
中国水稻科学 ›› 2022, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (3): 259-268.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2022
刘进1,2, 崔迪2, 余丽琴1, 张立娜2, 周慧颖1, 马小定2, 胡佳晓1, 韩冰2, 韩龙植2,*( ), 黎毛毛1,*(
), 黎毛毛1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2021-07-29
修回日期:2021-08-19
出版日期:2022-05-10
发布日期:2022-05-11
通讯作者:
韩龙植,黎毛毛
基金资助:
LIU Jin1,2, CUI Di2, YU Liqin1, ZHANG Lina2, ZHOU Huiying1, MA Xiaoding2, HU Jiaxiao1, HAN Bing2, HAN Longzhi2,*( ), LI Maomao1,*(
), LI Maomao1,*( )
)
Received:2021-07-29
Revised:2021-08-19
Online:2022-05-10
Published:2022-05-11
Contact:
HAN Longzhi, LI Maomao
摘要:
【目的】鉴定和筛选水稻极端耐热种质或基因,为培育耐高温水稻新品种提供技术支撑。【方法】以耐热等级和幼苗存活率为指标对不同类型水稻苗期耐热性进行鉴定评价,以筛选和鉴定耐热种质资源及主效QTL。【结果】不同类型水稻品种苗期耐热性存在明显差异,籼稻品种耐热性明显强于粳稻品种,籼稻和粳稻品种均存在极端耐热和极端敏感种质资源;共筛选出嘉育253、中优早8号、秀水09等20份耐热种质资源,高温处理后幼苗存活率和生长发育基本不受影响。RIL群体双亲耐热等级和幼苗存活率存在极显著差异,中优早8号耐热性较强,植株基本无枯死,龙稻5号对高温胁迫较敏感,不同株系间苗期耐热性存在较大幅度变异;共检测到12个苗期耐热相关QTL,分布于第1、3、4、5和8染色体上,耐热等级和存活率QTL存在明显的遗传重叠,主效QTL簇qHTS4和qHTS8表型贡献率较大。基于QTL初步定位结果,利用相对剩余杂合体RHL-F2群体,在第8染色体RM5808-RM556标记区域鉴定了一个苗期耐热性主效QTL qHTS8,该区域对苗期耐热性具有较强调控效应。【结论】筛选出20份苗期耐热性较强的水稻种质资源,鉴定了12个苗期耐热相关的QTL,定位和验证了一个调控水稻苗期耐热性的主效QTL qHTS8,研究结果可为水稻苗期耐热性生理生化机理与分子遗传机制的研究及育种利用奠定基础。
刘进, 崔迪, 余丽琴, 张立娜, 周慧颖, 马小定, 胡佳晓, 韩冰, 韩龙植, 黎毛毛. 水稻苗期耐热种质资源筛选及QTL定位[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(3): 259-268.
LIU Jin, CUI Di, YU Liqin, ZHANG Lina, ZHOU Huiying, MA Xiaoding, HU Jiaxiao, HAN Bing, HAN Longzhi, LI Maomao. Screening and QTL Mapping of Heat-tolerant Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Germplasm Resources at Seedling Stage[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(3): 259-268.
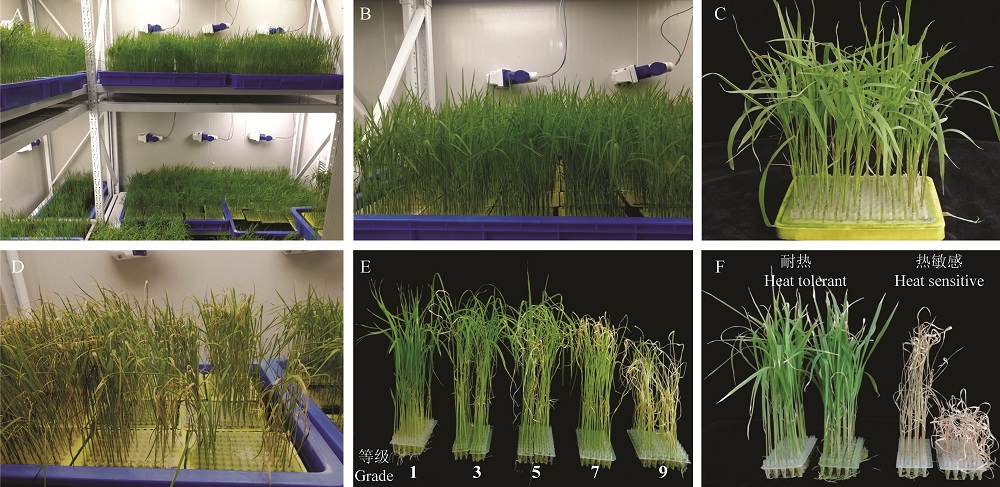

图1 水稻苗期耐热鉴定 A~C分别为正常温度培养水稻苗期培养环境及植株长势;D~F分别为45℃处理恢复后表型、耐热等级和极端材料表型。
Fig. 1. Identification of heat tolerance at seedling stage in rice. A-C, Plant phenotype at seedling stage under control; D-F, Plant phenotype, heat tolerance grade and extreme material after exposure to 45℃.
| 性状 Trait | 亚群 Group | 品种数量 Number of varieties | 均值±标准差 Mean±SD | 变幅 Range | 峰度 Skewness | 偏度 Kurtosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 耐热等级 Heat tolerance grade | 总体 Total | 738 | 6.04±2.38 | 1~9 | -0.498 | -0.749 |
| 籼稻 indica | 387 | 5.40±2.73 | 1~9 | -0.111 | -1.298 | |
| 粳稻 japonica | 351 | 6.74±1.67** | 3~9 | -0.417 | -0.568 | |
| 存活率 Survival rate under heat stress | 总体 Total | 738 | 42.41±30.42 | 0~100 | 0.226 | -1.174 |
| 籼稻 indica | 387 | 50.35±31.97 | 0~100 | -0.090 | -1.343 | |
| 粳稻 japonica | 351 | 33.64±25.98** | 0~100 | 0.436 | -0.787 |
表1 水稻种质资源苗期耐热性鉴定
Table 1. Screening of heat-tolerant rice germplasm resources at seedling stage.
| 性状 Trait | 亚群 Group | 品种数量 Number of varieties | 均值±标准差 Mean±SD | 变幅 Range | 峰度 Skewness | 偏度 Kurtosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 耐热等级 Heat tolerance grade | 总体 Total | 738 | 6.04±2.38 | 1~9 | -0.498 | -0.749 |
| 籼稻 indica | 387 | 5.40±2.73 | 1~9 | -0.111 | -1.298 | |
| 粳稻 japonica | 351 | 6.74±1.67** | 3~9 | -0.417 | -0.568 | |
| 存活率 Survival rate under heat stress | 总体 Total | 738 | 42.41±30.42 | 0~100 | 0.226 | -1.174 |
| 籼稻 indica | 387 | 50.35±31.97 | 0~100 | -0.090 | -1.343 | |
| 粳稻 japonica | 351 | 33.64±25.98** | 0~100 | 0.436 | -0.787 |
| 编号Number | 品种名称 Cultivar | 耐热等级 HTG | HTSR /% | 编号 Number | 品种名称Cultivar | 耐热等级 HTG | HTSR /% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | 嘉育253 Jiayu 253 | 1 | 100.0 | L11 | 秀水9号 Xiushui 9 | 3 | 93.8 | ||
| L2 | 早恢6号 Zaohui 6 | 1 | 100.0 | L12 | 苏资16 Suzi 16 | 4 | 87.5 | ||
| L3 | 龙红3号 Longhong 3 | 1 | 100.0 | L13 | 秀水12 Xiushui 12 | 4 | 87.5 | ||
| L4 | 闽泉2号 Minquan 2 | 1 | 100.0 | L14 | 云粳38 Yunjing 38 | 3 | 87.5 | ||
| L5 | 湘晚籼11 Xiangwanxian 11 | 1 | 100.0 | L15 | 秀水48 Xiushui 48 | 4 | 75.0 | ||
| L6 | 中优早8号 Zhongyouzao 8 | 1 | 97.0 | L16 | 嘉花1号 Jiahua 1 | 4 | 75.0 | ||
| L7 | 梅峰23号 Meifeng 23 | 1 | 90.6 | L17 | 南粳46 Nanjing 46 | 3 | 73.3 | ||
| L8 | 龙菲313 Longfei 313 | 1 | 90.6 | L18 | 甬糯34 Yongnuo 34 | 4 | 68.8 | ||
| L9 | 莲塘早 Liantangzao | 3 | 86.9 | L19 | 盐恢559 Yanhui 559 | 4 | 64.3 | ||
| L10 | 赣早籼58 Ganzaoxian 58 | 3 | 83.3 | L20 | 庄育3号 Zhuangyu 3 | 4 | 60.0 | ||
表2 水稻苗期极端耐热的种质资源
Table 2. Extreme heat resistant germplasm resources at seedling stage in rice.
| 编号Number | 品种名称 Cultivar | 耐热等级 HTG | HTSR /% | 编号 Number | 品种名称Cultivar | 耐热等级 HTG | HTSR /% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | 嘉育253 Jiayu 253 | 1 | 100.0 | L11 | 秀水9号 Xiushui 9 | 3 | 93.8 | ||
| L2 | 早恢6号 Zaohui 6 | 1 | 100.0 | L12 | 苏资16 Suzi 16 | 4 | 87.5 | ||
| L3 | 龙红3号 Longhong 3 | 1 | 100.0 | L13 | 秀水12 Xiushui 12 | 4 | 87.5 | ||
| L4 | 闽泉2号 Minquan 2 | 1 | 100.0 | L14 | 云粳38 Yunjing 38 | 3 | 87.5 | ||
| L5 | 湘晚籼11 Xiangwanxian 11 | 1 | 100.0 | L15 | 秀水48 Xiushui 48 | 4 | 75.0 | ||
| L6 | 中优早8号 Zhongyouzao 8 | 1 | 97.0 | L16 | 嘉花1号 Jiahua 1 | 4 | 75.0 | ||
| L7 | 梅峰23号 Meifeng 23 | 1 | 90.6 | L17 | 南粳46 Nanjing 46 | 3 | 73.3 | ||
| L8 | 龙菲313 Longfei 313 | 1 | 90.6 | L18 | 甬糯34 Yongnuo 34 | 4 | 68.8 | ||
| L9 | 莲塘早 Liantangzao | 3 | 86.9 | L19 | 盐恢559 Yanhui 559 | 4 | 64.3 | ||
| L10 | 赣早籼58 Ganzaoxian 58 | 3 | 83.3 | L20 | 庄育3号 Zhuangyu 3 | 4 | 60.0 | ||
| 性状 Trait | 亲本 Parent | 重组自交系群体 RIL population | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 龙稻5号 Longdao 5 | 中优早8号 Zhongyouzao 8 | 均值±标准差 Mean±SD | 变幅 Range | 峰度 Skewness | 偏度 Kurtosis | ||
| 耐热等级HTG | 8.0±1.2 | 1.7±1.0** | 6.5±1.8 | 1.7~9.0 | -0.55 | -0.28 | |
| HTSR/% | 17.5±6.5 | 90.8±3.0** | 39.1±16.5 | 0.0~100.0 | 0.23 | -0.77 | |
表3 亲本和RIL群体苗期耐热性表型分析
Table 3. Phenotype of heat tolerance from the parents and RIL populations at seedling stage.
| 性状 Trait | 亲本 Parent | 重组自交系群体 RIL population | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 龙稻5号 Longdao 5 | 中优早8号 Zhongyouzao 8 | 均值±标准差 Mean±SD | 变幅 Range | 峰度 Skewness | 偏度 Kurtosis | ||
| 耐热等级HTG | 8.0±1.2 | 1.7±1.0** | 6.5±1.8 | 1.7~9.0 | -0.55 | -0.28 | |
| HTSR/% | 17.5±6.5 | 90.8±3.0** | 39.1±16.5 | 0.0~100.0 | 0.23 | -0.77 | |
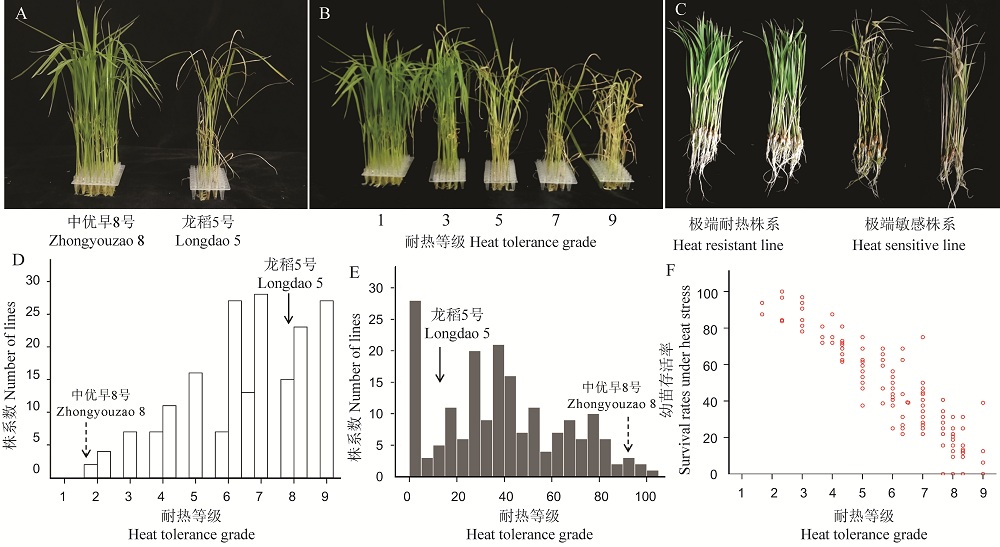
图3 水稻RIL群体苗期耐热性表型鉴定及相关性分析 A~C为高温处理后表型性状; D-幼苗耐热等级; E-幼苗存活率; F―耐热等级和幼苗存活率相关性。
Fig. 3. Identification of heat tolerance of RIL population and correlation at seedling stage. A-C is the phenotypic after high temperature treatment; D, Heat tolerance grade; E, Seedling survival distribution; F, Correlation between heat tolerance grade and seedling survival rate under heat stress.
| 性状 Trait | 位点 Locus | 位置 Position | 标记 Marker | LOD值 LOD value | 贡献率 Percentage variance explained / % | 加性效应 Additive effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 耐热等级 Heat tolerance grade | qHTG1.1 1 | 50.5 | RI02519-RM580 | 2.56 | 4.11 | 0.40 |
| qHTG1.2 | 152.5 | RM1198-RM1361.1 | 2.51 | 4.76 | 0.53 | |
| qHTG4 | 123.1 | RM3648-RM1113 | 2.54 | 12.46 | -0.41 | |
| qHTG5.1 | 111.0 | STS5.3-RM26 | 2.79 | 3.25 | -0.47 | |
| qHTG5.2 | 132.0 | RM19221-RM334 | 2.50 | 3.54 | -0.49 | |
| qHTG8 | 81.5 | RM7285-RM6976 | 4.34 | 14.57 | -1.63 | |
| 幼苗存活率 Survival rate under heat stress | qHTSR1 | 50.5 | RI02519-RM580 | 2.69 | 4.69 | -6.73 |
| qHTSR3 | 87.5 | MM3641-MM3720 | 2.54 | 2.39 | 6.20 | |
| qHTSR4.1 | 95.1 | R4M50-STS4.3 | 2.61 | 3.50 | 5.69 | |
| qHTSR4.2 | 123.1 | RM3648-RM1113 | 2.79 | 13.09 | 7.06 | |
| qHTSR5 | 108.0 | RM3321-RM3616 | 2.56 | 3.23 | 7.21 | |
| qHTSR8 | 80.5 | RM7285-RM6976 | 5.05 | 15.30 | 19.69 |
表4 水稻苗期耐热性QTL分析
Table 4. QTL for heat tolerance were detected at seedling stage.
| 性状 Trait | 位点 Locus | 位置 Position | 标记 Marker | LOD值 LOD value | 贡献率 Percentage variance explained / % | 加性效应 Additive effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 耐热等级 Heat tolerance grade | qHTG1.1 1 | 50.5 | RI02519-RM580 | 2.56 | 4.11 | 0.40 |
| qHTG1.2 | 152.5 | RM1198-RM1361.1 | 2.51 | 4.76 | 0.53 | |
| qHTG4 | 123.1 | RM3648-RM1113 | 2.54 | 12.46 | -0.41 | |
| qHTG5.1 | 111.0 | STS5.3-RM26 | 2.79 | 3.25 | -0.47 | |
| qHTG5.2 | 132.0 | RM19221-RM334 | 2.50 | 3.54 | -0.49 | |
| qHTG8 | 81.5 | RM7285-RM6976 | 4.34 | 14.57 | -1.63 | |
| 幼苗存活率 Survival rate under heat stress | qHTSR1 | 50.5 | RI02519-RM580 | 2.69 | 4.69 | -6.73 |
| qHTSR3 | 87.5 | MM3641-MM3720 | 2.54 | 2.39 | 6.20 | |
| qHTSR4.1 | 95.1 | R4M50-STS4.3 | 2.61 | 3.50 | 5.69 | |
| qHTSR4.2 | 123.1 | RM3648-RM1113 | 2.79 | 13.09 | 7.06 | |
| qHTSR5 | 108.0 | RM3321-RM3616 | 2.56 | 3.23 | 7.21 | |
| qHTSR8 | 80.5 | RM7285-RM6976 | 5.05 | 15.30 | 19.69 |
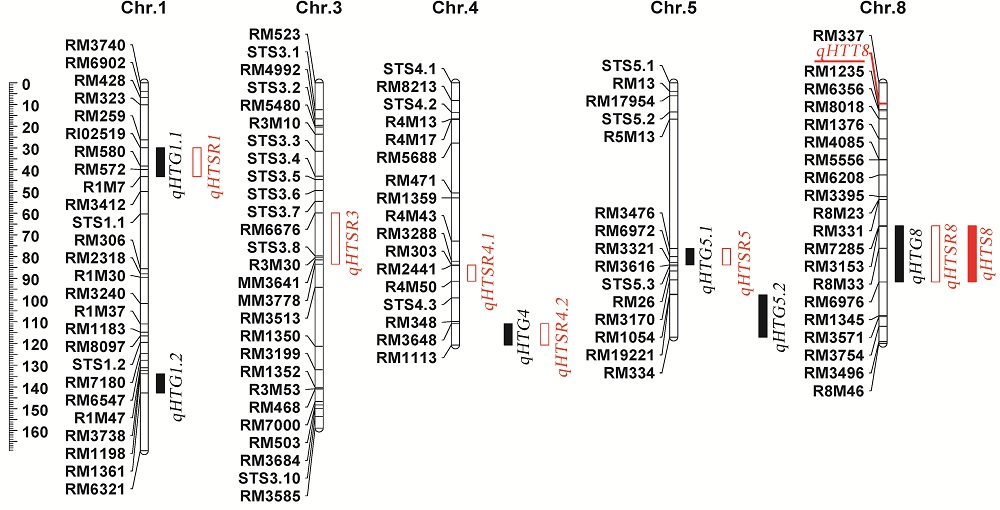
图4 水稻耐热等级(黑色)和幼苗存活率(红色)QTL在RIL群体中的染色体分布
Fig. 4. Location of QTL for heat tolerance grade(black) and seedling survival rate(red) detected at seedling stage on RIL populations genetic map.
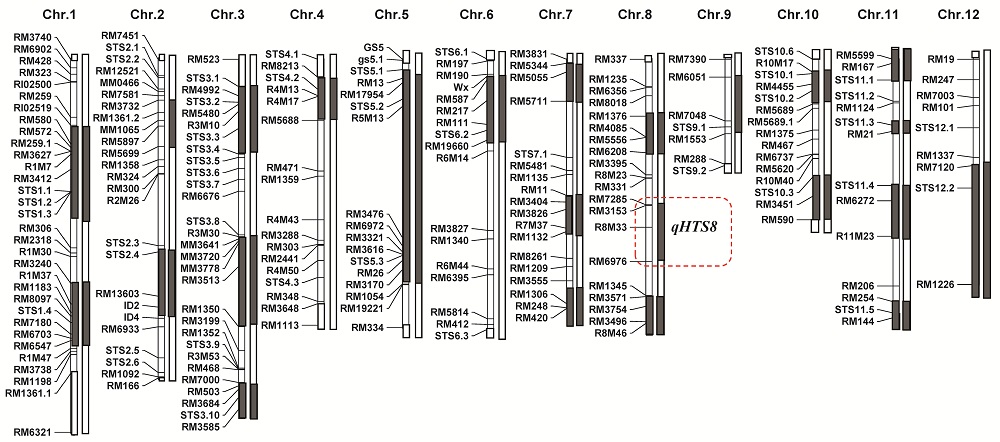
图5 水稻苗期耐热主效qHTS8定位相关的剩余杂合体基因型
Fig. 5. Residual heterozygous genotypes for identification of major QTL qHTS8 for heat tolerance at seedling stage in rice.
| [1] | Zhang G H, Li S Y, Wang L, Ye W J, Zeng D L, Rao Y C, Peng Y L, Hu J, Yang Y L, Xu J, Ren D Y, Gao Z Y, Zhu L, Dong G J, Hu X M, Yan M X, Guo L B, Li C Y, Qian Q. LSCHL4 from japonica cultivar, which is allelic to NAL1, increases yield of indica super rice 93-11[J]. Molecular Plant, 2014, 7: 1350-1364. |
| [2] | 田小海, 罗海伟, 周恒多, 吴晨阳. 中国水稻热害研究历史、进展与展望[J]. 中国农学通报, 2009, 25(22): 166-168. |
| Tian X H, Lu H W, Zhou H D, Wu C Y. Research on heat stress of rice in China: Progress and prospect[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2009, 25(22): 166-168. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 杨沈斌, 申双和, 赵小艳, 赵艳霞, 许吟隆, 王主玉, 刘娟, 张玮玮. 气候变化对长江中下游稻区水稻产量的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2010, 36(9): 1519-1528. |
| Yang S B, Shen S H, Zhao X Y, Zhao Y X, Xu Y L, Wang Z Y, Liu J, Zhang W W. Impacts of climate changes on rice production in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2010, 36(9): 1519-1528. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 方芳, 何序晨, 张志豪, 张勤, 关亚静, 胡晋, 胡伟民. 玉米自交系苗期对高温胁迫的响应机制及其抗逆性[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2019, 31(7): 1045-1056. |
| Fang F, He X C, Zhang Z H, Zhang Q, Guan Y J, Hu J, Hu W M. Response mechanism and stress resistance of maize inbred lines to high temperature stress at seedling stage[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2019, 31(7): 1045-1056. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | Longmei N, Gill G K, Zaidi P H, Kumar R, Vikal Y. Genome wide association mapping for heat tolerance in sub-tropical maize[J]. BMC Genomics, 2021, 22: 154. |
| [6] | Das S, Krishnan P, Nayak M, Ramakrishnan B. High temperature stress effects on pollens of rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes[J]. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2014, 101: 36-46. |
| [7] | Zhang X J, Zhang S Y, Li C Q, Zhang W H. Effects of high temperature stress on growth of stress-tolerant rice seedlings with resistibility[J]. Agricultural Science & Technology, 2014, 15(4): 576-578, 584. |
| [8] | Peng S B, Huang J L, Sheehy J E, Laza R C, Visperas R M, Zhong X, Centeno G S, Khush G S, Cassman K G. Rice yields decline with higher night temperature from global warming[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2004, 101(27): 9971-9975. |
| [9] | Zhao C, Liu B, Piao S L, Wang X H, Lobell D B, Huang Y, Huang M T, YaoY T, Bassu S, Ciais P, Durand J L, Elliott J, Ewert F, Janssens I A, Li T, Lin E, Liu Q, Martre P, Müller C, Peng S S, Peñuelas J, Ruane A C, Wallach D, Wang T, Wu D H, Liu Z, Zhu Y, Zhu Z C, Asseng S. Temperature increase reduces global yields of major crops in four independent estimates[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2017, 114: 9326-9331. |
| [10] | IPCC. Climate change 2013: The physical science basis contribution of working group I to the fifth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change[R]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2013: 1-36. |
| [11] | 朱镇, 赵庆勇, 张亚东, 陈涛, 姚姝, 周丽慧, 于新, 王才林. 抽穗扬花期极端自然高温胁迫对水稻结实率的影响研究[J]. 西南农业学报, 2015, 28(1): 1666-1671. |
| Zhu Z, Zhao Q Y, Zhang Y D, Chen T, Yao S, Zhou L H, Yu X, Wang C L. Effect of extreme natural high temperature at heading and flowering stage on seed setting rate of rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 28(1): 1666-1671. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 李小湘, 姚奕, 潘孝武, 黎用朝, 刘文强, 刘利成, 盛新年, 康旭梅, 段永红. 地方稻资源D43的开花期耐热特性研究[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2017, 18(2): 275-282. |
| Li X X, Yao Y, Pan X W, Li Y C, Liu W Q, Liu L C, Shen X N, Kang X M, Duan Y H. Heat resistance analysis of an early-morning-flowering landrace D43 at anthesis[J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2017, 18(2): 275-282. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | 刘业涛, 穆麒麟, 王毅, 高园, 田小海. 从非洲水稻材料中筛选耐高温种质资源[J]. 中国农学通报, 2019, 35(12): 8-12. |
| Liu Y T, Mu Q L, Wang Y, Gao Y, Tian X H. Selecting high temperature tolerant germplasms from Africa rice[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2019, 35(12): 8-12. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | 黎毛毛, 余丽琴, 熊玉珍, 杜慧, 吴锦文, 李慧, 张晓宁. 抽穗扬花期耐热水稻种质资源的筛选鉴定[J]. 江西农业学报, 2016, 28(6): 1-5. |
| Li M M, Yu L Q, Xiong Y Z, Du H, Wu J W, Li H, Zhang X N. Selection and identification of rice germplasm resources tolerant to high temperature at heading-flowering stage[J]. Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi, 2016, 28(6): 1-5. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 刘刚, 蔡海亚, 贾海涛, 张硕, 焦春海. 非洲水稻种质SDWG005苗期耐热生理基础[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2021, 22(3): 646-653 |
| Liu G, Cai H Y, Jia H T, Zhang S, Jiao C H. Physiological basis of heat tolerance of African rice germplasm SDWG005 at seedling stage[J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2021, 22(3): 646-653. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 方先文, 汤陵华, 王艳平. 水稻孕穗期耐热种质资源的初步筛选[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2006, 7(3): 342-344. |
| Fang X W, Tang L H, Wang Y P. Selection on rice germplasm tolerant to high temperature[J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2006, 7(3): 342-344. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | 黎毛毛, 廖家槐, 张晓宁, 马小定, 杜慧, 韩龙植. 江西省早稻品种抽穗扬花期耐热性鉴定评价研究[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2014, 15(5): 919-925. |
| Li M M, Liao J H, Zhang X N, Ma X D, Du H, Han L Z. Evaluation of heat tolerance at the heading-flowering stages for early-season rice varieties in Jiangxi Province[J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2014, 15(5): 919-925. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | 杨军, 章毅之, 贺浩华, 李迎春, 陈小荣, 边建民, 金国花, 李翔翔, 黄淑娥. 水稻高温热害的研究现状与进展[J]. 应用生态学报, 2020, 31(8): 2817-2830. |
| Yang J, Zhang Y Z, He H H, Li Y C, Chen X R, Bian J M, Jin G H, Li X X, Huang S E. Current status and research advances of high-temperature hazards in rice. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2020, 31(8): 2817-2830. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | 王志刚, 王磊, 林海, 庞乾林, 鄂志国, 张玉屏, 朱德峰. 水稻高温热害及耐热性研究进展[J]. 中国稻米, 2013, 19(1): 27-31. |
| Wang Z G, Wang L, Lin H, Pan Q L, E Z G, Zhang Y P, Zhu D F. Research progress on high temperature hot damages of rice[J]. China Rice, 2013, 19(1): 27-31. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | 唐婷, 陈艳艳, 杨洋, 杨远柱, 孟桂元, 周静. 水稻耐高温性研究进展[J]. 分子植物育种, 2017, 15(9): 3694-3700. |
| Tang T, Cheng Y Y, Yang Y, Yang Y Z, Meng G Y, Zhou J. Research progress of rice resistance to high temperature[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2017, 15(9): 3694-3700. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | Liu Y L, Liu X Y, Wang X, Gao K, Zheng S. Heterologous expression of heat stress responsive AtPLC9 confers heat tolerance in transgenic rice[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2020, 20: 514. |
| [22] | 穰中文, 周清明. 水稻高温胁迫的生理响应及耐热机理研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2015, 31(21): 249-258. |
| Xiang Z W, Zhou Q M. Research advances on physiological responses and tolerant mechanism to high temperature stress in rice[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2015, 31(21): 249-258. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 万丙良, 查中萍. 气候变暖对水稻生产的影响及水稻耐高温遗传改良[J]. 中国农学通报, 2012, 28(36): 1-7. |
| Wan B L, Zha Z P. Effects of climate warming on rice production and genetic improvement for rice heat- tolerance[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2012, 28(36): 1-7. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | 凌霄霞, 张作林, 翟景秋, 叶树春, 黄见良. 气候变化对中国水稻生产的影响研究进展[J]. 作物学报, 2019, 45(3): 323-334. |
| Ling X X, Zhang Z L, Zhai J Q, Ye S C, Huang J L. A review for impacts of climate change on rice production in China[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2019, 45(3): 323-334. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | 刘进, 姚晓云, 刘丹, 余丽琴, 李慧, 王棋, 王嘉宇, 黎毛毛. 不同生态环境下水稻穗部性状QTL鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(2): 124-134. |
| Liu J, Yao X Y, Liu D, Yu L Q, Li H, Wang Q, Wang J Y, Li M M. Identification of QTL for panicle traits under multiple environments in rice(Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2019, 33(2): 124-134. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | Wang J K, Li H H, Zhang L Y, Meng L. QTL IciMapping Version 4.2[OE/OL]. (2019-07-24) [2021-05-05]. http://www.isbreeding.net. |
| [27] | McCouch S R. Gene nomenclature system for rice[J]. Rice, 2008, 1: 72-84. |
| [28] | 熊伟, 冯灵芝, 居辉, 杨笛. 未来气候变化背景下高温热害对中国水稻产量的可能影响分析[J]. 地球科学进展, 2016, 31(5): 515-528. |
| Xiong W, Feng L Z, Ju H, Yang D. Possible impacts of high temperatures on china's rice yield under climate change[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2016, 31(5): 515-528. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | 冯活仪, 江浩林, 王孟, 唐湘如, 段美洋, 潘圣刚, 田华, 王树丽, 莫钊文. 不同香稻品种苗期耐高温的形态生理响应[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(1): 68-74. |
| Feng H Y, Jiang H L, Wang M, Tang X R, Duan M Y, Pan S G, Tian H, Wang S L, Mo Z W. Morpho- physiological responses of different scented rice varieties to high temperature at seedling stage[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2019, 33(1): 68-74. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | 段骅, 杨建昌. 高温对水稻的影响及其机制的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2012, 26(4): 393-400. |
| Du H, Yang J C. Research advances in the effect of high temperature on rice and its mechanism[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2012, 26(4): 393-400. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | 许红云, 许为军, 谭学林. 高温对粳稻品种发芽及幼苗生长发育影响的研究[J]. 西南农业学报, 2008, 21(3): 593-596. |
| Xu H Y, Xu W J, Tan X L. Effect of continuing high temperature on germination and seedling development of japonica rice[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2008, 21(3): 593-596. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [32] | 何洋, 刘洋, 方宝华, 何小娥, 杨坚, 滕振宁, 张玉烛. 不同生育期温度逆境处理对早稻产量的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2016, 32(24): 18-24 |
| He Y, Liu Y, Fang B H, He X E, Yang J, Teng Z N, Zhang Y Z. Effect of temperature on early rice yield at different growth stages[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2016, 32(24): 18-24. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [33] | 赵凌, 赵春芳, 王建, 陈涛, 赵庆勇, 姚姝, 王才林. 20个水稻引进资源的花药开裂及苗期耐热性评价[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2017, 18(5): 968-973. |
| Zhao L, Zhao C F, Wang J, Chen T, Zhao Q Y, Yao S, Wang C L. Analyzing of length dehiscence at basal part of thecae and heat resistance during seedling stage of 20 introduced rice germplasms[J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2017, 18(5): 968-973. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [34] | Yan C, Zhan GP, Hong X F, Yang D W. Identification and fine mapping of a major QTL, TT1-2, that plays significant roles in regulating heat tolerance in rice[J]. Plant Molecular Biology Reporter, 2021, 39: 376-385. |
| [35] | 刘鸣, 李玉花, 解莉楠. 水稻非生物胁迫相关QTL研究进展[J]. 植物生理学报, 2013, 49(12): 1301-1308. |
| Liu M, Li Y H, Xie L N. Progress in QTL research for abiotic stress in rice[J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 2013, 49(12): 1301-1308. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [36] | 王胜昌, 涂海甫, 胡丹, 吴奈, 岑祥, 熊立仲. 水稻抗非生物逆境功能基因的发掘[J]. 生命科学, 2016, 28(10): 1216-1229. |
| Wang S C, Tu H F, Hu D, Wu N, Qin X, Xiong L Z. The exploitation of rice functional genes for abiotic stress[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Life Sciences, 2016, 28(10): 1216-1229. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [37] | Wada H,. Hirata R, Matsuda R. New approaches combined with environmental control for enhancing heat-tolerant rice breeding in Japan//Iizumi T, Adaptation to Climate Change in Agriculture[M]. Singapore: Springer, 2019: 37-51. |
| [38] | Li G Y, Zhang C X, Zhang G H, Fu W M, Feng B H, Chen T T, Peng S B, Tao L X, Fu G F. Abscisic acid negatively modulates heat tolerance in rolled leaf rice by increasing leaf temperature and regulating energy homeostasis[J]. Rice, 2020, 13: 18. |
| [39] | Jagadish S V K, Cairns J, Lafitte R, Wheeler T R, Price A H, Craufurd P Q. Genetic analysis of heat tolerance at anthesis in rice[J]. Crop Science, 2010, 50(5): 1633-1641. |
| [40] | 潘孝武, 李小湘, 黎用朝, 姚奕, 刘文强, 盛新年. 水稻生殖发育期耐热性的分子遗传机制研究进展[J]. 生物技术通报, 2015, 31(4): 40-46. |
| Pan X W, Li X X, Li Y C, Yao Y, Liu W Q, Shen X N. Advances on molecular and genetic mechanisms of rice heat tolerance at the reproductive stage[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2015, 31(4): 40-46. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [41] | Raza Q, Riaz A, Bashir K, Sabar M. Reproductive tissues specific meta-QTLs and candidate genes for development of heat tolerant rice cultivars[J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 2020, 104: 97-112. |
| [42] | Li X M, Chao D Y, Wu Y, Huang X H, Chen K, Cui L G, Su L, Ye W W, Chen H, Chen H C, Dong N Q, Guo T, Shi M, Feng Q, Zhang P, Han B, Shan X J, Gao J P, Lin H X. Natural alleles of a proteasome α2 subunit gene contribute to thermos-tolerance and adaptation of African rice[J]. Nature Genetics, 2015, 47: 827-833. |
| [43] | Liu J, Zhang C, Wei C, Liu J P, Zhan C C, Wei C C, Liu X, Wang M G, Yu F F, Xie Q, Tu J M. The RING finger ubiquitin E3 ligase OsHTAS enhances heat tolerance by promoting H2O2-induced stomatal closure in rice[J]. Plant Physiology, 2016, 170: 429-443. |
| [44] | Wang D, Qin B X, Li X, Tang D, Zhang Y E, Cheng Z K, Xue Y B. Nucleolar DEAD-Box RNA helicase TOGR1 regulates thermos-tolerant growth as a Pre-rRNA chaperone in rice[J]. PLOS Genetics, 2016, 12(2): e1005844. |
| [45] | Ye C, Tenorio F A, Redona E D, Cortezano P S M, Cabrega G A, Jagadish K S V, Gregorio G B. Fine-mapping and validating qHTSF4.1 to increase spikelet fertility under heat stress at flowering in rice[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2015, 128: 1507-1517. |
| [46] | Chen L, Wang Q, Tang M Y, Zhang X L, Pan Y H, Yang X H, Gao G Q, Lü R H, Tao W, Jiang LG, Liang T F. QTL mapping and identification of candidate genes for heat tolerance at the flowering stage in rice[J]. Frontiers in Genetics, 2021, 11: 621871. |
| [47] | 朱玉君, 左紫薇, 张振华, 樊叶杨. 一种水稻微效QTL精细定位和克隆新途径[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(4): 407-414. |
| Zhu Y J, Zuo Z W, Zhang Z H, Fan Y Y. A new approach for fine-mapping and map-based cloning of minor-effect QTL in rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2021, 35(4): 407-414. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [48] | 杜成兴, 张华丽, 戴冬青, 吴明月, 梁敏敏, 陈俊宇, 马良勇. 水稻粒重粒形QTL 的定位及qTGW1.2/ qGL1.2的验证[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(4): 359-372. |
| Du C X, Zhang H L, Dai D Q, Wu M Y, Liang M M, Chen J Y, Ma L Y. QTL analysis for grain weight and shape and validation of qTGW1.2/qGL1.2[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2021, 35(4): 359-372. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [6] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [7] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [8] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [9] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [10] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [11] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [12] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [13] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| [14] | 许用强, 姜宁, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 水稻开花期高温热害响应机理及其调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 111-126. |
| [15] | 吕海涛, 李建忠, 鲁艳辉, 徐红星, 郑许松, 吕仲贤. 稻田福寿螺的发生、危害及其防控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 127-139. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||