
中国水稻科学 ›› 2020, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (2): 125-134.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2020.9125
李盼盼1, 朱玉君1, 郭梁2, 庄杰云1, 樊叶杨1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2019-11-21
修回日期:2019-12-28
出版日期:2020-03-10
发布日期:2020-03-10
通讯作者:
樊叶杨
基金资助:
Panpan LI1, Yujun ZHU1, Liang GUO2, Jieyun ZHUANG1, Yeyang FAN1,*( )
)
Received:2019-11-21
Revised:2019-12-28
Online:2020-03-10
Published:2020-03-10
Contact:
Yeyang FAN
摘要:
【目的】本研究旨在对前期在水稻第1染色体长臂521.8 kb的区间内定位到的qTGW1.1b进行精细定位。【方法】从qTGW1.1和qTGW1.2所在区间分别呈杂合的2个BC2F9单株配组衍生的F4群体中,筛选到Wn28826- RM1231区间内杂合片段呈梯系排列的3个单株,构建了3套F5:6近等基因系。2017年种植于浙江杭州,考查千粒重、粒长和粒宽。利用SAS软件的GLM程序进行双因素方差分析,对qTGW1.1b的效应进行了验证。在此基础上,筛选出杂合片段更小且呈交迭排列的6个剩余杂合体,发展了6套F8:9近等基因系,2018年种植于海南陵水。对每套近等基因系中双亲基因型株系的表型差异进行双因素方差分析。【结果】qTGW1.1b在2个试验中对粒长和千粒重均呈极显著差异,效应方向一致且大小稳定。密阳46等位基因能分别增加粒长0.027 mm和提高千粒重0.17 g,贡献率分别达到27.12%和19.09%。【结论】鉴于qTGW1.1b在前后试验中对粒长影响最为显著,而对粒宽作用不显著,故将qTGW1.1b重新命名为qGL1.1。通过比较各套近等基因系的分离区间的基因组位置,最终将qGL1.1定位于Wn29077和Wn29154之间约76.8 kb的区间内。
中图分类号:
李盼盼, 朱玉君, 郭梁, 庄杰云, 樊叶杨. 利用剩余杂合体衍生的近等基因系精细定位水稻粒长微效QTL qGL1.1[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(2): 125-134.
Panpan LI, Yujun ZHU, Liang GUO, Jieyun ZHUANG, Yeyang FAN. Fine Mapping of qGL1.1, a Minor QTL for Grain Length, Using Near Isogenic Lines Derived from Residual Heterozygotes in Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2020, 34(2): 125-134.
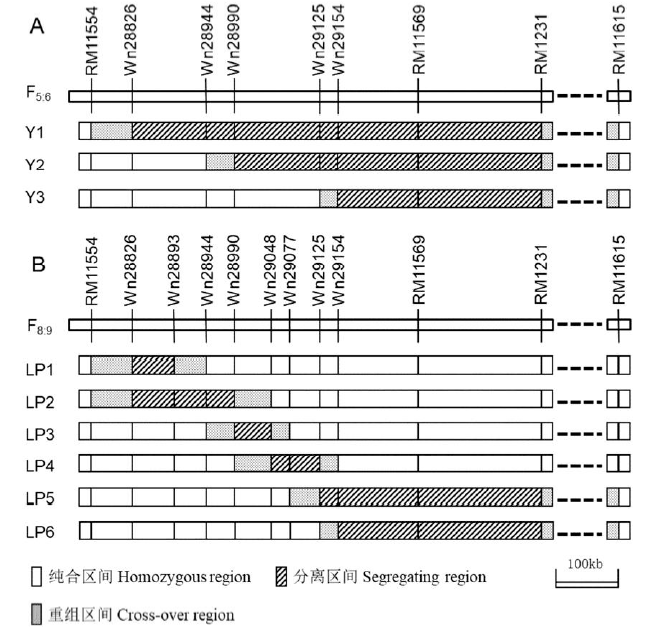
图2 9套近等基因系在目标区间的基因型组成 A-用于验证的3套F5:6近等基因系; B-用于精细定位的6套F8:9近等基因系。
Fig. 2. Genotypic compositions of the nine NILs sets in the target region. A, Three sets of NILs in F5:6 for validation. B, Six sets of NILs in F8:9 for fine-mapping.
| 标记名称 | 类型 | 限制性内切酶 | 正向引物(5'-3') | 反向引物(5'-3') |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Type | Restriction enzyme | Forward primer (5'-3') | Reverse primer (5'-3') |
| Wn28826 | CAPS | BstN I | GACAAGTTGGGATAATTCTTCGAT | TAACGTGTCGATCTCTGACC |
| Wn28893 | dCAPS | Hha I | GATCGCTCCCTTGTATACGCTGA | CCATTCCGCCCGGTTGATGAAACGC |
| Wn28944 | InDel | CATTACAAGGTAAATTGTAGATTGG | TCATTTAGGGATTATGTTGGTC | |
| Wn28990 | InDel | AGTTTATAAATCCGAAGCCAT | AGCACAAATAAGTAATTATGCCTA | |
| Wn29048 | dCAPS | N1a III | GAATAAGTCCACTTTACGCATCTTTCTCA | GGATCAAGATTTTCCGTATTGCAG |
| Wn29077 | dCAPS | Kpn I | CAGTTCACGGGATACGAAGC | CAGTTTGACCATCCTCTAAGCAAAGGGTA |
| Wn29125 | dCAPS | Sty I | AAGTGTGTACGGTCAAATGTTTGCCA | ACGTCAGTCAAAACAAATACGG |
| Wn29154 | CAPS | Xba I | TGGATTAATTAGGCTAGGTAGACA | TTCTCCCTCTCGTGATCGC |
表1 本研究新开发的DNA标记
Table 1 DNA markers developed in this study.
| 标记名称 | 类型 | 限制性内切酶 | 正向引物(5'-3') | 反向引物(5'-3') |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Type | Restriction enzyme | Forward primer (5'-3') | Reverse primer (5'-3') |
| Wn28826 | CAPS | BstN I | GACAAGTTGGGATAATTCTTCGAT | TAACGTGTCGATCTCTGACC |
| Wn28893 | dCAPS | Hha I | GATCGCTCCCTTGTATACGCTGA | CCATTCCGCCCGGTTGATGAAACGC |
| Wn28944 | InDel | CATTACAAGGTAAATTGTAGATTGG | TCATTTAGGGATTATGTTGGTC | |
| Wn28990 | InDel | AGTTTATAAATCCGAAGCCAT | AGCACAAATAAGTAATTATGCCTA | |
| Wn29048 | dCAPS | N1a III | GAATAAGTCCACTTTACGCATCTTTCTCA | GGATCAAGATTTTCCGTATTGCAG |
| Wn29077 | dCAPS | Kpn I | CAGTTCACGGGATACGAAGC | CAGTTTGACCATCCTCTAAGCAAAGGGTA |
| Wn29125 | dCAPS | Sty I | AAGTGTGTACGGTCAAATGTTTGCCA | ACGTCAGTCAAAACAAATACGG |
| Wn29154 | CAPS | Xba I | TGGATTAATTAGGCTAGGTAGACA | TTCTCCCTCTCGTGATCGC |
| 性状 | 试验 | 名称 | 平均 | 标准差 | 变异系数 | 范围 | 偏斜度 | 峰度 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trait | Trial | Name | Mean | SD | CV | Range | Skewness | Kurtosis | ||
| 千粒重 1000-grain weight /g | 杭州 | Y1 | 25.55 | 0.34 | 0.013 | 24.92~26.27 | 0.30 | -0.59 | ||
| Hangzhou | Y2 | 26.74 | 0.36 | 0.013 | 25.84~27.92 | 0.45 | 1.15 | |||
| Y3 | 25.67 | 0.26 | 0.010 | 25.05~26.17 | -0.27 | -0.38 | ||||
| 陵水 | LP1 | 30.16 | 0.36 | 0.012 | 29.42~30.89 | 0.07 | -0.34 | |||
| Lingshui | LP2 | 29.25 | 0.61 | 0.021 | 27.67~30.36 | -0.50 | -0.18 | |||
| LP3 | 29.93 | 0.29 | 0.010 | 29.26~30.57 | 0.07 | -0.43 | ||||
| LP4 | 30.74 | 0.31 | 0.010 | 30.04~31.37 | 0.24 | -0.52 | ||||
| LP5 | 29.81 | 0.48 | 0.016 | 28.35~30.79 | -0.31 | 0.28 | ||||
| LP6 | 29.73 | 0.52 | 0.017 | 28.69~30.68 | -0.27 | -0.71 | ||||
| 粒长 Grain length / mm | 杭州 | Y1 | 8.120 | 0.057 | 0.007 | 7.999~8.261 | -0.08 | -0.06 | ||
| Hangzhou | Y2 | 8.216 | 0.057 | 0.007 | 8.106~8.362 | 0.58 | 0.28 | |||
| Y3 | 8.136 | 0.050 | 0.006 | 8.033~8.264 | 0.02 | -0.34 | ||||
| 陵水 | LP1 | 8.106 | 0.037 | 0.005 | 8.034~8.191 | 0.30 | -0.39 | |||
| Lingshui | LP2 | 8.114 | 0.040 | 0.005 | 8.040~8.201 | 0.07 | -0.87 | |||
| LP3 | 8.097 | 0.041 | 0.005 | 8.003~8.199 | 0.16 | -0.10 | ||||
| LP4 | 8.268 | 0.047 | 0.006 | 8.138~8.358 | -0.44 | 0.02 | ||||
| LP5 | 8.094 | 0.054 | 0.007 | 7.978~8.217 | 0.13 | -0.47 | ||||
| LP6 | 8.164 | 0.045 | 0.005 | 8.051~8.245 | -0.15 | -0.29 | ||||
| 粒宽 Grain width / mm | 杭州 | Y1 | 2.958 | 0.022 | 0.008 | 2.899~3.024 | 0.13 | 0.81 | ||
| Hangzhou | Y2 | 3.053 | 0.018 | 0.006 | 3.014~3.103 | 0.35 | 0.43 | |||
| Y3 | 2.924 | 0.024 | 0.008 | 2.875~2.972 | 0.14 | -0.71 | ||||
| 陵水 | LP1 | 3.288 | 0.014 | 0.004 | 3.244~3.312 | -0.67 | 0.82 | |||
| Lingshui | LP2 | 3.218 | 0.044 | 0.014 | 3.091~3.290 | -0.78 | 0.48 | |||
| LP3 | 3.273 | 0.022 | 0.007 | 3.217~3.306 | -0.98 | 0.49 | ||||
| LP4 | 3.296 | 0.014 | 0.004 | 3.267~3.324 | -0.26 | -0.63 | ||||
| LP5 | 3.265 | 0.031 | 0.009 | 3.156~3.313 | -1.81 | 4.27 | ||||
| LP6 | 3.236 | 0.040 | 0.012 | 3.129~3.306 | -0.66 | -0.14 | ||||
表2 9套近等基因系千粒重、粒长和粒宽的表型变异
Table 2 Phenotypic variations of 1000-grain weight, grain length and grain width in nine sets of NILs.
| 性状 | 试验 | 名称 | 平均 | 标准差 | 变异系数 | 范围 | 偏斜度 | 峰度 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trait | Trial | Name | Mean | SD | CV | Range | Skewness | Kurtosis | ||
| 千粒重 1000-grain weight /g | 杭州 | Y1 | 25.55 | 0.34 | 0.013 | 24.92~26.27 | 0.30 | -0.59 | ||
| Hangzhou | Y2 | 26.74 | 0.36 | 0.013 | 25.84~27.92 | 0.45 | 1.15 | |||
| Y3 | 25.67 | 0.26 | 0.010 | 25.05~26.17 | -0.27 | -0.38 | ||||
| 陵水 | LP1 | 30.16 | 0.36 | 0.012 | 29.42~30.89 | 0.07 | -0.34 | |||
| Lingshui | LP2 | 29.25 | 0.61 | 0.021 | 27.67~30.36 | -0.50 | -0.18 | |||
| LP3 | 29.93 | 0.29 | 0.010 | 29.26~30.57 | 0.07 | -0.43 | ||||
| LP4 | 30.74 | 0.31 | 0.010 | 30.04~31.37 | 0.24 | -0.52 | ||||
| LP5 | 29.81 | 0.48 | 0.016 | 28.35~30.79 | -0.31 | 0.28 | ||||
| LP6 | 29.73 | 0.52 | 0.017 | 28.69~30.68 | -0.27 | -0.71 | ||||
| 粒长 Grain length / mm | 杭州 | Y1 | 8.120 | 0.057 | 0.007 | 7.999~8.261 | -0.08 | -0.06 | ||
| Hangzhou | Y2 | 8.216 | 0.057 | 0.007 | 8.106~8.362 | 0.58 | 0.28 | |||
| Y3 | 8.136 | 0.050 | 0.006 | 8.033~8.264 | 0.02 | -0.34 | ||||
| 陵水 | LP1 | 8.106 | 0.037 | 0.005 | 8.034~8.191 | 0.30 | -0.39 | |||
| Lingshui | LP2 | 8.114 | 0.040 | 0.005 | 8.040~8.201 | 0.07 | -0.87 | |||
| LP3 | 8.097 | 0.041 | 0.005 | 8.003~8.199 | 0.16 | -0.10 | ||||
| LP4 | 8.268 | 0.047 | 0.006 | 8.138~8.358 | -0.44 | 0.02 | ||||
| LP5 | 8.094 | 0.054 | 0.007 | 7.978~8.217 | 0.13 | -0.47 | ||||
| LP6 | 8.164 | 0.045 | 0.005 | 8.051~8.245 | -0.15 | -0.29 | ||||
| 粒宽 Grain width / mm | 杭州 | Y1 | 2.958 | 0.022 | 0.008 | 2.899~3.024 | 0.13 | 0.81 | ||
| Hangzhou | Y2 | 3.053 | 0.018 | 0.006 | 3.014~3.103 | 0.35 | 0.43 | |||
| Y3 | 2.924 | 0.024 | 0.008 | 2.875~2.972 | 0.14 | -0.71 | ||||
| 陵水 | LP1 | 3.288 | 0.014 | 0.004 | 3.244~3.312 | -0.67 | 0.82 | |||
| Lingshui | LP2 | 3.218 | 0.044 | 0.014 | 3.091~3.290 | -0.78 | 0.48 | |||
| LP3 | 3.273 | 0.022 | 0.007 | 3.217~3.306 | -0.98 | 0.49 | ||||
| LP4 | 3.296 | 0.014 | 0.004 | 3.267~3.324 | -0.26 | -0.63 | ||||
| LP5 | 3.265 | 0.031 | 0.009 | 3.156~3.313 | -1.81 | 4.27 | ||||
| LP6 | 3.236 | 0.040 | 0.012 | 3.129~3.306 | -0.66 | -0.14 | ||||
| 试验 Trial | 名称 Name | 分离区间 Segregating region | 性状 Trait | 表型值(平均值±标准差) | P | A | R2 / % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phenotype (Mean±SD) | |||||||||
| NILZS97 | NILMY46 | ||||||||
| 杭州 | Y1 | Wn28826-RM1231 | TGW/g | 25.42±0.30 | 25.69±0.32 | 0.0017 | 0.13 | 8.99 | |
| Hangzhou | GL/mm | 8.098±0.062 | 8.143±0.041 | 0.0018 | 0.023 | 8.13 | |||
| GW/mm | 2.950±0.019 | 2.966±0.023 | 0.0048 | 0.008 | 8.19 | ||||
| Y2 | Wn28990-RM1231 | TGW/g | 26.68±0.32 | 26.78±0.38 | 0.2372 | ||||
| GL/mm | 8.201±0.050 | 8.231±0.061 | 0.0343 | 0.015 | 5.33 | ||||
| GW/mm | 3.049±0.017 | 3.056±0.019 | 0.1553 | ||||||
| Y3 | Wn29154-RM1231 | TGW/g | 25.65±0.25 | 25.68±0.28 | 0.6181 | ||||
| GL/mm | 8.143±0.053 | 8.129±0.046 | 0.2623 | ||||||
| GW/mm | 2.922±0.023 | 2.927±0.025 | 0.3944 | ||||||
| 陵水 | LP1 | Wn28826-Wn28893 | TGW/g | 30.19±0.39 | 30.12±0.34 | 0.4894 | |||
| Lingshui | GL/mm | 8.110±0.034 | 8.104±0.040 | 0.5480 | |||||
| GW/mm | 3.291±0.013 | 3.286±0.014 | 0.1920 | ||||||
| LP2 | Wn28826-Wn28990 | TGW/g | 29.32±0.58 | 29.19±0.64 | 0.4124 | ||||
| GL/mm | 8.123±0.042 | 8.105±0.037 | 0.1011 | ||||||
| GW/mm | 3.224±0.041 | 3.212±0.046 | 0.3026 | ||||||
| LP3 | Wn28990-Wn29048 | TGW/g | 30.00±0.27 | 29.85±0.29 | 0.0394 | -0.08 | 4.30 | ||
| GL/mm | 8.109±0.043 | 8.086±0.035 | 0.0256 | -0.012 | 5.25 | ||||
| GW/mm | 3.275±0.022 | 3.272±0.023 | 0.6138 | ||||||
| LP4 | Wn29048-Wn29125 | TGW/g | 30.56±0.25 | 30.91±0.27 | <0.0001 | 0.17 | 19.09 | ||
| GL/mm | 8.241±0.043 | 8.296±0.033 | <0.0001 | 0.027 | 27.12 | ||||
| GW/mm | 3.297±0.015 | 3.295±0.014 | 0.7289 | ||||||
| LP5 | Wn29125-RM1231 | TGW/g | 29.84±0.44 | 29.78±0.52 | 0.6563 | ||||
| GL/mm | 8.083±0.049 | 8.105±0.057 | 0.1154 | ||||||
| GW/mm | 3.268±0.024 | 3.262±0.036 | 0.4580 | ||||||
| LP6 | Wn29154-RM1231 | TGW/g | 29.67±0.49 | 29.78±0.55 | 0.4381 | ||||
| GL/mm | 8.177±0.042 | 8.151±0.043 | 0.0206 | -0.013 | 6.03 | ||||
| GW/mm | 3.227±0.043 | 3.245±0.034 | 0.0711 | ||||||
| A-密阳46等位基因取代珍汕97等位基因所产生的遗传效应。R2-效应对表型方差的贡献率。 A, Additive effect of replacing a Zhenshan 97 allele with a Milyang 46 allele. R2, Proportion of phenotypic variance explained by the QTL effect. | |||||||||
表3 9套近等基因系千粒重、粒长和粒宽的QTL检测结果
Table 3 QTL analysis for 1000-grain weight, grain length and grain width in nine sets of NILs.
| 试验 Trial | 名称 Name | 分离区间 Segregating region | 性状 Trait | 表型值(平均值±标准差) | P | A | R2 / % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phenotype (Mean±SD) | |||||||||
| NILZS97 | NILMY46 | ||||||||
| 杭州 | Y1 | Wn28826-RM1231 | TGW/g | 25.42±0.30 | 25.69±0.32 | 0.0017 | 0.13 | 8.99 | |
| Hangzhou | GL/mm | 8.098±0.062 | 8.143±0.041 | 0.0018 | 0.023 | 8.13 | |||
| GW/mm | 2.950±0.019 | 2.966±0.023 | 0.0048 | 0.008 | 8.19 | ||||
| Y2 | Wn28990-RM1231 | TGW/g | 26.68±0.32 | 26.78±0.38 | 0.2372 | ||||
| GL/mm | 8.201±0.050 | 8.231±0.061 | 0.0343 | 0.015 | 5.33 | ||||
| GW/mm | 3.049±0.017 | 3.056±0.019 | 0.1553 | ||||||
| Y3 | Wn29154-RM1231 | TGW/g | 25.65±0.25 | 25.68±0.28 | 0.6181 | ||||
| GL/mm | 8.143±0.053 | 8.129±0.046 | 0.2623 | ||||||
| GW/mm | 2.922±0.023 | 2.927±0.025 | 0.3944 | ||||||
| 陵水 | LP1 | Wn28826-Wn28893 | TGW/g | 30.19±0.39 | 30.12±0.34 | 0.4894 | |||
| Lingshui | GL/mm | 8.110±0.034 | 8.104±0.040 | 0.5480 | |||||
| GW/mm | 3.291±0.013 | 3.286±0.014 | 0.1920 | ||||||
| LP2 | Wn28826-Wn28990 | TGW/g | 29.32±0.58 | 29.19±0.64 | 0.4124 | ||||
| GL/mm | 8.123±0.042 | 8.105±0.037 | 0.1011 | ||||||
| GW/mm | 3.224±0.041 | 3.212±0.046 | 0.3026 | ||||||
| LP3 | Wn28990-Wn29048 | TGW/g | 30.00±0.27 | 29.85±0.29 | 0.0394 | -0.08 | 4.30 | ||
| GL/mm | 8.109±0.043 | 8.086±0.035 | 0.0256 | -0.012 | 5.25 | ||||
| GW/mm | 3.275±0.022 | 3.272±0.023 | 0.6138 | ||||||
| LP4 | Wn29048-Wn29125 | TGW/g | 30.56±0.25 | 30.91±0.27 | <0.0001 | 0.17 | 19.09 | ||
| GL/mm | 8.241±0.043 | 8.296±0.033 | <0.0001 | 0.027 | 27.12 | ||||
| GW/mm | 3.297±0.015 | 3.295±0.014 | 0.7289 | ||||||
| LP5 | Wn29125-RM1231 | TGW/g | 29.84±0.44 | 29.78±0.52 | 0.6563 | ||||
| GL/mm | 8.083±0.049 | 8.105±0.057 | 0.1154 | ||||||
| GW/mm | 3.268±0.024 | 3.262±0.036 | 0.4580 | ||||||
| LP6 | Wn29154-RM1231 | TGW/g | 29.67±0.49 | 29.78±0.55 | 0.4381 | ||||
| GL/mm | 8.177±0.042 | 8.151±0.043 | 0.0206 | -0.013 | 6.03 | ||||
| GW/mm | 3.227±0.043 | 3.245±0.034 | 0.0711 | ||||||
| A-密阳46等位基因取代珍汕97等位基因所产生的遗传效应。R2-效应对表型方差的贡献率。 A, Additive effect of replacing a Zhenshan 97 allele with a Milyang 46 allele. R2, Proportion of phenotypic variance explained by the QTL effect. | |||||||||
| [1] | Xing Y Z, Zhang Q F.Genetic and molecular bases of rice yield[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2010, 61: 421-442. |
| [2] | Duan P G, Ni S, Wang J M, Zhang B L, Xu R, Wang Y X, Chen H Q, Zhu X D, Li Y H.Regulation of OsGRF4 by OsmiR396 controls grain size and yield in rice[J]. Nature Plants, 2016, 2: 15203. |
| [3] | Hu J, Wang Y X, Fang Y X, Zeng L J, Xu J, Yu H P, Shi Z Y, Pan J J, Zhang D, Kang S J, Zhu L, Dong G J, Guo L B, Zeng D L, Zhang G H, Xie L H, Xiong G S, Li J Y, Qian Q.A rare allele of GS2 enhances grain size and grain yield in rice[J]. Molecular Plant, 2015, 8: 1455-1465. |
| [4] | Yu J P, Xiong H Y, Zhu X Y, Zhang H L, Li H H, Miao J L, Wang W S, Tang Z S, Zhang Z Y, Yao G X, Zhang Q, Pan Y H, Wang X, Rashid M A R, Li J J, Gao Y M, Li Z K, Yang W C, Fu X D, Li Z C. OsLG3 contributing to rice grain length and yield was mined by Ho-LAMap[J]. BMC Biology, 2017, 15: 28. |
| [5] | Yu J P, Miao J L, Zhang Z Y, Xiong H Y, Zhu X Y, Sun X M, Pan Y H, Liang Y T, Zhang Q, Abdul Rehman R M, Li J J, Zhang H L, Li Z C. Alternative splicing of OsLG3b controls grain length and yield in japonica rice[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2018, 16: 1667-1678. |
| [6] | Liu Q, Han R X, Wu K, Zhang J Q, Ye Y F, Wang S S, Chen J F, Pan Y J, Li Q, Xu X P, Zhou J W, Tao D Y, Wu Y J, Fu X D.G-protein βγ subunits determine grain size through interaction with MADS-domain transcription factors in rice[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 852. |
| [7] | Fan C C, Xing Y Z, Mao H L, Lu T T, Han B, Xu C G, Li X H, Zhang Q F.GS3, a major QTL for grain length and weight and minor QTL for grain width and thickness in rice, encodes a putative transmembrane protein[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2006, 112: 1164-1171. |
| [8] | Qi P, Lin Y S, Song X J, Shen J B, Huang W, Shan J X, Zhu M Z, Jiang L W, Gao P J, Lin H X.The novel quantitative trait locus GL3.1 controls rice grain size and yield by regulating Cyclin-T1;3[J]. Cell Research, 2012, 22: 1666-1680. |
| [9] | Zhang X J, Wang J F, Huang J, Lan H X, Wang C L, Yin C F, Wu Y Y, Tang H J, Qian Q, Li J Y, Zhang H S.Rare allele of OsPPKL1 associated with grain length causes extra-large grain and a significant yield increase in rice[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2012, 109(52): 21534-21539. |
| [10] | Hu Z J, Lu S J, Wang M J, He H H, Sun L, Wang H R, Liu X H, Jiang L, Sun J L, Xin X Y, Kong W, Chu C C, Xue H W, Yang J S, Luo X J, Liu J X.A novel QTL qTGW3 encodes the GSK3/SHAGGY-like kinase OsGSK5/OsSK41 that interacts with OsARF4 to negatively regulate grain size and weight in rice[J]. Molecular Plant, 2018, 11:736-749. |
| [11] | Xia D, Zhou H, Liu R j, Dan W H, Li P B, Wu B, Chen J X, Wang L Q, Gao G J, Zhang Q L, He Y Q. GL3.3, a novel QTL encoding a GSK3/SHAGGY-like kinase, epistatically interacts with GS3 to produce extra-long grains in rice[J]. Molecular Plant, 2018, 11: 754-756. |
| [12] | Ying J Z, Ma M, Bai C, Huang X H, Liu J L, Fan Y Y, Song X J.TGW3, a major QTL that negatively modulates grain length and weight in rice[J]. Molecular Plant, 2018, 11: 750-753. |
| [13] | Wu W G, Liu X Y, Wang M H, Meyer R S, Luo X J, Ndjiondjop M N, Tan L B, Zhang J W, Wu J Z, Cai H W, Sun C Q, Wang X K, Wing R A, Zhu Z F.A single-nucleotide polymorphism causes smaller grain size and loss of seed shattering during African rice domestication[J]. Nature Plants, 2017, 3: 17064. |
| [14] | Wang A H, Hou Q Q, Si L Z, Huang X H, Luo J H, Lu D F, Zhu J J, Shangguan Y Y, Miao J S, Xie Y F, Wang Y C, Zhao Q, Feng Q, Zhou C C, Li Y, Fan D L, Lu Y Q, Tian Q L, Wang Z X, Han B.The PLATZ transcription factor GL6 affects grain length and number in rice[J]. Plant Physiology, 2019, 180 : 2077-2090. |
| [15] | Ishimaru K, Hirotsu N, Madoka Y, Murakami N, Hara N, Onodera H, Kashiwagi T, Ujiie K, Shimizu B I, Onishi A, Miyagawa H, Katoh E.Loss of function of the IAA-glucose hydrolase gene TGW6 enhances rice grain weight and increases yield[J]. Nature Genetics, 2013, 45(6): 707-711. |
| [16] | Si L Z, Chen J Y, Huang X H, Gong H, Luo J H, Hou Q Q, Zhou T Y, Lu T T, Zhu J J, Shangguan Y Y, Chen E W, Gong C X, Zhao Q, Jing Y F, Zhao Y, Li Y, Cui L L, Fan D L, Lu Y Q, Weng Q J, Wang Y C, Zhan Q L, Liu K Y, Wei X H, An K, An G, Han B.OsSPL13 controls grain size in cultivated rice[J]. Nature Genetics, 2016, 48(4): 447-456. |
| [17] | Song X J, Huang W, Shi M, Zhu M Z, Lin H X.A QTL for rice grain width and weight encodes a previously unknown RING-type E3 ubiquitin ligase[J]. Nature Genetics, 2007, 39(5): 623-630. |
| [18] | Li Y B, Fan C C, Xing Y Z, Jiang Y H, Luo L J, Sun L, Shao D, Xu C J, Li X H, Xiao J H, He Y Q, Zhang Q F.Natural variation in GS5 plays an important role in regulating grain size and yield in rice[J]. Nature Genetics, 2011, 43(12): 1266-1269. |
| [19] | Duan P G, Xu J S, Zeng D L, Zhang B L, Geng M F, Zhang G Z, Huang K, Huang L J, Xu R, Ge S, Qian Q, Li Y H.Natural variation in the promoter of GSE5 contributes to grain size diversity in rice[J]. Molecular Plant, 2017, 10: 685-694. |
| [20] | Liu J F, Chen J, Zheng X M, Wu F Q, Lin Q B, Heng Y Q, Tian P, Cheng Z J, Yu X W, Zhou K N, Zhang X, Guo X P, Wang J L, Wang H Y, Wan J M.GW5 acts in the brassinosteroid signaling pathway to regulate grain width and weight in rice[J]. Nature Plants, 2017, 3: 17043. |
| [21] | Wang S K, Wu K, Yuan Q B, Liu X Y, Liu Z B, Lin X Y, Zeng R Z, Zhu H T, Dong G J, Qian Q, Zhang G Q, Fu X D.Control of grain size, shape and quality by OsSPL16 in rice[J]. Nature Genetics, 2012, 44(8): 950-954. |
| [22] | Song X J, Kuroha T, Ayano M, Furuta T, Nagai K, Komeda N, Segami S, Miura K, Ogawa D, Kamura T, Suzuki T, Higashiyama T, Yamasaki M, Mori H, Inukai Y, Wu J Z, Kitano H, Sakakibara H, Jacobsen S E, Ashikari M.Rare allele of a previously unidentified histone H4 acetyltransferase enhances grain weight, yield, and plant biomass in rice[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2015, 112(1): 76-81. |
| [23] | Wang Y X, Xiong G S, Hu J, Jiang L, Yu H, Xu J, Fang Y X, Zeng L J, Xu E B, Xu J, Ye W J, Meng X B, Liu R F, Chen H Q, Jing Y H, Wang Y H, Zhu X D, Li J Y, Qian Q.Copy number variation at the GL7 locus contributes to grain size diversity in rice[J]. Nature Genetics, 2015, 47(8): 944-948. |
| [24] | Wang S K, Li S, Liu Q, Wu K, Zhang J Q, Wang S S, Wang Y, Chen X B, Zhang Y, Gao C X, Wang F, Huang H X, Fu X D.The OsSPL16-GW7 regulatory module determines grain shape and simultaneously improves rice yield and grain quality[J]. Nature Genetics, 2015, 47(8): 949-954. |
| [25] | Zhao D S, Li Q F, Zhang C Q, Zhang C, Yang Q Q, Pan L X, Ren X Y, Lu J, Gu M H, Liu Q Q.GS9 acts as a transcriptional activator to regulate rice grain shape and appearance quality[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 1240. |
| [26] | Li N, Xu R, Duan P G, Li Y H.Control of grain size in rice[J]. Plant Reproduction, 2018, 31: 237-251. |
| [27] | 刘喜,牟昌铃,周春雷,程治军,江玲,万建民. 水稻粒型基因克隆和调控机制研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学,2018, 32(1): 1-11. |
| Liu X, Mou C L, Zhou C L, Cheng Z J, Jiang L, Wang J M.Research progress on cloning and regulation mechanism of rice grain shape genes[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2018, 32(1): 1-11. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | Mackay T F C, Stone E A, Ayroles J F. The genetics of quantitative traits: challenges and prospects[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2009, 10: 565-577. |
| [29] | Kumar J, Gupta D S, Gupta S, Dubey S, Gupta P, Kumar S.Quantitative trait loci from identification to exploitation for crop improvement[J]. Plant Cell Reports, 2017, 36: 1187-1213. |
| [30] | Yamamoto T, Yonemaru J, Yano M.Towards the understanding of complex traits in rice: substantially or superficially[J]. DNA Research, 2009, 16: 141-154. |
| [31] | Zhang H W, Fan Y Y, Zhu Y J, Chen J Y, Yu S B, Zhuang J Y.Dissection of the qTGW1.1 region into two tightly-linked minor QTLs having stable effects for grain weight in rice[J]. BMC Genetics, 2016, 17: 98. |
| [32] | Guo L, Wang K, Chen J Y, Huang D R, Fan Y Y, Zhuang J Y.Dissection of two quantitative trait loci for grain weight linked in repulsion on the long arm of chromosome 1 of rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. The Crop Journal, 2013, 1: 70-76. |
| [33] | Zheng K L, Huang N, Bennett J, Khush G S.PCR-based marker-assisted selection in rice breeding//IRRI Discussion Paper Series No. 12. Los Banos: International Rice Research Institute, 1995. |
| [34] | Chen X, Temnykh S, Xu Y, Cho Y G, McCouch S R. Development of a microsatellite framework map providing genome-wide coverage in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 1997, 95: 553-567. |
| [35] | SAS Institute Inc.SAS/STAT User’s Guide[M]. Cary, NC: SAS Institute, 1999. |
| [36] | Dai W M, Zhang K Q, Wu J R, Wang L, Duan B W, Zheng K L, Cai R, Zhuang J Y.Validating a segment on the short arm of chromosome 6 responsible for genetic variation in the hull silicon content and yield traits of rice[J]. Euphytica, 2008, 160: 317-324. |
| [37] | Abiola O, Angel J M, Avner P, Bachmanov A A, Belknap J K, Bennett B, Blankenhorn E P, Blizard D A, Bolivar V, Brockmann G A, Buck K J, Bureau J F, Casley W L, Chesler E J, Cheverud J M, Churchill G A, Cook M, Crabbe J C, Crusio W E, Darvasi A, Haan G D, Dermant P, Doerge R W, Elliot R W, Farber C R, Flaherty L, Flint J, Gershenfeld H, Gibson J P, Gu J, Gu W, Himmelbauer H, Hitzemann R, Hsu H C, Hunter K, Iraqi F F, Jansen R C, Johnson T E, Jones B C, Kempermann G, Lammert F, Lu L, Manly K F, Matthews D B, Medrano J F, Mehrabian M, Mittlemann G, Mock B A, Mogil J S, Montagutelli X, Morahan G, Mountz J D, Nagase H, Nowakowski R S, O'Hara B F, Osadchuk A V, Paigen B, Palmer A A, Peirce J L, Pomp D, Rosemann M, Rosen G D, Schalkwyk L C, Seltzer Z, Settle S, Shimomura K, Shou S, Sikela J M, Siracusa L D, Spearow J L, Teuscher C, Threadgill D W, Toth L A, Toye A A, Vadasz C, Van Zant G, Wakeland E, Williams R W, Zhang H G, Zou F. Complex Trait Consortium. The nature and identification of quantitative trait loci: A community’s view[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2003, 4(11): 911-916. |
| [38] | Wang L L, Chen Y Y, Guo L, Zhang H W, Fan Y Y, Zhuang J Y.Dissection of qTGW1.2 to three QTLs for grain weight and grain size in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Euphytica, 2015, 202: 119-127. |
| [39] | Dong Q, Zhang Z H, Wang L L, Zhu Y J, Fan Y Y, Mou T M, Ma L Y, Zhuang J Y.Dissection and fine-mapping of two QTL for grain size linked in a 460-kb region on chromosome 1 of rice[J]. Rice, 2018, 11: 44. |
| [40] | Wang W H, Wang L L, Zhu Y J, Fan Y Y, Zhuang J Y.Fine-mapping of qTGW1.2a, a quantitative trait locus for 1000-grain weight in rice[J]. Rice Science, 2019, 26(4): 220-228. |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [6] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [7] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [8] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [9] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [10] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [11] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [12] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [13] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| [14] | 许用强, 姜宁, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 水稻开花期高温热害响应机理及其调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 111-126. |
| [15] | 吕海涛, 李建忠, 鲁艳辉, 徐红星, 郑许松, 吕仲贤. 稻田福寿螺的发生、危害及其防控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 127-139. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||