
中国水稻科学 ›› 2022, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (6): 562-571.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2022.220316
收稿日期:2022-03-31
修回日期:2022-06-06
出版日期:2022-11-10
发布日期:2022-11-10
通讯作者:
袁定阳
基金资助:
LI Xiaoxiu1, LÜ Qiming1,2, YUAN Dingyang1,2,*( )
)
Received:2022-03-31
Revised:2022-06-06
Online:2022-11-10
Published:2022-11-10
Contact:
YUAN Dingyang
摘要:
筛选和培育镉(Cd)低积累水稻品种是解决稻米镉污染问题最经济、有效的办法。现有研究表明OsNramp5是介导水稻Cd吸收最重要的基因,其功能缺失后,水稻籽粒Cd含量极显著下降,但同时会影响水稻必需元素锰(Mn)的吸收,而在前人关于OsNramp5变异影响水稻生长发育的研究中,结论并不一致。系统了解OsNramp5基因变异对水稻重要农艺性状的影响有助于推动低Cd优质水稻新品种的培育。本文重点对OsNramp5基因变异对水稻中金属离子的含量,水稻的生长发育、产量性状及米质的影响进行了综述,以期为利用OsNramp5基因突变选育低Cd积累水稻品种提供参考。
李小秀, 吕启明, 袁定阳. OsNramp5基因变异影响水稻重要农艺性状的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(6): 562-571.
LI Xiaoxiu, LÜ Qiming, YUAN Dingyang. Research Progress on the Effects of OsNramp5 Mutation on Important Agronomic Traits in Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(6): 562-571.
| 基因符号 Gene symbol | 组织表达 Tissue expression | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization | 金属转运功能 Metal transport function | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OsNramp1 | 根、叶 Root, leaf | 质膜Plasma membrane | Cd | [ |
| OsNramp2 | 地上部 Aboveground part | 液泡膜 Tonoplast | Fe | [ |
| OsNramp3 | 维管束 Vascular bundle | 质膜Plasma membrane | Mn | [ |
| OsNramp4 | 根 Root | 质膜Plasma membrane | Al | [ |
| OsNramp5 | 根 Root | 质膜Plasma membrane | Cd, Mn, Fe | [ |
| OsNramp6 | 不详 Unavailable | 质膜Plasma membrane | Fe, Mn | [ |
| OsNramp7 | 根、茎、幼穗 Root, culm, young panicle | 不详 Unavailable | Fe, Zn | [ |
表1 水稻NRAMP蛋白家族基因
Table 1. NRAMP protein family genes in rice.
| 基因符号 Gene symbol | 组织表达 Tissue expression | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization | 金属转运功能 Metal transport function | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OsNramp1 | 根、叶 Root, leaf | 质膜Plasma membrane | Cd | [ |
| OsNramp2 | 地上部 Aboveground part | 液泡膜 Tonoplast | Fe | [ |
| OsNramp3 | 维管束 Vascular bundle | 质膜Plasma membrane | Mn | [ |
| OsNramp4 | 根 Root | 质膜Plasma membrane | Al | [ |
| OsNramp5 | 根 Root | 质膜Plasma membrane | Cd, Mn, Fe | [ |
| OsNramp6 | 不详 Unavailable | 质膜Plasma membrane | Fe, Mn | [ |
| OsNramp7 | 根、茎、幼穗 Root, culm, young panicle | 不详 Unavailable | Fe, Zn | [ |
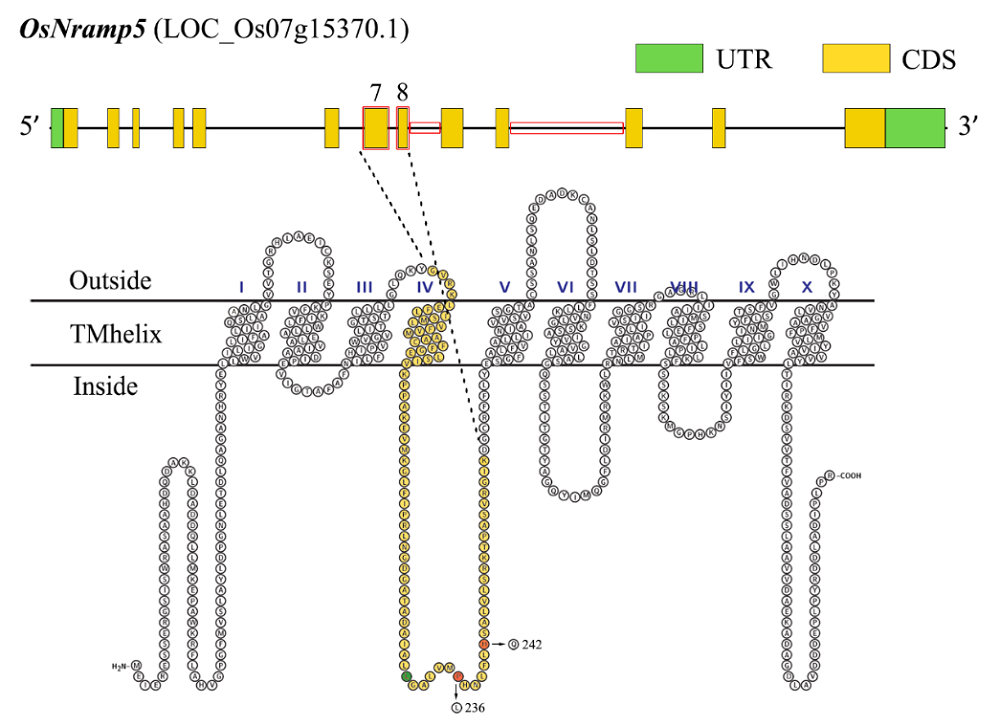
图1 OsNramp5基因结构及其编码蛋白跨膜结构模式图 OsNramp5蛋白根据预测具有10个跨膜结构,第7及第8外显子编码的氨基酸序列在第4及第5跨膜结构域之间,其中绿色和红色标注的氨基酸残基是在部分农艺性状无显著改变的突变体所携带的突变位点;绿色指OsNramp5基因1 bp碱基插入导致在该位置后的氨基酸序列改变,红色指OsNramp5基因单碱基突变导致该位置的氨基酸残基替换。
Fig. 1. OsNramp5 gene structure and transmembrane structure pattern of the protein. According to the prediction, OsNramp5 protein has 10 transmembrane helices, and the amino acid sequence encoded by exon 7 and exon 8 is between transmembrane domain 4 and 5. The green and red labeled amino acid residues are mutant sites with no significant change in agronomic traits in some previous studies. Green means that the insertion of the 1 bp base of the OsNramp5 gene leads to the change of the amino acid sequence after this position, and red means that the SNP mutation of the OsNramp5 gene leads to the substitution of the amino acid residue at this position.
| 变异位置 Mutation site | 变异来源Mutation method | 遗传背景Genetic background | 变异类型 Mutation type | 籽粒Cd、Mn含量Contents of Cd and Mn in grains | 其他金属含量 Other metal content | 产量及其他性状 Yield and other traits | 参考文献Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第1外显子 | CRISPR/Cas9技术 | 南粳46、 淮稻5号 | 1 bp插入 | Cd、Mn显著下降 | 对Fe无显著影响 | 产量、株高、每穗粒数、结实率均显著降低,穗数增加 | [ |
| 17 bp插入 | Cd、Mn显著下降 | 对Fe无显著影响 | 产量、株高、每穗粒数、结实率均显著降低 | [ | |||
| 11 bp插入 | Cd、Mn显著下降 | 对Fe无显著影响 | 产量、株高、每穗粒数、结实率均显著降低 | [ | |||
| 中花11 | 4 bp缺失 | Cd、Mn显著下降 | — | 生长严重受阻,根及地上部干质量显著降低 | [ | ||
| 第2外显子 | CRISPR/Cas9技术 | 黄华占 | 1 bp插入 | Cd、Mn显著下降 | 对Fe、Zn无显著影响 | 产量、每穗粒数、结实率、秸秆产量均显著降低,米质变劣,分蘖数增加 | [ |
| 第6外显子 | CRISPR/Cas9技术 | 黄华占 | 2 bp插入 | Cd、Mn显著下降 | 对Fe、Zn无显著影响 | 产量、每穗粒数、结实率、秸秆产量均显著降低,米质变劣 | [ |
| 第7外显子 | CRISPR/Cas9技术 | 锡稻1号 | 1 bp插入 | Cd显著下降 | — | 产量、其他性状无显著影响 | [ |
| EMS诱变 | 9311 | SNP变异 | Cd显著下降 | 对Fe、Zn、Cu无显著影响 | 其他性状无显著影响 | [ | |
| 第8外显子 | EMS诱变 | Hitomebore | SNP变异 | Cd、Mn显著下降 | — | 产量、其他性状无显著影响 | [ |
| 第9外显子 | 碳离子束辐射诱变 | 越光 | 1 bp缺失 | Cd<0.05 mg/kg, Mn显著下降 | 对Fe、Zn、Cu无显著 影响 | 产量、其他性状无显著影响 | [ |
| CRISPR/Cas9技术 | 华占 | 3 bp缺失+ 1 bp插入 | Cd<0.05 mg/kg, Mn极显著下降 | 对Cu、Zn无显著影响, Fe显著上升 | 产量、其他性状无显著影响 | [ | |
| 5 bp缺失 | Cd<0.05 mg/kg, Mn极显著下降 | 对Cu、Zn无显著影响, Fe显著上升 | 产量、其他性状无显著影响 | [ | |||
| 锡稻1号 | 33 bp缺失 | Cd显著下降 | — | 减产44.3%,生长严重受阻,株高降低 | [ | ||
| 黄华占 | 1 bp插入 | 均显著下降 | 对Fe、Zn无显著 影响 | 产量、每穗粒数、结实率、秸秆生物量均显著降低 | [ | ||
| 中花11 | 2 bp缺失+ 1 bp插入 | — | — | 产量、千粒重极显著降低,米质变劣 | [ | ||
| 中花11 | 5 bp缺失+ 1 bp插入 | — | — | 产量、千粒重极显著降低,米质变劣 | [ | ||
| 第10外显子 | 碳离子束辐射诱变 | 越光 | 433 bp插入 | Cd<0.05 mg/kg,Mn显著下降 | 对Fe、Zn、Cu 无显著影响 | 产量、其他性状无显著影响 | [ |
| CRISPR/Cas9技术 | 华占、 五丰B、 五山丝苗、 中早35 | 1-3 bp缺失+ 1 bp插入 | Cd、Mn显著下降 | 对Fe、Zn、Cu、Ca、 As、Se无显著影响 | 减产6.9%,株高、结实率、千粒重小幅降低,有效分蘖略微增加 | [ | |
| 第5内含子 | T-DNA插入 | 中花11 | 大片段插入 | — | 对K、Ca、Mg、Zn、 Cu无显著影响 | 生长受阻,叶片变黄 | [ |
| 第8内含子 | 碳离子束辐射诱变 | 隆臻36S、 华恢8612 | 18 bp缺失 | Cd、Mn显著下降 | — | 产量、其他性状无显著影响 | [ |
| 第10内含子 | 碳离子束辐射诱变 | 隆臻36S、 华恢8612 | 3 bp缺失 | Cd、Mn显著下降 | — | 产量、其他性状无显著影响 | [ |
| 第12内含子 | T-DNA插入 | 中花11 | 大片段插入 | Cd、Mn显著下降 | 对Fe、Zn、Cu无 显著影响 | 减产89%,生长受阻,叶片严重失绿 | [ |
| 全基因缺失 | 碳离子束辐射诱变 | 越光 | 227 kb缺失 | Cd<0.05 mg/kg, Mn显著下降 | 对Fe、Zn无显著影响, Cu显著上升 | 产量显著降低,抽穗早,株型小,穗数多,但秸秆产量低 | [ |
| 全基因缺失 | 60Co辐射诱变 | 粤泰B | 408 kb缺失 | Cd显著下降 | — | — | [ |
表2 OsNramp5不同变异类型对水稻植株金属含量及农艺性状的影响
Table 2. Effects of different mutation types of OsNramp5 on metal content and agronomic traits of rice.
| 变异位置 Mutation site | 变异来源Mutation method | 遗传背景Genetic background | 变异类型 Mutation type | 籽粒Cd、Mn含量Contents of Cd and Mn in grains | 其他金属含量 Other metal content | 产量及其他性状 Yield and other traits | 参考文献Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第1外显子 | CRISPR/Cas9技术 | 南粳46、 淮稻5号 | 1 bp插入 | Cd、Mn显著下降 | 对Fe无显著影响 | 产量、株高、每穗粒数、结实率均显著降低,穗数增加 | [ |
| 17 bp插入 | Cd、Mn显著下降 | 对Fe无显著影响 | 产量、株高、每穗粒数、结实率均显著降低 | [ | |||
| 11 bp插入 | Cd、Mn显著下降 | 对Fe无显著影响 | 产量、株高、每穗粒数、结实率均显著降低 | [ | |||
| 中花11 | 4 bp缺失 | Cd、Mn显著下降 | — | 生长严重受阻,根及地上部干质量显著降低 | [ | ||
| 第2外显子 | CRISPR/Cas9技术 | 黄华占 | 1 bp插入 | Cd、Mn显著下降 | 对Fe、Zn无显著影响 | 产量、每穗粒数、结实率、秸秆产量均显著降低,米质变劣,分蘖数增加 | [ |
| 第6外显子 | CRISPR/Cas9技术 | 黄华占 | 2 bp插入 | Cd、Mn显著下降 | 对Fe、Zn无显著影响 | 产量、每穗粒数、结实率、秸秆产量均显著降低,米质变劣 | [ |
| 第7外显子 | CRISPR/Cas9技术 | 锡稻1号 | 1 bp插入 | Cd显著下降 | — | 产量、其他性状无显著影响 | [ |
| EMS诱变 | 9311 | SNP变异 | Cd显著下降 | 对Fe、Zn、Cu无显著影响 | 其他性状无显著影响 | [ | |
| 第8外显子 | EMS诱变 | Hitomebore | SNP变异 | Cd、Mn显著下降 | — | 产量、其他性状无显著影响 | [ |
| 第9外显子 | 碳离子束辐射诱变 | 越光 | 1 bp缺失 | Cd<0.05 mg/kg, Mn显著下降 | 对Fe、Zn、Cu无显著 影响 | 产量、其他性状无显著影响 | [ |
| CRISPR/Cas9技术 | 华占 | 3 bp缺失+ 1 bp插入 | Cd<0.05 mg/kg, Mn极显著下降 | 对Cu、Zn无显著影响, Fe显著上升 | 产量、其他性状无显著影响 | [ | |
| 5 bp缺失 | Cd<0.05 mg/kg, Mn极显著下降 | 对Cu、Zn无显著影响, Fe显著上升 | 产量、其他性状无显著影响 | [ | |||
| 锡稻1号 | 33 bp缺失 | Cd显著下降 | — | 减产44.3%,生长严重受阻,株高降低 | [ | ||
| 黄华占 | 1 bp插入 | 均显著下降 | 对Fe、Zn无显著 影响 | 产量、每穗粒数、结实率、秸秆生物量均显著降低 | [ | ||
| 中花11 | 2 bp缺失+ 1 bp插入 | — | — | 产量、千粒重极显著降低,米质变劣 | [ | ||
| 中花11 | 5 bp缺失+ 1 bp插入 | — | — | 产量、千粒重极显著降低,米质变劣 | [ | ||
| 第10外显子 | 碳离子束辐射诱变 | 越光 | 433 bp插入 | Cd<0.05 mg/kg,Mn显著下降 | 对Fe、Zn、Cu 无显著影响 | 产量、其他性状无显著影响 | [ |
| CRISPR/Cas9技术 | 华占、 五丰B、 五山丝苗、 中早35 | 1-3 bp缺失+ 1 bp插入 | Cd、Mn显著下降 | 对Fe、Zn、Cu、Ca、 As、Se无显著影响 | 减产6.9%,株高、结实率、千粒重小幅降低,有效分蘖略微增加 | [ | |
| 第5内含子 | T-DNA插入 | 中花11 | 大片段插入 | — | 对K、Ca、Mg、Zn、 Cu无显著影响 | 生长受阻,叶片变黄 | [ |
| 第8内含子 | 碳离子束辐射诱变 | 隆臻36S、 华恢8612 | 18 bp缺失 | Cd、Mn显著下降 | — | 产量、其他性状无显著影响 | [ |
| 第10内含子 | 碳离子束辐射诱变 | 隆臻36S、 华恢8612 | 3 bp缺失 | Cd、Mn显著下降 | — | 产量、其他性状无显著影响 | [ |
| 第12内含子 | T-DNA插入 | 中花11 | 大片段插入 | Cd、Mn显著下降 | 对Fe、Zn、Cu无 显著影响 | 减产89%,生长受阻,叶片严重失绿 | [ |
| 全基因缺失 | 碳离子束辐射诱变 | 越光 | 227 kb缺失 | Cd<0.05 mg/kg, Mn显著下降 | 对Fe、Zn无显著影响, Cu显著上升 | 产量显著降低,抽穗早,株型小,穗数多,但秸秆产量低 | [ |
| 全基因缺失 | 60Co辐射诱变 | 粤泰B | 408 kb缺失 | Cd显著下降 | — | — | [ |
| [1] | Ye X X, Ma Y B, Sun B. Influence of soil type and genotype on Cd bioavailability and uptake by rice and implications for food safety[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2012, 24(9): 1647-1654. |
| [2] | Grant C A, Clarke J M, Duguid S, Chaney R L. Selection and breeding of plant cultivars to minimize cadmium accumulation[J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 2008, 390(2): 301-310. |
| [3] | Sui F Q, Chang J D, Tang Z, Liu W J, Huang X Y, Zhao F J. Nramp5 expression and functionality likely explain higher cadmium uptake in rice than in wheat and maize[J]. Plant and Soil, 2018, 433: 377-389. |
| [4] | Järup L, Akesson A. Current status of cadmium as an environmental health problem[J]. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 2009, 238(3): 201-208. |
| [5] | Rikans L E, Yamano T. Mechanisms of cadmium- mediated acute hepatotoxicity[J]. Journal of Biochemical and Molecular Toxicology, 2000, 14(2): 110-117. |
| [6] | Åkesson A, Barregard L, Bergdahl I A, Nordberg G F, Nordberg M, Skerfving S. Non-renal effects and the risk assessment of environmental cadmium exposure[J]. Environmental Health Perspectives, 2014, 122(5): 431-438. |
| [7] | Li H, Luo N, Li Y W, Cai Q Y, Li, H Y, Mo C H, Wong M H. Cadmium in rice: Transport mechanisms, influencing factors, and minimizing measures[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2017, 224: 622-630. |
| [8] | Jiang M, Jiang J, Li S, Li M, Tan Y Y, Song S Y, Shu Q Y, Huang J Z. Glutamate alleviates cadmium toxicity in rice via suppressing cadmium uptake and translocation[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 384: 121319. |
| [9] | Shan A, Kang K J, Xu H Z, Wu L, Lu M T, Lin Q, Pan M H, Wang G, He Z L, Yang X E. Cadmium accumulation in rice straws and derived biochars as affected by metal exposure, soil types and rice genotypes[J]. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 2021(1): 1-10. |
| [10] | Cattani I, Romani M, Boccelli R. Effect of cultivation practices on cadmium concentration in rice grain[J]. Agronomy for Sustainable Development, 2008, 28(2): 265-271. |
| [11] | Zhang Q, Li Z W, Huang B, Luo N L, Long L Z, Huang M, Zhai X Q, Zeng G M. Effect of land use pattern change from paddy soil to vegetable soil on the adsorption-desorption of cadmium by soil aggregates[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2017, 24(3): 2734-2743. |
| [12] | Mortensen L H, Rønn R, Vestergård M. Bioaccumulation of cadmium in soil organisms: With focus on wood ash application[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2018, 156: 452-462. |
| [13] | Yang Y, Li Y L, Wang M E, Chen W P, Dai Y T. Limestone dosage response of cadmium phytoavailability minimization in rice: A trade-off relationship between soil pH and amorphous manganese content[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 403: 123664. |
| [14] | Shao J F, Fujii-Kashino M, Yamaji N, Fukuoka S, Shen R F, Ma J F. Isolation and characterization of a rice line with high Cd accumulation for potential use in phytoremediation[J]. Plant and Soil, 2017, 410(1): 357-368. |
| [15] | Acosta J A, Abbaspour A, Martínez G R, Martínez- Martínez S, Zornoza R, Gabarrón M, Faz A. Phytoremediation of mine tailings with Atriplex halimus and organic/inorganic amendments: A five-year field case study[J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 204: 71-78. |
| [16] | 王林友, 竺朝娜, 王建军, 张礼霞, 金庆生, 石春海. 水稻镉、铅、砷低含量基因型的筛选[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2012, 24(1): 133-138. |
| Wang L Y, Zhu C N, Wang J J, Zhang L X, Jin Q S, Shi C H. Screening for rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes with lower Cd, Pb and As contents[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2012, 24(1): 133-138. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | 叶新新, 周艳丽, 孙波. 适于轻度Cd、As污染土壤种植的水稻品种筛选[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2012, 31(6): 1082-1088. |
| Ye X X, Zhou Y L, Sun B. Screening of suitable rice cultivars for the adaptation to lightly contaminated soil with Cd and As[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2012, 31(6): 1082-1088. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | Tang G H, Xie H J, Zhu M D, Xiao Y, Fu H R, Ling C Q, Yu Y H. Preliminary study on rice varieties with low cadmium accumulation by mixed planting[J]. Hunan Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 4: 17-20. |
| [19] | Shao J F, Xia J, Yamaji N, Shen R F, Ma J F. Effective reduction of cadmium accumulation in rice grain by expressing OsHMA3 under the control of the OsHMA2 promoter[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2018, 69(10): 2743-2752. |
| [20] | Wang T K, Li Y X, Fu Y F, Xie H J, Song S F, Qiu M D, Wen J, Chen M W, Chen G, Tian Y, Li C X, Yuan D Y, Wang J L, Li L. Mutation at different sites of metal transporter gene OsNramp5 affects Cd accumulation and related agronomic traits in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2019, 10: 1081. |
| [21] | Chang J D, Huang S, Konishi N, Wang P, Chen J, Huang X Y, Ma J F, Zhao F J. Overexpression of the manganese/cadmium transporter OsNRAMP5 reduces cadmium accumulation in rice grain[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2020, 71(18): 5705-5715. |
| [22] | Nevo Y, Nelson N. The NRAMP family of metal-ion transporters[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 2006, 1763(7): 609-620. |
| [23] | Bozzi A T, Gaudet R. Molecular mechanism of NRAMP-family transition metal transport[J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 2021, 433(16): 166991. |
| [24] | Petre B, Major I, Rouhier N, Duplessis S. Genome-wide analysis of eukaryote thaumatin-like proteins (TLPs) with an emphasis on poplar[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2011, 11(1): 33. |
| [25] | Nelson N. Metal ion transporters and homeostasis[J]. The EMBO Journal, 1999, 18(16): 4361-4371. |
| [26] | Mizuno T, Usui K, Horie K, Nosaka S, Mizuno N, Obata H. Cloning of three ZIP/Nramp transporter genes from a Ni hyperaccumulator plant Thlaspi japonicum and their Ni2+-transport abilities[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2005, 43(8): 793-801. |
| [27] | Oomen R J, Wu J, Lelièvre F, Blanchet S, Richaud P, Barbier-Brygoo H, Aarts M G, Thomine S. Functional characterization of NRAMP3 and NRAMP4 from the metal hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens[J]. The New Phytologist, 2009, 181(3): 637-650. |
| [28] | Wei W, Chai T Y, Zhang Y X, Han L, Xu J, Guan Z Q. The Thlaspi caerulescens NRAMP homologue TcNRAMP3 is capable of divalent cation transport[J]. Molecular Biotechnology, 2009, 41(1): 15-21. |
| [29] | Xiao H H, Yin L P, Xu X F, Li T Z, Han Z H. The iron-regulated transporter, MbNRAMP1, isolated from Malus baccata is involved in Fe, Mn and Cd trafficking[J]. Annals of Botany, 2008, 102(6): 881-889. |
| [30] | Ishikawa S, Abe T, Kuramata M, Yamaguchi M, Ando T, Yamamoto T, Yano M. A major quantitative trait locus for increasing cadmium-specific concentration in rice grain is located on the short arm of chromosome 7[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2010, 61(3): 923-934. |
| [31] | Takahashi R, Ishimaru Y, Senoura T, Shimo H, Ishikawa S, Arao T, Nakanishi H, Nishizawa N K. The OsNRAMP1 iron transporter is involved in Cd accumulation in rice[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2011, 62(14): 4843-4850. |
| [32] | Li Y, Li J J, Yu Y H, Dai X, Gong C Y, Gu D F, Xu E D, Liu Y H, Zou Y, Zhang P J, Chen X, Zhang W. The tonoplast-localized transporter OsNRAMP2 is involved in iron homeostasis and affects seed germination in rice[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2021, 72(13): 4839-4852. |
| [33] | Yamaji N, Sasaki A, Xia J X, Yokosho K, Ma J F. A node-based switch for preferential distribution of manganese in rice[J]. Nature Communications, 2013, 4: 2442. |
| [34] | Yang M, Zhang W, Dong H X, Zhang Y Y, Lü K, Wang D J, Lian X M. OsNRAMP3 is a vascular bundles-specific manganese transporter that is responsible for manganese distribution in rice[J]. PLoS ONE, 2013, 8(12): e83990. |
| [35] | Xia J, Yamaji N, Kasai T, Ma J F. Plasma membrane-localized transporter for aluminum in rice[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2010, 107(43): 18381-18385. |
| [36] | Li J Y, Liu J, Dong D, Jia X, McCouch S R, Kochian L V. Natural variation underlies alterations in Nramp aluminum transporter (NRAT1) expression and function that play a key role in rice aluminum tolerance[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2014, 111(17): 6503-6508. |
| [37] | Peris-Peris C, Serra-Cardona A, Sánchez-Sanuy F, Campo S, Ariño J, San Segundo B. Two NRAMP6 isoforms function as iron and manganese transporters and contribute to disease resistance in rice[J]. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 2017, 30(5): 385-398. |
| [38] | 吴天昊, 李曜魁, 孙远涛, 董家瑜, 莫伊凡, 唐丽, 赵炳然. 水稻OsNRAMP7基因的克隆、表达及生物信息学分析[J]. 分子植物育种, 2021, 19(7): 2103-2110. |
| Wu T H, Li Y K, Sun Y T, Dong J Y, Mo Y F, Tang L, Zhao B R. Cloning, expression and bioinformatical analysis of OsNAMP7 gene in rice[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2021, 19(7): 2103-2110. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [39] | Sperotto R A, Boff T, Duarte G L, Santos L S, Grusak M A, Fett J P. Identification of putative target genes to manipulate Fe and Zn concentrations in rice grains[J]. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2010, 167(17): 1500-1506. |
| [40] | Sasaki A, Yamaji N, Yokosho K, Ma J F. Nramp5 is a major transporter responsible for manganese and cadmium uptake in rice[J]. The Plant Cell, 2012, 24(5): 2155-2167. |
| [41] | Ishikawa S, Ishimaru Y, Igura M, Kuramata M, Abe T, Senoura T, Hase Y, Arao T, Nishizawa N K, Nakanishi H. Ion-beam irradiation, gene identification, and marker-assisted breeding in the development of low-cadmium rice[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2012, 109(47): 19166-19171. |
| [42] | Ishimaru Y, Bashir K, Nakanishi H, Nishizawa N K. OsNRAMP5, a major player for constitutive iron and manganese uptake in rice[J]. Plant Signaling & Behavior, 2012, 7(7): 763-766. |
| [43] | Yang M, Zhang Y Y, Zhang L J, Hu J T, Zhang X, Lu K, Dong H X, Wang D J, Zhao F J, Huang C F, Lian X M. OsNRAMP5 contributes to manganese translocation and distribution in rice shoots[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2014, 65(17): 4849-4961. |
| [44] | Uraguchi S, Fujiwara T. Cadmium transport and tolerance in rice: Perspectives for reducing grain cadmium accumulation[J]. Rice, 2012, 5(1): 5. |
| [45] | 杨猛. 水稻NRAMP家族基因在Mn和Cd转运中的功能研究[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2014. |
| Yang M. Functional Analysis of Rice NRAMP Genes in Mn and Cd Transport[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [46] | Tang L, Mao B G, Li Y K, Lü Q M, Zhang L P, Chen C Y, He H J, Wang W P, Zeng X F, Shao Y, Pan Y L, Hu Y Y, Peng Y, Fu X Q, Li H Q, Xia S T, Zhao B R. Knockout of OsNramp5 using the CRISPR/Cas9 system produces low Cd-accumulating indica rice without compromising yield[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 14438. |
| [47] | Yang C H, Zhang Y, Huang C F. Reduction in cadmium accumulation in japonica rice grains by CRISPR/Cas9- mediated editing of OsNRAMP5[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2019, 18: 688-697. |
| [48] | Liu S M, Jiang J, Liu Y, Meng J, Xu S L, Tan Y Y, Li Y F, Shu Q Y, Huang J Z. Characterization and evaluation of OsLCT1 and OsNramp5 mutants generated through CRISPR/Cas9-mediated mutagenesis for breeding low Cd rice[J]. Rice Science, 2019, 26(2): 88-97. |
| [49] | 龙起樟, 黄永兰, 唐秀英, 王会民, 芦明, 袁林峰, 万建林. 利用CRISPR/Cas9敲除OsNramp5基因创制低镉籼稻[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(5): 407-420. |
| Long Q Z, Huang Y L, Tang X Y, Wang H M, Lu M, Yuan L F, Wan J L. Creation of Low-Cd-accumulating indica rice by disruption of OsNramp5 gene via CRISPR/Cas9[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2019, 33(5): 407-420. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [50] | 胡黎明, 彭彦, 郑文杰, 周凯, 毛慧, 唐丽, 毛毕刚. 利用CRISPR/Cas9技术创制镉低积累香型水稻[J]. 杂交水稻, 2021, 36(6): 77-83. |
| Hu L M, Peng Y, Zheng W J, Zhou K, Mao H, Tang L, Mao B G. Using CRISPR/Cas9 technology to create low cadmium accumulation and aromatic rice[J]. Hybrid Rice, 2021, 36(6): 77-83. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [51] | Tanaka N, Nishida S, Kamiya T, Fujiwara T. Large-scale profiling of brown rice ionome in an ethyl methanesulphonate-mutagenized hitomebore population and identification of high- and low-cadmium lines[J]. Plant and Soil, 2016, 407(1): 109-117. |
| [52] | Cao Z Z, Lin X Y, Yang Y J, Guan M Y, Xu P, Chen M X. Gene identification and transcriptome analysis of low cadmium accumulation rice mutant (lcd1) in response to cadmium stress using MutMap and RNA-seq[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2019, 19(1): 250. |
| [53] | Tang L, Dong J, Qu M, Lü Q, Zhang L, Peng C, Hu Y, Li Y, Ji Z, Mao B, Peng Y, Shao Y, Zhao B. Knockout of OsNRAMP5 enhances rice tolerance to cadmium toxicity in response to varying external cadmium concentrations via distinct mechanisms[J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 832: 155006. |
| [54] | Ishimaru Y, Takahashi R, Bashir K, Shimo H, Senoura T, Sugimoto K, Ono K, Yano M, Ishikawa S, Arao T, Nakanishi H, Nishizawa N K. Characterizing the role of rice NRAMP5 in manganese, iron and cadmium transport[J]. Scientific Reports, 2012, 2: 286. |
| [55] | 刘松梅. 水稻镉运输基因OsLCT1和OsNramp5的特征与突变分析[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2019. |
| Liu S H. Characterization and mutational analysis of cadmium transport genes OsLCTl and OsNramp5 in rice[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [56] | Tsunemitsu Y, Yamaji N, Ma J F, Kato S I, Iwasaki K, Ueno D. Rice reduces Mn uptake in response to Mn stress[J]. Plant Signaling & Behavior, 2018, 13(1): 2476-2491. |
| [57] | Chang J D, Huang S, Yamaji N, Zhang W W, Ma J F, Zhao F J. OsNRAMP1 transporter contributes to cadmium and manganese uptake in rice[J]. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2020, 43(10): 2476-2491. |
| [58] | 董家瑜, 吴天昊, 孙远涛, 何含杰, 李曜魁, 彭彦, 冀中英, 孟前程, 赵炳然, 唐丽. 不同锰浓度环境下OsNRAMP5突变对水稻耐热性和主要经济性状的影响[J]. 杂交水稻, 2021, 36(2): 79-88. |
| Dong J Y, Wu T H, Sun Y T, He H J, Li Y K, Peng Y, Ji Z Y, Meng Q C, Zhao B R, Tang L. Effects of OsNRAMP5 mutation on heat tolerance and main economic traits of rice under the conditions of different manganese concentration[J]. Hybrid Rice, 2021, 36(2): 79-88. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [59] | Sasaki A, Yamaji N, Ma J F. Overexpression of OsHMA3 enhances Cd tolerance and expression of Zn transporter genes in rice[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2014, 65(20): 6013-6021. |
| [60] | Lu C, Zhang L X, Tang Z, Huang X Y, Ma J F, Zhao F J. Producing cadmium-free Indica rice by overexpressing OsHMA3[J]. Environment International, 2019, 126: 619-626. |
| [61] | Lü Q M, Li W G, Sun Z Z, Ouyang N, Jing X, He Q, Wu J, Zheng J K, Zheng J T, Tang S Q, Zhu R S, Tian Y, Duan M J, Tan Y N, Yu D, Sheng X B, Sun X W, Jia G F, Gao H Z, Zeng Q, Li Y F, Tang L, Xu Q S, Zhao B R, Huang Z Y, Lu H F, Li N, Zhao J, Zhu L H, Li D, Yuan L P, Yuan D Y. Resequencing of 1,143 indica rice accessions reveals important genetic variations and different heterosis patterns[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 4778. |
| [62] | 王天抗, 李懿星, 宋书锋, 傅岳峰, 余应弘, 柏连阳, 李莉. 水稻籽粒镉低积累资源挖掘及其新材料创制[J]. 杂交水稻, 2021, 36(1): 68-74. |
| Wang T K, Li Y X, Song S F, Fu Y F, Yu Y H, Bai L Y, Li L. Excavation of rice resources with low cadmium accumulation in grains and development of new materials[J]. Hybrid Rice, 2021, 36(1): 68-74. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [63] | 韶也, 彭彦, 毛毕刚, 余丽霞, 唐丽, 李曜魁, 胡远艺, 张丹, 袁智成, 罗武中, 彭选明, 李文建, 周利斌, 柏连阳, 赵炳然. M_1TDS技术及镉低积累杂交水稻亲本创制与组合选育[J]. 杂交水稻, 2022, 37(1): 1-11. |
| Shao Y, Peng Y, Mao B G, Yu L X, Tang L, Li Y K, Hu Y Y, Zhang D, Yuan Z C, Luo W Z, Peng X M, Li W J, Zhou L B, Bai L Y, Zhao B R. M_1TDS technology and creation of low-cadmium accumulation parents for hybrid rice breeding[J]. Hybrid Rice, 2022, 37(1): 1-11. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [6] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [7] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [8] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [9] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [10] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [11] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [12] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [13] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| [14] | 许用强, 姜宁, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 水稻开花期高温热害响应机理及其调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 111-126. |
| [15] | 吕海涛, 李建忠, 鲁艳辉, 徐红星, 郑许松, 吕仲贤. 稻田福寿螺的发生、危害及其防控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 127-139. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||