
中国水稻科学 ›› 2020, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (5): 470-478.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2020.9109
• 研究报告 • 上一篇
朱华珺1,2,3, 周瑚1,2,3, 任佐华1,2, 刘二明1,2,3,*( )
)
收稿日期:2019-10-12
修回日期:2019-12-23
出版日期:2020-09-10
发布日期:2020-09-10
通讯作者:
刘二明
基金资助:
Huajun ZHU1,2,3, Hu ZHOU1,2,3, Zuohua REN1,2, Erming LIU1,2,3,*( )
)
Received:2019-10-12
Revised:2019-12-23
Online:2020-09-10
Published:2020-09-10
Contact:
Erming LIU
摘要:
【目的】检测枯草芽孢杆菌JN005产生的胞外抗菌物质的稳定性和对稻瘟病菌的生物活性,及其对水稻叶瘟的防治效果。【方法】通过不同培养基检测枯草芽孢杆菌JN005产生的抑菌物质,结合平板对峙法、光学显微镜观察、室内离体和活体接种来检测JN005菌株胞外抗菌物质对稻瘟病菌拮抗活性和对水稻叶瘟防治效果。【结果】枯草芽孢杆菌JN005能分泌蛋白酶、纤维素酶、淀粉酶和β-1, 3-葡聚糖酶,其胞外抗菌物质对稻瘟病菌生长具有抑制作用。胞外抗稻瘟病菌物质在0℃~100℃和pH 2~12范围内活性较为稳定,且经蛋白酶K处理后不影响其活性,紫外照射12 h以及4℃保存3个月仍有活性。胞外抗菌物质能引起稻瘟病菌菌丝形态畸变,并抑制分生孢子的萌发。室内湘晚籼12号稻瘟病离体叶片接种表明,先用100倍胞外抗菌物质稀释液处理水稻叶片,24 h后接种稻瘟病菌分生孢子悬浮液(1×105个/mL),其叶瘟发病率为34.07%,效果接近稀释500倍的40%稻瘟灵EC;而先接种稻瘟病菌分生孢子悬浮液,24 h后用100倍胞外抗菌物质稀释液处理,其发病率为38.52%,与稀释1500倍的75%三环唑(WP)和稀释500倍的40%稻瘟灵(EC)有显著性差异。活体喷雾接种试验表明,于湘晚籼12号秧苗长至3叶1心时,接种稻瘟病菌分生孢子悬浮液前24 h喷施稀释100倍的胞外抗菌物质稀释液,其叶瘟防效为75.32%;接种稻瘟病菌分生孢子悬浮液后24 h喷施稀释100倍的胞外抗菌物质稀释液,其防效为71.49%。【结论】JN005菌株胞外抗菌物质对稻瘟病菌的菌丝生长和孢子萌发有直接抑制作用,且对环境稳定性较好,对稻瘟病有较好的预防和治疗作用,有进一步的开发潜力。
中图分类号:
朱华珺, 周瑚, 任佐华, 刘二明. 枯草芽孢杆菌JN005胞外抗菌物质及对水稻叶瘟防治效果[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(5): 470-478.
Huajun ZHU, Hu ZHOU, Zuohua REN, Erming LIU. Extracellular Antimicrobial Substances Produced by Bacillus subtilis JN005 and Its Control Efficacy on Rice Leaf Blast[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2020, 34(5): 470-478.
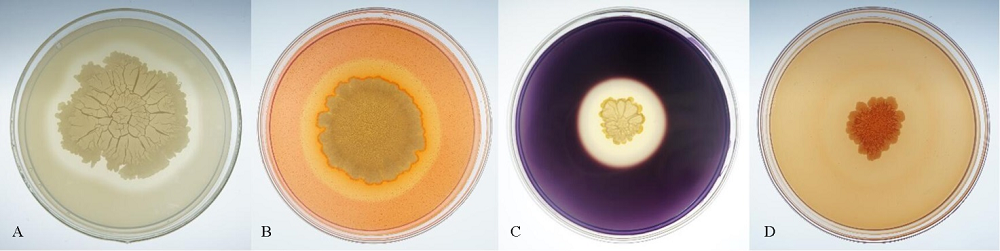
图1 JN005菌株产蛋白酶(A)、纤维素酶(B)、淀粉酶(C)和β-1, 3-葡聚糖酶(D)的检测
Fig. 1. Test of protease(A), cellulase(B), amylase(C) and β-1, 3-glucanase(D) produced by JN005 strain.
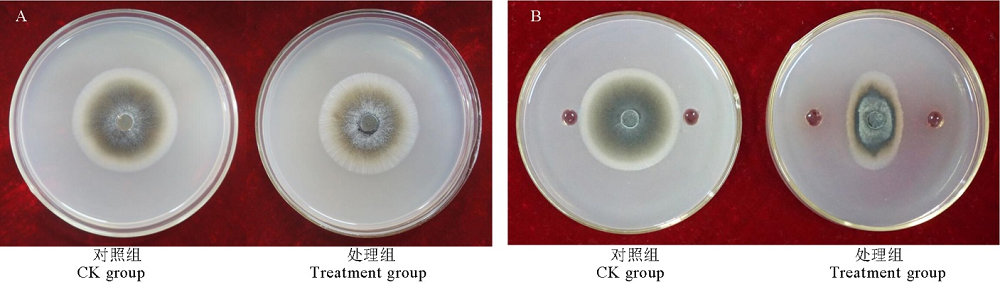
图2 JN005菌株挥发性气体(A)和胞外抗菌物质(B)对稻瘟病菌的影响
Fig. 2. Effects of volatile compounds(A) and extracellular antimicrobial substances(B) of JN005 strain on M. oryzae.
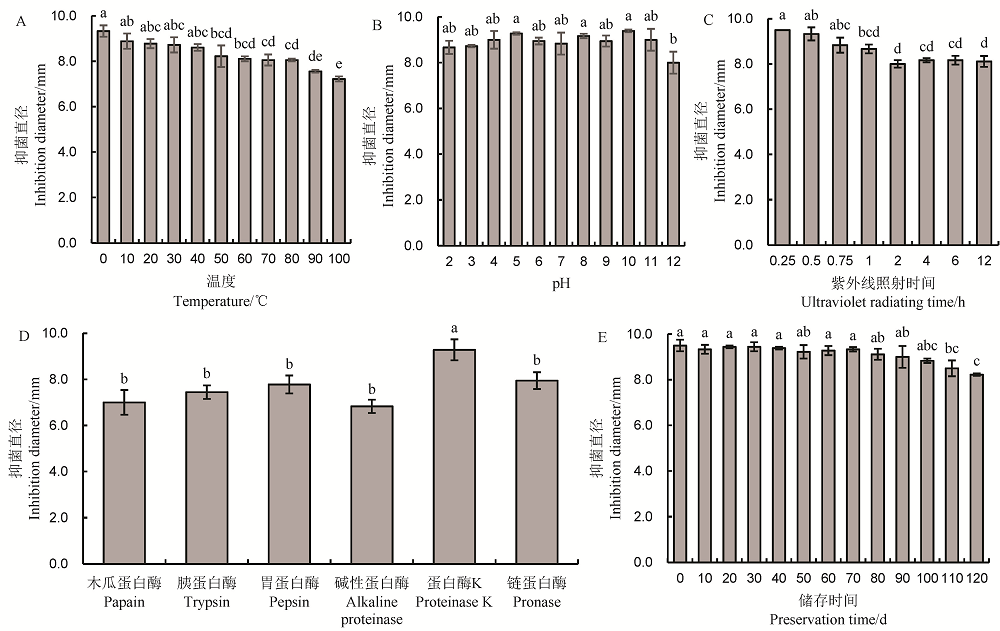
图3 不同处理对JN005菌株胞外抗菌物质抑制稻瘟病菌菌丝生长稳定性的影响
Fig. 3. Effect of different treatments on activity of extracellular antimicrobial substances of JN005 strain against M. oryzae.
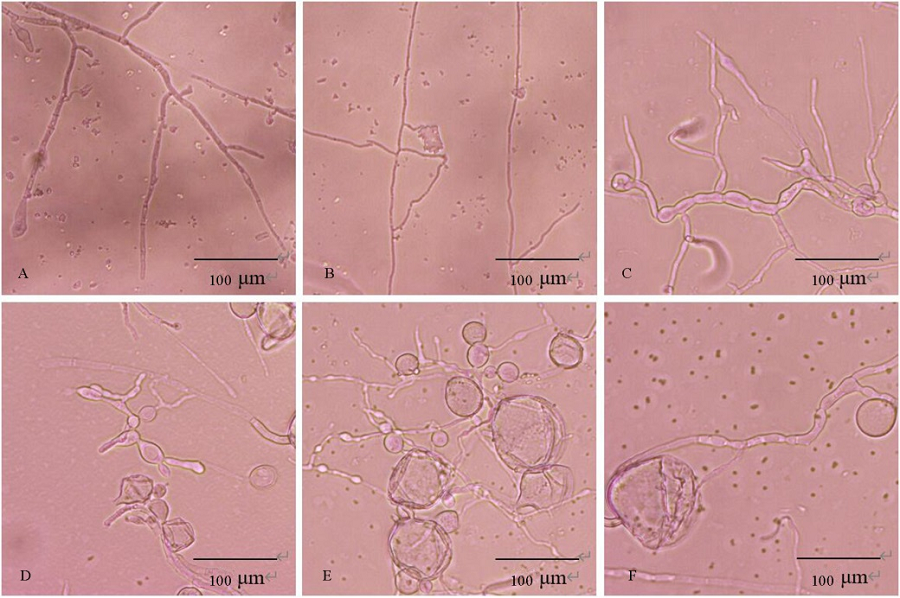
图4 JN005菌株胞外抗菌物质对稻瘟病菌菌丝生长的影响 A为无菌水处理,B为PBS缓冲液处理,C~F为胞外抗菌物质粗提液处理。
Fig. 4. Effect of extracellular antimicrobial substances of JN005 strain on mycelia of M. oryzae. A, Treated with sterile water; B, Treated with PBS buffer; C-F, Treated with crude extract of extracellular antimicrobial substances.
| 处理 Treatment | 稀释倍数 Dilution ratio | 试验组A Test group A | 试验组B Test group B |
|---|---|---|---|
| 发病率 Disease incidence/% | 发病率 Disease incidence/% | ||
| 清水 Water | 0 | 98.5±0.7 a | 97.8±1.3 a |
| PBS缓冲液 PBS buffer | 0 | 97.0±2.0 a | 99.3±0.7 a |
| 40%稻瘟灵乳油 40% isoprothiolane (EC) | 500 | 30.4±3.0 b | 29.6±2.7 c |
| 75%三环唑可湿性粉剂 75% tricyclazole (WP) | 1500 | 20.0±1.3 c | 23.0±1.5 d |
| 胞外抗菌物质粗提液 Extracellular antimicrobial substances crude extract | 100 | 34.1±3.2 b | 38.5±2.7 b |
表1 JN005菌株胞外抗菌物质粗提液对叶瘟的防效(离体接种)
Table 1 Control efficacy of crude extracts of JN005 extracellular antimicrobial substances on leaf blast (indoor detached-leaf inoculation).
| 处理 Treatment | 稀释倍数 Dilution ratio | 试验组A Test group A | 试验组B Test group B |
|---|---|---|---|
| 发病率 Disease incidence/% | 发病率 Disease incidence/% | ||
| 清水 Water | 0 | 98.5±0.7 a | 97.8±1.3 a |
| PBS缓冲液 PBS buffer | 0 | 97.0±2.0 a | 99.3±0.7 a |
| 40%稻瘟灵乳油 40% isoprothiolane (EC) | 500 | 30.4±3.0 b | 29.6±2.7 c |
| 75%三环唑可湿性粉剂 75% tricyclazole (WP) | 1500 | 20.0±1.3 c | 23.0±1.5 d |
| 胞外抗菌物质粗提液 Extracellular antimicrobial substances crude extract | 100 | 34.1±3.2 b | 38.5±2.7 b |
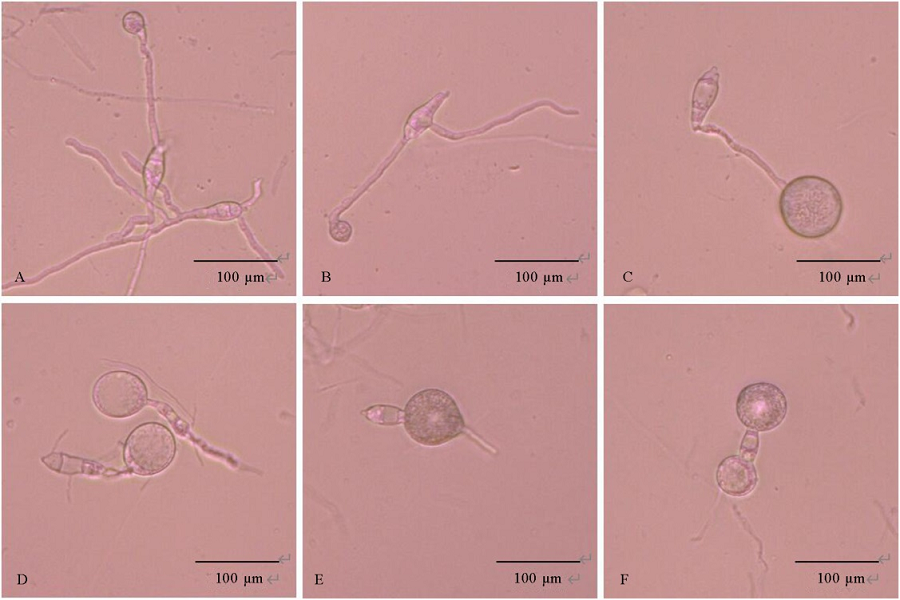
图5 JN005菌株胞外抗菌物质对稻瘟病菌孢子的影响 A为无菌水处理;B为PBS缓冲液处理,C~F为胞外抗菌物质粗提液。
Fig. 5. Effect of extracellular antimicrobial substances of JN005 strain on conidia of M. oryzae. A, Treated with sterile water; B, Treated with PBS buffer; C-F, Treated with crude extract of extracellular antimicrobial substances.
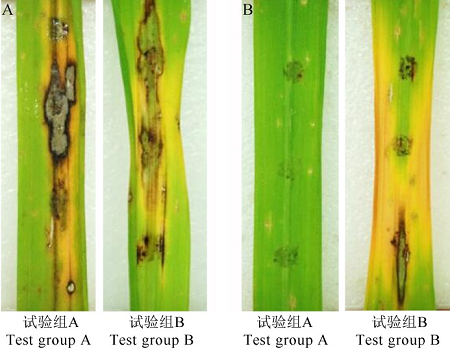
图6 JN005菌株胞外抗菌物质对叶瘟的防治效果(离体接种) A为清水处理;B为胞外抗菌物质处理。
Fig. 6. Control efficacy of extracellular antimicrobial substances on rice leaf blast(indoor detached-leaf inoculation). A, Water treatment; B, Extracellular antimicrobial substances treatment.
| 处理 Treatment | 稀释倍数 Dilution ratio | 试验组C Test group C | 试验组D Test group D | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 发病率 Disease incidence/% | 病情指数 Disease index | 防治效果 Control efficicy/% | 发病率 Disease incidence/% | 病情指数 Disease index | 防治效果 Control efficicy/% | ||
| 清水 Water | 0 | 97.8±1.1 a | 82.1±0.9 a | / | 96.7±1.9 a | 80.3±0.9 a | / |
| PBS缓冲液 PBS buffer | 0 | 94.4±1.1 a | 80.3±0.7 a | 2.2±0.9 d | 95.6±2.9 a | 79.3±0.6 a | 1.2±0.5 c |
| 40%稻瘟灵乳油 | 500 | 35.6±2.9 b | 15.1±0.4 c | 81.7±0.5 b | 37.8±2.9 b | 13.7±0.7 c | 83.0±0.9 a |
| 40% isoprothiolane (EC) | |||||||
| 75%三环唑可湿性粉剂 | 1500 | 25.6±2.9 c | 11.3±0.7 d | 86.3±0.7 a | 27.8±1.1 c | 12.5±0.8 c | 84.4±1.1 a |
| 75% tricyclazole (WP) | |||||||
| 胞外抗菌物质粗提液 | 100 | 40.0±3.3 b | 20.3±1.6 b | 75.3±1.8 c | 43.3±3.9 b | 22.9±0.9 b | 71.5±1.1 b |
| Crude extracts of extracellular antimicrobial substances | |||||||
表2 JN005菌株胞外抗菌物质粗提液对叶瘟的防效(活体接种)
Table 2 Control efficacy of crude extracts of JN005 extracellular antimicrobial substances on leaf blast(indoor live inoculation).
| 处理 Treatment | 稀释倍数 Dilution ratio | 试验组C Test group C | 试验组D Test group D | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 发病率 Disease incidence/% | 病情指数 Disease index | 防治效果 Control efficicy/% | 发病率 Disease incidence/% | 病情指数 Disease index | 防治效果 Control efficicy/% | ||
| 清水 Water | 0 | 97.8±1.1 a | 82.1±0.9 a | / | 96.7±1.9 a | 80.3±0.9 a | / |
| PBS缓冲液 PBS buffer | 0 | 94.4±1.1 a | 80.3±0.7 a | 2.2±0.9 d | 95.6±2.9 a | 79.3±0.6 a | 1.2±0.5 c |
| 40%稻瘟灵乳油 | 500 | 35.6±2.9 b | 15.1±0.4 c | 81.7±0.5 b | 37.8±2.9 b | 13.7±0.7 c | 83.0±0.9 a |
| 40% isoprothiolane (EC) | |||||||
| 75%三环唑可湿性粉剂 | 1500 | 25.6±2.9 c | 11.3±0.7 d | 86.3±0.7 a | 27.8±1.1 c | 12.5±0.8 c | 84.4±1.1 a |
| 75% tricyclazole (WP) | |||||||
| 胞外抗菌物质粗提液 | 100 | 40.0±3.3 b | 20.3±1.6 b | 75.3±1.8 c | 43.3±3.9 b | 22.9±0.9 b | 71.5±1.1 b |
| Crude extracts of extracellular antimicrobial substances | |||||||
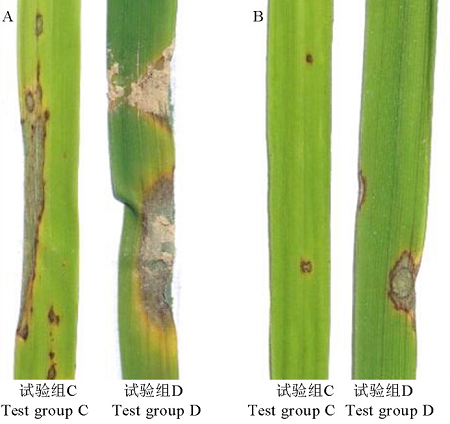

图7 胞外抗菌物质对叶瘟的防效(活体接种) A为清水处理;B为胞外抗菌物质处理。
Fig. 7. Control efficacy of extracellular antimicrobial substances on leaf blast(indoor live inoculation). A, Water treatment; B, Extracellular antimicrobial substances treatment.
| [1] | Guo F F, Chen X L, Lu M H, Yang L, Wang S W, Wu B M.Spatial analysis of rice blast in China at three different scales[J]. Phytopathology, 2018, 108(11): 1276-1286. |
| [2] | Wightwick A, Walters R, Allinson G, Reichman S, Menzies N.Environmental risks of fungicides used in horticultural production systems[J]. Fungicides, 2010: 273-304. |
| [3] | Leadbeater A J.Plant health management: Fungicides and antibiotics. Encyclopedia of Agriculture and Food Systems[J]. 2014: 408-424. |
| [4] | Hollomon D W.Fungicide resistance: Facing the challenge: A review[J]. Plant Protection Science, 2015, 51(4): 170-176. |
| [5] | Barratt B I P, Moran V C, Bigler F, van Lenteren J C. The status of biological control and recommendations for improving uptake for the future[J]. BioControl, 2018, 63(1): 155-167. |
| [6] | Hajek A E, Eilenberg J. Natural enemies: An introduction to biological control[M]. Cambridge University Press, 2018. |
| [7] | Velivelli S L, De Vos P, Kromann P, Declerck S, Prestwich B D.Biological control agents: From field to market, problems, and challenges[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2014, 32(10): 493-496. |
| [8] | Wang X Q, Zhao D L, Shen L L, Jing C L, Zhang C S.Application and mechanisms of Bacillus subtilis in biological control of plant disease[M]//Role of rhizospheric microbes in soil. Singapore: Springer, 2018: 225-250. |
| [9] | 沙月霞. 防治稻瘟病芽胞杆菌的筛选及生防机制研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2016. |
| Sha Y X.Screening of Bacillus strains against rice blast and research of biocontrol mechanism[D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2016. | |
| [10] | Zhang L, Sun C.Fengycins, cyclic lipopeptides from marine Bacillus subtilis strains, kill the plant-pathogenic fungus Magnaporthe oryzae by inducing reactive oxygen species production and chromatin condensation[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2018, 84(18): 1-46. |
| [11] | Sowanpreecha R, Kanchanabanca C, Sangvanich P, Rerngsamran P.Bacillus subtilis N3 as a biocontrol agent for Curvularia lunata and its antifungal protein properties[J]. International Journal of Agriculture and Biology, 2018, 20(3): 531-538. |
| [12] | Rishad K S, Rebello S, Shabanamol P S, Jisha M S.Biocontrol potential of halotolerant bacterial chitinase from high yielding novel Bacillus pumilus MCB-7 autochthonous to mangrove ecosystem[J]. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 2017, 137: 36-41. |
| [13] | 中国农药信息网. 农药登记数据[DB/OL]. , 2019-09-10. |
| China pesticide information network. Pesticide registration data[DB/OL]. , 2019-09-10. | |
| [14] | 刘二明, 任佐华, 管玲莉, 刘敏捷, 周鑫钰. 枯草芽孢杆菌JN005及其在防治水稻稻瘟病中的应用. 中国: 201510426569.9[P].2015-10-14. |
| Liu E M, Ren Z H, Guan L L, Liu M J, Zhou X Y. Bacillus subtilis JN005 and its application in rice blast control. China: 201510426569.9[P].2015-10-14. | |
| [15] | 管玲莉. 水稻稻瘟病生防菌的筛选及其防治效果[D]. 长沙:湖南农业大学, 2016. |
| Guan L L.Screening of biocontrol bacteria and their performance against rice blast[D]. Changsha: Hunan Agricultural University, 2016. | |
| [16] | 周瑚. 湖南稻瘟病菌遗传多样性分析及水稻品种抗瘟基因型推定[D]. 长沙:湖南农业大学, 2017. |
| Zhou H.Genetic diversity analysis of Magnaporthe oryzae and presumption of resistance blast genotypes of rice cultivars in Hunan[D]. Changsha: Hunan Agricultural University, 2017. | |
| [17] | 中华人民共和国农业农村部. 水稻稻瘟病抗性室内离体叶片鉴定技术规程: NY/T 3257—2018[S]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2018: 2-4. |
| Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China. Technical code of practice for wounding inoculation of detached leaves for evaluation of rice resistance to the blast fungus (Magnaporthe oryzae): NY/T 3257-2018[S]. Beijing: China Agricultural Press, 2018: 2-4. | |
| [18] | Jacobsen B J, Zidack N K, Larson B J.The role of Bacillus-based biological control agents in integrated pest management systems: Plant diseases[J]. Phytopathology, 2004, 94(11): 1272-1275. |
| [19] | Yan L, Jing T, Yujun Y, Bin L I, Hui L I, Chun L I.Biocontrol efficiency of Bacillus subtilis SL-13 and characterization of an antifungal chitinase[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2011, 19(1): 128-134. |
| [20] | Mnif I, Grau-Campistany A, Coronel-León J, Hammami I, Triki M A, Manresa A, Ghribi D.Purification and identification of Bacillus subtilis SPB1 lipopeptide biosurfactant exhibiting antifungal activity against Rhizoctonia bataticola and R. solani[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2016, 23(7): 6690-6699. |
| [21] | Yaseen Y, Diop A, Gancel F, Béchet M, Jacques P, Drider D.Polynucleotide phosphorylase is involved in the control of lipopeptide fengycin production in Bacillus subtilis[J]. Archives of Microbiology, 2018: 1-9. |
| [22] | Cruz-Martín M, Mena E, Acosta-Suárez M, Pichardo T, Rodriguez E, Alvarado-Capó Y.Protein compounds of Bacillus subtilis with in vitro antifungal activity against Pseudocercospora fijiensis (Morelet)[J]. Brazilian Journal of Microbiology, 2019: 1-5. |
| [23] | Wang N N, Yan X, Gao X N, Niu H J, Kang Z S, Huang L L.Purification and characterization of a potential antifungal protein from Bacillus subtilis E1R-J against Valsa mali[J]. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2016, 32(4): 63. |
| [24] | 郑小亮, 董超, 牛瑞艳, 齐新月, 孙超, 王星星, 刘超, 贾桂燕, 陈志宝. 枯草芽孢杆菌 Zl-2 抗菌蛋白特性及对小麦赤霉病菌的抑制作用[J]. 黑龙江大学自然科学学报, 2018, 35(2): 206-211. |
| Zheng X L, Dong C, Niu R Y, Qi X Y, Sun C, Wang X X, Liu C, Jia G Y, Chen Z B.Characterization and inhibition effects of antifungal protein from Bacillus subtilis Zl-2[J]. Journal of Natural Science of Heilongjiang University, 2018, 35(2): 206-211. | |
| [25] | 黄华毅, 黄咏槐, 黄焕华, 梁英梅, 田呈明. 枯草芽孢杆菌 STO-12 脂肽类物质抑菌活性及其特性分析[J]. 广东林业科技, 2018 (4): 8-14. |
| Huang H Y, Huang Y H, Huang H H, Liang Y M, Tian C M.Antifungal activities and characterization of lipopeptides produced by Bacillus subtilis STO-12[J]. Forestry and Environmental Science, 2018 (4): 8-14. | |
| [26] | 张晓云. 枯草芽孢杆菌菌株 CAB-1 抑菌物质的分离鉴定及活性分析[D]. 石家庄河北农业大学, 2011. |
| Zhang X Y.Isolation and analysis of antifungal compounds produced by Bacillus subtilis CAB-1[D]. Shijiazhuang: Agricultural University of Hebei, 2011. | |
| [27] | Yan L, Jing T, Yujun Y, Bin L I, Hui L I, Chun L I.Biocontrol efficiency of Bacillus subtilis SL-13 and characterization of an antifungal chitinase[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2011, 19(1): 128-134. |
| [28] | 吴艳清, 王游游, 王畅, 沙梦莹. 枯草芽孢杆菌 WL2 脂肽粗提物对致病疫霉的抑制作用及其分离鉴定[J]. 河北大学学报: 自然科学版, 2018, 38(6): 632-639. |
| Wu Y Q, Wang Y Y, Wang C, Sha M Y.Inhibitory effect of lipopeptide crude extract produced by Bacillus subtilis WL2 on Phytophthora infestans and its isolation and identification[J]. Journal of Hebei University: Natural Science Edition, 2018, 38(6): 632-639. | |
| [29] | 黄娜. 枯草芽孢杆菌粗蛋白的提取纯化及抑菌作用[D]. 合肥: 安徽农业大学, 2015. |
| Huang N.Extraction and purification of crude protein from Bacillus subtilis against pathogenic fungus[D]. Hefei: Anhui Agricultural University, 2015. | |
| [30] | Yamaguchi I.Overview on the chemical control of rice blast disease[M]//Rice Blast: Interaction with Rice and Control. Dordrecht: Springer, 2004: 1-13. |
| [31] | Cawoy H, Bettiol W, Fickers P, Ongena M.Bacillus -based biological control of plant diseases[M] //Margarita S. Pesticides in the Modern World-pesticides Use and Management. Rieka, Croatia: InTech, 2011. |
| [1] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [2] | 童琪, 王春燕, 阙亚伟, 肖宇, 王政逸. 稻瘟病菌热激蛋白(HSP)40编码基因MoMHF6的鉴定及功能研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(6): 563-576. |
| [3] | 陈明亮, 熊文涛, 沈雨民, 熊焕金, 罗世友, 吴小燕, 胡兰香, 肖叶青. 广谱抗稻瘟病水稻保持系赣香B的抗性遗传解析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(5): 470-477. |
| [4] | 李刚, 高清松, 李伟, 张雯霞, 王健, 程保山, 王迪, 高浩, 徐卫军, 陈红旗, 纪剑辉. 定向敲除SD1基因提高水稻的抗倒性和稻瘟病抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(4): 359-367. |
| [5] | 王雨, 孙全翌, 杜海波, 许志文, 吴科霆, 尹力, 冯志明, 胡珂鸣, 陈宗祥, 左示敏. 利用抗稻瘟病基因Pigm和抗纹枯病数量性状基因qSB-9TQ、qSB-11HJX改良南粳9108的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(2): 125-132. |
| [6] | 周永林, 申小磊, 周立帅, 林巧霞, 王朝露, 陈静, 冯慧捷, 张振文, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsLOX10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(4): 348-356. |
| [7] | 陈奕璇, 覃贵亮, 周晓欣, 黄军军, 蒙全, 吴俊辉, 闫晓静, 袁会珠. 不同植保机械喷施雾滴在水稻冠层沉积分布规律及对病虫害防效比较[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(2): 207-214. |
| [8] | 曹煜东, 肖湘谊, 叶乃忠, 丁晓雯, 易晓璇, 刘金灵, 肖应辉. 生长素调控因子OsGRF4协同调控水稻粒形和稻瘟病抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(6): 629-638. |
| [9] | 刘树芳, 董丽英, 李迅东, 周伍民, 杨勤忠. 持有Pi9基因的水稻单基因系IRBL9-W对稻瘟病菌苗期和成株期抗性差异[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(3): 303-310. |
| [10] | 许赵蒙, 李利华, 高晓庆, 袁正杰, 李莘, 田旭丹, 王岚岚, 瞿绍洪. 转Pi9抗稻瘟病基因水稻株系的比较转录组分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(3): 245-255. |
| [11] | 孟峰, 张亚玲, 靳学慧. 黑龙江省稻瘟病菌无毒基因AVR-Pita及其同源基因的检测与分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(2): 143-149. |
| [12] | 李金璐, 张慧, 焦泽宇, 刘剑宇, 韩光煜, 卓晓轩, 罗琼. 水稻子预44和江南香糯基因组比较鉴定稻瘟病抗性相关基因[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(1): 8-16. |
| [13] | 陈涛, 孙旭超, 张善磊, 梁文化, 周丽慧, 赵庆勇, 姚姝, 赵凌, 赵春芳, 朱镇, 张亚东, 王才林. 稻瘟病广谱抗性基因Pigm特异性分子标记的开发和应用[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(1): 28-36. |
| [14] | 曹妮, 陈渊, 季芝娟, 曾宇翔, 杨长登, 梁燕. 水稻抗稻瘟病分子机制研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(6): 489-498. |
| [15] | 徐鹏, 王宏, 涂燃冉, 刘群恩, 吴玮勋, 傅秀民, 曹立勇, 沈希宏. 利用CRISPR/Cas9系统定向改良水稻稻瘟病抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(4): 313-322. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||