
中国水稻科学 ›› 2018, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (6): 529-537.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2018.8001
张敏娟1,2, 李帅军1,2, 陈琼琼1, 景秀清1, 陈坤明1, 石春海3,*( ), 李文强1,*(
), 李文强1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2018-01-07
修回日期:2018-02-10
出版日期:2018-11-27
发布日期:2018-11-10
通讯作者:
石春海,李文强
Minjuan ZHANG1,2, Shuaijun LI1,2, Qiongqiong CHEN1, Xiuqing JING1, Kunming CHEN1, Chunhai SHI3,*( ), Wenqiang LI1,*(
), Wenqiang LI1,*( )
)
Received:2018-01-07
Revised:2018-02-10
Online:2018-11-27
Published:2018-11-10
Contact:
Chunhai SHI, Wenqiang LI
摘要:
目的 株高是农作物的重要农艺性状之一。导致株高变矮的原因很多,最受关注的是赤霉素(GA)和油菜素内酯(BR)对株高的影响,其调控机制的阐明对于植物科学基础研究及遗传育种研究均具有重要意义。方法 利用γ射线诱变水稻材料9311,获得一个矮化少蘖突变体,命名为dlt3 (dwarf and low-tillering 3),通过形态学调查手段分析dlt3突变体的株高、分蘖数、叶夹角、叶形态和结实率等性状,通过叶枕部位的伸直情况和α-淀粉酶活性检测分析其对外源BR和GA应答的敏感性,通过构建遗传群体和筛选分子标记对其进行基因定位,并利用基于iTRAQ的定量蛋白质组学技术分析dlt3突变体的蛋白质组表达谱。结果 表型分析显示dlt3突变体具有半矮化、少分蘖、叶夹角减小、叶表面皱褶、叶形变短变宽和结实率降低等多个突变表型;突变体对GA正常应答,而对BR处理表现为不应答。遗传分析显示dlt3突变因单个基因隐性突变导致;利用分子标记将dlt3基因定位在第6染色体标记RM2615和R6M14之间。定量蛋白质组学分析在dlt3突变体中鉴定到330个差异表达蛋白,包括222个上调和108个下调表达蛋白。其中,4个差异表达蛋白与BR信号途径直接相关;多个差异表达蛋白与水稻株高或生长发育调控直接相关;此外,多个差异表达蛋白,如丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶、Ca2+结合蛋白和锌指结构域蛋白等在dlt3突变体中大量富集。结论 dlt3是一个BR不敏感的矮化少蘖突变体,DLT3基因突变引起BR信号途径的异常,进而可能导致胞内蛋白磷酸化信号转导和转录激活途径受到广泛影响,从而引起植株生长发育等多方面性状异常。
中图分类号:
张敏娟, 李帅军, 陈琼琼, 景秀清, 陈坤明, 石春海, 李文强. 水稻矮化少蘖突变体dlt3的基因定位和蛋白质组学分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(6): 529-537.
Minjuan ZHANG, Shuaijun LI, Qiongqiong CHEN, Xiuqing JING, Kunming CHEN, Chunhai SHI, Wenqiang LI. Genetic Mapping and Proteomic Analysis of the Dwarf and Low-tillering Mutant dlt3 in Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2018, 32(6): 529-537.
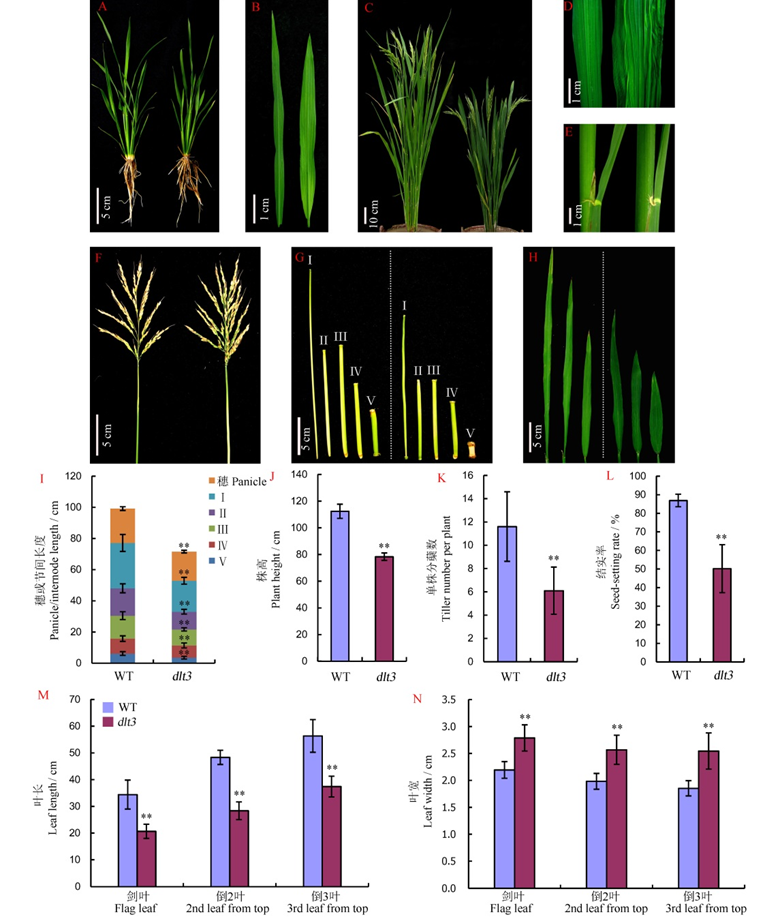
图1 野生型与突变体dlt3的表型特征及农艺性状比较^ A, B分别为分蘖期植株和叶片;C~H分别为成熟期的植株(C)、叶中部(D)、叶枕(E)、穗(F)、茎秆各节间(G)和植株上部三片功能叶的形态(H)。左为野生型,右为突变体dlt3。图中所显示数值为平均数±标准差(n=12)。**表示突变体与野生型间的差异达0.01显著水平。
Fig. 1. Phenotypic characterization of WT and dlt3 mutant.^ A and B, Plant and leaf blade at the tillering stage. C to H, Morphology of mature plant, middle portion of blade, lamina joint, panicle, internodes and top three leaf blades. The left represents wild type and the right the dlt3 mutant. Mean±SD, n=12. **Difference between mutant and WT was significant at 0.01 level.
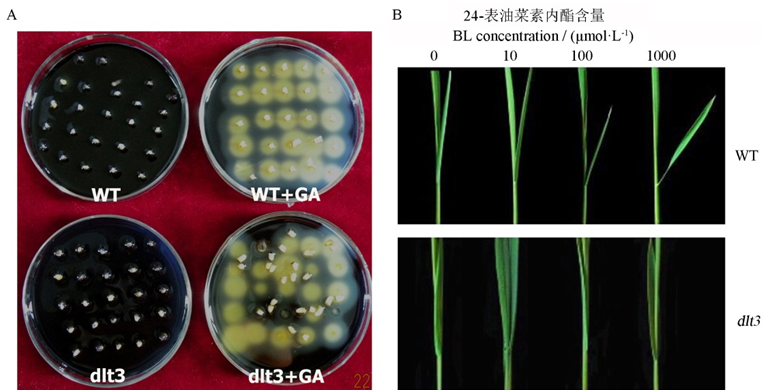
图2 野生型与突变体dlt3对外源GA(A)和BR(B)的应答分析
Fig. 2. Responses of WT and dlt3 to exogenous GA and BR based on the changes of α-amylase activity(A) and lamina inclination(B).
| 标记名称 Marker name | 正向引物序列(5′-3′) Forward primer sequence | 反向引物序列(5′-3′) Reverse primer sequence | 染色体 Chromosome | 物理位置 Physical position/kb |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RM1163 | TGGACGCGGATAGGAGGAGACG | TCCTCCGCAAGGTCGGTTTCC | 6 | 4021 |
| RM3408 | AGTGAATCCCATCAGATCACTCC | CATATCAAATCGCCGAGAAGG | 6 | 4608 |
| RM19556 | TTCTGGCCTATGAGGGATGATCG | ACCAAATATCAAGCCTGCACAGC | 6 | 5249 |
| RM19570 | CCCAGATATTCTGTGTGATCATGAGG | GAGTGAATGTGAGCCGTCTATTGG | 6 | 5422 |
| RM2615 | ATCTCGTTCATACTGCTTGACC | GACTGGTTTCCTTCATGTTACC | 6 | 5970 |
| RM276 | GTCCTCCATCGAGCAGTATCAGC | CTAGCAAGACATGGACCTCAACG | 6 | 6241 |
| RM19638 | CCACACTGTACCGGTCGAAGACG | CTCTACAACTTGCAGCCCTGTCAGC | 6 | 6387 |
| R6M14 | AAATGTCCATGTGTTTGCTTC | CATGTGTGGAATGTGGTTG | 6 | 7710 |
| RM527 | CGGTTTGTACGTAAGTAGCATCAGG | TCCAATGCCAACAGCTATACTCG | 6 | 9874 |
表1 本研究中dlt3基因定位所用分子标记及序列
Table 1 Molecular markers and its sequences used for genetic mapping of dlt3 in this study.
| 标记名称 Marker name | 正向引物序列(5′-3′) Forward primer sequence | 反向引物序列(5′-3′) Reverse primer sequence | 染色体 Chromosome | 物理位置 Physical position/kb |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RM1163 | TGGACGCGGATAGGAGGAGACG | TCCTCCGCAAGGTCGGTTTCC | 6 | 4021 |
| RM3408 | AGTGAATCCCATCAGATCACTCC | CATATCAAATCGCCGAGAAGG | 6 | 4608 |
| RM19556 | TTCTGGCCTATGAGGGATGATCG | ACCAAATATCAAGCCTGCACAGC | 6 | 5249 |
| RM19570 | CCCAGATATTCTGTGTGATCATGAGG | GAGTGAATGTGAGCCGTCTATTGG | 6 | 5422 |
| RM2615 | ATCTCGTTCATACTGCTTGACC | GACTGGTTTCCTTCATGTTACC | 6 | 5970 |
| RM276 | GTCCTCCATCGAGCAGTATCAGC | CTAGCAAGACATGGACCTCAACG | 6 | 6241 |
| RM19638 | CCACACTGTACCGGTCGAAGACG | CTCTACAACTTGCAGCCCTGTCAGC | 6 | 6387 |
| R6M14 | AAATGTCCATGTGTTTGCTTC | CATGTGTGGAATGTGGTTG | 6 | 7710 |
| RM527 | CGGTTTGTACGTAAGTAGCATCAGG | TCCAATGCCAACAGCTATACTCG | 6 | 9874 |
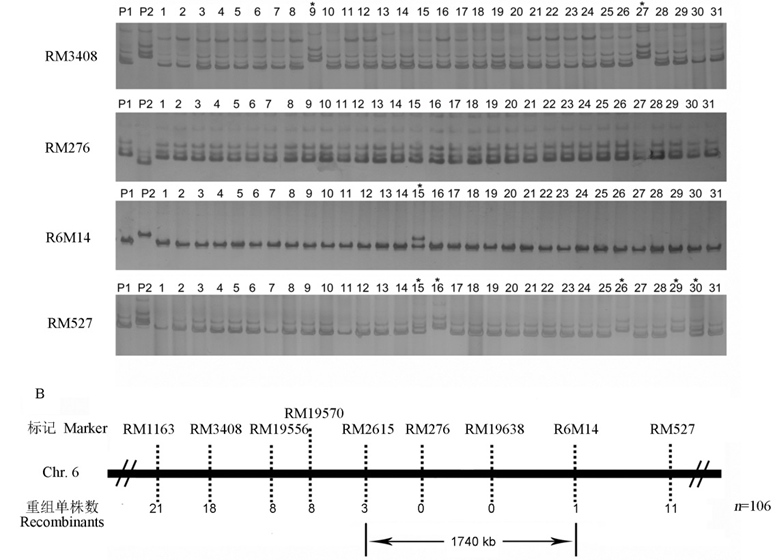
图3 分子标记连锁分析及基因定位^ A为dlt3基因的连锁分子标记RM3408、RM276、R6M14和RM527检测部分F2突变体单株的电泳分析结果;B为dlt3基因的初定位结果,目的基因被定位在第6染色体分子标记RM2615和R6M14区间。*代表重组单株。
Fig. 3. Genetic linkage analysis and molecular mapping of dlt3 gene.^ A, Genotyping of F2 mutant plants by dlt3-linked molecular markers RM3408, RM276, R6M14 and RM527; B, Genetic mapping of dlt3 gene by the molecular markers. *Recombinant.
| 蛋白登录号 Protein accession | 水稻基因号 RAP_locus | 蛋白质功能描述 Protein description | 表达量变化 Ratio (dlt3/WT) | P值 P-value | 上(下)调 Regulation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 油菜素内酯相关蛋白 Brassinosteroid related proteins | |||||
| Q6Z730 | Os02g0122300 | Translation initiation factor eIF3 subunit domain containing protein, Brassinosteroid receptor kinase (BRI1)-interacting protein 121, BIP121 | 0.651 | 1.08×10-2 | Down |
| Q0JBZ3 | Os04g0501600 | AT hook, DNA-binding, conserved site domain containing protein, brassinosteroid receptor kinase (BRI1)-interacting protein 106, BIP106 | 1.372 | 9.26×10-3 | Up |
| Q6K624 | Os02g0612800 | AT hook, DNA-binding, conserved site domain containing protein, brassinosteroid receptor kinase (BRI1)-interacting protein 135, BIP135 | 1.374 | 4.11×10-2 | Up |
| Q0J5J5 | Os08g0430500 | 14-3-3 protein, Florigen receptor, G-box factor 14-3-3c protein, OsGF14c | 3.355 | 3.15×10-3 | Up |
| 生长素相关蛋白 Auxin related proteins | |||||
| Q0DSY8 | Os03g0280000 | Similar to MDR-like ABC transporter, P-Glycoprotein 13, OsABCB13, OsPGP13 | 1.329 | 2.71×10-2 | Up |
| Q0IR61 | Os11g0673200 | Similar to Auxin-induced beta-glucosidase | 1.828 | 1.65×10-2 | Up |
| Q84QW4 | Os08g0524400 | Protein of unknown function DUF568, DOMON-like domain containing protein, auxin-responsive family protein AIR12 | 1.857 | 4.48×10-2 | Up |
| 激酶和磷酸酯酶相关蛋白 Kinase and phosphatase related proteins | |||||
| Q0D6J6 | Os07g0472400 | Serine/threonine protein kinase-related domain containing protein | 0.548 | 1.01×10-2 | Down |
| Q69NF8 | Os09g0529900 | Pyruvate/Phosphoenolpyruvate kinase, catalytic core domain containing protein | 0.716 | 8.12E-03 | Down |
| Q5Z8F2 | Os01g0337600 | Suppressor of Mek, PH domain-like protein | 0.697 | 1.38×10-2 | Down |
| Q0D4F7 | Os07g0628700 | Similar to Receptor protein kinase | 1.328 | 1.51×10-2 | Up |
| Q5QLG3 | Os01g0682500 | Similar to Protein Kinase C630.09c | 1.431 | 1.86×10-3 | Up |
| Q2R2T6 | Os11g0549615 | Ser/Thr protein phosphatase family protein, purple acid phosphatase 3a | 1.889 | 2.72×10-2 | Up |
| Q0IP84 | Os12g0236400 | Adenylate kinase A (EC 2.7.4.3) (ATP-AMP transphosphorylase) | 1.471 | 1.44×10-2 | Up |
| Q60DT7 | Os05g0190500 | Similar to acid phosphatase, HAD superfamily phosphatase, VEGETATIVE STORAGE PROTEIN 2, OsVSP2 | 1.550 | 3.50×10-2 | Up |
| Q6AVA8 | Os05g0405000 | floury endosperm 4, pyruvate orthophospate dikinase, OsPBDK | 1.641 | 7.29×10-4 | Up |
| Q6H444 | Os09g0279400 | Rhodanese-like domain containing protein, Rhodanese / Cell cycle control phosphatase superfamily protein | 2.096 | 8.54×10-3 | Up |
| Q0IPL3 | Os12g0189300 | Pyruvate/Phosphoenolpyruvate kinase, catalytic core domain containing protein | 2.248 | 6.06×10-4 | Up |
| Q6KA61 | Os02g0285800 | Similar to GTP-binding protein typA (Tyrosine phosphorylated protein A) | 3.491 | 3.91×10-4 | Up |
| Q7XQZ5 | Os04g0661300 | ATP/GTP binding protein | 1.356 | 1.09×10-2 | Up |
| Q0JQ62 | Os01g0179700 | Similar to GTP-binding protein YPTM2, ras-related protein, OsRab1 | 1.302 | 2.27×10-2 | Up |
| Q0DH67 | Os05g0489600 | ADP-ribosylation factor, Ras-related small GTP-binding family protein | 1.608 | 3.99×10-3 | Up |
| Q84T71 | Os03g0854100 | Similar to ARF GAP-like zinc finger-containing protein ZIGA2, GTPase-activating protein | 1.322 | 3.38×10-3 | Up |
| 钙结合蛋白 Ca2+ binding related proteins | |||||
| Q6F334 | Os05g0491000 | EF-Hand type domain containing protein, calmodulin-like protein 9, OsCML9 | 0.621 | 1.71×10-3 | Down |
| Q84VG0 | Os08g0117400 | Calmodulin-related calcium sensor protein, Ser/Thr kinase/calmodulin, OsCML7, OsSTKC | 0.732 | 7.55×10-3 | Down |
| Q0DFA8 | Os06g0104400 | IQ calmodulin-binding motif family protein | 1.458 | 1.17×10-4 | Up |
| Q0D7H6 | Os07g0246200 | Similar to calreticulin, CRT | 1.325 | 6.48×10-6 | Up |
| 锌指结构域蛋白 Zinc finger containing proteins | |||||
| Q6K977 | Os02g0831100 | Zinc finger CCCH domain-containing protein 19 | 0.400 | 4.02×10-3 | Down |
| Q2R4J4 | Os11g0472000 | Zinc finger CCCH-type domain containing protein 63 | 0.436 | 2.02×10-3 | Down |
| Q6Z6E6 | Os02g0203700 | Zinc finger family protein, SRZ1 | 0.563 | 5.50×10-3 | Down |
| Q5NAV3 | Os01g0257400 | Zinc finger CCCH-type domain containing protein, OsC3H5 | 0.638 | 1.30×10-2 | Down |
| Q6YUR8 | Os02g0121100 | Zinc finger CCHC-type domain containing protein, cold shock domain protein 1, CSD protein 1 | 0.679 | 8.90×10-3 | Down |
| Q6K4N0 | Os02g0789400 | Similar to 9G8-like SR protein, RNA recognition motif and CCHC-type zinc finger domains containing protein | 1.332 | 4.31×10-2 | Up |
| Q75LJ7 | Os03g0836200 | Similar to RNA-binding protein RZ-1, zinc finger-containing glycine-rich RNA-binding protein 1 | 1.374 | 2.39×10-3 | Up |
| Q6YTY3 | Os07g0608400 | PHD/F-BOX containing protein, PHD zinc finger protein ALFIN-LIKE 9 | 1.313 | 1.73×10-2 | Up |
| 水稻株型调控相关蛋白 Regulation of plant architecture and growth related proteins | |||||
| Q6EU14 | Os02g0672200 | Similar to AGO1 homologous protein, OsAGO1a | 0.471 | 1.96×10-3 | Down |
| Q2QN08 | Os12g0583500 | Broad Complex BTB domain with non-phototropic hypocotyl 3 NPH3 domain, BTB domain containing protein | 0.375 | 9.84×10-3 | Down |
| Q0J0F4 | Os09g0513000 | Similar to TGB12K interacting protein 3, ankyrin repeat domain containing protein, XA21 binding protein 25 | 0.712 | 3.06×10-2 | Down |
| Q10L71 | Os03g0356700 | Villin/gelsolin superfamily protein, Actin binding protein, Regulation of plant architecture, VLN2 | 1.350 | 2.66×10-2 | Up |
| Q0ITK1 | Os11g0247300 | Tubulin/FtsZ domain containing protein, Cell elongation and division, TWISTED DWARF 1, Tubulin alpha-2, small and round seed 5, TID1, TubA2, SRS5 | 2.936 | 3.45×10-3 | Up |
| Q0DH37 | Os05g0494000 | Cytochrome P450 | 1.507 | 4.15×10-3 | Up |
| Q2R176 | Os11g0615200 | SSXT family protein, GRF-interacting factor 2, protein binding/transcription coactivator | 1.428 | 2.04×10-2 | Up |
| Q7XHW8 | Os07g0681000 | Zinc-binding domain of translation initiation factor 2 beta | 1.429 | 4.84×10-4 | Up |
| Q0JAK9 | Os04g0592400 | Protein transport protein-related, t-snare domain containing protein | 1.574 | 9.88×10-4 | Up |
| Q0JP92 | Os01g0235400 | Similar to Importin-alpha re-exporter, Cellular apoptosis susceptibility protein homolog | 2.102 | 1.54×10-2 | Up |
表2 iTRAQ定量蛋白质组学分析鉴定到的部分差异表达蛋白
Table 2 Selected differentially expressed proteins identified by iTRAQ-based quantitative proteomic analysis.
| 蛋白登录号 Protein accession | 水稻基因号 RAP_locus | 蛋白质功能描述 Protein description | 表达量变化 Ratio (dlt3/WT) | P值 P-value | 上(下)调 Regulation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 油菜素内酯相关蛋白 Brassinosteroid related proteins | |||||
| Q6Z730 | Os02g0122300 | Translation initiation factor eIF3 subunit domain containing protein, Brassinosteroid receptor kinase (BRI1)-interacting protein 121, BIP121 | 0.651 | 1.08×10-2 | Down |
| Q0JBZ3 | Os04g0501600 | AT hook, DNA-binding, conserved site domain containing protein, brassinosteroid receptor kinase (BRI1)-interacting protein 106, BIP106 | 1.372 | 9.26×10-3 | Up |
| Q6K624 | Os02g0612800 | AT hook, DNA-binding, conserved site domain containing protein, brassinosteroid receptor kinase (BRI1)-interacting protein 135, BIP135 | 1.374 | 4.11×10-2 | Up |
| Q0J5J5 | Os08g0430500 | 14-3-3 protein, Florigen receptor, G-box factor 14-3-3c protein, OsGF14c | 3.355 | 3.15×10-3 | Up |
| 生长素相关蛋白 Auxin related proteins | |||||
| Q0DSY8 | Os03g0280000 | Similar to MDR-like ABC transporter, P-Glycoprotein 13, OsABCB13, OsPGP13 | 1.329 | 2.71×10-2 | Up |
| Q0IR61 | Os11g0673200 | Similar to Auxin-induced beta-glucosidase | 1.828 | 1.65×10-2 | Up |
| Q84QW4 | Os08g0524400 | Protein of unknown function DUF568, DOMON-like domain containing protein, auxin-responsive family protein AIR12 | 1.857 | 4.48×10-2 | Up |
| 激酶和磷酸酯酶相关蛋白 Kinase and phosphatase related proteins | |||||
| Q0D6J6 | Os07g0472400 | Serine/threonine protein kinase-related domain containing protein | 0.548 | 1.01×10-2 | Down |
| Q69NF8 | Os09g0529900 | Pyruvate/Phosphoenolpyruvate kinase, catalytic core domain containing protein | 0.716 | 8.12E-03 | Down |
| Q5Z8F2 | Os01g0337600 | Suppressor of Mek, PH domain-like protein | 0.697 | 1.38×10-2 | Down |
| Q0D4F7 | Os07g0628700 | Similar to Receptor protein kinase | 1.328 | 1.51×10-2 | Up |
| Q5QLG3 | Os01g0682500 | Similar to Protein Kinase C630.09c | 1.431 | 1.86×10-3 | Up |
| Q2R2T6 | Os11g0549615 | Ser/Thr protein phosphatase family protein, purple acid phosphatase 3a | 1.889 | 2.72×10-2 | Up |
| Q0IP84 | Os12g0236400 | Adenylate kinase A (EC 2.7.4.3) (ATP-AMP transphosphorylase) | 1.471 | 1.44×10-2 | Up |
| Q60DT7 | Os05g0190500 | Similar to acid phosphatase, HAD superfamily phosphatase, VEGETATIVE STORAGE PROTEIN 2, OsVSP2 | 1.550 | 3.50×10-2 | Up |
| Q6AVA8 | Os05g0405000 | floury endosperm 4, pyruvate orthophospate dikinase, OsPBDK | 1.641 | 7.29×10-4 | Up |
| Q6H444 | Os09g0279400 | Rhodanese-like domain containing protein, Rhodanese / Cell cycle control phosphatase superfamily protein | 2.096 | 8.54×10-3 | Up |
| Q0IPL3 | Os12g0189300 | Pyruvate/Phosphoenolpyruvate kinase, catalytic core domain containing protein | 2.248 | 6.06×10-4 | Up |
| Q6KA61 | Os02g0285800 | Similar to GTP-binding protein typA (Tyrosine phosphorylated protein A) | 3.491 | 3.91×10-4 | Up |
| Q7XQZ5 | Os04g0661300 | ATP/GTP binding protein | 1.356 | 1.09×10-2 | Up |
| Q0JQ62 | Os01g0179700 | Similar to GTP-binding protein YPTM2, ras-related protein, OsRab1 | 1.302 | 2.27×10-2 | Up |
| Q0DH67 | Os05g0489600 | ADP-ribosylation factor, Ras-related small GTP-binding family protein | 1.608 | 3.99×10-3 | Up |
| Q84T71 | Os03g0854100 | Similar to ARF GAP-like zinc finger-containing protein ZIGA2, GTPase-activating protein | 1.322 | 3.38×10-3 | Up |
| 钙结合蛋白 Ca2+ binding related proteins | |||||
| Q6F334 | Os05g0491000 | EF-Hand type domain containing protein, calmodulin-like protein 9, OsCML9 | 0.621 | 1.71×10-3 | Down |
| Q84VG0 | Os08g0117400 | Calmodulin-related calcium sensor protein, Ser/Thr kinase/calmodulin, OsCML7, OsSTKC | 0.732 | 7.55×10-3 | Down |
| Q0DFA8 | Os06g0104400 | IQ calmodulin-binding motif family protein | 1.458 | 1.17×10-4 | Up |
| Q0D7H6 | Os07g0246200 | Similar to calreticulin, CRT | 1.325 | 6.48×10-6 | Up |
| 锌指结构域蛋白 Zinc finger containing proteins | |||||
| Q6K977 | Os02g0831100 | Zinc finger CCCH domain-containing protein 19 | 0.400 | 4.02×10-3 | Down |
| Q2R4J4 | Os11g0472000 | Zinc finger CCCH-type domain containing protein 63 | 0.436 | 2.02×10-3 | Down |
| Q6Z6E6 | Os02g0203700 | Zinc finger family protein, SRZ1 | 0.563 | 5.50×10-3 | Down |
| Q5NAV3 | Os01g0257400 | Zinc finger CCCH-type domain containing protein, OsC3H5 | 0.638 | 1.30×10-2 | Down |
| Q6YUR8 | Os02g0121100 | Zinc finger CCHC-type domain containing protein, cold shock domain protein 1, CSD protein 1 | 0.679 | 8.90×10-3 | Down |
| Q6K4N0 | Os02g0789400 | Similar to 9G8-like SR protein, RNA recognition motif and CCHC-type zinc finger domains containing protein | 1.332 | 4.31×10-2 | Up |
| Q75LJ7 | Os03g0836200 | Similar to RNA-binding protein RZ-1, zinc finger-containing glycine-rich RNA-binding protein 1 | 1.374 | 2.39×10-3 | Up |
| Q6YTY3 | Os07g0608400 | PHD/F-BOX containing protein, PHD zinc finger protein ALFIN-LIKE 9 | 1.313 | 1.73×10-2 | Up |
| 水稻株型调控相关蛋白 Regulation of plant architecture and growth related proteins | |||||
| Q6EU14 | Os02g0672200 | Similar to AGO1 homologous protein, OsAGO1a | 0.471 | 1.96×10-3 | Down |
| Q2QN08 | Os12g0583500 | Broad Complex BTB domain with non-phototropic hypocotyl 3 NPH3 domain, BTB domain containing protein | 0.375 | 9.84×10-3 | Down |
| Q0J0F4 | Os09g0513000 | Similar to TGB12K interacting protein 3, ankyrin repeat domain containing protein, XA21 binding protein 25 | 0.712 | 3.06×10-2 | Down |
| Q10L71 | Os03g0356700 | Villin/gelsolin superfamily protein, Actin binding protein, Regulation of plant architecture, VLN2 | 1.350 | 2.66×10-2 | Up |
| Q0ITK1 | Os11g0247300 | Tubulin/FtsZ domain containing protein, Cell elongation and division, TWISTED DWARF 1, Tubulin alpha-2, small and round seed 5, TID1, TubA2, SRS5 | 2.936 | 3.45×10-3 | Up |
| Q0DH37 | Os05g0494000 | Cytochrome P450 | 1.507 | 4.15×10-3 | Up |
| Q2R176 | Os11g0615200 | SSXT family protein, GRF-interacting factor 2, protein binding/transcription coactivator | 1.428 | 2.04×10-2 | Up |
| Q7XHW8 | Os07g0681000 | Zinc-binding domain of translation initiation factor 2 beta | 1.429 | 4.84×10-4 | Up |
| Q0JAK9 | Os04g0592400 | Protein transport protein-related, t-snare domain containing protein | 1.574 | 9.88×10-4 | Up |
| Q0JP92 | Os01g0235400 | Similar to Importin-alpha re-exporter, Cellular apoptosis susceptibility protein homolog | 2.102 | 1.54×10-2 | Up |
| [1] | Sasaki A, Ashikari M, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Itoh H, Nishimura A, Swapan D, Ishiyama K, Saito T, Kobayashi M, Khush G S, Kitano H, Matsuoka M.Green revolution: A mutant gibberellin-synthesis gene in rice.Nature, 2002, 416(6882): 701-702. |
| [2] | Hedden P.The genes of the green revolution.Trends Genet, 2003, 19(1): 5-9. |
| [3] | Smith S M, Li C, Li J.1-Hormone function in plants.Horm Metabol Signal Plants, 2017: 1-38. |
| [4] | Santner A, Calderon-Villalobos L I A,Estelle M. Plant hormones are versatile chemical regulators of plant growth.Nat Chem Biol, 2009, 5(5): 301-307. |
| [5] | Hedden P, Phillips A L.Gibberellin metabolism: New insights revealed by the genes.Trends Plant Sci, 2000, 5(12): 523-530. |
| [6] | Clouse S D, Sasse J M.Brassinosteroids: Essential regulators of plant growth and development.Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol, 1998, 49(49): 427-451. |
| [7] | Lanahan M B, Ho T H (1988) Slender barley: A constitutive gibberellin-response mutant.Planta, 1988, 175(1): 107-114. |
| [8] | Tong H N, Jin Y, Liu W B, Li F, Fang J, Yin Y H, Qian Q, Zhu L H, Chu C C.DWARF AND LOW-TILLERING, a new member of the GRAS family, plays positive roles in brassinosteroid signaling in rice. Plant J, 2009, 58(5): 803-816. |
| [9] | Murray M G, Thompson W F.Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA.Nucl Acids Res, 1980, 8(19): 4321-4325. |
| [10] | Wang Z Q, Xu X Y, Gong Q Q, Xie C, Fan W, Yang J L, Lin Q S, Zheng S J.Root proteome of rice studied by iTRAQ provides integrated insight into aluminum stress tolerance mechanisms in plants.J Proteomics, 2014, 98(4): 189-205. |
| [11] | 李磊, 薛芗, 左示敏, 陈宗祥, 张亚芳, 李前前, 朱俊凯, 马玉银, 潘学彪, 潘存红. 抑制OsAGO1a基因的表达导致水稻叶片近轴面卷曲. 中国水稻科学, 2013, 27(3): 223-230. |
| Li L, Xue X, Zuo S M, Chen Z X, Zhang Y F, Li Q Q, Zhu J K, Ma Y Y, Pan X B, Pan C H.Suppressed expression ofOsAGO1a leads to adaxial leaf rolling in rice. Chin J Rice Sci, 2013, 27(3): 223-230. | |
| [12] | Wu S Y, Xie Y R, Zhang J J, Ren Y L, Zhang X, Wang J L, Guo X P, Wu F Q, Sheng P K, Wang J, Wu C, Wang H, Huang S, Wan [J]. VLN2 regulates plant architecture by affecting microfilament dynamics and polar auxin transport in rice. Plant Cell, 2015, 27(10): 2829-2845. |
| [13] | Sunohara H, Kawai T, Shimizu-Sato S, Sato Y, Sato K, Kitano H.A dominant mutation of TWISTED DWARF 1 encoding an alpha-tubulin protein causes severe dwarfism and right helical growth in rice. Genes Genet Syst, 2009, 84(3): 209-218. |
| [14] | Li W, Wu J, Weng S, Zhang Y, Zhang D, Shi C.Identification and characterization of dwarf 62, a loss-of-function mutation in DLT/OsGRAS-32 affecting gibberellin metabolism in rice. Planta, 2010, 232(6): 1383-1396. |
| [15] | Tong H N, Liu L C, Jin Y, Du L, Yin Y H, Qian Q, Zhu L H, Chu C C.DWARF AND LOW-TILLERING acts as a direct downstream target of a GSK3/SHAGGY-like kinase to mediate brassinosteroid responses in rice. Plant Cell, 2012, 24(6): 2562-2577. |
| [16] | Hirano K, Yoshida H, Aya K, Kawamura M, Hayashi M, Hobo T, Sato-Izawa K, Kitano H, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Matsuoka M.SMALL ORGAN SIZE 1 and SMALL ORGAN SIZE 2/DWARF AND LOW-TILLERING form a complex to integrate auxin and brassinosteroid signaling in rice. Mol Plant, 2017, 10(4): 590-604. |
| [17] | Sun L, Li X, Fu Y, Zhu Z, Tan L, Liu F, Sun X, Sun X, Sun C.GS6, a member of the GRAS gene family, negatively regulates grain size in rice. J Integr Plant Biol, 2013, 55(10): 938-949. |
| [18] | Li D, Wang L, Wang M, Xu Y Y, Luo W, Liu Y J, Xu Z H, Li J, Chong K.EngineeringOsBAK1 gene as a molecular tool to improve rice architecture for high yield. Plant Biotechnol J, 2009, 7(8): 791-806. |
| [19] | Tanaka A, Nakagawa H, Tomita C, Shimatani Z, Ohtake M, Nomura T, Jiang C, Dubouzet J G, Kikuchi S, Sekimoto H, Yokota T, Asami T, Kamakura T, Mori M.BRASSINOSTEROID UPREGULATED1, encoding a helix-loop-helix protein, is a novel gene involved in brassinosteroid signaling and controls bending of the lamina joint in rice. Plant Physiol, 2009, 151(2): 669-680. |
| [20] | Sakamoto T, Morinaka Y, Inukai Y, Kitano H, Fujioka S.Auxin signal transcription factor regulates expression of the brassinosteroid receptor gene in rice. Plant J, 2013, 73(4): 676-688. |
| [21] | Purwestri Y A, Ogaki Y, Tamaki S, Tsuji H, Shimamoto K.The 14-3-3 protein GF14c acts as a negative regulator of flowering in rice by interacting with the florigen Hd3a.Plant Cell Physiol, 2009, 50(3): 429-438. |
| [22] | Bai M Y, Zhang L Y, Gampala S S, Zhu S W, Song W Y, Chong K, Wang Z Y.Functions of OsBZR1 and 14-3-3 proteins in brassinosteroid signaling in rice.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2007, 104(34): 13839-13844. |
| [23] | Boonburapong B, Buaboocha T.Genome-wide identification and analyses of the rice calmodulin and related potential calcium sensor proteins. .BMC Plant Biol, 2007, 7(1): 4. |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [6] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [7] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [8] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [9] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [10] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [11] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [12] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [13] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| [14] | 许用强, 姜宁, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 水稻开花期高温热害响应机理及其调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 111-126. |
| [15] | 吕海涛, 李建忠, 鲁艳辉, 徐红星, 郑许松, 吕仲贤. 稻田福寿螺的发生、危害及其防控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 127-139. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||