
中国水稻科学 ›› 2020, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (2): 135-142.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2020.9086
曹志斌1, 李瑶2, 曾博虹1, 毛凌华1, 蔡耀辉1, 吴晓峰1,*, 袁林峰1,*
收稿日期:2019-07-26
修回日期:2019-10-17
出版日期:2020-03-10
发布日期:2020-03-10
通讯作者:
吴晓峰,袁林峰
作者简介:#共同第一作者
基金资助:Zhibin CAO1, Yao LI2, Bohong ZENG1, Linghua MAO1, Yaohui CAI1, Xiaofeng WU1,*, Linfeng YUAN1,*
Received:2019-07-26
Revised:2019-10-17
Online:2020-03-10
Published:2020-03-10
Contact:
Xiaofeng WU, Linfeng YUAN
About author:#These authors contributed equally to this work
摘要:
【目的】本研究旨在定位一个稻米垩白粒率高温耐性QTL,为外观品质育种及解析垩白粒率高温耐性的遗传机制提供依据。【方法】以非洲栽培稻耐热品种IRGC102309(Oryza glaberrima Steud.)和籼稻品种R9311(O. sativa L. subsp. indica Kato.)为亲本构建的栽培稻种间染色体片段导入系CSIL05-23为材料构建次级分离群体,结合人工气候室模拟灌浆期高温胁迫处理,采用垩白粒率高温钝感值为评价指标,对非洲栽培稻垩白粒率高温耐性 QTL 进行检测。【结果】 在BC6F2分离群体,利用单标记分析,发现第5染色体上的SSR标记RM1200与垩白粒率耐热性状极显著正相关(P=0.0005)。进一步利用BC6F3和BC6F4分离群体,采用QTL Cartographer 2.5软件和复合区间作图法在水稻第5染色体上的SSR标记RM1200-RM5796区间重复检测到一个灌浆期垩白粒率耐热性QTL, 命名为qHTCGR5,分别解释11.4%和17.5%表型变异。根据BC6F4分离群体的纯合重组体表型分组,利用置换作图方法将目标QTL同样定位在SSR标记RM1200-RM5796之间,遗传图距为1.3 cM,物理图距约为333.4 kb。【结论】 控制垩白粒率耐热性的qHTCGR5是一个能够用于稻米外观品质育种的新QTL。
中图分类号:
曹志斌, 李瑶, 曾博虹, 毛凌华, 蔡耀辉, 吴晓峰, 袁林峰. 非洲栽培稻垩白粒率耐热性QTL的定位[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(2): 135-142.
Zhibin CAO, Yao LI, Bohong ZENG, Linghua MAO, Yaohui CAI, Xiaofeng WU, Linfeng YUAN. QTL Mapping for Heat Tolerance of Chalky Grain Rate of Oryza glaberrima Steud.[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2020, 34(2): 135-142.
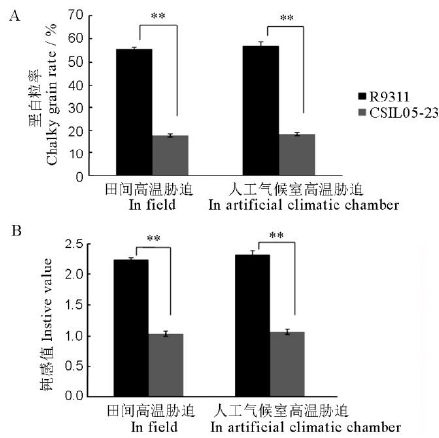
图1 CSIL05-23与R9311在田间及人工气候室高温胁迫处理下垩白粒率耐热性 **差异极显著(p<0.01), t检验。
Fig. 1. Comparison of heat tolerance of chalky grain rate of CSIL05-23 and R9311 in field and artificial climatic chambers. **Significant differences at 0.01 level, t-test.
| 世代 Generation | 供体亲本 Donor parent (IRGC102309) | 受体亲本 Recipient parent (R9311) | 群体Population | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均 Mean | 范围 Range | 标准差 SD | 峰度 Kurtosis | 偏度 Skewness | |||
| BC6F2(n=200) | 1.074 | 2.36 | 2.18 | 1.52-2.62 | 0.23 | 0.17 | 0.12 |
| BC6F3(n=368) | 1.054 | 2.23 | 2.11 | 1.48-2.68 | 0.31 | 0.23 | 0.32 |
| BC6F4(n=430) | 1.082 | 2.06 | 2.03 | 1.42-2.56 | 0.27 | 0.17 | 0.12 |
表1 亲本及BC6F2、BC6F3、BC6F4群体垩白粒率高温钝感值的表型变异
Table 1 Phenotypic variation of insensitive value of heat tolerance of chalky grain rate in BC6F2, BC6F3 and BC6F4 population and their parents.
| 世代 Generation | 供体亲本 Donor parent (IRGC102309) | 受体亲本 Recipient parent (R9311) | 群体Population | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均 Mean | 范围 Range | 标准差 SD | 峰度 Kurtosis | 偏度 Skewness | |||
| BC6F2(n=200) | 1.074 | 2.36 | 2.18 | 1.52-2.62 | 0.23 | 0.17 | 0.12 |
| BC6F3(n=368) | 1.054 | 2.23 | 2.11 | 1.48-2.68 | 0.31 | 0.23 | 0.32 |
| BC6F4(n=430) | 1.082 | 2.06 | 2.03 | 1.42-2.56 | 0.27 | 0.17 | 0.12 |

图2 垩白粒率耐热性QTL遗传连锁图和似然区间 左右箱线图分别表示来自BC6F3和BC6F4群体的1 LOD 和2 LOD 似然区间位置。
Fig. 2. Genetic linkage map and likelihood intervals for QTL associated with heat tolerance of chalky grain rate. The left and right bars and whiskers indicate 1 logarithm of the odds (LOD) and 2 LOD likelihood intervals from BC6F3 and BC6F4 populations, respectively.
| 性状 Character | 群体 Population | 区间 Interval | LOD | 表型方差 Phenotypic variance/% | 加性效应 Additive effect/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 垩白粒率高温钝感值IV | BC6F3 | RM1200-RM5796 | 6.3 | 11.3 | -5.9 |
| BC6F4 | RM1200-RM5796 | 7.4 | 17.5 | -11.8 | |
| 高温胁迫下的垩白粒率X1 | BC6F3 | RM1200-RM5796 | 5.9 | 9.5 | -5.6 |
| BC6F4 | RM1200-RM5796 | 6.9 | 16.7 | -12.5 | |
| 正常温度条件下的垩白粒率X2 | BC6F3 | RM1200-RM5796 | 6.2 | 12.6 | -5.7 |
| BC6F4 | RM1200-RM5796 | 7.1 | 16.5 | -11.2 |
表2 BC6F3与BC6F4世代灌浆期高温胁迫后垩白粒率耐热性QTL分析
Table 2 QTL analysis of heat tolerance of chalky grain rate in BC6F3 and BC6F4 populations.
| 性状 Character | 群体 Population | 区间 Interval | LOD | 表型方差 Phenotypic variance/% | 加性效应 Additive effect/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 垩白粒率高温钝感值IV | BC6F3 | RM1200-RM5796 | 6.3 | 11.3 | -5.9 |
| BC6F4 | RM1200-RM5796 | 7.4 | 17.5 | -11.8 | |
| 高温胁迫下的垩白粒率X1 | BC6F3 | RM1200-RM5796 | 5.9 | 9.5 | -5.6 |
| BC6F4 | RM1200-RM5796 | 6.9 | 16.7 | -12.5 | |
| 正常温度条件下的垩白粒率X2 | BC6F3 | RM1200-RM5796 | 6.2 | 12.6 | -5.7 |
| BC6F4 | RM1200-RM5796 | 7.1 | 16.5 | -11.2 |
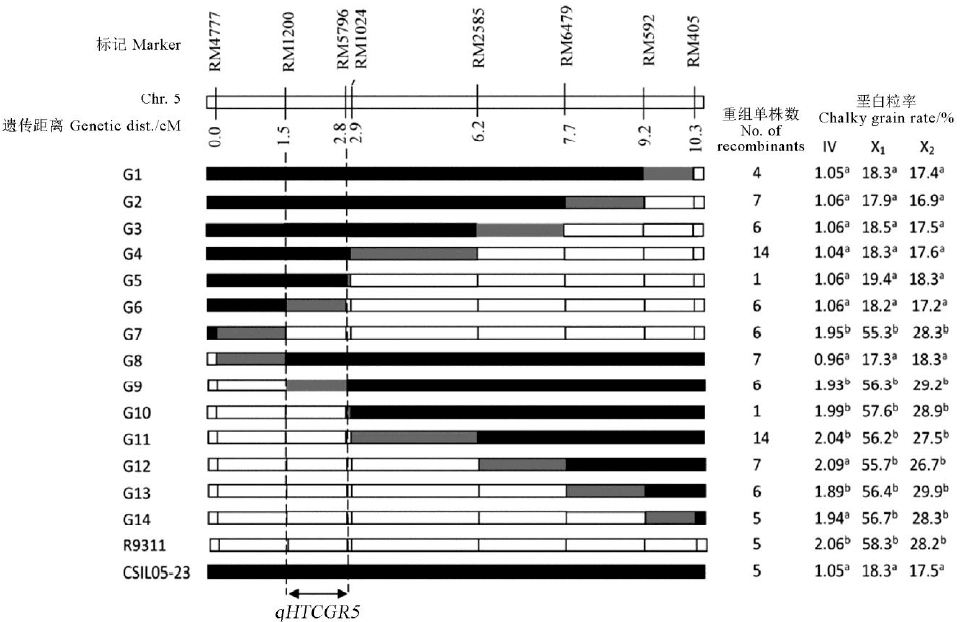
图3 利用置换作图法定位qHTCGR5 由380个BC6F3单株的分析数据构建QTL区域的连锁图。BC6F4纯合重组体的后代在灌浆期模拟高温逆境处理后, 根据垩白粒率及钝感值(IV=X1/X2)调查结果将qHTCGR5定位在RM1200和RM5796之间, 根据基因型将90个重组体分为14组。每组的重组体数目及与R9311和染色体片段导入系CSIL05-23之间的垩白粒率高温钝感表型差异显著性在右边标出。“a”表示重组体与R9311的表型值在0.05水平无显著差异:“b”表示重组体与CSIL05-23的表型值在0.05水平无显著差异。
Fig. 3. Mapping of qHTCGR5 by a substitution mapping strategy. Linkage map of the QTLs region produced with 380 BC6F3 plants. The number of recombinants between adjacent markers is indicated under the linkage map. Progeny testing of BC6F4 homozygous recombinants delimited the qHTCGR5 locus to the region between markers RM1200 and RM5796. The 90 recombinants were grouped into 14 groups based on genotypes. The numbers of recombinants in each group and phenotypic difference of each group from the controls CSIL05-23 and R9311 for mean insensitive value of heat tolerance of chalky grain rate are shown on the right. An “a” following the phenotypic value indicates that the mean phenotypic value of recombinant was not significantly different from that of R9311 at P < 0.05;a “b”indicates that the mean phenotypic value of recombinant was not significantly different from that of CSIL05-23 at P < 0.05.
| [1] | Carriger S, Vallée D.More crop per drop[J]. Rice Today, 2007, 6(2): 10-13. |
| [2] | Hockley N, Gibbons J M, Edwards-Jones G.Risks of extreme heat and unpredictability[J]. Science, 2009, 324(5924): 177-179. |
| [3] | Battisti D S, Naylor R L.Historical warnings of future food insecurity with unprecedented seasonal heat[J]. Science, 2009, 323(5911): 240-244. |
| [4] | Fitzgerald M A, McCouch S R, Hall R D. Not just a grain of rice: the quest for quality[J]. Trends Plant Science, 2009, 14(3): 133-139. |
| [5] | 森谷国男,. 徐正进, 译. 水稻高温胁迫抗性遗传育种研究概况[M]. 杂交水稻, 1992(1): 47-48. |
| Sengu G N,.Translated by Xu Z J. General Research on Genetic Breeding of Resistance to High Temperature Stress in Rice[M]. Hybrid Rice, 1992(1): 47-48. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 李木英, 熊伟, 石庆华, 胡志红, 潘晓华, 谭雪明. 高温胁迫对早稻不同品种灌浆结实和稻米品质的影响[J]. 江西农业学学报, 2006, 28(4): 483-487. |
| Li M Y, Xiong W, Shi Q H, Hu Z H, Pan X H, Pan X M.Effect of high temperature stress on endosperm filling and grain quality of early rice varieties[J]. Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis, 2006, 28(4): 483-487. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 赵海燕, 姚凤梅, 张勇, 徐宾, 袁静, 胡亚南, 许吟隆. 长江中下游水稻开花灌浆期气象要素与结实率和粒重的相关性分析[J]. 中国农业科学, 2006, 39(9): 1765-1771. |
| Zhao H Y, Yao F M, Zhang Y, Xu B, Yuan J, Hu Y N, Xu Y L.Correlation analysis of rice seed setting rate and weight of 1000-grain and agro-meteorology over the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2006, 39(9): 1765-1771. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | 李林, 沙国栋, 陆景淮. 水稻灌浆期温光因子对稻米品质的影响[J]. 中国农业气象, 1989, 10(3): 33-38. |
| Li L, Sha G D, Lu J H.Effect of temperature and light on rice quality[J]. Chinese Journal of Agromemorology, 1989, 10(3): 33-38. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 程方明, 张蒿午, 吴永常. 灌浆结实期温度对稻米垩白形成的影响[J]. 西北农业学报, 1996, 5(2): 31-34. |
| Cheng F M, Zhang H W, Wu Y C.Effect of high temperature stress on chalkiness at filling stage[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occidentalis Sinica, 1996, 5(2): 31-34. | |
| [10] | Zhong L, Cheng F, Wen X, Sun Z X, Zhang G P.The deterioration of eating and cooking quality caused by high temperature during grain filling in early-season indica rice cultivars[J]. Journal of Agronomy and Crop Science-Zeitschrift Fur Acker Und Pflanzenbau, 2005, 191(3): 218-225. |
| [11] | Mei D Y, Zhu Y J, Yu Y H, Fan Y Y, Huang D R, Zhuang J Y.Quantitative trait loci for grain chalkiness and endosperm transparency detected in three recombinant inbred line populations of indica rice[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2013, 12(1): 1-11. |
| [12] | 周立军, 刘喜, 江玲, 郑蕾娜, 陈亮明, 刘世家, 翟虎渠, 万建民. 利用CSSL和BIL群体分析稻米垩白粒率QTL 及互作效应. 中国农业科学, 2009, 42(4): 1129-1135. |
| Zhou L J, Liu X, Jiang L, Zheng L N, Chen L M, Liu S J, Zhai H Q, Wan J M.Analysis of QTL and GE effects on PGWC in rice (Oryza sativa L.) using CSSL and BIL populations. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2009, 42(4): 1129-1135. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | Liu X, Wang Y, Wang S W.QTL analysis of percentage of grains with chalkiness in japonica rice (Oryza sativa)[J]. Genetics and Molecular Research, 2012, 11(1): 717-724. |
| [14] | 晁园, 冯付春, 高冠军, 朱雪萍, 何予卿. 利用重组自交系群体定位水稻品质相关性状的QTL[J]. 华中农业大学学报, 2012, 31(4): 397-403. |
| Chao Y, Feng F C, Gao G J, Zhu X P, He Y Q.Mapping quantitative trait loci for qualities of rice grains using a Recombinant inbred(RIL) population[J]. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University, 2012, 31(4): 397-403. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 杨亚春, 倪大虎, 宋丰顺, 李泽福, 易成新, 杨剑波. 不同生态地点下稻米外观品质性状的QTL定位分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2011, 25(1): 43-51. |
| Yang Y C, Ni D H, Song F S, Li Z F, Yi C X, Chen J B.Identification of QTLs of rice appearance quality traits across different ecological sites[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2011, 25(1): 43-51. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 王林森, 陈亮明, 王沛然, 王卓然, 郑海, 马宏阳, 江玲, 赵志刚, 万建民. 利用高世代回交群体检测水稻垩白相关性状 QTL[J]. 南京农业大学学报, 2016, 39(2): 183-190. |
| Wang L S, Chen L M, Wang P R, Wang Z R, Zheng L, Ma H Y, Jiang L, Zhao Z G, Wan J M.Detecting the QTL of rice chalkiness traits using advanced backcrossing population[J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 2016, 39(2): 183-190. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | 朱昌兰. 稻低直链淀粉含量的遗传及品质形成对高温耐性的QTL分析. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2004. |
| Zhu C L.Identifying QTLs for thermo-tolerance of quality formation and inheritance of low amylose content in rice. Nanjing: Nanjing Agriculture University, 2004. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | 朱昌兰, 肖应辉, 王春明, 江玲, 翟虎渠, 万建民. 水稻灌浆期耐热害的数量性状基因位点分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2005, 19(2): 117-121. |
| Zhu C L, Xiao Y H, Wang C M, Jiang L, Zhai H Q, Wan J M.Mapping QTLs for heat tolerance during grain filling in rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2005, 19(2): 117-121. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | Kobayashi A, Bao G, Ye S, Tomita K.Detection of quantitative trait loci for white-back and basal white kernels under high temperature stress in japonica rice varieties[J]. Breeding Science, 200, 57(2): 107-116. |
| [20] | Shirasawa K.QTL analysis of high-temperature-stress tolerance in filling period based on rice grain quality[J]. Breeding Research, 2006, 8(1): 155. |
| [21] | Tabata M, Hirabayashi H, Takeuchi Y, Ando I.Mapping of quantitative trait loci for the occurrence of white-back kernels associated with high temperatures during the ripening period of rice(Oryza sativa L)[J]. Breeding Science, 2007, 57(1): 47-52. |
| [22] | 张桂莲, 廖斌, 唐文帮, 陈立云, 肖应辉. 稻米垩白性状对高温耐性的QTL分析. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(3): 257-264. |
| Zhang GL, Liao B, Tang W B, Chen L Y, Xiao Y H.Identifying QTLs for thermo-tolerance of grain chalkiness trait in rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2017, 31(3): 257-264. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 钟秉强, 杨正林, 冉启良, 何光华. 美国水稻品种农艺性状和品质性状的温度钝感特性研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2005, 21(2): 118-121. |
| Zhong B Q, Yang Z L, Ran Q L, He g H. Study on temperature insensitivity of characters of agronomy and quality in the American rice variety[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2005, 21(2): 118-121. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | Rogers S O, Bendich A J.Extraction of DNA from plant tissues[M]. Plant molecular Biology Manual. Springer, Dordrecht, 1989: 73-83. |
| [25] | Lander E S, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daly M J, Lincoln S E, Newberg L A.MAPMAKER: An interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations[J]. Genomics, 1987, 1(2): 174-181. |
| [26] | Kosambi D D.The estimation of map distances from recombination values[J]. Annals of Eugenics, 1943, 12(YRS 1943/5): 172-175. |
| [27] | Wang S C, Basten C J, Zeng Z B.Windows QTL Cartographer 2.5. Statistical Genetics, Raleigh, NC: North Carolina State, 2012. |
| [28] | Zeng Z B.Precision mapping of quantitative trait loci.Genetics, 1994, 136: 1457-1468. |
| [29] | 王慧, 喻德跃, 吴巧娟, 盖钧镒. 大豆对斜纹夜蛾抗生性基因的微卫星标记(SSR)的研究[J]. 大豆科学, 2004, 23(2): 91-95. |
| Wang H, Yu D Y, Wu Q J, Gai J Y.Characterization of resistance genes to cotton worm with SSR markers in soybean[J]. Soybean Science, 2004, 23(2): 91-95. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | 徐吉臣, 邹亮星. 利用相关性分析鉴定与水稻根部性状表达相关的分子标记[J]. 遗传学报, 2002, 29(3): 245-249. |
| Xu J C, Zou L X.Identification of molecular markers associated with rice root traits by correlation coefficient analysis[J]. Acta Genetica Sinica, 2002, 29(3): 245-249. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | McCouch S R, Cho Y G, Yano M, Paul E, Blinstrub M, Morishima H, Kinoshita T. Report on QTL nomenclature[J]. Rice Genetic Newsletter, 1997, 14: 11-13. |
| [32] | Li X M, Chao D Y, Wu Y, Huang X H, Chen K, Cui L G, Su L, Ye W W, Chen H, Chen H C, Dong N Q, Guo T, Shi M, Feng Q, Zhang P, Han B, Shan J X, Gao J P, Lin H X.Natural alleles of a proteasome α2 subunit gene contribute to thermos-tolerance and adaptation of African rice[J]. Nature Genetics, 2015, 47(7): 827. |
| [33] | Liu X, Wang Y, Wang S W.QTL analysis of percentage of grains with chalkiness in Japonica rice (Oryza sativa)[J]. Genetics and Molecular Research, 2012, 11(1): 717-724. |
| [34] | 高方远, 邱玲, 陆贤军, 任鄄胜, 吴贤婷, 任光俊, 曾礼华. 杂交籼稻骨干保持系岗46B稻谷粒形及垩白的QTL分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2014, 28(3): 235-242. |
| Gao F Y, Qiu L, Lu X J, Ren J S, Wu X T, Ren G J, Zeng L H.QTL analysis on grain shape and chalkiness of an elite maintainer line Gang 46B in hybrid rice(Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2014, 28(3): 235-242. | |
| [35] | Paterson A H, Deverna J W, Lanini B, Tanksley S D.Fine mapping of quantitative trait loci using selected overlapping recombinant chromosomes, in an interspecies cross of tomato[J]. Genetics, 1990, 124(3): 735-742. |
| [36] | Tanksley S D, Ganal M W, Martin G B.Chromosome landing: a paradigm for map-based gene cloning in plants with large genomes[J]. Trends in Genetics, 1995, 11(2): 63-68. |
| [37] | Alpert K B, Tanksley S D.High-resolution mapping and isolation of a yeast artificial chromosome contig containing fw2.2: A major fruit weight quantitative trait locus in tomato[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1996, 93(26): 15503-15507. |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [6] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [7] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [8] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [9] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [10] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [11] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [12] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [13] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| [14] | 许用强, 姜宁, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 水稻开花期高温热害响应机理及其调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 111-126. |
| [15] | 吕海涛, 李建忠, 鲁艳辉, 徐红星, 郑许松, 吕仲贤. 稻田福寿螺的发生、危害及其防控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 127-139. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||