
中国水稻科学 ›› 2018, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (4): 349-356.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2018.7131
齐岳翰1,2, 李瑞莉2,3, 王芳2, 刘洪家2,*( ), 易可可4, 朱诚1,*(
), 易可可4, 朱诚1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2017-11-01
修回日期:2018-02-06
出版日期:2018-07-10
发布日期:2018-07-10
通讯作者:
刘洪家,朱诚
基金资助:
Yuehan QI1,2, Ruili LI2,3, Fang WANG2, Hongjia LIU2,*( ), Keke YI4, Cheng ZHU1,*(
), Keke YI4, Cheng ZHU1,*( )
)
Received:2017-11-01
Revised:2018-02-06
Online:2018-07-10
Published:2018-07-10
Contact:
Hongjia LIU, Cheng ZHU
摘要: 【目的】本研究旨在鉴定和克隆水稻温敏转绿新基因,揭示其参与叶绿体发生发育和光合作用的分子机制,为高光效育种提供理论支撑。【方法】利用辐射诱变的方法,从粳稻品种日本晴中筛选获得叶片黄化突变体osv15,并对其表型、农艺性状和遗传方式进行详细分析。构建了突变体与Kasalath的F2群体,利用多态性分子标记对目的基因进行定位和测序分析。【结果】osv15幼苗期在22℃低温下叶片黄化,叶绿素含量仅为野生型的10%,光化学效率下降,叶绿体结构异常;随着温度的升高,osv15的叶色由黄转绿,30℃时叶绿素含量恢复到野生型的68%,光化学效率和叶绿体发育与野生型相近。在自然环境下,osv15突变体从苗期至成熟期均表现为叶片黄化,且株高、分蘖数和产量等农艺性状与野生型相比差异显著。遗传分析表明osv15突变体的表型由一对隐性核基因控制。将OsV15基因定位到第6染色体多态性标记S4和S5之间84 kb的区间内,定位区间测序发现突变体中编码分子伴侣蛋白的基因Cpn60β1(LOC_Os06g02380)发生单碱基缺失。【结论】osv15是一个新的水稻温敏转绿突变体,Cpn60β1可能为突变基因。
中图分类号:
齐岳翰, 李瑞莉, 王芳, 刘洪家, 易可可, 朱诚. 水稻温敏转绿突变体osv15的鉴定和遗传分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(4): 349-356.
Yuehan QI, Ruili LI, Fang WANG, Hongjia LIU, Keke YI, Cheng ZHU. Identification and Genetic Analysis of Thermo-sensitive Mutant osv15 in Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2018, 32(4): 349-356.
| 标记名称 Marker name | 正向引物(5′-3′) Forward primer(5′-3′) | 反向引物(5′-3′) Reverse primer(5′-3′) | 所在BAC BAC location |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | TAACACGCACTCAAAACGTG | TGCCGACTCTCATTGATCTG | AP001552 |
| S2 | CAACCCCTAACGACCATAGC | CACATGCATGACACGATCAA | AP001552 |
| S3 | CCAACTCTACATGCTCCTTCTG | CCCCAGAGAAGATCTCCTAGC | AP001389 |
| S4 | TCCTCACCTCCTCCTCCTTT | CACAAGCTTCTCTCTTCCCTTC | AP001389 |
| S5 | AGAGGCAATGTCGCAGTATG | GGTGGTTCTGCTCCCATTTA | AP002837 |
| S6 | ACAACTTCGCTTCTCGGTTG | GTACCTGACAGAGGCGATCC | AP002838 |
表1 用于精细定位的多态性STS标记
Table 1 Polymorphic STS markers used in fine mapping.
| 标记名称 Marker name | 正向引物(5′-3′) Forward primer(5′-3′) | 反向引物(5′-3′) Reverse primer(5′-3′) | 所在BAC BAC location |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | TAACACGCACTCAAAACGTG | TGCCGACTCTCATTGATCTG | AP001552 |
| S2 | CAACCCCTAACGACCATAGC | CACATGCATGACACGATCAA | AP001552 |
| S3 | CCAACTCTACATGCTCCTTCTG | CCCCAGAGAAGATCTCCTAGC | AP001389 |
| S4 | TCCTCACCTCCTCCTCCTTT | CACAAGCTTCTCTCTTCCCTTC | AP001389 |
| S5 | AGAGGCAATGTCGCAGTATG | GGTGGTTCTGCTCCCATTTA | AP002837 |
| S6 | ACAACTTCGCTTCTCGGTTG | GTACCTGACAGAGGCGATCC | AP002838 |
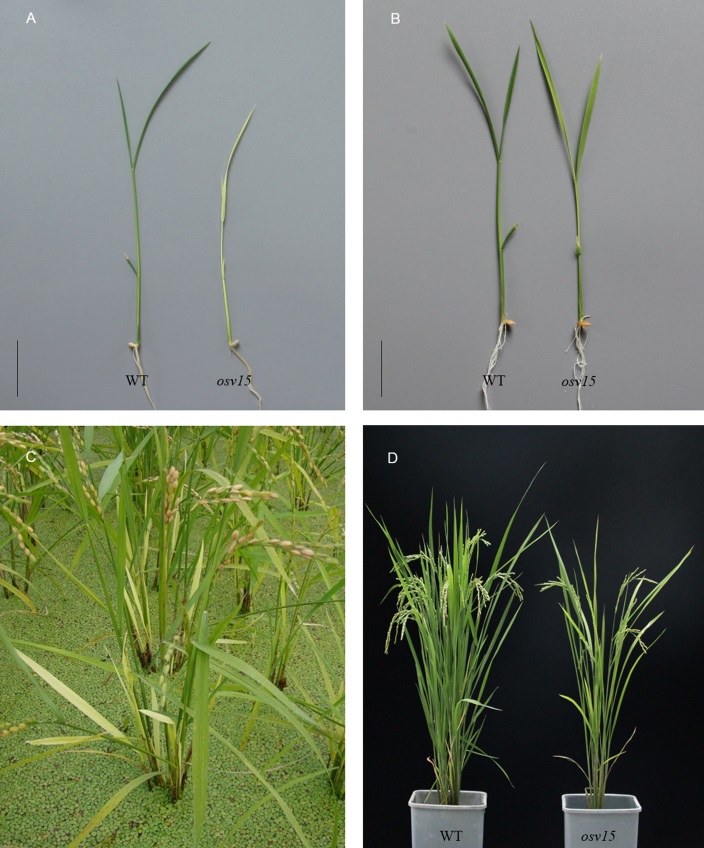

图1 不同时期野生型(WT)和突变体表型 A–22℃培养箱生长14 d;B–30℃培养箱生长9 d;C–成熟期(11月);D–成熟期(7月)。标尺=3 cm。
Fig. 1. Phenotype of the wild type (WT) and mutant at different growth stages. A, 14 d-old seedlings at 22℃; B, 9 d-old seedlings at 30℃; C, At maturity stage in November; D, At maturity stage in July. Bar=3 cm.
| 材料 Material | 株高 Plant height / cm | 分蘖数 Tiller number | 有效穗数 No. of productive panicles | 穗长 Panicle length / cm | 叶长 Leaf length / cm | 叶宽 Leaf width / cm | 结实率 Seed setting rate / % | 千粒重 1000-grain weight / g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | 87.3±2.0 | 15.8±2.2 | 14.3±2.1 | 21.5±0.6 | 31.5±1.3 | 1.3±0.1 | 91.4±2.1 | 25.8±0.6 |
| osv15 | 80.2±1.9** | 8.6±1.4** | 6.8±1.0** | 20.1±1.0 | 29.9±1.5 | 1.2±0.1 | 80.1±4.0** | 22.8±1.8** |
表2 野生型和突变体农艺性状分析
Table 2 Agronomic traits of the wild type and mutant.
| 材料 Material | 株高 Plant height / cm | 分蘖数 Tiller number | 有效穗数 No. of productive panicles | 穗长 Panicle length / cm | 叶长 Leaf length / cm | 叶宽 Leaf width / cm | 结实率 Seed setting rate / % | 千粒重 1000-grain weight / g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | 87.3±2.0 | 15.8±2.2 | 14.3±2.1 | 21.5±0.6 | 31.5±1.3 | 1.3±0.1 | 91.4±2.1 | 25.8±0.6 |
| osv15 | 80.2±1.9** | 8.6±1.4** | 6.8±1.0** | 20.1±1.0 | 29.9±1.5 | 1.2±0.1 | 80.1±4.0** | 22.8±1.8** |
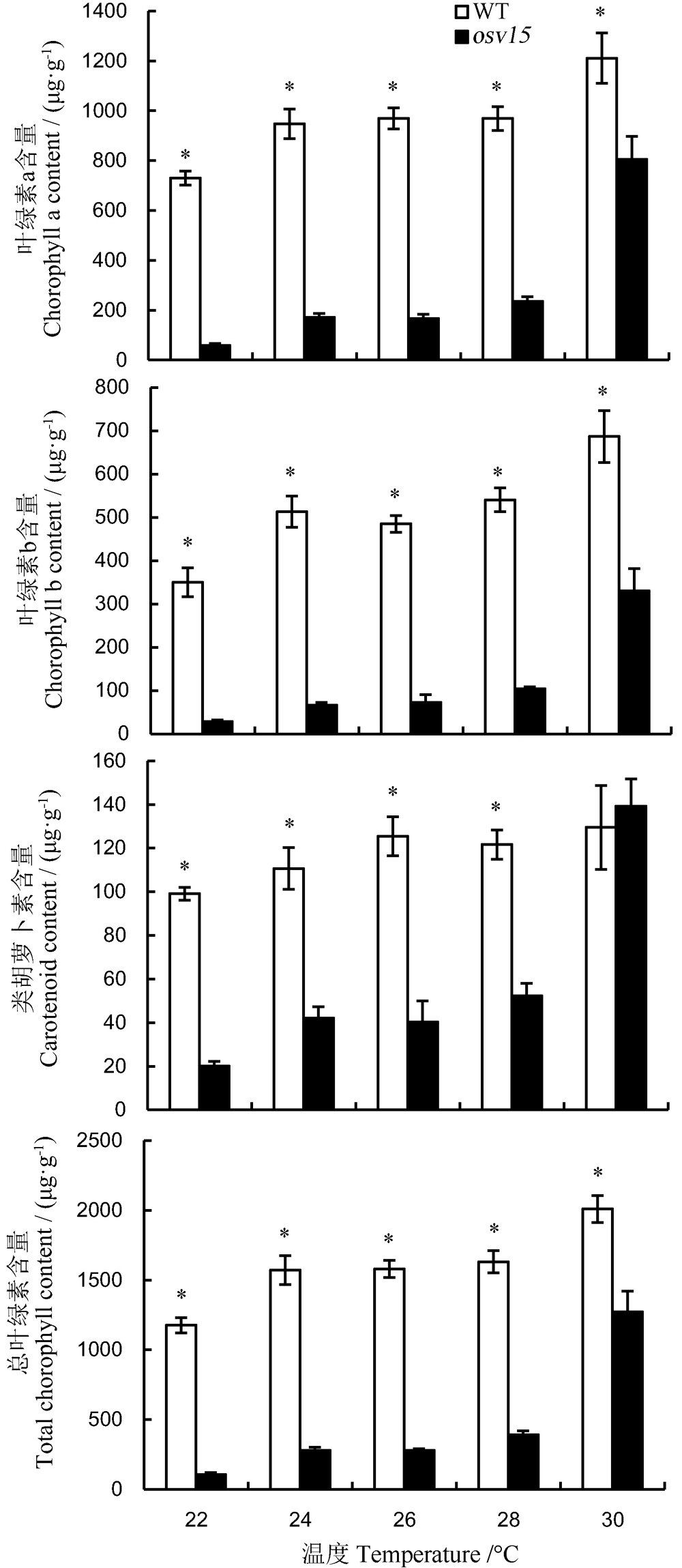
图2 不同温度下野生型和突变体光合色素含量 *表示野生型与突变体在0.05水平上差异显著。
Fig. 2. Photosynthetic pigment contents in leaves of the wild type(WT) and mutant at different temperatures. *Difference between WT and mutant was significant at 0.05 level.
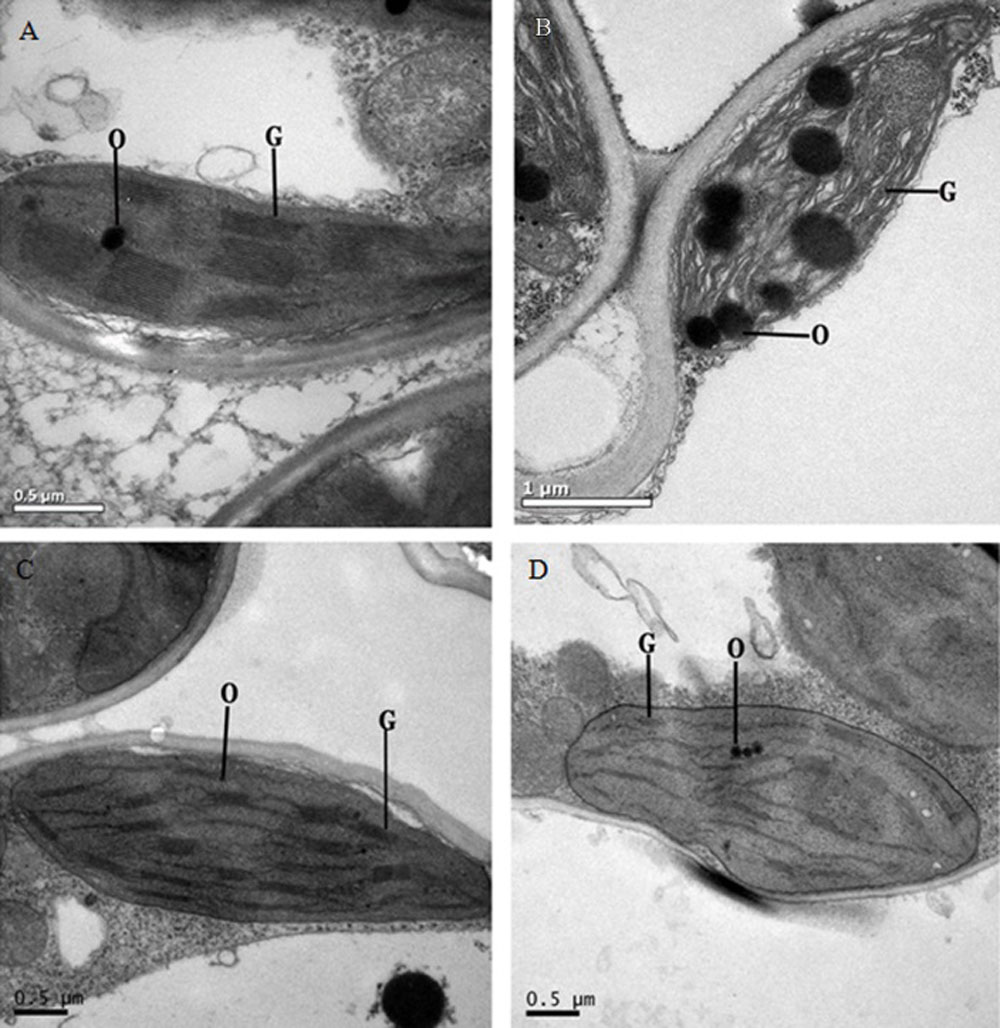
图3 野生型和突变体叶绿体超微结构 A–22℃条件下野生型;B–22℃条件下突变体;C–30℃条件下野生型;D–30℃条件下突变体。G–基粒;O–嗜锇粒。
Fig. 3. Chloroplast ultrastructure of the wild type and mutant. A, The wild type under 22℃; B, Mutant under 22℃; C, The wild type under 30℃; D, Mutant under 30℃. G, Granum; O, Osmiophilic globule.
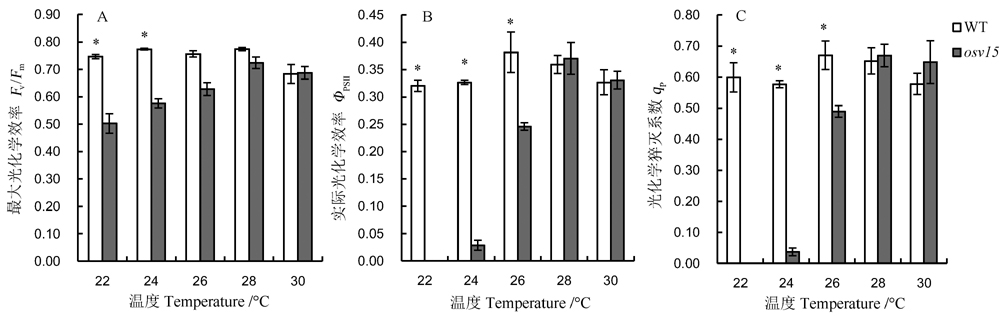
图4 不同温度下野生型和突变体叶绿素荧光动力学参数 A–最大光化学效率(Fv/Fm);B–实际光化学效率(ΦPSII);C–光化学猝灭系数(qP)。
Fig. 4. Chlorophyll fluorescence kinetics parameters of the wild type(WT) and mutant at different temperatures. A, Maximum photochemical efficiency(Fv/Fm); B, Actual photochemical efficiency(ΦPSII); C, Photochemical quenching coefficient(qP).
| 组合 Combination | 绿苗株数 Number of green-leaf plants | 黄苗株数 Number of yellow leaf plants | 总株数 Total number of plants | 分离比 Segregation | χ2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| osv15/Nipponbare osv15/Kasalath | 310 279 | 95 88 | 405 367 | 3∶1 3∶1 | 0.53 0.29 |
表3 突变体后代叶色性状的分离分析
Table 3 Segregation of leaf color of progenies derived from mutant.
| 组合 Combination | 绿苗株数 Number of green-leaf plants | 黄苗株数 Number of yellow leaf plants | 总株数 Total number of plants | 分离比 Segregation | χ2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| osv15/Nipponbare osv15/Kasalath | 310 279 | 95 88 | 405 367 | 3∶1 3∶1 | 0.53 0.29 |
| [1] | Mullet J E.Dynamic regulation of chloroplast transcription.Plant Physiol, 1993, 103(2): 309-313. |
| [2] | Abdallah F, Salamini F, Leister D.A prediction of the size and evolutionary origin of the proteome of chloroplasts of Arabidopsis. Trends Plant Sci, 2000, 5(4): 141-142. |
| [3] | 何冰, 刘玲珑, 张文伟, 万建民. 植物叶色突变体. 植物生理学报, 2006, 42(1): 1-9. |
| He B, Liu L L, Zhang W W, Wan J M.Plant leaf color mutants.Plant Physiol J, 2006, 42(1): 1-9. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 刘艳霞, 林冬枝, 董彦君. 水稻温敏感叶色突变体研究进展. 中国水稻科学, 2015, 29(4): 439-446. |
| Liu Y X, Lin D Z, Dong Y J.Research advances in thermo-sensitive leaf coloration mutants in rice.Chin J Rice Sci, 2015, 29(4): 439-446. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | 初志战, 刘小林, 陈远玲, 刘耀光. 一个水稻白化致死突变基因的精细定位和遗传研究. 中国水稻科学, 2016, 30(2): 136-142. |
| Chu Z Z, Liu X L, Chen Y L, Liu Y G.Genetic analysis and gene mapping of an albino lethal mutant in rice. Chin J Rice Sci, 2016, 30(2): 136-142. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 李自壮, 徐乾坤, 余海平, 周亭亭, 薛大伟, 曾大力, 郭龙彪, 钱前, 任德勇. 水稻淡黄叶矮化突变体yld的遗传分析及基因定位. 作物学报, 2017, 43(4): 522-529. |
| Li Z Z, Xu Q K, Yu H P, Zhou T T, Xue D W, Zeng D L, Guo L B, Qian Q, Ren D Y.Genetic analysis and gene mapping of Yellow leaf and dwarf ( yld ) mutant in rice. Act Agron Sin, 2017, 43(4): 522-529. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 刘胜, 魏祥进, 邵高能, 唐绍清, 胡培松. 一个水稻“斑马叶”叶色突变体基因zebra leaf2(zl2)的图位克隆. 中国水稻科学, 2013, 27(3): 231-239. |
| Liu S, Wei J X, Shao G N, Tang S Q, Hu P S.Map-based cloning of a zebra leaf mutant gene zl2 in rice.Chin J Rice Sci, 2013, 27(3): 231-239. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | 王亚琴, 施军琼, 张婷, 李燕, 张天泉, 张小龙, 桑贤春, 凌英华, 何光华. 水稻黄绿叶突变体ygl13的鉴定及候选基因分析. 中国农业科学, 2015, 48(21): 4197-4208. |
| Wang Y Q, Shi J Q, Zhang T, Li Y, Zhang T Q, Zhang X L, Sang X C, Ling Y H, He G H .Characterization and candidate gene analysis of Yellow-Green Leaf mutant ygl13 in rice(Oryza sativa). Sci Agric Sin, 2015, 48(21): 4197-4208. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 涂政军, 邹国兴, 黄李超, 陈龙, 代丽萍, 高易宏, 冷语佳, 朱丽, 张光恒, 胡江, 任德勇, 高振宇, 董国军, 陈光, 郭龙彪, 钱前, 曾大力. 水稻淡绿叶基因PGL11的鉴定与精细定位. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(5): 489-499. |
| Tu Z J, Zou G X, Huang L C, Chen L, Dai L P, Gao Y H, Leng Y J, Zhu L, Zhang G H, Hu J, Ren D Y, Gao Z Y, Dong G J, Chen G, Guo L B, Qian Q, Zeng D L.Identification and fine mapping of pale green leaf PGL11 in rice. Chin J Rice Sci, 2017, 31(5): 489-499. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | 邹金财, 张维林, 夏明辉, 邱洋松, 王长春, 杨玲, 张小明. 水稻阶段性温敏白化转绿突变体stgra254的特征和基因定位. 华北农学报, 2017, 32(3): 1-6. |
| Zhou J C, Zhang W L, Xia M H, Qiu Y S, Wang C C, Yang L, Zhang X M.Characterization and gene mapping of stage thermo-sensitive green-revertible albino mutant stgra254 in rice. Acta Agric Boreali-Sin, 2017, 32(3): 1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 朱环环, 刘艳霞, 潘倩文, 郑凯伦, 林冬枝, 董彦君. 一个水稻白化致死突变体abl25鉴定及其基因定位. 上海师范大学学报: 自然科学版, 2014, 43(3): 238-244. |
| Zhu H H, Liu Y X, Pan Q W, Zheng K W, Lin D Z, Dong Y J.Identification and gene mapping of a novel rice albino lethal abl25 mutant. J Shanghai Normal Univ: Nat Sci, 2014, 43(3): 238-244. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 高小丽, 李素娟, 邵健丰, 刘洪家, 陶跃之. 水稻POR基因的分离、定位与功能的初步研究. 植物生理学报, 2015, 51(6): 860-868. |
| Gao X L, LI S J, Shao J F, Liu H J, Tao Y Z.Preliminary study on isolation, mapping, and function of NADPH: Proto-chlorophyllide oxidoreductase( POR) gene in rice(Oryza sativa). Plant Physiol J, 2015, 51(6): 860-868. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | Li Q, Zhu F Y, Gao X, Sun Y, Li S, Tao Y, Lo C, Liu H.Young Leaf Chlorosis 2 encodes the stroma-localized heme oxygenase 2 which is required for normal tetrapyrrole biosynthesis in rice. Planta, 2014, 240(4): 701-712. |
| [14] | Zhou K, Ren Y, Lv J, Wang Y, Liu F, Zhou F, Zhao S, Chen S, Peng C, Zhang X.Young Leaf Chlorosis 1 , a chloroplast-localized gene required for chlorophyll and lutein accumulation during early leaf development in rice. Planta, 2013, 237(1): 279. |
| [15] | Chen H, Cheng Z, Ma X, Wu H, Liu Y, Zhou K, Chen Y, Ma W, Bi J, Zhang X.A knockdown mutation of YELLOW-GREEN LEAF2 blocks chlorophyll biosynthesis in rice. Plant Cell Rep, 2013, 32(12): 1855. |
| [16] | Archer E K, Bonnett H T.Characterization of a virescent chloroplast mutant of tobacco.Plant Physiol, 1987, 83(4): 920-925. |
| [17] | 谭炎宁, 孙学武, 袁定阳, 孙志忠, 余东, 何强, 段美娟, 邓华凤, 袁隆平. 水稻单叶独立转绿型黄化突变体grc2的鉴定与基因精细定位. 作物学报, 2015, 41(6): 831-837. |
| Tan Y N, Sun X W, Yuan D Y, Sun Z Z, Yu D, He Q, Duan M J, Deng H F, Yuan L P.Identification and fine mapping of green-revertible chlorina gene grc2 in rice(Oryza sativa L.) Act Agron Sin, 2015, 41(6): 831-837. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | Iba K, Takamiya K I, Toh Y, Satoh H, Nishimura M.Formation of functionally active chloroplasts is determined at a limited stage of leaf development in virescent mutants of rice. Genesis, 2010, 12(5): 342-348. |
| [19] | Kusumi K, Mizutani A, Nishimura M, Iba K.A virescent gene V1 determines the expression timing of plastid genes for transcription/translation apparatus during early leaf development in rice. Plant J, 1997, 12(6): 1241-1250. |
| [20] | Sugimoto H, Kusumi K, Noguchi K, Yano M, Yoshimura A, Iba K.The rice nuclear gene, VIRESCENT 2 , is essential for chloroplast development and encodes a novel type of guanylate kinase targeted to plastids and mitochondria. Plant J, 2007, 52(3): 512-527. |
| [21] | Yoo S C, Cho S H, Sugimoto H, Li J, Kusumi K, Koh H J, Iba K, Paek N C. Rice virescent3 and stripe1 encoding the large and small subunits of ribonucleotide reductase are required for chloroplast biogenesis during early leaf development. Plant Physiol, 2009, 150(1): 388-401. |
| [22] | Gong X, Su Q, Lin D, Jiang Q, Xu J, Zhang J, Teng S, Dong Y.The rice OsV4 encoding a novel pentatricopeptide repeat protein is required for chloroplast development during the early leaf stage under cold stress. J Integr Plant Biol, 2014, 56(4): 400-410. |
| [23] | Liu H, Li Q, Yang F, Zhu F, Sun Y, Tao Y, Lo C.Differential regulation of protochlorophyllide oxidoreductase abundances by VIRESCENT 5A (OsV5A) and VIRESCENT 5B (OsV5B) in rice seedlings. Plant Cell Physiol, 2016, 57(11): 2392-2402. |
| [24] | Jiang Q, Mei J, Gong X D, Xu J L, Zhang J H, Teng S, Lin D Z, Dong Y J.Importance of the riceTCD9 encoding α subunit of chaperonin protein 60(Cpn60α) for the chloroplast development during the early leaf stage. Plant Sci, 2014(215/216): 172-179. |
| [25] | Liu W, Fu Y, Hu G, Si H, Zhu L, Wu C, Sun Z.Identification and fine mapping of a thermo-sensitive chlorophyll deficient mutant in rice ( Oryza sativa L.). Planta, 2007, 226(3): 785-795. |
| [26] | Murray M G, Thompson W F.Rapid isolation of high weight plant DNA.Nucleic Acids Res, 1980, 8(19): 4321-4325. |
| [27] | 张其德. 测定叶绿素的几种方法. 植物学报, 1985, 3(5): 60-64. |
| Zhang Z D.Methods of determination of chlorophyll.Chin Bull Bot, 1985, 3(5): 60-64. (in Chinese) | |
| [28] | 吕典华, 宗学凤, 王三根, 凌英华, 桑贤春, 何光华. 两个水稻叶色突变体的光合特性研究. 作物学报, 2009, 35(12): 2304-2308. |
| Lv D H, Zong X F, Wang S G, Ling Y H, Sang X C, He G H.Characteristics of photosynthesis in two leaf color mutants of rice. Act Agron Sin, 2009, 35(12): 2304-2308. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | 郭鹏. 水稻温敏黄转绿突变体v5的鉴定和基因克隆. 金华: 浙江师范大学, 2011. |
| Guo P.Identification and gene mapping of a rice thermo-sensitivevirescent mutant v5. Jinhua: Zhejiang Normal University, 2011. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | 王文娟, 吴兰兰, 雷晓庆, 赵怀玉, 林冬枝, 董彦君. 一个新水稻低温敏感叶色突变体tcm11的鉴定及基因定位. 上海师范大学学报: 自然科学版, 2017, 46(2): 319-325. |
| Wang W J, Wu L L, Lei X Q, Zhao H Y, Lin D Z, Dong Y J.Identification and gene mapping of a novel low temperature sensitive leaf color mutant tcm11 in rice(Oryza sativa L.). J Shanghai Normal Univ: Nat Sci, 2017, 46(2): 319-325. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | 张天雨, 周春雷, 刘喜, 孙爱伶, 曹鹏辉, Nguyen T, 田云录, 翟虎渠, 江玲. 一个水稻温敏黄化突变体的表型分析和基因定位. 作物学报, 2017, 43(10): 1426-1433. |
| Zhang T Y, Zhou C L, Liu X, Sun A L, Cao P H, Nguyen T, Tian Y L, Zhai H Q, Jiang L.Phenotypes and gene mapping of a thermo-sensitive yellow leaf mutant of rice. Act Agron Sin, 2017, 43(10): 1426-1433. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [32] | Peng Y, Zhang Y, Lv J, Zhang J H, Li P, Shi X L, Wang Y F, Zhang H L, He Z H, Teng S.Characterization and fine mapping of a novel rice albino mutant low temperature albino 1. J Gene Genom, 2012, 39(8): 385-396. |
| [33] | Peng L W, Fukao Y, Myouga F, Motohashi R, Shinozaki K, Shikanai T.A chaperonin subunit with unique structures is essential for folding of a specific substrate.Plos Biol, 2011, 9(4): e1001040. |
| [34] | Suzuki K, Nakanishi H, Bower J, Yoder D W, Osteryoung K W, Miyagishima S Y.Plastid chaperonin proteins Cpn60α and Cpn60β are required for plastid division in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol, 2009, 9(1): 38. |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [6] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [7] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [8] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [9] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [10] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [11] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [12] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [13] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| [14] | 许用强, 姜宁, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 水稻开花期高温热害响应机理及其调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 111-126. |
| [15] | 吕海涛, 李建忠, 鲁艳辉, 徐红星, 郑许松, 吕仲贤. 稻田福寿螺的发生、危害及其防控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 127-139. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||