID |
| [32] | Chen S H, Yang Y, Shi W W, Ji Q, He F, Zhang Z D, Cheng Z K, Liu X N, Xu M L. Badh2, encoding betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase, inhibits the biosynthesis of 2-Acetyl-1-Pyrroline, a major component in rice fragrance[J]. The Plant Cell, 2008, 20(7): 1850-1861. |
| [33] | 钟群, 唐湘如. 氮肥施用对香稻香气含量的影响及其机理[J]. 广东农业科学, 2014, 41(4): 85-87. |
| Zhong Q, Tang X R. Effects of nitrogen application on aroma of aromatic rice and their mechanism[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 41(4): 85-87. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [34] | Prodhan Z H,. Faruq G, Rashid K A, Taha R M. Effects of temperature on volatile profile and aroma quality in rice[J]. International Journal of Agriculture and Biology, 2017, 19(5): 1065-1072. |
| [35] | 黄忠林, 唐湘如, 王玉良, 陈慕娇, 赵正琨, 段美洋, 潘圣刚. 增香栽培对香稻香气和产量的影响及其相关生理机制[J]. 中国农业科学, 2012, 45(6): 1054-1065. |
| Huang Z L, Tang X R, Wang Y L, Chen M J, Zhao Z K, Duan M Y, Pan S G. Effects of increasing aroma cultivation on aroma and grain yield of aromatic rice and their mechanism[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2012, 45(6): 1054-1065. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [36] | Liang H L, Tao D B, Zhang Q, Zhang S, Wang J Y, Liu L F, Wu Z X, Sun W T. Nitrogen fertilizer application rate impacts eating and cooking quality of rice after storage[J]. Plos ONE, 2021, 16(6): e0253189. |
| [1] | 蒋鹏, 张林, 周兴兵, 郭晓艺, 朱永川, 刘茂, 郭长春, 熊洪, 徐富贤. 冬水田轻简化栽培杂交稻蓄留再生稻产量形成特点 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 544-554. |
| [2] | 熊家欢, 张义凯, 向镜, 陈惠哲, 徐一成, 王亚梁, 王志刚, 姚坚, 张玉屏. 覆膜稻田施用炭基肥对水稻产量及氮素利用的影响 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 567-576. |
| [3] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [4] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [5] | 吕宙, 易秉怀, 陈平平, 周文新, 唐文帮, 易镇邪. 施氮量与移栽密度对小粒型杂交水稻产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| [6] | 赵艺婷, 谢可冉, 高逖, 崔克辉. 水稻分蘖期干旱锻炼对幼穗分化期高温下穗发育和产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 277-289. |
| [7] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [8] | 肖正午, 方升亮, 曹威, 胡丽琴, 黎星, 解嘉鑫, 廖成静, 康玉灵, 胡玉萍, 张珂骞, 曹放波, 陈佳娜, 黄敏. 米粉质构特性与稻米理化性状的关系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 316-323. |
| [9] | 彭显龙, 董强, 张辰, 李鹏飞, 李博琳, 刘智蕾, 于彩莲. 不同土壤条件下秸秆还田量对土壤还原性物质及水稻生长的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 198-210. |
| [10] | 景秀, 周苗, 王晶, 王岩, 王旺, 王开, 郭保卫, 胡雅杰, 邢志鹏, 许轲, 张洪程. 穗分化末期-灌浆初期干旱胁迫对优质食味粳稻根系形态和叶片光合特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(1): 33-47. |
| [11] | 雍明玲, 叶苗, 张雨, 陶钰, 倪川, 康钰莹, 张祖建. 不同食味水稻品种稻米淀粉结构与理化特性及其对氮素响应的差异[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(1): 57-71. |
| [12] | 易晓璇, 刘玮琦, 曾盖, 罗丽华, 肖应辉. 灌浆期高温胁迫对早籼稻品质性状的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(1): 72-80. |
| [13] | 谢开珍, 张建明, 程灿, 周继华, 牛付安, 孙滨, 张安鹏, 闻伟军, 代雨婷, 胡启琰, 邱越, 曹黎明, 储黄伟. 低直链淀粉含量水稻种质资源的鉴定与QTL定位分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(6): 609-616. |
| [14] | 朱旺, 张翔, 耿孝宇, 张哲, 陈英龙, 韦还和, 戴其根, 许轲, 朱广龙, 周桂生, 孟天瑶. 盐-旱复合胁迫下水稻根系的形态和生理特征及其与产量形成的关系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(6): 617-627. |
| [15] | 吴玉红, 李艳华, 王吕, 秦宇航, 李杉杉, 郝兴顺, 张庆路, 崔月贞, 肖飞. 陕南稻区紫云英稻草联合还田配施减量氮肥协同提升水稻产量与稻米品质[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(6): 628-641. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||