
中国水稻科学 ›› 2022, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (6): 586-600.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2022.211203
任维晨, 常庆霞, 张亚军, 朱宽宇( ), 王志琴, 杨建昌(
), 王志琴, 杨建昌( )
)
收稿日期:2021-12-02
修回日期:2022-06-17
出版日期:2022-11-10
发布日期:2022-11-10
通讯作者:
朱宽宇,杨建昌
基金资助:
REN Weichen, CHANG Qingxia, ZHANG Yajun, ZHU Kuanyu( ), WANG Zhiqin, YANG Jianchang(
), WANG Zhiqin, YANG Jianchang( )
)
Received:2021-12-02
Revised:2022-06-17
Online:2022-11-10
Published:2022-11-10
Contact:
ZHU Kuanyu, YANG Jianchang
摘要:
【目的】探明不同氮利用率水稻品种的氮素积累与转运特征及其机制。【方法】2个氮高效品种(武运粳30号和连粳7号)和2个氮低效品种(扬粳4038和宁粳1号)种植于大田,设置2个施氮量:全生育期不施氮(0 N)和全生育期施氮180 kg/hm2 (180N),比较分析了不同氮利用率粳稻品种干物质生产、氮素积累与转运差异及其机制。【结果】与氮低效品种相比,氮高效品种具有较高的产量、氮肥利用率、总颖花量和结实率,较高的花前干物质转运量和花后干物质积累量,分蘖至穗分化始期和抽穗至成熟期较高的净同化率和作物生长率,抽穗期较高的糖花比,灌浆期较高的籽粒库活性、籽粒中脱落酸与1-氨基环丙烷-1-羧酸含量的比值和茎鞘中较高的非结构性碳水化合物的转运和蔗糖合成相关酶活性以及蔗糖转运蛋白基因的表达量,抽穗后较高的氮转运、氮素吸收量,灌浆期较高的比叶氮含量、叶片中细胞分裂素含量、氮代谢酶活性以及氮素转运相关基因的表达量。【结论】氮高效品种穗分化前和抽穗后较高的物质生产效率以及灌浆期较高的碳氮转运与积累是产量和氮肥利用率协同提高的重要机制。
任维晨, 常庆霞, 张亚军, 朱宽宇, 王志琴, 杨建昌. 不同氮利用率粳稻品种的碳氮积累与转运特征及其生理机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(6): 586-600.
REN Weichen, CHANG Qingxia, ZHANG Yajun, ZHU Kuanyu, WANG Zhiqin, YANG Jianchang. Characteristics and Physiological Mechanism of Carbon and Nitrogen Accumulation and Translocation of japonica Rice Varieties Differing in Nitrogen Use Efficiency[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(6): 586-600.
| 品种 Variety | 选育单位 Breeding institution | 生育期 Growth period/d |
|---|---|---|
| 武运粳30号 Wuyunjing 30 | 江苏(武进)水稻研究所 | 156 |
| 连粳7号 Lianjing 7 | 连云港市农业科学研究院 | 153 |
| 宁粳1号 Ningjing 1 | 南京农业大学水稻研究所 | 152 |
| 扬粳4038 Yangjing 4038 | 江苏里下河地区农业科学研究所 | 154 |
表1 供试品种信息
Table 1. Information of test varieties.
| 品种 Variety | 选育单位 Breeding institution | 生育期 Growth period/d |
|---|---|---|
| 武运粳30号 Wuyunjing 30 | 江苏(武进)水稻研究所 | 156 |
| 连粳7号 Lianjing 7 | 连云港市农业科学研究院 | 153 |
| 宁粳1号 Ningjing 1 | 南京农业大学水稻研究所 | 152 |
| 扬粳4038 Yangjing 4038 | 江苏里下河地区农业科学研究所 | 154 |
| 基因名称 Gene | 引物序列 Primer sequence | 调控蛋白(酶) Encoding protein (enzyme) |
|---|---|---|
| OsActin | F-AGCAGCATGAAGATCAAGGTGGTC R-CCTTGGCAATCCACATCTGCTG | 内参蛋白 Actin |
| OsAMT1.1 | F-GGTTTCTCTCCCTCTCCGAT R-CCACCTTCACACCACACATT | 铵态氮转运蛋白1.1 Ammonium transporter 1.1 |
| OsAMT1.2 | F-AAGCACATGCCGCAGACA R-GACGCCCGACTTGAACAG | 铵态氮转运蛋白1.2 Ammonium transporter 1.2 |
| OsNRT1.1B | F-GGCAGGCTCGACTACTTCTA R-AGGCGCTTCTCCTTGTAGAC | 硝态氮转运蛋白1.1B Nitrate transporter 1.1B |
| OsNRT2.3a | F-CTCATCCGCGACACCCTC R-GATGGAGGAGCAGTACACCG | 硝态氮转运蛋白2.3a Nitrate transporter 2.3a |
| OsNPF2.4 | F-TAGGATTAAGTGGGTGAGG R-GTCAAACAGCAAGTAGCG | 硝态氮转运蛋白2.4 Nitrate transporter 2.4 |
| OsSUT1 | F-TTACAAGGACAACCGCGTCC R-GGCGTATCCCTTCATGGTGT | 蔗糖转运蛋白1 Sucrose transporter 1 |
| OsTPP7 | F-TCAAGGTGTGGTACGTGGTG R-CGAGGTCATAGCCCATCTTC | 海藻糖-6-磷酸磷酸酶7 Trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase 7 |
表2 氮素转运相关基因引物序列
Table 2. Genes primers sequences related to nitrogen transport.
| 基因名称 Gene | 引物序列 Primer sequence | 调控蛋白(酶) Encoding protein (enzyme) |
|---|---|---|
| OsActin | F-AGCAGCATGAAGATCAAGGTGGTC R-CCTTGGCAATCCACATCTGCTG | 内参蛋白 Actin |
| OsAMT1.1 | F-GGTTTCTCTCCCTCTCCGAT R-CCACCTTCACACCACACATT | 铵态氮转运蛋白1.1 Ammonium transporter 1.1 |
| OsAMT1.2 | F-AAGCACATGCCGCAGACA R-GACGCCCGACTTGAACAG | 铵态氮转运蛋白1.2 Ammonium transporter 1.2 |
| OsNRT1.1B | F-GGCAGGCTCGACTACTTCTA R-AGGCGCTTCTCCTTGTAGAC | 硝态氮转运蛋白1.1B Nitrate transporter 1.1B |
| OsNRT2.3a | F-CTCATCCGCGACACCCTC R-GATGGAGGAGCAGTACACCG | 硝态氮转运蛋白2.3a Nitrate transporter 2.3a |
| OsNPF2.4 | F-TAGGATTAAGTGGGTGAGG R-GTCAAACAGCAAGTAGCG | 硝态氮转运蛋白2.4 Nitrate transporter 2.4 |
| OsSUT1 | F-TTACAAGGACAACCGCGTCC R-GGCGTATCCCTTCATGGTGT | 蔗糖转运蛋白1 Sucrose transporter 1 |
| OsTPP7 | F-TCAAGGTGTGGTACGTGGTG R-CGAGGTCATAGCCCATCTTC | 海藻糖-6-磷酸磷酸酶7 Trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase 7 |
| 处理 Treatment | 品种 Variety | 产量 Grain yield /(t·hm-2) | 单位面积穗数 Number of panicles per 1 m2 | 每穗粒数 Spikelets per panicle | 总颖花数 Total spikelets /(×103·m−2) | 结实率 Seed setting rate/% | 千粒重 1000-grain weight/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0N | 武运粳30号Wuyujing 30 | 6.44±0.33 c | 220±9 d | 125±5 d | 27.5±0.5 e | 83.7±1.9 a | 28.3±0.3 a |
| 连粳7号Lianjing 7 | 6.53±0.39 c | 234±4 c | 131±4 c | 30.7±1.4 d | 84.9±2.8 a | 28.7±0.3 a | |
| 宁粳1号Ningjing 1 | 5.89±0.25 d | 218±6 d | 120±6 e | 26.1±0.4 f | 76.1±2.1 cd | 27.9±0.5 a | |
| 扬粳4038 Yangjing 4038 | 5.82±0.17 d | 230±8 c | 114±4 f | 26.2±0.6 f | 80.5±2.4 b | 28.7±0.5 a | |
| 180N | 武运粳30号Wuyunjing 30 | 9.16±0.36 a | 290±9 a | 146±5 a | 42.3±2.3 a | 79.4±1.6 b | 28.1±0.6 a |
| 连粳7号Lianjing 7 | 9.38±0.27 a | 284±5 a | 150±8 a | 42.6±3.0 a | 80.4±3.4 b | 28.5±0.7 a | |
| 宁粳1号Ningjing 1 | 8.17±0.32 b | 273±13 b | 134±6 b | 36.5±1.4 c | 73.9±1.2 d | 27.9±0.8 a | |
| 扬粳4038 Yangjing 4038 | 8.23±0.21 b | 285±10 a | 138±6 b | 39.3±1.1 b | 78.3±2.3 bc | 28.5±0.4 a | |
| 方差分析ANOVA | |||||||
| 氮肥Nitrogen(N) | *** | *** | *** | *** | ** | NS | |
| 品种Variety(V) | *** | NS | *** | *** | *** | NS | |
| 氮肥×品种N×V | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | |
表3 不同氮利用率粳稻品种的产量及其构成因素
Table 3. Yield and its components of japonica rice varieties differing in nitrogen use efficiency.
| 处理 Treatment | 品种 Variety | 产量 Grain yield /(t·hm-2) | 单位面积穗数 Number of panicles per 1 m2 | 每穗粒数 Spikelets per panicle | 总颖花数 Total spikelets /(×103·m−2) | 结实率 Seed setting rate/% | 千粒重 1000-grain weight/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0N | 武运粳30号Wuyujing 30 | 6.44±0.33 c | 220±9 d | 125±5 d | 27.5±0.5 e | 83.7±1.9 a | 28.3±0.3 a |
| 连粳7号Lianjing 7 | 6.53±0.39 c | 234±4 c | 131±4 c | 30.7±1.4 d | 84.9±2.8 a | 28.7±0.3 a | |
| 宁粳1号Ningjing 1 | 5.89±0.25 d | 218±6 d | 120±6 e | 26.1±0.4 f | 76.1±2.1 cd | 27.9±0.5 a | |
| 扬粳4038 Yangjing 4038 | 5.82±0.17 d | 230±8 c | 114±4 f | 26.2±0.6 f | 80.5±2.4 b | 28.7±0.5 a | |
| 180N | 武运粳30号Wuyunjing 30 | 9.16±0.36 a | 290±9 a | 146±5 a | 42.3±2.3 a | 79.4±1.6 b | 28.1±0.6 a |
| 连粳7号Lianjing 7 | 9.38±0.27 a | 284±5 a | 150±8 a | 42.6±3.0 a | 80.4±3.4 b | 28.5±0.7 a | |
| 宁粳1号Ningjing 1 | 8.17±0.32 b | 273±13 b | 134±6 b | 36.5±1.4 c | 73.9±1.2 d | 27.9±0.8 a | |
| 扬粳4038 Yangjing 4038 | 8.23±0.21 b | 285±10 a | 138±6 b | 39.3±1.1 b | 78.3±2.3 bc | 28.5±0.4 a | |
| 方差分析ANOVA | |||||||
| 氮肥Nitrogen(N) | *** | *** | *** | *** | ** | NS | |
| 品种Variety(V) | *** | NS | *** | *** | *** | NS | |
| 氮肥×品种N×V | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | |
| 处理 Treatment | 品种 Variety | 氮肥农学利用率 AEN /(kg·kg−1) | 氮肥偏生产力 PFPN /(kg·kg−1) | 籽粒氮素利用率 IEN /(kg·kg−1) | 氮肥回收利用率 REN/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0N | 武运粳30号 Wuyunjing 30 | 66.0±2.5 a | |||
| 连粳7号Lianjing 7 | 66.2±1.9 a | ||||
| 宁粳1号Ningjing 1 | 63.4±2.2 b | ||||
| 扬粳4038 Yangjing 4038 | 62.1±1.5 b | ||||
| 180N | 武运粳30号 Wuyunjing 30 | 15.1±0.7 a | 50.9±2.0 a | 54.6±1.1 c | 39.1±1.5 a |
| 连粳7号Lianjing 7 | 15.8±2.1 a | 52.1±1.5 a | 54.9±1.4 c | 40.2±1.4 a | |
| 宁粳1号Ningjing 1 | 12.7±1.0 b | 45.4±1.8 b | 51.7±1.3 d | 36.2±1.2 b | |
| 扬粳4038 Yangjing 4038 | 13.2±1.2 b | 45.7±1.2 b | 51.4±1.7 d | 36.9±1.7 b | |
| 方差分析ANOVA | |||||
| 氮肥Nitrogen(N) | *** | ||||
| 品种Variety(V) | *** | *** | ** | ** | |
| 氮肥×品种N×V | NS | NS | NS | NS | |
表4 不同氮利用率粳稻品种的氮肥利用率
Table 4. Nitrogen uptake and utilization of japonica rice varieties differing in nitrogen use efficiency.
| 处理 Treatment | 品种 Variety | 氮肥农学利用率 AEN /(kg·kg−1) | 氮肥偏生产力 PFPN /(kg·kg−1) | 籽粒氮素利用率 IEN /(kg·kg−1) | 氮肥回收利用率 REN/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0N | 武运粳30号 Wuyunjing 30 | 66.0±2.5 a | |||
| 连粳7号Lianjing 7 | 66.2±1.9 a | ||||
| 宁粳1号Ningjing 1 | 63.4±2.2 b | ||||
| 扬粳4038 Yangjing 4038 | 62.1±1.5 b | ||||
| 180N | 武运粳30号 Wuyunjing 30 | 15.1±0.7 a | 50.9±2.0 a | 54.6±1.1 c | 39.1±1.5 a |
| 连粳7号Lianjing 7 | 15.8±2.1 a | 52.1±1.5 a | 54.9±1.4 c | 40.2±1.4 a | |
| 宁粳1号Ningjing 1 | 12.7±1.0 b | 45.4±1.8 b | 51.7±1.3 d | 36.2±1.2 b | |
| 扬粳4038 Yangjing 4038 | 13.2±1.2 b | 45.7±1.2 b | 51.4±1.7 d | 36.9±1.7 b | |
| 方差分析ANOVA | |||||
| 氮肥Nitrogen(N) | *** | ||||
| 品种Variety(V) | *** | *** | ** | ** | |
| 氮肥×品种N×V | NS | NS | NS | NS | |
| 处理 Treatment | 品种 Variety | 氮积累量 Nitrogen accumulation/(kg·hm−2) | 氮转运量 NT/(kg·hm−2) | 氮转运率 NTE/% | 氮收获指数HIN/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 抽穗期 HT | 成熟期 MA | 抽穗-成熟 HT-MA | ||||||
| 0N | 武运粳30号 Wuyujing 30 | 82.8±1.5 c | 97.6±2.7 c | 14.8±2.9 c | 41.2±1.4 c | 55.9±1.6 a | 67.4±2.4 a | |
| 连粳7号 Lianjing 7 | 82.1±2.7 c | 98.6±2.5 c | 16.5±2.0 c | 39.4±1.1 c | 55.2±2.0 a | 67.0±1.9 a | ||
| 宁粳1号 Ningjing 1 | 81.4±1.3 c | 92.8±1.6 d | 11.4±1.6 d | 38.2±1.1 c | 52.1±1.2 b | 61.8±3.3 b | ||
| 扬粳4038 Yangjing 4038 | 81.5±2.4 c | 93.6±1.4 d | 12.1±2.4 d | 37.5±1.2 c | 52.5±1.6 b | 62.3±2.0 b | ||
| 180N | 武运粳30号 Wuyunjing 30 | 141.0±3.9 a | 169.0±5.0 a | 28.0±1.4 a | 56.7±1.1 a | 45.5±1.6 c | 60.4±1.2 b | |
| 连粳7号 Lianjing 7 | 142.0±4.0 a | 171.0±4.0 a | 29.0±2.3 a | 57.5±1.9 a | 46.8±0.7 c | 61.2±1.5 b | ||
| 宁粳1号 Ningjing 1 | 135.0±1.8 b | 158.0±7.0 b | 23.0±2.7 b | 48.0±1.2 b | 40.2±2.1 d | 54.7±0.7 c | ||
| 扬粳4038 Yangjing 4038 | 136.0±3.6 b | 160.0±6.0 b | 24.0±1.7 b | 49.2±1.1 b | 40.7±1.1 d | 55.2±1.7 c | ||
| 方差分析 ANOVA | ||||||||
| 氮肥 Nitrogen(N) | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | ||
| 品种 Variety(V) | * | ** | *** | *** | *** | *** | ||
| 氮肥×品种 N×V | NS | NS | NS | *** | NS | NS | ||
表5 不同氮利用率粳稻品种的氮素积累和转运
Table 5. Nitrogen accumulation and translocation in japonica rice varieties differing in nitrogen use efficiency.
| 处理 Treatment | 品种 Variety | 氮积累量 Nitrogen accumulation/(kg·hm−2) | 氮转运量 NT/(kg·hm−2) | 氮转运率 NTE/% | 氮收获指数HIN/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 抽穗期 HT | 成熟期 MA | 抽穗-成熟 HT-MA | ||||||
| 0N | 武运粳30号 Wuyujing 30 | 82.8±1.5 c | 97.6±2.7 c | 14.8±2.9 c | 41.2±1.4 c | 55.9±1.6 a | 67.4±2.4 a | |
| 连粳7号 Lianjing 7 | 82.1±2.7 c | 98.6±2.5 c | 16.5±2.0 c | 39.4±1.1 c | 55.2±2.0 a | 67.0±1.9 a | ||
| 宁粳1号 Ningjing 1 | 81.4±1.3 c | 92.8±1.6 d | 11.4±1.6 d | 38.2±1.1 c | 52.1±1.2 b | 61.8±3.3 b | ||
| 扬粳4038 Yangjing 4038 | 81.5±2.4 c | 93.6±1.4 d | 12.1±2.4 d | 37.5±1.2 c | 52.5±1.6 b | 62.3±2.0 b | ||
| 180N | 武运粳30号 Wuyunjing 30 | 141.0±3.9 a | 169.0±5.0 a | 28.0±1.4 a | 56.7±1.1 a | 45.5±1.6 c | 60.4±1.2 b | |
| 连粳7号 Lianjing 7 | 142.0±4.0 a | 171.0±4.0 a | 29.0±2.3 a | 57.5±1.9 a | 46.8±0.7 c | 61.2±1.5 b | ||
| 宁粳1号 Ningjing 1 | 135.0±1.8 b | 158.0±7.0 b | 23.0±2.7 b | 48.0±1.2 b | 40.2±2.1 d | 54.7±0.7 c | ||
| 扬粳4038 Yangjing 4038 | 136.0±3.6 b | 160.0±6.0 b | 24.0±1.7 b | 49.2±1.1 b | 40.7±1.1 d | 55.2±1.7 c | ||
| 方差分析 ANOVA | ||||||||
| 氮肥 Nitrogen(N) | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | ||
| 品种 Variety(V) | * | ** | *** | *** | *** | *** | ||
| 氮肥×品种 N×V | NS | NS | NS | *** | NS | NS | ||
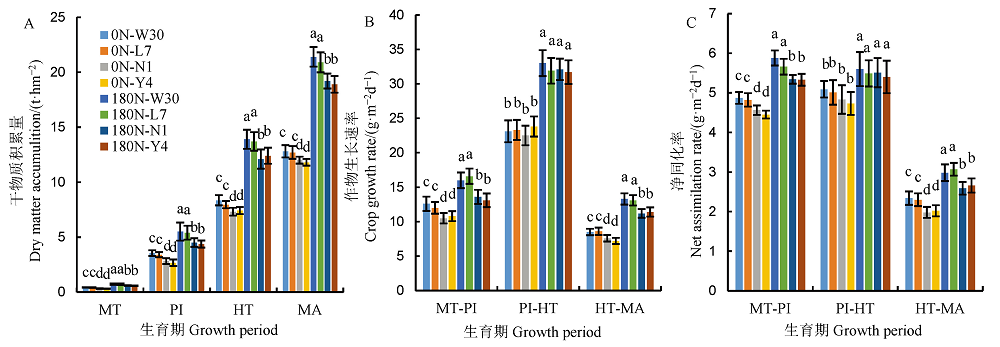
图1 不同氮利用率粳稻品种各生育期干物重积累(A)、作物生长速率(B)和净同化率(C) 0N-不施氮;180N-180 kg/hm2;W30-武运粳30号;L7-连粳7号;N1-宁粳1号;Y4-扬粳4038。MT-分蘖中期;PI-穗分化始期;HT-抽穗期;MA-成熟期;MT-PI-分蘖中期至穗分化始期;PI-HT-穗分化始期至抽穗期;HT-MA-抽穗至成熟期。柱形上方线条为标准差,n=3。同一生育时期或持续期内柱形上不同字母表示在P = 0.05水平上差异显著。下同。
Fig. 1. Dry matter accumulation(A), crop growth rate(B) and net assimilation rate(C) of japonica rice varieties differing in nitrogen use efficiency at different growth stages. 0N, Nitrogen omission; 180N, 180 kg/hm2; W30, Wuyunjing 30; L7, Lianjing 7; N1, Ningjing 1; Y4, Yangjing 4038. MT, Middle tillering; PI, Panicle initiation; HT, Heading time; MA, Maturity; MT-PI, Mid-tillering to panicle initiation; PI-HT, Panicle initiation to heading; HT-MA, Heading to maturity. Vertical bars above the column represent the standard deviations of the mean(n=3) where these exceed the size of the symbol. Different letters above the column indicate statistical significance at P = 0.05 level within the same growing stage. The same as below.
| 处理 Treatment | 品种 Variety | 抽穗至成熟期干物质量 DMAHT-MA/(t·hm−2) | 花前物质转运量 MT/(t·hm−2) | 物质转运率 MTE/% | 收获指数 Harvest index/% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0N | 武运粳30号 Wuyunjing 30 | 4.38±0.14 c | 1.71±0.05 c | 21.6±0.4 a | 51.2±1.3 a | |
| 连粳7号 Lianjing 7 | 4.33±0.11 c | 1.69±0.06 c | 21.2±0.4 a | 50.8±2.7 a | ||
| 宁粳1号 Ningjing 1 | 4.10±0.20 d | 1.36±0.07 d | 18.3±0.4 b | 48.3±0.5 b | ||
| 扬粳4038 Yangjing 4038 | 4.06±0.15 d | 1.32±0.05 d | 17.9±0.6 b | 49.1±2.0 b | ||
| 180N | 武运粳30号 Wuyunjing 30 | 7.12±0.16 a | 2.11±0.03 a | 17.0±0.2 c | 45.8±0.8 c | |
| 连粳7号 Lianjing 7 | 6.94±0.24 a | 2.15±0.05 a | 16.6±0.4 c | 45.0±0.5 c | ||
| 宁粳1号 Ningjing 1 | 6.39±0.14 b | 1.80±0.08 b | 14.8±0.3 d | 42.4±0.7 d | ||
| 扬粳4038 Yangjing 4038 | 6.31±0.13 b | 1.82±0.03 b | 14.4±0.5 d | 42.2±2.1 d | ||
| 方差分析ANOVA | ||||||
| 氮肥 Nitrogen(N) | *** | *** | *** | *** | ||
| 品种 Variety(V) | *** | *** | *** | ** | ||
| 氮肥×品种 N×V | NS | NS | * | NS | ||
表6 不同氮利用率粳稻品种的花后物质积累和转运
Table 6. Matter accumulation and translocation of japonica rice varieties differing in nitrogen use efficiency.
| 处理 Treatment | 品种 Variety | 抽穗至成熟期干物质量 DMAHT-MA/(t·hm−2) | 花前物质转运量 MT/(t·hm−2) | 物质转运率 MTE/% | 收获指数 Harvest index/% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0N | 武运粳30号 Wuyunjing 30 | 4.38±0.14 c | 1.71±0.05 c | 21.6±0.4 a | 51.2±1.3 a | |
| 连粳7号 Lianjing 7 | 4.33±0.11 c | 1.69±0.06 c | 21.2±0.4 a | 50.8±2.7 a | ||
| 宁粳1号 Ningjing 1 | 4.10±0.20 d | 1.36±0.07 d | 18.3±0.4 b | 48.3±0.5 b | ||
| 扬粳4038 Yangjing 4038 | 4.06±0.15 d | 1.32±0.05 d | 17.9±0.6 b | 49.1±2.0 b | ||
| 180N | 武运粳30号 Wuyunjing 30 | 7.12±0.16 a | 2.11±0.03 a | 17.0±0.2 c | 45.8±0.8 c | |
| 连粳7号 Lianjing 7 | 6.94±0.24 a | 2.15±0.05 a | 16.6±0.4 c | 45.0±0.5 c | ||
| 宁粳1号 Ningjing 1 | 6.39±0.14 b | 1.80±0.08 b | 14.8±0.3 d | 42.4±0.7 d | ||
| 扬粳4038 Yangjing 4038 | 6.31±0.13 b | 1.82±0.03 b | 14.4±0.5 d | 42.2±2.1 d | ||
| 方差分析ANOVA | ||||||
| 氮肥 Nitrogen(N) | *** | *** | *** | *** | ||
| 品种 Variety(V) | *** | *** | *** | ** | ||
| 氮肥×品种 N×V | NS | NS | * | NS | ||
| 处理 Treatment | 品种 Variety | NSC积累量 NSC accumulation/(g·m−2) | NSC转运率 NSC remobilization rate/% | 糖花比 Sugar-spikelets ratio/(mg·spikelet−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 抽穗期 Heading | 成熟期 Maturity | ||||
| 0 N | 武运粳30号Wuyujing 30 | 183±19 c | 81.7±11 c | 55.4±3.5 a | 6.65±0.40 a |
| 连粳7号Lianjing 7 | 193±16 c | 78.3±7 c | 59.4±4.7 a | 6.29±0.10 b | |
| 宁粳1号Ningjing 1 | 156±10 d | 78.6±9 c | 49.7±2.2 b | 5.99±0.09 c | |
| 扬粳4038 Yangjing 4038 | 154±12 d | 76.8±4 c | 50.0±2.0 b | 5.86±0.13 c | |
| 180N | 武运粳30号Wuyunjing 30 | 249±25 a | 124±7 a | 50.2±0.9 b | 5.89±0.18 c |
| 连粳7号Lianjing 7 | 247±9 a | 120±8 a | 51.4±1.2 b | 5.80±0.20 c | |
| 宁粳1号Ningjing 1 | 200±8 bc | 108±5 b | 46.0±1.4 c | 5.48±0.15 d | |
| 扬粳4038 Yangjing 4038 | 210±20 b | 112±6 b | 46.7±1.0 c | 5.34±0.22 d | |
| 方差分析ANOVA | |||||
| 氮肥Nitrogen(N) | *** | *** | *** | *** | |
| 品种Variety(V) | * | ** | *** | *** | |
| 氮肥×品种N×V | NS | NS | NS | NS | |
表7 不同氮利用率粳稻品种的茎中NSC转运率和糖花比
Table 7. Non-structual carbohydrate (NSC) in stems and NSC to the number of spikelets at heading and NSC remobilization of japonica rice varieties differing in nitrogen use efficiency.
| 处理 Treatment | 品种 Variety | NSC积累量 NSC accumulation/(g·m−2) | NSC转运率 NSC remobilization rate/% | 糖花比 Sugar-spikelets ratio/(mg·spikelet−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 抽穗期 Heading | 成熟期 Maturity | ||||
| 0 N | 武运粳30号Wuyujing 30 | 183±19 c | 81.7±11 c | 55.4±3.5 a | 6.65±0.40 a |
| 连粳7号Lianjing 7 | 193±16 c | 78.3±7 c | 59.4±4.7 a | 6.29±0.10 b | |
| 宁粳1号Ningjing 1 | 156±10 d | 78.6±9 c | 49.7±2.2 b | 5.99±0.09 c | |
| 扬粳4038 Yangjing 4038 | 154±12 d | 76.8±4 c | 50.0±2.0 b | 5.86±0.13 c | |
| 180N | 武运粳30号Wuyunjing 30 | 249±25 a | 124±7 a | 50.2±0.9 b | 5.89±0.18 c |
| 连粳7号Lianjing 7 | 247±9 a | 120±8 a | 51.4±1.2 b | 5.80±0.20 c | |
| 宁粳1号Ningjing 1 | 200±8 bc | 108±5 b | 46.0±1.4 c | 5.48±0.15 d | |
| 扬粳4038 Yangjing 4038 | 210±20 b | 112±6 b | 46.7±1.0 c | 5.34±0.22 d | |
| 方差分析ANOVA | |||||
| 氮肥Nitrogen(N) | *** | *** | *** | *** | |
| 品种Variety(V) | * | ** | *** | *** | |
| 氮肥×品种N×V | NS | NS | NS | NS | |
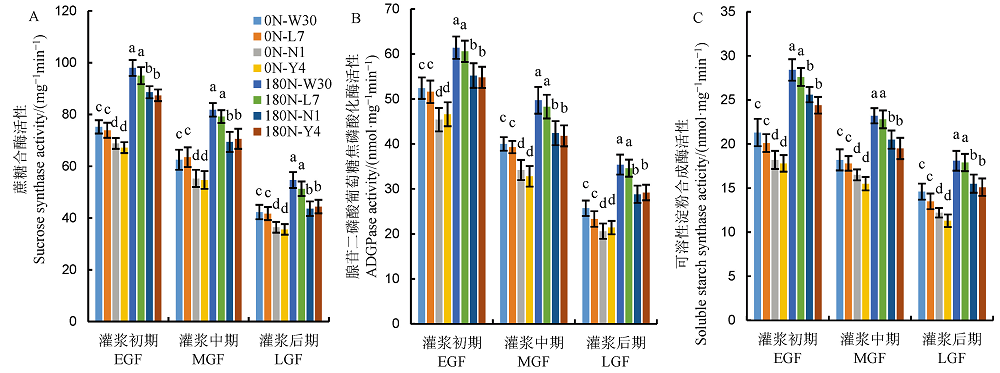
图2 不同氮利用率粳稻品种籽粒蔗糖合酶活性(A)、腺苷二磷酸葡萄糖焦磷酸化酶活性(B)和可溶性淀粉合成酶活性(C) W30-武运粳30号;L7-连粳7号;N1-宁粳1号;Y4-扬粳4038;下图同。
Fig. 2. Activities of sucrose synthase (A), adenosine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase (B) and soluble starch synthase (C) in the grains of japonica rice varieties differing in nitrogen use efficiency. EGF, Early grain filling stage; MGF, Middle grain filling stage; LGF, Late grain filling stage. W30, Wuyunjing 30; L7, Lianjing 7; N1, Ningjing 1;Y4, Yangjing 4038. The same below.
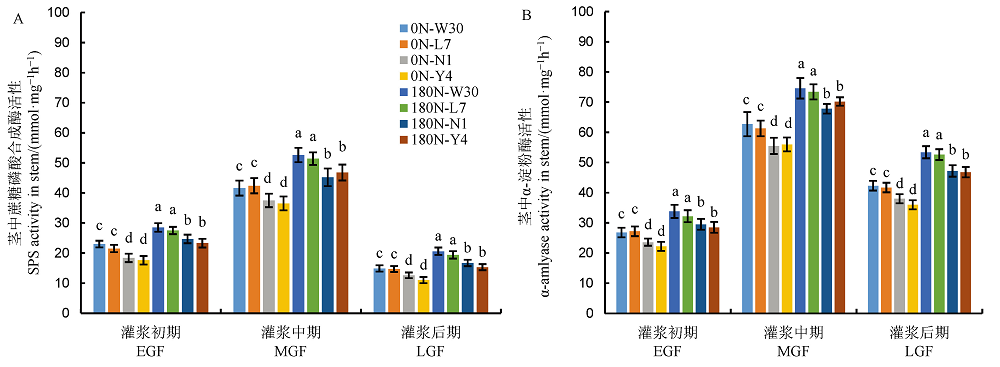
图3 不同氮利用率粳稻品种茎鞘中蔗糖磷酸合酶活性(A)和α-淀粉酶活性(B)
Fig. 3. Activities of sucrose phosphosynthase (A) and α -amylase (B) in the stems of japonica rice varieties in nitrogen use efficiency.
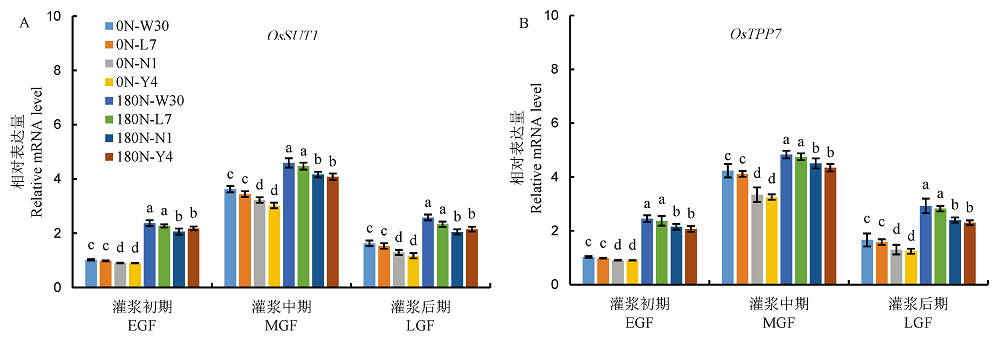
图4 不同氮利用率粳稻品种灌浆期茎鞘中OsSUT1(A)和OsTPP7(B)的表达水平
Fig. 4. OsSUT1 (A) and OsTPP7 (B) expression levels in stems of japonica varieties differing in nitrogen use efficiency during grain filling.
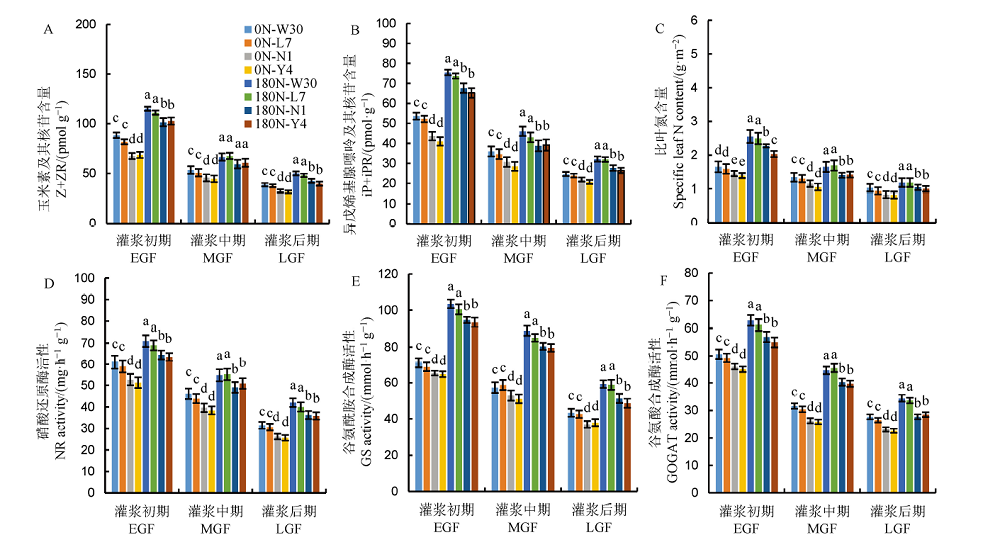
图5 不同氮利用率水稻品种灌浆期剑叶中细胞分裂素(A, B)、比叶氮含量(C)和氮代谢酶活性(D~F)
Fig. 5. Cytokinin and specific leaf N contents and the activities of the enzymes related to nitrogen metabolism in flag leaves of japonica varieties differing in nitrogen use efficiency during grain filling.
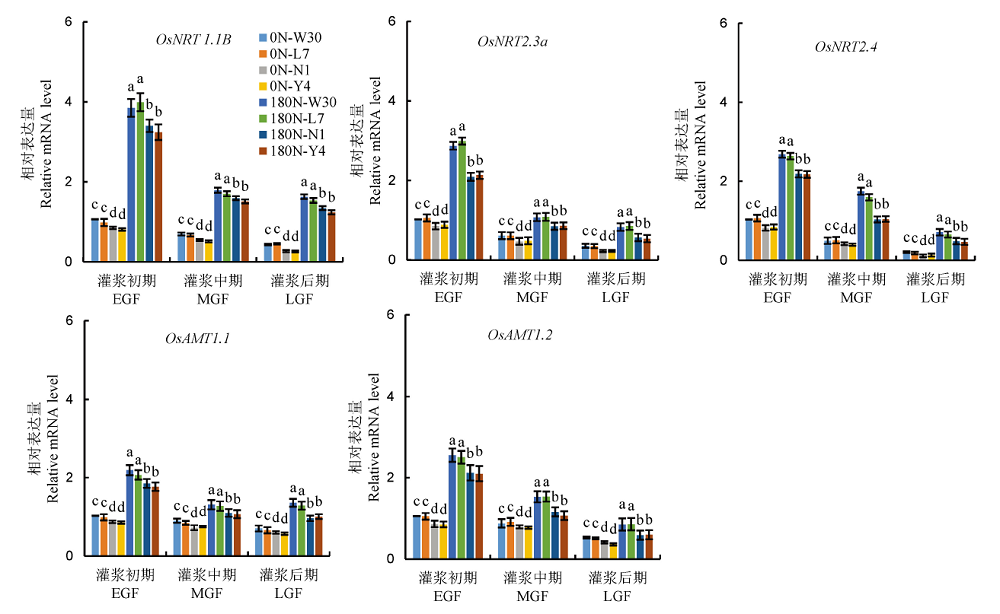
图6 不同氮利用率粳稻品种灌浆期剑叶中氮转运相关基因的表达水平
Fig. 6. Gene expression levels related to nitrogen transport of japonica rice varieties differing in nitrogen use efficiency during grain filling.
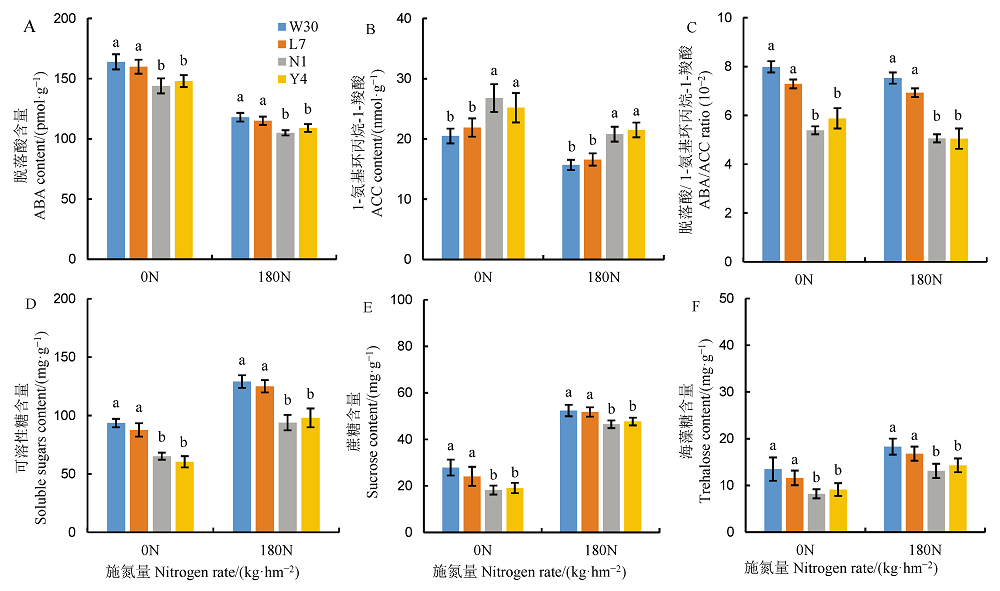
图7 不同氮利用率粳稻品种灌浆中期籽粒中脱落酸(A)、乙烯合成前体1-氨基环丙烷-1-羧酸(B)含量、ABA与ACC比值(C)以及茎鞘中可溶性总糖(D)、蔗糖(E)和海藻糖含量(F)
Fig. 7. Contents of abscisic acid (A) and 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid (ACC) (B), the ratio of ABA to ACC, and the contents of soluble sugars, sucrose and trehalose of japonica rice varieties differing in nitrogen use efficiency during mid-grain filling.
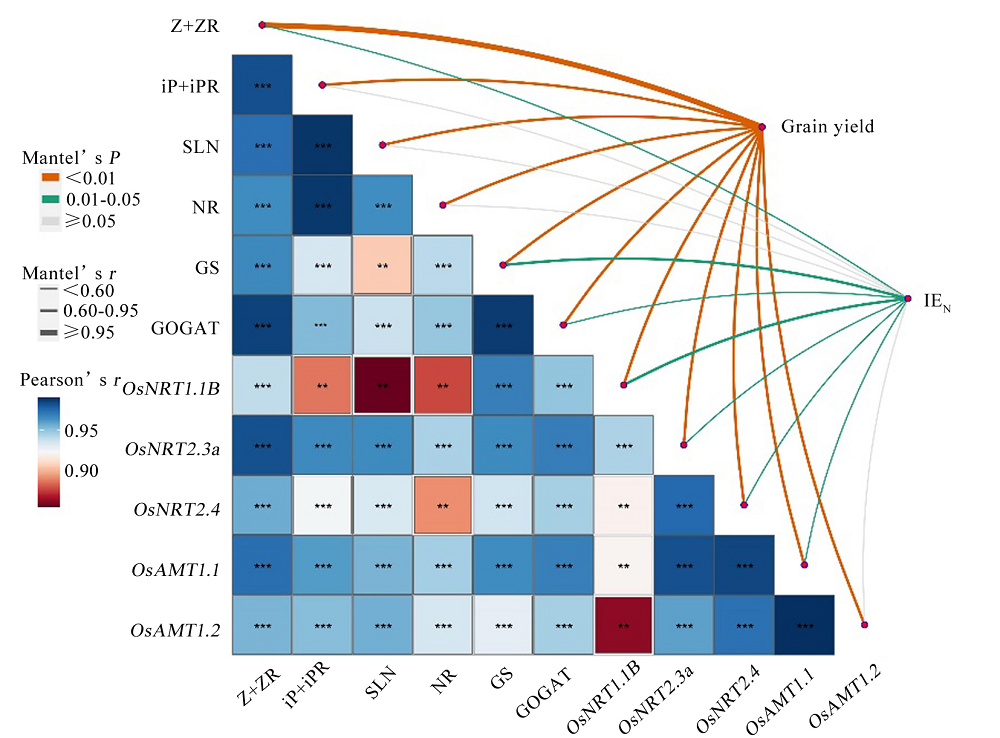
图8 植株灌浆期主要生理性状、氮转运相关基因表达水平与产量和氮肥利用率的相关性分析 **,***表示在P = 0.01和P = 0.001水平上差异显著(n = 8)。
Fig. 8. Correlation analysis of grain yield and NUE with plant main physiological traits and the expression levels of genes involved in nitrogen transport during grain filling. **, *** Significant at the P = 0.01 and P = 0.001 probability levels, respectively (n = 8).
| [1] | 叶利庭, 宋文静, 吕华军, 栗艳霞, 沈其荣, 张丽亚. 不同氮效率水稻生育后期氮素积累转运特征[J]. 土壤学报, 2010, 47(2): 303-310. |
| Ye L T, Song W J, Lü H J, Li Y X, Shen Q R, Zhang L Y. Accumulation and translocation of nitrogen at late-growth stage in rices different in cultivar nitrogen use efficiency[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2010, 47(2): 303-310. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | 杨京平, 姜宁, 陈杰. 水稻吸氮量和干物质积累的模拟试验研究[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2002, (3): 318-324. |
| Yang J P, Jiang N, Chen J. The validation of modeling effects of different nitrogen levels on the leaf nitrogen and yield dynamics of rice[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2002, 32(3): 318-324. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 魏海燕, 张洪程, 马群, 戴其根, 霍中洋, 许轲, 张庆, 黄丽芬. 不同氮肥吸收利用效率水稻基因型叶片衰老特性[J]. 作物学报, 2010, 36(4): 645-654. |
| Wei H Y, Zhang H C, Ma Q, Dai Q G, Huo Z Y, Xu K, Zhang Q, Huang L F. Characteristics of leaf senescence in rice genotypes with different nitrogen use efficiencies[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2010, 36(4): 645-654. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | Pan J, Cui K, Wei D, Huang J L, Xiang J, Nie L X. Relationships of non-structural carbohydrates accumulation and translocation with yield formation in rice recombinant inbred lines under two nitrogen levels[J]. Physiologia Plantarum, 2011, 141(4): 321-331. |
| [5] | Xiong J, Ding C Q, Wei G B, Ding Y F, Wang S H. Characteristic of dry matter accumulation and nitrogen uptake of super high-yielding early rice in China[J]. Agronomy Journal, 2013, 105(4): 1142-1150. |
| [6] | Li G, Hu Q, Shi Y, Cui K H, Nie L X, Huang J L, Peng S B. Low nitrogen application enhances starch-metabolizing enzyme activity and improves accumulation and translocation of non-structural carbohydrates in rice stems[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2018, 9: 1128. |
| [7] | Nagata K, Yoshinaga S, Takanashi J, Terao T. Effects of dry matter production, translocation of nonstructural carbohydrates and nitrogen application on grain filling in rice cultivar Takanari, a cultivar bearing a large number of spikelets[J]. Plant Production Science, 2001, 4(3): 173-183. |
| [8] | Peng Y, Sun Y J, Jiang M J, Xu H, Qin J, Yang Z Y, Ma J. Effects of water management and slow controlled release nitrogen fertilizer on biomass and nitrogen accumulation, translocation, and distribution in rice[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2014, 40(5): 859-870. |
| [9] | Zhong C, Cao X C, Hu J J, Zhu L F, Zhang J H, Huang J F, Jin Q Y. Nitrogen metabolism in adaptation of photosynthesis to water stress in rice grown under different nitrogen levels[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2017, 8: 1079. |
| [10] | 叶利庭, 吕华军, 宋文静, 图尔迪, 沈其荣, 张亚丽. 不同氮效率水稻生育后期氮代谢酶活性的变化特征[J]. 土壤学报, 2011, 48(1): 132-40. |
| Ye L T, Lü H J, Song W J, Tu E D, Shen Q R, Zhang Y L. Variation of activity of N metabolizing enzymes in rice plants different in N use efficiency at their late growth stages[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2011, 48(1): 132-40. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 孙永健, 孙园园, 严奉君, 杨志远, 徐徽, 李玥, 王海月, 马均. 氮肥后移对不同氮效率水稻花后碳氮代谢的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2017, 43(3): 407-419. |
| Sun Y J, Sun Y Y, Yan F J, Yang Z Y, Xu H, Li Y, Wang H Y, Ma J. Effects of postponing nitrogen topdressing on post-anthesis carbon and nitrogen metabolism in rice cultivars with different nitrogen use efficiencies[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2017, 43(3): 407-419. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 程建峰, 戴廷波, 曹卫星, 姜东, 潘晓云. 不同氮收获指数基因型的氮代谢特征[J]. 作物学报, 2007, 33(3): 497-502. |
| Cheng J F, Dai T B, Cao W X, Jiang D, Pan X Y. Nitrogen metabolic characteristics in rice genotypes with different nitrogen harvest index[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2007, 33(3): 497-502. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | 王平. 不同氮效率类型小麦氮代谢差异及其机理分析[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2011. |
| Wang P. Genotypic differences in nitrogen metabolism and the analysis of physiological mechanism[D]. Tai’an: Shandong Agricultural University, 2011. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | Kamada-Nobusada T, Makita N, Kojima M, Sakakibara H. Nitrogen-dependent regulation of de novo cytokinin biosynthesis in rice: the role of glutamine metabolism as an additional signal[J]. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2013, 54(11): 1881-1893. |
| [15] | Zhu K, Zhou Q, Shen Y, Yan J Q, Xu Y J, Wang Z Q, Yang J C. Agronomic and physiological performance of an indica-japonica rice variety with a high yield and high nitrogen use efficiency[J]. Crop Science, 2020, 60(3): 1556-1568. |
| [16] | Gu J F, Li Z K, Mao Y Q, Struik P C, Zhang H, Liu L J, Wang Z Q, Yang J C. Roles of nitrogen and cytokinin signals in root and shoot communications in maximizing of plant productivity and their agronomic applications[J]. Plant Science, 2018, 274: 320-331. |
| [17] | Frank M, Cortleven A, Novák O, Schmulling T. Root-derived trans-zeatin cytokinin protects Arabidopsis plants against photoperiod stress[J]. Plant Cell & Environment, 2020, 43(11): 2637-2649. |
| [18] | 王留艳. 缺氮胁迫下细胞分裂素对水稻幼苗氮素分配及叶片衰老的调控作用[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2017. |
| Wang L Y. The regulation of cytokinin on nitrogen distribution and leaf senescence in rice seedlings under nitrogen deficiency[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | Yoshida S, Forno D A, Cock J H. Laboratory Manual for Physiological Studies of Rice[M]. Los Baños, The Philippines: International Rice Research Institute, 1976: 24-79. |
| [20] | Krapp A, Saliba-Colombani V, Daniel-Vedele F. Analysis of C and N metabolisms and of C/N interactions using quantitative genetics[J]. Photosynthesis Research, 2005, 83: 251-263. |
| [21] | 申丽霞, 王璞. 玉米穗位叶碳氮代谢的关键指标测定[J]. 中国农学通报, 2009: 155-157. |
| [22] | Ntanos D A, Koutroubas S D. Dry matter and N accumulation and translocation for Indica and Japonica rice under Mediterranean conditions[J]. Field Crops Research, 2002, 74(1): 93-101. |
| [23] | 魏海燕, 张洪程, 杭杰, 戴其根, 霍中洋, 张胜飞, 马群, 张庆, 张军. 不同氮素利用效率基因型水稻氮素积累与转移的特性[J]. 作物学报, 2008, 34(1): 119-125. |
| Wei H Y, Zhang H C, Hang J, Dai Q G, Huo Z Y, Zhang S F, Ma Q, Zhang Q, Zhang J. Characteristics of N accumulation and translocation in rice genotypes with different N use efficiencies[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2008, 34(1): 119-125. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | 剧成欣. 不同水稻品种对氮素响应的差异及其农艺生理性状[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2017. |
| Ju C X. Agronomic and physiological traits for rice cultivars differing in response to nitrogen[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | Zhu K Y, Yan J Q, Shen Y, Zhang W Y, Xu Y J, Wang Z Q, Yang J C. Deciphering the physio-morphological traits for high yield potential in nitrogen efficient varieties (NEVs): A japonica rice case study[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2021, 21(4): 947-963. |
| [26] | Zhang T, Shi Y Y, Piao F Z, Sun Z Q. Effects of different LED sources on the growth and nitrogen metabolism of lettuce[J]. Plant Cell, 2018, 134(2): 231-240. |
| [27] | 常二华. 根系化学讯号与稻米品质的关系及其调控技术[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2008. |
| Chang E H. Relationship between root chemical signals and grain qualiy of rice and its regulation techniques[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2008. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | Cheng C Y, Lur H S. Ethylene may be involved in abortion of the maize caryopsis[J]. Physiologia Plantarum, 1996, 98: 245-252. |
| [29] | Chu G, Wang Z Q, Zhang H, Yang J C, Zhang J H. Agronomic and physiological performance of rice under integrative crop management[J]. Agronomy Journal, 2016, 108(1): 117-128. |
| [30] | 许阳东, 朱宽宇, 章星传, 王志琴, 杨建昌. 绿色超级稻品种的农艺与生理性状分析[J]. 作物学报, 2019, 45(1): 70-80. |
| Xu Y D, Zhu K Y, Zhang X C, Wang Z Q, Yang J C. Analysis in agronomic and physiological traits of green super rice[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2019, 45(1): 70-80. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | Huang L Y, Yang D S, Li X X, Peng S B, Wang F. Coordination of high grain yield and high nitrogen use efficiency through large sink size and high post-heading source capacity in rice[J]. Field Crops Research, 2019, 233: 49-58. |
| [32] | Kato T, Takeda K. Associations among characters related to yield sink capacity in space-planted rice[J]. Crop Science, 1996: 36, 1135-1139. |
| [33] | Xing Y Y, Jiang W T, He X L, Fiaz S, Ahmad S, Lei X, Wang W Q, Wang Y F, Wang X K. A review of nitrogen translocation and nitrogen-use efficiency[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 2019, 42(19): 2624-2641. |
| [34] | Peng S B, Khush G S, Virk P, Tang Q Y, Zou Y B. Progress in ideotype breeding to increase rice yield potential[J]. Field Crops Research, 2008, 108: 32-38. |
| [35] | 李国辉, 崔克辉. 氮对水稻叶蔗糖磷酸合成酶的影响及其与同化物积累和产量的关系[J]. 植物生理学报, 2018, 54(7): 1195-1204. |
| Li G H, Cui K H. The effect of nitrogen on leaf sucrose phosphate synthase and its relationships with assimilate accumulation and yield in rice[J]. Acta Phytophysiological Sinica, 2018, 54(7): 1195-1204. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [36] | 张国, 崔克辉. 水稻茎鞘非结构性碳水化合物积累与转运研究进展[J]. 植物生理学报, 2020, 56(6): 1127-1136. |
| Zhang G, Cui K H. Research advances on accumulation and translocation of stem non-structural carbohydrates in rice[J]. Acta Phytophysiological Sinica, 2020, 56(6): 1127-1136. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [37] | Li G H, Pan J F, Cui K H, Yuan M S, Hu Q Q, Wang W C, Mohapatra P K, Nie L X, Huang J L, Peng S B. Limitation of unloading in the developing grains is a possible cause responsible for low stem non-structural carbohydrate translocation and poor grain yield formation in rice through verification of recombinant inbred lines[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2017, 8: 1369. |
| [38] | 李志永. SRN1-Tre6P-SnRK1正向调控回路协调水稻源-库碳源分配的机制研究[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2021. |
| Li Z Y. A SRN1-Tre6P-SnRK1 feed-forward loop regulates source to sink carbon partitioning in rice[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [39] | 李国辉. 水稻茎鞘非结构性碳水化合物积累转运和颖果韧皮部卸载机理[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2018. |
| Li G H. Mechanisms of accumulation and translocation of stem non-structural carbohydrates and phloem unloading of caryopsis in rice[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [40] | 李孟珠, 王高鹏, 巫月, 任怡, 李刚华, 刘正辉, 丁艳锋, 陈琳. 水稻蔗糖转运蛋白OsSUT4参与蔗糖转运的功能研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(6): 491-498. |
| Li M Z, Wang G P, Wu Y, Ren Y, Li G H, Liu Z H, Ding Y F, Chen L. Function analysis of sucrose transporter OsSUT4 in Sucrose transport in rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2020, 34(6): 491-498. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [41] | 冯冰, 孙雅菲, 艾昊, 刘秀丽, 杨晶, 刘璐, 高飞燕, 徐国华, 孙淑斌. 超表达蔗糖转运蛋白基因OsSUT1对水稻形态和生理的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(6): 549-556. |
| Feng B, Sun Y F, AI H, Liu X L, Yang J, L Liu L, Gao F Y, Xu G H, Sun S B. Overexpression of sucrose transporter OsSUT1 affects rice morphology and physiology[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2018, 32(6): 549-556. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [42] | 陈素丽, 彭瑜, 周华, 于波, 董彦君, 滕胜. 植物海藻糖代谢及海藻糖-6-磷酸信号研究进展[J]. 植物生理学报, 2014, 50(3): 233-242. |
| Chen S L, Peng Y, Zhou H, Yu B, Dong Y J, Teng S. Research advances in trehalose metabolism and trehalose-6-phosphate signaling in plants[J]. Acta Phytophysiological Sinica, 2014, 50(3): 233-242. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [43] | Zhu G H, Ye N H, Yang J C, Peng X X, Zhang J H. Regulation of expression of starch synthesis genes by ethylene and ABA in relation to the development of rice inferior and superior spikelets[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2011, 62(11): 3907-3916. |
| [44] | Xu G W, Zhang J H, Lam H M, Wang Z Q, Yang J C. Hormonal changes are related to the poor grain filling in the inferior spikelets of rice cultivated under non-flooded and mulched condition[J]. Field Crops Research, 2007, 101(1): 53-61. |
| [45] | Wu X Y, Ding C H, Baerson S R, Lian F Z, Lin X H, Zhang L Q, Wu C F, Hwang S Y, Zeng R S, Song Y Y. The roles of jasmonate signaling in nitrogen uptake and allocation in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Plant Cell & Environment, 2019, 42(2): 659-672. |
| [46] | Liu K L, Qin J T, Zhang B, Zhao Y W. Physiological traits, yields and nitrogen translocation of ratoon rice in response to different cultivations and planting periods[J]. African Journal of Agricultural Research, 2012, 7(16): 2539-2545. |
| [47] | Takashima T, Hikosaka K, Hirose T. Photosynthesis or persistence: Nitrogen allocation in leaves of evergreen and deciduous Quercus species[J]. Plant Cell & Environment, 2010, 27(8): 1047-1054. |
| [48] | Su Y H, McGrath S P, Zhao F J. Rice is more efficient in arsenite uptake and translocation than wheat and barley[J]. Plant and Soil, 2010, 328(1): 27-34. |
| [49] | 刘奇华, 孙召文, 信彩云, 马加清. 孕穗期施硅对高温下扬花灌浆期水稻干物质转运及产量的影响[J]. 核农学报, 2016, 30(9): 1833-1839. |
| Liu Q H, Sun Z W, Xin C Y, Ma J Q. Effects of silicon on dry matter remobilization,distribution and grain yield of rice under high air temperature[J]. Journal Nuclear Agricultural Science, 2016, 30(9): 1833-1839. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [50] | Wu H, Xiang J, Zhang Y P, Zhang Y K, Peng S B, Chen H Z, Zhu D F. Effects of post-anthesis nitrogen uptake and translocation on photosynthetic production and rice yield[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 12891. |
| [51] | 李敏, 张洪程, 杨雄, 葛梦捷, 马群, 魏海燕, 戴其根, 霍中洋, 许轲. 水稻高产氮高效型品种的物质积累与转运特性[J]. 作物学报, 2013, 39(1): 101-109. |
| Li M, Zhang H C, Yang X, Ge M J, Ma Q, Wei H Y, Dai Q G, Huo Z Y, Xu K. Characteristics of dry matter accumulation and translocation in rice cultivars with high yield and high nitrogen use efficiency[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2013, 39(1): 101-109. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [52] | 赵全志, 黄丕生, 凌启鸿. 水稻群体光合速率和茎鞘贮藏物质与产量关系的研究[J]. 中国农业科学, 2001(3): 304-310. |
| Zhao Q Z, Huang P S, Lin Q H. Relations between canopy apparent photosynthesis and store matter iin stem and sheath between and yield and nitrogen regulations in rice[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2001(3): 304-310. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [53] | Vinod K K, Heuer S. Approaches towards nitrogen-and phosphorus-efficient rice[J]. AoB Plants, 2012: pls028. |
| [54] | Gansel X, Munos S, Tillard P, Gojon A. Differential regulation of the NO3- and NH4+ transporter genes AtNrt2.1 and AtAmt1.1 in Arabidopsis: relation with long-distance and local controls by N status of the plant[J]. Plant Journal, 2001, 26: 143-155. |
| [55] | Ruffel S, Krouk G, Ristova D, Shasha D, Birnbaum K D, Coruzzi G M. Nitrogen economics of root foraging: transitive closure of the nitrate-cytokinin relay and distinct systemic signaling for N supply vs. demand[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2011, 108: 18524-18529. |
| [56] | Castaings L, Camargo A, Pocholle D, Gaudon V, Texier Y, Boutet-Mercey S, Taconnat L, Renou J P. The nodule inception-like protein 7 modulates nitrate sensing and metabolism in Arabidopsis[J]. Plant Journal, 2009, 57: 426-435. |
| [57] | Cerezo M, Tillard P, Filleur S, Munos S, Daniel-Vedele F, Gojon A. Major alterations of the regulation of root NO3- uptake are associated with the mutation of NRT2.1 and NRT2.2 genes in Arabidopsis[J]. Plant Physiology, 2001, 127: 262-271. |
| [58] | Criado M V, Caputo C, Roberts I N, Castro M A, Barneix A J. Cytokinin-induced changes of nitrogen remobilization and chloroplast ultrastructure in wheat (Triticum aestivum)[J]. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2009, 166(16): 1775-1785. |
| [59] | Boonman A, Prinsen E, Gilmer F, Schurr U, Peeters A J M, Voesenek L A C J, Pons T L. Cytokinin import rate as a signal for photosynthetic acclimation to canopy light gradients[J]. Plant Physiology, 2007, 143(4): 1841-1852. |
| [60] | Gallais A, Coque M. 2005. Genetic variation and selection for nitrogen use efficiency in maize: A synthesis. Maydica, 2005, 50: 531-547. |
| [61] | 田纪春, 陈建省, 王延训, 张永祥. 氮素追肥后移对小麦籽粒产量和旗叶光合特性的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2001, 34: 101-103. |
| Tian J C, Chen J S, Wang Y X, Zhang Y X. Effects of delayed-nitrogen application on grain yield and photosynthetic characteristics in flag leaves of wheat cultivars[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2001, 34:101-103. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [62] | Zhu K Y, Ren W C, Yan J Q, Zhang Y J, Zhang W Y, Xu Y J, Wang Z Q, Yang J C. Grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency are increased by exogenous cytokinin application through the improvement in root physiological traits of rice[J]. Plant Growth Regulation, 2022, 97(1): 157-169. |
| [63] | Kakimoto T. Identification of plant cytokinin biosynthetic enzymes as dimethylallyl diphosphate: ATP/ADP isopentenyltransferases[J]. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2001, 42(7): 677-685. |
| [64] | Sakakibara H. Cytokinin biosynthesis and transport for systemic nitrogen signaling[J]. The Plant Journal, 2021, 105(2): 421-430. |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 吕宙, 易秉怀, 陈平平, 周文新, 唐文帮, 易镇邪. 施氮量与移栽密度对小粒型杂交水稻产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| [4] | 赵艺婷, 谢可冉, 高逖, 崔克辉. 水稻分蘖期干旱锻炼对幼穗分化期高温下穗发育和产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 277-289. |
| [5] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [6] | 彭显龙, 董强, 张辰, 李鹏飞, 李博琳, 刘智蕾, 于彩莲. 不同土壤条件下秸秆还田量对土壤还原性物质及水稻生长的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 198-210. |
| [7] | 朱旺, 张翔, 耿孝宇, 张哲, 陈英龙, 韦还和, 戴其根, 许轲, 朱广龙, 周桂生, 孟天瑶. 盐-旱复合胁迫下水稻根系的形态和生理特征及其与产量形成的关系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(6): 617-627. |
| [8] | 邹宇傲, 吴启侠, 周乾顺, 朱建强, 晏军. 孕穗期杂交中稻对淹涝胁迫的响应[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(6): 642-656. |
| [9] | 袁沛, 周旋, 杨威, 尹凌洁, 靳拓, 彭建伟, 荣湘民, 田昌. 化肥减氮配施对洞庭湖区双季稻产量和田面水氮磷流失风险的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(5): 518-528. |
| [10] | 肖大康, 胡仁, 韩天富, 张卫峰, 侯俊, 任科宇. 氮肥用量和运筹对我国水稻产量及其构成因子影响的整合分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(5): 529-542. |
| [11] | 黄亚茹, 徐鹏, 王乐乐, 贺一哲, 王辉, 柯健, 何海兵, 武立权, 尤翠翠. 外源海藻糖对粳稻品系W1844籽粒灌浆特性及产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(4): 379-391. |
| [12] | 高欠清, 任孝俭, 翟中兵, 郑普兵, 吴源芬, 崔克辉. 头季穗肥和促芽肥对再生稻再生芽生长及产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(4): 405-414. |
| [13] | 王文婷, 马佳颖, 李光彦, 符卫蒙, 李沪波, 林洁, 陈婷婷, 奉保华, 陶龙兴, 符冠富, 秦叶波. 高温下不同施肥量对水稻产量品质形成的影响及其与能量代谢的关系分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(3): 253-264. |
| [14] | 杨晓龙, 王彪, 汪本福, 张枝盛, 张作林, 杨蓝天, 程建平, 李阳. 不同水分管理方式对旱直播水稻产量和稻米品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(3): 285-294. |
| [15] | 魏晓东, 宋雪梅, 赵凌, 赵庆勇, 陈涛, 路凯, 朱镇, 黄胜东, 王才林, 张亚东. 硅锌肥及其施用方式对南粳46产量和稻米品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(3): 295-306. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||