
中国水稻科学 ›› 2021, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (5): 495-502.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2021.210202
王亚梁, 朱德峰*( ), 陈惠哲, 张玉屏, 向镜, 王志刚, 张义凯
), 陈惠哲, 张玉屏, 向镜, 王志刚, 张义凯
收稿日期:2021-02-02
修回日期:2021-03-25
出版日期:2021-09-10
发布日期:2021-09-10
通讯作者:
朱德峰
基金资助:
Yaliang WANG, Defeng ZHU*( ), Huizhe CHEN, Yuping ZHANG, Jing XIANG, Zhigang WANG, Yikai ZHANG
), Huizhe CHEN, Yuping ZHANG, Jing XIANG, Zhigang WANG, Yikai ZHANG
Received:2021-02-02
Revised:2021-03-25
Online:2021-09-10
Published:2021-09-10
Contact:
Defeng ZHU
摘要:
【目的】明确精准条播育秧机插对籼粳杂交稻产量形成的影响及其在减氮条件下降低产量损失的作用。【方法】以甬优538和甬优1540为供试品种,精准条播(precision drill sowing, PS)16条机插,并以相同播种量传统撒播(broadcast sowing, BS)机插为对照,同时设置不施氮肥(0 kg/hm2, zero-nitrogen application rate, 0N)、适氮(240 kg/hm2, suitable nitrogen application rate, SN)、减氮15%(204 kg/hm2,reduced nitrogen application rate, RN)等3个氮肥施用梯度处理,分析比较产量形成、植株均匀度、干物质积累及氮利用效率。【结果】1)与撒播相比,精准条播通过提高有效穗数使籼粳杂交稻产量平均提高4.3%,减氮条件下精准条播处理的水稻产量降幅小于撒播。2) 精准条播显著降低漏秧率,提高机插苗数均匀度以及有效穗数均匀度。与撒播相比,精准条播处理提高减氮下高峰苗数,两个品种趋势一致。3)与撒播相比,精准条播增加抽穗期叶面积指数,同时增加了抽穗期和抽穗开花后的干物质积累和氮吸收总量,其中减氮处理下表现尤为明显。4) 除0N外,氮素干物质积累量和氮素稻谷生产效率在不同品种方式及氮处理间无显著差异,但精准条播处理显著提高了氮肥吸收利用效率和氮肥农学利用效率,两个品种趋势一致。【结论】精准条播机插能够提高籼粳杂交稻植株均匀度,增加高峰苗数和叶面积指数,促进干物质积累和氮素吸收,进而提高产量,有效减少氮肥减施下籼粳杂交稻的产量损失。
王亚梁, 朱德峰, 陈惠哲, 张玉屏, 向镜, 王志刚, 张义凯. 籼粳杂交稻精准条播育秧机插减氮增产的效应研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(5): 495-502.
Yaliang WANG, Defeng ZHU, Huizhe CHEN, Yuping ZHANG, Jing XIANG, Zhigang WANG, Yikai ZHANG. Effects of Precise Drill Sowing-based Seedling Raising of indica-japonica Hybrid Rice for Mechanical Transplanting on Yield Increase Under Nitrogen Reduction Conditions[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2021, 35(5): 495-502.
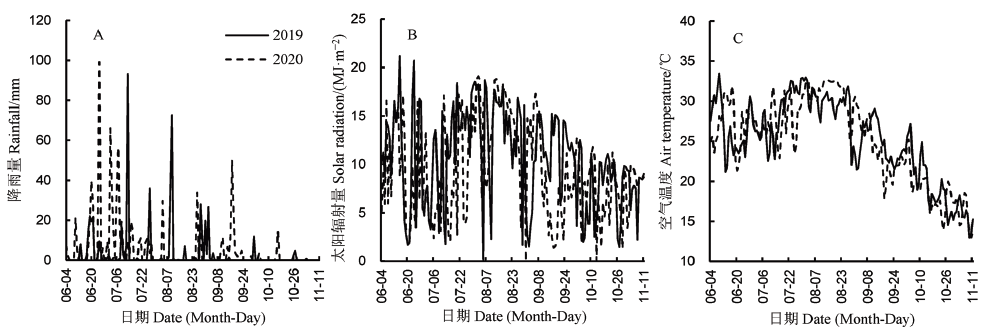
图1 水稻生长期间空气温度、太阳辐射量和降雨量A–降雨量;B–太阳辐射量;C–气温。
Fig. 1. Air temperature, solar radiation and rainfall during growth duration of rice.A, Rainfall; B, Solar radiation; C, Air temperature.
| 品种 Cultivar | 处理 Treatment | 有效穗数 Number of productive Panicles/(×105·hm-2) | 每穗粒数 Number of spikelet per panicle | 结实率 Seed-setting rate /% | 千粒重 1000-grain weight /g | 产量 Yield /(t·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 甬优538 Yongyou 538 | BS+0N | 14.8±0.1 e | 257.5±3.9 c | 87.0±2.2 a | 23.1±0.0 a | 7.7±0.0 e |
| BS+SN | 17.4±0.2 b | 346.8±7.1 a | 81.0±0.8 b | 23.1±0.1 a | 11.3±0.2 c | |
| BS+RN | 17.0±0.1 c | 332.0±3.0 b | 81.4±0.6 b | 23.1±0.1 a | 10.6±0.1 d | |
| PS+0N | 15.7±0.4 d | 256.5±10.5 c | 85.7±2.6 a | 23.1±0.1 a | 7.7±0.0 e | |
| PS+SN | 17.9±0.2 bc | 352.7±3.2 a | 80.7±1.1 b | 23.2±0.1 a | 11.8±0.1 a | |
| PS+RN | 17.3±0.1 b | 341.5±6.1 ab | 80.8±0.5 b | 23.1±0.0 a | 11.0±0.2 c | |
| 甬优1540 Yongyou 1540 | BS+0N | 12.8±0.5 d | 309.2±6.8 c | 83.9±0.9 a | 23.0±0.5 a | 7.6±0.4 d |
| BS+SN | 19.0±0.3 b | 361.2±2.7 ab | 83.8±1.0 a | 23.2±0.2 a | 13.3±0.0 b | |
| BS+RN | 18.2±0.1 c | 354.2±1.2 ab | 83.2±0.4 a | 23.5±0.1 a | 12.6±0.1 c | |
| PS+0N | 13.2±0.2 d | 306.1±5.4 c | 84.6±0.9 a | 22.9±0.5 a | 7.8±0.2 d | |
| PS+SN | 19.9±0.4 a | 358.7±2.7 a | 84.0±1.1 a | 23.1±0.3 a | 13.8±0.1 a | |
| PS+RN | 19.1±0.2 b | 353.0±4.1 b | 84.0±1.0 a | 23.4±0.3 a | 13.3±0.2 b |
表1 不同播种方式及氮梯度处理水稻产量及其结构的比较
Table 1 Comparison of grain yield and its components by various sowing methods under nitrogen gradient treatments.
| 品种 Cultivar | 处理 Treatment | 有效穗数 Number of productive Panicles/(×105·hm-2) | 每穗粒数 Number of spikelet per panicle | 结实率 Seed-setting rate /% | 千粒重 1000-grain weight /g | 产量 Yield /(t·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 甬优538 Yongyou 538 | BS+0N | 14.8±0.1 e | 257.5±3.9 c | 87.0±2.2 a | 23.1±0.0 a | 7.7±0.0 e |
| BS+SN | 17.4±0.2 b | 346.8±7.1 a | 81.0±0.8 b | 23.1±0.1 a | 11.3±0.2 c | |
| BS+RN | 17.0±0.1 c | 332.0±3.0 b | 81.4±0.6 b | 23.1±0.1 a | 10.6±0.1 d | |
| PS+0N | 15.7±0.4 d | 256.5±10.5 c | 85.7±2.6 a | 23.1±0.1 a | 7.7±0.0 e | |
| PS+SN | 17.9±0.2 bc | 352.7±3.2 a | 80.7±1.1 b | 23.2±0.1 a | 11.8±0.1 a | |
| PS+RN | 17.3±0.1 b | 341.5±6.1 ab | 80.8±0.5 b | 23.1±0.0 a | 11.0±0.2 c | |
| 甬优1540 Yongyou 1540 | BS+0N | 12.8±0.5 d | 309.2±6.8 c | 83.9±0.9 a | 23.0±0.5 a | 7.6±0.4 d |
| BS+SN | 19.0±0.3 b | 361.2±2.7 ab | 83.8±1.0 a | 23.2±0.2 a | 13.3±0.0 b | |
| BS+RN | 18.2±0.1 c | 354.2±1.2 ab | 83.2±0.4 a | 23.5±0.1 a | 12.6±0.1 c | |
| PS+0N | 13.2±0.2 d | 306.1±5.4 c | 84.6±0.9 a | 22.9±0.5 a | 7.8±0.2 d | |
| PS+SN | 19.9±0.4 a | 358.7±2.7 a | 84.0±1.1 a | 23.1±0.3 a | 13.8±0.1 a | |
| PS+RN | 19.1±0.2 b | 353.0±4.1 b | 84.0±1.0 a | 23.4±0.3 a | 13.3±0.2 b |
| 品种 Cultivar | 处理 Treatment | 机插每穴苗数 Number of seedling per hill under mechanical transplanting | 漏秧率 Unplanted hill percent/% | 机插苗数均匀度 Uniformity of the seedling number under mechanical transplanting /% | 高峰苗数 Peak number of tillers /(×105·hm-2) | 成穗率 Productive tiller percentage/% | 有效穗数均匀度 Uniformity of the number of productive tillers/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 甬优538 Yongyou 538 | BS+0N | 2.7±0.1 a | 10.4±0.8 a | 43.8±2.1 b | 19.8±1.1 c | 71.4±4.7 a | 50.4±1.4 b |
| BS+SN | 2.7±0.1 a | 10.6±0.5 a | 43.3±1.8 b | 28.3±0.6 ab | 60.7±0.8 b | 49.5±1.5 b | |
| BS+RN | 2.7±0.1 a | 11.0±0.2 a | 45.1±1.4 b | 26.5±0.6 b | 62.1±2.2 b | 49.1±1.7 b | |
| PS+0N | 2.7±0.1 a | 3.7±0.4 b | 82.2±2.8 a | 21.5±0.8 c | 71.8±3.2 a | 71.2±6.1 a | |
| PS+SN | 2.7±0.1 a | 3.3±0.7 b | 82.3±2.4 a | 29.0±1.7 a | 61.8±3.0 b | 66.4±3.7 a | |
| PS+RN | 2.7±0.0 a | 3.3±1.1 b | 81.0±2.6 a | 28.2±1.5 ab | 61.4±3.1 b | 71.1±2.7 a | |
| 甬优1540 Yongyou 1540 | BS+0N | 2.7±0.0 a | 10.7±0.5 a | 43.9±1.2 b | 16.8±0.3 c | 74.3±1.3 a | 40.3±4.7 b |
| BS+SN | 2.7±0.0 a | 9.8±0.8 a | 42.9±2.4 b | 29.4±0.7 b | 65.1±1.2 b | 39.1±8.1 b | |
| BS+RN | 2.7±0.0 a | 10.9±1.2 a | 44.1±1.6 b | 28.9±0.4 b | 63.1±1.1 b | 40.2±8.4 b | |
| PS+0N | 2.6±0.1 a | 3.7±0.9 b | 79.1±2.5 a | 17.7±0.4 c | 74.4±0.9 a | 66.2±1.7 a | |
| PS+SN | 2.6±0.1 a | 3.3±0.7 b | 80.4±0.8 a | 30.5±0.2 a | 66.0±0.4 b | 63.5±4.2 a | |
| PS+RN | 2.6±0.1 a | 3.3±0.7 b | 81.0±2.0 a | 29.5±0.1 b | 63.8±0.6 b | 65.1±4.6 a |
表2 不同播种方式及氮梯度处理水稻机插苗均匀度及群体分蘖特性的比较
Table 2 Comparison of the uniformity of the seedling under mechanical transplanting and tillering characteristics by various sowing methods at different nitrogen gradient levels.
| 品种 Cultivar | 处理 Treatment | 机插每穴苗数 Number of seedling per hill under mechanical transplanting | 漏秧率 Unplanted hill percent/% | 机插苗数均匀度 Uniformity of the seedling number under mechanical transplanting /% | 高峰苗数 Peak number of tillers /(×105·hm-2) | 成穗率 Productive tiller percentage/% | 有效穗数均匀度 Uniformity of the number of productive tillers/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 甬优538 Yongyou 538 | BS+0N | 2.7±0.1 a | 10.4±0.8 a | 43.8±2.1 b | 19.8±1.1 c | 71.4±4.7 a | 50.4±1.4 b |
| BS+SN | 2.7±0.1 a | 10.6±0.5 a | 43.3±1.8 b | 28.3±0.6 ab | 60.7±0.8 b | 49.5±1.5 b | |
| BS+RN | 2.7±0.1 a | 11.0±0.2 a | 45.1±1.4 b | 26.5±0.6 b | 62.1±2.2 b | 49.1±1.7 b | |
| PS+0N | 2.7±0.1 a | 3.7±0.4 b | 82.2±2.8 a | 21.5±0.8 c | 71.8±3.2 a | 71.2±6.1 a | |
| PS+SN | 2.7±0.1 a | 3.3±0.7 b | 82.3±2.4 a | 29.0±1.7 a | 61.8±3.0 b | 66.4±3.7 a | |
| PS+RN | 2.7±0.0 a | 3.3±1.1 b | 81.0±2.6 a | 28.2±1.5 ab | 61.4±3.1 b | 71.1±2.7 a | |
| 甬优1540 Yongyou 1540 | BS+0N | 2.7±0.0 a | 10.7±0.5 a | 43.9±1.2 b | 16.8±0.3 c | 74.3±1.3 a | 40.3±4.7 b |
| BS+SN | 2.7±0.0 a | 9.8±0.8 a | 42.9±2.4 b | 29.4±0.7 b | 65.1±1.2 b | 39.1±8.1 b | |
| BS+RN | 2.7±0.0 a | 10.9±1.2 a | 44.1±1.6 b | 28.9±0.4 b | 63.1±1.1 b | 40.2±8.4 b | |
| PS+0N | 2.6±0.1 a | 3.7±0.9 b | 79.1±2.5 a | 17.7±0.4 c | 74.4±0.9 a | 66.2±1.7 a | |
| PS+SN | 2.6±0.1 a | 3.3±0.7 b | 80.4±0.8 a | 30.5±0.2 a | 66.0±0.4 b | 63.5±4.2 a | |
| PS+RN | 2.6±0.1 a | 3.3±0.7 b | 81.0±2.0 a | 29.5±0.1 b | 63.8±0.6 b | 65.1±4.6 a |
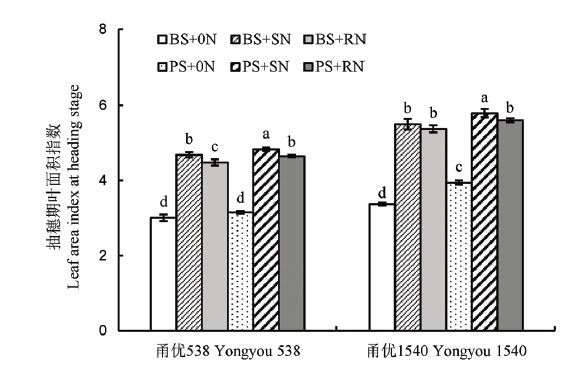
图2 不同播种方式及氮肥处理下水稻群体抽穗期叶面积指数数据为平均数±标准差;不同小写字母表示处理间差异显著(P<0.05, n=3)。下同。
Fig. 2. Comparison of leaf area index of rice population by various sowing methods at different nitrogen application levels.Values are Mean±SD; Bars superscripted by different lowercase letters are significantly different at 0.05 level among treatments(n=3). The same as below.
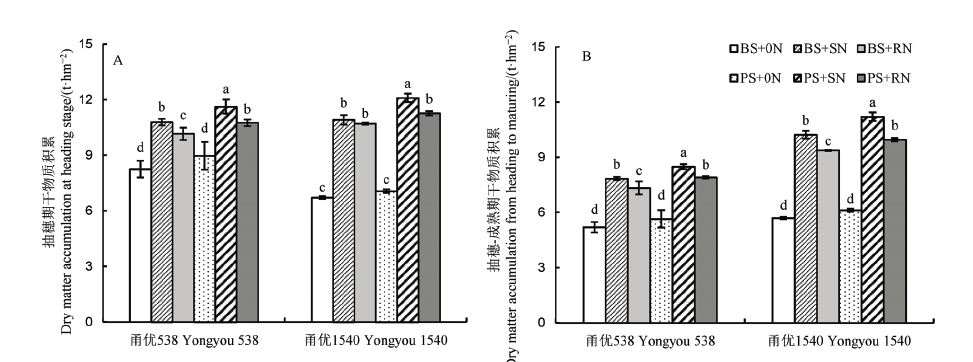
图3 不同播种方式及氮肥处理下水稻群体干物质积累量A–抽穗期干物质积累; B–抽穗-成熟期干物质积累。
Fig. 3. Comparison of dry matter accumulation of rice population by various sowing methods at different nitrogen application levels.A, Dry matter accumulation at heading stage; B, Dry matter accumulation from heading to maturing.
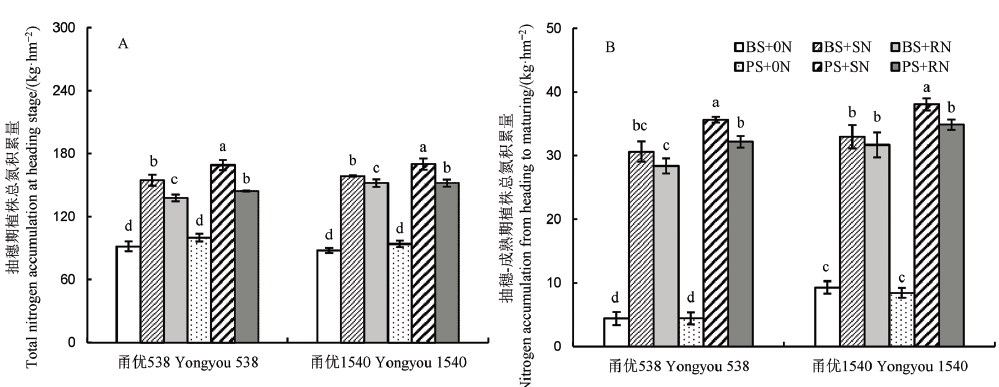
图4 不同播种方式及氮梯度处理水稻群体总氮积累量A–抽穗期总氮积累量; B–抽穗-成熟期总氮积累量。
Fig. 4. Comparison of total nitrogen accumulation of rice population by various sowing methods at different nitrogen application levels.A, Nitrogen accumulation at heading stage; B, Nitrogen accumulation from heading to maturing.
| 品种 Cultivar | 处理 Treatment | 氮素干物质生产效率 Nitrogen dry matter production efficiency/(kg·kg-1) | 氮素稻谷生产效率 Nitrogen grain production efficiency/(kg·kg-1) | 氮肥吸收利用率 Nitrogen recovery efficiency/% | 氮肥农学利用效率 Nitrogen agronomic use efficiency/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 甬优538 Yongyou 538 | BS+0N | 139.9±1.7 a | 79.7±3.7 a | ||
| BS+SN | 90.9±1.5 bc | 61.8±1.9 b | 34.7±1.8 b | 15.2±0.8 bc | |
| BS+RN | 94.3±2.2 b | 63.2±1.1 b | 33.6±1.6 b | 14.6±0.1 c | |
| PS+0N | 142.4±5.5 a | 75.3±6.1 a | |||
| PS+SN | 88.2±0.8 c | 59.6±0.3 b | 41.0±0.9 a | 17.0±0.6 a | |
| PS+RN | 92.0±1.9 bc | 60.7±0.6 b | 40.4±1.8 a | 16.4±0.8 ab | |
| 甬优1540 Yongyou 1540 | BS+0N | 125.3±5.7 a | 75.2±5.6 ab | ||
| BS+SN | 103.9±1.3 b | 68.9±0.5 c | 38.1±1.0 b | 23.7±0.3 c | |
| BS+RN | 105.0±2.2 b | 68.2±1.1 c | 40.6±2.1 ab | 24.3±0.5 bc | |
| PS+0N | 128.4±0.9 a | 76.5±0.9 a | |||
| PS+SN | 107.4±0.7 b | 68.7±1.2 c | 41.3±1.4 a | 25.0±0.3 b | |
| PS+RN | 108.1±0.7 b | 71.6±1.7 bc | 40.5±0.9 ab | 26.5±0.9 a |
表3 不同播种方式及氮梯度处理水稻群体氮吸收和利用效率
Table 3 Comparison of nitrogen absorption and utilization efficiency by various sowing methods at different nitrogen application levels.
| 品种 Cultivar | 处理 Treatment | 氮素干物质生产效率 Nitrogen dry matter production efficiency/(kg·kg-1) | 氮素稻谷生产效率 Nitrogen grain production efficiency/(kg·kg-1) | 氮肥吸收利用率 Nitrogen recovery efficiency/% | 氮肥农学利用效率 Nitrogen agronomic use efficiency/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 甬优538 Yongyou 538 | BS+0N | 139.9±1.7 a | 79.7±3.7 a | ||
| BS+SN | 90.9±1.5 bc | 61.8±1.9 b | 34.7±1.8 b | 15.2±0.8 bc | |
| BS+RN | 94.3±2.2 b | 63.2±1.1 b | 33.6±1.6 b | 14.6±0.1 c | |
| PS+0N | 142.4±5.5 a | 75.3±6.1 a | |||
| PS+SN | 88.2±0.8 c | 59.6±0.3 b | 41.0±0.9 a | 17.0±0.6 a | |
| PS+RN | 92.0±1.9 bc | 60.7±0.6 b | 40.4±1.8 a | 16.4±0.8 ab | |
| 甬优1540 Yongyou 1540 | BS+0N | 125.3±5.7 a | 75.2±5.6 ab | ||
| BS+SN | 103.9±1.3 b | 68.9±0.5 c | 38.1±1.0 b | 23.7±0.3 c | |
| BS+RN | 105.0±2.2 b | 68.2±1.1 c | 40.6±2.1 ab | 24.3±0.5 bc | |
| PS+0N | 128.4±0.9 a | 76.5±0.9 a | |||
| PS+SN | 107.4±0.7 b | 68.7±1.2 c | 41.3±1.4 a | 25.0±0.3 b | |
| PS+RN | 108.1±0.7 b | 71.6±1.7 bc | 40.5±0.9 ab | 26.5±0.9 a |
| [1] | 黄玛兰, 李晓云, 曾琳琳. 农村劳动力价格上涨与劳动力转移对作物种植结构的区域性影响差异[J]. 农业现代化研究, 2019, 40(1): 98-108. |
| Huang M, Li X Y, Zeng L L. Different reginal impacts of rural labor price increase and rural labor mitigation on crop structure[J]. Research of Agricultural Modernization, 2019, 40(1): 98-108. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | 王飞, 彭少兵. 水稻绿色高产栽培技术研究进展[J]. 生命科学, 2018, 30: 1129-1136. |
| Wang F, Peng S B. Research progress in rice green and high-yield management practices[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Life Sciences, 2018, 30: 1129-1136. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 林建荣, 宋昕蔚, 吴明国, 程式华. 籼粳超级杂交稻育种技术创新与品种培育[J]. 中国农业科学, 2016, 49(2): 207-218. |
| Lin J R, Song X W, Wu M G, Cheng S H. Breeding technology innovation of indica-japonica super hybrid rice and varietal breeding[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2016, 49(2): 207-218. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 朱德峰, 张玉屏, 陈惠哲, 向镜, 张义凯. 中国水稻高产栽培技术创新与实践[J]. 中国农业科学, 2015, 48: 3404-3414. |
| Zhu D F, Zhang Y P, Chen H Z, Xiang J, Zhang Y K. Innovation and practice of high-yield rice cultivation technology in China[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2015, 48: 3404-3414. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | 何文洪, 陈惠哲, 朱德峰, 徐一成, 林贤青, 张玉屏. 不同播种量对水稻机插秧苗素质及产量的影响[J]. 中国稻米, 2008(3): 60-62. |
| He W H, Chen H Z, Zhu D F, Xu Y C, Lin X Q, Zhang Y P. Effects of different sowing rates on the rice seedlings quality and rice yield[J]. China Rice, 2008(3): 60-62. (in Chinese) | |
| [6] | 彭少兵. 转型时期杂交水稻的困境与出路[J]. 作物学报, 2016, 42(3): 313-319. |
| Peng S B. Dilemma and way-out of hybrid rice during the transition period in China[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2016, 42(3): 313-319. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 陈子薇, 应珊珊, 刘银秀, 叶波, 董越勇, 姜培坤. 不同施肥类型对稻田氮素流失的影响[J].水土保持学报, 2021, 35(1): 36-43. |
| Chen Z W, Ying S S, Liu Y X, Ye B, Dong Y Y, Jiang P K. Effects of different fertilizer types on nitrogen loss in paddy field[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2021, 35(1): 36-43. | |
| [8] | Zhao C, Heng H, Jiang Z H, Liu H X, Huo Z Y. Effect of side deep placement of nitrogen on yield and nitrogen use efficiency of single season late japonica rice[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2020, 19: 2-17. |
| [9] | 李超, 肖小平, 唐海明, 汤文光, 程凯凯, 郭立君, 汪柯, 唐友云. 减氮增密对机插双季稻生物学特性及周年产量的影响[J]. 核农学报, 2019, 33(12): 2451-2459. |
| Li C, Xiao X P, Tang H M, Tang W G, Cheng K K, Guo L J, Wang K, Tang Y Y. Biological characteristics and annual yield of double machine-transplanted rice under nitrogen-reduction and density-increase measures[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 33(12): 2451-2459. | |
| [10] | 胡雅杰, 吴培, 朱明, 邢志鹏, 戴其根, 霍中洋, 许轲, 魏海燕, 郭保卫, 张洪程. 钵苗机插水稻氮素吸收与利用特征[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(3): 257-264. |
| Hu Y J, Wu P, Zhu M, Xing Z P, Dai Q G, Huo Z Y, Xu K, Wei H Y, Guo B W, Zhang H C. Characteristics of nitrogen uptake and utilization of mechanically- transplanted pot-tray-nursed rice seedlings[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2018, 32(3): 257-264. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 王亚梁, 朱德峰, 向镜, 陈惠哲, 张玉屏, 徐一成, 张义凯. 杂交稻低播量精量播种育秧及机插取秧特性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(4): 332-338. |
| Wang Y L, Zhu D F, Xiang J, Chen H Z, Zhang Y P, Xu Y C, Zhang Y K. Characteristics of seedling raising and mechanized transplanting of hybrid rice with a low seedling rate by precise seeding method[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2020, 34(4): 332-338. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 吴文革, 杨剑波, 张健美, 周永进, 蔡海涛, 许有尊, 吴然然, 陈刚. 穴基本苗对机插杂交中籼稻群体构建及产量的影响[J]. 安徽农业大学学报, 2014, 41: 401-405. |
| Wu W G, Yang J B, Zhang J M, Zhou Y J, Cai H T, Xu Y Z, Wu R R, Chen G. Effects of seedling number per hole on population quality and yield of mechanical transplanting middle-season indica hybrid rice[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural University, 2014, 41: 401-405. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | 汪洋. 氮素营养对水稻分蘖的产量异质性影响及调控[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2017. |
| Wang Y. Heterogeneity and regulations of rice tillers yield by nitrogen nutrition[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2017. | |
| [14] | 杜永林, 缪学宽, 李刚华, 张俊, 王绍华, 刘正辉, 唐设, 丁艳锋. 江苏机插水稻大面积均衡增产共性特征分析[J]. 作物学报, 2014, 40(12): 2183-2191. |
| Du Y L, Miao X K, Li G H, Zhang J, Wang S H, Liu Z H, Tang S, Ding Y F. Common characteristics of balanced yield increase in a large area of mechanical transplanted rice in Jiangsu Province[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2014, 40(12): 2183-2191. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 李应洪, 王海月, 吕腾飞, 张绍文, 蒋明金, 何巧林, 孙永健, 马均. 不同秧龄下机插方式与密度对杂交稻光合生产及产量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(3): 265-277. |
| Li Y H, Wang H Y, Lü T F, Zhang S W, Jiang M J, He Q M, Sun Y J, Ma J. Effects of mechanically-transplanted modes and density on photosynthetic production and yield in hybrid rice at different seedling-ages[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2017, 31(3): 265-277. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 赵海新, 杨丽敏, 陈书强, 姜树坤, 黄晓群, 单莉莉, 潘国君. 行距对两个不同类型水稻品种冠层结构与产量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2011, 25(5): 488-494. |
| Zhao H X, Yang L M, Chen S Q, Jiang S K, Huang X Q, Shan L L, Pan G J. Effects of row-spacing on canopy structure and yield in different type rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2011, 25(5): 488-494. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | 钟晓媛, 赵敏, 李俊杰, 陈多, 田青兰, 王丽, 黄光忠, 任万军. 播栽期对机插超级杂交籼稻分蘖成穗的影响及与气象因子的关系[J]. 作物学报, 2016, 42(11): 1708-1720. |
| Zhong X Y, Zhao M, Li J J, Chen D, Tian Q L, Wang L, Huang G, Ren W J. Effect of different seedling and transplanting dates on tillering characteristics of super indica hybrid rice with mechanized seeding and planting and its relationships with meteorological factors[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2016, 42(11): 1708-1720. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | 韦还和, 孟天瑶, 李超, 张洪程, 史天宇, 马荣荣, 王晓燕, 杨筠文, 戴其根, 霍中洋, 许轲, 魏海燕, 郭保卫. 甬优籼粳杂交稻花后干物质积累模型与特征分析[J]. 作物学报, 2016, 42(2): 265-277. |
| Wei H H, Meng T Y, Li C, Zhang H C, Shi T Y, Ma R R, Wang X Y, Yang J W, Dai Q G, Huo Z Y, Xu K, Wei H Y, Guo B W. Dynamic model and its characteristics analysis for dry matter production after heading of indica/japonica hybrid rice of Yongyou series[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2016, 42(20): 265-277. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | 程慧煌, 商庆银, 易振波, 郑厚亮, 曾勇军. 不同产量水平超级杂交稻产量形成特征及其对施肥量的响应[J]. 中国稻米, 2017, 23(4): 81-88. |
| Cheng H H, Shang Q Y, Yi Z B, Zheng H L, Zeng Y J. Effects of fertilizer application rate on yield and population quality of super hybrid rice at different yield levels[J]. China Rice, 2017, 23(4): 81-88. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | Wang Y L, Wang L, Zhou J X, Hu S B, Chen H Z, Xiang J, Zhang Y, Zeng Y J, Shi Q H, Zhu D F, Zhang Y P. Research progress on heat stress of rice at flowering stage[J]. Rice Science, 2019, 26(1): 1-10. |
| [21] | Wu H, Xiang J, Zhang Y P, Zhang Y K, Peng S B, Chen H Z, Zhu D F. Effects of post-anthesis nitrogen uptake and translocation on photosynthetic production and rice yield[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): e12891. |
| [22] | 许轲, 周兴涛, 曹利强, 张洪程, 郭保卫, 陈厚存, 吴中华, 朱聪聪, 杨岩. 不同类型钵苗及摆栽密度对粳型超级稻氮素吸收利用与转运特征的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2013, 46(23): 4876-4892. |
| Xu K, Zhou X T, Cao L Q, Zhang H C, Guo B W, Chen H C, Wu Z H, Zhu C C, Yang Y. Effects of different types of bowl seedlings and densities on characteristics of nitrogen uptake, utilization and translocation of bowl transplanted japonica super rice[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2013, 46(23): 4876-4892. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 陈明亮, 曾细华, 沈雨民, 罗世友, 胡兰香, 熊文涛, 熊焕金, 吴小燕, 肖叶青. 籼粳亚种间育性位点分型及籼粳杂交稻育性位点模式研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 386-396. |
| [2] | 吴玉红, 李艳华, 王吕, 秦宇航, 李杉杉, 郝兴顺, 张庆路, 崔月贞, 肖飞. 陕南稻区紫云英稻草联合还田配施减量氮肥协同提升水稻产量与稻米品质[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(6): 628-641. |
| [3] | 张小祥, 邵士梅, 赵步洪, 张耗, 季红娟, 肖宁, 潘存红, 李育红, 吴云雨, 蔡跃, 刘建菊, 吉春明, 张秀琴, 刘广青, 周长海, 黄年生, 李爱宏. 氮肥减施模式对不同穗型迟熟中粳水稻产量及氮素吸收利用的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(3): 278-294. |
| [4] | 孙园园, 张桥, 孙永健, 唐源, 郭长春, 刘芳艳, 武云霞, 杨志远, 马均. 不同育秧方式下播种量和插秧机具对机插稻氮素利用和产量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(6): 595-605. |
| [5] | 周娟, 舒小伟, 赖上坤, 许高平, 黄建晔, 姚友礼, 杨连新, 董桂春, 王余龙. 不同类型水稻品种产量和氮素吸收利用对大气CO2浓度升高响应的差异[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(6): 561-573. |
| [6] | 孟天瑶, 葛佳琳, 张徐彬, 韦还和, 周桂生, 戴其根. 甬优中熟籼粳杂交稻栽后植株磷素积累特征与模型分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(3): 256-265. |
| [7] | 曾研华, 张玉屏, 潘晓华, 朱德峰, 向镜, 陈惠哲, 张义凯, 曾勇军. 花后不同时段低温对籼粳杂交稻稻米品质性状的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(2): 166-174. |
| [8] | 曾研华, 张玉屏, 王亚梁, 向镜, 陈惠哲, 朱德峰. 甬优系列杂交稻组合开花期耐冷性评价[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2015, 29(3): 291-298. |
| [9] | 侯红乾1,2 ,冀建华1,2,刘光荣1,2 ,刘益仁1,2 ,刘秀梅1,2,*,程正新3,杨俊诚4,文石林5. 南方红壤区稻稻连作体系下氮肥减施模式研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2012, 26(5): 555-562. |
| [10] | 曹立勇,申宗坦. 籼粳杂交稻早熟性的研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 1997, 11(3): 187-189 . |
| [11] | 高勇, 滕利生, 申宗坦. 有关三系籼粳杂交稻的广亲和测验种的探讨[J]. 中国水稻科学, 1995, 9(1): 49-52 . |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||