
中国水稻科学 ›› 2019, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (5): 407-420.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2019.9026
龙起樟, 黄永兰, 唐秀英, 王会民, 芦明, 袁林峰, 万建林*( )
)
收稿日期:2019-03-05
修回日期:2019-05-24
出版日期:2019-09-10
发布日期:2019-09-10
通讯作者:
万建林
基金资助:
Qizhang LONG, Yonglan HUANG, Xiuying TANG, Huimin WANG, Ming LU, Linfeng YUAN, Jianlin WAN*( )
)
Received:2019-03-05
Revised:2019-05-24
Online:2019-09-10
Published:2019-09-10
Contact:
Jianlin WAN
摘要:
【目的】 为了尝试快速培育低镉籼稻,【方法】 选取广泛应用的杂交水稻亲本华占和五丰B以及常规品种五山丝苗和中早35为材料,通过CRISPR/Cas9技术创制OsNramp5基因突变株系,在镉污染及正常土壤中种植并测定突变株系籽粒(糙米)镉含量,其他相关元素含量亦同时在镉污染土壤种植条件下测定,在非镉污染土壤种植条件下考查OsNramp5基因敲除对农艺性状的影响。【结果】 成功获得了前述品种的OsNramp5基因敲除株系;非镉污染条件下种植的4个品种OsNramp5基因敲除株系籽粒镉含量低于0.02 mg/kg,平均较野生型降低85.5%;而在镉污染土壤种植时,不同品种OsNramp5基因敲除株系籽粒镉含量低于0.1 mg/kg,平均比野生型降低94.8%;锰含量也降低52.7%,铬含量增加59.5%,铅含量在华占中增加79.1%,而在其他品种中无变化;铜、铁、锌、钙、硒和砷含量(后4种元素只在华占及衍生品系中检测)受影响较小或不受影响;OsNramp5基因敲除株系株高、结实率和千粒重较野生型小幅降低,而有效分蘖略微增加,产量平均减少6.9%。【结论】 通过OsNramp5基因敲除,可以显著降低镉积累,但在某些种植条件下,代价为小幅产量损失;通过本研究获得的低镉OsNramp5基因敲除品系在镉污染地区具有较好利用潜力。
中图分类号:
龙起樟, 黄永兰, 唐秀英, 王会民, 芦明, 袁林峰, 万建林. 利用CRISPR/Cas9敲除OsNramp5基因创制低镉籼稻[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(5): 407-420.
Qizhang LONG, Yonglan HUANG, Xiuying TANG, Huimin WANG, Ming LU, Linfeng YUAN, Jianlin WAN. Creation of Low-Cd-accumulating indica Rice by Disruption of OsNramp5 Gene via CRISPR/Cas9[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2019, 33(5): 407-420.
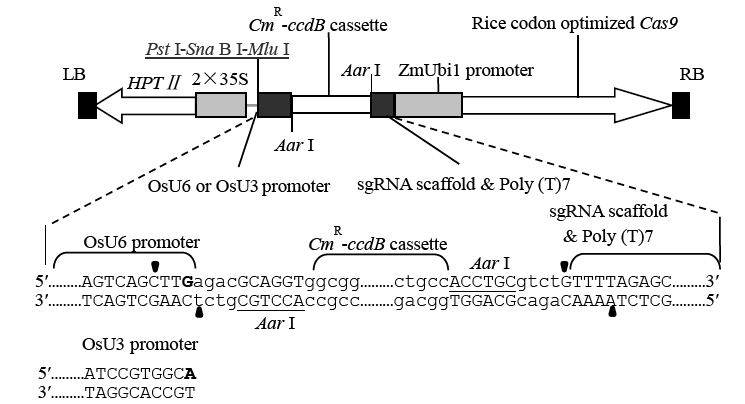
图1 农杆菌转化使用的CRISPR/Cas9 Ti质粒双元载体pCUbi1390Cas9-U6/U3 T-DNA区结构 LB、RB分别为T-DNA的左、右边界;HPTⅡ-潮霉素抗性标记;2×35S-串联的35S启动子;CmR-ccdB cassette-氯霉素抗性基因及自杀基因表达盒;sgRNA scaffold & Poly (T)7-sgRNA骨架及7个T碱基组成的终止子;ZmUbi1 promoter-玉米Ubi1基因启动子;Rice codon optimized Cas9-水稻密码子优化的Cas9基因;AarⅠ-供向导序列克隆的TypeⅡ限制性酶识别位点(黑色三角示剪切点);PstⅠ-Sna BⅠ-MluⅠ-三个单一限制性内切酶识别位点;图中省略了HPT和Cas9基因各自表达所需的终止子CaMV 3′ UTR和Nos polyA信号序列;pCUbi1390Cas9-U6和pCUbi1390Cas9-U3载体的区别仅在于sgRNA启动子及转录起始碱基不同。
Fig. 1. Structure of the T-DNA region of the CRISPR/Cas9 Ti binary vectors pCUbi1390Cas9-U6/U3. LB, T-DNA left border; RB, T-DNA right border; HPTⅡ, Hygromycin resistant gene; 2×35S, Duplicated 35S promoter; CmR-ccdB cassette, Chloramphenicol resistant gene and ccdB suicide gene; Aar I, typeⅡ restriction enzyme recognition site for guide DNA cloning (the cut sites were indicated by black triangles); Pst I-Sna B I-Mlu I, Restriction enzyme sites for further use; The CaMV 3′ UTR and Nos polyA signal of the HPT II and the Cas9 genes are not shown; The only difference between the vectors pCUbi1390Cas9-U6 and pCUbi1390Cas9-U3 is that the two vectors use different sgRNA promoters together with different transcription start bases.
| 基因型 Genotype | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 靶位点1 Target site 1 | 靶位点2 Target site 2 | ||||||
| 华占 Huazhan | 五丰B Wufeng B | 五山丝苗 Wushansimiao | 中早35 Zhongzao 35 | Kasalath | 合计 Sum | Kasalath | |
| 野生型Wild type | 5(36%) | 6(30%) | 22(61%) | 7(41%) | 1(10%) | 41(42%) | 0 |
| 杂合Heterozygous | 0 | 0 | 3(8%) | 0 | 1(10%) | 4(4%) | 2(50%) |
| 双等位基因Biallelic | 9(64%) | 14(70%) | 11(31%) | 10(59%) | 8(80%) | 52(54%) | 1(25%) |
| 纯合Homozygous | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 嵌合体Chimeric | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1(25%) |
| 合计Sum | 14(100%) | 20(100%) | 36(100%) | 17(100%) | 10(100%) | 97(100%) | 4(100%) |
表1 不同品种阳性转化株基因突变情况统计
Table 1 Occurrence frequency of the four genotypes among the positive transgenic lines of the five cultivars.
| 基因型 Genotype | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 靶位点1 Target site 1 | 靶位点2 Target site 2 | ||||||
| 华占 Huazhan | 五丰B Wufeng B | 五山丝苗 Wushansimiao | 中早35 Zhongzao 35 | Kasalath | 合计 Sum | Kasalath | |
| 野生型Wild type | 5(36%) | 6(30%) | 22(61%) | 7(41%) | 1(10%) | 41(42%) | 0 |
| 杂合Heterozygous | 0 | 0 | 3(8%) | 0 | 1(10%) | 4(4%) | 2(50%) |
| 双等位基因Biallelic | 9(64%) | 14(70%) | 11(31%) | 10(59%) | 8(80%) | 52(54%) | 1(25%) |
| 纯合Homozygous | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 嵌合体Chimeric | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1(25%) |
| 合计Sum | 14(100%) | 20(100%) | 36(100%) | 17(100%) | 10(100%) | 97(100%) | 4(100%) |
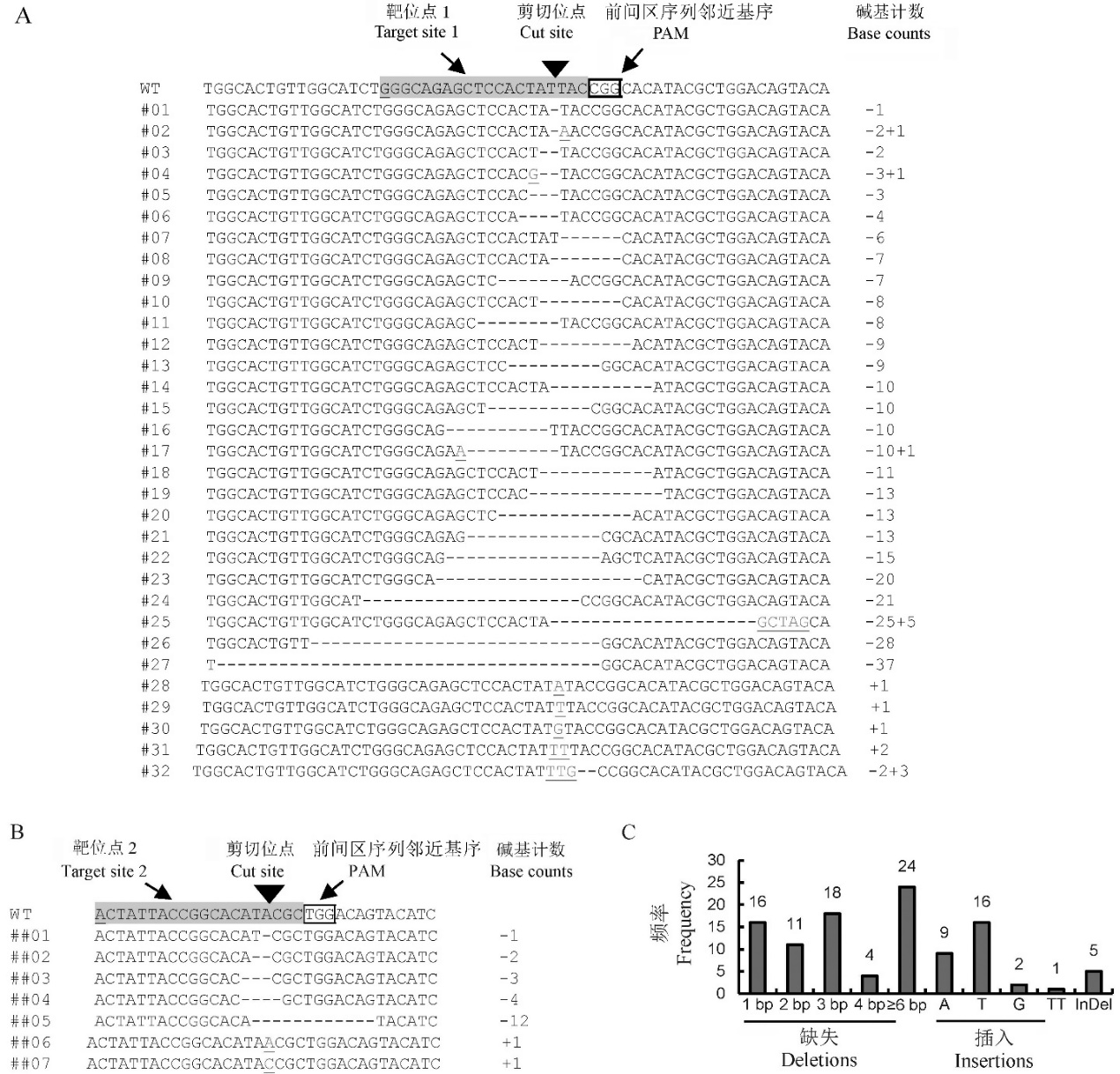
图2 基因编辑株系中OsNramp5基因靶位点突变情况 A和B,靶位点1和2的序列突变情况。WT-野生型;#**或##**,突变类型编号;野生型序列中Cas9靶位点、Cas9系统中U6和U3启动子A图和B图分别为靶位点1和靶位点2的突变情况。起始转录碱基以及PAM位点分别用灰色阴影、加下划线及加框标示,黑色倒三角指示Cas9切割位点,所有序列方向均为5′-3′;突变体序列中缺失碱基用短线代替,插入碱基加下划线显示,其余为与野生型相同者;图右边数字表示缺失(用“-”表示)或插入(用“+”表示)的碱基数。C-靶位点1不同突变类型发生频率统计。突变体类型分3类,即包含缺失1 bp、2 bp、3 bp、4 bp和≥6 bp六种类型的缺失突变,包含插入1个碱基A、T或G及插入2个碱基TT四种类型的插入突变,以及同时含有缺失和插入即InDel;一共统计56个独立转化株系,106个突变等位基因。
Fig. 2. Target site mutations of OsNramp5 in the genetically edited lines. A and B, The sequence changes in Target sites 1 and 2 of the OsNramp5 gene, respectively. WT, Wild type; #** or ##**, Mutation type numbers; In the WT sequence, the target site, the cut site and the PAM site are indicated with the bases highlighted in grey (The underlined base “G” or “A” indicates the transcription start site of the rice U6 or U3 promoter in the CRISPR/Cas9 system), reverse black triangle and the bases in underlined bold font, respectively; In the mutation sequences, the deleted bases are indicated by dashed lines, the inserted ones are underlined, and those identical with the wild type are shown normally; The numbers on the right indicate the counts of the deleted or inserted bases. C, The occurrence frequency of various mutation types in Target site 1. The mutations were summarized as three types, which are deletions, insertions and InDels. The deletion type includes five subtypes, which are those with 1 bp, 2 bp, 3 bp, 4 bp and ≥6 bp deletion respectively. The insertion type includes four subtypes, which are those with one A, one T, one G and double T insertion, respectively. The data are derived from the analysis of 106 mutation alleles from 56 independent transgenic lines.
| 株系号Line number | 等位 基因 Allele | 基因型Genotype | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 靶位点1 Target site 1 | 靶位点2 Target site 2 | ||||||
| 华占 Huazhan | 五丰B Wufeng B | 五山丝苗 Wushansimiao | 中早35 Zhongzao 35 | Kasalath | Kasalath | ||
| L01 | 1 | #05 | #26 | WT | #03 | #05 | WT |
| 2 | #31 | #30 | #28 | #29 | #29 | ##04 | |
| L02 | 1 | #06 | #03 | #15 | #03 | #03 | ##01 |
| 2 | #09 | #05 | #28 | #29 | #13 | ##06 | |
| L03 | 1 | #05 | #02 | #05 | #29 | WT | WT |
| 2 | #28 | #29 | #24 | ? | #21 | ##07 | |
| L04 | 1 | #01 | #06 | #03 | #05 | #01 | ##02 |
| 2 | #09 | #27 | #05 | #25 | #29 | ##03 | |
| 3 | - | - | - | - | - | ##05 | |
| L05 | 1 | #01 | #05 | #05 | #01 | #05 | - |
| 2 | #29 | #29 | #18 | #05 | ? | - | |
| L06 | 1 | #01 | #01 | #18 | #11 | #01 | - |
| 2 | #05 | #32 | #28 | #17 | #10 | - | |
| L07 | 1 | #07 | #05 | WT | #01 | #01 | - |
| 2 | #15 | #28 | #16 | #09 | #04 | - | |
| L08 | 1 | #03 | #03 | #05 | #03 | #12 | - |
| 2 | #19 | #08 | #10 | #14 | #29 | - | |
| L09 | 1 | #05 | #01 | #03 | #01 | #03 | - |
| 2 | #28 | #29 | #29 | #05 | #20 | - | |
| L10 | 1 | - | #05 | #01 | #06 | - | - |
| 2 | - | #28 | #29 | #29 | - | - | |
| L11 | 1 | - | #06 | #23 | - | - | - |
| 2 | - | #29 | #29 | - | - | - | |
| L12 | 1 | - | #03 | #01 | - | - | - |
| 2 | - | #30 | #28 | - | - | - | |
| L13 | 1 | - | #01 | #22 | - | - | - |
| 2 | - | #05 | #28 | - | - | - | |
| L14 | 1 | - | #01 | WT | - | - | - |
| 2 | - | #29 | #01 | - | - | - | |
表2 五个品种基因编辑株系中OsNramp5靶位点的基因型
Table 2 Genotypes of all OsNramp5 edited lines derived from five cultivars.
| 株系号Line number | 等位 基因 Allele | 基因型Genotype | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 靶位点1 Target site 1 | 靶位点2 Target site 2 | ||||||
| 华占 Huazhan | 五丰B Wufeng B | 五山丝苗 Wushansimiao | 中早35 Zhongzao 35 | Kasalath | Kasalath | ||
| L01 | 1 | #05 | #26 | WT | #03 | #05 | WT |
| 2 | #31 | #30 | #28 | #29 | #29 | ##04 | |
| L02 | 1 | #06 | #03 | #15 | #03 | #03 | ##01 |
| 2 | #09 | #05 | #28 | #29 | #13 | ##06 | |
| L03 | 1 | #05 | #02 | #05 | #29 | WT | WT |
| 2 | #28 | #29 | #24 | ? | #21 | ##07 | |
| L04 | 1 | #01 | #06 | #03 | #05 | #01 | ##02 |
| 2 | #09 | #27 | #05 | #25 | #29 | ##03 | |
| 3 | - | - | - | - | - | ##05 | |
| L05 | 1 | #01 | #05 | #05 | #01 | #05 | - |
| 2 | #29 | #29 | #18 | #05 | ? | - | |
| L06 | 1 | #01 | #01 | #18 | #11 | #01 | - |
| 2 | #05 | #32 | #28 | #17 | #10 | - | |
| L07 | 1 | #07 | #05 | WT | #01 | #01 | - |
| 2 | #15 | #28 | #16 | #09 | #04 | - | |
| L08 | 1 | #03 | #03 | #05 | #03 | #12 | - |
| 2 | #19 | #08 | #10 | #14 | #29 | - | |
| L09 | 1 | #05 | #01 | #03 | #01 | #03 | - |
| 2 | #28 | #29 | #29 | #05 | #20 | - | |
| L10 | 1 | - | #05 | #01 | #06 | - | - |
| 2 | - | #28 | #29 | #29 | - | - | |
| L11 | 1 | - | #06 | #23 | - | - | - |
| 2 | - | #29 | #29 | - | - | - | |
| L12 | 1 | - | #03 | #01 | - | - | - |
| 2 | - | #30 | #28 | - | - | - | |
| L13 | 1 | - | #01 | #22 | - | - | - |
| 2 | - | #05 | #28 | - | - | - | |
| L14 | 1 | - | #01 | WT | - | - | - |
| 2 | - | #29 | #01 | - | - | - | |
| 样品编号 | 镉1 Cd1 | 镉2 Cd2 | 锰1 Mn1 | 铁1 Fe1 | 铜1 Cu1 | 铅1 Pb1 | 铬1 Cr1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample number | /(μg∙kg-1) | /(μg∙kg-1) | /(mg∙kg-1) | /(mg∙kg-1) | /(mg∙kg-1) | /(μg∙kg-1) | /(μg∙kg-1) |
| HZ-WT | 2010.3±400.5(3) | 134.7±22.5(3) | 60.1±13.9(3) | 10.4±1.1(3) | 4.7±0.4(3) | 114.2±40.4(3) | 80.8±39.1(3) |
| HZ-L01-#05/#05 | 137.6(1) | 11.0(1) | 25.0(1) | 13.3(1) | 5.4(1) | 211.0(1) | 153.0(1) |
| HZ-L01-#31/#31 | 46.4(1) | 13.5(1) | 24.2(1) | 27.5(1) | 5.4(1) | 344.3(1) | 169.1(1) |
| HZ-L04-#09/#09 | 39.1±11.2(2) | 11.8±0.2(2) | 20.5±1.5(2) | 13.3±1.5(2) | 5.1±0.2(2) | 165.1±15.5(2) | 97.2±16.7(2) |
| HZ-L08-#03/#03 | 47.4±10.6(3) | 11.7±1.0(3) | 20.3(1) | 11.7±2.1(3) | 5.4±1.1(3) | 191.0±58.2(3) | 109.2±19.7(3) |
| HZ-L08-#19/#19 | 91.0±64.2(2) | 12.6±5.3(2) | 22.5±0.7(2) | 11.9±0.1(2) | 4.7±0.1(2) | 191.3±48.2(2) | 173.5±42.2(2) |
| HZ-MUT3 | 65.2±41.4(9)* | 12.0±2.1(9)* | 22.2±2.0(7)* | 14.0±5.2(9) | 5.2±0.6(9) | 204.6±64.2(9)* | 132.3±38.9(9) |
| WF-WT | 1753.7±167.5(3) | 123.7±31.3(3) | 42.6±7.0(3) | 12.8±0.9(3) | 4.5±0.3(3) | 168.0±34.7(3) | 60.8±5.0(3) |
| WF-L03-#02/#02 | 30.5(1) | 13.3(1) | 22.9(1) | 13.8(1) | 4.7(1) | 138.6(1) | 124.4(1) |
| WF-L03-#29/#29 | 29.1(1) | 14.6(1) | 21.1(1) | 14.8(1) | 3.9(1) | 100.9(1) | 54.6(1) |
| WF-L04-#27/#27 | 42.0(1) | 14.1(1) | 16.8(1) | 14.2(1) | 4.4(1) | 183.4(1) | 104.8(1) |
| WF-L05-#29/#29 | 68.3±33.5(2) | 15.9±0.7(2) | 16.0±0.6(2) | 13.6±0.1(2) | 4.5±0.2(2) | 161.7±32.5(2) | 108.7±39.5(2) |
| WF-L08-#03/#03 | 82.2±0.3(2) | 18.9±0.2(2) | 17.9±0.6(2) | 14.5±0.6(2) | 5.1±0.2(2) | 166.4±43.7(2) | 66.6±5.0(2) |
| WF-L08-#08/#08 | 29.1(1) | 15.0(1) | 17.1(1) | 14.9(1) | 4.7(1) | 149.0(1) | 73.9(1) |
| WF-MUT3 | 53.9±26.9(8)** | 15.8±2.1(8)* | 18.2±2.5(8)* | 14.2±0.6(8)** | 4.6±0.4(8) | 153.5±32.4(8) | 88.5±30.0(8) |
| WS-WT | 1765.6±246.4(6) | 129.2±32.3(3) | 37.1±5.1(3) | 9.5±0.7(3) | 4.6±0.2(3) | 133.9±41.5(3) | 74.0±23.9(3) |
| WS-L01-#28/#28 | 134.2±150.4(2) | 17.7±1.4(2) | 16.6±1.3(2) | 12.3±1.1(2) | 4.3±0.1(2) | 124.9±4.9(2) | 114.0±29.6(2) |
| WS-L02-#15/#15 | 42.6±8.2(2) | 15.6±0.4(2) | 15.8±0.6(2) | 12.4±2.1(2) | 4.6±0.1(2) | 170.2±60.7(2) | 119.6±13.1(2) |
| WS-L02-#28/#28 | 187.3(1) | 13.6(1) | 16.9(1) | 11.9(1) | 4.6(1) | 128.2(1) | 100.1(1) |
| WS-MUT3 | 108.2±98.6(5)** | 16.0±1.9(5)* | 16.3±0.9(5)* | 12.2±1.2(5)* | 4.5±0.2(5) | 143.7±38.9(5) | 113.4±18.0(5)* |
| ZZ-WT | 1140.3±143.0(3) | 69.9±12.7(3) | 29.1±1.2(3) | 14.4±1.3(3) | 5.0±0.1(3) | 123.7±3.2(3) | 56.9±9.5(3) |
| ZZ-L01-#03/#03 | 121.5(1) | 13.6(1) | 23.8(1) | 17.4(1) | 4.5(1) | 196.6(1) | 85.5(1) |
| ZZ-L01-#29/#29 | 31.9(1) | 14.1(1) | 16.7(1) | 14.8(1) | 4.7(1) | 131.9(1) | 109.0(1) |
| ZZ-L08-#03/#03 | 99.4±89.9(2) | 18.9±4.7(2) | 17.0±0.6(2) | 14.4±1.3(2) | 4.2±0.2(2) | 139.6±8.8(2) | 109.4±13.4(2) |
| ZZ-L08-#14/#14 | 107.2±95.7(2) | 17.3±1.3(2) | 20.3±2.8(2) | 17.5±2.7(2) | 4.2±0.1(2) | 119.0±17.1(2) | 93.1±8(2) |
| ZZ-MUT3 | 94.4±66.7(6)** | 16.7±3.2(6)* | 19.2±3.1(6)** | 16.0±2.1(6) | 4.4±0.2(6)** | 140.9±30.1(6) | 99.9±12.7(6)** |
表3 OsNramp5基因敲除株系籽粒的矿物元素含量变化
Table 3 Changes of mineral element contents in the grains of the OsNramp5 knockout lines.
| 样品编号 | 镉1 Cd1 | 镉2 Cd2 | 锰1 Mn1 | 铁1 Fe1 | 铜1 Cu1 | 铅1 Pb1 | 铬1 Cr1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample number | /(μg∙kg-1) | /(μg∙kg-1) | /(mg∙kg-1) | /(mg∙kg-1) | /(mg∙kg-1) | /(μg∙kg-1) | /(μg∙kg-1) |
| HZ-WT | 2010.3±400.5(3) | 134.7±22.5(3) | 60.1±13.9(3) | 10.4±1.1(3) | 4.7±0.4(3) | 114.2±40.4(3) | 80.8±39.1(3) |
| HZ-L01-#05/#05 | 137.6(1) | 11.0(1) | 25.0(1) | 13.3(1) | 5.4(1) | 211.0(1) | 153.0(1) |
| HZ-L01-#31/#31 | 46.4(1) | 13.5(1) | 24.2(1) | 27.5(1) | 5.4(1) | 344.3(1) | 169.1(1) |
| HZ-L04-#09/#09 | 39.1±11.2(2) | 11.8±0.2(2) | 20.5±1.5(2) | 13.3±1.5(2) | 5.1±0.2(2) | 165.1±15.5(2) | 97.2±16.7(2) |
| HZ-L08-#03/#03 | 47.4±10.6(3) | 11.7±1.0(3) | 20.3(1) | 11.7±2.1(3) | 5.4±1.1(3) | 191.0±58.2(3) | 109.2±19.7(3) |
| HZ-L08-#19/#19 | 91.0±64.2(2) | 12.6±5.3(2) | 22.5±0.7(2) | 11.9±0.1(2) | 4.7±0.1(2) | 191.3±48.2(2) | 173.5±42.2(2) |
| HZ-MUT3 | 65.2±41.4(9)* | 12.0±2.1(9)* | 22.2±2.0(7)* | 14.0±5.2(9) | 5.2±0.6(9) | 204.6±64.2(9)* | 132.3±38.9(9) |
| WF-WT | 1753.7±167.5(3) | 123.7±31.3(3) | 42.6±7.0(3) | 12.8±0.9(3) | 4.5±0.3(3) | 168.0±34.7(3) | 60.8±5.0(3) |
| WF-L03-#02/#02 | 30.5(1) | 13.3(1) | 22.9(1) | 13.8(1) | 4.7(1) | 138.6(1) | 124.4(1) |
| WF-L03-#29/#29 | 29.1(1) | 14.6(1) | 21.1(1) | 14.8(1) | 3.9(1) | 100.9(1) | 54.6(1) |
| WF-L04-#27/#27 | 42.0(1) | 14.1(1) | 16.8(1) | 14.2(1) | 4.4(1) | 183.4(1) | 104.8(1) |
| WF-L05-#29/#29 | 68.3±33.5(2) | 15.9±0.7(2) | 16.0±0.6(2) | 13.6±0.1(2) | 4.5±0.2(2) | 161.7±32.5(2) | 108.7±39.5(2) |
| WF-L08-#03/#03 | 82.2±0.3(2) | 18.9±0.2(2) | 17.9±0.6(2) | 14.5±0.6(2) | 5.1±0.2(2) | 166.4±43.7(2) | 66.6±5.0(2) |
| WF-L08-#08/#08 | 29.1(1) | 15.0(1) | 17.1(1) | 14.9(1) | 4.7(1) | 149.0(1) | 73.9(1) |
| WF-MUT3 | 53.9±26.9(8)** | 15.8±2.1(8)* | 18.2±2.5(8)* | 14.2±0.6(8)** | 4.6±0.4(8) | 153.5±32.4(8) | 88.5±30.0(8) |
| WS-WT | 1765.6±246.4(6) | 129.2±32.3(3) | 37.1±5.1(3) | 9.5±0.7(3) | 4.6±0.2(3) | 133.9±41.5(3) | 74.0±23.9(3) |
| WS-L01-#28/#28 | 134.2±150.4(2) | 17.7±1.4(2) | 16.6±1.3(2) | 12.3±1.1(2) | 4.3±0.1(2) | 124.9±4.9(2) | 114.0±29.6(2) |
| WS-L02-#15/#15 | 42.6±8.2(2) | 15.6±0.4(2) | 15.8±0.6(2) | 12.4±2.1(2) | 4.6±0.1(2) | 170.2±60.7(2) | 119.6±13.1(2) |
| WS-L02-#28/#28 | 187.3(1) | 13.6(1) | 16.9(1) | 11.9(1) | 4.6(1) | 128.2(1) | 100.1(1) |
| WS-MUT3 | 108.2±98.6(5)** | 16.0±1.9(5)* | 16.3±0.9(5)* | 12.2±1.2(5)* | 4.5±0.2(5) | 143.7±38.9(5) | 113.4±18.0(5)* |
| ZZ-WT | 1140.3±143.0(3) | 69.9±12.7(3) | 29.1±1.2(3) | 14.4±1.3(3) | 5.0±0.1(3) | 123.7±3.2(3) | 56.9±9.5(3) |
| ZZ-L01-#03/#03 | 121.5(1) | 13.6(1) | 23.8(1) | 17.4(1) | 4.5(1) | 196.6(1) | 85.5(1) |
| ZZ-L01-#29/#29 | 31.9(1) | 14.1(1) | 16.7(1) | 14.8(1) | 4.7(1) | 131.9(1) | 109.0(1) |
| ZZ-L08-#03/#03 | 99.4±89.9(2) | 18.9±4.7(2) | 17.0±0.6(2) | 14.4±1.3(2) | 4.2±0.2(2) | 139.6±8.8(2) | 109.4±13.4(2) |
| ZZ-L08-#14/#14 | 107.2±95.7(2) | 17.3±1.3(2) | 20.3±2.8(2) | 17.5±2.7(2) | 4.2±0.1(2) | 119.0±17.1(2) | 93.1±8(2) |
| ZZ-MUT3 | 94.4±66.7(6)** | 16.7±3.2(6)* | 19.2±3.1(6)** | 16.0±2.1(6) | 4.4±0.2(6)** | 140.9±30.1(6) | 99.9±12.7(6)** |
| 样品编号 Sample number | 株高 Plant height /cm | 有效分蘖数 Effective tiller number | 每穗总粒数 Total grain number per panicle | 每穗实粒数 Filled grain number per panicle | 结实率 Seed setting rate/% | 千粒重 1000-grain weight/g | 理论产量 Theoretical yield /(kg∙hm-2) | 增产率 Yield increasing rate/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HZ-WT | 115.3±3.6(68) | 8.8±2.4(68) | 239.1±91.5(115) | 192.9±75.0(115) | 81±11(115) | 19.6±0.1(2) | 9009.0 | - |
| HZ-L01-#31/#31 | 111.4±3.1(57)** | 9.2±2.2(57) | 257.1±97.6(89) | 178.7±69.9(89) | 70±12(89)** | 18.9±0.1(2)* | 8376.0 | -7.0 |
| HZ-L04-#09/#09 | 112.1±2.6(71)** | 8.8±2.3(71) | 235.9±63.7(105) | 181.9±53.7(105) | 77±9(105)** | 19.4±0.0(2) | 8418.0 | -6.6 |
| HZ-L08-#19/#19 | 107.9±4.4(70)** | 9.7±2.6(70) | - | - | - | 18.6±0.2(2)* | - | - |
| P值 P value | 0.000 | 0.129 | 0.211 | 0.322 | 0.000 | 0.003 | - | - |
| WF-WT | 78.9±2.1(46) | 7.3±1.6(46) | 129.8±26.1(73) | 121.3±26.5(73) | 93±5(73) | 24.0±0.1(2) | 5760.0 | - |
| WF-L03-#02/#02 | 74.6±1.8(46)** | 7.6±1.5(46) | 120.8±26.2(81) | 109.5±27.5(81)* | 90±7(81)** | 23.6±0.1(2) | 5310.0 | -7.8 |
| WF-L03-#29/#29 | 77.7±2.4(46)* | 7.3±2.1(46) | 130.8±24.2(75) | 117.4±24.4(75) | 89±6(75)** | 23.7±0.0(2) | 5512.5 | -4.3 |
| P值 P value | 0.000 | 0.664 | 0.028 | 0.018 | 0.000 | 0.083 | - | - |
| WS-WT | 116.2±3.8(45) | 8.7±2.4(45) | 223.8±70.2(103) | 201.7±61.7(103) | 90±4(103) | 20.4±0.0(2) | 9660.0 | - |
| WS-L01-#28/#28(1) | 110.4±2.9(46)** | 8.5±1.6(46) | 229.2±92.1(104) | 190.4±75.7(104) | 84±9(104)** | 19.6±0.1(2)** | 8596.5 | -11.0 |
| WS-L01-#28/#28(2) | 110.8±3.3(46)** | 9.6±2.6(46) | 211.6±58.0(96) | 187.8±50.7(96) | 89±7(96) | 19.3±0.0(2)** | 9435.0 | -2.3 |
| WS-L02-#15/#15 | 109.6±4.1(46)** | 9.2±1.8(46) | 183.5±68.3(103)** | 164.7±61.0(103)** | 90±3(103) | 20.1±0.1(2)* | 8220.0 | -14.9 |
| WS-L02-#28/#28 | 111.1±3.2(38)** | 9.6±2.2(38) | - | - | - | 19.9±0.0(2)** | - | - |
| P值 P value | 0.000 | 0.034 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | - | - |
| ZZ-WT | 83.8±3.1(46) | 7.2±1.9(46) | 115.2±42.7(83) | 101.0±41.3(83) | 86±8(83) | 29.4±0.2(2) | 5770.5 | - |
| ZZ-L08-#14/#14 | 78.1±2.3(45)** | 7.8±1.9(45) | 106.6±41.7(88) | 92.7±35.6(88) | 87±6(88) | 27.8±0.1(2)** | 5458.5 | -5.4 |
表4 OsNramp5基因敲除对株高、产量性状的影响
Table 4 Effects of OsNramp5 disruption on plant height and yield traits.
| 样品编号 Sample number | 株高 Plant height /cm | 有效分蘖数 Effective tiller number | 每穗总粒数 Total grain number per panicle | 每穗实粒数 Filled grain number per panicle | 结实率 Seed setting rate/% | 千粒重 1000-grain weight/g | 理论产量 Theoretical yield /(kg∙hm-2) | 增产率 Yield increasing rate/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HZ-WT | 115.3±3.6(68) | 8.8±2.4(68) | 239.1±91.5(115) | 192.9±75.0(115) | 81±11(115) | 19.6±0.1(2) | 9009.0 | - |
| HZ-L01-#31/#31 | 111.4±3.1(57)** | 9.2±2.2(57) | 257.1±97.6(89) | 178.7±69.9(89) | 70±12(89)** | 18.9±0.1(2)* | 8376.0 | -7.0 |
| HZ-L04-#09/#09 | 112.1±2.6(71)** | 8.8±2.3(71) | 235.9±63.7(105) | 181.9±53.7(105) | 77±9(105)** | 19.4±0.0(2) | 8418.0 | -6.6 |
| HZ-L08-#19/#19 | 107.9±4.4(70)** | 9.7±2.6(70) | - | - | - | 18.6±0.2(2)* | - | - |
| P值 P value | 0.000 | 0.129 | 0.211 | 0.322 | 0.000 | 0.003 | - | - |
| WF-WT | 78.9±2.1(46) | 7.3±1.6(46) | 129.8±26.1(73) | 121.3±26.5(73) | 93±5(73) | 24.0±0.1(2) | 5760.0 | - |
| WF-L03-#02/#02 | 74.6±1.8(46)** | 7.6±1.5(46) | 120.8±26.2(81) | 109.5±27.5(81)* | 90±7(81)** | 23.6±0.1(2) | 5310.0 | -7.8 |
| WF-L03-#29/#29 | 77.7±2.4(46)* | 7.3±2.1(46) | 130.8±24.2(75) | 117.4±24.4(75) | 89±6(75)** | 23.7±0.0(2) | 5512.5 | -4.3 |
| P值 P value | 0.000 | 0.664 | 0.028 | 0.018 | 0.000 | 0.083 | - | - |
| WS-WT | 116.2±3.8(45) | 8.7±2.4(45) | 223.8±70.2(103) | 201.7±61.7(103) | 90±4(103) | 20.4±0.0(2) | 9660.0 | - |
| WS-L01-#28/#28(1) | 110.4±2.9(46)** | 8.5±1.6(46) | 229.2±92.1(104) | 190.4±75.7(104) | 84±9(104)** | 19.6±0.1(2)** | 8596.5 | -11.0 |
| WS-L01-#28/#28(2) | 110.8±3.3(46)** | 9.6±2.6(46) | 211.6±58.0(96) | 187.8±50.7(96) | 89±7(96) | 19.3±0.0(2)** | 9435.0 | -2.3 |
| WS-L02-#15/#15 | 109.6±4.1(46)** | 9.2±1.8(46) | 183.5±68.3(103)** | 164.7±61.0(103)** | 90±3(103) | 20.1±0.1(2)* | 8220.0 | -14.9 |
| WS-L02-#28/#28 | 111.1±3.2(38)** | 9.6±2.2(38) | - | - | - | 19.9±0.0(2)** | - | - |
| P值 P value | 0.000 | 0.034 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | - | - |
| ZZ-WT | 83.8±3.1(46) | 7.2±1.9(46) | 115.2±42.7(83) | 101.0±41.3(83) | 86±8(83) | 29.4±0.2(2) | 5770.5 | - |
| ZZ-L08-#14/#14 | 78.1±2.3(45)** | 7.8±1.9(45) | 106.6±41.7(88) | 92.7±35.6(88) | 87±6(88) | 27.8±0.1(2)** | 5458.5 | -5.4 |
| 样品编号 Sample number | 整精米长 Head rice length /mm | 整精米宽 Head rice width /mm | 长宽比 Length/width | 垩白粒率 Chalky grain percentage/% | 垩白度 Chalkiness degree/% | 蛋白质含量 Protein content/% | 直链淀粉含量 Amylose content/% | 食味分 Taste score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HZ-WT | 5.59±0.02 | 1.80±0.00 | 3.11±0.02 | 4.50±0.12 | 1.25±0.06 | 8.20±0.03 | 12.18±0.25 | - |
| HZ-L04-#09/#09 | 5.67±0.01 | 1.74±0.01** | 3.27±0.01** | 3.85±0.45 | 1.18±0.12 | 8.47±0.02** | 12.05±0.27 | - |
| HZ-L08-#19/#19 | 5.55±0.03 | 1.72±0.00** | 3.23±0.02** | 4.06±0.65 | 0.97±0.18 | 8.41±0.03** | 11.54±0.17 | - |
| HZ-L01-#31/#31 | 5.61±0.01 | 1.73±0.01** | 3.25±0.01** | 3.27±0.51 | 0.94±0.19 | 8.77±0.01** | 11.66±0.18 | - |
| P值 P value | 0.015 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.400 | 0.402 | 0.000 | 0.202 | - |
| WF-WT | 5.28±0.01 | 2.21±0.00 | 2.39±0.00 | 37.36±1.03 | 6.94±0.50 | 9.02±0.01 | 9.00±0.63 | - |
| WF-L03-#02/#02 | 5.46±0.01** | 2.17±0.00** | 2.52±0.00** | 34.45±0.54 | 6.99±0.02 | 9.33±0.01** | 7.85±0.21 | - |
| WF-L03-#29/#29 | 5.38±0.00** | 2.15±0.00** | 2.50±0.00** | 35.17±1.96 | 6.80±0.61 | 9.03±0.01 | 7.93±0.27 | - |
| P值 P value | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.338 | 0.952 | 0.000 | 0.166 | - |
| WS-WT | 5.74±0.01 | 1.81±0.00 | 3.19±0.01 | 3.96±0.47 | 0.82±0.05 | 8.43±0.04 | 18.10±0.27 | 88.03±0.16 |
| WS-L02-#15/#15 | 5.91±0.01** | 1.81±0.00 | 3.26±0.01** | 2.82±0.31 | 0.45±0.04** | 8.72±0.02** | 17.93±0.11 | 88.16±0.30 |
| WS-L01-#28/#28 | 5.70±0.01 | 1.77±0.01** | 3.24±0.01** | 3.69±0.34 | 1.18±0.18 | 8.87±0.01** | 18.51±0.17 | 86.11±0.24** |
| WS-L02-#28/#28 | 5.81±0.00** | 1.80±0.00 | 3.24±0.00** | 2.68±0.68 | 0.55±0.08 | 8.63±0.04** | 18.52±0.01 | 87.88±0.01 |
| P值 P value | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.229 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.106 | 0.000 |
| ZZ-WT | 5.50±0.01 | 2.56±0.01 | 2.16±0.00 | 98.22±0.35 | 40.92±0.87 | 9.10±0.01 | 34.68±0.94 | - |
| ZZ-L08-#14/#14 | 5.60±0.01** | 2.49±0.00** | 2.26±0.01** | 91.65±0.74** | 36.60±0.68* | 9.38±0.01* | 30.32±0.49* | - |
表5 OsNramp5基因敲除株系的米质变化
Table 5 Quality change of the milled rice from the OsNramp5 knockout lines relative to those from the wild type.
| 样品编号 Sample number | 整精米长 Head rice length /mm | 整精米宽 Head rice width /mm | 长宽比 Length/width | 垩白粒率 Chalky grain percentage/% | 垩白度 Chalkiness degree/% | 蛋白质含量 Protein content/% | 直链淀粉含量 Amylose content/% | 食味分 Taste score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HZ-WT | 5.59±0.02 | 1.80±0.00 | 3.11±0.02 | 4.50±0.12 | 1.25±0.06 | 8.20±0.03 | 12.18±0.25 | - |
| HZ-L04-#09/#09 | 5.67±0.01 | 1.74±0.01** | 3.27±0.01** | 3.85±0.45 | 1.18±0.12 | 8.47±0.02** | 12.05±0.27 | - |
| HZ-L08-#19/#19 | 5.55±0.03 | 1.72±0.00** | 3.23±0.02** | 4.06±0.65 | 0.97±0.18 | 8.41±0.03** | 11.54±0.17 | - |
| HZ-L01-#31/#31 | 5.61±0.01 | 1.73±0.01** | 3.25±0.01** | 3.27±0.51 | 0.94±0.19 | 8.77±0.01** | 11.66±0.18 | - |
| P值 P value | 0.015 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.400 | 0.402 | 0.000 | 0.202 | - |
| WF-WT | 5.28±0.01 | 2.21±0.00 | 2.39±0.00 | 37.36±1.03 | 6.94±0.50 | 9.02±0.01 | 9.00±0.63 | - |
| WF-L03-#02/#02 | 5.46±0.01** | 2.17±0.00** | 2.52±0.00** | 34.45±0.54 | 6.99±0.02 | 9.33±0.01** | 7.85±0.21 | - |
| WF-L03-#29/#29 | 5.38±0.00** | 2.15±0.00** | 2.50±0.00** | 35.17±1.96 | 6.80±0.61 | 9.03±0.01 | 7.93±0.27 | - |
| P值 P value | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.338 | 0.952 | 0.000 | 0.166 | - |
| WS-WT | 5.74±0.01 | 1.81±0.00 | 3.19±0.01 | 3.96±0.47 | 0.82±0.05 | 8.43±0.04 | 18.10±0.27 | 88.03±0.16 |
| WS-L02-#15/#15 | 5.91±0.01** | 1.81±0.00 | 3.26±0.01** | 2.82±0.31 | 0.45±0.04** | 8.72±0.02** | 17.93±0.11 | 88.16±0.30 |
| WS-L01-#28/#28 | 5.70±0.01 | 1.77±0.01** | 3.24±0.01** | 3.69±0.34 | 1.18±0.18 | 8.87±0.01** | 18.51±0.17 | 86.11±0.24** |
| WS-L02-#28/#28 | 5.81±0.00** | 1.80±0.00 | 3.24±0.00** | 2.68±0.68 | 0.55±0.08 | 8.63±0.04** | 18.52±0.01 | 87.88±0.01 |
| P值 P value | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.229 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.106 | 0.000 |
| ZZ-WT | 5.50±0.01 | 2.56±0.01 | 2.16±0.00 | 98.22±0.35 | 40.92±0.87 | 9.10±0.01 | 34.68±0.94 | - |
| ZZ-L08-#14/#14 | 5.60±0.01** | 2.49±0.00** | 2.26±0.01** | 91.65±0.74** | 36.60±0.68* | 9.38±0.01* | 30.32±0.49* | - |
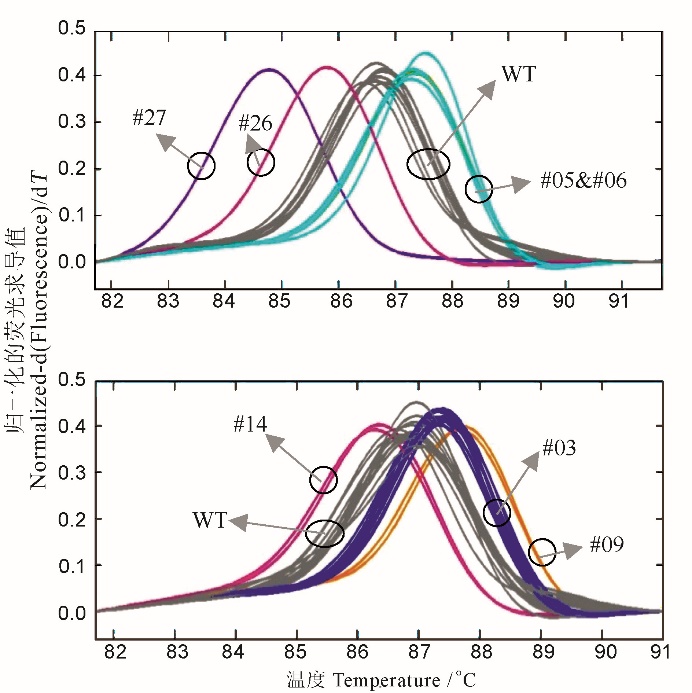
图3 几种突变类型与野生型在HRM分型时的溶解曲线其中基因型WT(上图)、WT(下图)、#03、#05、#06、#09、#14、#26和#27的样品数(n)分别为9、13、11、2、4、2、2、1和1。
Fig. 3. Melting curves of various mutation alleles and the wild type in HRM analysis. The sample sizes (n) for the genotypes WT(upper panel), WT(lower panel), #03, #05, #06, #09, #14, #26 and #27 are 9, 13, 11, 2, 4, 2, 2, 1 and 1, respectively.
| [1] | Grant C A, Clarke J M, Duguid S, Chaney R L.Selection and breeding of plant cultivars to minimize cadmium accumulation.Sci Total Environ, 2008, 390: 301-310. |
| [2] | Sebastian A, Prasad M N V. Cadmium minimization in rice. A review.Agron Sustain Dev, 2014, 34(1): 155-173. |
| [3] | Järup L, Åkesson A.Current status of cadmium as an environmental health problem.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol , 2009, 238: 201-208. |
| [4] | Arao T, Ae N.Genotypic variations in cadmium levels of rice grain.Soil Sci Plant Nutr, 2003, 49(4): 473-479 |
| [5] | Liu J, Zhu Q, Zhang Z, Xu J, Yang J, Wong M H.Variations in cadmium accumulation among rice cultivars and types and the selection of cultivars for reducing cadmium in the diet.J Sci Food Agric, 2005, 85: 147-153. |
| [6] | 王林友, 竺朝娜, 王建军, 张礼霞, 金庆生, 石春海. 水稻镉、铅、砷低含量基因型的筛选. 浙江农业学报, 2012, 24(1): 133-138. |
| Wang L Y, Zhu C N, Wang J J, Zhang L X, Jin Q S, Shi C H.Screening for rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotyeps with lower Cd, Pb and As contents. Acta Agric Zhejiang, 2012, 24(1): 133-138. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 叶新新, 周艳丽, 孙波. 适于轻度Cd、As污染土壤种植的水稻品种筛选. 农业环境科学学报, 2012, 31(6): 1082-1088. |
| Ye X X, Zhou Y L, Sun B.Screening of suitable rice cultivars for the adaptation to lightly contaminated soil with Cd and As.J Agro-Environ Sci, 2012, 31(6): 1082-1088. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | Uraguchi S, Fujiwara T.Rice breaks ground for cadmium-free cereals.Curr Opin Plant Biol, 2013, 16(3): 328-334. |
| [9] | Uraguchi S, Fujiwara T.Cadmium transport and tolerance in rice: Perspectives for reducing grain cadmium accumulation.Rice, 2012, 5(1): 5. |
| [10] | Satoh-Nagasawa N, Mori M, Nakazawa N, Kawamoto T, Nagato Y, Sakurai K, Takahashi H, Watanabe A, Akagi H.Mutations in rice (Oryza sativa) heavy metal ATPase 2 (OsHMA2) restrict the translocation of zinc and cadmium. Plant Cell Physiol, 2012, 53(1): 213-224. |
| [11] | Takahashi R, Ishimaru Y, Shimo H, Ogo Y, Senoura T, Nishizawa N K, Nakanishi H.The OsHMA2 transporter is involved in root-to-shoot translocation of Zn and Cd in rice.Plant Cell Environ, 2012, 35(11): 1948-1957. |
| [12] | Yamaji N, Xia J, Mitani-Ueno N, Yokosho K, Feng M J.Preferential delivery of zinc to developing tissues in rice is mediated by P-type heavy metal ATPase OsHMA2.Plant Physiol, 2013, 162(2): 927-939. |
| [13] | Ueno D, Yamaji N, Kono I, Huang C F, Ando T, Yano M, Ma J F.Gene limiting cadmium accumulation in rice.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2010, 107(38): 16 500-16 505. |
| [14] | Uraguchi S, Kamiya T, Sakamoto T, Kasai K, Sato Y, Nagamura Y, Yoshida A, Kyozuka J, Ishikawa S, Fujiwara T.Low-affinity cation transporter (OsLCT1) regulates cadmium transport into rice grains.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2011, 108(52): 20 959-20 964. |
| [15] | Shimo H, Ishimaru Y, An G, Yamakawa T, Nakanishi H, Nishizawa N K.Low cadmium (LCD), a novel gene related to cadmium tolerance and accumulation in rice. J Exp Bot, 2011, 62(15): 5727-5734. |
| [16] | Ishikawa S, Ishimaru Y, Igura M, Kuramata M, Abe T, Senoura T, Hase Y, Arao T, Nishizawa N K, Nakanishi H.Ion-beam irradiation, gene identification, and marker-assisted breeding in the development of low-cadmium rice.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2012, 109(47): 19 166-19 171. |
| [17] | Ishimaru Y, Takahashi R, Bashir K, Shimo H, Senoura T, Sugimoto K, Ono K, Yano M, Ishikawa S, Arao T, Nakanishi H, Nishizawa N K.Characterizing the role of rice NRAMP5 in manganese, iron and cadmium transport.Sci Rep, 2012, 2: 286. |
| [18] | Sasaki A, Yamaji N, Yokosho K, Ma J F.Nramp5 is a major transporter responsible for manganese and cadmium uptake in rice.Plant Cell, 2012, 24(5): 2155-2167. |
| [19] | Belhaj K, Chaparro-Garcia A, Kamoun S, Nekrasov V.Plant genome editing made easy: Targeted mutagenesis in model and crop plants using the CRISPR/Cas system.Plant Methods, 2013, 9(1): 39. |
| [20] | Peng H, Zhang Q, Li Y, Lei C, Zhai Y, Sun X, Sun D, Sun Y, Lu T.A putative leucine-rich repeat receptor kinase, OsBRR1, is involved in rice blast resistance.Planta, 2009, 230(2): 377-385. |
| [21] | Miao J, Guo D, Zhang J, Huang Q, Qin G, Zhang X, Wan J, Gu H, Qu L J.Targeted mutagenesis in rice using CRISPR-Cas system.Cell Res, 2013, 23(10): 1233-1236. |
| [22] | Feng Z, Zhang B, Ding W, Liu X, Yang D L, Wei P, Cao F, Zhu S, Zhang F, Mao Y, Zhu J K.Efficient genome editing in plants using a CRISPR/Cas system.Cell Res, 2013, 23(10): 1229-1232. |
| [23] | Cong L, Ran F A, Cox D, Lin S, Barretto R, Habib N, Hsu P D, Wu X, Jiang W, Marraffini L A, Zhang F.Multiplex genome engineering using CRISPR/Cas systems.Science, 2013, 339(6121): 819-823. |
| [24] | Liu H, Ding Y, Zhou Y, Jin W, Xie K, Chen L L.CRISPR-P 2.0: An improved CRISPR-Cas9 tool for genome editing in plants.Mol Plant, 2017, 10(3): 530-532. |
| [25] | Lei Y, Lu L, Liu H Y, Li S, Xing F, Chen L L.CRISPR-P: A web tool for synthetic single-guide RNA design of CRISPR-system in plants.Mol Plant, 2014, 7(9): 1494-1496. |
| [26] | Holsters M, de Waele D, Depicker A, Messens E, van Montagu M, Schell J. Transfection and transformation ofAgrobacterium tumefaciens. Mol Gen Genet, 1978, 163(2): 181-187. |
| [27] | Toki S, Hara N, Ono K, Onodera H, Tagiri A, Oka S, Tanaka H.Early infection of scutellum tissue with Agrobacterium allows high-speed transformation of rice.Plant J, 2006, 47(6): 969-976. |
| [28] | Allen G C, Flores-Vergara M A, Krasynanski S, Kumar S, Thompson W F. A modified protocol for rapid DNA isolation from plant tissues using cetyltrimethy- lammonium bromide.Nat Protoc, 2006, 1(5): 2320-2325. |
| [29] | 刘巧泉, 陈秀花, 王兴稳, 彭凌涛, 顾铭洪. 一种快速检测转基因水稻中潮霉素抗性的简易方法. 农业生物技术学报, 2001, 9(3): 264-268. |
| Liu Q Q, Chen X H, Wang X Y, Peng T L, Gu M H.A rapid simple method of assaying hygromysin resistance in transgenic rice. J Agric Biotechnol, 2001, 9(3): 264-268. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | Tang L, Mao B, Li Y, Lv Q, Zhang L, Chen C, He H, Wang W, Zeng X, Shao Y, Pan Y, Hu Y, Peng Y, Fu X, Li H, Xia S, Zhao B.Knockout ofOsNramp5 using the CRISPR/Cas9 system produces low Cd-accumulating indica rice without compromising yield. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1): 14 438. |
| [31] | Rizwan M, Ali S, Adrees M, Rizvi H, Zia-Ur-Rehman M, Hannan F, Qayyum M F, Hafeez F, Ok Y S.Cadmium stress in rice: Toxic effects, tolerance mechanisms, and management: A critical review.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int, 2016, 23(18): 17 859-17 879. |
| [32] | 吴平. 应用RFLP标记分析水稻株高与分蘖的遗传相关性. 中国科学C辑: 生命科学, 1996, 26(3): 264-270. |
| Wu P.Genetic correlation analysis of rice plant height and tiller number using RFLP markers.Sci China: Ser C, 1996, 26(3): 264-270. (in Chinese; the title was translated into English by us) | |
| [33] | Allen F, Crepaldi L, Alsinet C, Strong A J, Kleshchevnikov V, De Angeli P, Páleníková P, Khodak A, Kiselev V, Kosicki M, Bassett A R, Harding H, Galanty Y, Muñoz-Martínez F, Metzakopian E, Jackson S P, Parts L.Predicting the mutations generated by repair of Cas9-induced double-strand breaks.Nat Biotechnol, 2018, 37: 64-72. |
| [34] | Wang C, Guo W, Ye S, Wei P, Ow D W.Reduction of Cd in rice through expression ofOXS3-like gene fragments. Mol Plant, 2016, 9(2): 301-304 |
| [35] | Uraguchi S, Kamiya T, Clemens S, Fujiwara T.Characterization of OsLCT1, a cadmium transporter from indica rice (Oryza sativa). Physiol Plant, 2014, 151(3): 339-347. |
| [36] | Hao X, Zeng M, Wang J, Zeng Z, Dai J, Xie Z, Yang Y, Tian L, Chen L, Li D.A node-expressed transporter OsCCX2 is involved in grain cadmium accumulation of rice.Front Plant Sci, 2018, 9: 476. |
| [1] | 唐志伟, 朱相成, 张俊, 邓艾兴, 张卫建. 水分调控下绿肥种植和石灰施用对双季稻稻米镉含量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 211-222. |
| [2] | 梁楚炎, 巫明明, 黄凤明, 翟荣荣, 叶靖, 朱国富, 俞法明, 张小明, 叶胜海. 基因编辑及全基因组选择技术在水稻育种中的应用展望[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(1): 1-12. |
| [3] | 侯本福, 杨传铭, 张喜娟, 杨贤莉, 王立志, 王嘉宇, 李红宇, 姜树坤. 利用龙稻5号/中优早8号RIL群体定位粒形QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(1): 13-24. |
| [4] | 易晓璇, 刘玮琦, 曾盖, 罗丽华, 肖应辉. 灌浆期高温胁迫对早籼稻品质性状的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(1): 72-80. |
| [5] | 黄奇娜, 徐有祥, 林光号, 党洪阳, 郑振权, 张燕, 王晗, 邵国胜, 尹献远. 硅对镉胁迫下水稻苗期抗氧化酶系统及镉离子吸收和转运相关基因表达水平的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(5): 486-496. |
| [6] | 李刚, 高清松, 李伟, 张雯霞, 王健, 程保山, 王迪, 高浩, 徐卫军, 陈红旗, 纪剑辉. 定向敲除SD1基因提高水稻的抗倒性和稻瘟病抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(4): 359-367. |
| [7] | 陈丽明, 杨陶陶, 熊若愚, 谭雪明, 黄山, 曾勇军, 潘晓华, 石庆华, 张俊, 曾研华. 开放式主动增温对双季优质籼稻籽粒淀粉积累及其关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(2): 166-177. |
| [8] | 张佳, 王慧杰, 何正权, 刘文真. 农杆菌介导的籼稻9311和华占遗传转化体系的研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(2): 213-224. |
| [9] | 裴峰, 王广达, 高鹏, 冯志明, 胡珂鸣, 陈宗祥, 陈红旗, 崔傲, 左示敏. 敲除OsNramp5基因创制低镉优质粳稻新材料的应用评价[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(1): 16-28. |
| [10] | 巫明明, 曾维, 翟荣荣, 叶靖, 朱国富, 俞法明, 张小明, 叶胜海. 水稻耐盐分子机制与育种研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(6): 551-561. |
| [11] | 李小秀, 吕启明, 袁定阳. OsNramp5基因变异影响水稻重要农艺性状的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(6): 562-571. |
| [12] | 尹丽颖, 张元野, 李荣田, 何明良, 王芳权, 许扬, 刘欣欣, 潘婷婷, 田晓杰, 卜庆云, 李秀峰. 利用CRISPR/Cas9技术创制高效抗除草剂水稻[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(5): 459-466. |
| [13] | 周永林, 申小磊, 周立帅, 林巧霞, 王朝露, 陈静, 冯慧捷, 张振文, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsLOX10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(4): 348-356. |
| [14] | 张宇杰, 王志强, 马鹏, 杨志远, 孙永健, 马均. 麦秆还田下水氮耦合对水稻氮素吸收利用及产量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(4): 388-398. |
| [15] | 李兆伟, 孙聪颖, 零东兰, 曾慧玲, 张晓妹, 范凯, 林文雄. 利用CRISPR/Cas9创建osarf7突变体及其农艺性状调查[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(3): 237-247. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||