
中国水稻科学 ›› 2020, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (3): 217-227.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2020.9120
姚姝1, 张亚东1, 刘燕清1, 赵春芳1, 周丽慧1, 陈涛1, 赵庆勇1, 朱镇1, Balakrishna PILLAY2,*, 王才林1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2019-11-24
修回日期:2020-02-05
出版日期:2020-05-15
发布日期:2020-05-10
通讯作者:
Balakrishna PILLAY,王才林
基金资助:
Shu YAO1, Yadong ZHANG1, Yanqing LIU1, Chunfang ZHAO1, Lihui ZHOU1, Tao CHEN1, Qingyong ZHAO1, Zhen ZHU1, PILLAY Balakrishna2,*, Cailin WANG1,*( )
)
Received:2019-11-24
Revised:2020-02-05
Online:2020-05-15
Published:2020-05-10
Contact:
PILLAY Balakrishna, Cailin WANG
摘要:
【目的】分析在同一主效基因(Wxmp)背景下可溶性淀粉合成酶基因SSⅡa和去分支酶基因PUL对稻米蒸煮食味品质的影响,以期为水稻品质遗传改良提供依据。【方法】选择在SSⅡa和PUL存在多态性而其他淀粉合成酶相关基因没有多态性的半糯品系宁0145和粳稻品种武运粳21进行杂交,获得F2群体与F3株系。利用分子标记,选择含有Wxmp基因的F2单株与F3株系,将这些F2单株与F3株系分成SSⅡanPULn、SSⅡanPULw、SSⅡawPULn和SSⅡawPULw4种基因型(n和w分别表示该基因来源于宁0145和武运粳21),分析不同基因型蒸煮食味品质性状的差异,探讨同一Wxmp基因背景下不同SSⅡa和PUL等位基因对蒸煮食味品质性状的影响。【结果】不同基因型间蒸煮食味品质性状均存在显著差异,来源于武运粳21的SSⅡaw基因和PULw基因分别使直链淀粉含量增加0.29%~1.00%和0.62%~1.18%,且PUL的效应大于SSⅡa,两者间存在互作效应。SSⅡaw基因和PULw基因降低胶稠度和崩解值,提高了热浆黏度、冷胶黏度、消减值和回复值,对糊化温度、峰值黏度和峰值时间的作用较小。【结论】明确了Wxmp背景下SSⅡa和PUL基因对稻米蒸煮食味品质的遗传效应,该研究结果为SSⅡa和PUL基因的分子标记辅助选择改良稻米品质提供了理论依据。
中图分类号:
姚姝, 张亚东, 刘燕清, 赵春芳, 周丽慧, 陈涛, 赵庆勇, 朱镇, Balakrishna PILLAY, 王才林. Wxmp基因背景下可溶性淀粉合成酶基因SSⅡa和去分支酶基因PUL对水稻蒸煮食味品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(3): 217-227.
Shu YAO, Yadong ZHANG, Yanqing LIU, Chunfang ZHAO, Lihui ZHOU, Tao CHEN, Qingyong ZHAO, Zhen ZHU, PILLAY Balakrishna, Cailin WANG. Allelic Effects on Eating and Cooking Quality of SSⅡa and PUL Genes Under Wxmp Background in Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2020, 34(3): 217-227.
| 基因 Gene | 引物序列 Primer sequence(5′-3′) | 产物大小 Product size/bp | 退火温度 Annealing temperature/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wxmp | O-F: ATGTTGTGTTCTTGTGTTCTTTGCAGGC | 439/200 | 65 |
| O-R: GTAGATCTTCTCACCGGTCTTTCCCCAA | |||
| I-F: GGGTGAGGTTTTTCCATTGCTACAATCG | 439/292 | 65 | |
| I-R: GTCGATGAACACACGGTCGACTCAAT | |||
| SSIIa(Y12) | F: CCAATACCGTAAACTAGCGACTATG | 90/81 | 55 |
| R: TACAGGTAGAATGGCAGTGGTG | |||
| PUL(Y38) | F: AGTTCGCTAGTCATCTGCTCG | 198/194 | 55 |
| R: CCACATGTCCTTGTCTCCACTT |
表1 试验使用的Wxmp、SSIIa和PUL基因分子标记
Table 1 Molecular markers of Wxmp, SSIIa and PUL genes used in this study.
| 基因 Gene | 引物序列 Primer sequence(5′-3′) | 产物大小 Product size/bp | 退火温度 Annealing temperature/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wxmp | O-F: ATGTTGTGTTCTTGTGTTCTTTGCAGGC | 439/200 | 65 |
| O-R: GTAGATCTTCTCACCGGTCTTTCCCCAA | |||
| I-F: GGGTGAGGTTTTTCCATTGCTACAATCG | 439/292 | 65 | |
| I-R: GTCGATGAACACACGGTCGACTCAAT | |||
| SSIIa(Y12) | F: CCAATACCGTAAACTAGCGACTATG | 90/81 | 55 |
| R: TACAGGTAGAATGGCAGTGGTG | |||
| PUL(Y38) | F: AGTTCGCTAGTCATCTGCTCG | 198/194 | 55 |
| R: CCACATGTCCTTGTCTCCACTT |
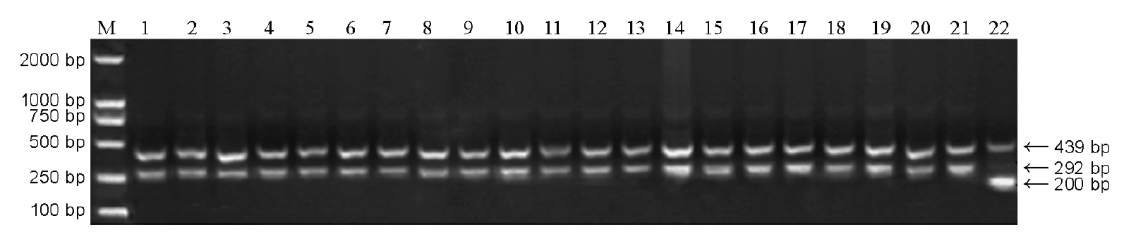
图1 F3半糯品系中Wxmp基因的检测M-DL 2000标记;泳道1~20:部分半糯单株;泳道21-宁0145;泳道22-武运粳21。
Fig. 1. Detection of the Wxmp gene in semi-glutinous F3 lines. M, DL 2000 marker;Lanes 1 to 20, Part of the semi-glutinous plants; Lane 21, Ning 0145; Lane 22, Wuyunjing 21.
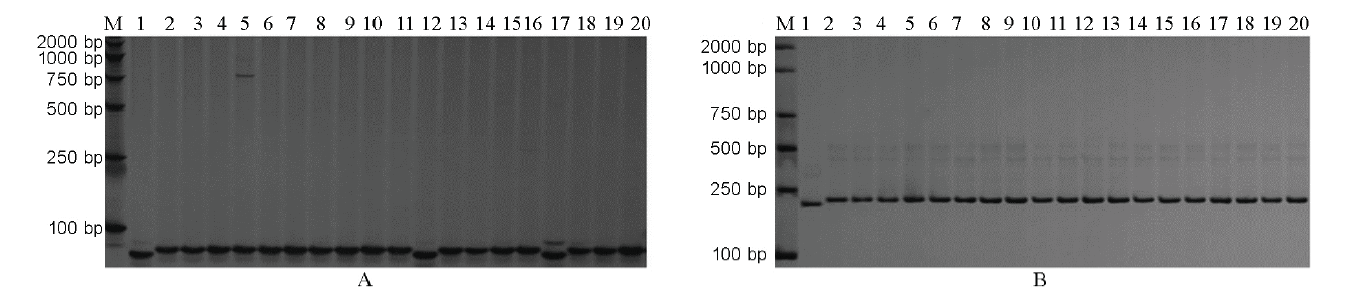
图2 F2代SSIIa(A)和PUL(B)基因的检测M-DL 2000标记;泳道1-武运粳21;泳道2-宁0145;泳道3~20-部分F2代。
Fig. 2. Detection of SSIIa(A) and PUL(B) genes in F2 population. M, DL 2000 marker; Lane 1, Wuyunjing 21; Lane 2, Ning 0145; Lanes 3 to 20, Part of F2 population.
| 基因型 Genotype | F2单株数 No. of F2 plants | F3株系数 No. of F3 lines | 基因型 Genotype | F2单株数 No. of F2 plants | F3株系数 No. of F3 lines |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSⅡanSSⅡan | 63 | 40 | SSⅡanPULn | 46 | 20 |
| SSⅡawSSⅡaw | 12 | 51 | SSⅡanPULw | 17 | 20 |
| PULnPULn | 53 | 41 | SSⅡawPULn | 7 | 21 |
| PULwPULw | 22 | 50 | SSⅡawPULw | 5 | 30 |
表2 来源于宁0145/武运粳21的75个F2单株和91个F3株系SSIIa和PUL位点的基因型
Table 2 Genotypes of SSIIa and PUL locus for 75 F2 plants and 91 F3 lines derived from Ning 0145/Wuyunjing 21 with Wxmp.
| 基因型 Genotype | F2单株数 No. of F2 plants | F3株系数 No. of F3 lines | 基因型 Genotype | F2单株数 No. of F2 plants | F3株系数 No. of F3 lines |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSⅡanSSⅡan | 63 | 40 | SSⅡanPULn | 46 | 20 |
| SSⅡawSSⅡaw | 12 | 51 | SSⅡanPULw | 17 | 20 |
| PULnPULn | 53 | 41 | SSⅡawPULn | 7 | 21 |
| PULwPULw | 22 | 50 | SSⅡawPULw | 5 | 30 |
| 变异来源 Source of variation | 自由度 df | 平方和 SS | 均方 MS | F值 F value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 重复 Repeat | 1 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.23 |
| F2单株间 Among F2 plants | 30 | 61.20 | 2.04 | 5.22** |
| 基因型间 Among genotypes | 3 | 50.64 | 16.88 | 35.54** |
| 基因型内 Within genotypes | 27 | 10.56 | 0.39 | 0.82 |
| 误差 Error | 30 | 14.25 | 0.48 | |
| 总变异 Total variation | 61 | 75.56 |
表3 31个F2单株直链淀粉含量的方差分析
Table 3 ANOVA of the amylose content in 31 F2 plants.
| 变异来源 Source of variation | 自由度 df | 平方和 SS | 均方 MS | F值 F value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 重复 Repeat | 1 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.23 |
| F2单株间 Among F2 plants | 30 | 61.20 | 2.04 | 5.22** |
| 基因型间 Among genotypes | 3 | 50.64 | 16.88 | 35.54** |
| 基因型内 Within genotypes | 27 | 10.56 | 0.39 | 0.82 |
| 误差 Error | 30 | 14.25 | 0.48 | |
| 总变异 Total variation | 61 | 75.56 |
| 参数 Parameter | 直链淀粉含量AC/% | 胶稠度GC/mm | 糊化温度GT/℃ | 峰值黏度PV/cP | 热浆黏度HPV/cP | 崩解值BDV/cP | 冷胶黏度CPV/cP | 消减值SBV/cP | 回复值CSV/cP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最小值 Min | 9.12 | 28.00 | 70.00 | 2445 | 1086 | 1109 | 1712 | -1214 | 626 |
| 最大值 Max | 12.69 | 103.50 | 76.10 | 4124 | 2312 | 2092 | 3356 | 11 | 1403 |
| 平均 Mean | 10.42 | 53.55 | 72.84 | 3366 | 1834 | 1532 | 2831 | -535 | 997 |
| 标准差 SD | 0.72 | 16.61 | 1.15 | 312.17 | 228.52 | 219.69 | 282.26 | 306.53 | 153.78 |
| 变异系数 CV/% | 6.92 | 31.02 | 1.58 | 9.27 | 12.46 | 14.34 | 9.97 | -57.31 | 15.42 |
表4 91个F3株系蒸煮食味品质性状的统计参数
Table 4 Statistical parameters of eating and cooking quality traits for 91 F3 lines.
| 参数 Parameter | 直链淀粉含量AC/% | 胶稠度GC/mm | 糊化温度GT/℃ | 峰值黏度PV/cP | 热浆黏度HPV/cP | 崩解值BDV/cP | 冷胶黏度CPV/cP | 消减值SBV/cP | 回复值CSV/cP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最小值 Min | 9.12 | 28.00 | 70.00 | 2445 | 1086 | 1109 | 1712 | -1214 | 626 |
| 最大值 Max | 12.69 | 103.50 | 76.10 | 4124 | 2312 | 2092 | 3356 | 11 | 1403 |
| 平均 Mean | 10.42 | 53.55 | 72.84 | 3366 | 1834 | 1532 | 2831 | -535 | 997 |
| 标准差 SD | 0.72 | 16.61 | 1.15 | 312.17 | 228.52 | 219.69 | 282.26 | 306.53 | 153.78 |
| 变异系数 CV/% | 6.92 | 31.02 | 1.58 | 9.27 | 12.46 | 14.34 | 9.97 | -57.31 | 15.42 |
| 变异来源 Source of variation | 自由度df | 直链淀粉含量AC | 胶稠度GC | 糊化温度GT | 峰值黏度PV | 热浆黏度HPV | 崩解值BDV | 冷胶黏度CPV | 消减值SBV | 回复值CSV | 峰值时间Peak time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 重复 | 1 | 2.34* | 3.12* | 1.05 | 2.18 | 1.48 | 1.95 | 1.67 | 2.16 | 2.41* | 0.92 |
| Repeat | |||||||||||
| F3株系间 | 90 | 3.60** | 90.81** | 1.07** | 97.74** | 101.90** | 124.92** | 73.51** | 90.80** | 79.48** | 1.43 |
| Among F3 plants | |||||||||||
| 基因型间 | 3 | 76.17** | 2682.83** | 2.98** | 1740.20** | 2290.05** | 2445.70** | 1627.99** | 1844.13** | 1739.01** | 2.33 |
| Among genotypes | |||||||||||
| 基因型内 | 87 | 1.09** | 1.43* | 1.00** | 41.10** | 26.45** | 44.90** | 19.91** | 30.34** | 22.25** | 1.39 |
| Within genotypes | |||||||||||
| 误差 | 90 | 0.58 | 0.98 | 0.53 | 0.76 | 0.48 | 0.63 | 0.68 | 0.44 | 0.54 | 2.83 |
| Error | |||||||||||
表5 91个F3株系蒸煮食味品质性状的方差分析
Table 5 ANOVA of the eating and cooking quality traits in 91 F3 lines.
| 变异来源 Source of variation | 自由度df | 直链淀粉含量AC | 胶稠度GC | 糊化温度GT | 峰值黏度PV | 热浆黏度HPV | 崩解值BDV | 冷胶黏度CPV | 消减值SBV | 回复值CSV | 峰值时间Peak time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 重复 | 1 | 2.34* | 3.12* | 1.05 | 2.18 | 1.48 | 1.95 | 1.67 | 2.16 | 2.41* | 0.92 |
| Repeat | |||||||||||
| F3株系间 | 90 | 3.60** | 90.81** | 1.07** | 97.74** | 101.90** | 124.92** | 73.51** | 90.80** | 79.48** | 1.43 |
| Among F3 plants | |||||||||||
| 基因型间 | 3 | 76.17** | 2682.83** | 2.98** | 1740.20** | 2290.05** | 2445.70** | 1627.99** | 1844.13** | 1739.01** | 2.33 |
| Among genotypes | |||||||||||
| 基因型内 | 87 | 1.09** | 1.43* | 1.00** | 41.10** | 26.45** | 44.90** | 19.91** | 30.34** | 22.25** | 1.39 |
| Within genotypes | |||||||||||
| 误差 | 90 | 0.58 | 0.98 | 0.53 | 0.76 | 0.48 | 0.63 | 0.68 | 0.44 | 0.54 | 2.83 |
| Error | |||||||||||
| 基因型 Genotype | F2株数 No. of F2 plants | F2直链淀粉含量AC in F2/% | F3 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 株系数 No. of lines | 直链淀粉含量AC/% | 胶稠度GC/mm | 糊化温度GT/℃ | 峰值黏度PV/cP | 热浆黏度HPV/cP | 崩解值BDV/cP | 冷胶黏度CPV/cP | 消减值SBV/cP | 回复值CSV/cP | 峰值时间Peak time /min | |||
| SSIIan | 19 | 9.60 | 40 | 10.26 | 55.11 | 72.77 | 3365 | 1817 | 1548 | 2794 | -571 | 977 | 6.13 |
| SSIIaw | 12 | 10.61 | 51 | 10.55 | 52.32 | 72.89 | 3367 | 1848 | 1519 | 2860 | -507 | 1013 | 6.20 |
| PULn | 17 | 9.46 | 41 | 10.08 | 53.72 | 72.87 | 3356 | 1785 | 1570 | 2754 | -602 | 968 | 6.12 |
| PULw | 14 | 10.64 | 50 | 10.70 | 53.41 | 72.81 | 3375 | 1875 | 1500 | 2895 | -479 | 1021 | 6.21 |
| SSIIanPULn | 10 | 8.70 | 20 | 10.08 | 58.23 | 73.09 | 3387 | 1807 | 1580 | 2737 | -650 | 930 | 6.09 |
| SSIIanPULw | 9 | 10.60 | 20 | 10.44 | 52.00 | 72.45 | 3343 | 1828 | 1515 | 2852 | -491 | 1024 | 6.16 |
| SSIIawPULn | 7 | 10.54 | 21 | 10.09 | 49.43 | 72.66 | 3327 | 1765 | 1562 | 2769 | -557 | 1004 | 6.14 |
| SSIIawPULw | 5 | 10.70 | 30 | 10.88 | 54.35 | 73.05 | 3396 | 1906 | 1490 | 2924 | -471 | 1019 | 6.25 |
表6 F2和F3不同基因型的蒸煮食味品质性状
Table 6 Eating and cooking quality traits for different genotypes of SSIIa and PUL in 31 F2 plants and 91 F3 lines.
| 基因型 Genotype | F2株数 No. of F2 plants | F2直链淀粉含量AC in F2/% | F3 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 株系数 No. of lines | 直链淀粉含量AC/% | 胶稠度GC/mm | 糊化温度GT/℃ | 峰值黏度PV/cP | 热浆黏度HPV/cP | 崩解值BDV/cP | 冷胶黏度CPV/cP | 消减值SBV/cP | 回复值CSV/cP | 峰值时间Peak time /min | |||
| SSIIan | 19 | 9.60 | 40 | 10.26 | 55.11 | 72.77 | 3365 | 1817 | 1548 | 2794 | -571 | 977 | 6.13 |
| SSIIaw | 12 | 10.61 | 51 | 10.55 | 52.32 | 72.89 | 3367 | 1848 | 1519 | 2860 | -507 | 1013 | 6.20 |
| PULn | 17 | 9.46 | 41 | 10.08 | 53.72 | 72.87 | 3356 | 1785 | 1570 | 2754 | -602 | 968 | 6.12 |
| PULw | 14 | 10.64 | 50 | 10.70 | 53.41 | 72.81 | 3375 | 1875 | 1500 | 2895 | -479 | 1021 | 6.21 |
| SSIIanPULn | 10 | 8.70 | 20 | 10.08 | 58.23 | 73.09 | 3387 | 1807 | 1580 | 2737 | -650 | 930 | 6.09 |
| SSIIanPULw | 9 | 10.60 | 20 | 10.44 | 52.00 | 72.45 | 3343 | 1828 | 1515 | 2852 | -491 | 1024 | 6.16 |
| SSIIawPULn | 7 | 10.54 | 21 | 10.09 | 49.43 | 72.66 | 3327 | 1765 | 1562 | 2769 | -557 | 1004 | 6.14 |
| SSIIawPULw | 5 | 10.70 | 30 | 10.88 | 54.35 | 73.05 | 3396 | 1906 | 1490 | 2924 | -471 | 1019 | 6.25 |
| 基因型 Genotype | F2直链淀粉含量 AC of F2/% | F3直链 淀粉含量 AC of F3/% | 胶稠度GC /mm | 糊化 温度GT/℃ | 峰值 黏度PV /cP | 热浆 黏度HPV /cP | 崩解值BDV /cP | 冷胶 黏度CPV /cP | 消减值SBV /cP | 回复值CSV /cP | 峰值时间Peak time /min |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSIIaw-SSIIan | 1.01 | 0.29 | -2.79 | 0.12 | 2 | 30 | -28 | 66 | 64 | 36 | 0.07 |
| PULw-PULn | 1.18 | 0.62 | -0.31 | -0.06 | 19 | 89 | -70 | 142 | 123 | 53 | 0.10 |
| SSIIanPULw-SSIIanPULn | 1.90 | 0.35 | -6.23 | -0.64 | -44 | 21 | -65 | 115 | 158 | 94 | 0.07 |
| SSIIawPULn-SSIIanPULn | 1.83 | 0.01 | -8.80 | -0.43 | -60 | -42 | -18 | 33 | 93 | 74 | 0.05 |
| SSIIawPULw-SSIIawPULn | 0.16 | 0.79 | 4.92 | 0.39 | 69 | 140 | -72 | 155 | 86 | 14 | 0.11 |
| SSIIawPULw-SSIIanPULw | 0.10 | 0.44 | 2.35 | 0.60 | 52 | 77 | -25 | 72 | 20 | -5 | 0.08 |
| SSIIawPULw-SSIIanPULn | 2.00 | 0.80 | -3.88 | -0.04 | 9 | 99 | -90 | 187 | 178 | 89 | 0.15 |
表7 SSIIa和PUL等位基因对蒸煮食味品质性状的影响
Table 7 Allelic effects of SSIIa and PUL locus originated from different parents on eating and cooking quality traits.
| 基因型 Genotype | F2直链淀粉含量 AC of F2/% | F3直链 淀粉含量 AC of F3/% | 胶稠度GC /mm | 糊化 温度GT/℃ | 峰值 黏度PV /cP | 热浆 黏度HPV /cP | 崩解值BDV /cP | 冷胶 黏度CPV /cP | 消减值SBV /cP | 回复值CSV /cP | 峰值时间Peak time /min |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSIIaw-SSIIan | 1.01 | 0.29 | -2.79 | 0.12 | 2 | 30 | -28 | 66 | 64 | 36 | 0.07 |
| PULw-PULn | 1.18 | 0.62 | -0.31 | -0.06 | 19 | 89 | -70 | 142 | 123 | 53 | 0.10 |
| SSIIanPULw-SSIIanPULn | 1.90 | 0.35 | -6.23 | -0.64 | -44 | 21 | -65 | 115 | 158 | 94 | 0.07 |
| SSIIawPULn-SSIIanPULn | 1.83 | 0.01 | -8.80 | -0.43 | -60 | -42 | -18 | 33 | 93 | 74 | 0.05 |
| SSIIawPULw-SSIIawPULn | 0.16 | 0.79 | 4.92 | 0.39 | 69 | 140 | -72 | 155 | 86 | 14 | 0.11 |
| SSIIawPULw-SSIIanPULw | 0.10 | 0.44 | 2.35 | 0.60 | 52 | 77 | -25 | 72 | 20 | -5 | 0.08 |
| SSIIawPULw-SSIIanPULn | 2.00 | 0.80 | -3.88 | -0.04 | 9 | 99 | -90 | 187 | 178 | 89 | 0.15 |
| [1] | Zeng D L, Tian Z X, Rao Y C, Dong G J, Yang Y L, Huang L C, Leng Y J, Xu J, Sun C, Zhang G H, Gao Z Y, Hu X M, Guo L B, Xiong G S, Wang Y H, Li J Y, Qian Q.Rational design of high-yield and superior-quality rice[J/OL].Nature Plants, 2017, 3: 17031. |
| [2] | 严长杰, 田舜, 张正球, 韩月澎, 陈峰, 李欣, 顾铭洪. 水稻栽培品种淀粉合成相关基因来源及其对品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2005, 39(5): 865-871. |
| Yan C J, Tian X, Zhang Z Q, Han Y P, Chen F, Li X, Gu M H.The source of genes related to rice grain starch synthesis among cultivated varieties and its contribution to quality[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2005, 39(5): 865-871. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | Vandeputte G E, Delcour J A.From sucrose to starch granule to starch physical behavior: A focus on rice starch[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2004, 58: 245-266. |
| [4] | 张昌泉, 赵冬生, 李钱峰, 顾铭洪, 刘巧泉. 稻米品质性状基因的克隆与功能研究进展[J]. 中国农业科学, 2016, 49(22): 4267-4283. |
| Zhang C Q, Zhao D S, Li Q F, Gu M H, Liu Q Q.Progresses in research on cloning and functional analysis of key genes involving in rice grain quality[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2016, 49(22): 4267-4283. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | Li K H, Bao J S, Corke H, Sun M. Genotypic diversity and environmental stability of starch physicochemical properties in the USDA rice mini-core collection[J]. Food Chemistry, 2017, 221: 1186-1196. |
| [6] | 黄祖六, 许如根, 陈德辉, 陈勇. 中泰软米资源直链淀粉含量的遗传研究[J]. 扬州大学学报: 农业与生命科学版, 2003, 24(1): 34-36. |
| Huang Z L, Xu R G, Chen D H, Chen Y.Research on inheritance for amylose content of soft rice from China and Thailand[J]. Journal of Yangzhou University: Agriculture and Life Science Edition, 2003, 24(1): 34-36. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | Suto M, Ando I, Numaguchi K.Breeding of low amylose content paddy rice variety Milk Queen with good eating quality[J]. Japan Breeding, 1996, 46(1): 221-224. |
| [8] | 赵春芳, 岳红亮, 黄双杰, 周丽慧, 赵凌, 张亚东, 陈涛, 朱镇, 赵庆勇, 姚姝, 梁文化, 路凯, 王才林. 南粳系列水稻品种的食味品质与稻米理化特性[J]. 中国农业科学, 2019, 52(5): 909-920. |
| Zhao C F, Yue H L, Huang S J, Zhou L H, Zhao L, Zhang Y D, Chen T, Zhu Z, Zhao Q Y, Yao S, Liang W H, Lu K, Wang C L.Study on eating quality and physicochemical properties in Nanjing rice varieties[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2019, 52(5): 909-920. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | Sato H, Suzuki Y, Okuno K, Hirano H, Imbe T.Genetic analysis of low amylose content in a rice variety, Milky Queen[J]. Japan Breeding Research, 2001, 3(1): 13-19. |
| [10] | Tomita K, Horiuchi H, Terada K.New-hikari, a new rice cultivar[J]. Bulletin of the Fukui Agricultural Experiment Station, 2007, 44(6): 1-20. |
| [11] | 王才林, 陈涛, 张亚东, 朱镇, 赵凌, 林静. 通过分子标记辅助选择培育优良食味水稻新品种[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2009, 23(1): 25-30. |
| Wang C L, Chen T, Zhang Y D, Zhu Z, Zhao L, Lin J.Breeding of a new rice variety with good eating quality by marker assisted selection[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2009, 23(1): 25-30. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 王才林, 张亚东, 朱镇, 陈涛, 赵庆勇, 赵凌, 周丽慧, 姚姝. 优良食味粳稻新品种南粳5055的选育及利用[J]. 农业科技通讯, 2012(2): 84-87. |
| Wang C L, Zhang Y D, Zhu Z, Chen T, Zhao Q Y, Zhao L, Zhou L H, Yao S, Breeding and application of new good eating quality rice variety Nanjing5055[J]. Bulletin of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2012(2): 84-87. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | 王才林, 张亚东, 朱镇, 姚姝, 赵庆勇, 陈涛, 周丽慧, 赵凌. 优良食味粳稻新品种南粳9108的选育与利用[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2013, 41(9): 86-88. |
| Wang C L, Zhang Y D, Zhu Z, Yao S, Zhao Q Y, Chen T, Zhou L H, Zhao L.Breeding and application of new good eating quality rice variety Nanjing 9108[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2013, 41(9): 86-88. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | 陈涛, 张亚东, 赵庆勇, 朱镇, 姚姝, 周丽慧, 赵凌, 赵春芳, 王波, 王才林. 优良食味抗病高产晚粳稻新品种南粳3908的选育和栽培技术[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2019, 47(19): 72-74. |
| Chen T, Zhang Y D, Zhao Q Y, Zhu Z, Yao S, Zhou L H, Zhao L, Zhao C F, Wang B, Wang C L.Breeding and cultivation technique of a new japonica rice variety Nanjing 3908 with good eating quality, resistant diseases and high yield[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 47(19): 72-74. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 于新, 赵庆勇, 赵春芳, 张亚东, 朱镇, 赵凌, 陈涛, 周丽慧, 姚姝, 王才林. 携带Wx-mq基因的不同类型水稻新品种(系)直链淀粉含量分析[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2012, 28(6): 1218-1222. |
| Yu X, Zhao Q Y, Zhao C F, Zhang Y D, Zhu Z, Zhao L, Chen T, Zhou L H, Yao S, Wang C L.Analysis of amylose content in different types of new rice varieties (lines) carrying Wx-mq gene[J]. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2012, 28(6): 1218-1222. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 姚姝, 于新, 周丽慧, 陈涛, 赵庆勇, 朱镇, 张亚东, 赵春芳, 赵凌, 王才林. 氮肥用量和播期对优良食味粳稻直链淀粉含量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2016, 30(5): 535-549. |
| Yao S, Yu X, Zhou L H, Chen T, Zhao Q Y, Zhu Z, Zhang Y D, Zhao C F, Zhao L, Wang C L.Effects of nitrogen and sowing date on amylose content in good eating quality rice (Oryza sativa L. japonica)[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2016, 30(5): 535-549. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | Gomez K A.Effect of environment on protein and amylose content of rice[C]//Proceedings of the Workshop on Chemical Aspects of Rice Grain Quality. Philippines: International Rice Research Institute, 1979: 59-68. |
| [18] | Sato H.Genetics and breeding of high eating quality rice: Status and perspectives on the researches of low amylose content rice[J]. Japan Agriculture and Horticulture, 2002, 77(5): 20-28. |
| [19] | Umemoto T, Yano M, Satoh H, Shomura A, Nakamura Y, Mapping of a gene responsible for the difference in amylopectin structure between japonica-type and indica-type rice varieties[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2002, 104: 1-8. |
| [20] | Li Q F, Zhang G Y, Dong Z W, Yu H X, Gu M H, Sun S S M, Liu Q Q. Characterization of expression of the OsPUL gene encoding a pullulanase-type debranching enzyme during seed development and germination in rice[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2009, 47: 351-358. |
| [21] | Kubo A, Fujita N, Harada K, Matsuda T, Satoh H, Nakamura Y.The starch debraching enzymes isoamylase and pullulanase are both involved in amylopectin biosynthesis in rice endosperm[J]. Plant Physiology, 1999, 121: 399-409. |
| [22] | 许顺菊, 向珣朝, 康翠芳, 龙小林, 苏文丽, 杨博文, 吴家富. 回交重组自交系中 SSIII-1、SBE3和PUL基因对稻米蒸煮品质的影响[J]. 西北植物学报, 2015, 35(10): 1978-1988. |
| Xu S J, Xiang X C, Kang C F, Long X L, Su W L, Yang B W, Wu J F.Effects of SSIII-1, SBE3 and PUL on eating and cooking qualities of rice under the background of backcross inbred lines quality[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali Occidentalia Sinica, 2015, 35(10): 1978-1988. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 康翠芳, 向珣朝, 龙小林, 苏文丽, 许顺菊. 籼爪交水稻F2群体的蒸煮食味品质研究[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2015, 16(3): 561-568. |
| Kang C F, Xiang X C, Long X L, Su W L, Xu S J.Studies on cooking and eating quality of F2 population of indica / javanica rice[J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2015, 16(3): 561-568. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | 刘燕清, 强新涛, 赵春芳, 于新, 姚姝, 周丽慧, 陈涛, 赵庆勇, 朱镇, 张亚东, 王才林. 水稻淀粉合成相关基因分子标记的筛选与利用[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2015, 31(3): 471-476. |
| Liu Y Q, Qiang X T, Zhao C F, Yu X, Yao S, Zhou L H, Chen T, Zhao Q Y, Zhu Z, Zhang Y D, Wang C L.Selection and application of molecular markers for starch synthesis-related genes in rice[J]. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 31(3): 471-476. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | Rogers S O, Bandit A J.Extraction of DNA from plant tissues[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2012, 54(12): 979-990. |
| [26] | 陈涛, 骆名瑞, 张亚东, 朱镇,、赵庆勇, 赵凌, 周丽慧, 姚姝, 王才林. 利用四引物扩增受阻突变体系PCR技术检测水稻低直链淀粉含量基因Wx-mp[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2013, 27(5): 529-534. |
| Chen T, Luo M R, Zhang Y D, Zhu Z, Zhao Q Y, Zhao L, Zhou L H, Yao S, Wang C L.Detection of Wx-mp gene for low amylose content by tatre-amplification refractory mutation system PCR in-rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2013, 27(5): 529-534. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | 万映秀. 水稻淀粉生物合成途径中关键酶基因分子标记的开发及应用[D]. 雅安: 四川农业大学, 2006. |
| Wan Y X.Development and application of the key enzyme gene sequence-tagged molecular markers of starch biosynthesis in rice (Oryza sativa L.) [D]. Yaan: Sichuan Agricultural University, 2006. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | 中华人民共和国农业部. 米质测定方法NY147-88[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 1988: 4-6. |
| Ministry of Agriculture of the People's Republic of China. Rice Quality Measurement Method of NY147-88[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 1988: 4-6. (in Chinese) | |
| [29] | 中华人民共和国国家标准. 粮油检验—大米胶稠度的测定: GB/T22294-2008[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2009. |
| The People’s Republic of China. Inspection of the grain and oil—Determination of rice adhesive strength: GB/T 22294-2008[S]. Beijing: Standard Press of China, 2009. (in Chinese) | |
| [30] | 莫惠栋. 农业试验统计[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 1992: 151-166. |
| Mo H D.Agricultural Experiment Statistics[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technology Press, 1992: 151-166. (in Chinese) | |
| [31] | Tian Z X, Qian Q, Liu Q Q, Yan M, Liu X, Yan C J, Liu G, Gao Z, Tang S, Zeng D, Wang Y, Yu J, Gu M H, Li J Y.Allelic diversities in rice starch biosynthesis lead to a diverse array of rice eating and cooking qualities[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2009, 106: 21 760-21 765. |
| [32] | He Y, Han Y P, Jiang L, Xu C W, Lu J F, Xu M L.Functional analysis of starch-synthesis genes in determining rice eating and cooking qualities[J]. Molecular Breeding, 2006, 18(4): 277-290. |
| [33] | Fujita N, Yoshida M, Asakura N, Ohdan T, Miyao A, Hirochika H, Nakamura Y.Function and characterization of starch synthase I using mutants in rice[J]. Plant Physiology, 2006, 140(11): 1070-1084. |
| [34] | 吴洪恺, 梁国华, 顾燕娟, 单丽丽, 王芳, 韩月澎, 顾铭洪. 水稻淀粉合成相关基因对稻米RVA谱特征的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2006, 32(11): 159-163. |
| Wu H K, Liang G H, Gu Y J, Shan L L, Wang F, Han Y P, Gu M H.The effect of the starch-synthesizing genes on RVA profile characteristics in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2006, 32(11): 159-163. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [35] | 康翠芳, 向珣朝, 龙小林, 苏文丽, 许顺菊. 水稻淀粉合成相关基因SSI、SSIII-1和PUL 对稻米品质的影响[J]. 农业生物技术学报, 2015, 23(3): 311-319. |
| Kang C F, Xiang X C, Long X L, Su W L, Xu S J.Effects of the starch- synthesizing genes SSI, SSIII-1 and PUL on rice (Oryza sativa L.) quality[J]. Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology, 2015, 23(3): 311-319. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [36] | 杨博文, 向珣朝, 许顺菊, 许亮. 回交重组自交系中SSI、SSIII-1和PUL不同等位基因互作对稻米蒸煮食味品质的影响[J]. 农业生物技术学报, 2017, 25(10): 1566-1574. |
| Yang B W, Xiang X C, Xu S J, Xu L.Influences on rice (Oryza sativa) eating and cooking qualities for interaction of different alleles of SSI, SSIII-1 and PUL in backcross recombinant inbred lines[J]. Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology, 2017, 25(10): 1566-1574. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [37] | Xu Y J, Ying Y N, Ouyang S H, Duan X L, Sun H, Jiang S K, Sun S C, Bao J S.Factors affecting sensory quality of cooked japonica rice[J]. Rice Science, 2018(2): 330-339. |
| [38] | Champagne E T, Bett-Garber K L, Fitzgerald M A, Grimm C C, Lea J, Ohtsubo K I, Jongdee S, Xie L H, Bassinello P Z, Resurreccion A, Ahmad R, Habibi F, Reinke R. Important sensory properties differentiating premium rice varieties[J]. Rice, 2010(3): 270-281. |
| [39] | Sreenivasulu N, Butardo V M J, Misra G, Cuevas R P, Anacleto R, Kavi Kishor P B. Designing climate-resilient rice with ideal grain quality suited for high-temperature stress[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2015, 66(7): 1737-1748. |
| [40] | Zhang C Q, Chen S J, Ren X Y, Lu Y, Liu D R, Cai X L, Li Q F, Gao J P, Liu Q Q.Molecular structure and physicochemical properties of starches from rice with different amylose contents resulting from modification of OsGBSSⅠ activity[J/OL]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2017, 65: 2222. |
| [41] | Nakamura Y.Towards a better understanding of the metabolic system for amylopectin biosynthesis in plants: Rice endosperm a model tissue[J]. Plant Cell Physiology, 2002, 43(7): 718-725. |
| [42] | 陈雅玲, 包劲松. 水稻胚乳淀粉合成相关酶的结构、功能及其互作研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(1): 1-12. |
| Chen Y L, Bao J S.Progress in structures, functions and interactions of starch synthesis related enzymes in rice endosperm[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2017, 31(1): 1-12. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 姚姝, 赵春芳, 陈涛, 路凯, 周丽慧, 赵凌, 朱镇, 赵庆勇, 梁文化, 赫磊, 王才林, 张亚东. 低谷蛋白半糯型粳稻营养品质与蒸煮食味品质特征分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(2): 178-188. |
| [2] | 田铮, 赵春芳, 张亚东, 赵庆勇, 朱镇, 赵凌, 陈涛, 姚姝, 周丽慧, 梁文化, 路凯, 王才林, 张红生. 江苏省半糯型粳稻蒸煮食味品质性状的差异分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(3): 249-258. |
| [3] | 石吕, 张新月, 孙惠艳, 曹先梅, 刘建, 张祖建. 不同类型水稻品种稻米蛋白质含量与蒸煮食味品质的关系及后期氮肥的效应[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(6): 541-552. |
| [4] | 曲莹,金正勋*,刘海英,徐振华,朱立楠,郑冠龙,朱方旭,张忠臣. 粳稻杂种后代胚乳可溶性淀粉合成酶及同工型基因表达特性分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2014, 28(1): 23-31. |
| [5] | 赖穗春1, 河野元信2, 王志东1, 三上隆司2, 黄道强1, 李宏1, 卢德城1, 周德贵1, 周少川1, * . 米饭食味计评价华南籼稻食味品质[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2011, 25(4): 435-438. |
| [6] | 吴洪恺,刘世家,江 玲,张文伟,王益华,任玉龙,韩小华,刘 峰. 稻米蛋白质组分及总蛋白质含量与淀粉RVA谱特征值的关系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2009, 23(4): 421-426 . |
| [7] | 刘奇华,蔡建,刘敏,柴廷友,李天. 两个籼稻品种垩白对稻米蒸煮食味与营养品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2007, 21(3): 327-330 . |
| [8] | 钱春荣,冯延江,杨静,刘海英,金正勋,. 水稻籽粒蛋白质含量选择对杂种早代蒸煮食味品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2007, 21(3): 323-326 . |
| [9] | 金正勋,钱春荣,杨静,刘海英. 水稻灌浆成熟期籽粒谷氨酰胺合成酶活性变化及其与稻米品质关系的初步研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2007, 21(1): 103-106 . |
| [10] | 刘海英,杨静,钱春荣,金正勋. 6-苄氨基嘌呤对水稻灌浆成熟期籽粒氮代谢及蒸煮食味品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2006, 20(6): 667-669 . |
| [11] | 金正勋,杨静,钱春荣,刘海英,金学泳,秋太权. 灌浆成熟期温度对水稻籽粒淀粉合成关键酶活性及品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2005, 19(4): 377-380 . |
| [12] | 曾亚文, 申时全, 汪禄祥, 刘家富, 普晓英, 杜娟. 云南稻种矿质元素含量与形态及品质性状的关系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2005, 19(2): 127-131 . |
| [13] | 罗玉坤,闵捷,吴戌君. 香港市场稻米品质的初步研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 1987, 1(3): 192-197 . |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||