
中国水稻科学 ›› 2019, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (1): 47-56.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2019.8078
何爱斌1, 于朋超1, 陈乾1, 姜广磊1, 王慰亲1, 聂立孝1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2018-06-19
修回日期:2018-07-23
出版日期:2019-01-10
发布日期:2019-01-10
通讯作者:
聂立孝
基金资助:
Aibin HE1, Pengchao YU1, Qian CHEN1, Guanglei JIANG1, Weiqin WANG1, Lixiao NIE1,2,*( )
)
Received:2018-06-19
Revised:2018-07-23
Online:2019-01-10
Published:2019-01-10
Contact:
Lixiao NIE
摘要:
【目的】研究不同氮肥运筹处理下,超优1000、甬优4949作再生稻种植时的产量、氮肥偏生产力以及再生力的表现,以期为超优1000和甬优4949引入再生稻系统提供理论依据。【方法】试验为裂区设计,主区为氮肥处理,共设置了6个不同的氮肥处理,分别为N1(120main150ratoon)、N2(120main225ratoon)、N3(185main150ratoon)、N4(185main225ratoon)、N5(250main150ratoon)、N6(250main225ratoon);品种为副区(甬优4949、超优1000,两优6326作为再生稻大面积种植的对照品种)。测定不同品种在不同氮肥运筹下株高、分蘖数、叶面积指数、地上部生物量、产量、产量构成因子和成熟籽粒氮含量。【结果】试验结果表明,在头季,两优6326、超优1000、甬优4949最高产量分别为9.16 t/hm2、9.08 t/hm2和11.15 t/hm2,其对应的施氮量分别为185 kg/hm2、120 kg/hm2和185 kg/hm2。三个品种在高施氮量下(225 kg/hm2)的平均再生季产量分别为5.41 t/hm2、4.98 t/hm2、6.02 t/hm2,在低施氮量下(150 kg/hm2)的平均再生季产量分别为5.78 t/hm2、5.41 t/hm2、6.49 t/hm2。然而,三个品种在低氮处理下的氮肥偏生产力均显著高于高氮处理。综合产量和氮肥偏生产力,甬优4949的最优氮肥运筹应与两优6326保持一致(185main150ratoon),而超优1000在目前的产量水平下的头季施氮量低于两优6326(120 kg/ hm2),而再生季可与两优6326保持一致。【结论】甬优4949可在华中地区作再生稻种植并且氮肥运筹模式可与两优6326保持一致,而超优1000由于生育期太长,再生季不能完全成熟,不适合在华中地区作再生稻种植。
中图分类号:
何爱斌, 于朋超, 陈乾, 姜广磊, 王慰亲, 聂立孝. 甬优4949和超优1000在华中地区再生稻种植的氮肥运筹研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(1): 47-56.
Aibin HE, Pengchao YU, Qian CHEN, Guanglei JIANG, Weiqin WANG, Lixiao NIE. Optimizing the Nitrogen Management for Yongyou 4949 and Chaoyou 1000 in Ratoon Rice System in Central China[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2019, 33(1): 47-56.
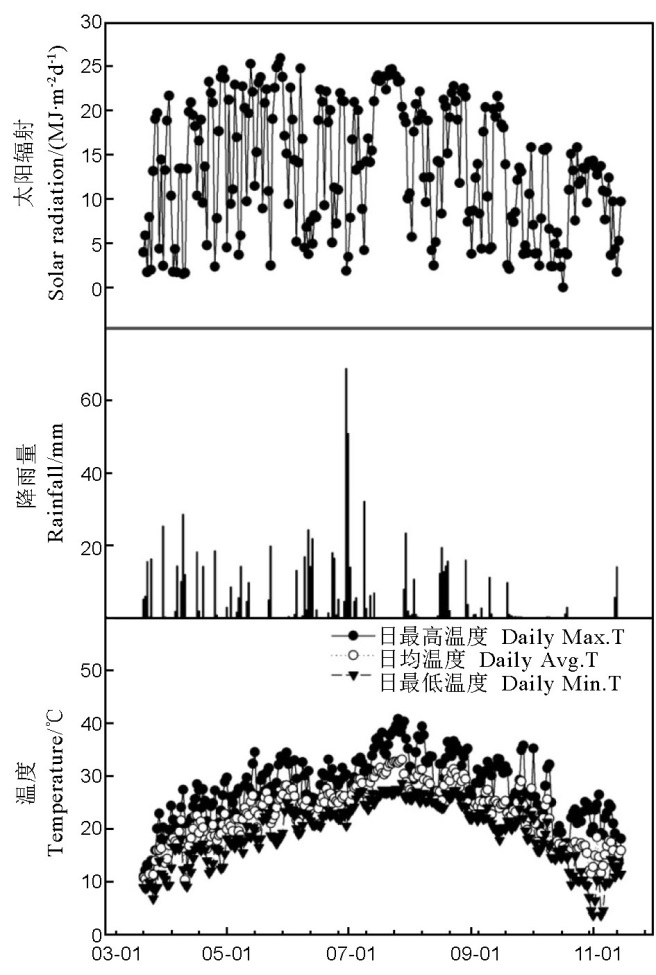
图1 全生育时期光照辐射、降雨量及温度
Fig. 1. Temperature (daily maximum, daily average and daily minimum), solar radiation and rainfall during the rice-growing season.
| 品种 Variety | 头季施氮量 Nitrogen level of main season /(kg·hm-2) | 头季 Main season | 再生季施氮量Nitrogen level of ratoon season /(kg·hm-2) | 再生季 Ratoon season | 周年生育期 Whole crop growth duration/d | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 播种期Sowing date | 齐穗期Heading stage | 成熟期Mature stage | 生育期Growth duration/d | 齐穗期 Heading stage | 成熟期Mature stage | 生育期Growth duration/d | ||||
| 两优6326 LY6326 | 120 | 03-16 | 06-26 | 07-29 | 135 | 150 | 09-11 | 10-25 | 88 | 223 |
| 225 | 09-11 | 10-25 | 88 | 223 | ||||||
| 185 | 03-16 | 06-26 | 08-02 | 139 | 150 | 09-11 | 10-29 | 88 | 227 | |
| 225 | 09-11 | 10-29 | 88 | 227 | ||||||
| 225 | 03-16 | 06-26 | 08-02 | 139 | 150 | 09-11 | 10-29 | 88 | 227 | |
| 225 | 09-11 | 10-29 | 88 | 227 | ||||||
| 超优1000 CY1000 | 120 | 03-16 | 07-10 | 08-15 | 152 | 150 | 09-22 | 11-14 | 91 | 243 |
| 225 | 09-22 | 11-14 | 91 | 243 | ||||||
| 185 | 03-16 | 07-12 | 08-15 | 152 | 150 | 09-22 | 11-14 | 91 | 243 | |
| 225 | 09-22 | 11-14 | 91 | 243 | ||||||
| 225 | 03-16 | 07-12 | 08-15 | 152 | 150 | 09-22 | 11-14 | 91 | 243 | |
| 225 | 09-22 | 11-14 | 91 | 243 | ||||||
| 甬优4949 YY4949 | 120 | 03-16 | 06-30 | 08-05 | 142 | 150 | 09-15 | 11-02 | 89 | 231 |
| 225 | 09-15 | 11-02 | 89 | 231 | ||||||
| 185 | 03-16 | 06-30 | 08-09 | 146 | 150 | 09-15 | 11-06 | 89 | 237 | |
| 225 | 09-15 | 11-06 | 89 | 237 | ||||||
| 225 | 03-16 | 06-30 | 08-09 | 146 | 150 | 09-15 | 11-06 | 89 | 237 | |
| 225 | 09-15 | 11-06 | 89 | 237 | ||||||
表1 不同氮肥运筹对两优6326、超优1000及甬优4949生育期的影响
Table 1 Growth duration of LL6326, CY1000 and YY4949 under various nitrogen treatments.
| 品种 Variety | 头季施氮量 Nitrogen level of main season /(kg·hm-2) | 头季 Main season | 再生季施氮量Nitrogen level of ratoon season /(kg·hm-2) | 再生季 Ratoon season | 周年生育期 Whole crop growth duration/d | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 播种期Sowing date | 齐穗期Heading stage | 成熟期Mature stage | 生育期Growth duration/d | 齐穗期 Heading stage | 成熟期Mature stage | 生育期Growth duration/d | ||||
| 两优6326 LY6326 | 120 | 03-16 | 06-26 | 07-29 | 135 | 150 | 09-11 | 10-25 | 88 | 223 |
| 225 | 09-11 | 10-25 | 88 | 223 | ||||||
| 185 | 03-16 | 06-26 | 08-02 | 139 | 150 | 09-11 | 10-29 | 88 | 227 | |
| 225 | 09-11 | 10-29 | 88 | 227 | ||||||
| 225 | 03-16 | 06-26 | 08-02 | 139 | 150 | 09-11 | 10-29 | 88 | 227 | |
| 225 | 09-11 | 10-29 | 88 | 227 | ||||||
| 超优1000 CY1000 | 120 | 03-16 | 07-10 | 08-15 | 152 | 150 | 09-22 | 11-14 | 91 | 243 |
| 225 | 09-22 | 11-14 | 91 | 243 | ||||||
| 185 | 03-16 | 07-12 | 08-15 | 152 | 150 | 09-22 | 11-14 | 91 | 243 | |
| 225 | 09-22 | 11-14 | 91 | 243 | ||||||
| 225 | 03-16 | 07-12 | 08-15 | 152 | 150 | 09-22 | 11-14 | 91 | 243 | |
| 225 | 09-22 | 11-14 | 91 | 243 | ||||||
| 甬优4949 YY4949 | 120 | 03-16 | 06-30 | 08-05 | 142 | 150 | 09-15 | 11-02 | 89 | 231 |
| 225 | 09-15 | 11-02 | 89 | 231 | ||||||
| 185 | 03-16 | 06-30 | 08-09 | 146 | 150 | 09-15 | 11-06 | 89 | 237 | |
| 225 | 09-15 | 11-06 | 89 | 237 | ||||||
| 225 | 03-16 | 06-30 | 08-09 | 146 | 150 | 09-15 | 11-06 | 89 | 237 | |
| 225 | 09-15 | 11-06 | 89 | 237 | ||||||
| 品种 Variety | 头季施氮量 Main season treatment/(kg·hm-2) | 头季产量 Main season yield/(t·hm-2) | 生物量 Biomass /(t·hm-2) | 收获指数Harvest index /% | 每1m2穗数 Panicle number per squaremeter | 每穗颖花数Grain number per panicle | 千粒重1000-grain weight/g | 结实率 Seed-setting rate/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 两优6326 LY6326 | 120 | 8.71 b | 14.78 b | 54.2 a | 240 b | 169 a | 25.1 a | 68.9 a |
| 185 | 9.47 a | 15.99 ab | 52.3 a | 276 ab | 153 a | 25.2 a | 68.8 a | |
| 250 | 9.30 a | 17.39 a | 52.2 a | 294 a | 160 a | 24.9 a | 66.7 a | |
| 平均Mean | 9.16 B | 16.05 B | 52.9 B | 270 A | 161 B | 25.0 A | 68.1 B | |
| 超优1000 CY1000 | 120 | 9.19 a | 15.21 a | 49.9 a | 204 a | 229 a | 20.7 b | 70.9 a |
| 185 | 9.15 a | 15.35 a | 51.6 a | 210 a | 237 a | 21.1 a | 72.3 a | |
| 250 | 8.90 a | 16.88 a | 50.1 a | 222 a | 264 a | 20.8 b | 65.9 a | |
| 平均Mean | 9.08 B | 15.81 B | 50.5 C | 212 C | 243 A | 20.8 B | 69.7 B | |
| 甬优4949 YY4949 | 120 | 10.57 b | 17.00 b | 56.6 a | 216 b | 246 a | 20.0 a | 87.0 a |
| 185 | 11.45 a | 17.84 ab | 56.3 a | 246 a | 241 a | 19.6 b | 80.4 b | |
| 250 | 11.43 a | 18.91 a | 57.0 a | 258 a | 246 a | 19.4 b | 81.2 b | |
| 平均Mean | 11.15 A | 17.91 A | 56.6 A | 240 B | 244 A | 19.7 C | 83.1 A |
表2 不同氮肥运筹对两优6326、超优1000及甬优4949头季产量及其产量构成的影响
Table 2 Effects of different nitrogen treatments on yield and its components of LY6326, CY1000 and LY4949 in main season.
| 品种 Variety | 头季施氮量 Main season treatment/(kg·hm-2) | 头季产量 Main season yield/(t·hm-2) | 生物量 Biomass /(t·hm-2) | 收获指数Harvest index /% | 每1m2穗数 Panicle number per squaremeter | 每穗颖花数Grain number per panicle | 千粒重1000-grain weight/g | 结实率 Seed-setting rate/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 两优6326 LY6326 | 120 | 8.71 b | 14.78 b | 54.2 a | 240 b | 169 a | 25.1 a | 68.9 a |
| 185 | 9.47 a | 15.99 ab | 52.3 a | 276 ab | 153 a | 25.2 a | 68.8 a | |
| 250 | 9.30 a | 17.39 a | 52.2 a | 294 a | 160 a | 24.9 a | 66.7 a | |
| 平均Mean | 9.16 B | 16.05 B | 52.9 B | 270 A | 161 B | 25.0 A | 68.1 B | |
| 超优1000 CY1000 | 120 | 9.19 a | 15.21 a | 49.9 a | 204 a | 229 a | 20.7 b | 70.9 a |
| 185 | 9.15 a | 15.35 a | 51.6 a | 210 a | 237 a | 21.1 a | 72.3 a | |
| 250 | 8.90 a | 16.88 a | 50.1 a | 222 a | 264 a | 20.8 b | 65.9 a | |
| 平均Mean | 9.08 B | 15.81 B | 50.5 C | 212 C | 243 A | 20.8 B | 69.7 B | |
| 甬优4949 YY4949 | 120 | 10.57 b | 17.00 b | 56.6 a | 216 b | 246 a | 20.0 a | 87.0 a |
| 185 | 11.45 a | 17.84 ab | 56.3 a | 246 a | 241 a | 19.6 b | 80.4 b | |
| 250 | 11.43 a | 18.91 a | 57.0 a | 258 a | 246 a | 19.4 b | 81.2 b | |
| 平均Mean | 11.15 A | 17.91 A | 56.6 A | 240 B | 244 A | 19.7 C | 83.1 A |
| 品种 Variety | 头季施氮量 Main season treatment/(kg·hm-2) | 再生季施氮量 Ratoon season treatment/(kg·hm-2) | 再生季产量Ratoon season yield/(t·hm-2) | 生物量 Biomass /(t·hm-2) | 收获指数Harvest index/% | 每1 m2穗数 Panicle number per square meter | 每穗颖花数Grain number per panicle | 千粒重1000-grain weight/g | 结实率 Seed-setting rate/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 两优6326 LY6326 | 120 | 150 | 5.55 ab | 11.10 b | 50.5 a | 337 b | 71 a | 25.0 a | 81.8 a |
| 225 | 5.99 a | 13.15 ab | 45.9 ab | 370 ab | 82 a | 24.5 ab | 78.3 ab | ||
| 185 | 150 | 5.45 ab | 12.97 ab | 42.1 bc | 368 ab | 82 a | 24.0 ab | 79.3 ab | |
| 225 | 5.54 ab | 14.28 a | 38.9 c | 417 a | 82 a | 23.7 ab | 74.2 b | ||
| 250 | 150 | 5.25 b | 14.02 a | 37.5 c | 380 ab | 81 a | 23.2 b | 73.2 b | |
| 225 | 5.81 ab | 13.45 a | 42.4 bc | 414 a | 83 a | 23.7 ab | 72.0 b | ||
| 平均Mean | 5.60 B | 13.16 A | 45.5 B | 381 A | 80 B | 24.0 A | 76.5 B | ||
| 超优1000 CY1000 | 120 | 150 | 5.17 ab | 12.43 a | 44.5 ab | 355 a | 112 ab | 20.7 a | 59.0 a |
| 225 | 5.29 ab | 13.53 a | 44.5 ab | 377 a | 116 ab | 20.2 a | 60.8 a | ||
| 185 | 150 | 5.06 ab | 12.24 a | 46.3 ab | 335 a | 118 a | 20.7 a | 60.7 a | |
| 225 | 5.57 a | 13.70 a | 46.6 a | 381 a | 117 ab | 20.6 a | 61.4 a | ||
| 250 | 150 | 4.72 b | 13.38 a | 44.6 ab | 393 a | 107 b | 20.4 a | 61.7 a | |
| 225 | 5.38 a | 13.09 a | 43.7 b | 378 a | 113 ab | 20.3 a | 57.8 a | ||
| 平均Mean | 5.20 C | 13.06 A | 45.0 B | 370 A | 114 A | 20.5 B | 60.3 C | ||
| 甬优4949 YY4949 | 120 | 150 | 6.20 ab | 13.23 a | 50.0 ab | 310 a | 118 a | 20.0 a | 84.1 a |
| 225 | 6.36 ab | 13.27 a | 50.8 a | 313 a | 125 a | 19.9 a | 83.2 a | ||
| 185 | 150 | 6.21 ab | 14.43 a | 49.3 ab | 326 a | 119 a | 20.0 a | 84.0 a | |
| 225 | 6.33 ab | 13.73 a | 50.1 ab | 339 a | 118 a | 20.1 a | 84.3 a | ||
| 250 | 150 | 5.65 b | 13.72 a | 48.4 b | 328 a | 105 b | 22.2 a | 83.0 a | |
| 225 | 6.79 a | 14.17 a | 49.1 ab | 335 a | 120 a | 20.1 a | 84.9 a | ||
| 平均Mean | 6.26 A | 13.76 A | 49.6 A | 325 B | 118 A | 20.4 B | 83.9 A | ||
表3 不同氮肥运筹对两优6326、超优1000及甬优4949的再生季产量及其构成的影响
Table 3 Effects of different nitrogen treatments on yield and its components of LY6326, CY1000 and LY4949 in ratoon season.
| 品种 Variety | 头季施氮量 Main season treatment/(kg·hm-2) | 再生季施氮量 Ratoon season treatment/(kg·hm-2) | 再生季产量Ratoon season yield/(t·hm-2) | 生物量 Biomass /(t·hm-2) | 收获指数Harvest index/% | 每1 m2穗数 Panicle number per square meter | 每穗颖花数Grain number per panicle | 千粒重1000-grain weight/g | 结实率 Seed-setting rate/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 两优6326 LY6326 | 120 | 150 | 5.55 ab | 11.10 b | 50.5 a | 337 b | 71 a | 25.0 a | 81.8 a |
| 225 | 5.99 a | 13.15 ab | 45.9 ab | 370 ab | 82 a | 24.5 ab | 78.3 ab | ||
| 185 | 150 | 5.45 ab | 12.97 ab | 42.1 bc | 368 ab | 82 a | 24.0 ab | 79.3 ab | |
| 225 | 5.54 ab | 14.28 a | 38.9 c | 417 a | 82 a | 23.7 ab | 74.2 b | ||
| 250 | 150 | 5.25 b | 14.02 a | 37.5 c | 380 ab | 81 a | 23.2 b | 73.2 b | |
| 225 | 5.81 ab | 13.45 a | 42.4 bc | 414 a | 83 a | 23.7 ab | 72.0 b | ||
| 平均Mean | 5.60 B | 13.16 A | 45.5 B | 381 A | 80 B | 24.0 A | 76.5 B | ||
| 超优1000 CY1000 | 120 | 150 | 5.17 ab | 12.43 a | 44.5 ab | 355 a | 112 ab | 20.7 a | 59.0 a |
| 225 | 5.29 ab | 13.53 a | 44.5 ab | 377 a | 116 ab | 20.2 a | 60.8 a | ||
| 185 | 150 | 5.06 ab | 12.24 a | 46.3 ab | 335 a | 118 a | 20.7 a | 60.7 a | |
| 225 | 5.57 a | 13.70 a | 46.6 a | 381 a | 117 ab | 20.6 a | 61.4 a | ||
| 250 | 150 | 4.72 b | 13.38 a | 44.6 ab | 393 a | 107 b | 20.4 a | 61.7 a | |
| 225 | 5.38 a | 13.09 a | 43.7 b | 378 a | 113 ab | 20.3 a | 57.8 a | ||
| 平均Mean | 5.20 C | 13.06 A | 45.0 B | 370 A | 114 A | 20.5 B | 60.3 C | ||
| 甬优4949 YY4949 | 120 | 150 | 6.20 ab | 13.23 a | 50.0 ab | 310 a | 118 a | 20.0 a | 84.1 a |
| 225 | 6.36 ab | 13.27 a | 50.8 a | 313 a | 125 a | 19.9 a | 83.2 a | ||
| 185 | 150 | 6.21 ab | 14.43 a | 49.3 ab | 326 a | 119 a | 20.0 a | 84.0 a | |
| 225 | 6.33 ab | 13.73 a | 50.1 ab | 339 a | 118 a | 20.1 a | 84.3 a | ||
| 250 | 150 | 5.65 b | 13.72 a | 48.4 b | 328 a | 105 b | 22.2 a | 83.0 a | |
| 225 | 6.79 a | 14.17 a | 49.1 ab | 335 a | 120 a | 20.1 a | 84.9 a | ||
| 平均Mean | 6.26 A | 13.76 A | 49.6 A | 325 B | 118 A | 20.4 B | 83.9 A | ||
| 品种 Variety | 头季施氮量 Main season treatment/(kg·hm-2) | 头季籽粒氮素含量 Grain N content of main season/(kg·hm-2) | 头季氮肥偏生产力 Nitrogen partial factor productivity of main season/(kg·kg-1) | 再生季施氮量 Ratoon season treatment/(kg·hm-2) | 再生季籽粒氮素含量Grain N content of ratoon season/(kg·hm-2) | 再生季氮肥偏生产力Nitrogen partial factor productivity of ratoon season/(kg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 两优6326 LY6326 | 120 | 115.51 b | 72.5 a | 150 | 59.81 b | 37.0 a |
| 225 | 68.91 ab | 26.6 b | ||||
| 185 | 119.68 b | 51.2 b | 150 | 60.41 b | 36.3 a | |
| 225 | 86.04 a | 24.6 b | ||||
| 250 | 129.21 a | 37.2 c | 150 | 69.39 ab | 35.0 a | |
| 225 | 77.57 ab | 25.2 b | ||||
| 平均Mean | 121.47 B | 53.6 B | 70.35 AB | 30.8 B | ||
| 超优1000 CY1000 | 120 | 114.81 a | 76.6 a | 150 | 46.22 c | 34.4 a |
| 225 | 73.99 a | 23.5 b | ||||
| 185 | 119.81 a | 49.4 b | 150 | 57.77 bc | 33.7 a | |
| 225 | 71.47 ab | 24.8 b | ||||
| 250 | 124.04 a | 35.6 c | 150 | 63.99 ab | 31.4 a | |
| 225 | 67.82 ab | 23.9 b | ||||
| 平均Mean | 119.55 B | 53.9 B | 63.55 B | 28.6 C | ||
| 甬优4949 YY4949 | 120 | 150.48 a | 88.1 a | 150 | 74.49 a | 41.3 a |
| 225 | 83.08 a | 28.3 b | ||||
| 185 | 150.67 a | 61.9 b | 150 | 70.30 a | 41.4 a | |
| 225 | 76.66 a | 28.1 b | ||||
| 250 | 165.12 a | 45.7 c | 150 | 51.19 b | 37.7 a | |
| 225 | 82.83 a | 30.2 b | ||||
| 平均Mean | 155.42 A | 65.2 A | 73.09 A | 34.5 A |
表4 不同氮肥处理下两优6326、超优1000及甬优4949的籽粒氮素含量以及氮肥偏生产力
Table 4 Grain nitrogen content and nitrogen partial factor productivity of LY6326, CY1000 and YY4949 under various nitrogen treatments.
| 品种 Variety | 头季施氮量 Main season treatment/(kg·hm-2) | 头季籽粒氮素含量 Grain N content of main season/(kg·hm-2) | 头季氮肥偏生产力 Nitrogen partial factor productivity of main season/(kg·kg-1) | 再生季施氮量 Ratoon season treatment/(kg·hm-2) | 再生季籽粒氮素含量Grain N content of ratoon season/(kg·hm-2) | 再生季氮肥偏生产力Nitrogen partial factor productivity of ratoon season/(kg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 两优6326 LY6326 | 120 | 115.51 b | 72.5 a | 150 | 59.81 b | 37.0 a |
| 225 | 68.91 ab | 26.6 b | ||||
| 185 | 119.68 b | 51.2 b | 150 | 60.41 b | 36.3 a | |
| 225 | 86.04 a | 24.6 b | ||||
| 250 | 129.21 a | 37.2 c | 150 | 69.39 ab | 35.0 a | |
| 225 | 77.57 ab | 25.2 b | ||||
| 平均Mean | 121.47 B | 53.6 B | 70.35 AB | 30.8 B | ||
| 超优1000 CY1000 | 120 | 114.81 a | 76.6 a | 150 | 46.22 c | 34.4 a |
| 225 | 73.99 a | 23.5 b | ||||
| 185 | 119.81 a | 49.4 b | 150 | 57.77 bc | 33.7 a | |
| 225 | 71.47 ab | 24.8 b | ||||
| 250 | 124.04 a | 35.6 c | 150 | 63.99 ab | 31.4 a | |
| 225 | 67.82 ab | 23.9 b | ||||
| 平均Mean | 119.55 B | 53.9 B | 63.55 B | 28.6 C | ||
| 甬优4949 YY4949 | 120 | 150.48 a | 88.1 a | 150 | 74.49 a | 41.3 a |
| 225 | 83.08 a | 28.3 b | ||||
| 185 | 150.67 a | 61.9 b | 150 | 70.30 a | 41.4 a | |
| 225 | 76.66 a | 28.1 b | ||||
| 250 | 165.12 a | 45.7 c | 150 | 51.19 b | 37.7 a | |
| 225 | 82.83 a | 30.2 b | ||||
| 平均Mean | 155.42 A | 65.2 A | 73.09 A | 34.5 A |
| [1] | 章秀福, 王丹英, 方福平, 曾衍坤, 廖西元. 中国粮食安全和水稻生产. 农业现代化研究, 2005, 26(2): 85-88. |
| Zhang X F, Wang D Y, Fang F P, Zeng Y K, Liao X Y, Food safety and rice production in China.Res Agric Moder, 2005, 26(2): 85-88. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | Peng S B, Tang Q Y, Ying Z.Current status and challenges of rice production in China.Plant Prod Sci, 2009, 12(1): 3-8. |
| [3] | Ray D K, Foley J A.Increasing global crop harvest frequency: Recent trends and future directions.Environ Res Lett, 2013, 8: 44041-44050. |
| [4] | 熊洪, 冉茂林, 徐富贤, 洪松. 南方稻区再生稻研究进展及发展. 作物学报, 2000, 26(3): 1-5. |
| Xiong H, Ran M L, Xu F X, Hong S.Achievements and developments of ratooning rice in South of China.Acta Agron Sin, 2000, 26(3): 1-5. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | 朱永川, 熊洪, 徐富贤, 郭晓艺, 张林, 刘茂, 周兴兵. 再生稻栽培技术的研究进展. 中国农学通报, 2013, 29(36): 1-8. |
| Zhu Y H, Xiong H, Xu F X, Guo X Y, Zhang L, Liu M, Zhou X B.Progress on research of ratoon rice cultivation technology.Chin Agric Sci Bull, 2013, 29(36): 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 谢华安. 超级稻作再生稻高产栽培特性的研究. 杂交水稻, 2010(S1): 17-26. |
| Xie H A.Studies on high-yielding cultivation characteristics of super hybrid rice grown as ratoon rice..Hybrid Rice, 2010(S1): 17-26. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | Dong H L, Peng S B, Huang J L, Cui K H, Nie L X.The growth and yield of a wet-seeded rice-ratoon rice system in central China.Field Crops Res, 2017, 208: 55-59. |
| [8] | 孟天瑶,许俊伟, 邵子彬, 葛梦婕, 张洪程, 魏海燕, 戴淇根, 霍中洋, 许轲, 荆培培. 甬优系列籼粳杂交稻氮肥群体最高生产力的优势及形成特征. 作物学报, 2015, 41(11): 1711-1725. |
| Meng T Y, Xu J W, Shao Z B, Ge M J, Zhang H C, Wei H Y, Dai Q G, Huo Z Y, Xu K, Jing P P.Advantages and their formation characteristics of the highest population productivity of nitrogen fertilization in japonica/indica hybrid rice of Yongyou series.Acta Agron Sin, 2015, 41(11): 1711-1725. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 韦还和, 李超, 孟天瑶, 葛梦婕, 张洪程, 魏海燕, 戴其根, 霍中洋, 许轲, 郭保卫, 荆培培. 甬优系列籼粳杂交稻高产栽培与生理特性研究进展. 扬州大学学报: 农业与生命科学版, 2015, 36(4): 79-84. |
| Wei H H, Li C, Meng T Y, Ge M J, Zhang H C, Wei H Y, Dai Q G, Huo Z Y, Xu K, Guo B W, Jing P P.Research advances in physiological characteristics and high-yielding cultivation of Yongyou hybrid rice.J Yangzhou Univ: Agric Life Sci, 2015, 36(4): 79-84. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | 李梦婷. 氮肥运筹对籼粳亚种间杂交中稻甬优4949产量形成及氮肥吸收利用的影响研究. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2015. |
| Li M T.Effects of different nitrogen management on yield formation and nitrogen absorption and utilization of the subspecific hybrid medium rice. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 熊渠, 王文丰, 李爱武, 王记安, 马琼瑶, 刘丹. 籼粳杂交稻新组合甬优4949在湖北孝感种植表现及栽培技术. 杂交水稻, 2016, 31(5): 41-43. |
| Xiong Q, Wang W F, Li A W, Wang J A, Ma Q Y, Liu D.Performance and cultural techniques of new indica-japonica hybrid rice combination Yongyou 4949 planted at Xiaogan,Hubei.Hybrid Rice, 2016, 31(5): 41-43. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 魏中伟, 马国辉. 超高产杂交水稻超优1000的生物学特性及抗倒性研究. 杂交水稻, 2015, 30(1): 58-63. |
| Wei Z W, Ma G H.Study on the biological characteristics and anti-inversion of super high yield hybrid rice CY 1000.Hybrid Rice, 2015, 30(1): 58-63. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | 陈健晓, 孟卫东, 林朝上. 超级稻苗头组合超优1000在海南三亚6.82 hm2连片高产示范表现及栽培技术. 杂交水稻, 2016, 31(3): 40-42. |
| Chen X J, Meng W D, Lin C S.Performance and cultivation techniques of promising super hybrid rice combination Chaoyou 1000 in the 6.82 hm2 large demonstrative production at Sanya, Hainan.Hybrid Rice, 2016, 31(3): 40-42. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | 郑景生, 林文雄, 李义珍, 姜照伟, 卓传营. 再生稻头季不同施氮水平的双季氮素吸收及产量效应研究. 中国生态农业学报, 2004, 12(3): 78-82. |
| Zheng J S, Lin We X, Li Y Z, Jiang Z W, Zhuo C Y.Nitrogen uptake and grain yield effects of double-cropping rice at different nitrogen application rates in the first crop of ratoon rice.Chin J Eco-Agric, 2004, 12(3): 78-82. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 陈鸿飞,杨东,梁义元,张志兴,梁康迳,林文雄.头季稻氮肥运筹对再生稻干物质积累、产量及氮素利用率的影响. 中国生态农业学报, 2010, 18(1):50-56. |
| Chen H F, Yang D, Liang Y Y, Zhang Z X, Liang K J, Lin W X.Effect of nitrogen application strategy in the first cropping rice on dry matter accumulation, grain yield and nitrogen utilization efficiencyof the first cropping rice and its ratoon rice crop.Chin J Eco-Agric, 2010, 18(1): 50-56. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 徐富贤, 熊洪, 朱永川,张林. 促芽肥施用量对杂交中稻再生力的影响与组合间源库结构的关系. 西南农业学报, 2008, 21(3): 688-694. |
| Xu F X, Xiong H, Zhu Y C, Zhang L.The relationship between the effects of fertilizer application on the regenerative capacity of hybrid middle rice and the structure of the source sink of hybrid rice.Southwest China J Agric Sci, 2008, 21(3): 688-694. | |
| [17] | 方军. 水稻新品种超优1000引进试种初报. 安徽农学通报, 2016, 22(03-04): 43-44. |
| Fang J.Evaluting the growth performance of a newly developed variety Chaoyou 1000.Anhui Agric Sci Bull, 2016, 22(03-04): 43-44.(in Chinese) | |
| [18] | 张玉葵,叶尔太. 凯氏定氮(半微量)法测定牛乳中蛋白质含量的方法. 中国乳业, 2005(6): 35-36. |
| Zhang Y K, Ye R T, Kjeldahl nitrogen determination (semi micro) method for determination of protein content in milk.China Dairy, 2005(6): 35-36. (in Chinese) | |
| [19] | 钱太平, 方锡文, 张继新, 邹春华, 陈建军, 徐志进,肖齐圣. 杂交中稻-再生稻品种筛选试验. 湖北农业科学, 2012, 51(19): 4193-4195. |
| Qian T P, Fang X W, Zhang J X,, Zou C H, Chen J J, Xu Z J, Xiao Q S.Selection experiment of Hybrid middle rice-ratoon rice varieties.Hubei Agric Sci, 2012, 51(19), 4193-4195. (in Chinese) | |
| [20] | 刘丹, 黄修荣, 王记安,高长清,罗珍美,程建平. 孝感市再生稻品种的筛选试验. 湖北农业科学, 2016(11): 2739-2742. |
| Liu D, Huang X R, Wang J A, Gao C Q, Luo Z M, Cheng J P.Selection experiment of Ratoon rice varieties in Xiaogan.Hubei Agric Sci, 2016(11): 2739-2742. | |
| [21] | 谢春甫, 王记安, 刘红平, 刘华曙, 高长清, 刘长兵, 乐菊, 汤汉华, 林忠辉, 汪新胜, 王伟刚, 郑明. 不同品种作再生稻筛选试验. 现代农业科技, 2014(2): 64-65. |
| Xie C P, Wang J A, Liu H P, Liu H S, Gao C Q, Liu C B, Le J, Tang H H, Lin Z H, Wang X S, Wang W G, Zheng M.Selection experiment of different varieties for Ratoon rice.Mod Agric Sci Technol, 2014(2): 64-65. (in Chinese) | |
| [22] | 刘芳, 梁华东, 刘涛,张淑贞,何迅,贺立源,徐能海. 湖北省近三十年耕地土壤肥力变化解析. 华中农业大学学报, 2016, 35(6): 79-85. |
| Liu F, Liang H D, Liu T, Zhang S Z, He X, He L Y, Xu H N.Analysis of soil fertility changes of cultivated land in Hubei Province in recent thirty years.J Huazhong Agric Univ, 2016, 35(6): 79-85. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 王书裕. 水稻灌浆与气温. 中国农业气象, 1980, 1(1): 19-25. |
| Wang S Y.Rice grain filling and temperature.Agron Meteorol China, 1980, 1(1): 19-25. (in Chinese) | |
| [24] | 刘代银, 丁明忠. 洪水再生稻的蓄留及管理技术. 四川农业科技, 2007(8): 23. |
| Liu D Y, Ding M Z.Storage and management technology of flood regenerated rice.Sichuan Agric Sci Technol, 2007(8): 23. | |
| [25] | 何红卫. 湖北:再生稻如何绿色“再生”. 农民日报, 2017-11-13. |
| He H W. Hubei: Green “regeneration” of ratoon rice. Farmers’ Daily, 2017-11-13. (in Chinese) | |
| [26] | Perez C M, Juliano B O, Liboon S P, Alcantara M, Cassman K G.Effects of late nitrogen fertilizer application on head rice yield, protein content, and grain quality of rice.Cereal Chem, 1996, 73(5): 556-560. |
| [27] | Leesawatwong M, Jamjod S, Kuo J, Dell B, Rerkasem B.Nitrogen fertilizer increases seed protein and milling quality of rice.Cereal Chem, 2005, 82(5): 588-593. |
| [28] | 慕永红, 于杨, 王安东, 张莉萍, 王智敏. 施肥对稻米品质的影响. 现代化农业, 2009(4): 7-9. |
| Mu Y H, Gan Y, Wang A D, Zhang L P, Wang Z M.Effects of fertilization on the quality of rice.Mod Agric, 2009(4): 7-9. (in Chinese) | |
| [29] | 杨静, 罗秋香, 钱春荣, 刘海英, 金正勋. 氮素对稻米蛋白质组分含量及蒸煮食味品质的影响. 东北农业大学学报, 2006, 37(2): 145-150. |
| Yang J, Luo Q X, Qian C R, Liu H Y, Jin Z X.Effects of nitrogen on protein content and cooking and eating quality of rice.J Northeast Agric Univ, 2006, 37(2): 145-150. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | 王德仁, 卢婉芳, 陈苇. 施氮对稻米蛋白质、氨基酸含量的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2001, 7(3):353-356. |
| Wang D R, Lu W F, Chen W.Effects of nitrogen application on the contents of protein and amino acid in rice.J Plant Nutr Fert, 2001, 7(3): 353-356. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | Hamaker B, Griffin V K.Changing the viscoelastic properties of cooked rice through protein disruption.Cereal Chem, 1990, 67(3): 261-264. |
| [32] | Champagne E T, Lyon B G, Min B K, Vinyard B T, Bett K L, Barton,F, E I, Webb B D, Mcclung A M, Moldenhauer K A, Linscombe S, Mckenzie K S, Kohlwey D E. Effect of post-harvest processing on texture profile analysis of cooked rice.Cereal Chem, 1998, 75(2): 181-186. |
| [33] | 沈鹏, 罗秋香, 金正勋. 稻米蛋白质与蒸煮食味品质关系研究. 东北农业大学学报, 2003, 34(4): 378-381. |
| Shen P, Luo Q X, Jin Z X.Study on the relationship between rice protein and cooking and eating quality.J Northeast Agric Univ, 2003, 34(4): 378-381. |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 吕宙, 易秉怀, 陈平平, 周文新, 唐文帮, 易镇邪. 施氮量与移栽密度对小粒型杂交水稻产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| [4] | 赵艺婷, 谢可冉, 高逖, 崔克辉. 水稻分蘖期干旱锻炼对幼穗分化期高温下穗发育和产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 277-289. |
| [5] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [6] | 彭显龙, 董强, 张辰, 李鹏飞, 李博琳, 刘智蕾, 于彩莲. 不同土壤条件下秸秆还田量对土壤还原性物质及水稻生长的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 198-210. |
| [7] | 朱旺, 张翔, 耿孝宇, 张哲, 陈英龙, 韦还和, 戴其根, 许轲, 朱广龙, 周桂生, 孟天瑶. 盐-旱复合胁迫下水稻根系的形态和生理特征及其与产量形成的关系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(6): 617-627. |
| [8] | 邹宇傲, 吴启侠, 周乾顺, 朱建强, 晏军. 孕穗期杂交中稻对淹涝胁迫的响应[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(6): 642-656. |
| [9] | 袁沛, 周旋, 杨威, 尹凌洁, 靳拓, 彭建伟, 荣湘民, 田昌. 化肥减氮配施对洞庭湖区双季稻产量和田面水氮磷流失风险的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(5): 518-528. |
| [10] | 肖大康, 胡仁, 韩天富, 张卫峰, 侯俊, 任科宇. 氮肥用量和运筹对我国水稻产量及其构成因子影响的整合分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(5): 529-542. |
| [11] | 黄亚茹, 徐鹏, 王乐乐, 贺一哲, 王辉, 柯健, 何海兵, 武立权, 尤翠翠. 外源海藻糖对粳稻品系W1844籽粒灌浆特性及产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(4): 379-391. |
| [12] | 高欠清, 任孝俭, 翟中兵, 郑普兵, 吴源芬, 崔克辉. 头季穗肥和促芽肥对再生稻再生芽生长及产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(4): 405-414. |
| [13] | 王文婷, 马佳颖, 李光彦, 符卫蒙, 李沪波, 林洁, 陈婷婷, 奉保华, 陶龙兴, 符冠富, 秦叶波. 高温下不同施肥量对水稻产量品质形成的影响及其与能量代谢的关系分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(3): 253-264. |
| [14] | 杨晓龙, 王彪, 汪本福, 张枝盛, 张作林, 杨蓝天, 程建平, 李阳. 不同水分管理方式对旱直播水稻产量和稻米品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(3): 285-294. |
| [15] | 魏晓东, 宋雪梅, 赵凌, 赵庆勇, 陈涛, 路凯, 朱镇, 黄胜东, 王才林, 张亚东. 硅锌肥及其施用方式对南粳46产量和稻米品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(3): 295-306. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||