
中国水稻科学 ›› 2022, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (2): 171-180.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2022.210208
收稿日期:2021-02-06
修回日期:2021-06-03
出版日期:2022-03-10
发布日期:2022-03-11
通讯作者:
向珣朝
基金资助:
LIANG Cheng, XIANG Xunchao*( ), ZHANG Ouling, YOU Hui, XU Liang, CHEN Yongjun
), ZHANG Ouling, YOU Hui, XU Liang, CHEN Yongjun
Received:2021-02-06
Revised:2021-06-03
Online:2022-03-10
Published:2022-03-11
Contact:
XIANG Xunchao
摘要:
【目的】 理想株型水稻能提高光合作用效率、经济产量和抗病能力。通过探究两份新株型水稻种质的农艺性状变异和遗传特性,为水稻高产抗病育种提供优异理想株型种质资源。【方法】 以两个重组自交系中发现的两份自然重组的新株型种质08yi和RIL60以及由同一自交系选育出来的常规种质08yc和RILc为材料,进行不同生长时期的株型构成因子和产量性状的比较分析,同时对4份种质进行理想株型基因IPA1测序和糯性鉴定。【结果】 两份新种质与常规种质相比,在不同发育时期的功能叶性状、干物质积累量、穗部性状和产量构成因素上均存在显著变异,二者发生的有利变异包括功能叶叶角减小、功能叶叶长更合理、株型紧凑、单株有效穗数增加1~2穗,结实率分别提高了7.37%和5.09%;此外,新种质08yi叶绿素含量显著提高,RIL60的茎秆变粗,二者在逆境下的穗部性状表现更好,产量降幅更小,抗逆力增强。不利变异包括单穗重降低、穗长变短、每穗着粒数和每穗实粒数减少、枝梗长度和数量下降。IPA1基因测序结果显示与少蘖粳ipa1相比,两新种质并未突变,株型变异源自于其他因子。糯性鉴定结果表明RIL60存在糯性变异。【结论】 两个新种质的一些农艺性状发生了明确的有利变异,具有较理想的株型结构,可作为优异种质用于理想株型育种和株型研究。RIL60作为理想株型糯稻,由于具有非糯水稻的经济产量,具有巨大的应用价值。
梁程, 向珣朝, 张欧玲, 游慧, 许亮, 陈永军. 两份新株型水稻品系的农艺性状与遗传特性分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(2): 171-180.
LIANG Cheng, XIANG Xunchao, ZHANG Ouling, YOU Hui, XU Liang, CHEN Yongjun. Analyses on Agronomic Traits and Genetic Characteristics of Two New Plant-architecture Lines in Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(2): 171-180.
| 引物名称 Name of primer | 引物序列 Sequence of primer(5′-3′) | 产物大小 Product size/bp | 退火温度 Annealing temperature/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|
| IPA1扩增引物 IPA1 amplification primer | F: CGGTCGACTAGCTGCATCTGTTGG R: CATCGTGTTGCTGGTTTGGTCGAAG | 784 | 58.3 |
| IPA1测序引物 IPA1 sequencing primer | F: GATCTCCGGTGGTATCCAGT R: GAAGTGGGCATGATGGCTA | 457 | 55.9 |
| Wx M1 | F: CACAGCAACAGCTAGACAACCAC R: CACGACGACGGAGGGGAAC | 275/252 | 55.0 |
表1 引物信息
Table 1 Primer information.
| 引物名称 Name of primer | 引物序列 Sequence of primer(5′-3′) | 产物大小 Product size/bp | 退火温度 Annealing temperature/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|
| IPA1扩增引物 IPA1 amplification primer | F: CGGTCGACTAGCTGCATCTGTTGG R: CATCGTGTTGCTGGTTTGGTCGAAG | 784 | 58.3 |
| IPA1测序引物 IPA1 sequencing primer | F: GATCTCCGGTGGTATCCAGT R: GAAGTGGGCATGATGGCTA | 457 | 55.9 |
| Wx M1 | F: CACAGCAACAGCTAGACAACCAC R: CACGACGACGGAGGGGAAC | 275/252 | 55.0 |
| 生育期与材料 Growth stage and material | 叶长Leaf length/cm | 叶宽Leaf width/cm | 叶角度 Leaf angle/° | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 剑叶 Flag Leaf | 倒2叶 2nd leaf from top | 倒3叶 3rd leaf from top | 剑叶 Flag Leaf | 倒2叶 2nd leaf from top | 倒3叶 3rd leaf from top | 剑叶 Flag Leaf | 倒2叶 2nd leaf from top | 倒3叶 3rd leaf from top | |
| 乳熟期Milky maturity stage Milk-ripe stage | |||||||||
| 08yi | 26.80±2.89b | 43.17±1.45b | 40.20±0.73b | 2.58±0.03b | 1.85±0.03b | 1.64±0.02b | 10.80±1.18b | 9.77±0.37b | 22.50±0.71b |
| 08yc | 37.53±1.33a | 49.83±1.33a | 51.20±1.85a | 2.55±0.07b | 2.01±0.05b | 1.72±0.05b | 10.40±0.41b | 15.23±0.12a | 20.83±2.72b |
| RIL60 | 28.57±0.54b | 46.37±0.88ab | 46.77±2.56a | 2.87±0.04a | 2.38±0.07a | 2.03±0.02a | 19.23±1.02a | 16.27±0.90a | 21.10±0.82b |
| RILc | 31.67±2.15b | 46.43±2.72ab | 48.83±2.08a | 3.04±0.10a | 2.71±0.26a | 2.02±0.11a | 10.07±0.12b | 13.60±2.16a | 27.77±2.58a |
| 蜡熟期Dough maturity stage | |||||||||
| 08yi | 17.30±1.78b | 35.37±3.21b | 40.27±1.50c | 2.29±0.03b | 1.93±0.10a | 1.63±0.13b | 10.30±1.30c | 12.70±2.44b | 27.03±3.98a |
| 08yc | 30.97±3.81a | 47.83±1.57a | 50.03±0.82a | 2.21±0.22b | 1.81±0.07a | 1.47±0.10b | 10.03±0.87c | 10.87±0.66b | 17.07±1.32b |
| RIL60 | 27.90±1.35a | 45.13±1.54a | 47.03±1.68b | 2.72±0.02a | 2.24±0.04b | 2.00±0.01a | 17.07±1.60b | 19.03±1.64a | 22.30±3.19ab |
| RILc | 31.93±1.13a | 47.17±1.27a | 49.20±0.37ab | 2.80±0.01a | 2.32±0.02b | 2.06±0.04a | 30.77±2.87a | 22.93±3.07a | 22.47±0.77ab |
| 完熟期Full maturity stage | |||||||||
| 08yi | 12.33±1.03c | 28.50±1.51b | 39.83±0.29c | 2.33±0.12b | 2.01±0.09b | 1.49±0.06b | 10.07±0.12c | 15.60±1.37b | 28.10±3.04a |
| 08yc | 36.30±4.30a | 46.17±3.73a | 49.53±1.81a | 2.37±0.15b | 1.86±0.20b | 1.57±0.12b | 11.20±1.42c | 12.30±0.62b | 19.07±1.25b |
| RIL60 | 27.17±1.66b | 44.37±1.11a | 45.33±2.10b | 2.74±0.07a | 2.21±0.05ab | 1.99±0.02a | 17.13±1.77b | 21.74±1.72a | 23.83±2.78ab |
| RILc | 30.50±1.76ab | 47.37±1.05a | 49.47±0.54a | 2.80±0.05a | 2.32±0.03a | 2.07±0.03a | 29.27±2.74a | 22.97±1.84a | 23.37±0.96ab |
表2 不同种质的功能叶叶长、叶宽和叶角比较
Table 2 Length, width and angle of functional leaves for different germplasms.
| 生育期与材料 Growth stage and material | 叶长Leaf length/cm | 叶宽Leaf width/cm | 叶角度 Leaf angle/° | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 剑叶 Flag Leaf | 倒2叶 2nd leaf from top | 倒3叶 3rd leaf from top | 剑叶 Flag Leaf | 倒2叶 2nd leaf from top | 倒3叶 3rd leaf from top | 剑叶 Flag Leaf | 倒2叶 2nd leaf from top | 倒3叶 3rd leaf from top | |
| 乳熟期Milky maturity stage Milk-ripe stage | |||||||||
| 08yi | 26.80±2.89b | 43.17±1.45b | 40.20±0.73b | 2.58±0.03b | 1.85±0.03b | 1.64±0.02b | 10.80±1.18b | 9.77±0.37b | 22.50±0.71b |
| 08yc | 37.53±1.33a | 49.83±1.33a | 51.20±1.85a | 2.55±0.07b | 2.01±0.05b | 1.72±0.05b | 10.40±0.41b | 15.23±0.12a | 20.83±2.72b |
| RIL60 | 28.57±0.54b | 46.37±0.88ab | 46.77±2.56a | 2.87±0.04a | 2.38±0.07a | 2.03±0.02a | 19.23±1.02a | 16.27±0.90a | 21.10±0.82b |
| RILc | 31.67±2.15b | 46.43±2.72ab | 48.83±2.08a | 3.04±0.10a | 2.71±0.26a | 2.02±0.11a | 10.07±0.12b | 13.60±2.16a | 27.77±2.58a |
| 蜡熟期Dough maturity stage | |||||||||
| 08yi | 17.30±1.78b | 35.37±3.21b | 40.27±1.50c | 2.29±0.03b | 1.93±0.10a | 1.63±0.13b | 10.30±1.30c | 12.70±2.44b | 27.03±3.98a |
| 08yc | 30.97±3.81a | 47.83±1.57a | 50.03±0.82a | 2.21±0.22b | 1.81±0.07a | 1.47±0.10b | 10.03±0.87c | 10.87±0.66b | 17.07±1.32b |
| RIL60 | 27.90±1.35a | 45.13±1.54a | 47.03±1.68b | 2.72±0.02a | 2.24±0.04b | 2.00±0.01a | 17.07±1.60b | 19.03±1.64a | 22.30±3.19ab |
| RILc | 31.93±1.13a | 47.17±1.27a | 49.20±0.37ab | 2.80±0.01a | 2.32±0.02b | 2.06±0.04a | 30.77±2.87a | 22.93±3.07a | 22.47±0.77ab |
| 完熟期Full maturity stage | |||||||||
| 08yi | 12.33±1.03c | 28.50±1.51b | 39.83±0.29c | 2.33±0.12b | 2.01±0.09b | 1.49±0.06b | 10.07±0.12c | 15.60±1.37b | 28.10±3.04a |
| 08yc | 36.30±4.30a | 46.17±3.73a | 49.53±1.81a | 2.37±0.15b | 1.86±0.20b | 1.57±0.12b | 11.20±1.42c | 12.30±0.62b | 19.07±1.25b |
| RIL60 | 27.17±1.66b | 44.37±1.11a | 45.33±2.10b | 2.74±0.07a | 2.21±0.05ab | 1.99±0.02a | 17.13±1.77b | 21.74±1.72a | 23.83±2.78ab |
| RILc | 30.50±1.76ab | 47.37±1.05a | 49.47±0.54a | 2.80±0.05a | 2.32±0.03a | 2.07±0.03a | 29.27±2.74a | 22.97±1.84a | 23.37±0.96ab |
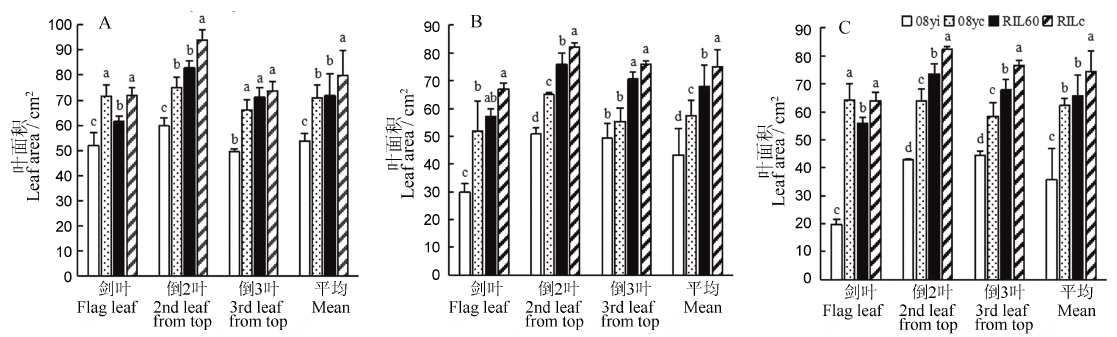
图1 不同种质在不同生育时期功能叶叶面积差异比较 A-乳熟期;B-蜡熟期;C-完熟期。均值±标准差,不同小写字母表示不同种质差异显著(P<0.05, n=4)(F检验)。
Fig. 1. Comparison of functional leaves area for different germplasms at different developmental stages. A, Milky maturity stage; B, Drought maturity stage; C, Full maturity stage. Mean±SD. Bars superscripted by different lowercase letters are significantly different at 0.05 level among germplasms by F-test (n=4).
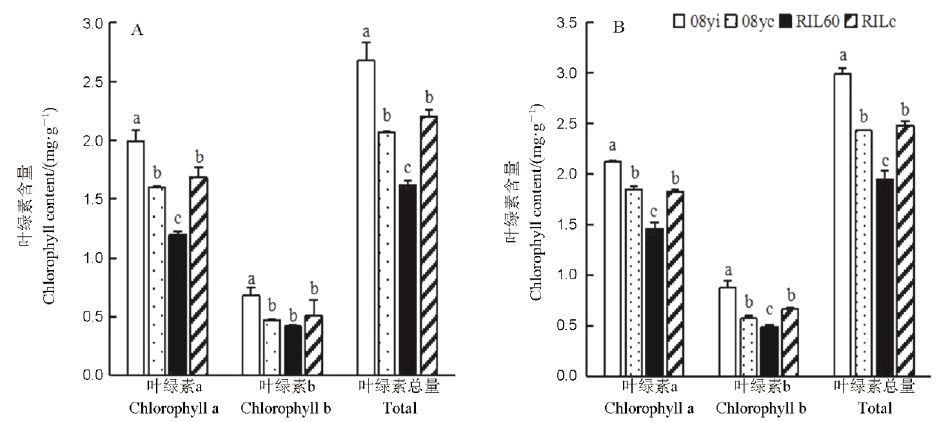
图2 不同种质在不同生育时期叶绿素含量差异比较 A-乳熟期;B-蜡熟期。均值±标准差,不同小写字母表示不同种质差异显著(P<0.05, n=4)(F检验)。
Fig. 2. Comparison of chlorophyll contents for different germplasms at different developmental stages. A, Milky maturity stage; B, Drought maturity stage. Mean±SD. Bars superscripted by different lowercase letters are significantly different at 0.05 level among germplasms by F-test (n=4).
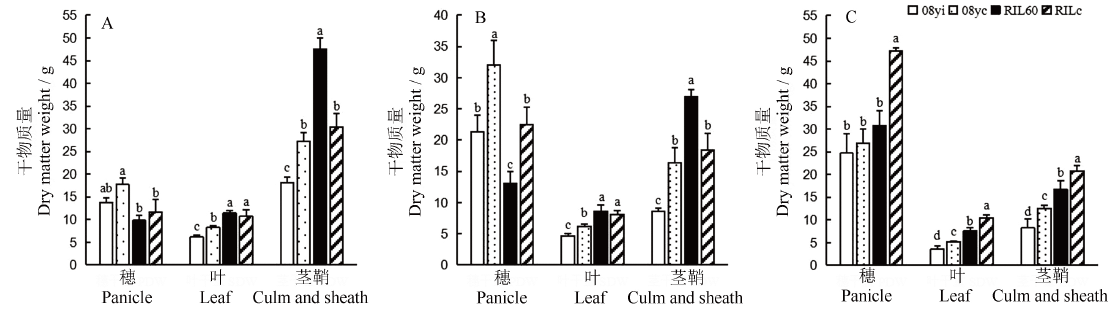
图3 不同种质在不同生育时期的干物质含量差异比较 A-乳熟期;B-蜡熟期;C-完熟期。均值±标准差,不同小写字母表示不同种质差异显著(P<0.05, n=4)(F检验)。
Fig. 3. Comparison of dry matter content of different germplasms at different developmental stages. A, Milky maturity stage; B, Drought maturity stage; C, Full maturity stage. Mean±SD. Bars superscripted by different lowercase letters are significantly different at 0.05 level among germplasms by F-test (n=4).
| 年份 Year | 种质Germplasm | 穗重 Single panicle weight / g | 穗长 Panicle length / cm | 一次枝梗数 Primary rachis branch number | 一次枝梗总长 Total length of primary rachis branch number / cm | 二次枝梗总数 Secondary rachis branch number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 08yi | 4.46±0.45 d | 16.01±0.52 d | 16.32±0.18 b | 129.27±9.64 d | 66.23±3.78 d |
| 08yc | 6.14±0.68 c | 20.09±0.76 c | 16.07±0.95 bc | 168.39±2.53 b | 83.73±8.02 b | |
| RIL60 | 7.34±0.26 b | 25.76±0.36 ab | 16.96±0.40 b | 203.35±2.10 a | 81.44±1.36 b | |
| RILc | 9.44±1.19 a | 26.10±0.93 a | 17.73±0.53 ab | 200.00±14.17 a | 104.12±5.33 a | |
| 2020 | 08yi | 3.66±0.19 d | 16.05±0.97 d | 17.96±0.41 a | 123.46±6.50 d | 67.57±2.38 d |
| 08yc | 5.43±0.52 cd | 20.25±0.74 c | 16.99±0.71 b | 158.22±10.83 bc | 77.86±3.40 bc | |
| RIL60 | 5.66±0.64 c | 24.79±0.42 b | 17.80±0.55 ab | 191.05±14.57 a | 66.37±8.15 d | |
| RILc | 5.74±0.93 bc | 25.05±0.57 b | 15.22±0.20 c | 149.58±5.79 c | 71.93±2.66 c |
表3 不同种质的穗部性状比较
Table 3 Comparison of panicle characters for different germplasms.
| 年份 Year | 种质Germplasm | 穗重 Single panicle weight / g | 穗长 Panicle length / cm | 一次枝梗数 Primary rachis branch number | 一次枝梗总长 Total length of primary rachis branch number / cm | 二次枝梗总数 Secondary rachis branch number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 08yi | 4.46±0.45 d | 16.01±0.52 d | 16.32±0.18 b | 129.27±9.64 d | 66.23±3.78 d |
| 08yc | 6.14±0.68 c | 20.09±0.76 c | 16.07±0.95 bc | 168.39±2.53 b | 83.73±8.02 b | |
| RIL60 | 7.34±0.26 b | 25.76±0.36 ab | 16.96±0.40 b | 203.35±2.10 a | 81.44±1.36 b | |
| RILc | 9.44±1.19 a | 26.10±0.93 a | 17.73±0.53 ab | 200.00±14.17 a | 104.12±5.33 a | |
| 2020 | 08yi | 3.66±0.19 d | 16.05±0.97 d | 17.96±0.41 a | 123.46±6.50 d | 67.57±2.38 d |
| 08yc | 5.43±0.52 cd | 20.25±0.74 c | 16.99±0.71 b | 158.22±10.83 bc | 77.86±3.40 bc | |
| RIL60 | 5.66±0.64 c | 24.79±0.42 b | 17.80±0.55 ab | 191.05±14.57 a | 66.37±8.15 d | |
| RILc | 5.74±0.93 bc | 25.05±0.57 b | 15.22±0.20 c | 149.58±5.79 c | 71.93±2.66 c |
| 年份 Year | 种质 Germplasm | 单株有效穗数 Effective panicle number per plant | 结实率 Seed setting rate / % | 千粒重 1000-grain weight /g | 着粒数 Number of grain per panicle | 实粒数 Filled grains per panicle |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 08yi | 6.33±0.58 ab | 79.42±6.95 ab | 20.88±0.58 c | 233.36±18.64 c | 185.08±17.76 cd |
| 08yc | 5.00±0.00 bc | 73.97±7.48 b | 22.38±0.76 b | 309.53±44.62 b | 226.87±21.66 c | |
| RIL60 | 5.67±0.58 b | 83.54±4.69 a | 25.04±0.84 a | 325.21±5.71 b | 271.84±16.10 b | |
| RILc | 4.33±0.58 c | 79.49±3.69 ab | 24.61±0.25 a | 441.72±31.77 a | 351.78±36.12 a | |
| 2020 | 08yi | 7.00±0.00 a | 64.34±1.33 c | 20.00±0.31 c | 273.38±10.63 bc | 175.86±6.94 d |
| 08yc | 5.67±0.58 b | 68.71±4.48 bc | 22.27±0.40 b | 306.58±31.12 b | 211.30±31.98 cd | |
| RIL60 | 5.67±0.58 b | 76.08±1.29 ab | 24.99±0.29 a | 273.20±37.18 bc | 207.52±24.52 cd | |
| RILc | 4.67±0.58 c | 63.39±3.30 c | 24.51±0.47 a | 293.42±14.70 b | 185.72±4.79 cd |
表4 不同种质单株产量性状比较
Table 4 Comparison of yield characters per plant of different germplasms.
| 年份 Year | 种质 Germplasm | 单株有效穗数 Effective panicle number per plant | 结实率 Seed setting rate / % | 千粒重 1000-grain weight /g | 着粒数 Number of grain per panicle | 实粒数 Filled grains per panicle |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 08yi | 6.33±0.58 ab | 79.42±6.95 ab | 20.88±0.58 c | 233.36±18.64 c | 185.08±17.76 cd |
| 08yc | 5.00±0.00 bc | 73.97±7.48 b | 22.38±0.76 b | 309.53±44.62 b | 226.87±21.66 c | |
| RIL60 | 5.67±0.58 b | 83.54±4.69 a | 25.04±0.84 a | 325.21±5.71 b | 271.84±16.10 b | |
| RILc | 4.33±0.58 c | 79.49±3.69 ab | 24.61±0.25 a | 441.72±31.77 a | 351.78±36.12 a | |
| 2020 | 08yi | 7.00±0.00 a | 64.34±1.33 c | 20.00±0.31 c | 273.38±10.63 bc | 175.86±6.94 d |
| 08yc | 5.67±0.58 b | 68.71±4.48 bc | 22.27±0.40 b | 306.58±31.12 b | 211.30±31.98 cd | |
| RIL60 | 5.67±0.58 b | 76.08±1.29 ab | 24.99±0.29 a | 273.20±37.18 bc | 207.52±24.52 cd | |
| RILc | 4.67±0.58 c | 63.39±3.30 c | 24.51±0.47 a | 293.42±14.70 b | 185.72±4.79 cd |
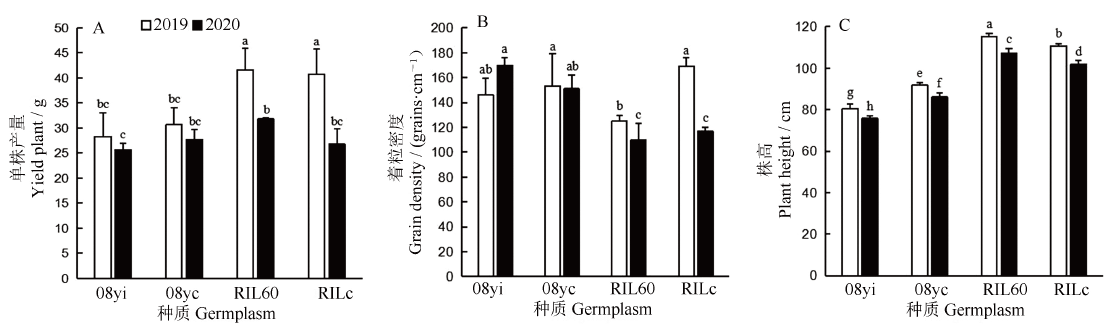
图4 不同种质单株产量及其构成因素差异比较 均值±标准差。不同小写字母表示不同种质间以及同一种质不同年份间差异显著(P<0.05, n=8, F-检验)。
Fig. 4. Comparison of yield per plant and its components for different germplasms. Mean±SD. Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference at P<0.05 by F-test (n=8).
| [1] | 吴比, 胡伟, 邢永忠. 中国水稻遗传育种历程与展望[J]. 遗传, 2018,40(10):841-857. |
| Wu B, Hu W, Xing Y Z. The history and prospect of rice genetic breeding in China[J]. Hereditas (Beijing), 2018,40(10):841-857. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | 胡娟, 林晗, 徐娜, 焦然, 戴志俊, 鲁草林, 饶玉春, 王跃星. 水稻叶倾角分子机制及育种应用的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019,33(5):391-400. |
| Hu J, Lin H, Xu N, Jiao R, Dai Z J, Lu C L, Rao Y C, Wang Y X. Advances in molecular mechanisms of rice leaf inclination and its application in breeding[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2019,33(5):391-400. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 李红, 何炜, 连玲, 魏毅东, 蔡秋华, 王颖姮, 谢华安, 张建福. 水稻株型的研究进展[J]. 福建稻麦科技, 2020,38(4):61-66. |
| Li H, He W, Lian L, Wei Y D, Cai Q H, Wang Y H, Xie H A, Zhang J F. Research advances on plant type of rice[J]. Fujian Science and Technology of Rice and Wheat, 2020,38(4):61-66. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | Guo W, Chen L, Herrera-Estrella L, Cao D, Tran L S P. Altering plant architecture to improve performance and resistance[J]. Trends in Plant Science, 2020,25(11):1154-1170. |
| [5] | Donald C M. The biological yield and harvest index of cereals as agronomic and plant breeding criteria[J]. Agronomy, 1976,28(4):361-405. |
| [6] | Khush G S. Prospects and approaches to increasing the genetic yield potential of rice[M]// Evenson R E, Herdt R N, Hossain M. Rice Research in Asia: Progress and Priorities. CAB International and IRRI, 1996: 59-71. |
| [7] | 杨守仁, 张龙步, 陈温福, 徐正进, 王进民. 水稻超高产育种的理论和方法[J]. 中国水稻科学, 1996,10(2):115-120. |
| Yang S R, Zhang L B, Cheng W F, Xun Z J, Wang J M. Theories and methods of rice breeding for maximum yield[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 1996,10(2):115-120. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | 马梦影, 巩文靓, 康雪蒙, 段海燕. 水稻理想株型改良的研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2020,36(29):1-6. |
| Ma M J, Gong W J, Kang X M, Duan H Y. The improvement of ideal plant type of rice: A review[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2020,36(29):1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | Chen W F, Xu Z J, Zhang W Z, Zhang L B, Yang S R. Creation of new plant type and breeding rice for super high yield[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2001,27(5):665-672. |
| [10] | Zhao S, Xiang J, Xue H. Studies on the rice LEAF INCLINATION1(LC1), an IAA-amido synthetase, reveal the effects of auxin in leaf inclination control[J]. Molecular Plant, 2013,6(1):174-187. |
| [11] | Jiao Y Q, Wang Y H, Xue D W, Wang J, Yan M, Liu G, Dong G, Zeng D, Lu Z, Zhu X. Regulation of OsSPL14 by OsmiR156 defines ideal plant architecture in rice[J]. Nature Genetics, 2010,42(6):541-544. |
| [12] | Miura K, Ikeda M, Matsubara A, Song X J, Ito M, Asano K, Matsuoka M, Kitano H, Ashikari M. OsSPL14 promotes panicle branching and higher grain productivity in rice[J]. Nature Genetics, 2010,42(6):545-549. |
| [13] | Wang J, Zhou L, Hui S, Mawsheng C, Hong Y, Hong Y, Min H, Yin J, Zhu X, Li Y. A single transcription factor promotes both yield and immunity in rice[J]. Science, 2018,361(6406):1026-1028. |
| [14] | Jeng T L, Wang C S, Tseng T H, Wu M T, Sung J M. Nucleotide polymorphisms in the waxy gene of NaN3-induced waxy rice mutants[J]. Journal of Cereal Science, 2009,49(1):112-116. |
| [15] | 刘巧泉, 王兴稳, 陈秀花, 王宗阳. 转反义Wx基因糯稻的显性遗传及对稻米粒重的效应分析. 中国农业科学, 2002,35(2):117-122. |
| Liu Q Q, Wang X Y, Chen X H, Wang Z Y. Effect of dominant waxy character on kernel weight of transgenic rice with antisense Wx gene. Scientia Agriculture Sinica, 2002,35(2):117-122. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 丁维龙, 谢涛, 徐利锋, 张义凯. 基于虚拟模型的水稻冠层叶面积计算方法[J]. 农业工程学报, 2017,33(2):192-198. |
| Ding W L, Xie T, Xu L F, Zhang Y K. Calculation method of rice canopy leaf area based on virtual model[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2017,33(2):192-198. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | 周振翔, 李志康, 陈颖, 王志琴, 杨建昌, 顾骏飞. 叶绿素含量降低对水稻叶片光抑制与光合电子传递的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2016,49(19):3709-3720. |
| Zhou Z X, Li Z K, Chen Y, Wang Z Q, Yang J C, Gu J F. Effects of reduced chlorophyll content on photo- inhibition and photosynthetic electron transport in rice leaves[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2016,49(19):3709-3720. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | 陈家润. 水稻品种试验田间记载及室内考种项目与标准[J]. 湖北农业科学, 1957(2):146-148. |
| Chen J R. Field records and laboratory test items and standards of rice variety test[J]. Hubei Agricultural Science, 1957(2):146-148. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | Wendland J, Lengeler K B, Kothe E. An instant preparation method for nucleic acids of filamentous fungi[J]. Fungal Genetics Reports, 1996,43(1):54-55. |
| [20] | 田志喜, 严长杰, 钱前, 严松, 谢会兰, 王芳, 徐洁芬, 刘贵富, 王永红, 刘巧泉, 汤述翥, 李家洋, 顾铭洪. 水稻淀粉合成相关基因分子标记的建立[J]. 科学通报, 2010,55(26):2591-2601. |
| Tian Z X, Yan C J, Qian Q, Yan S, Xie H L, Wang F, Xu J F, Liu G F, Wang Y H, Liu Q Q, Tang S Z, Li J Y, Gu M H. Establishment of molecular markers of rice starch synjournal related genes[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2010,55(26):2591-2601. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | 徐静, 王莉, 钱前, 张光恒. 水稻叶片形态建成分子调控机制研究进展[J]. 作物学报, 2013,39(5):767-774. |
| Xu J, Wang L, Qian Q, Zhang G H. Research advance in molecule regulation mechanism of leaf morphogenesis in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2013,39(5):767-774. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | 杨从党, 袁平荣, 周能, 朱德峰, 杨爱兵, 郑学玉, 黄庆宇, 应继锋. 叶型特性与产量构成因素的相关分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2001,15(1):71-73. |
| Yang C D, Yuan P R, Zhou N, Zhu D F, Yang A B, Zheng X Y, Huang Q Y, Ying J F. Analysis on relationship between characters of leaf type and yield components[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2001,15(1):71-73. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 贺勇, 孙焕良, 孟桂元. 水稻叶片形态研究进展[J]. 作物研究, 2008(S1):378-380. |
| He Y, Sun H L, Meng G Y. Advances in leaf morphology of rice[J]. Crop Research, 2008(S1):378-380. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | 罗赣丰, 马雪梅, 程建峰. 水稻剑叶角度与氮营养效率的关系[J]. 中国农学通报, 2014,30(18):29-34. |
| Luo G F, Ma X M, Cheng J F. The relationships between flag leaf angles of various rice germplasms and their nitrogen nutrition efficiencies[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2014,30(18):29-34. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | Easterling W, Apps M. Assessing the consequences of climate change for food and forest resources: A view from the IPCC[J]. Climate Change, 2005,70:165-189. |
| [26] | 孔飞扬, 江立庚, 文娟, 郝向阳. 直播水稻产量、产量构成因子和干物质积累的变化特点及其相互关系[J]. 华中农业大学学报, 2018,37(5):11-17. |
| Kong F Y, Jiang L G, Wen J, Hao X Y. Changes and relationships of yield, yield components and dry matter accumulation of direct-seeded rice[J]. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University, 2018,37(5):11-17. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | Peng S B, Li Y, Cui K H, Yu T T, Wang T, Xu L, Zhan X W, Huang J L, Nie L X. Yield performance of direct-seed, double-season rice using varieties with short growth durations in central China[J]. Field Crops Research, 2018,227:49-55. |
| [28] | 武玲, 向珣朝, 杨博文, 许亮, 颜李梅. 水稻籼爪交重组自交系穗部性状变异分析[J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2017,22(10):26-35. |
| Wu L, Xiang X C, Yang B W, Xu L, Yan L M. Analysis on the panicle traits variation of recombinant inbred line derived from the hybridization of indica and javanica[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2017,22(10):26-35. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | 陈小荣, 陈志彬, 贺浩华, 朱昌兰, 彭小松, 贺晓鹏, 傅军如, 欧阳林娟. 水稻单株有效穗数主基因+多基因混合遗传分析[J]. 生物数学学报, 2011,26(3):555-562. |
| Chen X R, Chen Z B, He H H, Zhu C L, Peng X S, He X P, Fu J R, OuYang L J. Genetic analysis of panicles per plant in rice by the major genes plus polygenes mixed inheritance model[J]. Journal of Biomathematics, 2011,26(3):555-562. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | 刘坚, 陶红剑, 施思, 叶卫军, 钱前, 郭龙彪. 水稻穗型的遗传和育种改良[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2012,26(2):227-234. |
| Liu J, Tao H J, Shi S, Ye W J, Qian Q, Gu L B. Genetics and breeding improvement for panicle type in rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2012,26(2):227-234. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | Li X, Qian Q, Fu Z, Wang Y, Xiong G, Zeng D, Wang X, Liu X, Sheng T, Hiroshi F. Control of tillering in rice[J]. Nature, 2003,422:618-621. |
| [32] | Jin J, Huang W, Gao J P, Yang J, Lin H X. Genetic control of rice plant architecture under domestication[J]. Nature Genetics, 2008,40:1365-1369. |
| [33] | Fan C, Xing Y, Mao H, Lu T, Zhang Q. GS3, a major QTL for grain length and weight and minor QTL for grain width and thickness in rice, encodes a putative transmembrane protein[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2006,112:1164-1171. |
| [34] | Feng Z, Wu C, Wang C, Roh J, Zhang L, Chen J, Zhang S, Zhang H, Yang C, Hu J, You X, Liu X, Yang X, Guo X, Zhang X, Wu F, Terzaghi W, Kim S K, Jiang L, Wan J. SLG controls grain size and leaf angle by modulating brassinosteroid homeostasis in rice[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2016,67(14):4241-4253. |
| [35] | Huang X, Qian Q, Liu Z, Sun H, He S, Luo D, Xia G, Chu C, Li J, Fu X. Natural variation at the DEP1 locus enhances grain yield in rice[J]. Nature Genetics, 2009,41:494-497. |
| [1] | 冯爱卿, 汪聪颖, 苏菁, 封金奇, 陈凯玲, 林晓鹏, 陈炳, 梁美玲, 杨健源, 朱小源, 陈深. 水稻细菌性条斑病抗性新品系的创制及其农艺性状分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(6): 587-596. |
| [2] | 兰金松, 庄慧. 水稻株型的分子机理研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(5): 449-458. |
| [3] | 李小秀, 吕启明, 袁定阳. OsNramp5基因变异影响水稻重要农艺性状的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(6): 562-571. |
| [4] | 乔胜锋, 邓亚萍, 瞿寒冰, 张伟杨, 顾骏飞, 张耗, 刘立军, 王志琴, 杨建昌. 不同籼稻品种对低磷响应的差异及其农艺生理性状[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(4): 396-406. |
| [5] | 杨晓龙, 程建平, 汪本福, 李阳, 张枝盛, 李进兰, 李萍. 灌浆期干旱胁迫对水稻生理性状和产量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(1): 38-46. |
| [6] | 彭永彬, 谢先芝. 表型组学在水稻研究中的应用[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(4): 300-306. |
| [7] | 李可, 禹晴, 徐云姬, 杨建昌. 水稻叶片早衰突变体的农艺与生理性状研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(2): 104-114. |
| [8] | 吕川根, 李霞, 宗寿余, 邹江石. 超级杂交稻两优培九的广适性分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(3): 191-205. |
| [9] | 陈宗祥, 冯志明, 王龙平, 冯凡, 张亚芳, 马玉银, 潘学彪, 左示敏. 水稻分蘖角基因TAC1的育种应用价值分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(6): 590-598. |
| [10] | 王琳琳, 陈玉宇, 郭梁, 张宏伟, 樊叶杨, 庄杰云. 水稻第1染色体qTGW1.2区域粒重组分性状QTL的剖析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2015, 29(3): 232-240. |
| [11] | 曹志斌, 谢红卫, 聂元元, 毛凌华, 李永辉, 蔡耀辉. 水稻抽穗扬花期耐热QTL(qHTH5) 定位及其遗传效应分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2015, 29(2): 119-125. |
| [12] | 李磊1,#,薛芗1,#,左示敏1,陈宗祥1,张亚芳1,李前前1,朱俊凯2,马玉银3,潘学彪1,*,潘存红2,*. 抑制OsAGO1a基因的表达导致水稻叶片近轴面卷曲[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2013, 27(3): 223-230. |
| [13] | 丁明亮1,2,# ,苏振喜2,# ,邹茜2 ,朱振华2 ,袁平荣2 ,陈于敏2 ,刘慰华2 ,陆树刚1 ,戴陆园2,*. 高原粳稻抗倒性与农艺性状及亲本抗倒性的关系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2012, 26(3): 325-330. |
| [14] | 刘传光1,周汉钦1,冯道基1,周新桥1,陈达刚1,李丽君1,李巨昌1,张桂权2,*,陈友订1,*. 影响华南稻区常规籼稻产量水平的主要农艺性状分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2012, 26(2): 182-188. |
| [15] | 李毓1,2庄伟建1,3, * 王乃元2洪国琴1戴飞3. 抑制水稻隐花色素基因OsCRY1a表达对水稻农艺性状的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2011, 25(6): 575-579. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||