
中国水稻科学 ›› 2022, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (3): 248-258.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2022.211007
梁敏敏#, 张华丽#, 陈俊宇, 戴冬青, 杜成兴, 王惠梅, 马良勇*( )
)
收稿日期:2021-10-25
修回日期:2021-12-20
出版日期:2022-05-10
发布日期:2022-05-11
通讯作者:
马良勇
作者简介:第一联系人:#共同第一作者
基金资助:
LIANG Minmin#, ZHANG Huali#, CHEN Junyu, DAI Dongqing, DU Chengxing, WANG Huimei, MA Liangyong*( )
)
Received:2021-10-25
Revised:2021-12-20
Online:2022-05-10
Published:2022-05-11
Contact:
MA Liangyong
About author:First author contact:#These authors contributed equally to this work
摘要:
【目的】创制新型抗稻瘟病香型早籼温敏核不育系,为高产优质杂交水稻选育提供资源。【方法】利用CRISPP/Cas9技术在水稻稻瘟病基因Pi21、温敏不育基因TMS5和香味基因Badh2的第1外显子处设计靶位点,构建多基因表达载体pC1300-2×35S::gTMS5-gBadh2-gPi21,转化优质常规籼稻品种中早70,测序鉴定分析获得纯合阳性稳定株系。利用稻瘟病喷雾接种和打孔接种方法对稻瘟病基因Pi21的纯合突变株系进行稻瘟病抗性鉴定,利用GC-MS技术对Badh2纯合突变株系的香味物质2-乙酰-1-吡咯啉(2-AP)含量进行测定。【结果】在T0转基因株系中,Pi21、TMS5和Badh2突变频率分别为87.5%、80.0%和87.5%,突变类型多为双等位突变。从T1代中筛选不含载体骨架的纯合突变株系,获得两种三突变纯合株系。稻瘟病接种结果表明,与野生型相比,T2代Pi21纯合变异株系的抗性显著提高。同时,接种后纯合突变体株系内相关防卫基因的表达量显著上调,ROS积累量也显著增加。tms5纯合变异株系表现出典型的温敏不育特性,TMS5基因的表达水平与野生型相比显著降低,高温下UbL404基因的表达水平明显高于野生型。与野生型相比,在Badh2纯合突变体植株中Badh2的表达水平显著下调,并且香味物质2-AP含量极显著增加。【结论】利用CRISPR/Cas9技术成功对Pi21、TMS5和Badh2基因同时进行定向编辑,获得了具有高抗稻瘟病的香型温敏不育系,为高抗、香型不育系材料的选育提供参考,加快高产优质杂交水稻的选育。
梁敏敏, 张华丽, 陈俊宇, 戴冬青, 杜成兴, 王惠梅, 马良勇. 利用CRISPR/Cas9技术创制抗稻瘟病香型早籼温敏核不育系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(3): 248-258.
LIANG Minmin, ZHANG Huali, CHEN Junyu, DAI Dongqing, DU Chengxing, WANG Huimei, MA Liangyong. Developing Fragrant Early indica TGMS Line with Blast Resistance by Using CRISPR/Cas9 Technology[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(3): 248-258.
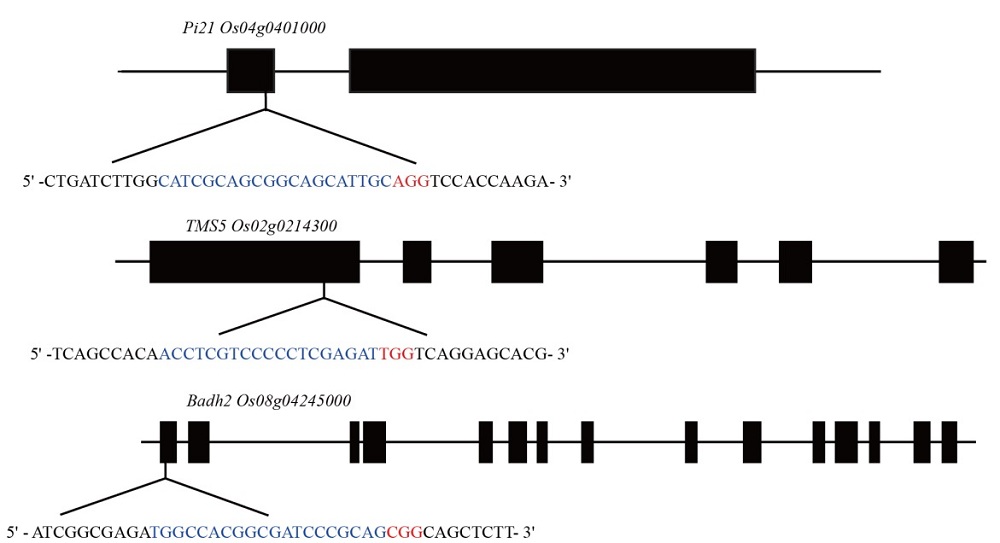
图1 Pi21、TMS5和Badh2基因结构和靶位点位置 蓝色字母表示靶点序列,红色字母表示PAM序列。线条表示内含子,黑盒子代表外显子。
Fig. 1. Schematic diagram of the targeted sites of Pi21, TMS5 and Badh2. Blue letters are the target sequence and red letters are the protospacer adjacent motif (PAM) sequences. The lines represent introns, black boxes exons.

图2 pC1300-2×35S::gTMS5-gBadh2-gPi21 载体示意图 Hyg-潮霉素磷酸转移酶基因;LB-载体左边界;RB-载体右边界;Cas9蛋白的启动子是35S;sgRNA的启动子为U3。
Fig. 2. Schematic diagram of the pC1300-2×35S::gTMS5-gBadh2-gPi21 vector. Hyg, Hygromycin phosphotransferase gene; LB, Left border; RB, Right border; The Cas9 cassette is driven by the 35S promoter, while the sgRNA is controlled by the U3 promoter.

图3 两种三基因纯合突变体的类型 蓝色字母表示靶点序列;红色字母表示碱基插入;红色连字符表示碱基缺失;+表示插入;―表示缺失;WT表示野生型。
Fig. 3. Two types of homozygous triple mutants. The initiation codon is highlighted in blue and insertions are represented by red letters. The deletions are shown by red hyphens; +, Insertion; ―, Deletion; WT, Wild-type.
| 基因 Gene | 株数 No. of plants | 突变基因型比率 Ratio of mutation genotypes / % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 纯合突变率Homozygous | 杂合突变率Heterozygous | 双等位突变率Bi-allele | ||
| Pi21 | 35 | 34.3 (12/35) | 8.6 (3/35) | 57.1 (20/35) |
| TMS5 | 35 | 11.4 (4/35) | 0.0 (0/35) | 80.0 (28/35) |
| Badh2 | 35 | 28.6 (10/35) | 5.7 (2/35) | 92.0 (23/35) |
表1 T0转基因株突变情况统计
Table 1. Ratios of mutant genotype and mutation types in T0 plants.
| 基因 Gene | 株数 No. of plants | 突变基因型比率 Ratio of mutation genotypes / % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 纯合突变率Homozygous | 杂合突变率Heterozygous | 双等位突变率Bi-allele | ||
| Pi21 | 35 | 34.3 (12/35) | 8.6 (3/35) | 57.1 (20/35) |
| TMS5 | 35 | 11.4 (4/35) | 0.0 (0/35) | 80.0 (28/35) |
| Badh2 | 35 | 28.6 (10/35) | 5.7 (2/35) | 92.0 (23/35) |
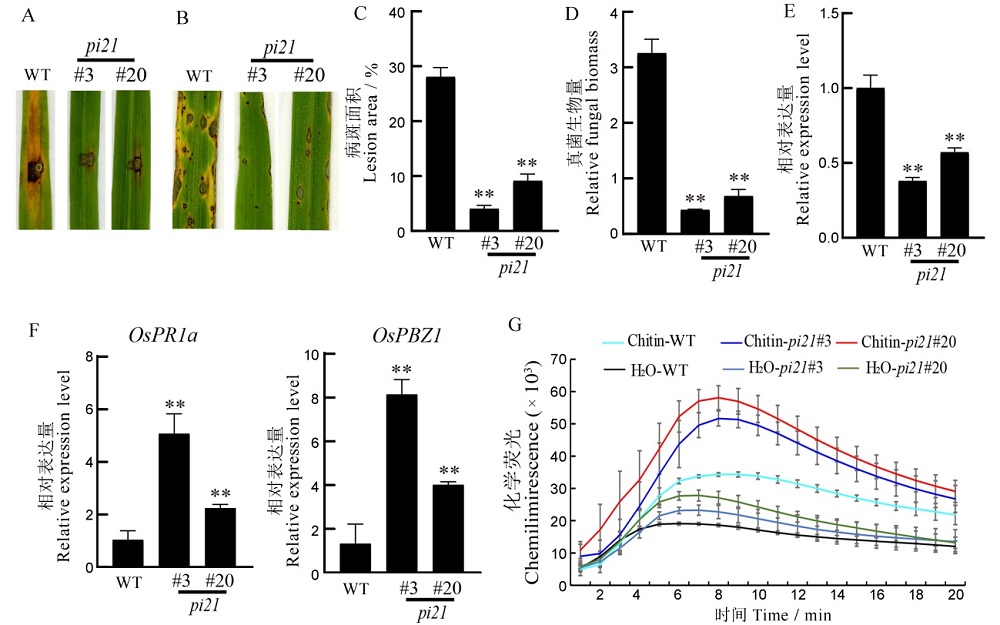
图4 稻瘟病抗性鉴定 A-纯合突变株系和野生型(WT)打孔接种;B-纯合突变株系和野生型喷雾接种;C-野生型和纯合突变株系的相对病斑面积;D-野生型和纯合突变株系的真菌生物量;E-纯合突变体及其野生型水稻Pi21相对表达量;F-野生型和纯合突变株系防卫基因的相对表达量;G-野生型和纯合突变株系ROS的积累量。数据为3次重复的平均数±标准误;**表示差异达0.01显著水平(t检验)。
Fig. 4. Identification of rice blast resistance. A, Punch inoculation of homozygous mutant lines and wild type. B, Spray inoculation of homozygous mutant lines and wild type. C, Lesion area of wild type and homozygous mutant lines. D, Relative fungal biomass of wild type and homozygous mutant lines. E. Relative expression levels of Pi21 in homozygous mutant lines and wild type; F, Relative expression levels of defense genes OsPR1a and OsPBZ1 in the wild type and the homozygous mutant lines. G, ROS accumulation in wild type and homozygous mutant lines. Data are shown as means ± SE of three biological replicates; **, Significant difference at 0.01 level(t-test).
| 株系 Line | 株高 Plant height / cm | 有效分蘖 Number of tillers per plant | 穗长 Panicle length / cm | 每穗粒数 Number of spikelets per panicle | 抽穗期 Heading date / d | 结实率 Seed setting rate / % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 野生型 WT | 100.05±0.85 | 17.00±1.67 | 23.11±0.68 | 166.61±22.84 | 52.67±1.37 | 87.32±0.09 |
| tms5#3 | 85.15±2.02** | 27.83±4.49** | 21.36±1.05** | 145.78±11.19** | 65.33±2.07** | 0** |
| tms5#20 | 84.10±2.27** | 28.83±3.19** | 20.85±0.96** | 141.28±16.31** | 65.50±1.87** | 0** |
表2 野生型和tms5纯合突变体的农艺性状
Table 2. Agronomic traits of the wild-type and tms5 homozygous mutant.
| 株系 Line | 株高 Plant height / cm | 有效分蘖 Number of tillers per plant | 穗长 Panicle length / cm | 每穗粒数 Number of spikelets per panicle | 抽穗期 Heading date / d | 结实率 Seed setting rate / % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 野生型 WT | 100.05±0.85 | 17.00±1.67 | 23.11±0.68 | 166.61±22.84 | 52.67±1.37 | 87.32±0.09 |
| tms5#3 | 85.15±2.02** | 27.83±4.49** | 21.36±1.05** | 145.78±11.19** | 65.33±2.07** | 0** |
| tms5#20 | 84.10±2.27** | 28.83±3.19** | 20.85±0.96** | 141.28±16.31** | 65.50±1.87** | 0** |
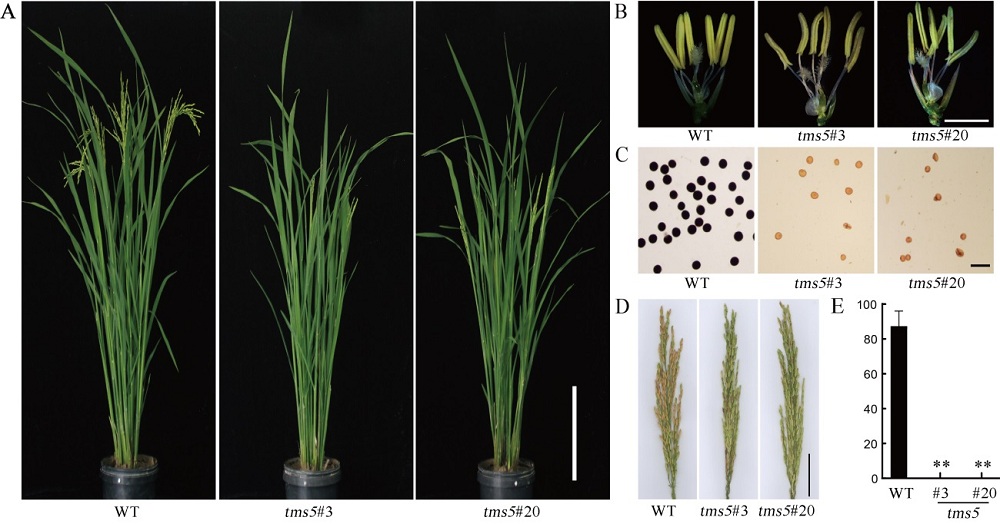

图5 野生型和tms5纯合突变体植株在田间生长下的形态特征 A-野生型和纯合突变体的株型,标尺为20 cm;B-野生型和纯合突变体的花药形态,标尺为0.5 cm;C-野生型和纯合突变体的花粉育性,标尺为100 μm;D-野生型和纯合突变体的穗,标尺为5 cm;E-野生型和纯合突变体的结实率。数据为平均数±标准差,n=3;**差异达0.01显著水平(t检验)。
Fig. 5. Phenotype of the wild-type and homozygous mutant grown in field during the normal rice growing season. A, Whole plant of the wild type and homozygous mutant lines, bars=20 cm. B, Anther morphology of the wild type and homozygous mutant lines, bars=0.5 cm. C, Pollen fertility of wild type and homozygous mutant lines, bars=100 μm. D, Panicles of the wild type and homozygous mutant lines, bars=5 cm. E, Seed setting rates of the wild type and homozygous mutant lines. Data are shown as means ± SD, n=3. **Significant difference at the 0.01 levels by t-test.
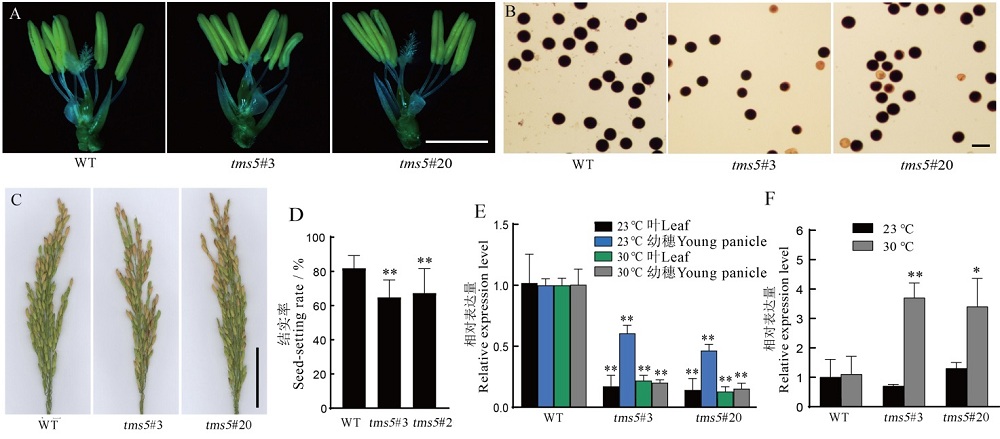
图6 野生型和纯合突变体植株的形态特征及TMS5和UbL404的表达量 A-野生型和纯合突变体在冷灌处理条件下的花药形态,标尺为0.5 cm;B-野生型和纯合突变体在冷灌处理条件下的花粉育性,标尺为100 μm;C-野生型和纯合突变体在冷灌处理条件下的穗子表型,标尺为5 m;D-野生型和纯合突变体在冷灌处理条件下的结实率;E-在不同温度下水稻叶片和幼穗TMS5基因的转录水平;F-野生型和纯合突变体在不同温度下UbL404的相对表达量。数据为平均数±标准差,n=3;*和**分别表示差异达0.05和0.01显著水平(t检验)。
Fig. 6. Phenotypes and expression of TMS5 and UbL404 in wild type and homozygous mutant plants. A, Phenotypes of wild type and homozygous mutant plants under cold irrigation conditions, bars=0.5 cm. B, Anther morphology of wild type and homozygous mutant plants under cold irrigation conditions, bars=100 μm. C, Panicle of wild type and homozygous mutant plants under cold irrigation conditions, bars=100 μm. D, Seed setting rates of wild type and homozygous mutant plants under cold irrigation conditions. E, Transcription of TMS5 as estimated by qRT-PCR in leaves and young panicle of plants grown at different temperature. F, Relative expression of UbL404 as estimated by qRT-PCR in wild type and homozygous mutant lines at different temperature. Data are shown as means ± SD, n=3; *and ** represent significant difference at the 0.05 and 0.01 levels by t-test, respectively.
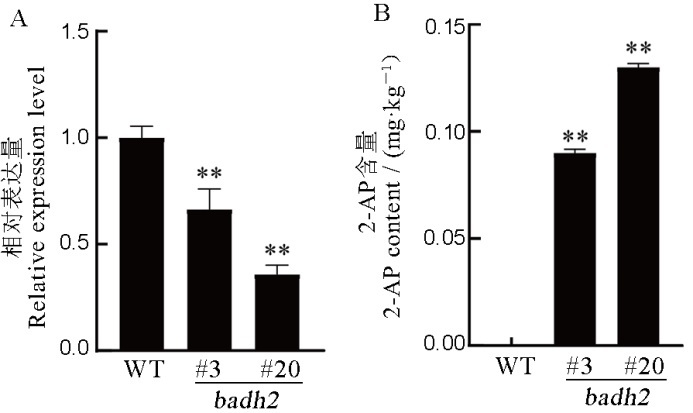
图7 Badh2基因的表达情况及2-AP的含量测定 A―野生型(WT)和纯合突变体Badh2基因的表达量;B―野生型和纯合突变体的2-AP含量。平均数±标准差(n=3);**表示差异达0.01显著水平(t检验)。
Fig. 7. Expression of Badh2 and content determination of 2-AP. A, Expression of Badh2 of the wild type and homozygous mutant lines. B, 2-AP levels of wild type and homozygous mutant lines. Data are shown as mean±SD (n=3); **, Significant difference at 0.01 level (t-test).
| [1] | Song S, Wang T, Li Y, Hu J, Kan R F, Qiu M, Deng Y D, Liu P X, Zhang L C, Dong H, Li C X, Yu D, Li X L, Yuan D Y, Li L. A novel strategy for creating a new system of third-generation hybrid rice technology using a cytoplasmic sterility gene and a genic male-sterile gene[J]. Plant Biotechnol Journal, 2021, 19(2): 251-260. |
| [2] | Zhou H, He M, Li J, Chen L, Huang Z F, Zheng S Y, Zhu L Y, Ni E D, Jiang D G, Zhao B R, Zhuang C X. Development of commercial thermo-sensitive genic male sterile rice accelerates hybrid rice breeding using the CRISPR/Cas9-mediated TMS5 editing system[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6(1): 1-12. |
| [3] | 陈家彬, 林纲, 赵德明, 江青山, 贺兵, 张杰, 姜方洪. 我国杂交籼稻选育进展[J]. 中国稻米, 2017, 23(1): 1-4. |
| Chen J B, Lin G, Zhao D M, Jiang Q S, He B, Zhang J, Jiang F H. Progress of breeding on indica hybrid rice in China[J]. China Rice, 2017, 23(1): 1-4. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | Huang M. The decreasing area of hybrid rice production in China: Causes and potential effects on Chinese rice self-sufficiency[J]. Food Security, 2022, 14: 267-272. |
| [5] | Ashraf M F, Peng G, Liu Z, Noman A, Alamri S, Hashem M, Qari S H, Zoubi O M. Molecular control and application of male fertility for two-line hybrid rice breeding[J]. International Journal of Molecular Biology, 2020, 21(21): 1-29. |
| [6] | 陈镇, 马雪丽, 曾汉来. 水稻光温敏核不育调控基因及作用机理研究进展[J]. 世界科技研究与发展, 2015, 37(1): 97-104. |
| Chen Z, Ma X L, Zeng H L. Research progress on photoperiod-thermo-sensitive genic male sterile regulatory genes and their functional mechanism[J]. World Sci-Tech R & D, 2015, 37(1): 97-104. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | Zhou H, Liu Q, Li J, Jiang D, Zhou L, Wu P, Lu S, Li F, Zhu L, Liu Z, Chen L, Liu Y G, Zhuang C X. Photoperiod- and thermo-sensitive genic male sterility in rice are caused by a point mutation in a novel noncoding RNA that produces a small RNA[J]. Cell Research, 2012, 22(4): 649-660. |
| [8] | Yu J, Han J, Kim Y J, Song M, Yang Z, He Y, Fu R, Luo Z, Hu J, Liang W, Zhang D. Two rice receptor-like kinases maintain male fertility under changing temperatures[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2017, 114(46): 12327-12332. |
| [9] | Fan Y, Yang J, Mathioni S M, Shen J, Yang X, Wang L, Zhang Q, Cai Z, Xu C, Li X, Xiao J, Meyers B C, Zhang Q,. PMS1T, producing phased small-interfering RNAs, regulates photoperiod-sensitive male sterility in rice[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2016, 113(52): 15144-15149. |
| [10] | Ding J H, Lu Q, Ouyang Y D, Mao H L, Zhang P B, Yao J L, Xu C G, Li X H, Xiao J H, Zhang Q F. A long noncoding RNA regulates photoperiod-sensitive male sterility, an essential component of hybrid rice[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2012, 109(7): 2654-2659. |
| [11] | 吴明基, 林艳, 刘华清, 陈建民, 付艳萍, 杨绍华, 王锋. 利用CRISPR/Cas9技术创制水稻温敏核不育系[J]. 福建农业学报, 2018, 33(10): 1011-1015. |
| Wu J M, Lin Y, Liu Q H, Chen J M, Fu Y P, Yang S H, Wang F. Development of thermo-sensitive male sterile rice with CRISPR/Cas9 technology[J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 33(10): 1011-1015. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | Zhou H, Zhou M, Yang Y Z, Li J, Zhu L Y, Jiang D G, Dong J F, Liu Q J, Gu L F, Zhou L Y, Feng M J, Qin P, Hu X C, Song C L, Shi J F, Song X W, Ni E D, Wu X J, Deng Q Y, Liu Z L, Chen M S, Liu Y G, Cao X F, Zhuang C X. RNase ZS1 processes UbL40 mRNAs and controls thermosensitive genic male sterility in rice[J]. Nature Communications, 2014, 5: 4884. |
| [13] | Barman H N, Sheng Z H, Fiaz S, Zhong M, Wu Y W, Cai Y C, Wang W, Jiao G A, Tang S Q, Wei X J, Hu P S. Generation of a new thermo-sensitive genic male sterile rice line by targeted mutagenesis of TMS5 gene through CRISPR/Cas9 system[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2019, 19(1): 1-9. |
| [14] | 黄忠明, 周延彪, 唐晓丹, 赵新辉, 周在为, 符星, 王凯, 史江伟, 李艳锋, 符辰建, 杨远柱. 基于CRISPR/Cas9技术的水稻温敏不育基因tms5突变体的构建[J]. 作物学报, 2018, 44(6): 844-851. |
| Huang Z M, Zhou Y B, Tang X D, Zhao X H, Zhou Z W, Fu X, Wang K, Shi J W, Li Y F, Fu C J, Yang Y Z. Construction of tms5 mutants in rice based on CRISPR/Cas9 technology[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2018, 44(6): 844-851. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | Shanthinie A, Dilip K R, Raveendran M. Comparative profiling of volatile compounds in the grains of rice varieties differing in their aroma[J]. Electronic Journal of Plant Breeding, 2019, 10(2): 614-619. |
| [16] | Li W B, Zeng X H, Li S L, Chen F B, Gao J. Development and application of two novel functional molecular markers of BADH2 in rice[J]. Electronic Journal of Biotechnology, 2020, 46: 1-7. |
| [17] | Usman B, Nawaz G, Zhao N, Liu Y G, Li R B. Generation of high yielding and fragrant rice (Oryza sativa L.) lines by CRISPR/Cas9 targeted mutagenesis of three homoeologs of cytochrome P450 gene family and OsBADH2 and transcriptome and proteome profiling of revealed changes triggered by mutations[J]. Plants, 2020, 9(6): 788. |
| [18] | Ballini E, Morel J B, Droc G, Price A, Courtois B, Notteghem J L, Tharreau D. A genome-wide meta-analysis of rice blast resistance genes and quantitative trait loci provides new insights into partial and complete resistance[J]. Molecular Plant-microbe Interactions, 2008, 21(7): 859-868. |
| [19] | Wang B H, Ebbole D J, Wang Z H. The arms race between Magnaporthe oryzae and rice: Diversity and interaction of Avr and R genes[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2017, 16(12): 2746-2760. |
| [20] | 赵夏夏, 王旭明, 许飘, 赵丽娜, 胡燕, 陈景阳, 黄永相, 李伟, 郭建夫. 水稻稻瘟病抗性研究与展望[J]. 湖北农业科学, 2019, 58(11): 5-9. |
| Zhao X X, Wang X M, Xu P, Zhao L N, Hu Y, Chen J Y, Huang Y X, Li W, Guo J F. Research and prospect of rice blast resistance[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 58(11): 5-9. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | 高清, 张亚玲, 葛欣, 李雨馨, 马宇欣, 斩学慧. 水稻抗稻瘟病基因研究进展[J]. 分子植物育种, 2021(1): 1-11. |
| Gao Q, Zhang Y L, Ge X, Li Y X, Ma Y X, Zhan X H. Advances in gene research on rice blast resistance[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2021(1): 1-11. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | Li W, Zhu Z, Chern M, Yin J J, Yang C, Ran L, Cheng M P, He M, Wang K, Zhou X G, Zhu X B, Chen Z X, Wang J X, Zhao W, Ma B T, Qin P, Chen W L, Wang Y P, Liu J L, Wang W M, Wu X J, Li P, Wang J R, Zhu L H, Li S G, Chen X W. A natural allele of a transcription factor in rice confers broad-spectrum blast resistance[J]. Cell, 2017, 170(1): 114-126. |
| [23] | 王芳权, 范方军, 李文奇, 朱金燕, 王军, 仲维功, 杨杰. 利用CRISPR/Cas9技术敲除水稻Pi21基因的效率分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2016, 30(5): 469-478. |
| Wang Q F, Fan F J, Li W Q, Zhu J Y, Wang J, Zhong W G, Yang J. Knock-out efficiency analysis of Pi21 gene using CRISPR/Cas9 in rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2016, 30(5): 469-478. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | 杨海河, 毕冬玲, 张玉, 邹小维, 高晓庆, 袁正杰, 曲海艳, 何海燕, 翟绍洪. 基于CRISPR/Cas9技术的水稻pi21基因编辑材料的创制及稻瘟病抗性鉴定[J]. 分子植物育种, 2017, 15(11): 4451-4465. |
| Yang H H, Bi D L, Zhang Y, Zou X W, Gao X Q, Yuan Z J, Qu H Y, He H Y, Zhai S H. Generation of rice pi21 gene editing lines based on CRISPR/Cas9 technology and evaluation of their blast resistance[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2017, 15(11): 4451-4465. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | 徐鹏, 王宏, 涂燃冉, 刘群恩, 吴玮勋, 傅秀民, 曹立勇, 沈希宏. 利用CRISPR/Cas9系统定向改良水稻稻瘟病抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(4): 313-322. |
| Xu P, Wang H, Tu R R, Liu Q E, Wu W X, Fu X M, Cao L Y, Shen X H, Orientation improvement of blast resistance in rice via CRISPR/Cas9 system[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2019, 33(4): 313-322. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | Nawaz G, Usman B, Peng H W, Zhao N, Yuan R Z, Liu Y G, Li R B. Knockout of Pi21 by CRISPR/Cas9 and iTRAQ-based proteomic analysis of mutants revealed new insights into M. oryzae resistance in elite rice line[J]. Genes, 2020, 11(7): 735. |
| [27] | Gaj T, Gersbach C A, Barbas C F. ZFN, TALEN, and CRISPR/Cas-based methods for genome engineering[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2013, 31(7): 397-405. |
| [28] | Shan Q W, Wang Y P, Li J, Gao G X. Genome editing in rice and wheat using the CRISPR/Cas system[J]. Nature Protocols, 2014, 9(10): 2395-2410. |
| [29] | Li J, Zhang H W, Si X M, Tian Y H, Chen K L. Generation of thermosensitive male-sterile maize by targeted knockout of the ZmTMS5 gene[J]. Journal of Genetics and Genomics, 2017, 44(9): 465-468. |
| [30] | 沈兰, 华宇峰, 付亚萍, 李健, 刘庆, 焦晓真, 辛高伟, 王俊杰, 王兴春, 严长杰, 王克剑. 利用CRISPR/Cas9多基因编辑系统在水稻中快速引入遗传多样性[J]. 中国科学, 2017, 47(11): 1186-1195. |
| Shen L, Hua Y J, Fu Y P, Li J, Liu Q, Jiao X Z, Xin G W, Wang J J, Wang X C, Yan C J, Wang K J. Rapid generation of genetic diversity by multiplex CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing in rice[J]. Science in China, 2017, 47(11): 1186-1195. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | 张向前, 邹金松, 朱海涛, 李晓燕, 曾瑞珍. 水稻早熟多子房突变体fon5的遗传分析和基因定位[J]. 遗传, 2008, 30(10): 1349-1355. |
| Zhang X Q, Zou J S, Zhu H T, Li X Y, Zeng R Z. Genetic analysis and gene mapping of an early flowering and multi-ovary mutant in rice[J]. Hereditas, 2008, 30(10): 1349-1355. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [32] | Liu W, Xie X, Ma X, Li J, Chen J, Liu Y G. DSDecode: A web-based tool for decoding of sequencing chromatograms for genotyping of targeted mutations[J]. Molecular Plant, 2015, 8(9): 1431-1433. |
| [33] | Park C H, Chen S, Shirsekar G, Zhou B, Khang C H, Songkunmarn P, Afzal A J, Ning Y, Wang R, Bellizzi M, Valent B, Wang G L. The Magnaporthe oryzae effector AvrPiz-t targets the RING E3 ubiquitin ligase APIP6 to suppress pathogen-associated molecular pattern-triggered immunity in rice[J]. The Plant Cell, 2012, 24(11): 4748-4762. |
| [34] | Park C H, Shirsekar G, Bellizzi M, Chen S, Songkumarn P, Xie X, Shi X, Ning Y, Zhou B, Suttiviriya P, Wang M, Umemura K, Wang G L. The E3 ligase APIP10 connects the effector AvrPiz-t to the NLR receptor Piz-t in rice[J]. PLoS Pathogens, 2016, 12(3): 1-23. |
| [35] | Hui S Z, Li H J, Mawia A M, Zhou L, Cai J Y, Ahmad S, Lai C K, Wang J X, Jiao G A, Xie L H, Shao G N, Sheng Z H, Tang S Q, Wang J L, Wei X J, Hu S K, Hu P S. Production of aromatic three-line hybrid rice using novel alleles of BADH2[J]. Plant Biotechnol Journal, 2022, 20(1): 59-74. |
| [36] | Ma X L, Zhang Q Y, Zhu Q L, Liu W, Chen Y, Qiu Rong, Wang B, Yang Z F, Li H Y, Lin Y R, Xie Y Y, Shen R X, Chen S F, Wang Z, Chen Y L, Guo J X, Chen L, Zhao Z C, Liu Y G. A robust CRISPR/Cas9 system for convenient, high-efficiency multiplex genome editing in monocot and dicot plants[J]. Molecular Plant, 2015, 8(8): 1274-1284. |
| [37] | Shen L, Hua Y F, Fu Y P, Li Jian, Liu Q, Jiao X Z, Xin G W, Wang J J, Wang X C, Yan C J, Wang K J. Rapid generation of genetic diversity by multiplex CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing in rice[J]. Science China Life Sciences, 2017, 60(5): 506-515. |
| [38] | Li S F, Shen L, Hu P, Liu Q, Zhu X D, Qian Q, Wang K J, Wang Y X. Developing disease-resistant thermosensitive male sterile rice by multiplex gene editing[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2019, 61(12): 1201-1205. |
| [39] | Tao H, Shi X, He F, Wang D, Xiao N, Fang H, Wang R, Zhang F, Wang M, Li A, Liu X, Wang G L, Ning Y. Engineering broad-spectrum disease-resistant rice by editing multiple susceptibility genes[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2021, 63(9): 1639-1648. |
| [40] | Fukuoka S, Saka N, Koga H, Ono K, Shimizu T, Ebana K, Hayashi N, Takahashi A, Hirochika H, Okuno K, Yano M. Loss of Function of a Proline-Containing Protein Confers Durable Disease Resistance in Rice[J]. Science, 2009, 325(5943): 998-1001. |
| [41] | Okpala N E, Mo Z W, Duan M Y, Tang X R. The genetics and biosynthesis of 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline in fragrant rice[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2019, 135: 272-276. |
| [42] | 孟庆彬, 黄健文, 冯国辉, 钟升, 韦鸿若. 优质三系香稻不育系耕香A的选育[J]. 杂交水稻, 2021, 36(5): 14-16. |
| Meng Q B, Huang J W, Feng G H, Zhong S, Wei H R. Breeding of high-quality aromatic CMS line Gengxiang A in rice[J]. Hybrid Rice, 2021, 36(5): 14-16. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [43] | 柳武革, 王丰, 李金华, 刘振荣, 朱满山, 廖亦龙, 付崇允, 刘迪林, 曾学勤, 马晓智. 籼型优质三系香稻不育系广泰A的选育及应用[J]. 杂交水稻, 2021, 36(2): 22-24. |
| Liu W G, Wang F, Li J H, Liu Z R, Zhu M S, Liao Y L, Fu C Y, Liu D L, Zeng X Q, Ma X Z. Breeding and application of aromatic indica CMS line Guangtai A with good grain quality in rice[J]. Hybrid Rice, 2021, 36(2): 22-24. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [44] | 张现伟, 唐永群, 肖人鹏, 刘强明, 文明, 李经勇. 优质香稻不育系渝香813A的选育[J]. 杂交水稻, 2020, 35(6): 18-20. |
| Zhang X W, Tang Y Q, Xiao R P, Liu Q M, Wen M, Li J Y. Breeding of aromatic CMS line Yuxiang 813A with good quality in rice[J]. Hybrid Rice, 2020, 35(6): 18-20. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [45] | 刘三雄, 李用朝, 刘利成, 闵军, 李小湘, 胡敏, 黄海明. 优质三系香稻不育系朝1A的选育[J]. 杂交水稻, 2020, 35(5): 22-24. |
| Liu S X, Li Y C, Liu L C, Min J, Li X X, Hu M, Huang H M. Breeding of CMS line Chao 1A with aroma and good quality in rice[J]. Hybrid Rice, 2020, 35(5): 22-24. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [46] | 莫海玲, 唐梅, 孙富, 罗敬昭, 邓晶. 优质香稻三系不育系野香A的选育与应用[J]. 杂交水稻, 2015, 30(4): 11-12. |
| Mo H L, Tang M, Sun F, Luo J Z, Deng J. Breeding and application of aromatic CMS line Yexiang A with fine grain quality in rice[J]. Hybrid Rice, 2015, 30(4): 11-12. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [47] | Wang J, Wang R, Fang H, Zhang C, Zhang F, Hao Z, You X, Shi X, Park C H, Hua K, He F, Bellizzi M, Xuan K T, Jeon J S, Ning Y, Wang G L. Two VOZ transcription factors link an E3 ligase and an NLR immune receptor to modulate immunity in rice[J]. Molecular Plant, 2020, 14(2): 253-266. |
| [48] | Liu W, Liu J, Ning Y, Ding B, Wang Z, Wang G L. Recent progress in understanding PAMP-and effector- triggered immunity against the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae[J]. Molecular Plant, 2013, 6(3): 605-620. |
| [49] | Liu X, Inoue H, Tang X, Tan Y, Xu X, Wang C, Jiang C J. Rice OsAAA-ATPase1 is induced during blast infection in a salicylic acid-dependent manner, and promotes blast fungus resistance[J]. Molecular Sciences, 2020, 21(4): 1443 |
| [50] | 陈日荣, 周延彪, 王黛君, 赵新辉, 唐晓丹, 许世冲, 唐倩莹, 符星学, 王凯, 刘选明, 杨远柱. 利用CRISPR/Cas9技术编辑水稻温敏不育基因TMS5[J]. 作物学报, 2020, 46(8): 1157-1165. |
| Chen R Z, Zhou Y B, Wang D J, Zhao X H, Tang X D, Xu S C, Tang Q Y, Fu X X, Wang K, Liu X M, Yang Y Z. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated editing of the thermo- sensitive genic male-sterile gene TMS5 in rice[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2020, 46(8): 1157-1165. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [51] | Chen S H, Yang Y, Shi W W, Ji Q, He Fei, Zhang Z D, Cheng Z K, Liu X N, Xu M L. Badh2, encoding betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase, inhibits the biosynthesis of 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline, a major component in rice fragrance[J]. The Plant Cell, 2008, 20(7): 1850-1861. |
| [52] | Ashokkumar S H, Jaganathan D, Ramanathan V, Rahman H, Palaniswamy P, Kambale R, Muthurajan. Creation of novel alleles of fragrance gene OsBADH2 in rice through CRISPR/Cas9 mediated gene editing[J]. PLoS One, 2020, 15(8): e0237018. |
| [53] | 孙慧宇, 宋佳, 王敬国, 刘化龙, 孙健, 莫天宇, 徐善斌, 郑洪亮, 邹德堂. 利用CRISPR/Cas9技术编辑Badh2基因改良粳稻香味[J]. 华北农学报, 2019, 34(4): 1-8. |
| Sun H Y, Song J, Wang J G, Liu H L, Sun J, Mo T Y, Xu S B, Zheng H L, Zou D T. Editing Badh2 gene to improve the fragrance of japonica rice by CRISPR/Cas9 technology[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2019, 34(4): 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [54] | 邵高能, 谢黎虹, 焦桂爱, 魏祥进, 圣忠华, 唐绍清, 胡培松. 利用CRISPR/CAS9技术编辑水稻香味基因Badh2[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(2): 216-222. |
| Shao G N, Xie L H, Jiao G A, Wei X J, Sheng Z H, Tang S Q, Hu P S. CRISPR/CAS9-mediated editing of the fragrant gene Badh2in rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2017, 31(2): 216-222. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [55] | Shan Q W, Zhang Y, Chen K L, Zhang K, Gao C X. Creation of fragrant rice by targeted knockout of the osbadh2gene using talen technology[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2015(1): 1-10. |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [6] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [7] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [8] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [9] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [10] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [11] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [12] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [13] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| [14] | 许用强, 姜宁, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 水稻开花期高温热害响应机理及其调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 111-126. |
| [15] | 吕海涛, 李建忠, 鲁艳辉, 徐红星, 郑许松, 吕仲贤. 稻田福寿螺的发生、危害及其防控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 127-139. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||