
中国水稻科学 ›› 2022, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (5): 476-486.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2022.210813
朱春权1,#, 魏倩倩1,2,#, 党彩霞3, 黄晶1, 徐青山1, 潘林1, 朱练峰1, 曹小闯1, 孔亚丽1, 项兴佳2, 刘佳4, 金千瑜1, 张均华1( )
)
收稿日期:2021-08-27
修回日期:2022-01-22
出版日期:2022-09-10
发布日期:2022-09-09
通讯作者:
张均华
作者简介:第一联系人:#共同第一作者
基金资助:
ZHU Chunquan1,#, WEI Qianqian1,2,#, DANG Caixia3, HUANG Jing1, XU Qingshan1, PAN Lin1, ZHU Lianfeng1, CAO Xiaochuang1, KONG Yali1, XIANG Xingjia2, LIU Jia4, JIN Qianyu1, ZHANG Junhua1( )
)
Received:2021-08-27
Revised:2022-01-22
Online:2022-09-10
Published:2022-09-09
Contact:
ZHANG Junhua
About author:First author contact:#These authors contributed equally to the work
摘要:
【目的】深入剖析水杨酸调控水稻低磷胁迫响应的生理与分子机制具有重要意义。【方法】选取常规水稻品种日本晴,外源添加水杨酸后测定水稻体内总磷含量、酸性磷酸酶活性、木质部汁液磷含量、水稻根系特征参数、磷转运子基因表达水平和一氧化氮含量等指标解析水杨酸缓解水稻缺磷胁迫的生理和分子机制。【结果】1)水杨酸对水稻磷吸收的调控存在剂量效应,1 μmol/L水杨酸显著提高低磷条件下水稻体内总磷含量,5 μmol/L水杨酸则降低水稻体内总磷含量。2)低磷条件下,1 μmol/L水杨酸使酸性磷酸酶活性提高了11.35%,根系总长增加了20.90%,根系表面积增加11.86%,根系体积增加了15.38%,总根数增加了23.55%,木质部汁液中的磷含量提高了22.67%。同时,1 μmol/L水杨酸提高了水稻根系磷转运子基因的表达,从而提高水稻对外界磷的吸收和体内磷的转运。3)水杨酸通过提高硝酸还原酶的活性增加水稻根系的一氧化氮含量,从而通过调控磷转运子基因的表达提高低磷条件下水稻对外界磷的吸收。【结论】水杨酸与信号分子一氧化氮互作缓解低磷胁迫。
朱春权, 魏倩倩, 党彩霞, 黄晶, 徐青山, 潘林, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 孔亚丽, 项兴佳, 刘佳, 金千瑜, 张均华. 水杨酸通过一氧化氮途径调控水稻缓解低磷胁迫[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(5): 476-486.
ZHU Chunquan, WEI Qianqian, DANG Caixia, HUANG Jing, XU Qingshan, PAN Lin, ZHU Lianfeng, CAO Xiaochuang, KONG Yali, XIANG Xingjia, LIU Jia, JIN Qianyu, ZHANG Junhua. Salicylic Acid Alleviates Low Phosphorus Stress in Rice via a Nitric Oxide-dependent Manner[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(5): 476-486.
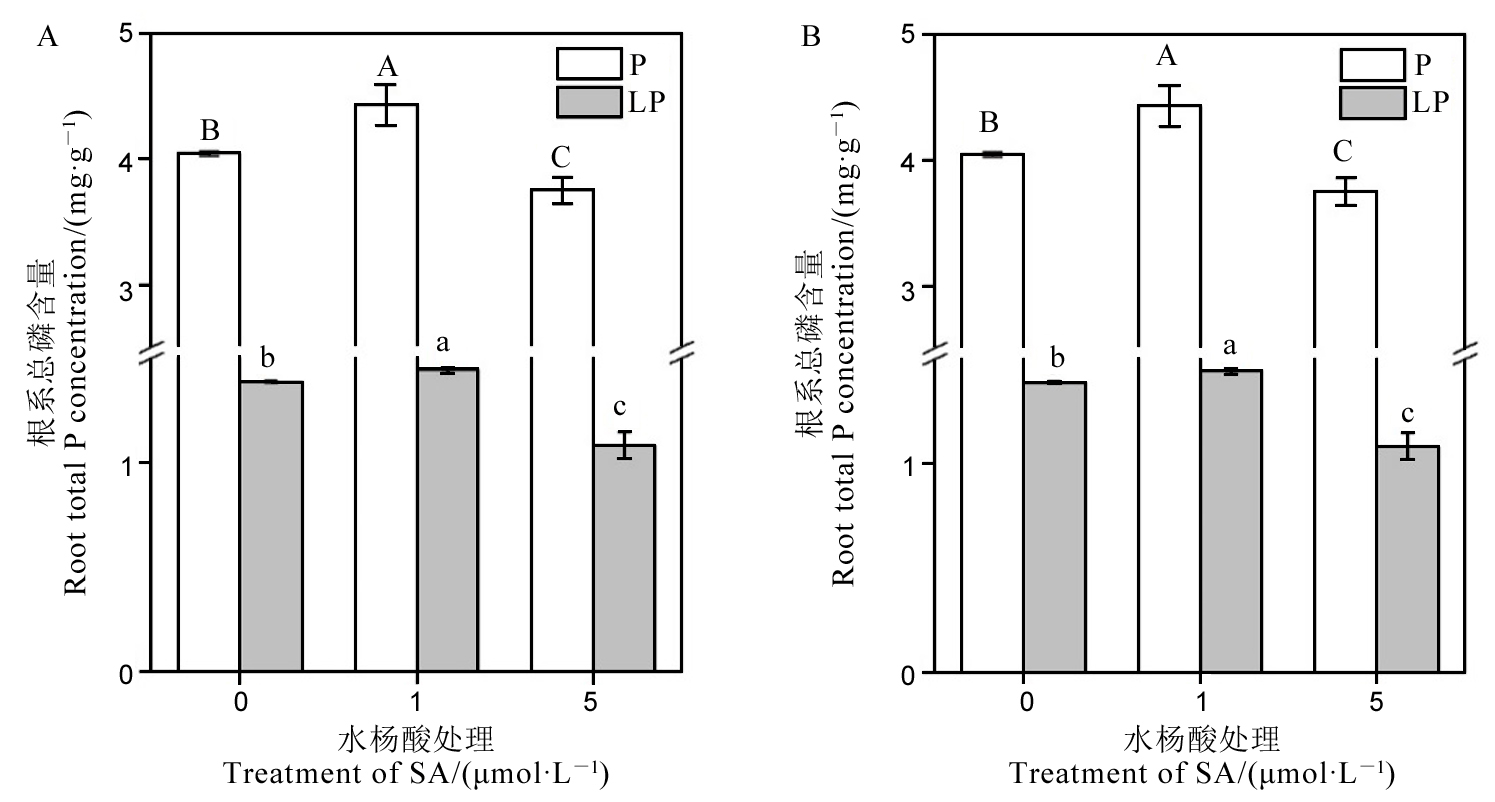
图 1 低磷和正常磷条件下水稻根部(A)和地上部(B)的总磷含量 数据用均值±标准差(n = 4)表示。不同的大小写字母代表处理间差异分别在P < 0.01和P < 0.05 水平上显著。P-180 mmol/L;LP-18 mmol/L。
Fig. 1. P contents in roots(A) and shoots (B) under low and normal P levels. Different letters above the bars mean significant difference at P < 0.05. P, 180 mmol/L; LP, 18 mmol/L.
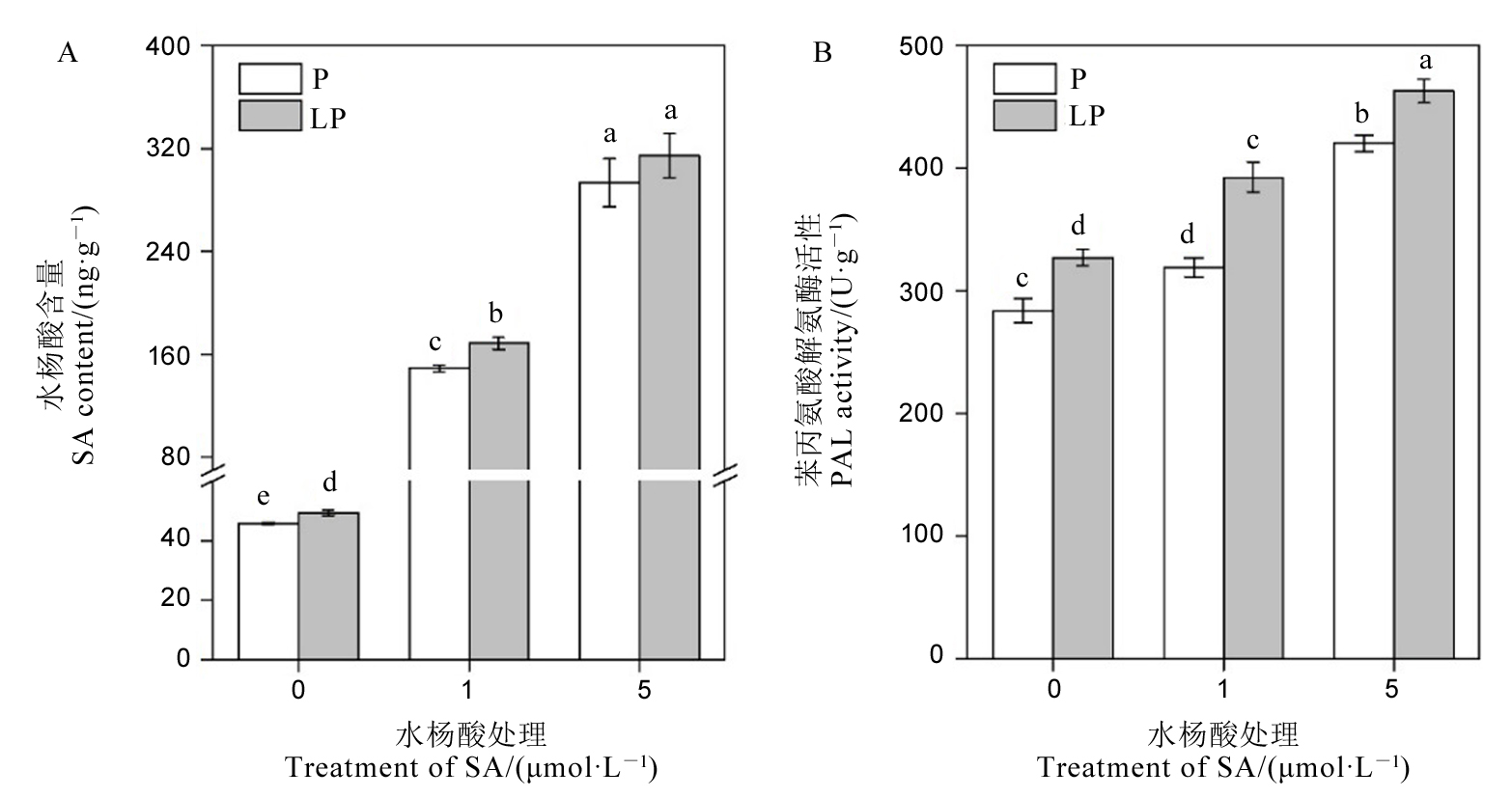
图2 不同浓度外源水杨酸处理下水稻水杨酸含量和苯丙氨酸解氨酶活性 数据用均值±标准差(n = 4)表示。不同的大小写字母代表处理间差异分别在P < 0.01和P < 0.05 水平上显著。P-180 mmol/L;LP-18 mmol/L。
Fig. 2. Salicylic acid content and phenylalanine ammonia lyase activity under different exogenous salicylic acid levels. Different letters above the bars mean significant difference at P < 0.05. P, 180 mmol/L; LP, 18 mmol/L.
| 处理 Treatment | 总根长 Total length/cm | 表面积 Surface area/cm2 | 平均直径 Average diameter/mm | 根系总体积 Root volume/cm3 | 总根尖数 Number of root tips |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P | 155.99±13.28 c | 14.45±0.97 c | 0.30±0.01 a | 0.11±0.01 c | 745.8±60.3 c |
| P+SA | 228.63±18.25 b | 21.00±1.00 ab | 0.28±0.02 a | 0.15±0.01 a | 1034.0±87.6 ab |
| LP | 208.66±17.94 b | 20.06±0.84 b | 0.30±0.03 a | 0.13±0.03 b | 1183.8±181.2 b |
| LP+SA | 252.27±15.07 a | 22.44±0.54 a | 0.29±0.01 a | 0.15±0.01 a | 1462.5±126.5 a |
表1 水稻根系发育相关指标
Table 1. Indicators associated with rice root development.
| 处理 Treatment | 总根长 Total length/cm | 表面积 Surface area/cm2 | 平均直径 Average diameter/mm | 根系总体积 Root volume/cm3 | 总根尖数 Number of root tips |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P | 155.99±13.28 c | 14.45±0.97 c | 0.30±0.01 a | 0.11±0.01 c | 745.8±60.3 c |
| P+SA | 228.63±18.25 b | 21.00±1.00 ab | 0.28±0.02 a | 0.15±0.01 a | 1034.0±87.6 ab |
| LP | 208.66±17.94 b | 20.06±0.84 b | 0.30±0.03 a | 0.13±0.03 b | 1183.8±181.2 b |
| LP+SA | 252.27±15.07 a | 22.44±0.54 a | 0.29±0.01 a | 0.15±0.01 a | 1462.5±126.5 a |
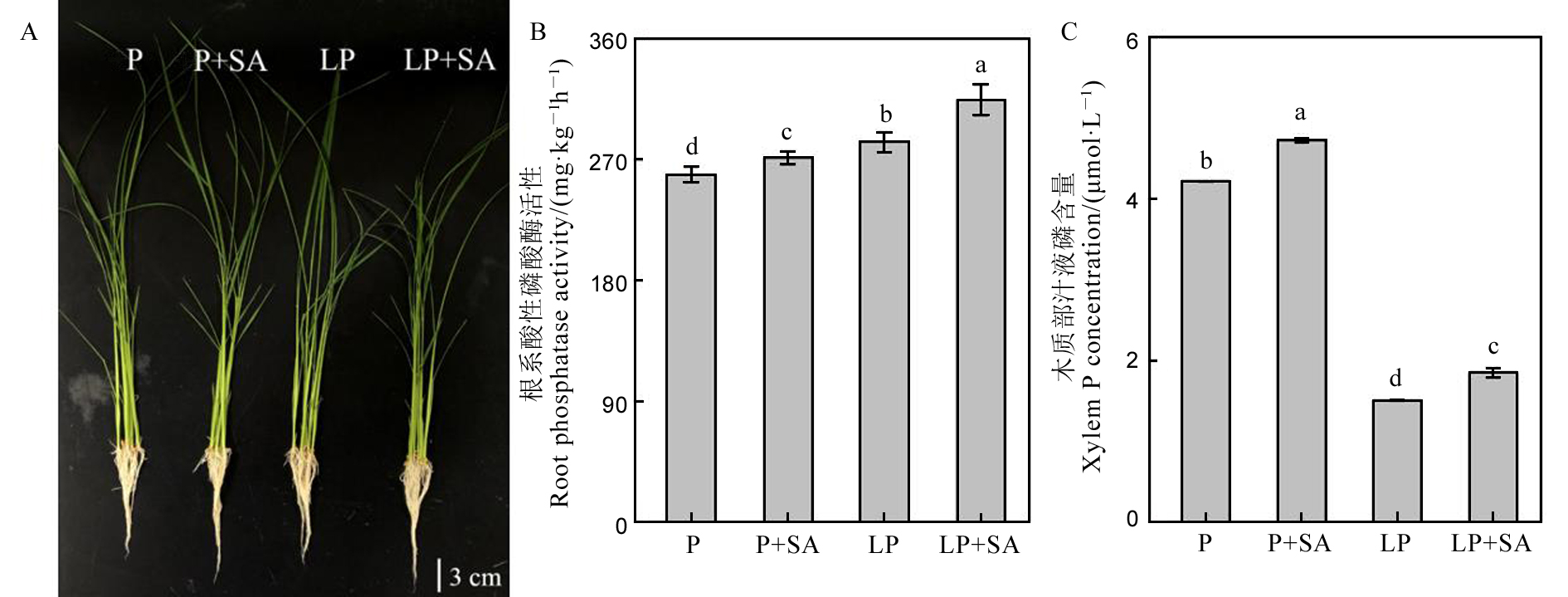
图3 水稻的表型和根部酸性磷酸酶活性和木质部汁液磷含量 数据用均值±标准差(n = 4)表示。不同的大小写字母代表处理间差异分别在P < 0.01和P < 0.05 水平上显著。P-180 mmol/L;LP-18 mmol/L;SA-1 μmol/L水杨酸。
Fig. 3. Phenotype of rice, acid phosphatase activity in rice roots and xylem P concentration. Different letters above the bars mean significant difference at P < 0.05. P, 180 mmol/L; LP, 18 mmol/L; SA,1 μmol/L salicylic acid.
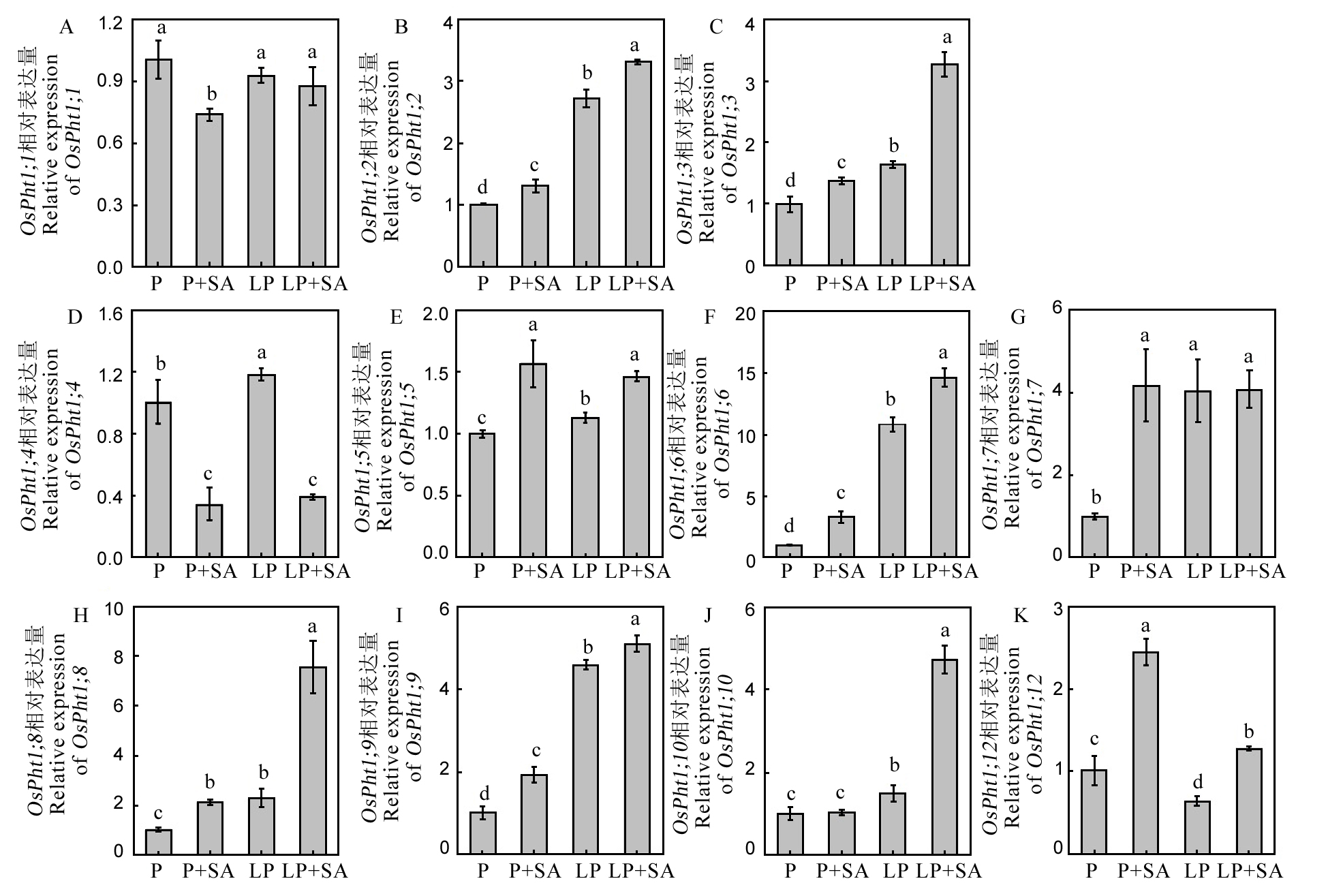
图4 水稻磷转运相关基因的表达 数据用均值±标准差(n = 4)表示。不同的大小写字母代表处理间差异分别在P < 0.01和P < 0.05 水平上显著。P-180 mmol/L;LP-18 mmol/L。
Fig. 4. Relative expression levels of P transporter genes. Different letters above the bars mean significant difference at P < 0.05. P, 180 mmol/L; LP, 18 mmol/L.
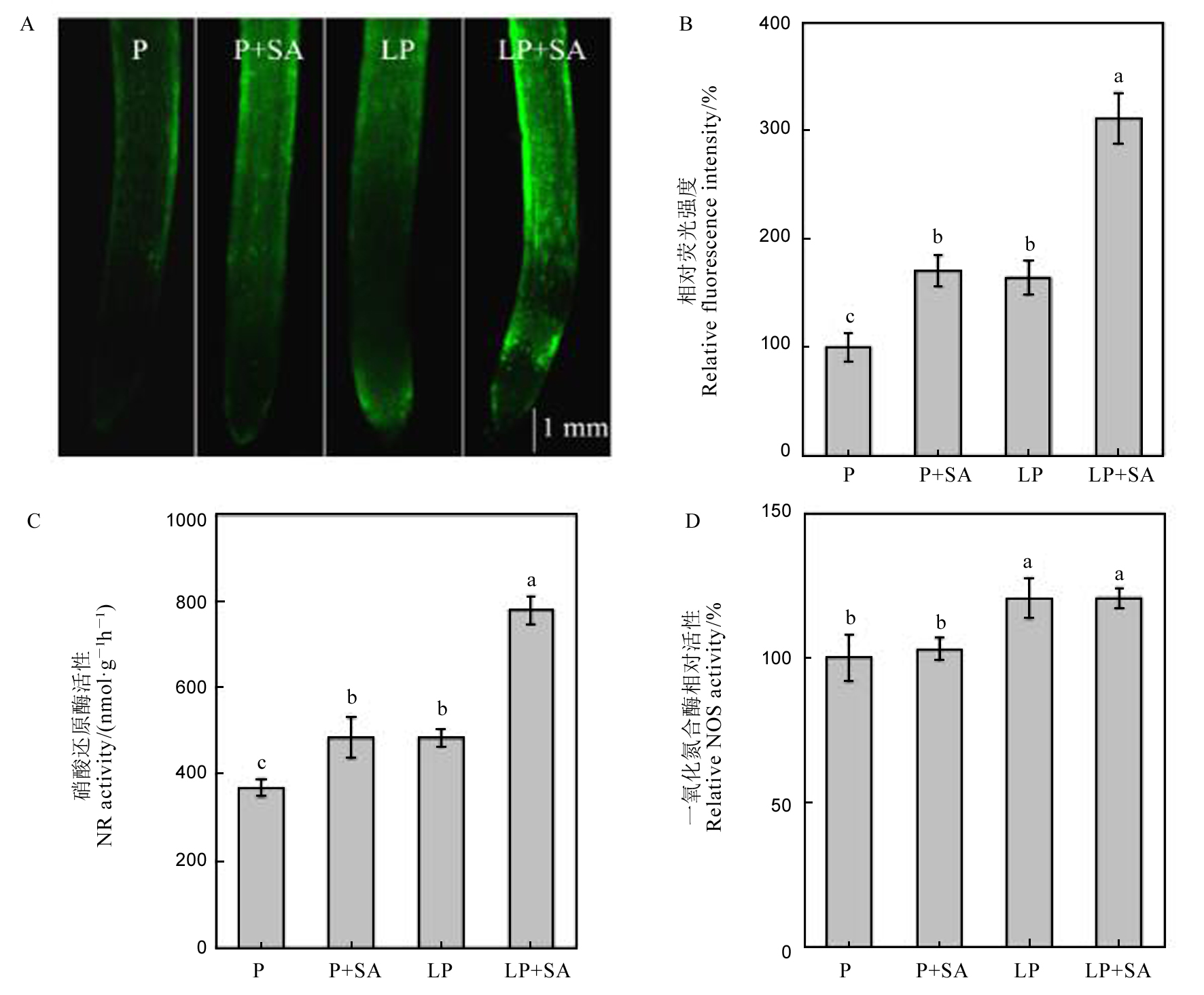
图5 水稻根尖一氧化氮荧光(A)、荧光强度(B)、硝酸还原酶活性(C)和一氧化氮合酶相对活性(D) 数据用均值±标准差(n = 4)表示。不同的小写字母代表处理间差异在 P < 0.05 水平上显著。P-180 mmol/L;LP-18 mmol/L;SA-1 μmol/L水杨酸。
Fig. 5. Nitric oxide fluorescence (A), fluorescence intensity (B), NR activity (C), and relative NOS activity (D). Mean±SD(n=4). Different letters above the bars mean significant difference at P < 0.05. P, 180 mmol/L; LP, 18 mmol/L; SA, 1 μmol/L salicylic acid.
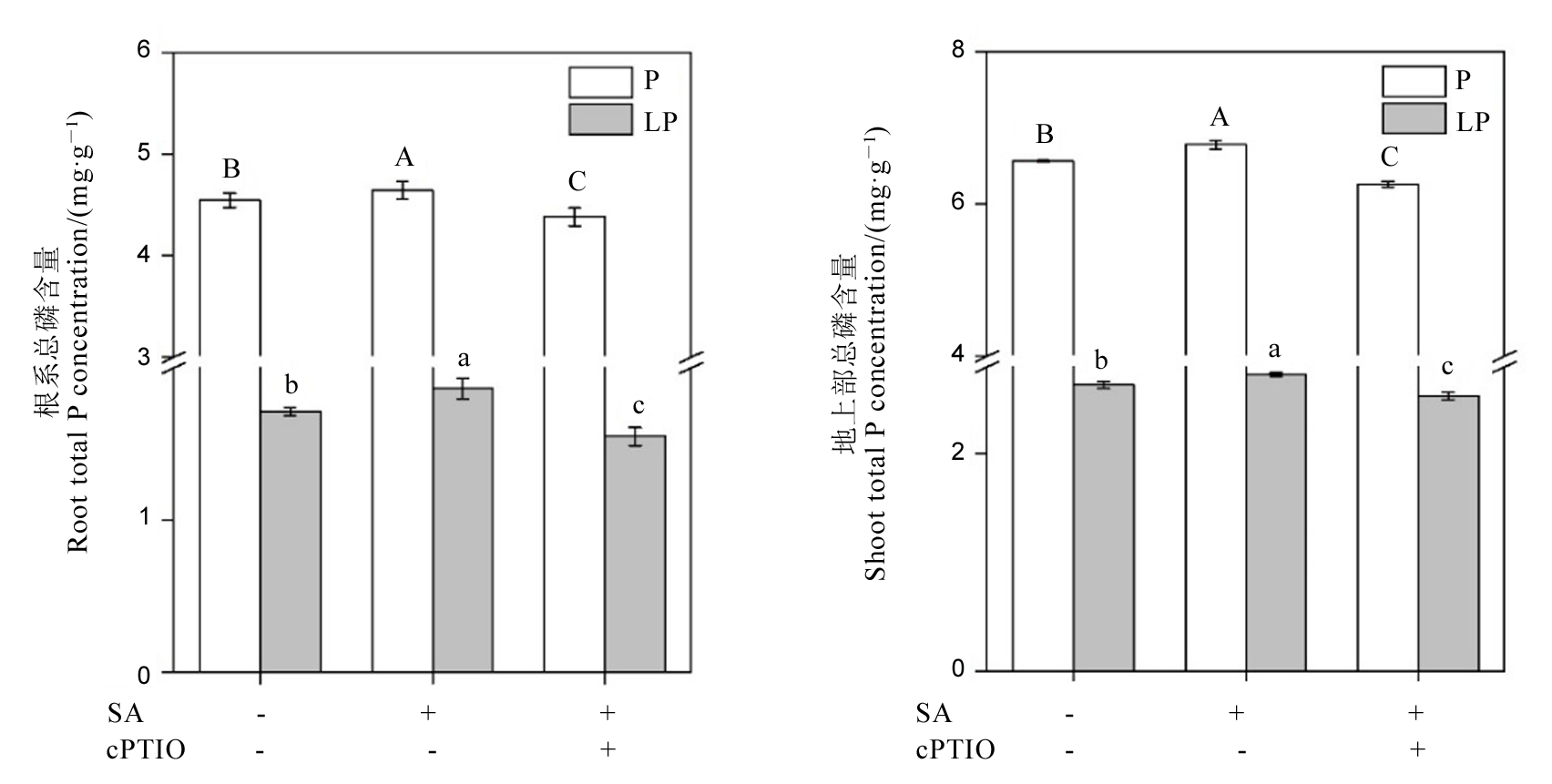
图6 添加c-PTIO后水稻根部(A)和地上部(B)的总磷含量 数据用均值±标准差(n = 4)表示。不同大小写字母代表处理间差异分别在P < 0.01和P < 0.05水平上显著。P-180 mmol/L;LP-18 mmol/L;SA-1 μmol/L;cPTIO-1 μmol/L。
Fig. 6. Total P content of rice roots (A) and shoots (B) after c-PTIO application. Mean±SD(n=4). Different letters above the bars mean significant difference at P < 0.05. P, 180 mmol/L; LP, 18 mmol/L; SA, 1 μmol/L; cPTIO, 1 μmol/L.
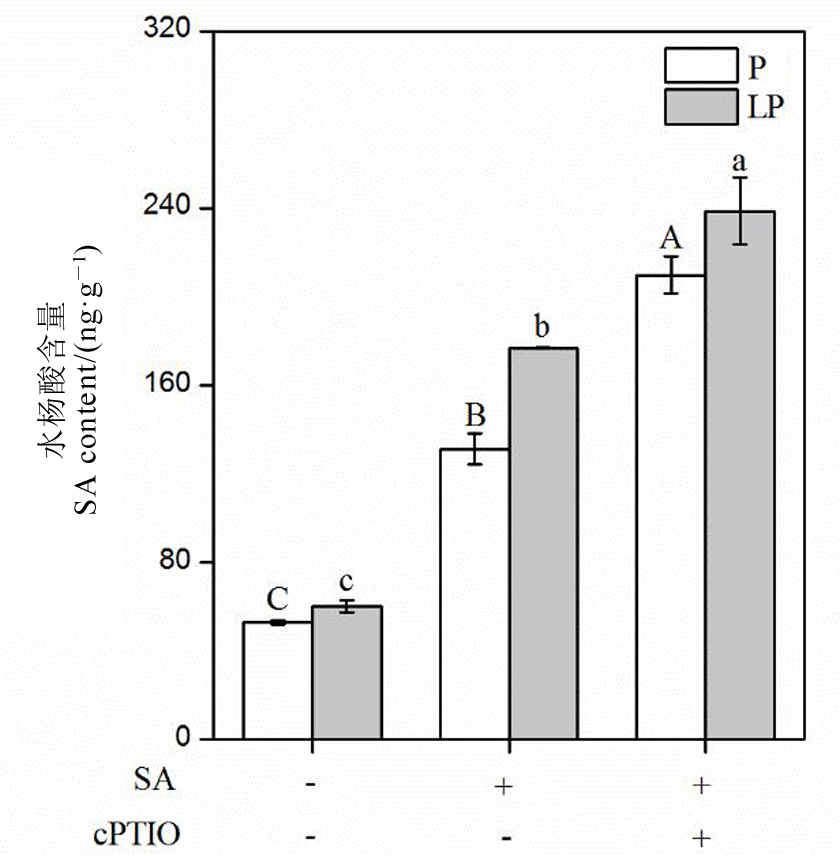
图7 添加1 μmol/L c-PTIO后水稻根部水杨酸含量 数据用均值±标准差(n = 4)表示。不同大小写字母代表处理间差异分别在 P < 0.01和P < 0.05 水平上显著。P-180 mmol/L;LP-18 mmol/L;SA-1 μmol/L;cPTIO-1 μmol/L。
Fig. 7. Salicylic acid content of rice roots after 1 μmol/L c-PTIO application. Mean±SD(n=4). Different letters above the bars mean significant difference at P < 0.05. P, 180 mmol/L; LP, 18 mmol/L; SA, 1 μmol/L salicylic acid; CP, 1 μmol/L cPTIO.
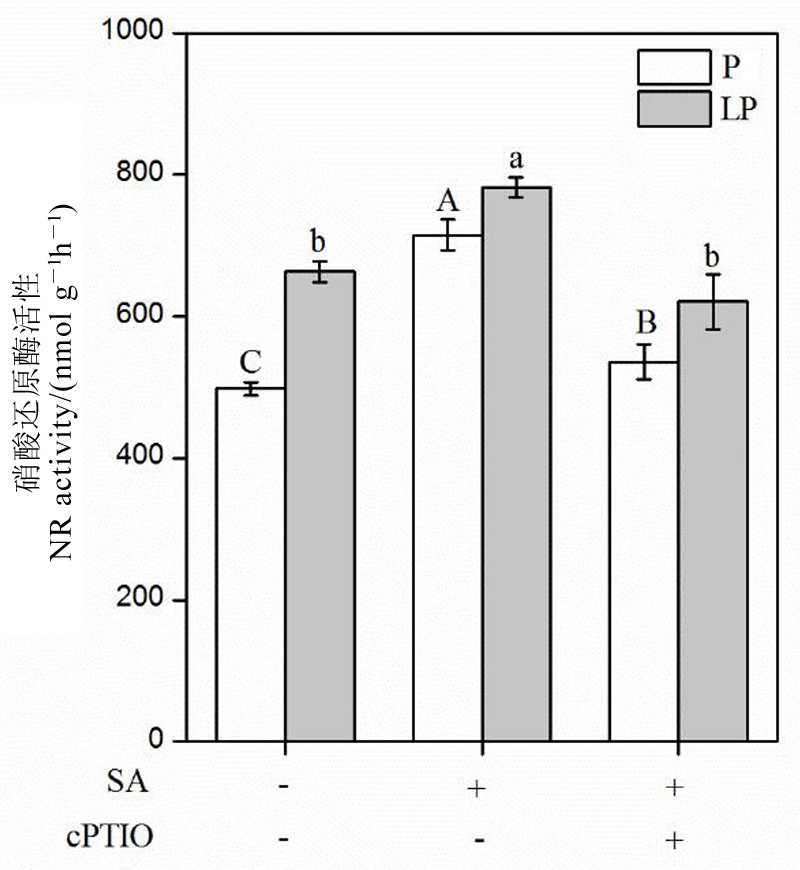
图8 添加1 μmol/L c-PTIO后水稻根部硝酸还原酶活性 数据用均值±标准差(n = 4)表示。不同的小写字母代表处理间差异在 P < 0.05 水平上显著。P-180 mmol/L,LP-18 mmol/L;SA-1 μmol/L;cPTIO-1 μmol/L。
Fig. 8. NR activity of rice roots after 1 μmol/L c-PTIO application. Mean±SD(n=4). Different letters above the bars mean significant difference at P < 0.05. P, 180 mmol/L, LP, 18 mmol/L; SA, 1 μmol/L salicylic acid; CP, 1 μmol/L cPTIO.

图9 水稻磷转运相关基因的表达 数据用均值±标准差(n = 4)表示。不同小写字母代表处理间差异在 P < 0.05 水平上显著。P-180 mmol/L; LP-18 mmol/L; SA-1 μmol/L水杨酸;CP-cPTIO,1 μmol/L。
Fig. 9. Relative expression levels of P transporter genes. Different letters above the bars mean significant difference at P < 0.05. P, 180 mmol/L; LP, 18 mmol/L; SA, 1 μmol/L salicylic acid; CP, 1 μmol/L cPTIO.
| [1] | 朱春权, 曹小闯, 朱练峰, 白志刚, 黄洁, 梁清铎, 金千瑜, 张均华. 硫化氢提高水稻磷吸收转运的生理和分子机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(6): 532-540. |
| Zhu C Q, Cao X C, Zhu L F, Bai Z G, Huang J, Liang Q D, Jin Q Y, Zhang J H. Physiological and molecular mechanisms of hydrogen sulfide enhancing phosphorus absorption and transportation in rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2019, 33(6): 532-540. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | 郎印海. 缺磷胁迫下植物应激反应初步研究及应激物质的诱导、提取分离[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2000. |
| Lang Y H. Preliminary study on plants response to phosphorus deficiency stress and the extraction and separation of stress induction substances[D]. Tai’an: Shandong Agricultural University, 2000. | |
| [3] | 张海伟, 黄宇, 叶祥盛, 徐芳森. 低磷胁迫下甘蓝型油菜酸性磷酸酶对磷效率的贡献分析[J]. 中国科学: C辑, 2010, 40(5): 418-427. |
| Zhang H W, Huang Y, Ye X S, Xu F S. Contribution analysis of phosphorus efficiency for acid phosphatase in Brassica napus L. under low phosphorus stress[J]. Scientia Sinica Vitae, 2010, 40(5): 418-427. (in Chinese) | |
| [4] | 李立芹. 植物低磷胁迫适应机制的研究进展[J]. 生物学通报, 2011, 46(2): 13-16. |
| Li L Q. Advances in the mechanism of plant adapt to low phosphorus stress[J]. Bulletin of Biology, 2011, 46(2): 13-16. (in Chinese) | |
| [5] | 李锋, 潘晓华. 植物适应缺磷胁迫的根系形态及生理特征研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2002, 18(5): 65-69, 76. |
| Li F, Pan X H. The research development of morphological and physiological characteristics of plant root system under phosphorus deficiency[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2002, 18(5): 65-69, 76. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | Plaxton W C, Carswell M C. Metabolic aspects of the phosphate starvation response in plants. Plant responses to environmental stresses: From phytohormones to genome reorganization Marcel Dekker, New York: 1999, 349-372. |
| [7] | Zhu X F, Wang Z W, Wan J X, Sun Y, Wu Y R, Li G X, Shen R F, Zheng S J. Pectin enhances rice (Oryza sativa) root phosphorus remobilization[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2015, 66(3): 1017-1024. |
| [8] | Yu B, Xu C, Benning C. Arabidopsis disrupted in SQD2 encoding sulfolipid synthase is impaired in phosphate-limited growth[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2002, 99(8): 5732-5737. |
| [9] | Bandurska H. An update on biosynthesis and action in plant response to water deficit and performance under drought[C]// Hayat S, Ahmad A, Alyemeni M N. Salicylic Acid, Springer, 2013: 1-14. |
| [10] | Yusuf M, Hayat S, Alyemeni M N, Fariduddin Q, Ahmad A. Salicylic acid: Physiological roles in plants[C]// Hayat S, Ahmad A, Alyemeni M N. Salicylic Acid, Springer, 2013: 15-30. |
| [11] | Pancheva T V, Popova L P, Uzunova A N. Effects of salicylic acid on growth and photosynthesis in barley plants[J]. Journal of Plant Physiology, 1996, 149(1-2): 57-63. |
| [12] | Pancheva T V, Popova L P. Effect of salicylic acid on the synthesis of ribulose-1, 5-bisphosphate carboxylase/ oxygenase in barley leaves[J]. Journal of Plant Physiology, 1998, 152(4): 381-386. |
| [13] | 张永福, 黄鹤平, 彭声静, 任禛, 陈泽斌, 刘佳妮, 陈瑞. 铝胁迫下水杨酸对水晶葡萄植株生长及营养积累的影响[J]. 中外葡萄与葡萄酒, 2015(2): 10-15. |
| Zhang Y F, Huang H P, Peng S J, Ren C, Chen Z B, Liu J N, Chen R. Effects of salicylic acid on growth and nutrition accumulation of Shuijing seedling under aluminum stress[J]. Sino-Overseas Grapevine & Wine, 2015(2): 10-15. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | Janda T, Szalai G, Tari I, Páldi E. Hydroponic treatment with salicylic acid decreases the effects of chilling injury in maize (Zea mays L.) plants[J]. Planta, 1999, 208(8): 175-180. |
| [15] | Tasgin E, Attici O, Nalbantoglu B. Effect of salicylic acid and cold on freezing tolerance in winter wheat leaves[J]. Plant Growth Regulation, 2003, 41(3): 231-236. |
| [16] | Glass A D. Influence of phenolic acids on ion uptake: I. Inhibition of phosphate uptake[J]. Plant Physiology, 1973, 51(6): 1037-1041. |
| [17] | Khorassani R, Hettwer U, Ratzinger A, Ursula H, Reza K, Norbert C. Citramalic acid and salicylic acid in sugar beet root exudates solubilize soil phosphorus[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2011, 11(1): 121. |
| [18] | Gunes A, Inal A, Alpaslan M, Cicek N, Guneri E, Eraslan F, Guzelordu T. Effects of exogenously applied salicylic acid on the induction of multiple stress tolerance and mineral nutrition in maize (Zea mays L.)[J]. Archives of Agronomy and Soil Science, 2005, 51(6): 687-695. |
| [19] | He J Y, Ren Y F, Chen X L, Chen H. Protective roles of nitric oxide on seed germination and seedling growth of rice (Oryza sativa L.) under cadmium stress[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2014, 108: 114-119. |
| [20] | Singh V P, Srivastava P K, Prasad S M. Nitric oxide alleviates arsenic-induced toxic effects in ridged Luffa seedlings[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2013, 71: 155-163. |
| [21] | 李鹏飞. 一氧化氮通过调节磷酸盐吸收与转运促进水稻磷营养[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学, 2017. |
| Li P F. Nitric oxide enhances phosphate nutrition in rice seedlings by regulating phosphate uptake and translocation[D]. Xiamen: Xiamen University, 2017. | |
| [22] | Zhu C Q, Zhu X F, Hu A Y, Wang C, Wang B, Dong X Y, Shen R F. Differential effects of nitrogen forms on cell wall phosphorus remobilization are mediated by nitric oxide, pectin content, and phosphate transporter expression[J]. Plant Physiology, 2016, 171: 1407-1417. |
| [23] | Shao R X, Xin L F, Guo J M, Zheng H F, Mao J, Han X P, Jia L, Jia S J, Du C G, Song R, Yang Q H, Elmore R W. Salicylic acid-induced photosynthetic adaptability of Zea mays L. to polyethylene glycol-simulated water deficit is associated with nitric oxide signaling[J]. Photosynthetica, 2018, 56: 1370-1377. |
| [24] | Zhang X B, Feng B H, Wang H M, Xu X, Shi Y F, He Y, Chen Z, Sathe A P, Shirle Y L, Wu J L. A substitution mutation in OsPELOTA confers bacterial blight resistance by activating the salicylic acid pathway[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2018, 60(2): 160-172. |
| [25] | You C, Zhu H, Xu B, Wang S, Ding Y, Liu Z, Li G, Chen L, Ding C. Effect of removing superior spikelets on grain filling of inferior spikelets in rice[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2016: 7. |
| [26] | 李忠光, 龚明. 磺胺比色法测定植物组织硝酸还原酶活性的改进[J]. 植物生理学通讯, 2009, 45(1): 67-68. |
| Li Z G, Gong M. Improvement of nitrate reductase activity measurement in plant tissues by sulfa colorimetry method[J]. Plant Physiology Communications, 2009, 45(1): 67-68. (in Chinese) | |
| [27] | 张志良. 植物生理学实验指导. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2003: 41-43. |
| Zhang Z L. Experimental Guidance in Plant Physiology. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2003: 41-43. (in Chinese) | |
| [28] | 徐畅, 安书成. 一氧化氮及一氧化氮合酶的测定[J]. 陕西师范大学继续教育学报, 2004, 21(1): 115-118. |
| Xu C, An S C. Determination of nitric oxide and nitric oxide synthase[J]. Journal of Further Education of Shanxi Normal University, 2004, 21(1): 115-118. (in Chinese) | |
| [29] | 穆师洋, 胡文忠, 姜爱丽. 水杨酸的信号分子作用及其在鲜切果蔬中的应用[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报, 2015(7): 2434-2438. |
| Mu S Y, Hu W Z, Jiang A L. The role of salicylic acid as signal molecule and its application in fresh-cut fruits and vegetables[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality, 2015(7): 2434-2438. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | 侯爽, 陈锦芬, 刘溶荣, 王瑞, 陈俊鸿, 邹聪明, 谢小玉. 外源水杨酸对烟草幼苗低温胁迫的缓解效应[J]. 湖南农业大学学报: 自然科学版, 2020, 46(1): 14-20. |
| Hou S, Chen J F, Liu R R, Wang R, Chen J H, Zou C M, Xie X Y. Mitigative effect of exogenous salicylic acid on low temperature stress in tobacco seedlings[J]. Journal of Hunan Agricultural University: Natural Sciences Edition, 2020, 46(1): 14-20. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | Liao H, Yan X L. Adaptive changes and genotypic variation for root architecture of common bean in response to phosphorus deficiency[J]. Acta Botanica Sinica, 2000, 42(2): 158-163. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [32] | 黄荣, 孙虎威, 刘尚俊, 宋文静, 刘言勋, 余超, 毛颖, 张亚丽, 徐国华. 低磷胁迫下水稻根系的发生及生长素的响应[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2012, 26(5): 563-568. |
| Huang R, Sun H W, Liu S J, Song W J, Liu Y X, Yu C, Mao Y, Zhang Y L, Xu G H. Rice Root Growth and Auxin Concentration in Response to Phosphate Deficiency[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2012, 26(5): 563-568. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [33] | Wissuwa M, Ae N. Genotypic variation for tolerance to phosphorus deficiency in rice and the potential for its exploitation in rice improvement[J]. Plant Breeding, 2001, 120: 43-48. |
| [34] | Li H, Guo L, Tao C, Yang L M, Wang X Z. Nonredundant regulation of rice arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis by two members of the PHOSPHATE TRANSPORTER1 gene family[J]. Plant Cell, 2012, 24: 4236-4251. |
| [35] | Paszkowski U, Kroken S, Roux C, Briggs S P. Rice phosphate transporters include an evolutionarily divergent gene specifically activated in arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science, 2002, 99: 13324-13329. |
| [36] | Wang X, Wang Y, Piñeros M A, Wang Z Y, Wang W X, Li C G, Wu Z C, Kochian L V, Wu P. Phosphate transporters OsPHT1;9 and OsPHT1;10 are involved in phosphate uptake in rice[J]. Plant, Cell and Environment, 2014, 37: 1159-1170. |
| [37] | 王文霞. 水稻磷酸盐转运体OsPht1;3和OsPht1;5的功能研究. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2014: 21-30. |
| Wang W X. Functional analysis of OsPhtl;3 and OsPht1;5 in Oryza sativa[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2014: 21-30. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [38] | Zhang F, Sun Y F, Pei W X, Jain A, Sun R, Cao Y, Wu X, Jiang T, Zhang L, Fan X, Chen A, Shen Q, Xu G, Sun S. Involvement of OsPht1;4 in phosphate acquisition and mobilization facilitates embryo development in rice[J]. Plant Journal, 2015, 82(4): 556-569. |
| [39] | Ai P H, Sun S B, Zhao J N, Fan X R, Xin W J, Guo Q, Yu L, Shen Q R, Wu P, Miller A J, Xu G H. Two rice phosphate transporters, OsPht1; 2 and OsPht1; 6, have different functions and kinetic properties in uptake and translocation[J]. The Plant Journal, 2009, 57(5): 798-809. |
| [40] | Jia H, Ren H, Gu M, Zhao J, Sun S, Zhang X, Chen J, Wu P, Xu G. The phosphate transporter gene OsPht1; 8 is involved in phosphate homeostasis in rice[J]. Plant Physiology, 2011, 156(3): 1164-1175. |
| [41] | 黄沆, 付崇允, 周德贵, 陈光辉, 周少川. 植物磷吸收的分子机理研究进展[J]. 分子植物育种, 2008, 6(1): 117-122. |
| Huang H, Fu Z Y, Zhou D G, Chen G H, Zhou S C. Progress in research of molecular mechanism of phosphorus absorption in plants[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2008, 6(1): 117-122. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [42] | Klessig D F, Durner J, Noad R, Navarre D A, Wendehenne D, Kumar D, Zhou J M, Shah J, Zhang S Q, Kachroo P, Trifa Y, Pontier D, Lam E, Silva H. Nitric oxide and salicylic acid signaling in plant defense[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science, 2000, 97(16): 8849-8855. |
| [43] | Song F, Goodman R M. Activity of nitric oxide is dependent on, but is partially required for function of, salicylic acid in the signaling pathway in tobacco systemic acquired resistance[J]. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 2001, 14(12): 1458-1462. |
| [44] | Zottini M, Costa A, Michele R D, Ruzzene M, Carimi F. Salicylic acid activates nitric oxide synthesis in Arabidopsis[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2007, 6 (58): 1397-1405. |
| [45] | Meng Z B, Chen L Q, Suo D, Li G X, Tang C X, Zheng S J. Nitric oxide is the shared signaling molecule in phosphorus- and iron-deficiency-induced formation of cluster roots in white lupin (Lupinus albus)[J]. Annals of Botany, 2012, 109: 1055-1064. |
| [46] | Shen J B, Yuan L X, Zhang J L, Li H G, Bai Z H, Chen H P, Zhang W F, Zhang F S. Phosphorus dynamics: From soil to plant[J]. Plant Physiology, 2011, 156: 997-1005. |
| [47] | Ae N, Shen R F. Root cell-wall properties are proposed to contribute to phosphorus (P) mobilization by groundnut and pigeonpea[J]. Plant and Soil, 2002, 245: 95-103. |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 伏荣桃, 陈诚, 王剑, 赵黎宇, 陈雪娟, 卢代华. 转录组和代谢组联合分析揭示稻曲病菌的致病因子[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 375-385. |
| [5] | 丁正权, 潘月云, 施扬, 黄海祥. 基于基因芯片的嘉禾系列长粒优质食味粳稻综合评价与比较[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 397-408. |
| [6] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [7] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [8] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [9] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [10] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [11] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [12] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [13] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [14] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [15] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||