
中国水稻科学 ›› 2020, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (6): 525-538.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2020.0701
张玉屏1,2,#, 王军可2,#, 王亚梁2, 陈燕华2, 朱德峰2, 陈惠哲2, 向镜2, 张义凯2, 刘小军1, 朱艳1, 曹卫星1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2020-07-01
修回日期:2020-09-11
出版日期:2020-11-10
发布日期:2020-11-10
通讯作者:
张玉屏,王军可,曹卫星
基金资助:
Yuping ZHANG1,2,#, Junke WANG2,#, Yaliang WANG2, Yanhua CHEN2, Dengfeng ZHU2, Huizhe CHEN2, Jing XIANG2, Yikai ZHANG2, Xiaojun LIU1, Yan ZHU1, Weixing CAO1,*( )
)
Received:2020-07-01
Revised:2020-09-11
Online:2020-11-10
Published:2020-11-10
Contact:
Yuping ZHANG, Junke WANG, Weixing CAO
摘要: 目的 探究夜温变化对水稻淀粉形成的影响及其生理机制【方法】以优质软米浙禾香2号为材料,在灌浆初期设置31℃/20℃ (LT)、31℃/24℃ (NT)、31℃/28℃ (HT)3个夜间温度模式,测定其直链淀粉和支链淀粉含量及合成关键酶活性及相关基因的表达。结果 1)与NT相比,LT和HT处理显著降低粒重和淀粉积累,降低糊化温度和胶稠度,并影响支链淀粉链长,降低支链淀粉含量,提高直链淀粉含量,HT的影响要大于LT;2) LT和HT处理对白天叶片净光合速率的影响不显著,但显著降低籽粒中非结构性碳水化合物积累,抑制蔗糖转运基因OsSUT1、OsSUT2和OsSUT4在夜间和白天表达;3) LT 和HT处理降低夜间和白天蔗糖水解相关酶活性,增加淀粉水解酶活性,导致可溶性糖含量升高,籽粒中糖利用受阻;4)与NT相比,LT和HT处理下腺苷二磷酸葡萄糖含量呈现白天降低而夜晚升高的趋势,腺苷二磷酸葡萄糖积累及利用受到抑制,颗粒结合淀粉合酶活性随处理时间延长而显著降低,且白天酶活性也受夜间温度的影响;5)与NT相比,LT和HT处理降低了夜间支链淀粉合成相关酶活性,抑制了夜间相关基因的表达,导致支链淀粉合成受阻,但对白天酶活及相关基因表达的影响不大。结论 夜间高温对淀粉积累的影响要大于夜温降低,夜间高温/低温抑制全天蔗糖转运及代谢,进而抑制淀粉积累;支链淀粉合成受阻是导致直链淀粉相对含量升高的主要原因,直链淀粉合成相关酶活性(白天)受夜温变化影响,而支链淀粉合成相关酶活性(白天)受夜温变化的影响不显著。
中图分类号:
张玉屏, 王军可, 王亚梁, 陈燕华, 朱德峰, 陈惠哲, 向镜, 张义凯, 刘小军, 朱艳, 曹卫星. 水稻淀粉合成对夜温变化的响应[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(6): 525-538.
Yuping ZHANG, Junke WANG, Yaliang WANG, Yanhua CHEN, Dengfeng ZHU, Huizhe CHEN, Jing XIANG, Yikai ZHANG, Xiaojun LIU, Yan ZHU, Weixing CAO. Response ofRice Starch Synthesis to Night Temperature Changes[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2020, 34(6): 525-538.
| 温度时段 Period | 夜间低温 LN | 夜间适温 NT | 夜间高温 HT |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0:00–6:30 | 20 | 24 | 28 |
| 6:30–9:30 | 28 | 28 | 28 |
| 9:30–17:30 | 31 | 31 | 31 |
| 17:30–22:30 | 28 | 28 | 28 |
| 22:30–24:00 | 20 | 24 | 28 |
| 平均Average | 26.3 | 27.7 | 29 |
表1 人工气候箱温度设置
Table 1 Temperature setting of different treatments in climate chambers.℃
| 温度时段 Period | 夜间低温 LN | 夜间适温 NT | 夜间高温 HT |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0:00–6:30 | 20 | 24 | 28 |
| 6:30–9:30 | 28 | 28 | 28 |
| 9:30–17:30 | 31 | 31 | 31 |
| 17:30–22:30 | 28 | 28 | 28 |
| 22:30–24:00 | 20 | 24 | 28 |
| 平均Average | 26.3 | 27.7 | 29 |
| 基因 Gene | 正向引物 Forward primer (5'→3') | 反向引物 Reverse primer (5'→3') |
|---|---|---|
| OsUBQ | GCACCCTCGCCGACTACAACATCCA | CCACCTTGTAGAACTGGAGCACGGC |
| OsSUT1 | ATGTGGCTCTGTGGTCCTATTGC | TCAACACACATCCTGTAAGAATA |
| OsSUT2 OsSUT4 | GCTGTGCCAACCTCAAGTCTGCC TCAAAGTATGGAAGAAGGAGACCGT | GTGAGGGCAGTAACAATCAAAAC GACCTTGAACTGTATTGTTTGCGAG |
| OsSSⅠ | CGTGTGATGGTTGTAATGCCGAG | CTGATTATCGCCAAAAGCACCAA |
| OsSSⅡa | GGTGTCTATGCGTTGTTGGAATG | CTCTTTGCTCTTGCGGATAACAG |
| OsSSⅢa | CCCACCGCCTTCCTTCCTGCTACT | GTGAAGGGCTGGCGGGGAGACGAG |
| OsBEⅡb | GGTGTTTGGGAGATTTTTCTGCCTA | GGTCTTTTAGGTTGAGGATGCTTGA |
表2 实时荧光定量PCR引物序列
Table 2 Primers used for quantitative real-time PCR.
| 基因 Gene | 正向引物 Forward primer (5'→3') | 反向引物 Reverse primer (5'→3') |
|---|---|---|
| OsUBQ | GCACCCTCGCCGACTACAACATCCA | CCACCTTGTAGAACTGGAGCACGGC |
| OsSUT1 | ATGTGGCTCTGTGGTCCTATTGC | TCAACACACATCCTGTAAGAATA |
| OsSUT2 OsSUT4 | GCTGTGCCAACCTCAAGTCTGCC TCAAAGTATGGAAGAAGGAGACCGT | GTGAGGGCAGTAACAATCAAAAC GACCTTGAACTGTATTGTTTGCGAG |
| OsSSⅠ | CGTGTGATGGTTGTAATGCCGAG | CTGATTATCGCCAAAAGCACCAA |
| OsSSⅡa | GGTGTCTATGCGTTGTTGGAATG | CTCTTTGCTCTTGCGGATAACAG |
| OsSSⅢa | CCCACCGCCTTCCTTCCTGCTACT | GTGAAGGGCTGGCGGGGAGACGAG |
| OsBEⅡb | GGTGTTTGGGAGATTTTTCTGCCTA | GGTCTTTTAGGTTGAGGATGCTTGA |
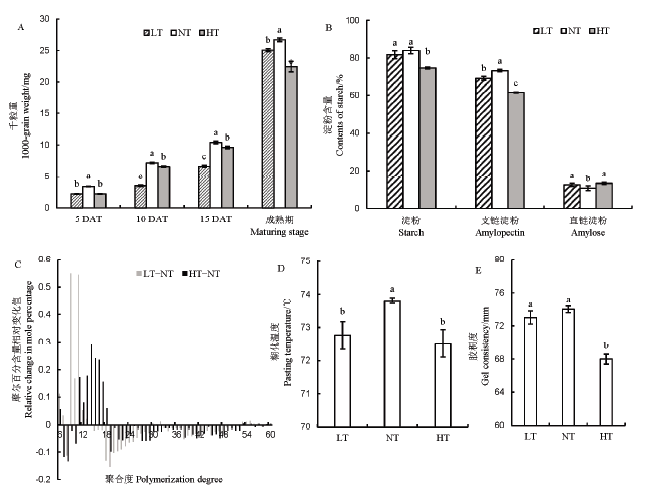
图1 不同夜温处理籽粒千粒重、淀粉含量、不同链长支链淀粉含量、糊化温度及胶稠度的比较 LT表示夜间低温处理; NT表示夜间适温处理; HT表示夜间高温处理; DAT表示处理后天数。数据为平均数±标准差;不同小写字母表示处理间差异显著(P<0.05, n=3)。下同。
Fig. 1. Comparison of 1000-grain weight, starch contents, amylopectin contents of different chain lengths, pasting temperature, and gel consistency of rice grain at different night temperatures. LT, Low night temperature treatment; NT, Normal night temperature treatment; HT, High night temperature treatment; DAT, Days after treatment. Values are Mean ± SD. Bars superscripted by different lowercase letters are significantly different at 0.05 level among treatments. The same as below.
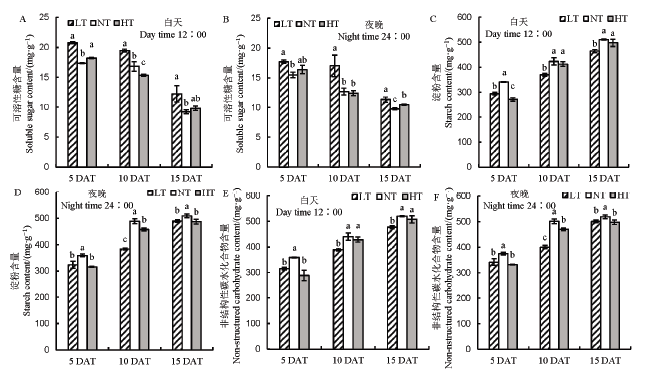
图2 不同夜温处理籽粒白天和夜间碳水化合物含量的比较 A–中午12点可溶性糖含量;B–夜晚24点可溶性糖含量;C–中午12点淀粉含量;D–夜晚24点淀粉含量;E–中午12点非结构性碳水化合物含量;F–夜晚24点非结构性碳水化合物含量。
Fig. 2. Comparison of carbohydrate accumulation in grain under different night temperature treatments. A, Contents of soluble sugar at 12:00 AM; B, Contents of soluble sugar at 24:00 PM; C, Contents of starch at 12:00 AM; D, Contents of starch at 24:00 PM; E, Non-structural carbohydrate contents at 12:00 AM; F, Non-structural carbohydrate contents at 24:00 PM.
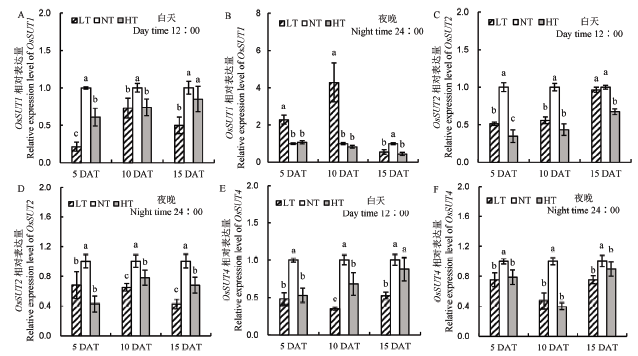
图3 不同夜温处理籽粒蔗糖转运基因表达的变化 A–中午12点OsSUT1相对表达量;B–夜晚24点OsSUT1相对表达量;C–中午12点OsSUT2相对表达量;D–夜晚24点OsSUT2相对表达量;E–中午12点OsSUT4相对表达量;F–夜晚24点OsSUT4相对表达量。
Fig. 3. Comparison of sucrose transporter gene expression under different night temperature treatments. A, Relative expression level of OsSUT1 at 12:00 AM; B, Relative expression level of OsSUT1 at 24:00 PM; C, Relative expression level of OsSUT2 at 12:00 AM; D, Relative expression level of OsSUT2 at 24:00 PM; E, Relative expression level of OsSUT4 at 12:00 AM; F, Relative expression level of OsSUT4 at 24:00 PM.
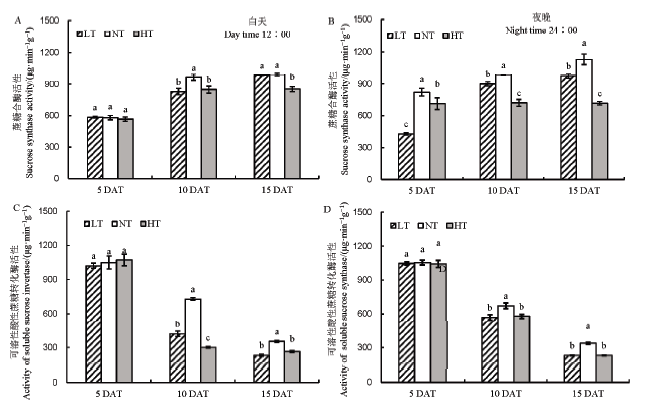
图4 不同夜温处理下蔗糖水解相关酶活性的比较 A–中午12点蔗糖合酶活性;B–夜晚24点蔗糖合酶活性;C–中午12点可溶性酸性蔗糖转化酶活性;D–夜晚24点可溶性酸性蔗糖转化酶活性。
Fig. 4. Comparison of sucrose hydrolysis-related enzymes under different night temperature treatments. A, Sucrose synthase activity at 12:00 AM; B, Sucrose synthase activity at 24:00 PM; C, Activity of soluble sucroseinvertase at 12:00 AM; D, Activity ofsoluble sucroseinvertase at 24:00 PM.
| 处理温度Treatment | 5 DAT | 10 DAT | 15 DAT |
|---|---|---|---|
| LT | 21.8±0.5 a | 22.8±0.5 a | 21.8±0.5 a |
| NT | 22.4±0.3 a | 21.4±0.3 a | 21.4±0.3 a |
| HT | 22.7±0.5 a | 21.7±0.5 a | 19.7±0.5 b |
表3 夜温处理对叶片净光合速率的影响
Table 3 Comparison of leaf net photosynthetic rate under different night temperature treatments.μmol/(m2·s)
| 处理温度Treatment | 5 DAT | 10 DAT | 15 DAT |
|---|---|---|---|
| LT | 21.8±0.5 a | 22.8±0.5 a | 21.8±0.5 a |
| NT | 22.4±0.3 a | 21.4±0.3 a | 21.4±0.3 a |
| HT | 22.7±0.5 a | 21.7±0.5 a | 19.7±0.5 b |
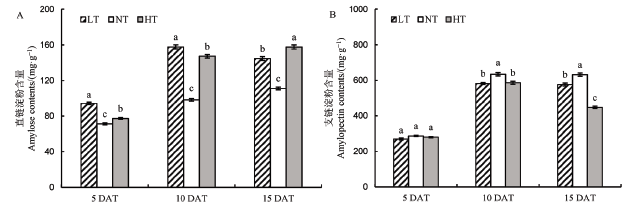
图5 不同夜温处理下直链淀粉和支链淀粉含量的比较 A–直链淀粉;B–支链淀粉。
Fig. 5. Comparison of amylose and amylopectin contents under different night temperature treatments. A, Amylose starch; B, Amylopectin.
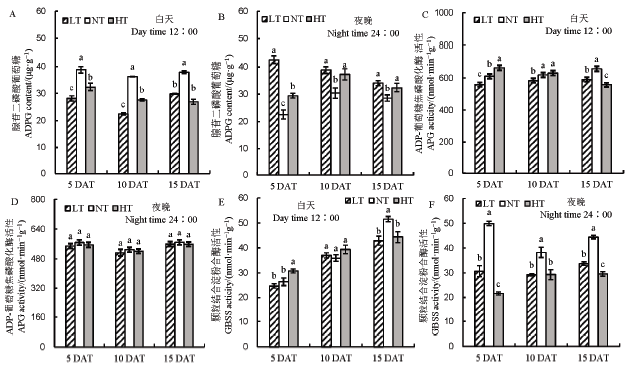
图6 不同夜温处理下直链淀粉合成相关酶活性的比较 A–中午12点腺苷二磷酸葡萄糖含量;B–夜晚24点腺苷二磷酸葡萄糖含量;C–中午12点ADP-葡萄糖焦磷酸化酶活性;D–夜晚24点ADP-葡萄糖焦磷酸化酶活性;E–中午12点颗粒结合淀粉合酶活性;F–夜晚24点颗粒结合淀粉合酶活性。
Fig. 6. Comparison of amylose synthase activity under different night temperature treatments. A, Content of glucose adenosine diphosphate at 12:00 AM; B, Content of glucose adenosine diphosphate at 24:00 PM; C, Activity of ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase at 12:00 AM; D, Activity of ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase at 24:00 PM; E, Activity of particle-binding starch synthase at 12:00 AM; F, Activity of granuce-bound starch synthase at 24:00 PM.
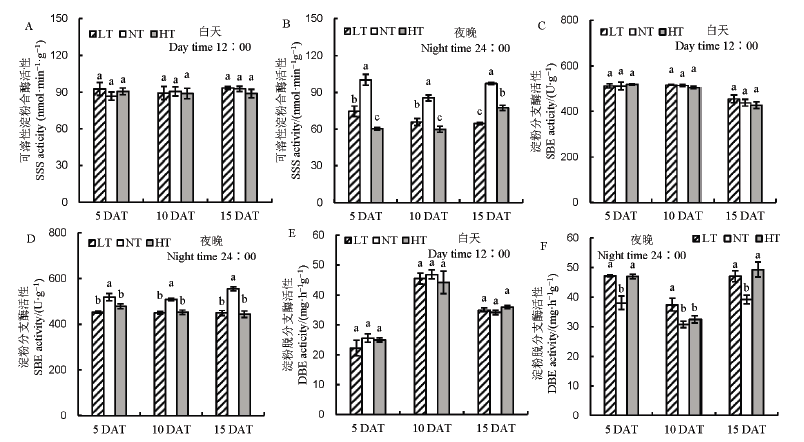
图7 不同夜温处理下支链淀粉形成相关酶活性的比较 A–中午12点可溶性淀粉合酶活性;B–夜晚24点可溶性淀粉合酶活性;C–中午12点淀粉分支酶活性;D–夜晚24点淀粉分支酶活性;E–中午12点淀粉分支酶活性;F–夜晚24点淀粉分支酶活性。
Fig. 7. Comparison of amylopectin formation-related enzyme activities under different night temperature treatments. A, Activity of soluble starch synthase (SSS) at 12:00 AM; B, Activity of soluble starch synthase (SSS) at 24:00 PM; C, Activity of amylase branching enzyme (SBE) at 12:00 AM; D, Activity of amylase branching enzyme (SBE) at 24:00 PM; E, Activity of amylase branching enzyme (DBE) at 12:00 AM; F, Activity of amylase branching enzyme (DBE) at 24:00 PM.
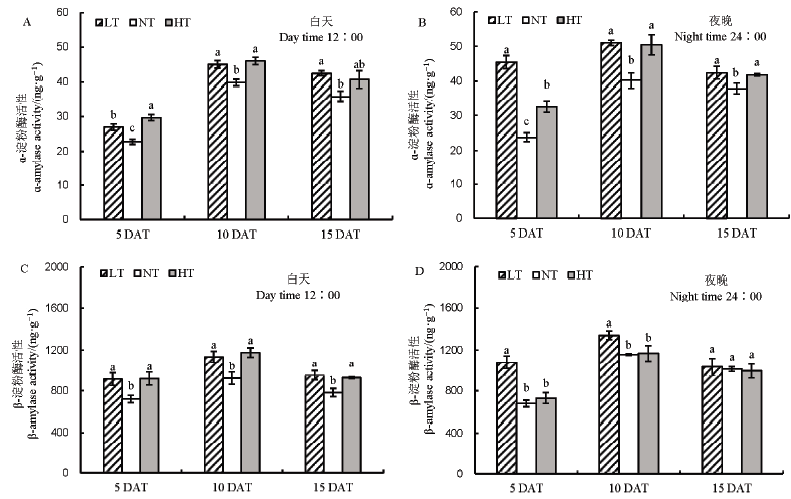
图8 不同夜温处理下淀粉水解相关酶活性的比较 A–中午12点ɑ-淀粉酶活性;B–夜晚24点ɑ-淀粉酶活性;C–中午12点β-淀粉酶活性;D–夜晚24点β-淀粉酶活性。
Fig. 8. Comparison of starch hydrolase-related enzyme activities under different night temperature treatments. A, Activity of ɑ-amylase activity at 12:00 AM; B, Activity of ɑ-amylase activity at 24:00 PM; C, β-amylase activity at 12:00 AM; D, β-amylase activity at 24:00 PM.
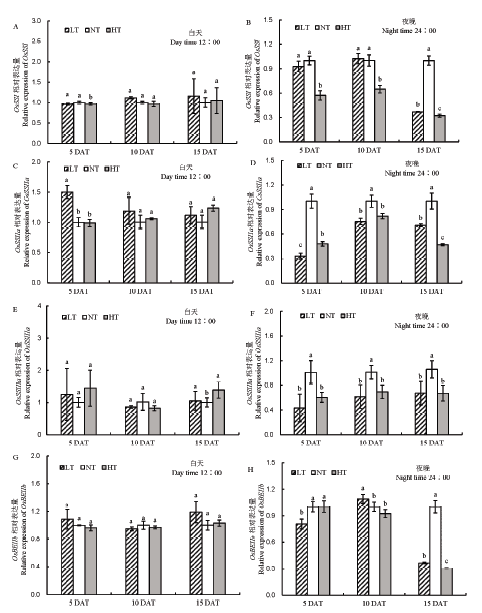
图9 不同夜温处理籽粒蔗糖转运基因表达量的比较 A–中午12点OsSSⅠ相对表达量;B–夜晚24点OsSSⅠ相对表达量;C–中午12点OsSSⅡa相对表达量;D–夜晚24点OsSSⅡa相对表达量;E–中午12点OsSSⅢa相对表达量;F–夜晚24点OsSSⅢa相对表达量; G–中午12点OsBEⅡb相对表达量;H–夜晚24点OsBEⅡb相对表达量。
Fig. 9. Comparison of sucrose transporter gene expression under different night temperatures. A, Relative expression level of OsSSⅠat 12:00 AM; B, Relative expression level of OsSSⅠat 24:00 PM; C, Relative expression level of OsSSⅡa at 12:00 AM; D, Relative expression level of OsSSⅡa at 24:00 PM; E, Relative expression level of OsSSⅢa at 12:00 AM; F, Relative expression level of OsSSⅢa at 24:00 PM; G, Relative expression level of OsBEⅡb at 12:00 AM; H, Relative expression level of OsBEⅡb at 24:00 PM.
| [1] | 陈波, 周年兵, 郭保卫, 黄大山, 陈忠平, 花劲, 霍中洋, 张洪程. 南方稻区“籼改粳”研究进展[J]. 扬州大学学报:农业与生命科学版, 2017, 38(1): 67-72, 88. |
| Chen B, Zhou N B, Guo B W, Huang D S, Chen Z P, Hua J, Huo Z Y, Zhang H C.Progress of “indicarice to japonicarice” in southern China[J]. Journal of Yangzhou University:Agricultural and Life Science Edition,2017, 38(1): 67-72, 88. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | 成臣, 黎星, 谭雪明, 商庆银, 曾研华, 石庆华, 曾勇军, 吕伟生, 王玮, 陈芸.播期对南方优质晚粳稻产量及稻米品质的调控效应研究[J].中国稻米, 2018, 24(5): 58-63. |
| Cheng C, Li X, Tan X M, Shang Q Y, Zeng Y H, Shi Q H, Zeng Y J, Lü W S, Wang W, Chen Y.Effects of sowing date on yield and quality of late japonica rice with high quality in southern China[J].China Rice, 2018, 24(5): 58-63. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 范晓磊,李应秋,陈专专,朱韵,刘巧泉.高温影响稻米品质形成机制研究及育种利用[C].2019年中国作物学会学术年会论文摘要集. 北京: 中国作物学会. 2019. |
| Fan X L, Li Y Q, Chen Z Z, Zhu Y, Liu Q Q.Study on the mechanism of high temperature influencing rice quality formation and breeding utilization[C].Proceedings of the Annual Conference of the Chinese Crop Society.Beijing: The Chinese Crop Society,2019. | |
| [4] | 杨军,章毅之,贺浩华,李迎春,陈小荣, 边建民,金国花,李翔翔,黄淑娥.水稻高温热害的研究现状与进展[J].应用生态学报,2020, 31(8): 2817-2830. |
| Yang J, Zhang YZ, He H H,Li Y C,Chen X R,Bian J M,Jin G H,LiX X,Huang S E.Current status and research advances of high-temperature hazards in rice[J].Chinese Journal ofApplied Ecology, 2020, 31(8): 2817-2830.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | 杨陶陶,解嘉鑫,黄山,谭雪明,潘晓华,曾勇军,石庆华,张俊,曾研华.花后增温对双季晚粳稻产量和稻米品质的影响[J].中国农业科学,2020,53(7):1338-1347. |
| Yang TT, Xie JX, Huang S, Tan X M, Pan XH, Zeng YJ,Shi QH, Zhang J, Zeng YH.The impacts of post-anthesiswarming on grain yield and quality oflate japonicarice in a double rice cropping system[J].Scientia AgriculturaSinica,2020,53(7):1338-1347. | |
| [6] | Zhang C X, Feng B H, Chen TT, Fu W M, Li H B, Li G Y, JinQ Y, Tao L X, Fu G F. Heat stress-reduced kernel weight in rice at anthesis is associated with impaired source-sink relationship and sugars allocation[J]. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2018, 155: 718-733. |
| [7] | 龚金龙, 张洪程, 胡雅杰, 龙厚元, 常勇, 王艳, 邢志鹏, 霍中洋. 灌浆结实期温度对水稻产量和品质形成的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2013, 32(2): 482-491. |
| Gong J L, Zhang H C, Hu Y J, Long H Y, Chang Y, Wang Y, Xing Z P, Huo Z Y.Effects of air temperature during rice grain-filling period on the formation of rice grain yield and its quality[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2013, 32(2): 482-491. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | 曹云英, 段骅, 杨立年, 王志琴,刘立军, 杨建昌. 抽穗和灌浆早期高温对耐热性不同籼稻品种产量的影响及其生理原因[J]. 作物学报, 2009, 35(3): 512-521. |
| Cao Y Y, Duan H, Yang L M, Wang Z Q, Liu L J, Yang C J.Effect of high temperature during heading and early grain filling on grain yield of indica rice cultivars differing in heat-tolerance and its physiological mechanism[J]. ActaAgronomicaSinica, 2009, 35(3): 512-521. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 曾凯, 居为民, 周玉, 管建丰, 王尚明, 张清霞. 高温逼熟等级对早稻品质与产量的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2011, 27(30): 120-125. |
| Zeng K, Ju W M, Zhou Y, Guan S M, Zhang Q X.Influences of high temperature induced maturity on the quality and yield characteristics of early rice[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2011, 27(30): 120-125. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | 朱昌兰, 贺浩华, 贺晓鹏, 彭小松, 傅军如, 欧阳林娟. 稻米支链淀粉的结构及其遗传调控研究进展[J]. 中国粮油学报, 2010, 25(12): 37-43. |
| Zhu C L, He H H, He X P, Peng X S, Fu J R, Ouyang L J.Advance in research on rice amylopectin structure and its genetic mechanism[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association, 2010, 25(12): 37-43. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | Houghton J, Ding Y, Griggs D J,Noguer M,van der Linden P J,Dai X,Maskell K,Johnson C A. IPCC, Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis[M].Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press, 2001, 881. |
| [12] | Peng S, Huang J, Sheehy J E,Laza R C,Visperas R M,Zhong X, Centeno G S,Khush G S,Cassman K G.Rice yields decline with higher night temperature from global warming[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2004, 101:9971-9975. |
| [13] | Jagadish SV, Murty M V,Quick W P. Rice responses to rising temperatures-challenges, perspectives and future directions[J]. Plant Cell Environment,2015, 38: 1686-1698. |
| [14] | Laza M R C, Sakai H, Cheng W,Tokida T, Peng S, Hasegawa T. Differential response of rice plants to high night temperatures imposed at varying developmental phases.Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 2015:209-210. |
| [15] | 吴自明, 时红, 石秀兰, 谭雪明, 石庆华, 潘晓华. 夜温升高对双季晚稻产量和品质影响[J]. 核农学报, 2014, 28(4): 708-713. |
| Wu Z M, Shi H, Shi X L, Tan X M, Shi Q H, Pan X H.The effects of the elevated nighttime temperature on the yield and quality of double season late rice[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 28(4): 708-713. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | Bahuguna R N, Solis C A, Shi W J, Jagadish K SV.Post-flowering night respiration and altered sink activity account for high night temperature-induced grain yield and quality loss in rice (Oryza sativa L.). PhysiologiaPlantarum, 2017, 159: 59-73. |
| [17] | 周倩兰, 李怡, 肖枫, 徐宏发, 李刚华, 王绍华, 丁艳锋, 刘正辉. 水稻植株温度的研究进展与展望[J]. 杂交水稻, 2019, 34(5): 1-6. |
| Zhou Q L, Li Y, Xiao F, Xu H F, Li G H, Wang S H, Ding Y F, Liu Z H.Advances in and future prospect of researches on rice plant temperature[J]. Hybrid Rice, 2019, 34(5): 1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | Czechowski T, Bari R P, Stitt M, Scheible W R, Udvardi M K.Real-time RT-PCR profiling of over 1400 Arabidopsis transcription factors: Unprecedented sensitivity reveals novel root- and shoot-specific genes[J]. Plant Journal, 2004, 38: 366-379. |
| [19] | 冯敏玉, 祝必琴, 雷俊, 朱建章,刘文英. 南昌高温逼熟发生规律及其对早稻产量的影响[J]. 中国农业气象, 2014, 35(3): 287-292. |
| Feng M Y, Zhu B Q, Lei J, Zhu J Z, Liu W Y.Characteristics of high-temperature forced maturity disaster and It's impacts on early rice in Nanchang area[J]. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 2014,35(3):287-292. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | 曾研华, 张玉屏, 潘晓华, 朱德峰, 向镜, 陈惠哲,张义凯. 花后低温对水稻籽粒灌浆与内源激素含量的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2016, 42(10): 1551-1559. |
| Zeng Y H, Zhang Y P, Pan X H, Zhu D F, Xang J, Chen H Z, Zheng Y K.Effect of low temperature after flowering on grain filling and plant hormones contents in rice[J]. ActaAgronomicaSinica, 2016,42(10):1551-1559. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | Bhat F M, Riar C S.Effect of composition, granular morphology and crystalline structure on the pasting, textural, thermal and sensory characteristics of traditional rice cultivars[J]. Food Chemistry, 2019, 280: 303-309. |
| [22] | 彭小松, 朱昌兰, 王方, 欧阳林娟, 贺晓鹏, 傅军如, 陈小荣, 刘琚珥, 贺浩华. 籼粳杂种后代支链淀粉结构及其与稻米糊化特性相关性分析[J].核农学报,2014,28(7):1219-1225. |
| Peng X S, Zhu C L, Wang F, Ouyang L J, He X P, Fu J R, Chen X R, Liu J E, He H H.The relationship between amylopectin structure and rice pastepropertyof indica/japonica cross progenies[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2014,28(7):1219-1225. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 韦克苏. 花后高温对水稻胚乳淀粉合成与蛋白积累的影响机理[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学,2012. |
| Wei K S.Effects of high temperature on starch synthesis and protein accumulation in rice endosperm at filling stage[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | Naoko F, Mayumi Y, Noriko A, Takashi O, Akio M, Hirohiko H, Yasunori N.Function and characterization of starch synthase I using mutants in rice[J]. Plant Physiology, 2006, 140(3):1070-1084. |
| [25] | 高振宇, 曾大力, 崔霞, 周奕华, 颜美仙, 黄大年, 李家洋, 钱前. 水稻稻米糊化温度控制基因ALK的图位克隆及其序列分析[J]. 中国科学: 生命科学, 2003, 46(6): 481-487. |
| Gao Z Y, Zeng D L, Cui X, Zhou Y H, Yan M X, Huang D N, Ji J Y, Qian Q.Map based cloning and sequence analysis of ALK gene for rice gelatinization temperature control[J]. Science in China:Life Sciences, 2003, 46(6):481-487. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | Jiang H, Dian W, Wu P.Effect of high temperature on fine structure of amylopectin in rice endosperm by reducing the activity of the starch branching enzyme[J]. Phytochemistry, 2003, 63(1):53-59. |
| [27] | 滕中华, 智丽, 吕俊, 宗学凤, 王三根, 何光华. 灌浆期高温对水稻光合特性、内源激素和稻米品质的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2010, 30(23): 6504-6511. |
| Teng Z H, Zhi L, Lü J, Zong X F, Wang S G, He G H.Effects of high temperature on photosynthesis characteristics, phytohormones and grain quality during filling-periods in rice[J]. ActaEcologicaSinica, 2010,30(23):6504-6511. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | 张彩霞, 符冠富, 奉保华, 陈婷婷, 陶龙兴. 水稻同化物转运及其对逆境胁迫响应的机理[J]. 中国农业气象, 2018, 39(2): 73-83. |
| Zhang C X, Fu G F, Feng B H, Chen T T, Tao L X.Mechanisms of assimilation transport in phloem of rice and its response to abiotic stress[J]. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 2018, 39(2): 73-83.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | 张彩霞. 高温影响水稻韧皮部同化物转运及代谢的作用机制及调控[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2018. |
| Zhang C X.The mechanism and regulation underlying the inhibition on the assimilates transport and metabolism in phloem of rice caused by heat stress [D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | 赵超, 王海燕, 刘美珍, 王文泉. 干旱胁迫下木薯茎杆可溶性糖、淀粉及相关酶的代谢规律[J]. 植物生理学报, 2017, 53(5): 795-806. |
| Zhao C, Wang H Y, Liu M Z, Wang W Q.Effect of drought on the contents of soluble sugars, starch and enzyme activities in cassava stem[J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 2017,53(5):795-806. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | 李天. 温光对水稻籽粒碳水化合物代谢及品质的影响[D]. 雅安: 四川农业大学, 2005. |
| Li T.Effects of temperature and light on carbohydrate metabolism and quality of rice grain[D]. Yaan: Sichuan Agricultural University, 2005. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [32] | 张文倩,王亚梁,朱德峰,陈惠哲,向镜,张义凯,张玉屏.花期夜温升高对水稻颖花开放及籽粒结实的影响[J]. 中国农业气象, 2019, 40(3): 180-185. |
| Zhang W Q,Wang YL,Zhu DF,Chen HZ,Xiang J,Zhang YK,Zhang YP.Effect of increasing night temperature on floret opening and grain setting of rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 2019,40(3):180-185. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [33] | 程方民, 丁元树, 朱碧岩. 稻米直链淀粉含量的形成及其与灌浆结实期温度的关系[J].生态学报, 2000, 20(4): 646-652. |
| Cheng F M, Ding Y S, Zhu B Y.The formation of amylose content in rice grain and its relation with field temperature[J]. ActaEcologicaSinica, 2000, 20(4): 646-652. |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [6] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [7] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [8] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [9] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [10] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [11] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [12] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [13] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| [14] | 许用强, 姜宁, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 水稻开花期高温热害响应机理及其调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 111-126. |
| [15] | 吕海涛, 李建忠, 鲁艳辉, 徐红星, 郑许松, 吕仲贤. 稻田福寿螺的发生、危害及其防控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 127-139. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||