
中国水稻科学 ›› 2022, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (5): 543-550.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2022.210811
• 研究报告 • 上一篇
曾文静, 邱岚英, 陈俊杰, 钱浩宇, 张楠, 丁艳锋, 江瑜( )
)
收稿日期:2021-08-19
修回日期:2022-03-06
出版日期:2022-09-10
发布日期:2022-09-09
通讯作者:
江瑜
基金资助:
ZENG Wenjing, QIU Lanying, CHEN Junjie, QIAN Haoyu, ZHANG Nan, DING Yanfeng, JIANG Yu( )
)
Received:2021-08-19
Revised:2022-03-06
Online:2022-09-10
Published:2022-09-09
Contact:
JIANG Yu
摘要:
【目的】明确秸秆还田下大气CO2浓度升高对水稻生长和稻田CH4排放的影响,为气候变化下温室气体排放评估和丰产低碳的稻作技术创新提供理论参考和科学依据。【方法】利用开顶式气室(Open top chamber, OTC)进行田间试验,设置两个CO2浓度处理,分别为正常大气CO2浓度处理(简称aCO2,CO2浓度约为0.04%)和大气CO2浓度升高处理(简称eCO2,CO2浓度约为0.055%),每个处理的田块混入等量的前茬小麦秸秆,探明秸秆还田下大气CO2浓度升高对水稻产量等生长特性、稻田CH4排放及微生物丰度的影响,揭示秸秆还田下大气CO2浓度升高对CH4排放的影响机制。【结果】大气CO2浓度升高显著促进水稻的生长,使剑叶叶面积增加25.0%,地上生物量增加22.0%,产量提高29.0%。大气CO2浓度升高显著增加了穗数、结实率和千粒重,但对穗粒数影响不显著。秸秆还田下,大气CO2浓度升高有降低稻田CH4排放的趋势,使单位产量CH4排放量降低了39.4%。大气CO2浓度升高使土壤甲烷氧化关键基因pmoA的拷贝数增加了20.0%,但对甲烷产生关键基因mcrA的拷贝数影响较小。【结论】秸秆还田条件下,未来大气CO2浓度升高不仅提高了水稻产量,而且有利于减少稻田温室气体CH4的排放。
曾文静, 邱岚英, 陈俊杰, 钱浩宇, 张楠, 丁艳锋, 江瑜. 秸秆还田下大气CO2浓度升高对水稻生长和CH4排放的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(5): 543-550.
ZENG Wenjing, QIU Lanying, CHEN Junjie, QIAN Haoyu, ZHANG Nan, DING Yanfeng, JIANG Yu. Effect of Elevated CO2 Concentration on Rice Growth and CH4 Emission from Paddy Fields Under Straw Incorporation[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(5): 543-550.
| 处理 Treatment | 株高 Plant height/cm | 叶面积系数 Leaf area index | 地上部生物量 Aboveground biomass/(g·m−2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 剑叶 Flag leaf | 倒2叶 Second leaf | |||
| aCO2 | 102.3 ± 0.8 a | 0.8 ± 0.0 a | 0.9 ± 0.1 a | 2067.8 ± 62.6 a |
| eCO2 | 104.0 ± 0.7 a | 1.0 ± 0.0 b | 1.1 ± 0.1 b | 2523.3 ± 105.1 b |
表1 大气CO2浓度升高对水稻株高、叶面积和生物量的影响
Table 1. Effects of elevated atmospheric CO2 concentration on rice plant height, leaf area and biomass.
| 处理 Treatment | 株高 Plant height/cm | 叶面积系数 Leaf area index | 地上部生物量 Aboveground biomass/(g·m−2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 剑叶 Flag leaf | 倒2叶 Second leaf | |||
| aCO2 | 102.3 ± 0.8 a | 0.8 ± 0.0 a | 0.9 ± 0.1 a | 2067.8 ± 62.6 a |
| eCO2 | 104.0 ± 0.7 a | 1.0 ± 0.0 b | 1.1 ± 0.1 b | 2523.3 ± 105.1 b |
| 处理 Treatment | 每平方米穗数 Panicle number per square meter | 每穗粒数 Spikelet number per panicle | 结实率 Seed-setting rate /% | 千粒重 1000-grain weight /g | 产量 Yield /(g·m−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| aCO2 | 232.0 ± 7.2 a | 203.7 ± 6.1 a | 69.6 ± 0.6 a | 23.4 ± 0.1 a | 846.4 ± 34.1 a |
| eCO2 | 276.0 ± 9.2 b | 205.1 ± 8.6 a | 74.2 ± 1.1 b | 24.1 ± 0.2 b | 1092.0 ± 56.1 b |
表2 大气CO2浓度升高对产量及产量构成因素的影响
Table 2. Effects of elevated atmospheric CO2 concentration on yield and its components.
| 处理 Treatment | 每平方米穗数 Panicle number per square meter | 每穗粒数 Spikelet number per panicle | 结实率 Seed-setting rate /% | 千粒重 1000-grain weight /g | 产量 Yield /(g·m−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| aCO2 | 232.0 ± 7.2 a | 203.7 ± 6.1 a | 69.6 ± 0.6 a | 23.4 ± 0.1 a | 846.4 ± 34.1 a |
| eCO2 | 276.0 ± 9.2 b | 205.1 ± 8.6 a | 74.2 ± 1.1 b | 24.1 ± 0.2 b | 1092.0 ± 56.1 b |
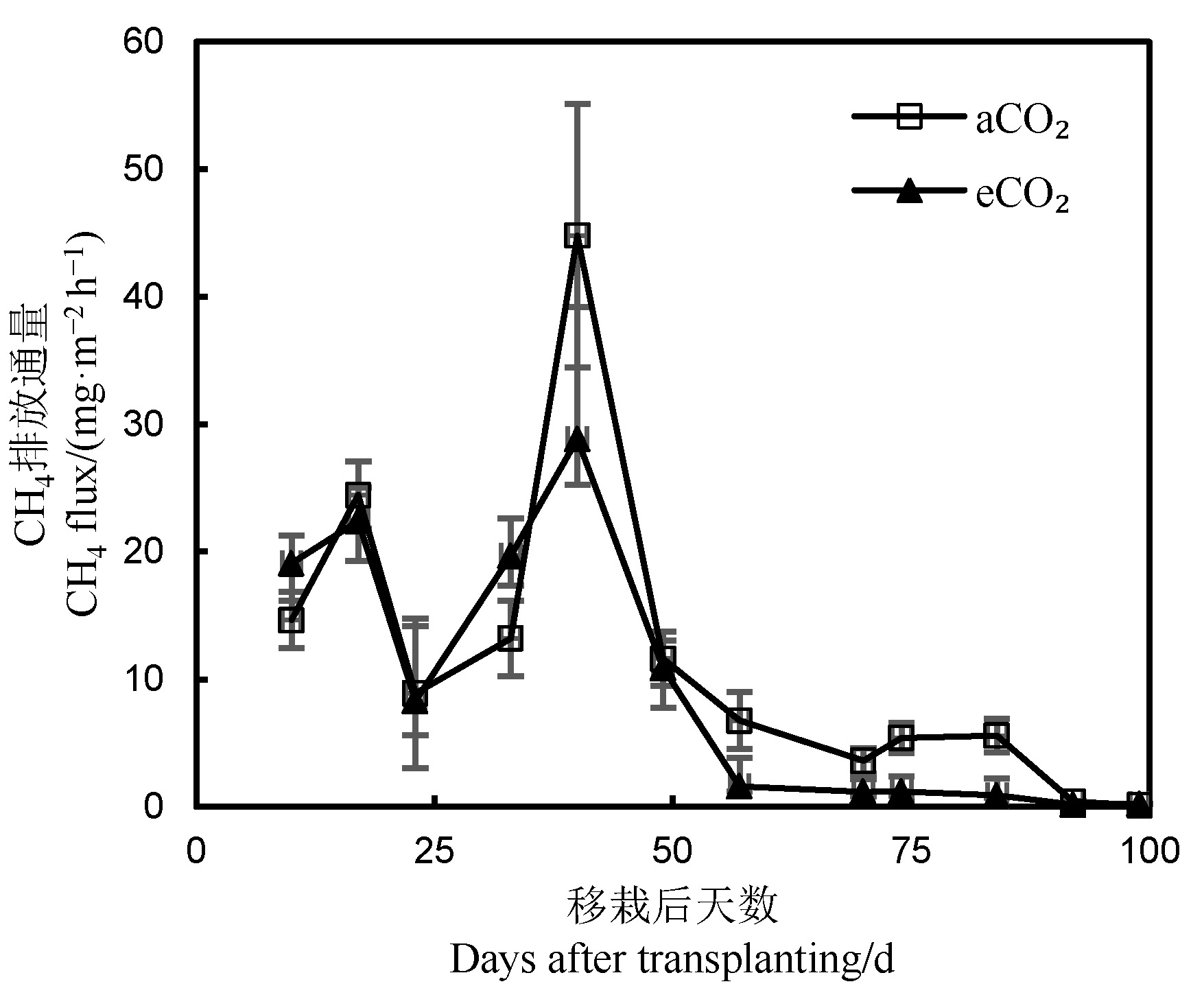
图1 大气CO2浓度升高对CH4排放动态的影响 图中误差线表示标准误。下同。
Fig. 1. Effects of elevated atmospheric CO2 concentration on CH4 emission dynamics. Error bars represent standard errors(n=6). The same as in the figures below.

图2 大气CO2浓度升高对CH4累积排放量(A)和单位产量CH4排放量(B)的影响
Fig. 2. Effects of elevated atmospheric CO2 concentration on CH4 emissions (A) and yield-scaled CH4 emission (B).
| [1] | FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations). FAOSTAT-Food and agriculture data[EB/OL]. 2021. http://www.fao.org/faostat/zh/#data/QC. |
| [2] | IRRI (International Rice Research Institute). Rice Today: Yield increase prospects for rice to 2050[EB/OL] // Fischer T. 2014. https://ricetoday.irri.org/yield-increase-prospects-for-rice-to-2050. |
| [3] | IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change). Working group I contribution to the fifth assessment report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Working group I contribution to the fifth assessment report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. //Stocker T F. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis[R]. Cambridge, UK, and New York, NY: Cambridge University Press, 2013: 95-123. |
| [4] | Yan X Y, Akiyama H, Yagi K, Akimoto H. Global estimations of the inventory and mitigation potential of methane emissions from rice cultivation conducted using the 2006 Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Guidelines[J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 2009, 23: GB2002. |
| [5] | 李彦生, 金剑, 刘晓冰. 作物对大气CO2浓度升高生理响应研究进展[J]. 作物学报, 2020, 46(12): 1819-1830. |
| Li Y S, Jin J, Liu X B. Research progress on physiological responses of crops to elevated atmospheric CO2 concentration[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2020, 46(12): 1819-1830. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | Zhu C W, Zhu J G, Cao J, Jiang Q, Liu G, Ziska L H. Biochemical and molecular characteristics of leaf photosynthesis and relative seed yield of two contrasting rice cultivars in response to elevated [CO2][J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2014, 65(20): 6049-6056. |
| [7] | van Groenigen K J, Kessel C, Hungate B A. Increased greenhouse-gas intensity of rice production under future atmospheric conditions[J]. Nature Climate Change, 2013, 3: 288-291. |
| [8] | 张坚超, 徐镱钦, 陆雅海. 陆地生态系统甲烷产生和氧化过程的微生物机理[J]. 生态学报 2015, 35(20): 6592-6603. |
| Zhang J C, Xu Y Q, Lu Y H. Microbial mechanisms of methane production and oxidation in terrestrial ecosystems[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2015, 35 (20): 6592-6603. | |
| [9] | van Groenigen K J, Osenberg C W, Hungate B A. Increased soil emissions of potent greenhouse gases under increased atmospheric CO2[J]. Nature, 2011, 475: 214-216. |
| [10] | 蔡祖聪, 徐华, 马静. 稻田生态系统CH4和N2O排放[M]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学出版社, 2009: 136-140. |
| Cai Z C, Xu H, Ma J. CH4 and N2O emissions from paddy ecosystem[M]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China Press, 2009: 136-140. (in Chinese) | |
| [11] | 田婷, 张青, 蒋华伟, 靖晶, 姜红卫, 李欣, 江君, 徐君. 水稻植株对稻田甲烷排放影响的研究进展[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2017, 45(20): 28-31. |
| Tian T, Zhang Q, Jiang H W, Jing J, Jiang H W, Li X, Jiang J, Xu J. Research progress on effects of rice plants on methane emission from paddy fields[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 45(20): 28-31. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | Liu G C, Tokida T, Matsunami T, Nakamura H, Okada M, Sameshima R, Hasegawa T, Sugiyama S. Microbial community composition controls the effects of climate change on methane emission from rice paddies[J]. Environmental Microbiology Reports. 2012, 4(6): 648-54. |
| [13] | Liu D Y, Tago K, Hayatsu M, Tokida T, Asakawa S. Effect of elevated CO2 concentration, elevated temperature and no nitrogen fertilization on methanogenic archaeal and methane-oxidizing bacterial community structures in paddy soil[J]. Microbes and Environments, 2016, 31(3): 349-356. |
| [14] | Okubo T, Liu D Y, Tsurumaru H, Ikeda S, Asakawa S, Tokida T, Tago K, Hayatsu M, Aoki N, Ishimaru K, Ujiie K, Usui Y, Nakamura H, Sakai H, Hayashi K, Hasegawa T, Minamisawa K. Elevated atmospheric CO2 levels affect community structure of rice root-associated bacteria[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2015, 6: 136. |
| [15] | 钟平, 张超旭, 王丽, 王福成, 汪春. 秸秆资源综合利用研究[J]. 现代农业, 2020(6): 4-5. |
| Zhong P, Zhang C X, Wang L, Wang F C, Wang C. Research on comprehensive utilization of straw resources[J]. Modern Agriculture, 2020(6): 4-5. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 张志才, 陈加银, 张永明. 丘陵地小麦秸秆全量还田对土壤肥力及水稻生长的影响[J]. 南方农业, 2021, 15(7): 43-46. |
| Zhang Z C, Chen J Y, Zhang Y M. Effects of total wheat straw returning on soil fertility and rice growth in hilly land[J]. South China Agriculture, 2021, 15(7): 43-46. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | 李凤博, 牛永志, 高文玲, 刘金根, 卞新民. 耕作方式和秸秆还田对直播稻田土壤理化性质及其产量的影响[J]. 土壤通报, 2008, 39(3): 549-552. |
| Li F B, Niu Y Z, Gao W L, Liu J G, Bian X M. Effects of tillage and straw returning on soil physicochemical properties and yield in direct-seeding rice field[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2008, 39(3): 549-552. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | 陈云峰, 夏贤格, 杨利, 刘波, 张敏敏, 聂新星. 秸秆还田是秸秆资源化利用的现实途径[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2020(6): 300. |
| Chen Y F, Xia X G, Yang L, Liu B, Zhang M M, Nie X X. Straw returning to field is a realistic approach to straw resource utilization[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Science in China, 2020(6): 300. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | Liu C, Lu M, Cui J, Li B, Fang C M. Effects of straw carbon input on carbon dynamics in agricultural soils: a meta-analysis[J]. Global Change Biology, 2014, 20(5): 1366-1381. |
| [20] | Jiang Y, Qian H Y, Huang S, Zhang X Y, Wang L, Zhang L, Shen M X, Xiao X P, Chen F, Zhang H L, Lu C Y, Li C, Zhang J, Deng A X, van Groenigen K J, Zhang W J. Acclimation of methane emissions from rice paddy fields to straw addition[J]. Science Advances, 2019, 5: eaau9038 |
| [21] | Hu S W, Wang Y X, Yang L X. Response of rice yield traits to elevated atmospheric CO2 concentration and its interaction with cultivar, nitrogen application rate and temperature: A meta-analysis of 20 years FACE studies[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 764: 142797. |
| [22] | 陈改苹, 朱建国, 庞静, 程磊, 谢祖彬, 曾青. CO2浓度升高对水稻抽穗期根系有关性状及根碳氮比的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2006, 20(1): 53-57. |
| Chen G P, Zhu J G, Pang J, Cheng L, Xie Z B, Zeng Q. Effects of elevated CO2 concentration on root traits and root C/N ratio at heading stage of rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2006, 20(1): 53-57. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 刘红江, 杨连新, 黄建晔, 董桂春, 朱建国, 刘钢, 王余龙. FACE对三系杂交籼稻汕优63根系生长动态的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2008, 27(6): 2291-2296. |
| Liu H J, Yang L X, Huang J Y, Dong G C, Zhu J G, Liu G, Wang Y L. Effects of FACE on root growth dynamics of three-line indica hybrid rice Shanyou 63[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2008, 27(6): 2291-2296. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | Wu J J, Kronzucker H J, Shi W M. Dynamic analysis of the impact of free-air CO2 enrichment (FACE) on biomass and N uptake in two contrasting genotypes of rice[J]. Functional Plant Biology, 2018, 45(7): 696-704. |
| [25] | Hasegawa T, Sakai H, Tokida T, Usui Y, Nakamura H, Wakatsuki H, Chen C P, Ikawa H, Zhang G, Nakano H. A high-yielding rice cultivar “Takanari” shows no N constraints on CO2 fertilization[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2019, 10: 361. |
| [26] | Cai C, Yin X Y, He S Q, Jiang W Y, Si C F, Struik P C, Luo W H, Li G, Xie Y T, Xiong Y, Pan G X. Responses of wheat and rice to factorial combinations of ambient and elevated CO2 and temperature in FACE experiments[J]. Global Change Biology, 2016, 22(2): 856-874. |
| [27] | 刘红江, 杨连新, 黄建晔, 董桂春, 朱建国, 刘钢, 王余龙. FACE对杂交籼稻汕优63干物质生产与分配的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2009, 28(1): 8-14. |
| Liu H J, Yang L X, Huang J Y, Dong G C, Zhu J G, Liu G, Wang Y L. Effects of FACE on dry matter production and distribution in indica hybrid rice Shanyou 63[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2009, 28(1): 8-14. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | Zhang G Y, Sakai H, Usui Y, Tokida T, Nakamurac H, Zhu C W, Fukuoka M, Kobayashi K, Hasegawa T. Grain growth of different rice cultivars under elevated CO2 concentrations affects yield and quality[J]. Field Crops Research, 2015, 179: 72-80. |
| [29] | Zhang G Y, Sakai H, Tokida T, Usui Y, Zhu C W, Nakamura H, Yoshimoto M Fukuoka M, Kobayashi K, Hasegawa T. The effects of free-air CO2 enrichment (FACE) on carbon and nitrogen accumulation in grains of rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2013, 64(11): 3179-3188. |
| [30] | Wang J Q, Liu X Y, Zhang X H, Smith P, Li L Q, Filley T R,. Cheng K, Shen M X, He Y B, Pan G X. Size and variability of crop productivity both impacted by CO2 enrichment and warming: A case study of 4 years field experiment in a Chinese paddy[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 2016, 221: 40-49. |
| [31] | Raj A, Chakrabarti B, Pathak H, Singh S D, Mina U, Purakayastha T J. Growth, yield and nitrogen uptake in rice crop grown under elevated carbon dioxide and different doses of nitrogen fertilizer[J]. Indian Journal of Experimental Biology, 2019, 57: 181-187. |
| [32] | Hu S W, Wang Y X, Yang L X. Response of rice yield traits to elevated atmospheric CO2 concentration and its interaction with cultivar, nitrogen application rate and temperature: A meta-analysis of 20 years FACE studies[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 764: 142797. |
| [33] | 周娟, 舒小伟, 赖上坤, 许高平, 黄建晔, 姚友礼, 杨连新, 董桂春, 王余龙. 不同类型水稻品种产量和氮素吸收利用对大气CO2浓度升高响应的差异[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(6): 561-573. |
| Zhou J, Shu X W, Lai S K, Xu G P, Huang J Y, Yao Y L, Yang L X, Dong G C, Wang Y L. Response of different rice varieties to elevated atmospheric CO2 concentration in response to yield and nitrogen uptake and utilization[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2020, 34(6): 561-573. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [34] | Yang L X, Huang J Y, Yang H J, Dong G C, Liu H J, Liu G, Zhu J G, Wang Y L. Seasonal changes in the effects of free-air CO2 enrichment (FACE) nitrogen (N) uptake and utilization of rice at three levels of N fertilization[J]. Field Crops Research, 2007, 100: 189. |
| [35] | 杨连新, 王余龙, 黄建晔, 杨洪建. 开放式空气 CO2 浓度增高对水稻生长发育影响的研究进展[J]. 应用生态学报, 2006, 17(7): 1333. |
| Yang L X, Wang Y L, Huang J Y, Yang H J. Effects of elevated CO2 concentration in open air on rice growth and development[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2006, 17(7): 1333. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [36] | Bai Z H, Li H G, Yang X Y, Zhou B K, Shi X J, Wang B, Li D C, Shen J B, Chen Q, Qin W, Oenema O, Zhang F. The critical soil P levels for crop yield, soil fertility and environmental safety in different soil types[J]. Plant and Soil, 2013, 372(1-2): 27-37. |
| [37] | Turmel M S, Speratti A, Baudron F, Verhulst N, Govaerts B. Crop residue management and soil health: A systems analysis[J]. Agricultural Systems, 2015, 134(3): 6-16. |
| [38] | Yang H J, Ma J X, Rong Z Y, Zeng D D, Wang Y C, Hu S J, Ye W W, Zheng X B. Wheat straw return influences nitrogen-cycling and pathogen associated soil microbiota in a wheat-soybean rotation system[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2019(10): 1811-1825. |
| [39] | Wang C, Jin Y G, Jia C, Zhang N, Song M Y, Kong D L, Liu S W, Zhang X H, Liu X Y, Zou J W, Lia S Q, Pan G X. An additive effect of elevated atmospheric CO2 and rising temperature on methane emissions related to methanogenic community in rice paddies[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 2018, 257: 165-174. |
| [40] | Zheng X H, Zhou Z X, Wang Y S, Zhu J G, Wang Y L, Yue J, Shi Y, Kobayashi K, Inubushi K, Huang Y, Han S H, Xu Z J, Xie B H, Butterbach-Bahl K, Yang L X. Nitrogen-regulated effects of free-air CO2enrichment on methane emissions from paddy rice fields[J]. Global Change Biology, 2006, 12: 1717-1732. |
| [41] | Inubushi K, Cheng W G, Aonuma S, Hooue M M, Kobayashi K, Miura S, Kim H Y, Okadas M. Effects of free-air CO2 enrichment (FACE) on CH4 emission from a rice paddy field[J]. Global Change Biology, 2003, 9: 1458-1464. |
| [42] | Qian H Y, Huang S, Chen J, Wang L, Hungate B A, van Kessel C, Zhang J, Deng A X, Jiang Y, van Groenigen K J, Zhang W J. Lower-than-expected CH4 emissions from rice paddies with rising CO2 concentrations[J]. Global Change Biology, 2020, 26: 2368-2376. |
| [43] | Henriksen T M, Brelamd T A. Carbon mineralization,fungal and bacterial growth,and enzyme activities as affected by contact between crop residues and soil[J]. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 2002, 35(1): 41-48. |
| [44] | Turmel M S, Speratti A, Baudron F. Crop residue management and soil health: A systems analysis[J]. Agricultural Systems, 2015, 134(3): 6-16. |
| [45] | Liu S W, Ji C, Wang C, Chen J, Jin Y G, Zou Z H, Li S Q, Niu S L, Zou J W. Climatic role of terrestrial ecosystem under elevated CO2: Abottom-up greenhouse gases budget[J]. Ecology Letters, 2018, 21: 1108-1118. |
| [46] | Watanabe A, Takeda T, Kimura M. Evaluation of carbon origins of CH4 emitted from rice paddies[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1999, 104: 13623-23630. |
| [47] | Hanson R S, Hanson T E. Methanotrophic bacteria[J]. Microbiological Reviews, 1996, 60: 439-471. |
| [48] | Van der Gon H A C, Neue H. Oxidation of methane in the rhizosphere of rice plants[J]. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 1996, 22(4): 359-366. |
| [49] | Schrope M K, Chanton J P, Allen L H, Baker J T. Effect of CO2 enrichment and elevated temperature on methane emissions from rice, Oryza sativa[J]. Global Change Biology, 1999, 5(5): 587-599. |
| [50] | Jiang Y, K J, Huang S, Hungate B A, van Kessel C, Hu S J, Zhang J, Wu L H, Yan X J, Wang L L, Chen J, Hang X N, Zhang Y, Horwath W R, Ye R Z, Linquist B A, Song Z W, Zheng C Y, Deng A X, Zhang W J. Higher yields and lower methane emissions with new rice cultivars[J]. Global Change Biology, 2017, 23: 4728-4738. |
| [51] | 沈学良, 田光蕾, 周元昌, 王缨. 水稻生物学特性对稻田甲烷排放的影响[J]. 农学学报, 2020, 10(2): 75-80. |
| Shen X L, Tian G L, Zhou Y C, Wang Y. Effects of biological characteristics of rice on methane emission from rice field[J]. Journal of Agronomy, 2020, 10(2): 75-80. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [52] | Ma K, Qiu Q F, Lu Y H. Microbial mechanism for rice variety control on methane emission from rice field soil[J]. Global Change Biology, 2010, 16: 3085-3095. |
| [53] | 江瑜, 管大海, 张卫建. 水稻植株特性对稻田甲烷排放的影响及其机制的研究进展[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2018, 26(2): 175-181. |
| Jiang Y, Guan D H, Zhang W J. Research progress of the effects of rice plant characteristics on methane emission from paddy fields and its mechanism[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2018, 26(2): 175-181. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [54] | 宋练, 蔡创, 朱春梧. [CO2]升高对粮食作物影响的研究进展[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2020, 39(4): 786-796. |
| Song L, Cai C, Zhu C W. Review on crop responses to rising atmospheric [CO2][J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2020, 39(4): 786-796. | |
| [55] | Yang L X, Liu H J, Wang Y X, Zhu J G, Huang J Y, Liu G, Dong G C, Wang Y L. Impact of elevated CO2 concentration on inter-subspecific hybrid rice cultivar Liangyoupeijiu under fully open-air field conditions[J]. Field Crops Research, 2009, 112: 7-15. |
| [56] | Cai Z C, Shan Y H, Xu H. Effects of nitrogen fertilization on CH4 emissions from rice fields[J]. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 2007, 53: 353-361. |
| [1] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [2] | 彭显龙, 董强, 张辰, 李鹏飞, 李博琳, 刘智蕾, 于彩莲. 不同土壤条件下秸秆还田量对土壤还原性物质及水稻生长的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 198-210. |
| [3] | 张宇杰, 王志强, 马鹏, 杨志远, 孙永健, 马均. 麦秆还田下水氮耦合对水稻氮素吸收利用及产量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(4): 388-398. |
| [4] | 杨通, 吴俊男, 鲍婷, 李凤博, 冯金飞, 周锡跃, 方福平. 耕作方式对双季稻田土壤剖面CH4和N2O分布特征的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(1): 78-88. |
| [5] | 彭志芸, 向开宏, 杨志远, 唐源, 谌洁, 张宇杰, 何艳, 严田蓉, 孙永健, 马均. 麦/油-稻轮作下秸秆还田与氮肥管理对直播杂交稻氮素利用特征的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(1): 57-68. |
| [6] | 殷尧翥, 郭长春, 孙永健, 武云霞, 余华清, 孙知白, 张桥, 王海月, 杨志远, 马均. 稻油轮作下油菜秸秆还田与水氮管理对杂交稻群体质量和产量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(3): 257-268. |
| [7] | 郭保卫, 胡雅杰, 钱海军, 曹伟伟, 邢志鹏, 张洪程, 戴其根, 霍中洋, 许轲, 魏海燕. 秸秆还田下适宜施氮量提高机插稻南粳9108产量和群体质量[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2015, 29(5): 511-518. |
| [8] | 裴鹏刚, 张均华, 朱练峰, 胡志华, 金千瑜. 秸秆还田耦合施氮水平对水稻光合特性、氮素吸收及产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2015, 29(3): 282-290. |
| [9] | 严奉君, 孙永健, 马均, 徐徽, 李玥, 代邹, 杨志远. 不同土壤肥力条件下麦秆还田与氮肥运筹对杂交稻氮素利用、产量及米质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2015, 29(1): 56-64. |
| [10] | 董春华1,2,3 ,曾闹华3 ,高菊生2,3,*,刘强1,* ,徐明岗3 ,文石林2,3 . 长期不同施肥模式下红壤性稻田水稻产量及有机碳含量变化特征[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2014, 28(2): 193-198. |
| [11] | 马义虎,顾道健,刘立军,王志琴,张耗,杨建昌*. 玉米秸秆源有机肥对水稻产量与温室气体排放的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2013, 27(5): 520-528. |
| [12] | 王丽丽1 ,闫晓君1 ,江瑜1 ,田云录3 ,邓艾兴2 ,张卫建1,2,*. 超级稻宁粳1号与常规粳稻CH4排放特征的比较分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2013, 27(4): 413-418. |
| [13] | 赵建国2 ,蒋开锋1 ,杨莉1 ,杨乾华1 ,万先齐1 ,曹应江1 ,游书梅1 ,罗婧1 ,张涛1,* ,郑家奎1,*. 水稻产量相关性状QTL定位[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2013, 27(4): 344-352. |
| [14] | 葛立立,马义虎,卞金龙,王志琴,杨建昌,刘立军*. 玉米秸秆还田与实地氮肥管理对水稻产量与米质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2013, 27(2): 153-160. |
| [15] | 陈培峰1 ,董明辉1,2 ,*,顾俊荣1,惠锋3,乔中英1,杨代凤1 ,刘腾飞1. 麦秸还田与氮肥运筹对超级稻强弱势粒粒重与品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2012, 26(6): 715-722. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||