
中国水稻科学 ›› 2019, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (2): 135-143.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2019.8057 135
农保选1,2,3, 秦碧霞4, 夏秀忠2,3, 杨行海2,3, 张宗琼2,3, 曾宇2,3, 邓国富2,3, 蔡健和4, 李战彪4, 刘丕庆1,*( ), 李丹婷2,3,*(
), 李丹婷2,3,*( )
)
收稿日期:2018-05-16
修回日期:2018-12-20
出版日期:2019-03-10
发布日期:2019-03-10
通讯作者:
刘丕庆,李丹婷
基金资助:
Baoxuan NONG1,2,3, Bixia QIN4, Xiuzhong XIA2,3, Xinghai YANG2,3, Zongqiong ZHANG2,3, Yu ZENG2,3, Guofu DENG2,3, Jianhe CAI4, Zhanbiao LI4, Piqing LIU1,*( ), Danting LI2,3,*(
), Danting LI2,3,*( )
)
Received:2018-05-16
Revised:2018-12-20
Online:2019-03-10
Published:2019-03-10
Contact:
Piqing LIU, Danting LI
摘要:
【目的】近年来由白背飞虱传播的南方水稻黑条矮缩病给水稻生产造成了巨大损失,开展该病的抗性遗传分析和基因精细定位,将为抗性育种提供材料和理论依据。【方法】分析了抗性材料D4对南方水稻黑条矮缩病的抗性特征,并通过广恢998/D4 F2群体分析该病抗性的遗传规律,利用QTL-seq技术联合遗传连锁分析定位主效抗性QTL。【结果】D4对南方水稻黑条矮缩病的抗性表现为抗病毒性而非抗虫性,且受主效基因和微效基因共同控制。QTL-seq和连锁分析将南方水稻黑条矮缩病主效抗性QTL定位于第9染色体上,命名为qSRBSDV9。利用代换作图法进一步将qSRBSDV9定位在102.3 kb的区间内,该区间包含21个预测基因,其中9个基因与赤霉素信号传导相关。【结论】揭示了D4对南方水稻黑条矮缩病的抗性特征及遗传规律,精细定位了南方水稻黑条矮缩病主效抗性QTL qSRBSDV9。这为该QTL的图位克隆及育种利用奠定了基础。
中图分类号:
农保选, 秦碧霞, 夏秀忠, 杨行海, 张宗琼, 曾宇, 邓国富, 蔡健和, 李战彪, 刘丕庆, 李丹婷. 南方水稻黑条矮缩病抗性的遗传分析及主效QTL的精细定位[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(2): 135-143.
Baoxuan NONG, Bixia QIN, Xiuzhong XIA, Xinghai YANG, Zongqiong ZHANG, Yu ZENG, Guofu DENG, Jianhe CAI, Zhanbiao LI, Piqing LIU, Danting LI. Genetic Analysis and Fine Mapping of a Major QTL for the Resistance to Southern Rice Black-Streaked Dwarf Disease[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2019, 33(2): 135-143.

图1 人工接种南方水稻黑条矮缩病后水稻D4和广恢998的表型 A-D4接种南方水稻黑条矮缩病毒的表型;B-广恢998接种南方水稻黑条矮缩病毒的表型。N-未接种对照;I-接种。
Fig. 1. Phenotype of D4 and Guanghui 998 by artificial inoculation of SRBSDV. A, Phenotype of D4 after artificial inoculation of SRBSDV; B, Phenotype of Guanghui 998 after artificial inoculation of SRBSDV. N, Control; I, Inoculation.
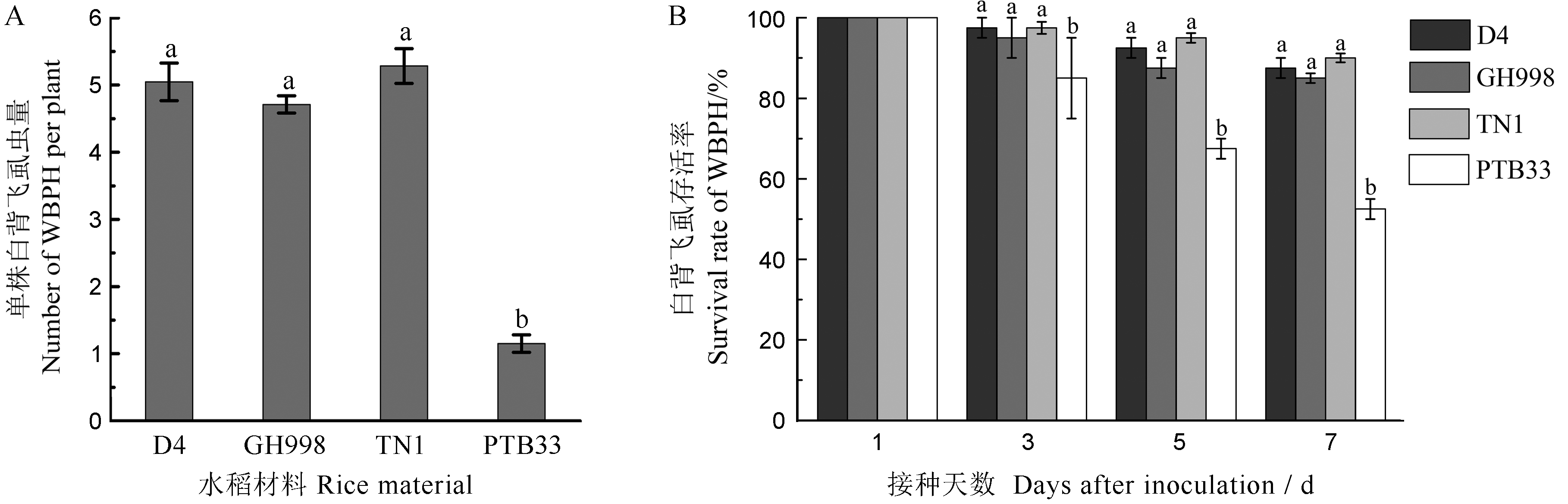
图2 D4和广恢998对白背飞虱的抗性分析 A-D4和广恢998(GH998)及两个对照品种对白背飞虱的排驱性表现;B-白背飞虱在D4和广恢998及两个对照品种中的存活率。数据用平均值±标准误表示, n=3。柱上相同字母表示差异未达0.01显著水平(t测验)。
Fig. 2. Resistance to white-backed planthoppers(WBPH) in D4 and Guanghui 998. A, Feeding preference of D4, Guanghui 998(GH998) and two control rice materials; B, Survival rates of D4, Guanghui 998(GH998) and two control rice materials. The error bars represent the SE(n=3). Bars superscripted by the same letter are not significantly different at the 0.01 level, by the Student’s t-test.
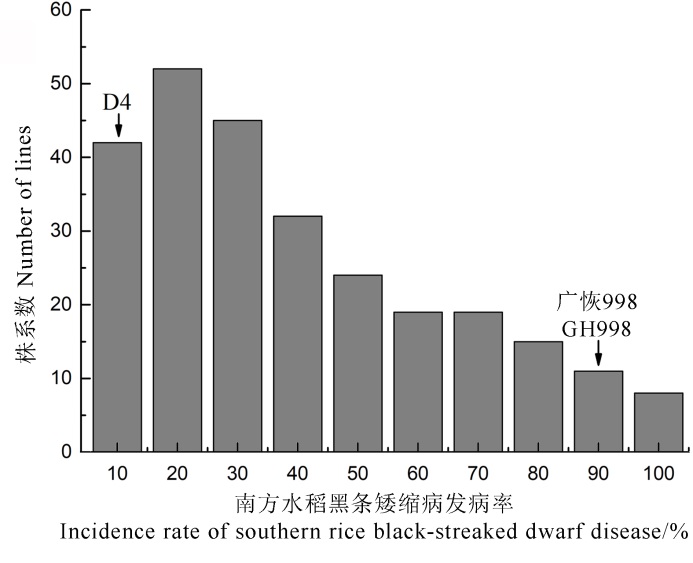
图3 广恢998/D4 F2:3株系接种南方水稻黑条矮缩病后的发病率频率分布
Fig. 3. Frequency distribution of the F2:3 lines derived from the cross between Guanghui 998(GH998) and D4 with southern rice black-streaked dwarf disease as determined by artificial inoculation identification.
| 样品Sample | Clean数据 Clean data/bp | HQ clean数据 HQ clean data/bp | 平均测序深度 Average depth/× | Read总数 Total reads | 比对read数 Mapped reads | 覆盖度 Coverage/% | GC含量 GC content/% | Q30含量 Q30 content/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D4 | 22 783 003 500 | 21 308 456 571 | 55.88 | 142 913 376 | 138 406 793 | 92.66 | 44.78 | 84.36 |
| GH998 | 30 069 649 500 | 29 089 431 251 | 76.28 | 195 193 248 | 189 390 713 | 93.26 | 43.45 | 94.56 |
| R-pool | 30 313 518 000 | 29 287 082 085 | 76.80 | 196 696 800 | 190 730 909 | 93.65 | 43.18 | 94.87 |
| S-pool | 27 220 437 600 | 26 367 983 261 | 69.14 | 177 553 354 | 171 577 580 | 93.35 | 45.11 | 95.02 |
表1 D4、广恢998(GH998)、抗池(R-pool)及感池(S-pool)测序结果数据统计
Table 1 Sequencing data statistics of D4, Guanghui 998(GH998), R-pool and S-pool.
| 样品Sample | Clean数据 Clean data/bp | HQ clean数据 HQ clean data/bp | 平均测序深度 Average depth/× | Read总数 Total reads | 比对read数 Mapped reads | 覆盖度 Coverage/% | GC含量 GC content/% | Q30含量 Q30 content/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D4 | 22 783 003 500 | 21 308 456 571 | 55.88 | 142 913 376 | 138 406 793 | 92.66 | 44.78 | 84.36 |
| GH998 | 30 069 649 500 | 29 089 431 251 | 76.28 | 195 193 248 | 189 390 713 | 93.26 | 43.45 | 94.56 |
| R-pool | 30 313 518 000 | 29 287 082 085 | 76.80 | 196 696 800 | 190 730 909 | 93.65 | 43.18 | 94.87 |
| S-pool | 27 220 437 600 | 26 367 983 261 | 69.14 | 177 553 354 | 171 577 580 | 93.35 | 45.11 | 95.02 |
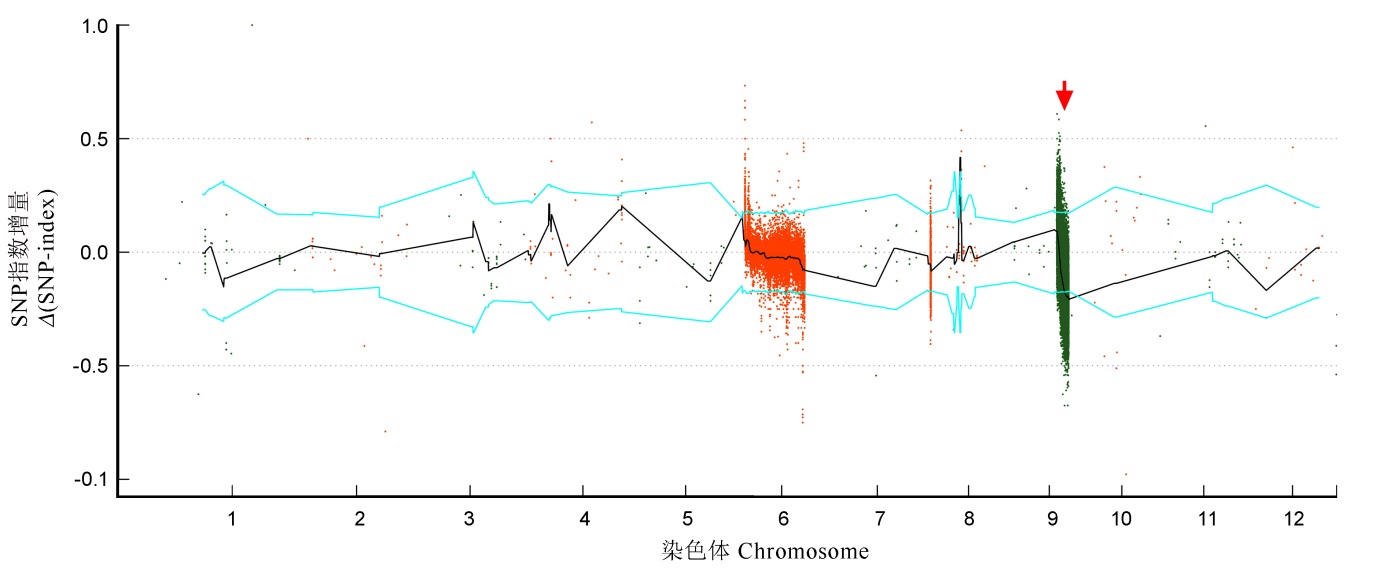
图4 单核苷酸多态性(SNP)指数增量在染色体上的分布横坐标表示染色体位置, 纵坐标表示SNP指数增量(突变型减去野生型)。图中每个点代表每个SNP指数增量, 相邻的染色体分别用橙色和绿色的点来表示, 黑线代表各个窗口SNP指数的平均值拟合线。蓝线代表95%置信水平的阈值线。
Fig. 4. Δ(SNP-index) value distribution in rice chromosomes. X-axis represents the chromosome position, and the y-axis represents the Δ(SNP-index) values. Dot on the map represents Δ(SNP-index) values, which were dyed orange and green of the neighboring chromosome, respectively. Black line represents the average SNP index values, as determined by sliding window analysis. Blue lines represents the threshold value(P<0.05).
| 引物 Primer | 正向引物序列 Forward primer (5'-3') | 反向引物序列 Reverse primer (5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
| Indel 4 | TGAAACTGGACAAATTACCC | AGGAGTACATGACAAGTGGG |
| Indel 5 | AAAATGAAACCCAACATGAC | CTTTATTTGCTTGCTCGATT |
| Indel 6 | AACCAGATATCTTGACCCCT | GAACGAAGACTCGGTCAATA |
| Indel 7 | AATTACGTTGTGGCAATACA | CGTAGCGATAAGAATGTGTG |
| Indel 18 | AGTCCCATCCAAACATAGTG | CAGAGCAGGTTGTCAACAG |
| Indel 22 | CTGTCAGACACGATCAGAGA | CATGCATGTCCTCTTGCT |
| Indel 23 | TTCTGCACACAATCTTTTTG | AGCCATGCTAGCTAGTTCAC |
| Indel 29 | ATCCTTTGCCATATCATCAG | AACGGTTGTACGAGTGAGAT |
| Indel 40 | AAATCCACGCAGTTCAAG | ACTAGGACCTGATTCCCATT |
| Indel 43 | AACCACTTGTCTTAGTCAAAAA | CACTGTTTGATCATTCGTCT |
| M1 | CAAAATAAGTTGGTTTTGGC | GTGTTTCTCCTTAATCTGCG |
| M2 | CTTCTCCGTCCAAACTACC | CCCCAGTAGAAGGTCATGT |
| M3 | TAATTAGTGTGTTGCACCGA | AAGCTAAACAGCACCATCAT |
| M4 | TGTGGGGTATCCACTAGTTC | AAGACGAGTGGTCAAACATT |
| M5 | GATAGATATAACGCGAGGCA | ATATTCCCCTATTCCACACC |
| M6 | AGCCAAAAACAACCTTACAA | AGCTCTCTGTCACTAGCTGC |
| M7 | TACGGTTTTGTAAACCTGCT | TCGGATCTAACAGGTGGTAA |
| M8 | AATGAATCAGCAGAAGGAAA | GGTAGTTGTGTCAAGGGCT |
| M9 | ACATGTTACTGGGCCTAAAA | CCCTTGAAAATGACGATAAG |
| M10 | ACTCTGGGAGTGGAGGAT | ACCTCACCTGTTCTGTGTTC |
| M11 | CCGTTTTTCTTATTCCTACG | GAACATATGATTGGGTTGGT |
| M12 | GAATCATCCACACACACAGA | GTTCACCTGCAGACTCTCTC |
| M13 | TAACGGCTGTTTCTTTCTTC | TATCTACAGTTTCCCGCTGT |
| M14 | TCTTTCCCTTCCTCTCTCTC | AAATATGCCACTCCAGAAAA |
| M15 | GTCGGTGCTGGAGGAACT | CCGCCTTCTTCCTCGTTAT |
表2 本研究中定位qSRBSDV9所用的InDel标记
Table 2 InDel primer used for mapping of qSRBSDV9 in this study.
| 引物 Primer | 正向引物序列 Forward primer (5'-3') | 反向引物序列 Reverse primer (5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
| Indel 4 | TGAAACTGGACAAATTACCC | AGGAGTACATGACAAGTGGG |
| Indel 5 | AAAATGAAACCCAACATGAC | CTTTATTTGCTTGCTCGATT |
| Indel 6 | AACCAGATATCTTGACCCCT | GAACGAAGACTCGGTCAATA |
| Indel 7 | AATTACGTTGTGGCAATACA | CGTAGCGATAAGAATGTGTG |
| Indel 18 | AGTCCCATCCAAACATAGTG | CAGAGCAGGTTGTCAACAG |
| Indel 22 | CTGTCAGACACGATCAGAGA | CATGCATGTCCTCTTGCT |
| Indel 23 | TTCTGCACACAATCTTTTTG | AGCCATGCTAGCTAGTTCAC |
| Indel 29 | ATCCTTTGCCATATCATCAG | AACGGTTGTACGAGTGAGAT |
| Indel 40 | AAATCCACGCAGTTCAAG | ACTAGGACCTGATTCCCATT |
| Indel 43 | AACCACTTGTCTTAGTCAAAAA | CACTGTTTGATCATTCGTCT |
| M1 | CAAAATAAGTTGGTTTTGGC | GTGTTTCTCCTTAATCTGCG |
| M2 | CTTCTCCGTCCAAACTACC | CCCCAGTAGAAGGTCATGT |
| M3 | TAATTAGTGTGTTGCACCGA | AAGCTAAACAGCACCATCAT |
| M4 | TGTGGGGTATCCACTAGTTC | AAGACGAGTGGTCAAACATT |
| M5 | GATAGATATAACGCGAGGCA | ATATTCCCCTATTCCACACC |
| M6 | AGCCAAAAACAACCTTACAA | AGCTCTCTGTCACTAGCTGC |
| M7 | TACGGTTTTGTAAACCTGCT | TCGGATCTAACAGGTGGTAA |
| M8 | AATGAATCAGCAGAAGGAAA | GGTAGTTGTGTCAAGGGCT |
| M9 | ACATGTTACTGGGCCTAAAA | CCCTTGAAAATGACGATAAG |
| M10 | ACTCTGGGAGTGGAGGAT | ACCTCACCTGTTCTGTGTTC |
| M11 | CCGTTTTTCTTATTCCTACG | GAACATATGATTGGGTTGGT |
| M12 | GAATCATCCACACACACAGA | GTTCACCTGCAGACTCTCTC |
| M13 | TAACGGCTGTTTCTTTCTTC | TATCTACAGTTTCCCGCTGT |
| M14 | TCTTTCCCTTCCTCTCTCTC | AAATATGCCACTCCAGAAAA |
| M15 | GTCGGTGCTGGAGGAACT | CCGCCTTCTTCCTCGTTAT |

图5 第9染色体上南方水稻黑条矮缩病主效抗性位点qSRBSDV9的验证及确认 A—连锁分析;B—利用代换作图精细定位qSRBSDV9。代换图中黑色条状区域代表来源于广恢998的导入片段; 空白条状区域代表来源于D4的导入片段;灰色条状区域代表杂合双亲基因的片段。
Fig. 5. Identification and validation of qSRBSDV9 in rice chromosome 9. A, Linkage analysis; B, Substitution mapping of qSRBSDV9 in an interval defined by InDel markers. Black bar, Homozygous segments from Guanghui 998(GH998); Blank bar, Homozygous segments from D4; Grey bar, Heterozygous segments.
| [1] | Zhou G H, Wen J J, Cai D J, Li P, Xu D L, Zhang S G. Southern rice black-streaked dwarf virus: A new proposed Fijivirus species in the family Reoviridae. Chin Sci Bull, 2008, 53(23): 3677-3685. |
| [2] | 周国辉, 许东林, 李华平. 广东发生水稻黑条矮缩病病原分子鉴定//中国植物病理学会2004年学术年会论文集. 北京: 中国农业科学技术出版社, 2004: 201-212. |
| Zhou G H, Xu D L, Li H P.Identification of Rice black-streaked dwarf virus in Guangdong. Chinese Academy of Plant Pathology 2004 Annual Conference, Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, 2004: 201-212. | |
| [3] | Mar T T, Liu W W, Wang X F.Proteomic analysis of interaction between P7-1 of Southern rice black-streaked dwarf virus and the insect vector reveals diverse insect proteins involved in successful transmission. J Proteom, 2014, 102: 83-97. |
| [4] | Cuong H V, Hai N V, Man V T, Matsumoto M.Rice dwarf disease in north Vietnam in 2009 is caused by southern rice black-streaked dwarf virus(SRBSDV). Bull Inst Trop Agric, Kyushu Univ, 2009, 32: 85-92. |
| [5] | 周国辉, 张曙光, 邹寿发, 许兆伟, 周志强. 水稻新病害南方水稻黑条矮缩病发生特点及危害趋势分析. 植物保护, 2010, 36(1): 144-146. |
| Zhou G H, Zhang S G, Zou S F, Xu Z W, Zhou Z J.Occurrence and damage analysis of a new rice dwarf disease caused by Southern rice black-streaked dwarf virus. Plant Prot, 2010, 36(1): 144-146. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | Hoang A T, Zhang H M, Yang J, Chen J P, Hébrard E, Zhou G H, Vinh V N, Cheng J A.Identification, characterization, and distribution of Southern rice black-streaked dwarf virus in Vietnam. Plant Dis, 2011, 95(9): 1063-1069. |
| [7] | 翟保平, 周国辉, 陶小荣, 陈晓, 沈慧梅. 稻飞虱暴发与南方水稻黑条矮缩病流行的宏观规律和微观机制. 应用昆虫学报, 2011, 48(3): 480-487. |
| Zhai B P, Zhou G H, Tao X R, Chen X, Shen H M.Macroscopic patterns and microscopic mechanisms of the outbreak of rice planthoppers and epidemic SRBSDV.Chin J Appl Entomol, 2011, 48(3): 480-487. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | 陈声祥, 张巧艳. 我国水稻黑条矮缩病和玉米粗缩病研究进展. 植物保护学报, 2005(1): 97-103. |
| Chen S X, Zhang Q Y. Advance in researches on rice black-streaked dwarf disease and maize rough dwarf disease in China.Acta Phytophyl Sin, 2005(1): 97-103. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | Zhang H M, Yang J, Chen J P, Adams M J.A black-streaked-dwarf disease on rice in China is caused by a novel Fjivirus. Arch Virol, 2008, 153: 1893-1898. |
| [10] | Xue J, Li J, Ta H A, Zhang H M, Yang J, Lv M F, Meng Y, Li P P, Chen J P.Complete genomic sequence of Southern rice blacked-dwarf virus, a novel Fijivirus, from Vietnam. Genome Announc, 2013, 1(3): e00212-13. |
| [11] | 阮义理, 陈声祥, 林瑞芬, 蒋文烈, 金登迪. 水稻黑条矮缩病的研究. 浙江农业科学, 1984(4): 185-187. |
| Ruan Y L, Chen S X, Lin R F, Jiang W L, Jin D D. Studies onRice black-streaked dwarf virus. Zhejiang Agric Sci, 1984(4): 185-187. (in Chinese) | |
| [12] | 王宝祥, 江玲, 陈亮明, 卢百关, 王琦, 黎光泉, 樊继伟, 程遐年, 翟虎渠, 徐大勇, 万建民. 水稻黑条矮缩病抗性资源的筛选和抗性QTL的定位. 作物学报, 2010, 36(8): 1258-1264. |
| Wang B X, Jiang L, Chen L M, Lu B G, Wang Q, Li G Q, Fan J W, Cheng X N, Zhai H Q, Xu D Y, Wan J M.Screening of rice resources against Rice black-streaked dwarf virus and mapping of resistant QTL. Acta Agron Sin, 2010, 36(8): 1258-1264. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | 郭荣, 周国辉, 张曙光. 水稻南方黑条矮缩病发生规律及防控对策初探. 中国植保导刊, 2010, 30(8): 17-20. |
| Guo R, Zhou G H, Zhang S G.Mechanisms and integrated control of the outbreak of southern rice black- streaked dwarf disease. Chin Plant Prot, 2010, 30(8): 17-20. (in Chinese) | |
| [14] | 刘琳琳. 24个水稻品种对南方水稻黑条矮缩病的抗性研究. 福州: 福建农林大学, 2012. |
| Liu L L.The resistance research of 24 rice varieties to southern black-streaked dwarf disease of rice. Fuzhou: Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 高瑞珍, 程兆榜, 杨荣明, 朱凤, 季英华, 任春梅, 吴丽莉, 周益军, 范永坚. 江苏省水稻矮缩病的病原鉴定. 华北农学报, 2012(5): 174-178. |
| Gao R Z, Cheng Z B, Yang R M, Zhu F, Ji Y H, Ren C M, Wu L L, Zhou Y J, Fan Y J. Identification of rice dwarf disease in Jiangsu.Acta Agric Bor Sin, 2012(5): 174-178. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 秦碧霞, 蔡健和, 李战彪, 黄所生, 崔丽贤, 黄凤宽, 吴碧球, 高汉亮, 麦接超, 谢慧婷. 广西水稻品种抗水稻南方黑条矮缩病鉴定. 南方农业学报, 2014, 45(1): 38-42. |
| Qin B X, Cai J H, Li Z B, Huang S S, Cui L X, Huang F K, Wu B Q, Gao H L, Mai J C, Xie H T.Resistance identification of rice cultivars to southern rice black-streaked dwarf disease in Guangxi.J South Agric, 2014, 45(1): 38-42. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | Zhang P, Mar T T, Liu W W, Li L, Wang X F.Simultaneous detection and differentiation of Rice black streaked dwarf virus(RBSDV) and Southern rice blacks streaked dwarf virus(SRBSDV) by duplex real time RT-PCR. Viro J, 2013, 10: 24. |
| [18] | Zhou T, Du L L, Lan Y, Sun F, Fan Y J, Zhou Y J.Development of SYBR green I-based one-step real time RT-PCR assay for quantifying Southern rice black-streaked dwarf virus in rice. J Phytopathol, 2014, 162: 26-32. |
| [19] | Li J, Xue J, Zhang H M, Yang J, Lv M F, Xie L, Meng Y, Li P P, Chen J P.Interactions between the P6 and P5-1 proteins of southern rice black-streaked dwarf Fijivirus in yeast and plant cells. Arch Virol, 2013, 158: 1649-1659. |
| [20] | [Li Y Q, Xia Z H, Peng J, Zhou T, Fan Z F.Evidence of recombination and genetic diversity in Southern rice black-streaked dwarf virus. Arch Virol, 2013, 158: 2147-2151. |
| [21] | Li J, Xue J, Zhang H M, Yang J, Xie L, Chen J P.Characterization of homologous and heterologous interactions between viroplasm proteins P6 and P9-1 of the Fijivirus southern rice black-streaked dwarf virus. Arch Virol, 2015, 160: 453-457. |
| [22] | Cheng Z B, Li S, Gao R Z, Sun F, Liu W C, Zhou G H, Wu J X, Zhou X P, Zhou Y J.Distribution and genetic diversity of Southern rice black-streaked dwarf virus in China. Viro J, 2013, 10(1): 307. |
| [23] | 汪涵, 许东林, 周国辉. 南方水稻黑条矮缩病及其防控技术研究进展. 中国植保导刊, 2014, 34(3): 17-20. |
| Wang H, Xu D L, Zhou G H.Research progress on southern rice black-streaked dwarf disease and its controlling techniques.China Plant Prot, 2014, 34(3): 17-20. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | 黄所生, 吴碧球, 秦碧霞, 李战彪, 李成, 孙祖雄, 谢慧婷, 黄凤宽, 蔡健和. 白背飞虱对南方水稻黑条矮缩病传毒效率的影响. 西南农业学报, 2016, 29(12): 2840-2844. |
| Huang S S, Wu B Q, Qin B X, Li Z B, Li C, Sun Z X, Xie H T, Huang F K, Cai J H.Effects of white-backed planthopper, Sogatella furcifera, Horvath on transmission rates of Southern rice black streaked dwarf virus. Southwest Chin J Agric Sci, 2016, 29(12): 2840-2844. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | 陈卓, 李向阳, 俞露, 宋宝安. 南方水稻黑条矮缩病防控药剂的创制与应用. 植物保护学报, 2017, 44(6): 905-918. |
| Chen Z, Li X Y, Yu L, Song B A.The development and application of pesticides against the disease caused by Southern rice black-streaked dwarf virus. J Plant Prot, 2017, 44(6): 905-918. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | 于文娟, 王建, 钟雪莲, 李红松, 姬红丽, 周雪平, 彭云良. 南方水稻黑条矮缩病综合防治技术研究. 西南农业学报, 2017, 30(12): 2705-2710. |
| Yu W J, Wang J, Zhong X L, Li H S, Ji H L, Zhou X P, Peng Y L.Studies on integrated control of southern rice black-streaked dwarf disease on hybrid rice.Southwest Chin J Agric Sci, 2017, 30(12): 2705-2710. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | 潘凤英, 廖咏梅, 海博, 周瑞阳. 19个水稻雄性不育系对南方水稻黑条矮缩病的抗性评价. 南方农业学报, 2011, 42(4): 399-402. |
| Pan F Y, Liao Y M, Hai B, Zhou R Y.Evaluation of nineteen rice male sterile lines for resistance to southern rice black-streaked dwarf disease.J South Agric, 2011, 42(4): 399-402. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | 余守武, 范天云, 杜龙岗, 黄益峰, 陈珊宇, 葛帅, 麻人方, 洪晓富, 阮关海. 抗南方水稻黑条矮缩病水稻光温敏核不育系的筛选和鉴定. 植物遗传资源学报, 2015, 16(1): 163-167. |
| Yu S W, Fan T Y, Du L G, Huang Y F, Chen S Y, Ge S, Ma R F, Hong X F, Ruan G H.Screening and identification of Photo-thermo-sensitive genic male sterile lines against Southern rice black-streaked dwarf virus. J Plant Genet Resour, 2015, 16(1): 163-167. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | Wang Q, Liu Y Q, He J, Zheng X M, Hu J L, Liu Y L, Dai H M, Zhang Y X, Wang B X, Wu W X, Gao H, Zhang Y H, Tao X R, Deng H F, Yuan D Y, Jiang L, Zhang X, Guo X P, Cheng X N, Wu C Y, Wang H Y, Yuan L P, Wan J M.STV11 encodes a sulphotransferase and confers durable resistance to Rice stripe virus. Nat Commun, 2014, 5: 4768. |
| [30] | Murray M G, Thompson W F.Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA.Nucleic Acids Res, 1980, 8(19): 4321-4325. |
| [31] | Yang X H, Xia X Z, Zhang Z Q, Nong B X, Zeng Y, Xiong F Q, Wu Y Y, Gao J, Deng G F, Li D T.QTL mapping by whole genome Re-sequencing and analysis of candidate genes for nitrogen use efficiency in rice.Front Plant Sci, 2017, 8: 1634. |
| [32] | Takagi H, Abe A, Yoshida K, Kosugi S, Natsume S, Mitsuoka C, Uemura A, Utsushi H, Tamiru M, Takuno S, Innan H, Cano L M, Kamoun S, Terauchi R. QTL-seq: rapid mapping of quantitative trait loci in rice by whole genome resequencing of DNA from two bulked populations. Plant J, 2013, 74: 174-183 |
| [33] | van Ooijen J W. Joinmap 4: Software for the calculation of genetic linkage maps in experimental populations. Wageningen, Netherlands: Kyazma B V, 2006. |
| [34] | van Ooijen J W. MapQTL6: Software for the mapping of quantitative trait loci in experimental populations of diplord species. Wageningen, Netherlands: Kyazma B V, 2009. |
| [35] | Zheng T Q, Yang J, Zhong W G, Zhai H Q, Zhu L H, Fan F J, Ali A J, Yang J H, Wang J, Zhu J Y, Uzokwe V N E, Xu J L, Li Z K. Novel loci for field resistance to black-streaked dwarf and stripe viruses identified in a set of reciprocal introgression lines of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol Breeding, 2012, 29: 925-938. |
| [36] | Zhou T, Du L L, Wang L J, Gao C Y, Lan Y, Sun F, Fan Y J, Wang G L, Zhou Y J.Genetic analysis and molecular mapping of QTLs for resistance to rice black-streaked dwarf disease in rice.Sci Rep, 2015, 5: 10509. |
| [37] | Moose S P, Mumm R H.Molecular plant breeding as the foundation for 21st century crop improvement. Plant Physiol, 2008, 147: 969-977. |
| [38] | 潘存红, 李爱宏, 陈宗祥, 吴林波, 戴正元, 张洪熙, 黄年生, 陈夕军, 张亚芳, 左示敏, 潘学彪. 水稻黑条矮缩病抗性QTL分析. 作物学报, 2009, 35(12): 2213-2217. |
| Pan C H, Li A H, Chen Z X, Wu L B, Dai Z Y, Zhang H X, Huang N S, Chen X J, Zhang Y F, Zuo S M, Pan X B.Detection of QTL for resistance to rice black-streaked dwarf viral disease.Acta Agron Sin, 2009, 35(12): 2213-2217. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [39] | Chen J, Huang D R, Wang L, Liu G J, Zhuang J Y.Identification of quantitative trait loci for resistance to whitebacked planthopper, Sogatella furcifera, from an interspecific cross Oryza sativa × O. rufipogon. Breed Sci, 2010, 60: 153-159. |
| [40] | Russell S L, Kimmins W C.Growth regulators and the effect of barley yellow dwarf virus on barley.Ann Bot, 1971, 35: 1037-1043. |
| [41] | Sridhar R, Mohanty S K, Mohanty S K,.Physiology of rice tungro virus disease: Gibberellins in the disease syndrome. Inter J Trop Plant Dis, 1987, 4: 85-92. |
| [42] | Zhu S F, Gao F, Cao X S, Chen M, Ye G Y, Wei C H, Yi L.The rice dwarf virus P2 protein interacts with ent-Kaurene oxidases in vivo, leading to reduced biosynthesis of gibberellins and rice dwarf symptoms. Plant Physiol, 2005, 139: 1935-1945. |
| [43] | 吴建国, 王萍, 谢荔岩, 林奇英, 吴祖建, 谢联辉. 水稻矮缩病毒对3种内源激素含量及代谢相关基因转录水平的影响. 植物病理学报, 2010, 40(2): 151-158. |
| Wu J G, Wang P, Xie L Y, Lin J Y, Wu Z J, Xie L H.Affection of rice dwarf virus on three phytohormones and transcriptional level of related genes in infected rice.Acta Phytopathol Sin, 2010, 40(2): 151-158. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [44] | 杨阳. 南方水稻黑条矮缩病与水稻激素的关系研究. 长沙: 湖南农业大学, 2015. |
| Yang Y.The relationship between Southern rice black-streaked dwarf virus and rice hormone. Changsha: Hunan Agricultural University, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [45] | Tao T, Zhou C J, Wang Q, Chen X R, Sun Q, Zhao T Y, Ye J C, Wang Y, Zhang Z Y, Zhang Y L, Guo Z J, Wang X B, Li D W, Yu J L, Han C G. Rice black streaked dwarf virus P7-2 forms a SCF complex through binding to Oryza sativa SKP1-like proteins, and interacts with GID2 involved in the gibberellin pathway. PloS One, 2017, 12(5): e0177518. |
| [46] | 杨行海, 夏秀忠, 农保选, 张宗琼, 曾宇, 李丹婷. 水稻苗期感染SRBSDV后赤霉素相关基因表达量及赤霉素含量的变化. 植物保护学报, 2017, 44(6): 1033-1039. |
| Yang H H, Xia X Z, Nong B X, Zhang Z Q, Zeng Y, Li D T.Analysis of the expression levels of the genes involved in gibberellin biosynthesis and gibberellin contents in rice during seedling stage after being infected by Southern rice black-streaked dwarf virus. J Plant Prot, 2017, 44(6): 1033-1039. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [2] | 侯本福, 杨传铭, 张喜娟, 杨贤莉, 王立志, 王嘉宇, 李红宇, 姜树坤. 利用龙稻5号/中优早8号RIL群体定位粒形QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(1): 13-24. |
| [3] | 胡佳晓, 刘进, 崔迪, 勒思, 周慧颖, 韩冰, 孟冰欣, 余丽琴, 韩龙植, 马小定, 黎毛毛. 利用东乡野生稻染色体片段置换系鉴定穗部性状主效QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(6): 597-608. |
| [4] | 谢开珍, 张建明, 程灿, 周继华, 牛付安, 孙滨, 张安鹏, 闻伟军, 代雨婷, 胡启琰, 邱越, 曹黎明, 储黄伟. 低直链淀粉含量水稻种质资源的鉴定与QTL定位分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(6): 609-616. |
| [5] | 姚晓云, 陈春莲, 熊运华, 黄永萍, 彭志勤, 刘进, 尹建华. 水稻加工和外观品质性状QTL鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(5): 507-517. |
| [6] | 沈雨民, 陈明亮, 熊焕金, 熊文涛, 吴小燕, 肖叶青. 水稻内外稃异常发育突变体blg1 (beak like grain 1)的表型分析与精细定位[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(3): 225-232. |
| [7] | 廉院训, 韦子芸, 张强, 李清, 任德勇, 胡江, 朱丽, 高振宇, 张光恒, 郭龙彪, 曾大力, 钱前, 沈兰. 水稻斑马叶突变体zl7的鉴定与基因的精细定位[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(2): 113-124. |
| [8] | 韦敏益, 马增凤, 黄大辉, 秦媛媛, 刘驰, 卢颖萍, 罗同平, 李振经, 张月雄, 秦钢. 基于QTL-Seq的水稻抗细菌性条斑病QTL定位[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(2): 133-141. |
| [9] | 黄涛, 王燕宁, 钟奇, 程琴, 杨朦朦, 王鹏, 吴光亮, 黄诗颖, 李才敬, 余剑峰, 贺浩华, 边建民. 利用染色体片段置换系群体定位和分析水稻粒重和粒型QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(2): 159-170. |
| [10] | 董铮, 王雅美, 黎用朝, 熊海波, 薛灿辉, 潘孝武, 刘文强, 魏秀彩, 李小湘. 基于MAGIC群体的水稻镉含量全基因组关联分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(1): 35-42. |
| [11] | 李杰, 田蓉蓉, 白天亮, 朱春艳, 宋佳伟, 田蕾, 马帅国, 吕建东, 胡慧, 王震宇, 罗成科, 张银霞, 李培富. 水稻回交群体剑叶性状综合评价及QTL定位[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(6): 573-585. |
| [12] | 褚晓洁, 芦涛, 叶涵斐, 王盛, 林晗, 吴先美, 何瑞, 严钢, 王跃星, 李三峰, 路梅, 胡海涛, 杨窑龙, 饶玉春. 水稻叶片衰老基因LPS1的克隆与功能研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(5): 427-438. |
| [13] | 陈喜娜, 袁泽科, 胡珍珍, 赵全志, 孙红正. 利用QTL-Seq定位粳稻整精米率QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(5): 449-454. |
| [14] | 王晨, 王备芳, 张迎信, 曹永润, 张越, 江敏, 边康吉, 张小惠, 刘群恩. 水稻类病斑突变体lm8015-2的鉴定与基因的精细定位[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(4): 352-358. |
| [15] | 杜成兴, 张华丽, 戴冬青, 吴明月, 梁敏敏, 陈俊宇, 马良勇. 水稻粒重粒形QTL的定位及qTGW1.2/qGL1.2的验证[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(4): 359-372. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||