
中国水稻科学 ›› 2018, Vol. 1 ›› Issue (1): 169-180.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2018.7041
收稿日期:2017-04-01
出版日期:2018-01-10
发布日期:2018-03-10
通讯作者:
吴良欢
基金资助:
Xuan ZHOU1,2,3, Rong JIN4, Lianghuan WU1,2,*( ), DAIFeng5
), DAIFeng5
Received:2017-04-01
Online:2018-01-10
Published:2018-03-10
Contact:
Lianghuan WU
摘要: 【目的】添加生化抑制剂是提高水稻肥料利用率的有效途径之一。本研究旨在结合不同施肥模式揭示其节肥增效的群体优势,寻找适合黄泥田地区水稻高产高效的施用方式。【方法】采用二因素随机区组设计,研究生化抑制剂组合与施肥模式(一次性和分次施肥)互作对黄泥田水稻群体质量的影响。【结果】尿素分次施用处理水稻有效茎蘖数、有效叶面积指数(LAI)、抽穗至成熟期干物质积累量、抽穗期SPAD值和籽粒产量较一次性施用处理分别显著提高0.8%、24.0%、9.3%、1.5%和14.2%。不同施肥模式下,配施生化抑制剂组合N-丁基硫代磷酰三胺/N-丙基硫代磷酰三胺+2-氯-6-(三氯甲基)吡啶(NBPT/NPPT+CP)显著提高水稻有效茎蘖数及茎蘖成穗率,增加抽穗后干物质积累量,增大有效LAI,增加抽穗期SPAD值,提高水稻粒叶比,改善源库关系。相关性分析表明,抽穗至成熟期干物质累积与水稻籽粒产量呈显著正相关。新型脲酶抑制剂N-丙基硫代磷酰三胺(NPPT)单独施用及与2-氯-6-(三氯甲基)吡啶(CP)配施的水稻群体质量与N-丁基硫代磷酰三胺(NBPT)相似。【结论】通过施肥技术和抑制剂配施的集成与优化,可以改善黄泥田水稻群体质量,提高光合产物转化,获得更高产量。
中图分类号:
周旋, 金蓉, 吴良欢, 戴锋. 生化抑制剂组合与施肥模式对黄泥田水稻群体质量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 1(1): 169-180.
Xuan ZHOU, Rong JIN, Lianghuan WU, DAIFeng. Effects of Combined Biochemical Inhibitors and Fertilization Models on Rice Population Quality in Yellow Clayey Field[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2018, 1(1): 169-180.
| 处理 | 施N量 | 抑制剂 | 抑制剂添加量(以N为基础) | 施肥方式 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment | N rate/(kg·hm-2) | Type | Rate/% | Application method |
| CK | 0 | 无N0 | 0 | 不施氮肥Zero nitrogen fertilizer application |
| U | 180 | 无N0 | 0 | 一次性基施One-off basal application |
| U+NBPT | 180 | NBPT | 0.5 | 一次性基施One-off basal application |
| U+NPPT | 180 | NPPT | 0.5 | 一次性基施One-off basal application |
| U+CP | 180 | CP | 0.3 | 一次性基施One-off basal application |
| U+NBPT+CP | 180 | NBPT+CP | 0.5+0.3 | 一次性基施One-off basal application |
| U+NPPT+CP | 180 | NPPT+CP | 0.5+0.3 | 一次性基施One-off basal application |
| U3 | 180 | 无N0 | 0 | m基肥:m分蘖肥:m穗肥=5:3:2 |
| U3+NBPT | 180 | NBPT | 0.5 | m基肥:m分蘖肥:m穗肥=5:3:2 |
| U3+NPPT | 180 | NPPT | 0.5 | m基肥:m分蘖肥:m穗肥=5:3:2 |
| U3+CP | 180 | CP | 0.3 | m基肥:m分蘖肥:m穗肥=5:3:2 |
| U3+NBPT+CP | 180 | NBPT+CP | 0.5+0.3 | m基肥:m分蘖肥:m穗肥=5:3:2 |
| U3+NPPT+CP | 180 | NPPT+CP | 0.5+0.3 | m基肥:m分蘖肥:m穗肥=5:3:2 |
表1 氮肥施用方式
Table 1 N application methods.
| 处理 | 施N量 | 抑制剂 | 抑制剂添加量(以N为基础) | 施肥方式 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment | N rate/(kg·hm-2) | Type | Rate/% | Application method |
| CK | 0 | 无N0 | 0 | 不施氮肥Zero nitrogen fertilizer application |
| U | 180 | 无N0 | 0 | 一次性基施One-off basal application |
| U+NBPT | 180 | NBPT | 0.5 | 一次性基施One-off basal application |
| U+NPPT | 180 | NPPT | 0.5 | 一次性基施One-off basal application |
| U+CP | 180 | CP | 0.3 | 一次性基施One-off basal application |
| U+NBPT+CP | 180 | NBPT+CP | 0.5+0.3 | 一次性基施One-off basal application |
| U+NPPT+CP | 180 | NPPT+CP | 0.5+0.3 | 一次性基施One-off basal application |
| U3 | 180 | 无N0 | 0 | m基肥:m分蘖肥:m穗肥=5:3:2 |
| U3+NBPT | 180 | NBPT | 0.5 | m基肥:m分蘖肥:m穗肥=5:3:2 |
| U3+NPPT | 180 | NPPT | 0.5 | m基肥:m分蘖肥:m穗肥=5:3:2 |
| U3+CP | 180 | CP | 0.3 | m基肥:m分蘖肥:m穗肥=5:3:2 |
| U3+NBPT+CP | 180 | NBPT+CP | 0.5+0.3 | m基肥:m分蘖肥:m穗肥=5:3:2 |
| U3+NPPT+CP | 180 | NPPT+CP | 0.5+0.3 | m基肥:m分蘖肥:m穗肥=5:3:2 |

图2 不同处理下水稻的株高 MT–分蘖盛期;PI–孕穗期;HS–抽穗期;MS–成熟期。下同。
Fig. 2. Plant height of rice under different treatments. MT, Mid-tillering stage; PI, Panicle initiation stage; HS, Heading stage; MS, Maturity stage.The same as below.
| 处理 Treatment | 最高茎蘖数 Maximum tiller number/(×104·hm-2) | 有效茎蘖数 Productive tiller number/(×104·hm-2) | 成穗率 Productive tiller rate/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 250.0±7.2 d | 216.7±6.3 d | 86.7±2.5 ab |
| U | 416.7±12.0 a | 272.9±7.9 c | 65.5±1.9 c |
| U+NBPT | 354.2±10.2 bc | 291.7±8.4 abc | 82.4±2.4 ab |
| U+NPPT | 343.8±9.9 bc | 280.2±8.1 bc | 81.5±2.4 ab |
| U+CP | 350.0±10.1 bc | 283.3±8.2 bc | 81.0±2.3 ab |
| U+NBPT+CP | 353.3±10.2 bc | 284.6±8.2 abc | 80.5±2.3 b |
| U+NPPT+CP | 341.7±9.9 bc | 285.5±8.2 abc | 83.5±2.4 ab |
| U3 | 415.8±12.0 a | 275.0±7.9 c | 66.1±1.9 c |
| U3+NBPT | 353.3±10.2 bc | 291.7±8.4 abc | 82.5±2.4 ab |
| U3+NPPT | 370.8±10.7 b | 300.0±8.7 ab | 80.9±2.3 ab |
| U3+CP | 366.7±10.6 bc | 300.0±8.7 ab | 81.8±2.4 ab |
| U3+NBPT+CP | 358.3±10.4 bc | 308.3±8.9 a | 86.0±2.5 ab |
| U3+NPPT+CP | 337.1±9.7 c | 299.0±8.6 ab | 88.7±2.6 a |
| ANOVA | |||
| F | ns | * | ns |
| I | *** | ns | *** |
| F × I | ns | ns | ns |
表2 不同处理下水稻的茎蘖成穗率
Table 2 Productive tiller rate of rice under different treatments
| 处理 Treatment | 最高茎蘖数 Maximum tiller number/(×104·hm-2) | 有效茎蘖数 Productive tiller number/(×104·hm-2) | 成穗率 Productive tiller rate/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 250.0±7.2 d | 216.7±6.3 d | 86.7±2.5 ab |
| U | 416.7±12.0 a | 272.9±7.9 c | 65.5±1.9 c |
| U+NBPT | 354.2±10.2 bc | 291.7±8.4 abc | 82.4±2.4 ab |
| U+NPPT | 343.8±9.9 bc | 280.2±8.1 bc | 81.5±2.4 ab |
| U+CP | 350.0±10.1 bc | 283.3±8.2 bc | 81.0±2.3 ab |
| U+NBPT+CP | 353.3±10.2 bc | 284.6±8.2 abc | 80.5±2.3 b |
| U+NPPT+CP | 341.7±9.9 bc | 285.5±8.2 abc | 83.5±2.4 ab |
| U3 | 415.8±12.0 a | 275.0±7.9 c | 66.1±1.9 c |
| U3+NBPT | 353.3±10.2 bc | 291.7±8.4 abc | 82.5±2.4 ab |
| U3+NPPT | 370.8±10.7 b | 300.0±8.7 ab | 80.9±2.3 ab |
| U3+CP | 366.7±10.6 bc | 300.0±8.7 ab | 81.8±2.4 ab |
| U3+NBPT+CP | 358.3±10.4 bc | 308.3±8.9 a | 86.0±2.5 ab |
| U3+NPPT+CP | 337.1±9.7 c | 299.0±8.6 ab | 88.7±2.6 a |
| ANOVA | |||
| F | ns | * | ns |
| I | *** | ns | *** |
| F × I | ns | ns | ns |
| 处理 Treatment | 抽穗期干质量 Biomass at heading /(t·hm-2) | 抽穗期干质量占总干质量比例 Biomass at heading to total biomass/% | 抽穗至成熟期干物质积累 Biomass from heading to maturity/(t·hm-2) | 花后干质量占总干质量比例 Post-anthesis biomass to total biomass/% | 成熟期干质量 Total biomass atmaturity/(t·hm-2) | 收获指数 Harvest index/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 9.8±0.3 b | 12.4±0.4 e | 1.4±0.1 f | 87.6±2.5 a | 11.2±0.3 g | 57.5±1.7 a |
| U | 10.8±0.3 a | 28.0±0.8 d | 4.2±0.1 e | 72.0±2.1 b | 15.0±0.4 f | 47.7±1.4 d |
| U+NBPT | 10.3±0.3 ab | 32.0±0.9 c | 4.9±0.1 d | 68.0±2.0 bcd | 15.2±0.4 ef | 50.1±1.4 cd |
| U+NPPT | 10.1±0.3 ab | 36.3±1.0 ab | 5.7±0.1 c | 63.7±1.8 de | 15.8±0.5 cdef | 52.5±1.5 bc |
| U+CP | 10.4±0.3 ab | 37.5±1.1 ab | 6.3±0.2 b | 62.5±1.8 de | 16.7±0.5 abcd | 51.5±1.5 bcd |
| U+NBPT+CP | 10.2±0.3 ab | 36.8±1.1 ab | 5.9±0.1 bc | 63.2±1.8 de | 16.2±0.5 abcdef | 52.6±1.5 bc |
| U+NPPT+CP | 10.6±0.3 ab | 35.4±1.0 b | 5.8±0.2 c | 64.6±1.9 de | 16.4±0.5 abcde | 51.1±1.5 bcd |
| U3 | 10.9±0.3 a | 29.7±0.9 cd | 4.6±0.1 de | 70.3±2.0 bc | 15.5±0.4 def | 52.1±1.5 bcd |
| U3+NBPT | 10.5±0.3 ab | 35.3±1.0 b | 5.7±0.2 c | 64.7±1.9 de | 16.2±0.5 abcdef | 52.6±1.5 bc |
| U3+NPPT | 10.4±0.3 ab | 35.3±1.0 b | 5.6±0.1 c | 64.7±1.9 cde | 16.0±0.5 bcdef | 52.7±1.5 bc |
| U3+CP | 10.9±0.3 a | 36.6±1.1 ab | 6.3±0.2 b | 63.4±1.8 de | 17.2±0.5 ab | 53.3±1.5 abc |
| U3+NBPT+CP | 10.8±0.3 a | 36.8±1.1 ab | 6.3±0.2 b | 63.2±1.8 de | 17.0±0.5 abc | 55.3±1.6 ab |
| U3+NPPT+CP | 10.7±0.3 ab | 38.8±1.1 a | 6.8±0.2 a | 61.2±1.8 e | 17.4±0.5 a | 54.2±1.6 abc |
| ANOVA | ||||||
| F | ns | ns | *** | ns | * | *** |
| I | ns | *** | *** | ** | ** | ns |
| F×I | ns | ns | * | ns | ns | ns |
表3 不同处理下水稻的干物质生产特性
Table 3 Properties of dry matter production of rice under different treatments.
| 处理 Treatment | 抽穗期干质量 Biomass at heading /(t·hm-2) | 抽穗期干质量占总干质量比例 Biomass at heading to total biomass/% | 抽穗至成熟期干物质积累 Biomass from heading to maturity/(t·hm-2) | 花后干质量占总干质量比例 Post-anthesis biomass to total biomass/% | 成熟期干质量 Total biomass atmaturity/(t·hm-2) | 收获指数 Harvest index/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 9.8±0.3 b | 12.4±0.4 e | 1.4±0.1 f | 87.6±2.5 a | 11.2±0.3 g | 57.5±1.7 a |
| U | 10.8±0.3 a | 28.0±0.8 d | 4.2±0.1 e | 72.0±2.1 b | 15.0±0.4 f | 47.7±1.4 d |
| U+NBPT | 10.3±0.3 ab | 32.0±0.9 c | 4.9±0.1 d | 68.0±2.0 bcd | 15.2±0.4 ef | 50.1±1.4 cd |
| U+NPPT | 10.1±0.3 ab | 36.3±1.0 ab | 5.7±0.1 c | 63.7±1.8 de | 15.8±0.5 cdef | 52.5±1.5 bc |
| U+CP | 10.4±0.3 ab | 37.5±1.1 ab | 6.3±0.2 b | 62.5±1.8 de | 16.7±0.5 abcd | 51.5±1.5 bcd |
| U+NBPT+CP | 10.2±0.3 ab | 36.8±1.1 ab | 5.9±0.1 bc | 63.2±1.8 de | 16.2±0.5 abcdef | 52.6±1.5 bc |
| U+NPPT+CP | 10.6±0.3 ab | 35.4±1.0 b | 5.8±0.2 c | 64.6±1.9 de | 16.4±0.5 abcde | 51.1±1.5 bcd |
| U3 | 10.9±0.3 a | 29.7±0.9 cd | 4.6±0.1 de | 70.3±2.0 bc | 15.5±0.4 def | 52.1±1.5 bcd |
| U3+NBPT | 10.5±0.3 ab | 35.3±1.0 b | 5.7±0.2 c | 64.7±1.9 de | 16.2±0.5 abcdef | 52.6±1.5 bc |
| U3+NPPT | 10.4±0.3 ab | 35.3±1.0 b | 5.6±0.1 c | 64.7±1.9 cde | 16.0±0.5 bcdef | 52.7±1.5 bc |
| U3+CP | 10.9±0.3 a | 36.6±1.1 ab | 6.3±0.2 b | 63.4±1.8 de | 17.2±0.5 ab | 53.3±1.5 abc |
| U3+NBPT+CP | 10.8±0.3 a | 36.8±1.1 ab | 6.3±0.2 b | 63.2±1.8 de | 17.0±0.5 abc | 55.3±1.6 ab |
| U3+NPPT+CP | 10.7±0.3 ab | 38.8±1.1 a | 6.8±0.2 a | 61.2±1.8 e | 17.4±0.5 a | 54.2±1.6 abc |
| ANOVA | ||||||
| F | ns | ns | *** | ns | * | *** |
| I | ns | *** | *** | ** | ** | ns |
| F×I | ns | ns | * | ns | ns | ns |
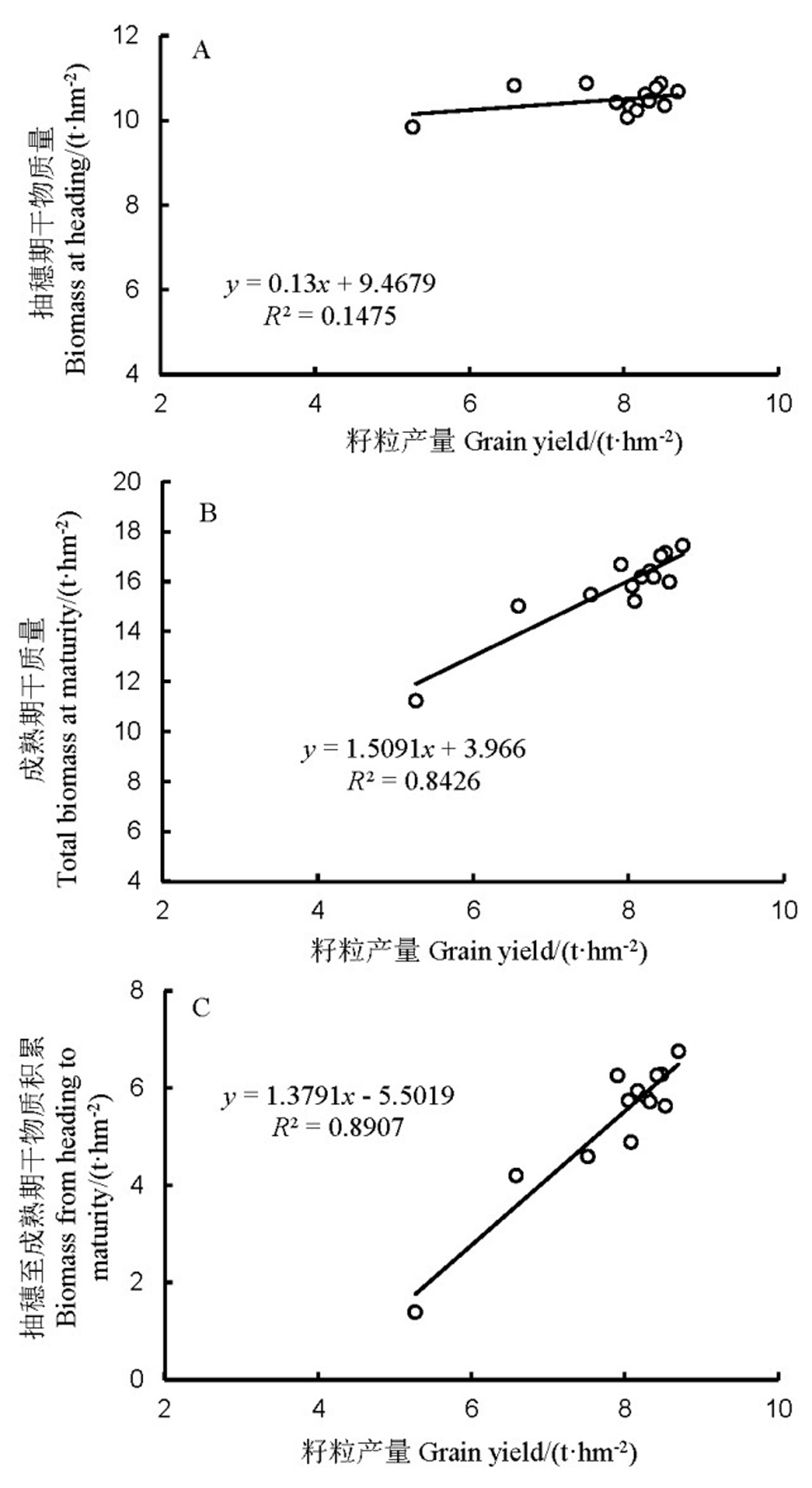
图3 不同处理下水稻籽粒产量与抽穗期干质量(A)、成熟期干质量(B)和抽穗至成熟期干物质积累(C)的相关性分析
Fig. 3. Correlation between grain yield and biomass at heading (A), at maturity (B), and from heading to maturity (C).
| 处理 Treatment | 总LAI Total LAI | 有效LAI Efficient LAI | 高效LAI High efficient LAI | 有效叶面积率 Efficient LAI rate/% | 高效叶面积率 High efficient LAI rate/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 5.5±0.2 g | 4.3±0.1 d | 2.2±0.1 f | 78.8±5.7 ab | 40.9±3.0 b |
| U | 9.5±0.3 de | 7.4±0.2 c | 5.2±0.2 d | 78.0±5.6 ab | 54.8±4.0 a |
| U+NBPT | 9.1±0.3 ef | 8.1±0.2 bc | 5.1±0.1 de | 89.7±6.5 ab | 55.9±4.0 a |
| U+NPPT | 9.6±0.3 de | 8.5±0.2 b | 5.8±0.2 c | 88.2±6.4 ab | 60.6±4.4 a |
| U+CP | 8.7±0.2 f | 8.0±0.2 bc | 5.2±0.2 d | 91.9±6.6 a | 60.0±4.3 a |
| U+NBPT+CP | 8.5±0.2 f | 7.8±0.2 bc | 4.6±0.1 e | 92.3±6.7 a | 54.2±3.9 a |
| U+NPPT+CP | 9.1±0.3 ef | 7.8±0.2 bc | 5.1±0.1 de | 85.6±6.2 ab | 55.7±4.0 a |
| U3 | 12.6±0.4 a | 9.2±0.3 a | 7.7±0.2 a | 73.3±5.3 b | 61.1±4.4 a |
| U3+NBPT | 10.8±0.3 b | 9.6±0.3 a | 6.5±0.2 b | 89.2±6.4 ab | 60.1±4.3 a |
| U3+NPPT | 9.9±0.3 cd | 9.4±0.3 a | 5.9±0.2 c | 94.4±6.8 a | 59.5±4.3 a |
| U3+CP | 11.4±0.3 b | 9.5±0.3 a | 6.8±0.2 b | 83.7±6.0 ab | 60.1±4.3 a |
| U3+NBPT+CP | 11.1±0.3 b | 9.7±0.3 a | 6.5±0.2 b | 88.1±6.4 ab | 58.9±4.3 a |
| U3+NPPT+CP | 10.7±0.3 bc | 9.7±0.3 a | 6.4±0.2 b | 91.4±6.6 ab | 60.4±4.4 a |
| ANOVA | |||||
| F | *** | *** | *** | ns | ns |
| I | ** | ns | *** | ns | ns |
| F×I | ** | ns | *** | ns | ns |
表4 不同处理下抽穗期水稻的总叶面积指数(LAI)、有效LAI和高效LAI
Table 4 Total leaf area index (LAI), efficient LAI, and high efficient LAI of rice at heading stage under different treatments.
| 处理 Treatment | 总LAI Total LAI | 有效LAI Efficient LAI | 高效LAI High efficient LAI | 有效叶面积率 Efficient LAI rate/% | 高效叶面积率 High efficient LAI rate/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 5.5±0.2 g | 4.3±0.1 d | 2.2±0.1 f | 78.8±5.7 ab | 40.9±3.0 b |
| U | 9.5±0.3 de | 7.4±0.2 c | 5.2±0.2 d | 78.0±5.6 ab | 54.8±4.0 a |
| U+NBPT | 9.1±0.3 ef | 8.1±0.2 bc | 5.1±0.1 de | 89.7±6.5 ab | 55.9±4.0 a |
| U+NPPT | 9.6±0.3 de | 8.5±0.2 b | 5.8±0.2 c | 88.2±6.4 ab | 60.6±4.4 a |
| U+CP | 8.7±0.2 f | 8.0±0.2 bc | 5.2±0.2 d | 91.9±6.6 a | 60.0±4.3 a |
| U+NBPT+CP | 8.5±0.2 f | 7.8±0.2 bc | 4.6±0.1 e | 92.3±6.7 a | 54.2±3.9 a |
| U+NPPT+CP | 9.1±0.3 ef | 7.8±0.2 bc | 5.1±0.1 de | 85.6±6.2 ab | 55.7±4.0 a |
| U3 | 12.6±0.4 a | 9.2±0.3 a | 7.7±0.2 a | 73.3±5.3 b | 61.1±4.4 a |
| U3+NBPT | 10.8±0.3 b | 9.6±0.3 a | 6.5±0.2 b | 89.2±6.4 ab | 60.1±4.3 a |
| U3+NPPT | 9.9±0.3 cd | 9.4±0.3 a | 5.9±0.2 c | 94.4±6.8 a | 59.5±4.3 a |
| U3+CP | 11.4±0.3 b | 9.5±0.3 a | 6.8±0.2 b | 83.7±6.0 ab | 60.1±4.3 a |
| U3+NBPT+CP | 11.1±0.3 b | 9.7±0.3 a | 6.5±0.2 b | 88.1±6.4 ab | 58.9±4.3 a |
| U3+NPPT+CP | 10.7±0.3 bc | 9.7±0.3 a | 6.4±0.2 b | 91.4±6.6 ab | 60.4±4.4 a |
| ANOVA | |||||
| F | *** | *** | *** | ns | ns |
| I | ** | ns | *** | ns | ns |
| F×I | ** | ns | *** | ns | ns |
| 处理 Treatment | 颖花数/叶面积 Spikelet number/leaf area/(cm-2) | 实粒数/叶面积 Filled grain number/leaf area/(cm-2) | 粒重/叶面积 Grain yield/leaf area/(mg·cm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0.88±0.02 a | 0.78±0.02 a | 12.2±0.4 a |
| U | 0.65±0.02 bcd | 0.53±0.02 cde | 8.9±0.3 def |
| U+NBPT | 0.67±0.02 bc | 0.55±0.01 cd | 9.9±0.3 bc |
| U+NPPT | 0.63±0.02 cde | 0.55±0.02 cd | 9.5±0.3 cd |
| U+CP | 0.66±0.02 bc | 0.55±0.01 c | 9.9±0.3 bc |
| U+NBPT+CP | 0.66±0.02 bc | 0.56±0.02 c | 10.5±0.3 b |
| U+NPPT+CP | 0.69±0.02 b | 0.61±0.02 b | 10.7±0.3 b |
| U3 | 0.59±0.02 ef | 0.48±0.01 f | 8.2±0.2 f |
| U3+NBPT | 0.55±0.01 f | 0.49±0.01 ef | 8.6±0.3 ef |
| U3+NPPT | 0.60±0.02 def | 0.51±0.01 def | 9.1±0.3 de |
| U3+CP | 0.57±0.02 f | 0.50±0.01 ef | 8.9±0.3 def |
| U3+NBPT+CP | 0.56±0.01 f | 0.49±0.01 ef | 8.6±0.3 ef |
| U3+NPPT+CP | 0.60±0.02 def | 0.52±0.01 cdef | 8.9±0.3 def |
| ANOVA | |||
| F | *** | *** | *** |
| I | ns | * | ** |
| F×I | ns | ns | ns |
表5 不同处理下水稻的粒叶比
Table 5 Grain-leaf ratio of rice under different treatments.
| 处理 Treatment | 颖花数/叶面积 Spikelet number/leaf area/(cm-2) | 实粒数/叶面积 Filled grain number/leaf area/(cm-2) | 粒重/叶面积 Grain yield/leaf area/(mg·cm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0.88±0.02 a | 0.78±0.02 a | 12.2±0.4 a |
| U | 0.65±0.02 bcd | 0.53±0.02 cde | 8.9±0.3 def |
| U+NBPT | 0.67±0.02 bc | 0.55±0.01 cd | 9.9±0.3 bc |
| U+NPPT | 0.63±0.02 cde | 0.55±0.02 cd | 9.5±0.3 cd |
| U+CP | 0.66±0.02 bc | 0.55±0.01 c | 9.9±0.3 bc |
| U+NBPT+CP | 0.66±0.02 bc | 0.56±0.02 c | 10.5±0.3 b |
| U+NPPT+CP | 0.69±0.02 b | 0.61±0.02 b | 10.7±0.3 b |
| U3 | 0.59±0.02 ef | 0.48±0.01 f | 8.2±0.2 f |
| U3+NBPT | 0.55±0.01 f | 0.49±0.01 ef | 8.6±0.3 ef |
| U3+NPPT | 0.60±0.02 def | 0.51±0.01 def | 9.1±0.3 de |
| U3+CP | 0.57±0.02 f | 0.50±0.01 ef | 8.9±0.3 def |
| U3+NBPT+CP | 0.56±0.01 f | 0.49±0.01 ef | 8.6±0.3 ef |
| U3+NPPT+CP | 0.60±0.02 def | 0.52±0.01 cdef | 8.9±0.3 def |
| ANOVA | |||
| F | *** | *** | *** |
| I | ns | * | ** |
| F×I | ns | ns | ns |
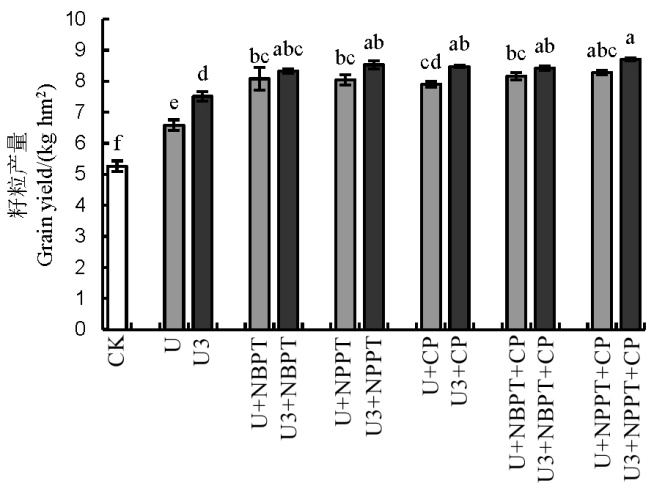
图6 不同处理下黄泥田水稻产量柱上不同小写字母代表处理间在5%水平差异显著(LSD)。图中数值为平均值±标准误(n=3)。
Fig. 6. Grain yield of rice in yellow clay field under different treatments. Different small letters above the bars mean significant difference among treatments at 5% level (LSD). Data in the figure are Mean±SE (n=3).
| [1] | 朱兆良, 金继运. 保障我国粮食安全的肥料问题. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2013, 19(2): 259-273. |
| Zhu Z L, Jin J Y.Fertilizer use and food security in China.Plant Nut FertilSci, 2013, 19(2): 259-273. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | Wang D J, Liu Q, Lin J H, Sun R J.Optimum nitrogen use and reduced nitrogen loss for production of rice and wheat in the Yangtse Delta Region.Environ Geochem Heal, 2004, 26(2): 221-227. |
| [3] | Jiang L G, Dong D F, Gan X Q, Wei S Q.Photosynthetic efficiency and nitrogen distribution under different nitrogen management and relationship with physiological N-use efficiency in three rice genotypes.Plant Soil, 2005, 271(1): 321-328. |
| [4] | Peng S B, Buresh R J, Huang J L, Yang J C, Zou Y B, Zhong X H, Wang G H, Zhang F S.Strategies for overcoming low agronomic nitrogen use efficiency in irrigated rice systems in China.Field Crops Res, 2006, 96(1):37-47. |
| [5] | Wopereispura M M, Watanabe H, Moreira J, Wopereis M C S. Effect of late nitrogen application on rice yield, grain quality and profitability in the Senegal River valley.Europ J Agron, 2002, 17(3): 191-198. |
| [6] | Xing G X, Zhu Z L.An assessment of N loss from agricultural fields to the environment in China.Nut CyclAgroecos, 2000, 57(1): 67-73. |
| [7] | Xie Y X, Xiong Z Q, Xing G X, Sun G Q, Zhu Z L.Assessment of nitrogen pollutant sources in surface waters of TaihuLake region.Pedosphere, 2007, 17(2): 200-208. |
| [8] | Qiao J, Yang L Z, Yan T M, Xue F, Zhao D.Nitrogen fertilizer reduction in rice production for two consecutive years in the Taihu Lake area.AgricEcosys Environ, 2012, 146(1): 103-112. |
| [9] | 朱兆良. 中国土壤氮素研究. 土壤学报, 2008, 45(5): 778-783. |
| Zhu Z L.Research on soil nitrogen in China.ActaPedol Sin, 2008, 45(5): 778-783.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | Huang J K, Huang Z R, Jia X P, Hu R, Xiang C.Long-term reduction of nitrogen fertilizer use through knowledge training in rice production in China.Agric Sys, 2015, 135(6): 105-111. |
| [11] | 孙海军, 闵炬, 施卫明, 冯彦房, 李卫正, 初磊. 硝化抑制剂施用对水稻产量与氨挥发的影响. 土壤, 2015, (6): 1027-1033. |
| Sun H J, Min J, Shi W M, Eeng Y F, Li W Z, Chu L.Effects of nitrification inhibitor on rice production and ammonia volatilization in paddy rice field.Soils, 2015, (6): 1027-1033.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | Wang Z P, Van Cleemput O, Demeyer P, Baert L.Effect of urease inhibitors on urea hydrolysis and ammonia volatilization.BiolFertil Soils, 1991, 11(1): 43-47. |
| [13] | Antisari L V, Marzadori C, Gioacchini P, Ricci S, Gessa C.Effects of the urease inhibitor N-(n-butyl)phosphorothioictriamide in low concentrations on ammonia volatilization and evolution of mineral nitrogen.BiolFertSoils, 1996, 22(3): 196-201. |
| [14] | 徐星凯, 周礼恺, Van Cleemput O.脲酶抑制剂/硝化抑制剂对植稻土壤中尿素N行为的影响. 生态学报, 2001, 21(10): 1682-1686. |
| Xu X K, Zhou L K, Van Cleemput O.Effect of urease/nitrification inhibitors on the behavior of urea-N in the soil planted to rice.ActaEcologicaSinica, 2001, 21(10): 1682-1686. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 张文学, 孙刚, 何萍, 梁国庆, 余喜初, 刘光荣, 周卫. 双季稻田添加脲酶抑制剂NBPT氮肥的最高减量潜力研究. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2014, 20(4): 821-830. |
| Zhang W X, Sun G, He P, Liang G Q, Yu X C, Liu G R,. Zhou W.Highest potential of subtracting nitrogen fertilizer through addition of urease inhibitor NBPT in double-cropping paddy fields.J Plant Nut FertilSci, 2014, 20(4): 821-830.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 周礼恺, 徐星凯, 陈利军, 李荣华, van Cleemput O.氢醌和双氰胺对种稻土壤N2O和CH4排放的影响. 应用生态学报, 1999, 10(2): 189-192. |
| Zhou L K, Xu X K, Chen L J, Li R H, Van Cleemput O.Effect of hydroquinone and dicyandiamide on N2O and CH4 emissions from lowland rice soil.Chin J ApplEcol, 1999, 10(2): 189-192. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | 李香兰, 马静, 徐华, 曹金留, 蔡祖聪, Yagi K.DCD不同施用时间对水稻生长期CH4和N2O排放的影响. 生态学报, 2008, 28(8): 3675-3681. |
| Li X L, Ma J, Xu H, Cao J L, Cai Z C, Yagi K.Effect of different application time of DCD on methane and nitrous oxide emissions during rice growth period.ActaEcol Sin, 2008, 28(8): 3675-3681.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | 王少先, 彭克勤, 萧浪涛, 夏石头, 童建华, 王若仲. 双氰胺对水稻根系及光合特性和经济性状的影响. 湖南农业大学学报:自然科学版, 2003, 29(1): 18-21. |
| Wang S X, Peng K Q, Xiao L T, Xia S T, Tong J H, Wang R Z.Study on the effects of Dicyandianmide on root system, photosynthetic and economic characteristics of rice.J Hunan AgricUniv, 2003, 29(1): 18-21.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | 朱德峰, 陈惠哲, 徐一成, 张玉屏. 我国双季稻生产机械化制约因子与发展对策. 中国稻米, 2013, 19(4): 1-4. |
| Zhu D F, Chen H Z, Xu Y C, Zhang Y P.Constraints and countermeasures of the mechanization of double rice production in China.China Rice, 2013, 19(4): 1-4.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | 王飞, 林诚, 李清华, 何春梅, 李昱, 林新坚. 长期不同施肥对南方黄泥田水稻子粒品质性状与土壤肥力因子的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2011, 17(2): 283-290. |
| Wang F, Lin C, Li Q H, Li Yu, Lin X J.Effects of long-term fertilization on rice grain qualities and soil fertility factors in yellow paddy fields of southern China.Plant Nut FertilSci, 2011, 17(2): 283-290.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | 林诚, 王飞, 李清华, 李昱, 何春梅, 林新坚. 不同施肥制度对黄泥田土壤酶活性及养分的影响. 中国土壤与肥料, 2009, (6): 24-27. |
| Lin C, Wang F, Li Q H, Li Yu, He C M, Lin X J.Effects of different fertilizer application strategies on nutrients and enzymatic activities in yellow clayey soil.Soil FertilSci China, 2009, (6): 24-27.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | 张宣. 南方中低产黄泥田科学施肥技术研究. 杭州:浙江大学, 2014. |
| Zhang X.Study on rational fertilization technology of low-medium yielding yellow-clayed paddy field in south China.Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2014.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 唐启源, 邹应斌, 米湘成, 汪汉林, 周美兰. 不同施氮条件下超级杂交稻的产量形成特点与氮肥利用. 杂交水稻, 2003, 18(1): 44-48. |
| Tang Q Y, Zou Y B, Mi X C, Wang H L, Zhou M L.Grain yield construction and N fertilizer efficiency of super hybrid rice under different N applications.Hybrid Rice, 2003, 18(1):44-48.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | 吴文革, 张四海, 赵决建, 吴桂成, 李泽福, 夏加发. 氮肥运筹模式对双季稻北缘水稻氮素吸收利用及产量的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2007, 13(5): 757-764. |
| Wu W G, Zhang S H, Zhao J J, Wu G C, Li Z F, Xia J F.Nitrogen uptake, utilization and rice yield in the north rimland of double-cropping rice region as affected by different nitrogen management strategies.Plant Nut FertilSci, 2007, 13(5): 757-764.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | 石丽红, 纪雄辉, 李永华, 朱校奇, 李洪顺, 彭华, 刘昭兵. 施氮量和时期运筹对超级杂交稻植株氮含量与籽粒产量的影响研究. 土壤, 2011, 43(4): 534-541. |
| Shi L H, Ji X H, Li Y H, Zhu X Q, Li H S, Peng H, Liu Z B.Effect of nitrogen application amount and stage management on nitrogen content in plant and grain yield of super hybrid rice.Soils, 2011, 22(1): 207-209.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | 周旋, 吴良欢, 戴锋. 生化抑制剂组合对黄泥田土壤尿素态氮转化的影响. 水土保持学报, 2015, 29(5): 95-100. |
| Zhou X, Wu L H, Dai F.Effects of combined biochemical inhibitors on transformation of urea-N in yellow clayey soil.J Soil Water Conser, 2015, 29(5): 95-100. | |
| (inChinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | 周旋, 吴良欢, 戴锋. 新型磷酰胺类脲酶抑制剂对不同质地土壤尿素转化的影响. 应用生态学报, 2016, 27(12): 4003-4012. |
| Zhou X, Wu L H, Dai F.Influence of a new phosphoramide urease inhibitor on urea-N transformation in different texture soil.Chin J ApplEcol, 2016, 27(12): 4003-4012.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | 凌启鸿. 作物群体质量. 上海:上海科学技术出版社, 2000. |
| Ling Q H.Crop population quality. Shanghai: Shanghai Scientific and Technical Publishers, 2000.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | 陈惠哲. 水稻物质运转规律及其产量形成的研究. 北京:中国农业科学院, 2007. |
| Chen H Z.Study on matter translocation characteristic and yield formation in rice (Oryza sativa L.).Beijing:Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2007.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | 李木英, 石庆华, 郑伟, 潘晓华, 谭雪明.杂交稻后期叶片早衰特征及其与叶片N含量和根系活力关系初探. 江西农业大学学报, 2008, 30(5): 757-765. |
| Li M Y, Shi Q H, Zheng W, Pan X H, Tan X M.A preliminary study on relationship between leaf premature senescence characteristic and leaf N content, roots activity in hybrid rice during grain filling stage.ActaAgricUniv Jiangxi, 2008, 30(5): 757-765. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | 薛利红, 覃夏, 李刚华, 杨林章.基蘖肥氮不同比例对直播早稻群体动态、氮素吸收利用及产量形成的影响. 土壤, 2010, 42(5): 815-821. |
| Xue L H, Qin X, Li G H, Yang L Z.Effect of basal and tiller nitrogen rates on population dynamics, nitrogen uptake and utilization, and yield formation of direct-seeding early rice.Soils, 2010, 42(5): 815-821.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [32] | 张慧, 彭显龙, 刘元英, 郁燕, 陈丽楠. 前氮后移对寒地水稻群体质量的影响. 土壤通报, 2011, 42(2): 402-406. |
| Zhang H, Peng X L, Liu Y Y, Yu Y, Chen L N.Effect of N application at later stages on population quality of rice in cold area.Chin J Soil Sci, 2011, 42(2): 402-406.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [33] | 俞巧钢, 陈英旭. 尿素添加硝化抑制剂DMPP对稻田土壤不同形态矿质态氮的影响. 农业环境科学学报, 2011, 30(7): 1357-1363. |
| Yu Q G, Chen Y X.Effect of the urea with nitrification inhibitor DMPP addition on different form nitrogen transformation in rice fields.J Agro-Environ Sci, 2011, 30(7): 1357-1363.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [34] | 张怡, 吕世华, 马静, 徐华, 袁江, 董瑜皎.覆膜栽培及抑制剂施用对稻田N2O排放的影响. 土壤, 2013, 45(5): 830-837. |
| Zhang Y, Lv S H, Ma J, Xu H, Yuan J, Dong Y J.Effects of cultivation pattern and inhibitor application on nitrous oxide emission from paddy fields.Soils, 2013, 45(5): 830-837. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [35] | Ghosh S, Majumdar D, Jain M C.Methane and nitrous oxide emissions from an irrigated rice of North India.Chemosphere, 2003, 51(3):181-195. |
| [36] | Chaiwanakupt P, Freney J R, Keerthisinghe D G, Phongpan S, Blakeley R L.Use of urease, algal inhibitors, and nitrification inhibitors to reduce nitrogen loss and increase the grain yield of flooded rice (Oryza sativa, L.). BiolFertil Soils, 1996, 22(1-2): 89-95. |
| [37] | 张文学, 孙刚, 何萍, 梁国庆, 王秀斌, 刘光荣,周卫.脲酶抑制剂与硝化抑制剂对稻田氨挥发的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2013, 19(6): 1411-1419. |
| Zhang W X, Sun G, He P, Liang G Q, Wang X B, Liu G R, Zhou W.Effects of urease and nitrification inhibitors on ammonia volatilization from paddy fields.J Plant NutrFertilSci, 2013, 19(6): 1411-1419.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [38] | 邹应斌, 敖和军, 王淑红,唐启源. 超级稻“三定”栽培法研究:Ⅰ.概念与理论依据. 中国农学通报, 2006, 22(5): 158-162. |
| Zou Y B, Ao H J, Wang S H, Tang Q Y.Studies on San-Ding cultivation method for super riceⅠ.The concept and the principle.Chin AgricSci Bull, 2006, 22(5): 158-162.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [39] | 吴文革, 张洪程, 吴桂成, 翟超群, 钱银飞, 陈烨, 徐军, 戴其根, 许珂. 超级稻群体籽粒库容特征的初步研究. 中国农业科学, 2007b, 40(2): 250-257. |
| Wu W G, Zhang H C, Wu G C, Zhai C Q, Qian Y F, Chen Y, Xu J, Dai Q G, Xu K.Preliminary study on super rice population sink characters.SciAgric Sin, 2007b, 40(2): 250-257.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [40] | 冯跃华, 潘剑, 何腾兵, 刘应春, 王尚有, 赵福胜, 田晋文, 潘兴书, 范乐乐. 不同施氮水平对超级稻源库特性的影响. 中国农学通报, 2010, 26(15): 252-256. |
| Feng Y H, Pan J, He T B, Liu Y C, Wang S Y, Zhao F S, Tian J W, Pan X S, Fan L L.Effect of different fertilizer-N application rate on source-sink characteristics of super hybrid rice. Chin AgricSci Bulletin, 2010, 26(15): 252-256.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [41] | 林忠成, 李土明, 吴福观, 张洪程, 戴其根, 叶世超, 郭宏文. 基蘖肥与穗肥氮比例对双季稻产量和碳氮比的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2011, 17(2): 269-275. |
| Lin Z C, Li T M, Wu F G, Zhang H C, Dai Q G, Ye S C, Guo H W.Effects of nitrogen application on yield and C/N of double-cropping rice.Plant NutrFertilSci, 2011, 17(2): 269-275.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [42] | 刘彦伶. 南方中低产黄泥田改良和产量提升技术研究. 杭州:浙江大学, 2013. |
| Liu Y L.Study on the technology of soil and grain yield improvement for low-medium yielding yellow-clayed paddy field in south China. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2013.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 陈云, 张亚军, 张宏路, 朱安, 黄健, 张耗, 顾骏飞, 刘立军, 杨建昌. 机插株距对优质食味水稻品种产量和群体质量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(6): 550-560. |
| [2] | 夏琼梅, 胡家权, 董林波, 钱文娟, 何永福, 李贵勇, 龙瑞平, 朱海平, 杨从党. 氮肥减量后移对云南高原水旱轮作下粳稻群体质量及产量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(3): 266-277. |
| [3] | 殷尧翥, 郭长春, 孙永健, 武云霞, 余华清, 孙知白, 张桥, 王海月, 杨志远, 马均. 稻油轮作下油菜秸秆还田与水氮管理对杂交稻群体质量和产量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(3): 257-268. |
| [4] | 郭长春, 孙知白, 孙永健, 殷尧翥, 武云霞, 唐源, 杨志远, 向开宏, 马均. 优质丰产杂交籼稻品种机直播产量构成及其群体质量研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(5): 462-474. |
| [5] | 张文学, 杨成春, 王少先, 孙刚, 刘增兵, 李祖章, 刘光荣. 脲酶抑制剂与硝化抑制剂对稻田土壤氮素转化的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(4): 417-424. |
| [6] | 郭保卫, 胡雅杰, 钱海军, 曹伟伟, 邢志鹏, 张洪程, 戴其根, 霍中洋, 许轲, 魏海燕. 秸秆还田下适宜施氮量提高机插稻南粳9108产量和群体质量[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2015, 29(5): 511-518. |
| [7] | 许轲1 ,张军1,2 ,张洪程1,* ,花劲1 ,霍中洋1 ,郭保卫1 ,戴其根1 ,魏海燕1 ,高辉1. 双季晚粳稻不同栽培方式生产力及其群体质量差异研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2014, 28(5): 503-513. |
| [8] | 卢婉芳,陈苇. 稻田脲酶抑制剂的应用效果及其与环境条件的关系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 1992, 6(3): 135-138 . |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||