
中国水稻科学 ›› 2018, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (4): 357-364.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2018.7098
高虹1,2,3, 姜楠4, 吕国依5, 夏英俊6, 王嘉宇2, 孙健2, 唐亮2, 徐正进2,*( ), 隋国民1,*(
), 隋国民1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2017-08-15
修回日期:2018-01-06
出版日期:2018-07-10
发布日期:2018-07-10
通讯作者:
徐正进,隋国民
基金资助:
Hong GAO1,2,3, Nan JIANG4, Guoyi LÜ5, Yingjun XIA6, Jiayu WANG2, Jian SUN2, Liang TANG2, Zhengjin XU2,*( ), Guomin SUI1,*(
), Guomin SUI1,*( )
)
Received:2017-08-15
Revised:2018-01-06
Online:2018-07-10
Published:2018-07-10
Contact:
Zhengjin XU, Guomin SUI
摘要: 【目的】随着籼粳稻杂交理想株型创造与超高产育种理论的应用,我国东北地区培育出大量高产粳稻品种,逐渐取代曾经占据主导地位的日本典型粳稻。本研究旨在通过分析中国东北粳稻与日本粳稻形态、遗传和产量的差异及原因,研究籼粳杂交对东北粳稻改良的影响。【方法】利用InDel和SSILP亚种特异性分子标记、程氏指数、维管束数目比分析比较中国东北与日本粳稻的籼粳成分和属性及与产量结构的关系。【结果】东北粳稻育成品种产量比日本典型粳稻高15.79%,每穗粒数多15.22%,粳型基因频率极显著低于日本粳稻。按程氏指数分类标准,东北粳稻籼粳类型是偏粳型。相关分析结果表明,籼型基因频率与穗数极显著负相关,与每穗粒数极显著正相关,且与一、二次枝梗数及其粒数正相关。【结论】东北粳稻籼型基因频率增加导致穗数减少,每穗粒数增加,同时将结实率和千粒重维持在较稳定水平是东北粳稻品种获得高产的关键。
中图分类号:
高虹, 姜楠, 吕国依, 夏英俊, 王嘉宇, 孙健, 唐亮, 徐正进, 隋国民. 中国东北粳稻与日本粳稻产量差异及原因分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(4): 357-364.
Hong GAO, Nan JIANG, Guoyi LÜ, Yingjun XIA, Jiayu WANG, Jian SUN, Liang TANG, Zhengjin XU, Guomin SUI. Dissection of Grain Yield Differences Between japonica Rice in Northeast China and in Japan[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2018, 32(4): 357-364.
| 地区 | 参数 | 产量 | 穗数Panicle number | 每穗粒数 | 结实率 | 千粒重 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Region | Parameter | Yield / (t·hm-2) | /(×104·hm-2) | SPP | SSR/% | GW/g |
| 日本Japan | 平均数Mean | 8.36±1.66 | 369.90±105.06 | 117.25±25.06 | 84.41±10.80 | 24.81±2.87 |
| CV/% | 19.83 | 28.40 | 21.38 | 12.80 | 11.58 | |
| 中国东北 | 平均数Mean | 9.68±1.38 | 343.63±74.75 | 135.10±28.50 | 87.35±6.36 | 24.87±1.84 |
| Northeast China | CV/% | 14.27 | 21.75 | 21.10 | 7.28 | 7.39 |
| 差异Difference /% | 15.79 | ―7.10 | 15.22 | 3.48 | 0.24 | |
| F值 F value | 11.37** | 1.29 | 5.49* | 2.20 | 0.01 |
表1 中国东北和日本粳稻育成品种产量及其构成因素的差异
Table 1 Differences in grain yield and its components between japonica cultivars in Northeast China and Japanese japonica cultivars.
| 地区 | 参数 | 产量 | 穗数Panicle number | 每穗粒数 | 结实率 | 千粒重 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Region | Parameter | Yield / (t·hm-2) | /(×104·hm-2) | SPP | SSR/% | GW/g |
| 日本Japan | 平均数Mean | 8.36±1.66 | 369.90±105.06 | 117.25±25.06 | 84.41±10.80 | 24.81±2.87 |
| CV/% | 19.83 | 28.40 | 21.38 | 12.80 | 11.58 | |
| 中国东北 | 平均数Mean | 9.68±1.38 | 343.63±74.75 | 135.10±28.50 | 87.35±6.36 | 24.87±1.84 |
| Northeast China | CV/% | 14.27 | 21.75 | 21.10 | 7.28 | 7.39 |
| 差异Difference /% | 15.79 | ―7.10 | 15.22 | 3.48 | 0.24 | |
| F值 F value | 11.37** | 1.29 | 5.49* | 2.20 | 0.01 |
| 地区 Region | 参数 Parameter | 程氏 指数 ChI | 大维管 束比 RLVB | 大小维管束比 RLSVB |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 日本Japan | Mean | 18.75 | 2.55 | 0.56 |
| 标准差SD | 0.98 | 0.19 | 0.04 | |
| CV/% | 5.25 | 7.29 | 7.61 | |
| 中国东北 Northeast China | Mean | 16.30 | 2.36 | 0.59 |
| 标准差SD | 1.44 | 0.27 | 0.07 | |
| CV/% | 8.86 | 11.56 | 12.39 | |
| 差异Difference /% | ―13.07 | –7.45 | 5.36 | |
| F值 F value | 48.86 | 5.05* | 5.56* | |
表2 中国东北粳稻与日本粳稻籼粳属性的差异
Table 2 Differences of the Cheng’s index, vascular bundle traits between japonica varieties in northeast China and Japanese japonica rice.
| 地区 Region | 参数 Parameter | 程氏 指数 ChI | 大维管 束比 RLVB | 大小维管束比 RLSVB |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 日本Japan | Mean | 18.75 | 2.55 | 0.56 |
| 标准差SD | 0.98 | 0.19 | 0.04 | |
| CV/% | 5.25 | 7.29 | 7.61 | |
| 中国东北 Northeast China | Mean | 16.30 | 2.36 | 0.59 |
| 标准差SD | 1.44 | 0.27 | 0.07 | |
| CV/% | 8.86 | 11.56 | 12.39 | |
| 差异Difference /% | ―13.07 | –7.45 | 5.36 | |
| F值 F value | 48.86 | 5.05* | 5.56* | |
| 性状 Characteristic | 产量 Yield / (t·hm-2) | 穗数 Panicles number /(×104·hm-2) | 穗粒数 SPP | 结实率 SSR/% | 千粒重 1000-grain weight/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 籼型基因频率Fi | –0.086 | –0.392** | 0.437** | 0.058 | –0.202** |
| 程氏指数ChI | –0.043 | 0.450** | –0.455** | –0.143 | 0.120** |
| 大维管束比RLVB | 0.158 | 0.405** | –0.427** | 0.014 | 0.299** |
| 大小维管束比RLSVB | 0.011 | –0.214** | 0.257** | –0.084 | –0.082** |
表3 籼粳成分和属性与产量及其构成因素的相关性
Table 3 Correlations of indica-type allele frequency, the Cheng’s index, vascular bundle characters and grain yield and its components.
| 性状 Characteristic | 产量 Yield / (t·hm-2) | 穗数 Panicles number /(×104·hm-2) | 穗粒数 SPP | 结实率 SSR/% | 千粒重 1000-grain weight/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 籼型基因频率Fi | –0.086 | –0.392** | 0.437** | 0.058 | –0.202** |
| 程氏指数ChI | –0.043 | 0.450** | –0.455** | –0.143 | 0.120** |
| 大维管束比RLVB | 0.158 | 0.405** | –0.427** | 0.014 | 0.299** |
| 大小维管束比RLSVB | 0.011 | –0.214** | 0.257** | –0.084 | –0.082** |
| 地区 Region | 参数 Parameter | 穗长 PL/cm | 一次枝梗The primary rachis branch | 二次枝梗The secondary rachis branch | 着粒密度 SD /(No.∙cm-1) | 二次粒率 SBGR /% | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 枝梗数 PBN | 粒数 GPB | 结实率 SSRPB/% | 枝梗数 SBN | 粒数 GSB | 结实率 SSRSB/% | |||||||
| 日本 | 平均数Mean | 18.9 | 10.4 | 52.3 | 91.2 | 19.6 | 46.5 | 77.0 | 6.2 | 49.14 | ||
| Japan | 标准差SD | 1.6 | 1.1 | 9.4 | 8.0 | 5.0 | 18.6 | 15.0 | 1.2 | 7.44 | ||
| CV/% | 8.5 | 10.9 | 18.0 | 8.8 | 25.4 | 40.1 | 19.5 | 18.5 | 15.15 | |||
| 中国东北 | 平均数Mean | 18.3 | 11.2 | 57.3 | 94.6 | 24.9 | 60.7 | 81.5 | 7.4 | 54.75 | ||
| Northeast China | 标准差SD | 1.9 | 2.0 | 13.2 | 4.6 | 6.4 | 18.4 | 9.4 | 1.7 | 6.72 | ||
| CV/% | 10.2 | 17.4 | 23.0 | 4.8 | 25.5 | 30.3 | 11.5 | 23.0 | 12.28 | |||
| 差异Difference/% | –3.1 | 7.6 | 9.5 | 3.7 | 27.1 | 30.4 | 5.9 | 19.5 | 11.42 | |||
| F值 F value | 1.2 | 2.5 | 2.2 | 5.4* | 9.7** | 8.1** | 2.5 | 7.5** | 8.12** | |||
表4 中国东北和日本水稻育成品种穗部性状的差异
Table 4 Differences of panicle traits between japonica varieties in northeast China and Japanese japonica rice.
| 地区 Region | 参数 Parameter | 穗长 PL/cm | 一次枝梗The primary rachis branch | 二次枝梗The secondary rachis branch | 着粒密度 SD /(No.∙cm-1) | 二次粒率 SBGR /% | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 枝梗数 PBN | 粒数 GPB | 结实率 SSRPB/% | 枝梗数 SBN | 粒数 GSB | 结实率 SSRSB/% | |||||||
| 日本 | 平均数Mean | 18.9 | 10.4 | 52.3 | 91.2 | 19.6 | 46.5 | 77.0 | 6.2 | 49.14 | ||
| Japan | 标准差SD | 1.6 | 1.1 | 9.4 | 8.0 | 5.0 | 18.6 | 15.0 | 1.2 | 7.44 | ||
| CV/% | 8.5 | 10.9 | 18.0 | 8.8 | 25.4 | 40.1 | 19.5 | 18.5 | 15.15 | |||
| 中国东北 | 平均数Mean | 18.3 | 11.2 | 57.3 | 94.6 | 24.9 | 60.7 | 81.5 | 7.4 | 54.75 | ||
| Northeast China | 标准差SD | 1.9 | 2.0 | 13.2 | 4.6 | 6.4 | 18.4 | 9.4 | 1.7 | 6.72 | ||
| CV/% | 10.2 | 17.4 | 23.0 | 4.8 | 25.5 | 30.3 | 11.5 | 23.0 | 12.28 | |||
| 差异Difference/% | –3.1 | 7.6 | 9.5 | 3.7 | 27.1 | 30.4 | 5.9 | 19.5 | 11.42 | |||
| F值 F value | 1.2 | 2.5 | 2.2 | 5.4* | 9.7** | 8.1** | 2.5 | 7.5** | 8.12** | |||
| 性状 Characteristic | 穗长 PL/cm | 一次枝梗The primary rachis branch | 二次枝梗 The secondary rachis branch | 着粒密度 SD/(No.∙cm-1) | 二次粒率 SBGR/% | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 枝梗数 Branch number | 粒数 Grain number | 结实率 SSR/% | 枝梗数 Branch number | 粒数 Grain number | 结实率 SSR/% | ||||||
| 籼型基因频率Fi | 0.034 | 0.259** | 0.263** | 0.110 | 0.470** | 0.493** | 0.078 | 0.386** | 0.336** | ||
| 程氏指数ChI | 0.115 | –0.488** | –0.405** | –0.110 | –0.429** | –0.422** | –0.168 | –0.504** | –0.145** | ||
| 大维管束比RLVB | 0.108 | –0.389** | –0.287** | –0.061 | –0.451** | –0.378** | –0.002 | –0.484** | –0.264** | ||
| 大小维管束比RLSVB | –0.036 | 0.226** | 0.168** | –0.057 | 0.292** | 0.197** | –0.049 | 0.289** | 0.150** | ||
表5 籼粳成分和属性与穗部性状的相关
Table 5 Correlations of indica-type allele frequency, the Cheng’s index, vascular bundle characters and panicle traits.
| 性状 Characteristic | 穗长 PL/cm | 一次枝梗The primary rachis branch | 二次枝梗 The secondary rachis branch | 着粒密度 SD/(No.∙cm-1) | 二次粒率 SBGR/% | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 枝梗数 Branch number | 粒数 Grain number | 结实率 SSR/% | 枝梗数 Branch number | 粒数 Grain number | 结实率 SSR/% | ||||||
| 籼型基因频率Fi | 0.034 | 0.259** | 0.263** | 0.110 | 0.470** | 0.493** | 0.078 | 0.386** | 0.336** | ||
| 程氏指数ChI | 0.115 | –0.488** | –0.405** | –0.110 | –0.429** | –0.422** | –0.168 | –0.504** | –0.145** | ||
| 大维管束比RLVB | 0.108 | –0.389** | –0.287** | –0.061 | –0.451** | –0.378** | –0.002 | –0.484** | –0.264** | ||
| 大小维管束比RLSVB | –0.036 | 0.226** | 0.168** | –0.057 | 0.292** | 0.197** | –0.049 | 0.289** | 0.150** | ||
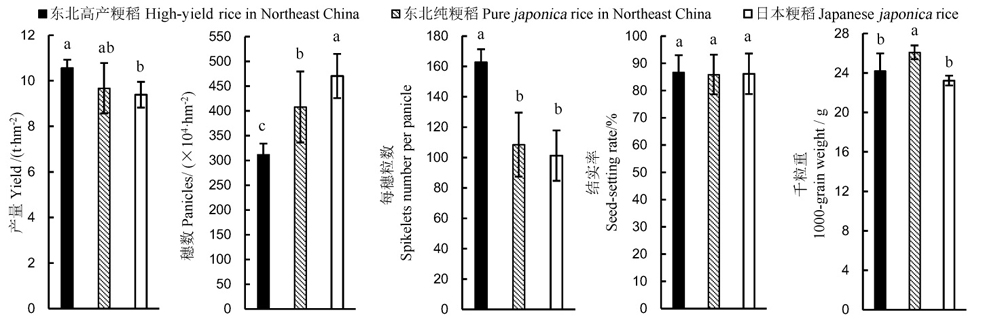
图2 中国东北高产粳稻、纯粳稻(籼型基因频率Fi<2%)与日本粳稻产量及产量相关性状的差异柱上标相同小写字母者表示差异未达0.05显著水平。
Fig. 2. Differences in yield and its components of high yield rice, pure japonica rice(indica-type allele frequency<2%) in northeast China and japonica in Japan. The same lowercase letters indicate no significant difference at the 0.05 level.
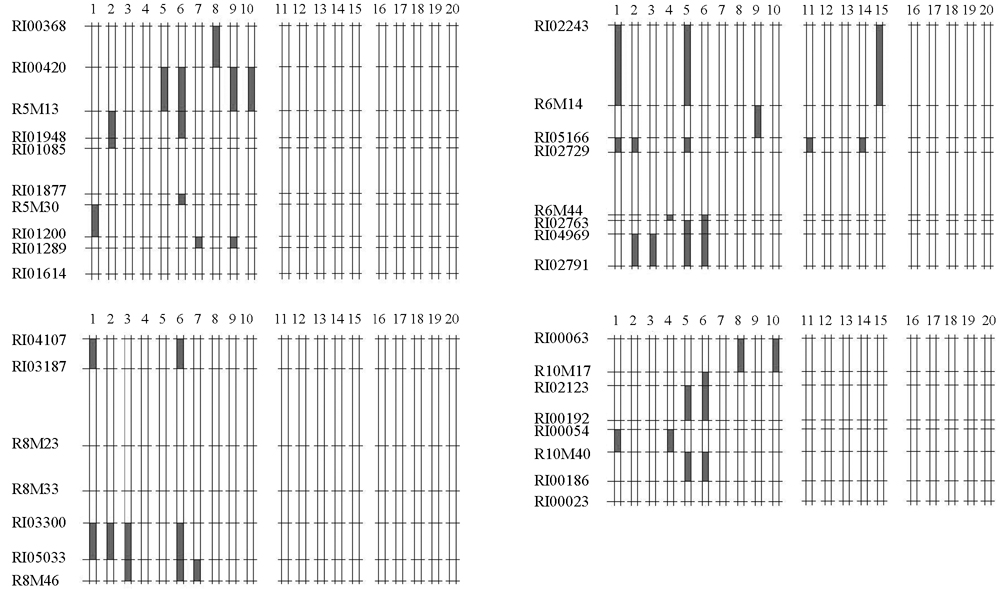
图3 中国东北高产粳稻、纯粳稻与日本粳稻籼型位点的分布1–辽星17;2–沈农9741;3–沈农9903;4–吉粳60;5–吉粳105;6–吉粳88;7–普选10;8–东农415;9–合江21;10–垦稻12;11–吉粳56;12–吉粳94;13–吉粳62;14–东农419;15–垦稻11;16–富士光;17–秋光;18–屉锦;19–里歌;20–一目惚。其中,1~10为中国东北高产粳稻;11~15为中国东北纯粳稻(籼型基因频率Fi<2%);16~20为日本粳稻。
Fig. 3. Distribution of indica-type loci of high yield rice, pure japonica rice in northeast China and japonica in Japan. 1, Liaoxing 17; 2, Shennong 9741; 3, Shennong 9903; 4, Jijing 60; 5, Jijing 105; 6, Jijing 88; 7, Puxuan 10; 8, Dongnong 415; 9, Hejiang 21; 10, Kendao 12; 11, Jijing 56; 12, Jijing 94; 13, Jijing 62; 14, Dongnong 419; 15, Kendao 11; 16, Fujihikari; 17, Akihikari; 18, Sasanishiki; 19, Satonouda; 20, Hitomebore. 1-10, High-yield rice in northeast China; 11-15, Pure japonica rice in northeast China(indica-type allele frequency<2%); 16-20, japonica in Japan.
| [1] | 陈温福, 徐正进, 唐亮. 中国超级稻育种研究进展与前景. 沈阳农业大学学报, 2012, 43(6): 643-649. |
| Chen W F, Xu Z J, Tang L.Advances and prospects in research on super rice breeding. J Shenyang Agric Univ,2014, 43(6): 643-649. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | 张洪程, 张军, 龚金龙, 常勇, 李敏, 高辉, 戴其根, 霍中洋, 许轲, 魏海燕. “籼改粳”的生产优势及其形成机理. 中国农业科学, 2013, 46(4): 686-704. |
| Zhang H C, Zhang J, Gong J L, Chang Y, Li M, Gao H, Dai Q G, Huo Z Y, Xv K, Wei H Y.The productive advantages and formation mechanisms of “indica rice to japonica rice”.Sci Agric Sin, 2013, 46(4): 686-704. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 徐正进,陈温福. 中国北方粳型超级稻研究进展. 中国农业科学, 2016, 49(2): 239-250. |
| Xu Z J, Chen W F.Research progress and related problems on japonica super rice in northern China.Sci Agric Sin, 2016, 49(2): 239-250. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 郭桂珍, 刘才哲, 丛文春, 周广春. 日本稻种资源在吉林省水稻常规育种上的利用. 吉林农业科学, 2002, 27(6): 20-25. |
| Guo G Z, Liu C Z, Cong W C, Zhou G C.The use of Japanese rice resources in Jilin Province conventional breeding.J Jilin Agric Sci, 2002, 27(6): 20-25. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | 齐永文, 张冬玲, 张洪亮, 王美兴, 孙俊立, 廖登群, 魏兴华, 裘宗恩, 汤圣祥, 曹永生, 王象坤, 李自超. 中国水稻选育品种遗传多样性及其近50年变化趋势. 科学通报, 2006, 51(6): 693-699. |
| Qi Y L, Zhang D L, Zhang H L, Wang M X, Sun J L, Liao D Q, Wei X H, Qiu Z E, Tang S X, Cao Y S, Wang X K, Li Z C.The genetic diversity and its changing trend in rice breeding varieties in China nearly 50 years.Chin Sci Bull, 2006, 51(6): 693-699. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 万建民. 中国水稻遗传育种与品种系谱. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2010: 1-23. |
| Wan J M.Rice Genetic Breeding and Variety Pedigree in China. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2010: 1-23. (in Chinese) | |
| [7] | 吴洪恺, 梁国华, 严长杰, 顾燕娟, 单丽丽, 王芳, 顾铭洪. 水稻不同生态型品种间直链淀粉含量的变异及其遗传分析. 作物学报, 2006, 32(9): 1301-1305. |
| Wu H K, Liang G H, Yan C J, Gu Y J, Shan L L, Wang F, Gu M H.Variation among varieties with different ecotypes and its genetic analysis of amylose content in rice ( Oryza sativa L.). Acta Agron Sin, 2006, 32(9): 1301-1305. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | Sun J, Liu D, Wang J Y, Ma D R, Tang L, Gao H, Xu Z J, Chen W F.The contribution of intersubspecific hybridization to the breeding of super-high-yielding japonica rice in northeast China.Theor Appl Genet, 2012, 125(6): 1149-1157. |
| [9] | Xu Q, Chen W F, Xu Z J.Relationship between grain yield and quality in cultivars grown across different rice-growing areas.Breeding Sci, 2015, 65: 226-232. |
| [10] | 李荣华, 夏岩石, 刘顺枝, 孙莉丽, 郭培国, 缪绅裕, 陈健辉. 改进的CTAB提取植物DNA方法. 实验室研究与探索, 2009, 28(9): 14-16. |
| Li R H, Xia Y S, Liu S Z, Sun L L, Guo P G, Miao K Y, Chen J H.CTAB-improved method of DNA extraction in plant. Res Exp Lab, 2009, 28(9): 14-16. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 程侃声. 亚洲栽培稻籼粳亚种的鉴别. 昆明: 云南科学技术出版社, 1993: 1-23. |
| Cheng K S.Identification of indica-japonica Subspecies in Asian Cultivated Rice. Kunming: Yunnan Science and Technology Publishers, 1993: 1-23. (in Chinese) | |
| [12] | 朱春杰, 徐海, 郭艳华, 王嘉宇, 刘宏光, 徐正进. 籼粳交重组自交系亚种属性判别及维管束性状变异. 中国水稻科学, 2007, 21(6): 619-624. |
| Zhu J, Xu H, Guo Y H, Wang J Y, Liu H G, Xu Z J.Discrimination of indica and japonica subspecies and variations of vascular bundle characteristics in recombinant inbred lines derived from an indica/japonica cross. Chin J Rice Sci, 2007, 21(6): 619-624. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | 周开达, 马玉清, 刘太清, 沈茂松. 杂交水稻亚种间重穗型组合的选育: 杂交水稻超高产育种的理论与实践. 四川农业大学学报, 1995, 13(4): 403-407. |
| Zhou K D, Ma Y Q, Liu T Q, Shen M S.The breeding of subspecific heavy ear hybrid rice-exploration about super-high yield breeding of hybrid rice.J Sichuan Agric Univ, 1995, 13(4): 403-407. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | 顾铭洪. 水稻高产育种中一些问题的讨论. 作物学报, 2010, 36(9): 1431-1439. |
| Gu M H.Discussion on the aspects of high-yielding breeding in rice.Acta Agron Sin, 2010, 36(9): 1431-1439. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 徐正进, 张龙步, 陈温福, 王进民, 董克. 从日本超高产品种(系)的选育看粳稻高产的方向. 沈阳农业大学学报, 1991, 22(S): 27-33. |
| Xu Z J, Zhang L B, Chen W F, Wang J M, Dong K.Judging the way forward of breeding Japonica rice for high yield from the advance of breeding super-high yield varieties in Japan.J Shenyang Agric Univ, 1991, 22(S): 27-33. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 王海泽, 刘迪, 唐亮. 东北地区主栽水稻品种的籼型位点频率及其与产量的关系. 沈阳农业大学学报, 2014, 45(6): 661-667. |
| Wang H Z, Liu D, Tang L.Indica genotype frequency of popular cultivars in the northeast of China and its relationship with yield.J Shenyang Agric Univ, 2014, 45(6): 661-667. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | 桂君梅, 王林友, 范小娟, 祁永斌, 张礼霞, 范宏环, 金庆生, 王建军. 基于InDel分子标记的籼粳杂交稻与粳粳杂交稻的杂种优势比较研究. 中国农业科学, 2016, 49(2): 219-231. |
| Gui J M, Wang L Y, Fan X J, Qi Y B, Zhang L X, Fan H H, Jin Q S, Wang J J.Comparison the heterosis of indica-japonica hybrids and japonica-japonica hybrids using InDel markers. Sci Agric Sin, 2016, 49(2): 219-231. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | 徐正进, 陈温福, 张文忠, 周淑清, 刘丽霞, 张龙步, 杨守仁. 北方粳稻新株型超高产育种研究进展. 中国农业科学, 2004, 37(10): 1407-1413. |
| Xu Z J, Chen W F, Zhang W Z, Zhou S Q, Liu L X, Zhang L B, Yang SR.New plant type breeding for super-high yielding northern japonica rice.Sci Agric Sin, 2004, 37(10): 1407-1413. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | Matsuo T M.Great Achievement of Rice Science. Tokyo: Nousangyoson Culture Society, 1990: 419-423. |
| [20] | 刘坚, 陶红剑, 施思, 叶卫军, 钱前, 郭龙彪. 水稻穗型的遗传和育种改良. 中国水稻科学, 2012, 26(2): 227-234. |
| Liu J, Tao H J, Shi S, Ye W J, Qian Q, Guo L B.Genetics and breeding improvement for panicle type in rice.Chin J Rice Sci, 2012, 26(2): 227-234. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | 袁隆平. 两系法杂交水稻研究的进展. 中国农业科学, 1990, 23(3): 1-6. |
| Yuan L P.Progress of two-line system hybrid rice breeding.Sci Agric Sin, 1990, 23(3): 1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | 龚金龙, 邢志鹏, 胡雅杰, 张洪程, 戴其根, 霍中洋, 许轲, 魏海燕, 高辉. 籼、粳超级稻产量构成特征的差异研究. 核农学报, 2014, 28(3): 500-511. |
| Gong J L, Xing Z P, Hu Y J, Zhang H C, Dai Q G, Huo Z Y, Xu K, Wei H Y, Gao H.Studies on the difference of yield components characteristics between indica and japonica super rice. J Nucl Agric Sci, 2014, 28(3): 500-511. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 王远征, 王晓菁, 李源, 徐海, 王嘉宇, 赵明辉, 唐亮, 马殿荣, 徐正进, 陈温福. 北方粳稻产量与品质性状及其相互关系分析. 作物学报, 2015, 41(6): 910-918. |
| Wang Y Z, Wang X J, LI Y, Xu H, Wang J Y, Zhao M H, Tang L, Ma D R, Xu Z J, Chen W F.Analysis of yield and quality traits and their relationship in japonica rice in northern China. Acta Agron Sin, 2015, 41(6): 910-918. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | 程式华, 曹立勇, 陈深广, 朱德峰, 王熹, 闵绍楷, 翟虎渠. 后期功能型超级杂交稻的概念及生物学意义. 中国水稻科学, 2005, 19(3): 280-284. |
| Cheng S H, Cao L Y, Chen S G, Zhu D F, Wang X, Min S K, Zhai H Q.Conception of late-stage vigor super hybrid rice and its biological significance.Chin J Rice Sci, 2005, 19(3): 280-284. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 丁正权, 潘月云, 施扬, 黄海祥. 基于基因芯片的嘉禾系列长粒优质食味粳稻综合评价与比较[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 397-408. |
| [4] | 吕宙, 易秉怀, 陈平平, 周文新, 唐文帮, 易镇邪. 施氮量与移栽密度对小粒型杂交水稻产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| [5] | 赵艺婷, 谢可冉, 高逖, 崔克辉. 水稻分蘖期干旱锻炼对幼穗分化期高温下穗发育和产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 277-289. |
| [6] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [7] | 彭显龙, 董强, 张辰, 李鹏飞, 李博琳, 刘智蕾, 于彩莲. 不同土壤条件下秸秆还田量对土壤还原性物质及水稻生长的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 198-210. |
| [8] | 景秀, 周苗, 王晶, 王岩, 王旺, 王开, 郭保卫, 胡雅杰, 邢志鹏, 许轲, 张洪程. 穗分化末期-灌浆初期干旱胁迫对优质食味粳稻根系形态和叶片光合特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(1): 33-47. |
| [9] | 朱旺, 张翔, 耿孝宇, 张哲, 陈英龙, 韦还和, 戴其根, 许轲, 朱广龙, 周桂生, 孟天瑶. 盐-旱复合胁迫下水稻根系的形态和生理特征及其与产量形成的关系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(6): 617-627. |
| [10] | 邹宇傲, 吴启侠, 周乾顺, 朱建强, 晏军. 孕穗期杂交中稻对淹涝胁迫的响应[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(6): 642-656. |
| [11] | 袁沛, 周旋, 杨威, 尹凌洁, 靳拓, 彭建伟, 荣湘民, 田昌. 化肥减氮配施对洞庭湖区双季稻产量和田面水氮磷流失风险的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(5): 518-528. |
| [12] | 肖大康, 胡仁, 韩天富, 张卫峰, 侯俊, 任科宇. 氮肥用量和运筹对我国水稻产量及其构成因子影响的整合分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(5): 529-542. |
| [13] | 黄亚茹, 徐鹏, 王乐乐, 贺一哲, 王辉, 柯健, 何海兵, 武立权, 尤翠翠. 外源海藻糖对粳稻品系W1844籽粒灌浆特性及产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(4): 379-391. |
| [14] | 高欠清, 任孝俭, 翟中兵, 郑普兵, 吴源芬, 崔克辉. 头季穗肥和促芽肥对再生稻再生芽生长及产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(4): 405-414. |
| [15] | 王文婷, 马佳颖, 李光彦, 符卫蒙, 李沪波, 林洁, 陈婷婷, 奉保华, 陶龙兴, 符冠富, 秦叶波. 高温下不同施肥量对水稻产量品质形成的影响及其与能量代谢的关系分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(3): 253-264. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||