
中国水稻科学 ›› 2019, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (5): 436-446.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2019.8084
钟雪梅1, 黄铁平2, 彭建伟1,*( ), 卢文璐3, 康兴蓉1, 孙梦飞1, 宋思明4, 唐启源1, 陈裕新5, 湛冬至3, 周旋6,*(
), 卢文璐3, 康兴蓉1, 孙梦飞1, 宋思明4, 唐启源1, 陈裕新5, 湛冬至3, 周旋6,*( )
)
收稿日期:2018-07-16
修回日期:2019-07-09
出版日期:2019-09-10
发布日期:2019-09-10
通讯作者:
彭建伟,周旋
基金资助:
Xuemei ZHONG1, Tieping HUANG2, Jianwei PENG1,*( ), Wenlu LU3, Xingrong KANG1, Mengfei SUN1, Siming SONG4, Qiyuan TANG1, Yuxin CHEN5, Dongzhi ZHAN3, Xuan ZHOU6,*(
), Wenlu LU3, Xingrong KANG1, Mengfei SUN1, Siming SONG4, Qiyuan TANG1, Yuxin CHEN5, Dongzhi ZHAN3, Xuan ZHOU6,*( )
)
Received:2018-07-16
Revised:2019-07-09
Online:2019-09-10
Published:2019-09-10
Contact:
Jianwei PENG, Xuan ZHOU
摘要:
【目的】 为保证水稻施肥的准确性,揭示水稻机插与同步一次性侧深减量施肥的养分利用特征,为机插双季稻的氮(N)肥高效利用提供依据。【方法】 在典型双季稻种植区,以测土配方施肥量为依据,结合精量施肥机,2017-2018年研究机插同步一次性精量施肥对双季稻养分吸收和利用的影响。【结果】 与常规施肥处理相比,机插同步一次性减N 10%~30%处理早稻N、P、K累积量分别提高7.9%~11.7%、9.4%~25.9%和2.0%~6.5%(2017),8.2%~15.0%、9.0%~12.1%和14.0%~18.1%(2018);晚稻分别提高-0.6%~5.7%、9.1%~14.4%和3.7%~19.6%(2017),6.1%~8.5%、9.4%~19.3%和18.7%~22.2%(2018);早稻N肥吸收利用率(NRE)、N肥农学利用率(NAE)、N肥偏生产力(NPFP)分别提高38.6%~92.7%、49.9%~103.6%和29.5%~71.7%(2017),35.4%~71.4%、46.0%~98.4%和20.7%~75.4%(2018);晚稻分别提高20.8%~43.1%、31.3%~64.2%和18.3%~48.5% (2017),26.8%~99.1%、60.0%~82.9%和26.6%~60.5%(2018)。其中,早晚稻以减N 20%~30%处理效果较好。水稻机插同步一次性精量施肥随着施N量的降低,双季稻NRE先增加后降低,NHI、NAE和NPFP呈上升趋势,而土壤碱解氮含量呈下降趋势。【结论】通过施肥技术和机插模式的集成与优化,能有效减少稻田N肥施入,利于N、P、K吸收积累,同步提高双季稻的产量和N肥利用效率。
中图分类号:
钟雪梅, 黄铁平, 彭建伟, 卢文璐, 康兴蓉, 孙梦飞, 宋思明, 唐启源, 陈裕新, 湛冬至, 周旋. 机插同步一次性精量施肥对双季稻养分累积及利用率的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(5): 436-446.
Xuemei ZHONG, Tieping HUANG, Jianwei PENG, Wenlu LU, Xingrong KANG, Mengfei SUN, Siming SONG, Qiyuan TANG, Yuxin CHEN, Dongzhi ZHAN, Xuan ZHOU. Effects of Machine-transplanting Synchronized with One-time Precision Fertilization on Nutrient Uptake and Use Efficiency of Double Cropping Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2019, 33(5): 436-446.
| 稻季 Season | 处理 Treatment | 基肥 Base fertilizer | 分蘖肥 Tillering fertilizer |
|---|---|---|---|
| 早稻 Early rice | T1 | 复混肥 Compound fertilizer(20-10-10) 450 kg/hm2 | 尿素130.5 kg/hm2+氯化钾75.0 kg/hm2 Urea 130.5 kg/hm2+KCl 75.0 kg/hm2 |
| T2 | 水稻生产专用肥 Special fertilizer(26.1-8.7-17.4) 517.3 kg/hm2 | ||
| T3 | 水稻生产专用肥 Special fertilizer(24.8-9.3-18.6) 483.9 kg/hm2 | ||
| T4 | 水稻生产专用肥 Special fertilizer(23.1-9.9-19.8) 454.6 kg/hm2 | ||
| T5 | 水稻生产专用肥 Special fertilizer(21.0-10.5-21.0) 428.6 kg/hm2 | ||
| CK | 过磷酸钙 Calcium superphosphate 375.0 kg/hm2+氯化钾KCl 75.0 kg/hm2 | 氯化钾75.0 kg/hm2 KCl 75.0 kg/hm2 | |
| 晚稻 Late rice | T1 | 复混肥 Compound fertilizer(20-8-12) 450 kg/hm2 | 尿素130.5 kg/hm2+氯化钾75.0 kg/hm2 Urea 130.5 kg/hm2+KCl 75.0 kg/hm2 |
| T2 | 水稻生产专用肥 Special fertilizer(28.9-7-17.5) 514.05 kg/hm2 | ||
| T3 | 水稻生产专用肥 Special fertilizer(27.1-7.4-18.5) 486.45 kg/hm2 | ||
| T4 | 水稻生产专用肥 Special fertilizer(25.4-7.9-19.8) 455.7 kg/hm2 | ||
| T5 | 水稻生产专用肥 Special fertilizer(23.1-8.4-21) 428.55 kg/hm2 | ||
| CK | 过磷酸钙 Calcium superphosphate 300.0 kg/hm2+氯化钾KCl 75.0 kg/hm2 | 氯化钾75.0 kg/hm2 KCl 75.0 kg/hm2 |
表1 施肥方式及施肥用量
Table 1 Fertilization method and application rate.
| 稻季 Season | 处理 Treatment | 基肥 Base fertilizer | 分蘖肥 Tillering fertilizer |
|---|---|---|---|
| 早稻 Early rice | T1 | 复混肥 Compound fertilizer(20-10-10) 450 kg/hm2 | 尿素130.5 kg/hm2+氯化钾75.0 kg/hm2 Urea 130.5 kg/hm2+KCl 75.0 kg/hm2 |
| T2 | 水稻生产专用肥 Special fertilizer(26.1-8.7-17.4) 517.3 kg/hm2 | ||
| T3 | 水稻生产专用肥 Special fertilizer(24.8-9.3-18.6) 483.9 kg/hm2 | ||
| T4 | 水稻生产专用肥 Special fertilizer(23.1-9.9-19.8) 454.6 kg/hm2 | ||
| T5 | 水稻生产专用肥 Special fertilizer(21.0-10.5-21.0) 428.6 kg/hm2 | ||
| CK | 过磷酸钙 Calcium superphosphate 375.0 kg/hm2+氯化钾KCl 75.0 kg/hm2 | 氯化钾75.0 kg/hm2 KCl 75.0 kg/hm2 | |
| 晚稻 Late rice | T1 | 复混肥 Compound fertilizer(20-8-12) 450 kg/hm2 | 尿素130.5 kg/hm2+氯化钾75.0 kg/hm2 Urea 130.5 kg/hm2+KCl 75.0 kg/hm2 |
| T2 | 水稻生产专用肥 Special fertilizer(28.9-7-17.5) 514.05 kg/hm2 | ||
| T3 | 水稻生产专用肥 Special fertilizer(27.1-7.4-18.5) 486.45 kg/hm2 | ||
| T4 | 水稻生产专用肥 Special fertilizer(25.4-7.9-19.8) 455.7 kg/hm2 | ||
| T5 | 水稻生产专用肥 Special fertilizer(23.1-8.4-21) 428.55 kg/hm2 | ||
| CK | 过磷酸钙 Calcium superphosphate 300.0 kg/hm2+氯化钾KCl 75.0 kg/hm2 | 氯化钾75.0 kg/hm2 KCl 75.0 kg/hm2 |
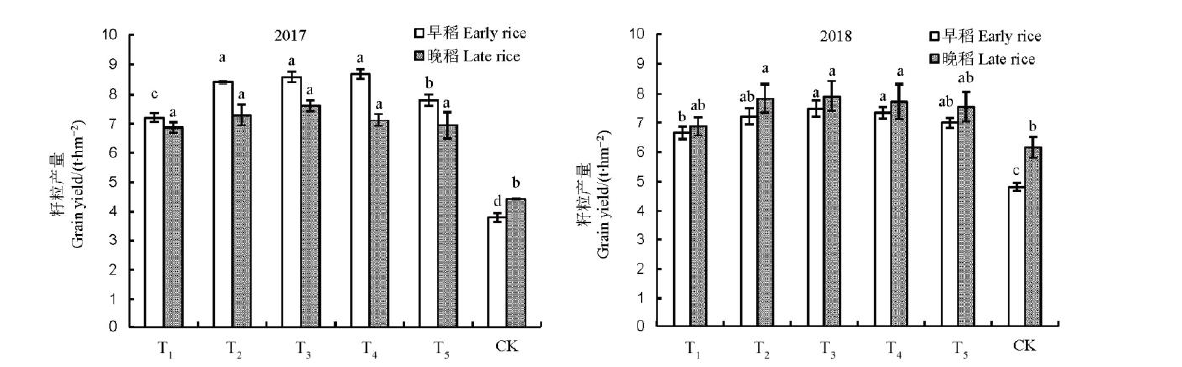
图1 不同施肥处理下机插双季稻籽粒产量柱上不同小写字母代表处理间在5%水平上差异显著(LSD)。图中数值为平均值±标准误(n=3)。
Fig. 1. Grain yield of machine-transplanted double-cropping rice under different fertilization treatments. Different small letters above the bars mean significant difference among treatments at 5% level (LSD). Data in the figure are Mean±SE (n=3).
| 年份 Year | 稻季 Season | 处理 Treatment | 各生育期干物质量 Dry matter accumulation at different growth stages/(t∙hm-2) | 收获指数 HI/% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 分蘖盛期 MT | 抽穗期 HS | 灌浆期 FS | 成熟期 MS | |||||
| 2017 | 早稻Early rice | T1 | 0.8 a | 3.5 a | 6.1 b | 12.5 ab | 59.4 ab | |
| T2 | 0.9 a | 4.0 a | 6.3 ab | 13.4 a | 58.1 b | |||
| T3 | 0.9 a | 4.0 a | 6.7 ab | 13.5 a | 59.7 ab | |||
| T4 | 1.0 a | 4.1 a | 6.9 a | 13.7 a | 61.0 ab | |||
| T5 | 0.8 a | 3.5 a | 6.3 ab | 12.0 b | 64.2 a | |||
| CK | 0.3 b | 1.8 b | 3.4 c | 9.4 c | 61.1 ab | |||
| 平均值Average | 0.8 | 3.5 | 5.9 | 12.4 | 60.6 | |||
| 晚稻Late rice | T1 | 1.3 ab | 6.6 ab | 8.8 a | 12.8 ab | 45.2 b | ||
| T2 | 1.4 ab | 7.1 a | 9.3 a | 13.4 ab | 45.2 b | |||
| T3 | 1.4 a | 6.9 ab | 9.1 a | 13.7 a | 46.8 b | |||
| T4 | 1.5 a | 6.6 ab | 9.0 a | 12.9 ab | 48.1 ab | |||
| T5 | 1.2 b | 6.0 b | 8.2 a | 12.4 b | 47.9 ab | |||
| CK | 0.6 c | 2.1 c | 4.3 b | 10.3 c | 53.4 a | |||
| 平均值Average | 1.2 | 5.9 | 8.1 | 12.6 | 47.8 | |||
| 2018 | 早稻Early rice | T1 | 1.6 a | 4.0 a | 11.0 a | 14.2 b | 46.9 a | |
| T2 | 1.5 ab | 4.2 a | 11.2 a | 14.9 ab | 48.5 a | |||
| T3 | 1.5 abc | 4.3 a | 11.2 a | 15.1 a | 51.2 a | |||
| T4 | 1.4 bc | 4.0 a | 10.9 a | 14.4 ab | 51.3 a | |||
| T5 | 1.4 c | 3.6 a | 10.7 a | 13.2 c | 53.1 a | |||
| CK | 0.8 d | 2.1 b | 8.5 b | 9.6 d | 50.1 a | |||
| 平均值Average | 1.4 | 3.7 | 10.6 | 13.6 | 50.2 | |||
| 晚稻Late rice | T1 | 4.0 a | 6.7 a | 12.5 ab | 17.9 b | 38.4 a | ||
| T2 | 2.9 b | 6.8 a | 13.8 ab | 19.0 ab | 41.3 a | |||
| T3 | 2.5 bc | 7.1 a | 14.4 a | 19.9 a | 39.6 a | |||
| T4 | 2.5 bcd | 7.0 a | 12.8 ab | 18.9 ab | 40.7 a | |||
| T5 | 1.8 cd | 6.4 a | 11.7 b | 17.8 b | 42.5 a | |||
| CK | 1.7 d | 4.9 b | 8.7 c | 13.7 c | 45.0 a | |||
| 平均值Average | 2.5 | 6.5 | 12.3 | 17.9 | 41.3 | |||
表2 不同施肥处理下机插双季稻各生育期干物质量和收获指数
Table 2 Dry matter accumulation at different growth stages and harvest index of machine-transplanted double-cropping rice under different fertilization treatments.
| 年份 Year | 稻季 Season | 处理 Treatment | 各生育期干物质量 Dry matter accumulation at different growth stages/(t∙hm-2) | 收获指数 HI/% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 分蘖盛期 MT | 抽穗期 HS | 灌浆期 FS | 成熟期 MS | |||||
| 2017 | 早稻Early rice | T1 | 0.8 a | 3.5 a | 6.1 b | 12.5 ab | 59.4 ab | |
| T2 | 0.9 a | 4.0 a | 6.3 ab | 13.4 a | 58.1 b | |||
| T3 | 0.9 a | 4.0 a | 6.7 ab | 13.5 a | 59.7 ab | |||
| T4 | 1.0 a | 4.1 a | 6.9 a | 13.7 a | 61.0 ab | |||
| T5 | 0.8 a | 3.5 a | 6.3 ab | 12.0 b | 64.2 a | |||
| CK | 0.3 b | 1.8 b | 3.4 c | 9.4 c | 61.1 ab | |||
| 平均值Average | 0.8 | 3.5 | 5.9 | 12.4 | 60.6 | |||
| 晚稻Late rice | T1 | 1.3 ab | 6.6 ab | 8.8 a | 12.8 ab | 45.2 b | ||
| T2 | 1.4 ab | 7.1 a | 9.3 a | 13.4 ab | 45.2 b | |||
| T3 | 1.4 a | 6.9 ab | 9.1 a | 13.7 a | 46.8 b | |||
| T4 | 1.5 a | 6.6 ab | 9.0 a | 12.9 ab | 48.1 ab | |||
| T5 | 1.2 b | 6.0 b | 8.2 a | 12.4 b | 47.9 ab | |||
| CK | 0.6 c | 2.1 c | 4.3 b | 10.3 c | 53.4 a | |||
| 平均值Average | 1.2 | 5.9 | 8.1 | 12.6 | 47.8 | |||
| 2018 | 早稻Early rice | T1 | 1.6 a | 4.0 a | 11.0 a | 14.2 b | 46.9 a | |
| T2 | 1.5 ab | 4.2 a | 11.2 a | 14.9 ab | 48.5 a | |||
| T3 | 1.5 abc | 4.3 a | 11.2 a | 15.1 a | 51.2 a | |||
| T4 | 1.4 bc | 4.0 a | 10.9 a | 14.4 ab | 51.3 a | |||
| T5 | 1.4 c | 3.6 a | 10.7 a | 13.2 c | 53.1 a | |||
| CK | 0.8 d | 2.1 b | 8.5 b | 9.6 d | 50.1 a | |||
| 平均值Average | 1.4 | 3.7 | 10.6 | 13.6 | 50.2 | |||
| 晚稻Late rice | T1 | 4.0 a | 6.7 a | 12.5 ab | 17.9 b | 38.4 a | ||
| T2 | 2.9 b | 6.8 a | 13.8 ab | 19.0 ab | 41.3 a | |||
| T3 | 2.5 bc | 7.1 a | 14.4 a | 19.9 a | 39.6 a | |||
| T4 | 2.5 bcd | 7.0 a | 12.8 ab | 18.9 ab | 40.7 a | |||
| T5 | 1.8 cd | 6.4 a | 11.7 b | 17.8 b | 42.5 a | |||
| CK | 1.7 d | 4.9 b | 8.7 c | 13.7 c | 45.0 a | |||
| 平均值Average | 2.5 | 6.5 | 12.3 | 17.9 | 41.3 | |||
| 年份 Year | 稻季 Season | 处理 Treatment | 各生育期N素累积量TNA at different stages/(kg∙hm-2) | N收获指数 NHI/% | 抽穗后N素积累 N accumulation after heading/(kg∙hm-2) | 抽穗后N素积累比例 N accumulation ratio after heading/% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 分蘖盛期 MT | 抽穗期 HS | 灌浆期 FS | 成熟期 MS | |||||||
| 2017 | 早稻Early rice | T1 | 23.3 a | 78.4 a | 77.8 b | 140.5 ab | 61.4 a | 62.1 a | 43.5 b | |
| T2 | 23.7 a | 82.8 a | 92.1 ab | 151.6 ab | 60.1 a | 68.9 a | 45.4 b | |||
| T3 | 24.0 a | 84.6 a | 99.5 a | 157.0 a | 61.9 a | 72.4 a | 46.0 b | |||
| T4 | 23.5 a | 87.8 a | 109.4 a | 156.2 a | 64.0 a | 68.4 a | 43.9 b | |||
| T5 | 22.2 a | 67.9 a | 99.3 a | 132.9 b | 66.6 a | 65.0 a | 49.8 b | |||
| CK | 15.9 b | 25.6 b | 33.9 c | 95.4 c | 63.6 a | 69.8 a | 73.2 a | |||
| 平均值Average | 17.5 | 71.2 | 85.3 | 138.9 | 62.9 | 67.8 | 50.3 | |||
| 晚稻Late rice | T1 | 32.3 ab | 99.2 ab | 119.6 ab | 165.0 a | 53.0 a | 65.8 a | 35.0 b | ||
| T2 | 38.4 a | 109.4 a | 149.9 a | 170.7 a | 54.0 a | 61.3 a | 35.9 b | |||
| T3 | 40.0 a | 108.5 a | 144.3 ab | 174.4 a | 55.2 a | 65.9 a | 37.6 b | |||
| T4 | 37.7 ab | 101.7 ab | 129.6 ab | 163.9 a | 55.8 a | 62.2 a | 37.8 b | |||
| T5 | 30.2 b | 90.6 b | 109.3 b | 146.1 ab | 54.9 a | 55.5 a | 38.1 b | |||
| CK | 9.6 c | 30.1 c | 49.1 c | 100.0 b | 52.8 a | 69.9 a | 69.5 a | |||
| 平均值Average | 31.4 | 89.9 | 117.0 | 153.3 | 54.3 | 63.4 | 42.3 | |||
| 2018 | 早稻Early rice | T1 | 27.8 a | 92.6 a | 103.2 a | 150.2 ab | 54.0 a | 57.6 a | 37.9 b | |
| T2 | 23.1 b | 94.1 a | 120.4 a | 162.6 ab | 57.6 a | 68.5 a | 41.1 ab | |||
| T3 | 22.1 bc | 96.8 a | 118.7 a | 172.8 a | 61.3 a | 76.1 a | 44.1 ab | |||
| T4 | 20.3 bc | 89.9 a | 111.7 a | 168.1 ab | 58.6 a | 78.2 a | 46.2 ab | |||
| T5 | 19.1 c | 78.9 a | 101.3 a | 143.4 b | 57.6 a | 71.7 a | 45.0 ab | |||
| CK | 7.1 d | 40.6 b | 58.6 b | 98.8 c | 55.3 a | 58.3 a | 58.3 a | |||
| 平均值Average | 19.9 | 82.2 | 102.3 | 149.3 | 48.6 | 68.4 | 45.4 | |||
| 晚稻Late rice | T1 | 96.9 a | 134.7 a | 152.0 a | 195.3 a | 49.5 a | 50.6 a | 31.0 a | ||
| T2 | 81.9 ab | 150.7 a | 174.6 a | 207.2 a | 46.9 a | 56.5 a | 26.6 a | |||
| T3 | 68.6 bc | 154.3 a | 176.4 a | 211.9 a | 44.7 a | 57.6 a | 27.7 a | |||
| T4 | 72.4 abc | 147.6 a | 156.7 a | 207.1 a | 48.6 a | 59.5 a | 28.8 a | |||
| T5 | 48.2 cd | 127.1 a | 140.6 ab | 192.4 a | 48.9 a | 75.9 a | 33.9 a | |||
| CK | 37.2 d | 83.4 b | 97.9 b | 153.1 b | 52.9 a | 69.7 a | 45.6 a | |||
| 平均值Average | 67.6 | 132.9 | 149.7 | 194.5 | 48.6 | 61.7 | 32.3 | |||
表3 不同施肥处理下机插双季稻各生育期N素吸收和N收获指数
Table 3 N uptake at different growth stages and N harvest index of machine-transplanted double-cropping rice under different fertilization treatments.
| 年份 Year | 稻季 Season | 处理 Treatment | 各生育期N素累积量TNA at different stages/(kg∙hm-2) | N收获指数 NHI/% | 抽穗后N素积累 N accumulation after heading/(kg∙hm-2) | 抽穗后N素积累比例 N accumulation ratio after heading/% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 分蘖盛期 MT | 抽穗期 HS | 灌浆期 FS | 成熟期 MS | |||||||
| 2017 | 早稻Early rice | T1 | 23.3 a | 78.4 a | 77.8 b | 140.5 ab | 61.4 a | 62.1 a | 43.5 b | |
| T2 | 23.7 a | 82.8 a | 92.1 ab | 151.6 ab | 60.1 a | 68.9 a | 45.4 b | |||
| T3 | 24.0 a | 84.6 a | 99.5 a | 157.0 a | 61.9 a | 72.4 a | 46.0 b | |||
| T4 | 23.5 a | 87.8 a | 109.4 a | 156.2 a | 64.0 a | 68.4 a | 43.9 b | |||
| T5 | 22.2 a | 67.9 a | 99.3 a | 132.9 b | 66.6 a | 65.0 a | 49.8 b | |||
| CK | 15.9 b | 25.6 b | 33.9 c | 95.4 c | 63.6 a | 69.8 a | 73.2 a | |||
| 平均值Average | 17.5 | 71.2 | 85.3 | 138.9 | 62.9 | 67.8 | 50.3 | |||
| 晚稻Late rice | T1 | 32.3 ab | 99.2 ab | 119.6 ab | 165.0 a | 53.0 a | 65.8 a | 35.0 b | ||
| T2 | 38.4 a | 109.4 a | 149.9 a | 170.7 a | 54.0 a | 61.3 a | 35.9 b | |||
| T3 | 40.0 a | 108.5 a | 144.3 ab | 174.4 a | 55.2 a | 65.9 a | 37.6 b | |||
| T4 | 37.7 ab | 101.7 ab | 129.6 ab | 163.9 a | 55.8 a | 62.2 a | 37.8 b | |||
| T5 | 30.2 b | 90.6 b | 109.3 b | 146.1 ab | 54.9 a | 55.5 a | 38.1 b | |||
| CK | 9.6 c | 30.1 c | 49.1 c | 100.0 b | 52.8 a | 69.9 a | 69.5 a | |||
| 平均值Average | 31.4 | 89.9 | 117.0 | 153.3 | 54.3 | 63.4 | 42.3 | |||
| 2018 | 早稻Early rice | T1 | 27.8 a | 92.6 a | 103.2 a | 150.2 ab | 54.0 a | 57.6 a | 37.9 b | |
| T2 | 23.1 b | 94.1 a | 120.4 a | 162.6 ab | 57.6 a | 68.5 a | 41.1 ab | |||
| T3 | 22.1 bc | 96.8 a | 118.7 a | 172.8 a | 61.3 a | 76.1 a | 44.1 ab | |||
| T4 | 20.3 bc | 89.9 a | 111.7 a | 168.1 ab | 58.6 a | 78.2 a | 46.2 ab | |||
| T5 | 19.1 c | 78.9 a | 101.3 a | 143.4 b | 57.6 a | 71.7 a | 45.0 ab | |||
| CK | 7.1 d | 40.6 b | 58.6 b | 98.8 c | 55.3 a | 58.3 a | 58.3 a | |||
| 平均值Average | 19.9 | 82.2 | 102.3 | 149.3 | 48.6 | 68.4 | 45.4 | |||
| 晚稻Late rice | T1 | 96.9 a | 134.7 a | 152.0 a | 195.3 a | 49.5 a | 50.6 a | 31.0 a | ||
| T2 | 81.9 ab | 150.7 a | 174.6 a | 207.2 a | 46.9 a | 56.5 a | 26.6 a | |||
| T3 | 68.6 bc | 154.3 a | 176.4 a | 211.9 a | 44.7 a | 57.6 a | 27.7 a | |||
| T4 | 72.4 abc | 147.6 a | 156.7 a | 207.1 a | 48.6 a | 59.5 a | 28.8 a | |||
| T5 | 48.2 cd | 127.1 a | 140.6 ab | 192.4 a | 48.9 a | 75.9 a | 33.9 a | |||
| CK | 37.2 d | 83.4 b | 97.9 b | 153.1 b | 52.9 a | 69.7 a | 45.6 a | |||
| 平均值Average | 67.6 | 132.9 | 149.7 | 194.5 | 48.6 | 61.7 | 32.3 | |||
| 年份 Year | 稻季 Season | 处理 Treatment | 氮肥吸收利用率 NRE/% | 氮肥农学利用率NAE/(kg·kg-1) | 氮肥偏生产力NPFP/(kg·kg-1) | 氮肥生理利用率NPE/(kg·kg-1) | 氮素干物质 生产效率 NBPE/(kg·kg-1) | 氮素稻谷生产效率NGPE/(kg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 早稻Early rice | T1 | 30.1 b | 22.8 d | 48.1 d | 80.9 a | 89.2 b | 51.8 a |
| T2 | 41.6 ab | 34.2 c | 62.3 c | 82.9 a | 88.3 b | 55.5 a | ||
| T3 | 51.3 a | 39.8 bc | 71.4 b | 78.9 a | 86.2 b | 54.7 a | ||
| T4 | 57.9 a | 46.4 a | 82.6 a | 83.3 a | 88.0 b | 55.7 a | ||
| T5 | 41.6 ab | 44.7 ab | 86.9 a | 110.8 a | 90.3 b | 59.4 a | ||
| CK | - | - | - | - | 98.8 a | 39.9 b | ||
| 平均值Average | 44.5 | 37.6 | 70.3 | 87.4 | 90.1 | 52.8 | ||
| 晚稻Late rice | T1 | 39.4 a | 11.8 b | 33.3 c | 39.3 a | 81.3 b | 35.2 a | |
| T2 | 47.6 a | 15.5 ab | 39.4 c | 32.7 a | 78.5 b | 34.3 a | ||
| T3 | 56.3 a | 19.4 a | 46.2 b | 36.2 a | 78.6 b | 35.1 a | ||
| T4 | 55.3 a | 18.7 a | 49.4 b | 39.0 a | 80.0 b | 35.3 a | ||
| T5 | 46.5 a | 20.4 a | 56.2 a | 45.4 a | 85.1 b | 38.3 a | ||
| CK | - | - | - | - | 103.7 a | 35.6 a | ||
| 平均值Average | 49.0 | 17.1 | 44.9 | 38.5 | 84.5 | 35.6 | ||
| 2018 | 早稻Early rice | T1 | 33.1 b | 12.2 c | 44.4 e | 49.0 a | 99.4 a | 45.0 a |
| T2 | 44.9 ab | 17.9 bc | 53.6 d | 38.3 a | 92.0 ab | 44.9 a | ||
| T3 | 56.8 a | 22.3 ab | 62.5 c | 37.2 a | 84.8 ab | 43.4 a | ||
| T4 | 53.7 a | 24.3 a | 70.2 b | 38.4 a | 83.8 b | 43.9 a | ||
| T5 | 45.9 ab | 22.8 ab | 77.8 a | 50.4 a | 88.6 ab | 47.0 a | ||
| CK | - | - | - | - | 97.9 ab | 49.0 a | ||
| 平均值Average | 46.9 | 19.9 | 61.7 | 42.7 | 91.1 | 45.6 | ||
| 晚稻Late rice | T1 | 26.1 b | 6.5 d | 41.7 d | 23.1 a | 93.8 a | 37.5 a | |
| T2 | 33.0 b | 10.3 c | 52.8 cd | 31.1 a | 92.8 a | 38.1 a | ||
| T3 | 51.9 a | 11.8 b | 60.0 bc | 35.7 a | 94.9 a | 37.7 a | ||
| T4 | 46.7 a | 11.8 b | 67.0 ab | 29.5 a | 91.8 a | 37.6 a | ||
| T5 | 45.2 a | 12.8 a | 76.3 a | 31.0 a | 89.1 a | 37.4 a | ||
| CK | - | - | - | - | 89.8 a | 40.3 a | ||
| 平均值Average | 40.6 | 10.7 | 59.6 | 30.1 | 92.0 | 38.1 |
表4 不同施肥处理下机插双季稻N肥利用效率
Table 4 N use efficiency of machine-transplanted double-cropping rice under different fertilization treatments.
| 年份 Year | 稻季 Season | 处理 Treatment | 氮肥吸收利用率 NRE/% | 氮肥农学利用率NAE/(kg·kg-1) | 氮肥偏生产力NPFP/(kg·kg-1) | 氮肥生理利用率NPE/(kg·kg-1) | 氮素干物质 生产效率 NBPE/(kg·kg-1) | 氮素稻谷生产效率NGPE/(kg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 早稻Early rice | T1 | 30.1 b | 22.8 d | 48.1 d | 80.9 a | 89.2 b | 51.8 a |
| T2 | 41.6 ab | 34.2 c | 62.3 c | 82.9 a | 88.3 b | 55.5 a | ||
| T3 | 51.3 a | 39.8 bc | 71.4 b | 78.9 a | 86.2 b | 54.7 a | ||
| T4 | 57.9 a | 46.4 a | 82.6 a | 83.3 a | 88.0 b | 55.7 a | ||
| T5 | 41.6 ab | 44.7 ab | 86.9 a | 110.8 a | 90.3 b | 59.4 a | ||
| CK | - | - | - | - | 98.8 a | 39.9 b | ||
| 平均值Average | 44.5 | 37.6 | 70.3 | 87.4 | 90.1 | 52.8 | ||
| 晚稻Late rice | T1 | 39.4 a | 11.8 b | 33.3 c | 39.3 a | 81.3 b | 35.2 a | |
| T2 | 47.6 a | 15.5 ab | 39.4 c | 32.7 a | 78.5 b | 34.3 a | ||
| T3 | 56.3 a | 19.4 a | 46.2 b | 36.2 a | 78.6 b | 35.1 a | ||
| T4 | 55.3 a | 18.7 a | 49.4 b | 39.0 a | 80.0 b | 35.3 a | ||
| T5 | 46.5 a | 20.4 a | 56.2 a | 45.4 a | 85.1 b | 38.3 a | ||
| CK | - | - | - | - | 103.7 a | 35.6 a | ||
| 平均值Average | 49.0 | 17.1 | 44.9 | 38.5 | 84.5 | 35.6 | ||
| 2018 | 早稻Early rice | T1 | 33.1 b | 12.2 c | 44.4 e | 49.0 a | 99.4 a | 45.0 a |
| T2 | 44.9 ab | 17.9 bc | 53.6 d | 38.3 a | 92.0 ab | 44.9 a | ||
| T3 | 56.8 a | 22.3 ab | 62.5 c | 37.2 a | 84.8 ab | 43.4 a | ||
| T4 | 53.7 a | 24.3 a | 70.2 b | 38.4 a | 83.8 b | 43.9 a | ||
| T5 | 45.9 ab | 22.8 ab | 77.8 a | 50.4 a | 88.6 ab | 47.0 a | ||
| CK | - | - | - | - | 97.9 ab | 49.0 a | ||
| 平均值Average | 46.9 | 19.9 | 61.7 | 42.7 | 91.1 | 45.6 | ||
| 晚稻Late rice | T1 | 26.1 b | 6.5 d | 41.7 d | 23.1 a | 93.8 a | 37.5 a | |
| T2 | 33.0 b | 10.3 c | 52.8 cd | 31.1 a | 92.8 a | 38.1 a | ||
| T3 | 51.9 a | 11.8 b | 60.0 bc | 35.7 a | 94.9 a | 37.7 a | ||
| T4 | 46.7 a | 11.8 b | 67.0 ab | 29.5 a | 91.8 a | 37.6 a | ||
| T5 | 45.2 a | 12.8 a | 76.3 a | 31.0 a | 89.1 a | 37.4 a | ||
| CK | - | - | - | - | 89.8 a | 40.3 a | ||
| 平均值Average | 40.6 | 10.7 | 59.6 | 30.1 | 92.0 | 38.1 |
| 年份 Year | 稻季 Season | 处理 Treatment | 各生育期P素累积量Total P accumulation at different stages/(kg·hm-2) | P收获指数 P harvest index/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 分蘖盛期MT | 抽穗期HS | 灌浆期FS | 成熟期MS | ||||
| 2017 | 早稻Early rice | T1 | 3.7 a | 8.6 a | 27.1 a | 49.5 c | 72.9 a |
| T2 | 4.2 a | 9.8 a | 27.7 a | 54.1 abc | 67.2 abc | ||
| T3 | 4.7 a | 10.2 a | 30.2 a | 58.0 ab | 65.9 bc | ||
| T4 | 5.1 a | 11.1 a | 31.9 a | 62.3 a | 67.2 abc | ||
| T5 | 4.1 a | 9.0 a | 28.0 a | 51.2 bc | 71.8 ab | ||
| CK | 1.5 b | 3.5 b | 13.8 b | 33.7 d | 64.8 c | ||
| 平均值Average | 3.9 | 8.7 | 26.5 | 51.4 | 68.3 | ||
| 晚稻Late rice | T1 | 3.0 a | 8.9 b | 31.5 a | 25.2 ab | 55.1 a | |
| T2 | 3.9 a | 14.7 a | 33.0 a | 27.5 ab | 52.7 a | ||
| T3 | 4.1 a | 14.9 a | 33.4 a | 28.9 a | 52.9 a | ||
| T4 | 4.1 a | 14.3 a | 32.7 a | 27.8 ab | 56.9 a | ||
| T5 | 3.6 a | 9.8 b | 30.5 a | 26.0 ab | 57.0 a | ||
| CK | 1.3 b | 3.2 c | 15.1 a | 20.8 b | 64.1 a | ||
| 平均值Average | 3.3 | 11.0 | 29.4 | 26.0 | 56.4 | ||
| 2018 | 早稻Early rice | T1 | 6.4 a | 14.8 a | 29.6 ab | 42.7 c | 56.1 a |
| T2 | 5.3 bc | 15.8 a | 31.9 ab | 46.2 ab | 54.5 a | ||
| T3 | 5.4 bc | 16.1 a | 34.3 a | 47.9 a | 53.6 a | ||
| T4 | 5.4 b | 16.0 a | 32.3 a | 46.6 ab | 56.2 a | ||
| T5 | 5.0 c | 14.2 a | 30.3 ab | 44.6 bc | 54.3 a | ||
| CK | 3.6 d | 7.7 b | 27.0 b | 32.3 d | 47.8 b | ||
| 平均值Average | 5.2 | 14.1 | 30.9 | 43.4 | 53.8 | ||
| 晚稻Late rice | T1 | 15.6 a | 28.2 a | 32.1 b | 34.5 a | 35.8 a | |
| T2 | 10.7 b | 31.1 a | 37.7 a | 37.7 a | 34.3 a | ||
| T3 | 10.7 b | 32.7 a | 39.0 a | 41.1 a | 32.5 a | ||
| T4 | 9.9 bc | 31.0 a | 36.4 ab | 38.5 a | 34.6 a | ||
| T5 | 6.9 bc | 28.4 a | 33.9 ab | 35.1 a | 37.2 a | ||
| CK | 6.5 c | 19.4 b | 21.9 c | 25.7 b | 37.7 a | ||
| 平均值Average | 10.1 | 28.5 | 33.5 | 35.4 | 35.3 | ||
表5 不同施肥处理下机插双季稻各生育期P素吸收和P收获指数
Table 5 P uptake at different growth stages and P harvest index of machine-transplanted double-cropping rice under different fertilization treatments.
| 年份 Year | 稻季 Season | 处理 Treatment | 各生育期P素累积量Total P accumulation at different stages/(kg·hm-2) | P收获指数 P harvest index/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 分蘖盛期MT | 抽穗期HS | 灌浆期FS | 成熟期MS | ||||
| 2017 | 早稻Early rice | T1 | 3.7 a | 8.6 a | 27.1 a | 49.5 c | 72.9 a |
| T2 | 4.2 a | 9.8 a | 27.7 a | 54.1 abc | 67.2 abc | ||
| T3 | 4.7 a | 10.2 a | 30.2 a | 58.0 ab | 65.9 bc | ||
| T4 | 5.1 a | 11.1 a | 31.9 a | 62.3 a | 67.2 abc | ||
| T5 | 4.1 a | 9.0 a | 28.0 a | 51.2 bc | 71.8 ab | ||
| CK | 1.5 b | 3.5 b | 13.8 b | 33.7 d | 64.8 c | ||
| 平均值Average | 3.9 | 8.7 | 26.5 | 51.4 | 68.3 | ||
| 晚稻Late rice | T1 | 3.0 a | 8.9 b | 31.5 a | 25.2 ab | 55.1 a | |
| T2 | 3.9 a | 14.7 a | 33.0 a | 27.5 ab | 52.7 a | ||
| T3 | 4.1 a | 14.9 a | 33.4 a | 28.9 a | 52.9 a | ||
| T4 | 4.1 a | 14.3 a | 32.7 a | 27.8 ab | 56.9 a | ||
| T5 | 3.6 a | 9.8 b | 30.5 a | 26.0 ab | 57.0 a | ||
| CK | 1.3 b | 3.2 c | 15.1 a | 20.8 b | 64.1 a | ||
| 平均值Average | 3.3 | 11.0 | 29.4 | 26.0 | 56.4 | ||
| 2018 | 早稻Early rice | T1 | 6.4 a | 14.8 a | 29.6 ab | 42.7 c | 56.1 a |
| T2 | 5.3 bc | 15.8 a | 31.9 ab | 46.2 ab | 54.5 a | ||
| T3 | 5.4 bc | 16.1 a | 34.3 a | 47.9 a | 53.6 a | ||
| T4 | 5.4 b | 16.0 a | 32.3 a | 46.6 ab | 56.2 a | ||
| T5 | 5.0 c | 14.2 a | 30.3 ab | 44.6 bc | 54.3 a | ||
| CK | 3.6 d | 7.7 b | 27.0 b | 32.3 d | 47.8 b | ||
| 平均值Average | 5.2 | 14.1 | 30.9 | 43.4 | 53.8 | ||
| 晚稻Late rice | T1 | 15.6 a | 28.2 a | 32.1 b | 34.5 a | 35.8 a | |
| T2 | 10.7 b | 31.1 a | 37.7 a | 37.7 a | 34.3 a | ||
| T3 | 10.7 b | 32.7 a | 39.0 a | 41.1 a | 32.5 a | ||
| T4 | 9.9 bc | 31.0 a | 36.4 ab | 38.5 a | 34.6 a | ||
| T5 | 6.9 bc | 28.4 a | 33.9 ab | 35.1 a | 37.2 a | ||
| CK | 6.5 c | 19.4 b | 21.9 c | 25.7 b | 37.7 a | ||
| 平均值Average | 10.1 | 28.5 | 33.5 | 35.4 | 35.3 | ||
| 年份 Year | 稻季 Season | 处理 Treatment | 各生育期K素累积量Total K accumulation at different stages/(kg·hm-2) | K收获指数 K harvest index/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 分蘖盛期MT | 抽穗期HS | 灌浆期FS | 成熟期MS | ||||
| 2017 | 早稻Early rice | T1 | 20.1 a | 82.9 a | 83.0 c | 72.4 a | 10.1 b |
| T2 | 24.5 a | 96.6 a | 88.8 bc | 73.8 a | 11.2 ab | ||
| T3 | 26.4 a | 98.2 a | 96.0 ab | 77.1 a | 11.6 ab | ||
| T4 | 27.5 a | 101.4 a | 101.5 a | 76.7 a | 12.6 a | ||
| T5 | 20.3 a | 88.1 a | 95.0 ab | 63.0 b | 12.6 a | ||
| CK | 6.6 a | 46.2 b | 55.1 d | 46.2 c | 12.2 ab | ||
| 平均值Average | 20.9 | 85.6 | 86.6 | 68.2 | 11.7 | ||
| 晚稻Late rice | T1 | 23.2 a | 69.2 ab | 72.6 a | 75.3 ab | 10.9 a | |
| T2 | 25.0 a | 75.5 a | 81.1 a | 84.1 a | 11.4 a | ||
| T3 | 25.6 a | 77.3 a | 83.2 a | 90.1 a | 11.0 a | ||
| T4 | 24.7 a | 67.8 ab | 86.7 a | 78.1 ab | 11.8 a | ||
| T5 | 19.0 a | 57.5 b | 67.9 a | 71.2 ab | 10.5 a | ||
| CK | 7.7 b | 19.4 c | 32.7 b | 58.5 b | 13.9 a | ||
| 平均值Average | 20.9 | 61.1 | 70.7 | 76.2 | 11.6 | ||
| 2018 | 早稻Early rice | T1 | 13.5 a | 40.6 b | 110.8 a | 114.1 c | 12.8 a |
| T2 | 14.0 a | 48.8 a | 112.4 a | 130.1 ab | 12.3 a | ||
| T3 | 14.4 a | 51.4 a | 120.9 a | 135.0 a | 13.2 a | ||
| T4 | 11.2 b | 49.4 a | 117.8 a | 131.5 ab | 13.5 a | ||
| T5 | 11.0 b | 40.7 b | 111.9 a | 120.5 bc | 12.0 a | ||
| CK | 9.1 b | 22.2 c | 72.1 b | 94.2 d | 14.2 a | ||
| 平均值Average | 12.7 | 42.2 | 107.7 | 120.9 | 13.0 | ||
| 晚稻Late rice | T1 | 42.4 a | 67.4 b | 81.9 bc | 97.7 b | 9.3 a | |
| T2 | 34.5 b | 74.9 b | 97.5 a | 116.0 a | 8.9 ab | ||
| T3 | 30.2 bc | 86.2 a | 98.0 a | 119.4 a | 9.1 ab | ||
| T4 | 27.3 c | 74.1 b | 99.3 a | 116.0 a | 8.8 ab | ||
| T5 | 25.4 c | 67.9 b | 91.9 ab | 112.7 a | 8.3 b | ||
| CK | 18.0 d | 49.6 c | 69.3 c | 89.8 b | 8.3 b | ||
| 平均值Average | 29.6 | 70.0 | 90.0 | 108.6 | 8.8 | ||
表6 不同施肥处理下机插双季稻各生育期K素吸收和K收获指数
Table 6 K uptake at different growth stages and K harvest index of machine-transplanted double-cropping rice under different fertilization treatments.
| 年份 Year | 稻季 Season | 处理 Treatment | 各生育期K素累积量Total K accumulation at different stages/(kg·hm-2) | K收获指数 K harvest index/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 分蘖盛期MT | 抽穗期HS | 灌浆期FS | 成熟期MS | ||||
| 2017 | 早稻Early rice | T1 | 20.1 a | 82.9 a | 83.0 c | 72.4 a | 10.1 b |
| T2 | 24.5 a | 96.6 a | 88.8 bc | 73.8 a | 11.2 ab | ||
| T3 | 26.4 a | 98.2 a | 96.0 ab | 77.1 a | 11.6 ab | ||
| T4 | 27.5 a | 101.4 a | 101.5 a | 76.7 a | 12.6 a | ||
| T5 | 20.3 a | 88.1 a | 95.0 ab | 63.0 b | 12.6 a | ||
| CK | 6.6 a | 46.2 b | 55.1 d | 46.2 c | 12.2 ab | ||
| 平均值Average | 20.9 | 85.6 | 86.6 | 68.2 | 11.7 | ||
| 晚稻Late rice | T1 | 23.2 a | 69.2 ab | 72.6 a | 75.3 ab | 10.9 a | |
| T2 | 25.0 a | 75.5 a | 81.1 a | 84.1 a | 11.4 a | ||
| T3 | 25.6 a | 77.3 a | 83.2 a | 90.1 a | 11.0 a | ||
| T4 | 24.7 a | 67.8 ab | 86.7 a | 78.1 ab | 11.8 a | ||
| T5 | 19.0 a | 57.5 b | 67.9 a | 71.2 ab | 10.5 a | ||
| CK | 7.7 b | 19.4 c | 32.7 b | 58.5 b | 13.9 a | ||
| 平均值Average | 20.9 | 61.1 | 70.7 | 76.2 | 11.6 | ||
| 2018 | 早稻Early rice | T1 | 13.5 a | 40.6 b | 110.8 a | 114.1 c | 12.8 a |
| T2 | 14.0 a | 48.8 a | 112.4 a | 130.1 ab | 12.3 a | ||
| T3 | 14.4 a | 51.4 a | 120.9 a | 135.0 a | 13.2 a | ||
| T4 | 11.2 b | 49.4 a | 117.8 a | 131.5 ab | 13.5 a | ||
| T5 | 11.0 b | 40.7 b | 111.9 a | 120.5 bc | 12.0 a | ||
| CK | 9.1 b | 22.2 c | 72.1 b | 94.2 d | 14.2 a | ||
| 平均值Average | 12.7 | 42.2 | 107.7 | 120.9 | 13.0 | ||
| 晚稻Late rice | T1 | 42.4 a | 67.4 b | 81.9 bc | 97.7 b | 9.3 a | |
| T2 | 34.5 b | 74.9 b | 97.5 a | 116.0 a | 8.9 ab | ||
| T3 | 30.2 bc | 86.2 a | 98.0 a | 119.4 a | 9.1 ab | ||
| T4 | 27.3 c | 74.1 b | 99.3 a | 116.0 a | 8.8 ab | ||
| T5 | 25.4 c | 67.9 b | 91.9 ab | 112.7 a | 8.3 b | ||
| CK | 18.0 d | 49.6 c | 69.3 c | 89.8 b | 8.3 b | ||
| 平均值Average | 29.6 | 70.0 | 90.0 | 108.6 | 8.8 | ||
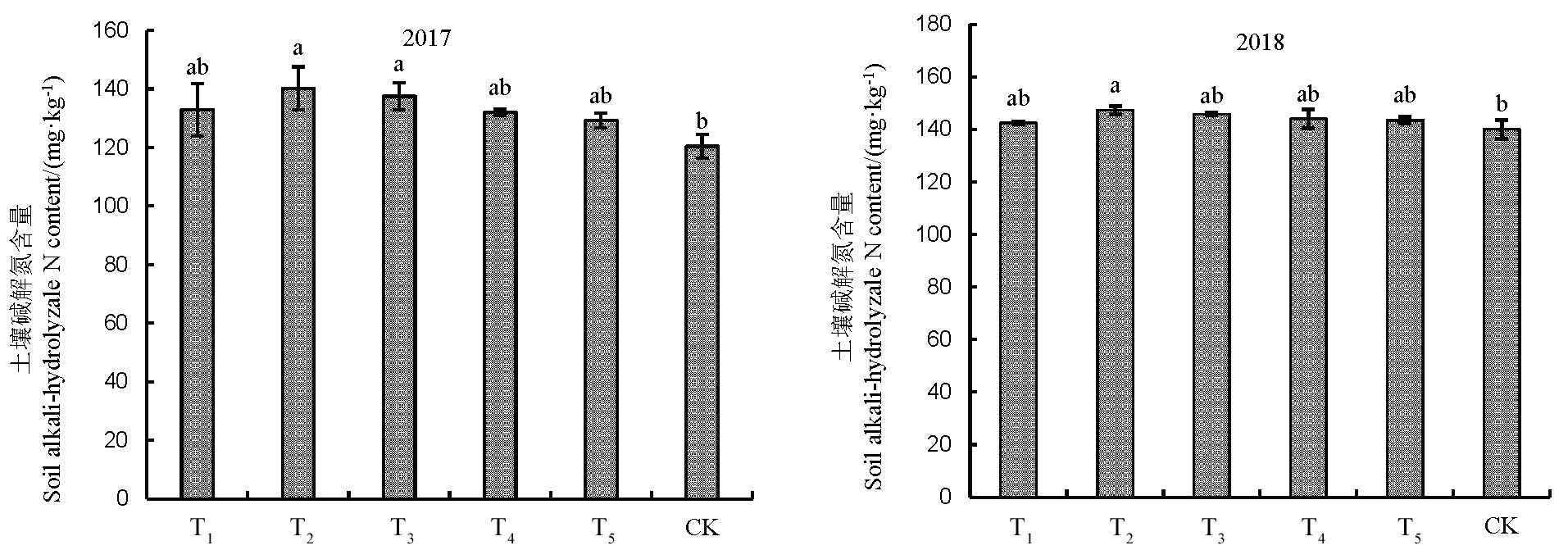
图2 不同施肥处理下机插双季稻土壤碱解氮含量柱上不同小写字母代表处理间在5%水平上差异显著(LSD)。图中数值为平均值±标准误(n=3)。
Fig. 2. Soil alkali-hydrolyzale N content of machine-transplanted double-cropping rice under different fertilization treatments. Different small letters above the bars mean significant difference among treatments at 5% level (LSD). Data in the figure are Mean±SE (n=3).
| [1] | 彭少兵, 黄见良, 钟旭华, 杨建昌, 王光火, 邹应斌, 张福锁, 朱庆森, Buresh R, Witt C.提高中国稻田氮肥利用率的研究策略. 中国农业科学, 2002, 35(9): 1095-1103. |
| Peng S B, Huang J L, Zhong X H, Yang J C, Wang G H, Zhou Y B, Zhang F S, Zhu Q S, Buresh R, Witt C.Research strategy in improving fertilizer-nitrogen use efficiency of irrigated rice in China.Sci Agric Sin, 2002, 35(9): 1095-1103. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | 刘立军, 杨立年, 孙小淋, 王志琴, 杨建昌. 水稻实地氮肥管理的氮肥利用效率及其生理原因. 作物学报, 2009, 35(9): 1672-1680. |
| Liu L J, Yang L N, Sun X L, Wang Z Q, Yang J C.Fertilizer-nitrogen use efficiency and its physiological mechanism under site-specific nitrogen management in rice.Acta Agron Sin, 2009, 35(9): 1672-1680. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | Ju X T, Xing G X, Chen X P, Zhang S L, Zhang L J, Liu, X J, Cui Z L, Yin B, Christie P, Zhu Z L, Zhang F S. Reducing environmental risk by improving N management in intensive Chinese agricultural systems.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2009, 106(9): 3041-3046. |
| [4] | Xu X P, He P, Zhao S C, Qiu S J, Johnston A M, Wei Z.Quantification of yield gap and nutrient use efficiency of irrigated rice in China.Field Crops Res, 2016, 186. |
| [5] | Bodirsky B L, Müller C.Robust relationship between yields and nitrogen inputs indicates three ways to reduce nitrogen pollution.Environ Res Lett, 2014, 9(11): 111005. |
| [6] | 朱德峰, 陈惠哲, 徐一成, 张玉屏. 我国双季稻生产机械化制约因子与发展对策. 中国稻米, 2013, 19(4): 1-4. |
| Zhu D F, Chen H Z, Xu Y C, Zhang Y P.Mechanization constraints and development counter measures of double cropping rice production in China.China Rice, 2013, 19(4): 1-4. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 邹应斌. 长江流域双季稻栽培技术发展. 中国农业科学, 2011, 44(2): 254-262. |
| Zou Y B.Development of Cultivation Technology for double cropping rice along the Changjiang River Valley.Sci Agric Sin, 2011, 44(2): 254-262. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | 朱德峰, 陈惠哲. 水稻机插秧发展与粮食安全. 中国稻米, 2009, 20(6): 4-7. |
| Zhu D F, Chen H Z.Development and food security of rice transplanting.China Rice, 2009, 20(6): 4-7. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 张文毅, 袁钊和, 吴崇友, 金梅. 水稻种植机械化进程分析研究——水稻种植机械化由快速向高速发展的进程. 中国农机化, 2011(1): 19-22. |
| Zhang W Y, Yuan Z H, Wu C Y, Jin M.Analysis and research on the process of rice planting mechanization: The rapid development of rice planting mechanization.J Chin Agric Mechan, 2011(1): 19-22. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | 陈佳娜, 曹放波, 谢小兵, 单双吕, 高伟, 李志斌, 黄敏, 邹应斌. 机插条件下低氮密植栽培对“早晚兼用”双季稻产量和氮素吸收利用的影响. 作物学报, 2016, 42(8): 1176-1187. |
| Chen J N, Cao F B, Xie X B, Dan S L, Gao W, Li Z B, Huang M, Zhou Y B.Effect of low nitrogen rate combined with high plant density on yield and nitrogen use efficiency of machine-transplanted early-late season double cropping rice.Acta Agron Sin, 2016, 42(8): 1176-1187. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 毕春辉, 陈长海, 李明金, 吴家安, 张宝库. 浅谈水稻侧深施肥技术. 农业装备技术, 2011, 37(6): 24-25. |
| Bi C H, Chen C H, Li M J, Wu J A, Zhang B K.Brief discussion on side deep fertilization technology of rice.Agric Equip & Technol, 2011, 37(6): 24-25. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 侯朋福, 薛利祥, 俞映倞, 薛利红, 范立慧, 杨林章. 缓控释肥侧深施对稻田氨挥发排放的控制效果. 环境科学, 2017, 38(12): 5326-5332. |
| Hou P F, Xue L X, Yu Y J, Xue L H, Fan L H, Yang L Z.Control effect of side deep fertilization with slow-release fertilizer on ammonia volatilization from paddy fields.Environ Sci, 2017, 38(12): 5326-5332. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | Alimata B, Fofana B, Sansan Y, Ebenezer S, Robert A, Opoku A.Effect of fertilizer deep placement with urea supergranule on nitrogen use efficiency of irrigated rice in Sourou Valley (Burkina Faso).Nut Cyc Agroeco, 2015, 102(1): 79-89. |
| [14] | 夏艳涛, 吴亚晶. 寒地水稻侧深施肥技术研究. 北方水稻, 2014(1): 30-32. |
| Xia Y T, Wu Y J.Study on side deep fertilizing of rice in cold area.North Rice, 2014(1): 30-32. (in Chinese) | |
| [15] | 白雪, 郑桂萍, 王宏宇, 潘世驹, 蔡永胜, 王安东. 寒地水稻侧深施肥效果的研究. 黑龙江农业科学, 2014(6): 40-43. |
| Bai X, Zheng G P, Wang H Y, Pan S X, Cai Y S, Wang A D.Study on the effect of deep lateral fertilization on rice in cold region.Heilongjiang Agric Sci, 2014(6): 40-43. (in Chinese) | |
| [16] | 马昕, 杨艳明, 刘智蕾, 孙彦坤, 于彩莲, 彭显龙. 机械侧深施控释掺混肥提高寒地水稻的产量和效益. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2017, 23(4): 1095-1103. |
| Ma X, Yang Y M, Liu Z L, Sun Y K, Yu C L, Peng X L.Yield increasing effect of mechanical topdressing of polymer-coated urea mixed with compound fertilizer in cold area rice.J Plant Nutr Fert, 2017, 23(4): 1095-1103. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | 林玉萍, 聂录, 姜灏, 丁亮. 水稻侧深施肥技术研究. 现代化农业, 2017(3): 19-21. |
| Lin Y P, Nie L, Jiang H, Ding L.Study on deep side fertilization technology of rice.Mod Agric, 2017 (3): 19-21. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | 马增奇, 周成, 刘卫东. 机械式强排侧深施肥技术的应用. 现代化农业, 2017(12): 53-54. |
| Ma Z G, Zhou C, Liu W D.Application of mechanical strong drainage side deep fertilization technology.Mod Agric, 2017(12): 53-54. (in Chinese) | |
| [19] | 敖和军, 王淑红, 邹应斌, 彭少兵, 程兆伟, 刘武, 唐启源. 不同施肥水平下超级杂交稻对氮、磷、钾的吸收累积. 中国农业科学, 2008(10): 3123-3132. |
| Ao H J, Wang S H, Zou Y B, Peng S B, Chen Z W, Liu W, Tang Q Y.Characteristics of nutrient uptake and utilization of super hybrid rice under different fertilizer application rates.Sci Agric Sin, 2008, 41(10): 3123-3132. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | 袁嫚嫚, 叶舒娅, 刘枫, 李敏, 吴学忠. 氮肥施用方法对水稻产量和氮肥利用率的影响. 河北农业科学, 2011, 15(3): 39-41. |
| Yuan W W, Ye S Y, Liu F, Li M, Wu X Z.Effects of nitrogen application methods on rice yield and nitrogen fertilizer utilization.J Hebei Agric Sci, 2011, 15(3): 39-41. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | 黄巧义, 唐拴虎, 张发宝, 张木, 黄旭, 黄建凤, 李苹, 付弘婷. 减氮配施控释尿素对水稻产量和氮肥利用的影响. 中国生态农业学报, 2017, 25(6): 829-838. |
| Huang Q Y, Tang S H, Zhang F B, Zhang M, Huang X, Huang J F, Li P, Fu H T.Effect of combined application of controlled-release urea and conventional urea under reduced N rate on yield and N utilization efficiency of rice.Chin J Eco-Agric, 2017, 25(6): 829-838. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | 张满利, 陈盈, 隋国民, 侯守贵, 于广星, 李海波, 王有芬, 吴凯. 氮肥对水稻产量和氮肥利用率的影响. 中国农学通报, 2010, 26(13): 230-234. |
| Zhang M L, Chen Y, Sui G M, Hou S G, Yu G X, Li H B, Wang Y F, Wu K.Effect of N fertilizer on the yield and nitrogen use efficiency in rice.Chin Agric Sci Bull, 2010, 26(13): 230-234. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 孙永健, 孙园园, 李旭毅, 张荣萍, 郭翔, 马均. 水氮互作对水稻氮磷钾吸收、转运及分配的影响. 作物学报, 2010, 36(4): 655-664. |
| Sun Y J, Sun Y Y, Li X Y, Zhang R P, Guo X, Ma J.Effects of water-nitrogen interaction on absorption, translocation and distribution of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium in rice.Acta Agron Sin, 2010, 36(4): 655-664. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | 王海月, 李玥, 孙永健, 李应洪, 蒋明金, 王春雨, 赵建红, 孙园园, 徐徽, 严奉君, 马均. 不同施氮水平下缓释氮肥配施对机插稻氮素利用特征及产量的影响. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(1): 50-64. |
| Wang H Y, Li Y, Sun Y J, Li Y H, Jiang M J, Wang C Y, Zhao J H, Sun Y Y, Xu H, Yan F J, Ma J.Effects of slow-release urea on nitrogen utilization and yield in mechanically-trans-planted rice under different nitrogen application rates.Chin Rice Sci, 2017, 31(1): 50-64. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | 谢小兵, 周雪峰, 蒋鹏, 陈佳娜, 张瑞春, 伍丹丹, 曹放波, 单双吕, 黄敏, 邹应斌. 低氮密植栽培对超级稻产量和氮素利用率的影响. 作物学报, 2015, 41(10): 1591-1602. |
| Xie X B, Zhou X F, Jiang P, Chen J N, Zhang R C, Wu D D, Cao F B, Shan S L, Huang M, Zhou Y B.Effect of low nitrogen rate combined with high plant density on grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency in super rice.Acta Agron Sin, 2015, 41(10): 1591-1602. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | 杨成林, 王丽妍, 赵红玉. 侧深施肥对寒地水稻产量及肥料利用率的影响. 广东农业科学, 2017, 44(8): 61-65. |
| Yang C L, Wang L Y, Zhao H Y.Effects of different application rates of side deep fertilization on yield and fertilizer use efficiency of rice in cold region.Guangdong Agric Sci, 2017, 44(8): 61-65. (in Chinese) |
| [1] | 唐志伟, 朱相成, 张俊, 邓艾兴, 张卫建. 水分调控下绿肥种植和石灰施用对双季稻稻米镉含量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 211-222. |
| [2] | 杨陶陶, 邹积祥, 伍龙梅, 包晓哲, 江瑜, 张楠, 张彬. 开放式增温对华南双季稻稻米品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(1): 66-77. |
| [3] | 任维晨, 常庆霞, 张亚军, 朱宽宇, 王志琴, 杨建昌. 不同氮利用率粳稻品种的碳氮积累与转运特征及其生理机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(6): 586-600. |
| [4] | 张宇杰, 王志强, 马鹏, 杨志远, 孙永健, 马均. 麦秆还田下水氮耦合对水稻氮素吸收利用及产量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(4): 388-398. |
| [5] | 王丰, 廖亦龙, 柳武革, 刘迪林, 曾学勤, 傅友强, 朱满山, 李金华, 付崇允, 马晓智, 霍兴. 籼型杂交稻恢复系动态株型与光能利用率评价[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(2): 141-154. |
| [6] | 杨通, 吴俊男, 鲍婷, 李凤博, 冯金飞, 周锡跃, 方福平. 耕作方式对双季稻田土壤剖面CH4和N2O分布特征的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(1): 78-88. |
| [7] | 叶春, 李艳大, 曹中盛, 黄俊宝, 孙滨峰, 舒时富, 吴罗发. 不同育秧盘对机插双季稻株型与产量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(5): 435-442. |
| [8] | 徐飞, 隋文志, 张拓, 怀宝东, 杨雪. 叶龄调控下水肥耦合对寒地水稻生物学特征及水肥利用效率的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(4): 339-347. |
| [9] | 王海月, 张桥, 武云霞, 严奉君, 郭长春, 孙永健, 徐徽, 杨志远, 马均. 不同株距下氮肥减量配施运筹对机插杂交稻的产量及光合特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(5): 447-456. |
| [10] | 陈中督, 徐春春, 纪龙, 方福平. 基于农户调查的长江中游地区双季稻生产碳足迹及其构成[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(6): 601-609. |
| [11] | 杨陶陶, 胡启星, 黄山, 曾研华, 谭雪明, 曾勇军, 潘晓华, 石庆华, 张俊. 双季优质稻产量和品质形成对开放式主动增温的响应[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(6): 572-580. |
| [12] | 陈中督 徐春春 纪龙 方福平*. 基于农户调查的长江中游地区双季稻生产碳足迹及其构成[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(6): 601-609. |
| [13] | 王海月, 郭长春, 孙永健, 李应洪, 蒋明金, 严奉君, 殷尧翥, 何艳, 徐徽, 杨志远, 马均. 缓释氮肥减量配施和株距对机插杂交籼稻氮素利用的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(4): 374-386. |
| [14] | 田昌, 周旋, 谢桂先, 刘强, 荣湘民, 张玉平, 谭力彰, 彭建伟. 控释尿素减施对双季稻田氨挥发损失和氮肥利用率的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(4): 387-397. |
| [15] | 张浪, 周玲红, 魏甲彬, 成小琳, 徐华勤, 肖志祥, 唐启源, 唐剑武. 冬季种养结合对双季稻生长与土壤肥力的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(3): 226-236. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||