
中国水稻科学 ›› 2017, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (6): 631-642.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2017.6168
田蕾, 陈亚萍, 刘俊, 马晓刚, 王娜, 杨兵, 李莹, 郭海东, 李娟, 胡慧, 张银霞, 李培富*( )
)
出版日期:2017-11-25
发布日期:2017-11-10
通讯作者:
李培富
基金资助:
Lei TIAN, Yaping CHEN, Jun LIU, Xiaogang MA, Na WANG, Bing YANG, Ying LI, Haidong GUO, Juan LI, Hui HU, Yinxia ZHANG, Peifu LI*( )
)
Online:2017-11-25
Published:2017-11-10
Contact:
Peifu LI
摘要:
【目的】 土壤盐渍化是危害水稻生产的重要非生物胁迫之一。鉴定水稻种质资源发芽期耐盐性,筛选耐盐指标,培育耐盐品种,对水稻生产的发展具有重要意义。【方法】 利用125 mmol/L NaCl溶液对64份粳稻种质资源进行盐胁迫,于胁迫后3 d测定发芽数;胁迫5 d、10 d后,测定发芽数、芽长和根长,并计算相对芽长、根长、发芽势、发芽率、盐害率,发芽指数和活力指数。运用多种统计学方法对各种质资源的芽期耐盐性进行综合评价,分析典型耐盐和盐敏感种质盐胁迫条件下的发芽特征。【结果】 相对盐害率与相对根长、相对发芽势、相对发芽率、发芽指数和活力指数均极显著负相关;除相对芽长外各指标间的相关性均达到极显著水平。通过聚类分析将64份粳稻种质资源划分成4个类群。第Ⅰ、Ⅳ类群分别为典型的盐敏感和耐盐类群,第Ⅱ类群为弱耐盐种质为主的混合类群,第Ⅲ类群主要由耐盐种质组成。通过主成分分析将7个评价指标转换为3个主成分,应用隶属函数和权重,获得了客观评价粳稻种质资源耐盐性的综合评价值 D。分别选取D值最高和最低的5份种质资源进行芽期耐盐指标的差异显著性分析,结果表明,两组种质资源盐胁迫5 d的各评价指标差异均达到极显著水平,10 d的评价指标除相对芽长外,均达到了显著差异水平。【结论】 水稻芽期对盐胁迫较为敏感,且耐盐性不同的种质间差异显著。利用逐步回归和主成分分析获得发芽指数、相对根长和相对盐害率3个指标,可作为快速鉴定粳稻种质资源芽期耐盐性的重要指标,若采用多元统计方法评价可靠性更高。
中图分类号:
田蕾, 陈亚萍, 刘俊, 马晓刚, 王娜, 杨兵, 李莹, 郭海东, 李娟, 胡慧, 张银霞, 李培富. 粳稻种质资源芽期耐盐性综合评价与筛选[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(6): 631-642.
Lei TIAN, Yaping CHEN, Jun LIU, Xiaogang MA, Na WANG, Bing YANG, Ying LI, Haidong GUO, Juan LI, Hui HU, Yinxia ZHANG, Peifu LI. Comprehensive Evaluation and Selection of Rice (Oryza sativa japonica) Germplasm for Saline Tolerance at Germination Stage[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2017, 31(6): 631-642.
| 编号ID. | 种质资源名称 Name of germplasm | 原产地或来源 Origin | D值 D value | 排名 Ranking | 编号ID. | 种质资源名称 Name of germplasm | 原产地或来源 Origin | D值 D value | 排名Ranking |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OB1 | 合江21 Hejiang 21 | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 0.235 | 63 | OB33 | 罗平懒汉谷 Luopinglanhangu | 云南 Yunnan | 0.819 | 6 |
| OB2 | 吉粳44 Jijing 44 | 吉林 Jilin | 0.540 | 50 | OB34 | Daniela | 巴西 Brazil | 0.961 | 1 |
| OB3 | Hungarian No.1 | 澳大利亚 Australia | 0.594 | 45 | OB35 | Arborio | 意大利 Italy | 0.843 | 4 |
| OB4 | Banat 725 | 澳大利亚 Australia | 0.709 | 16 | OB36 | 湟罗 Huangluo | 苏联 The Soviet Union | 0.810 | 8 |
| OB5 | 东北小粒种 Dongbeixiaolizhong | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 0.491 | 56 | OB37 | Gostima | 阿尔巴尼亚 Aerbaerya | 0.868 | 2 |
| OB6 | 罗萨马启蒂Rosa Marchetti | 意大利 Italy | 0.715 | 15 | OB38 | Rocca | 意大利 Italy | 0.722 | 12 |
| OB7 | 意大利3号Italy 3 | 意大利 Italy | 0.769 | 10 | OB39 | 越光 Koshihikari | 日本 Japan | 0.670 | 27 |
| OB8 | Roma | 意大利 Italy | 0.548 | 47 | OB40 | 水原1号 Suwon 1 | 韩国 Korea | 0.719 | 13 |
| OB9 | Banat2951 | 澳大利亚 Australia | 0.638 | 35 | OB41 | Rossi | 意大利 Italy | 0.823 | 5 |
| OB10 | Cigalon | 法国 France | 0.666 | 29 | OB42 | 京香2号 Jingxiang 2 | 北京 Peking | 0.535 | 51 |
| OB11 | Agostono | 意大利 Italy | 0.645 | 33 | OB43 | 幸实 Sachiminori | 日本 Japan | 0.542 | 49 |
| OB12 | Rizzotto | 意大利 Italy | 0.521 | 54 | OB44 | 咸南22 Xiannan 22 | 朝鲜 North Korea | 0.698 | 22 |
| OB13 | 水原55 Suwon 55 | 韩国 Korea | 0.642 | 34 | OB45 | Hrborio Cyauco | 南斯拉夫 Yugoslavia | 0.851 | 3 |
| OB14 | 秋铃 Qiuling | 安徽 Anhui | 0.546 | 48 | OB46 | 新竹8号 Xinzhu 8 | 台湾 Taiwan | 0.684 | 24 |
| OB15 | 宁粳16 Ningjing 16 | 宁夏 Ningxia | 0.211 | 64 | OB47 | 镇稻2号 Zhendao 2 | 江苏 Jiangsu | 0.701 | 21 |
| OB16 | 嘉南8号 Jianan 8 | 台湾 Taiwan | 0.607 | 43 | OB48 | 嘉农485 Jianong 485 | 上海 Shanghai | 0.299 | 62 |
| OB17 | Balilla | 意大利 Italy | 0.610 | 42 | OB49 | YR251 | 澳大利亚 Australia | 0.795 | 9 |
| OB18 | 荒木 Araki | 日本 Japan | 0.502 | 55 | OB50 | Calrose | 美国 America | 0.675 | 26 |
| OB19 | 加合1号 Jiahe 1 | 浙江 Zhejiang | 0.428 | 58 | OB51 | 山福利亚 Shanfuliya | 西非几内亚 Guinea | 0.705 | 19 |
| OB20 | 嘉湖3号 Jiahu 3 | 浙江 Zhejiang | 0.636 | 37 | OB52 | 日本晴 Nipponbare | 日本 Japan | 0.651 | 31 |
| OB21 | Cristal | 法国 France | 0.633 | 38 | OB53 | 中花17 Zhonghua 17 | 北京 Peking | 0.623 | 40 |
| OB22 | 漾濞光壳陆稻Yangbiguangkeludao | 云南 Yunnan | 0.814 | 7 | OB54 | 早生光头 Zaoshengguangtou | 东北 Northeast of China | 0.603 | 44 |
| OB23 | Bertone | 葡萄牙 Portugal | 0.716 | 14 | OB55 | 小白芒 Xiaobaimang | 浙江 Zhejiang | 0.709 | 17 |
| OB24 | Farry | 法国 France | 0.528 | 52 | OB56 | 法国稻 Faguodao | 法国 France | 0.637 | 36 |
| OB25 | 中花9号 Zhonghua 9 | 北京 Beijing | 0.525 | 53 | OB57 | 陆羽132 Luyu 132 | 日本 Japan | 0.681 | 25 |
| OB26 | Amepukahmib | 意大利 Italy | 0.669 | 28 | OB58 | 芦苇稻 Luweidao | 东北 Northeast of China | 0.745 | 11 |
| OB27 | Kele (34978) | 孟加拉 Bengal | 0.484 | 57 | OB59 | 红尖 Hongjian | 浙江 Zhejiang | 0.648 | 32 |
| OB28 | Galhardo | 葡萄牙 Portugal | 0.706 | 18 | OB60 | 早糯稻 Zaonuodao | 山东 Shandong | 0.702 | 20 |
| OB29 | Kele (34979) | 孟加拉 Bengal | 0.629 | 39 | OB61 | 露水稻 Lushuidao | 河南 Henan | 0.570 | 46 |
| OB30 | 辽丰8号 Liaofeng 8 | 辽宁 Liaoning | 0.361 | 60 | OB62 | 永德3号 Yongde 3 | 韩国 Korea | 0.611 | 41 |
| OB31 | 千重浪 Qianchonglang | 日本 Japan | 0.394 | 59 | OB63 | 新竹4号 Xinzhu 4 | 台湾 Taiwan | 0.685 | 23 |
| OB32 | 圭陆1号 Guilu 1 | 云南 Yunnan | 0.660 | 30 | OB64 | ARC7042 | 印度 India | 0.313 | 61 |
表1 64份粳稻种质资源名称、来源、综合评价值及排名
Table 1 Origin and names of 64 japonica rice germplasm and their D values, comprehensive ranking.
| 编号ID. | 种质资源名称 Name of germplasm | 原产地或来源 Origin | D值 D value | 排名 Ranking | 编号ID. | 种质资源名称 Name of germplasm | 原产地或来源 Origin | D值 D value | 排名Ranking |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OB1 | 合江21 Hejiang 21 | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 0.235 | 63 | OB33 | 罗平懒汉谷 Luopinglanhangu | 云南 Yunnan | 0.819 | 6 |
| OB2 | 吉粳44 Jijing 44 | 吉林 Jilin | 0.540 | 50 | OB34 | Daniela | 巴西 Brazil | 0.961 | 1 |
| OB3 | Hungarian No.1 | 澳大利亚 Australia | 0.594 | 45 | OB35 | Arborio | 意大利 Italy | 0.843 | 4 |
| OB4 | Banat 725 | 澳大利亚 Australia | 0.709 | 16 | OB36 | 湟罗 Huangluo | 苏联 The Soviet Union | 0.810 | 8 |
| OB5 | 东北小粒种 Dongbeixiaolizhong | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 0.491 | 56 | OB37 | Gostima | 阿尔巴尼亚 Aerbaerya | 0.868 | 2 |
| OB6 | 罗萨马启蒂Rosa Marchetti | 意大利 Italy | 0.715 | 15 | OB38 | Rocca | 意大利 Italy | 0.722 | 12 |
| OB7 | 意大利3号Italy 3 | 意大利 Italy | 0.769 | 10 | OB39 | 越光 Koshihikari | 日本 Japan | 0.670 | 27 |
| OB8 | Roma | 意大利 Italy | 0.548 | 47 | OB40 | 水原1号 Suwon 1 | 韩国 Korea | 0.719 | 13 |
| OB9 | Banat2951 | 澳大利亚 Australia | 0.638 | 35 | OB41 | Rossi | 意大利 Italy | 0.823 | 5 |
| OB10 | Cigalon | 法国 France | 0.666 | 29 | OB42 | 京香2号 Jingxiang 2 | 北京 Peking | 0.535 | 51 |
| OB11 | Agostono | 意大利 Italy | 0.645 | 33 | OB43 | 幸实 Sachiminori | 日本 Japan | 0.542 | 49 |
| OB12 | Rizzotto | 意大利 Italy | 0.521 | 54 | OB44 | 咸南22 Xiannan 22 | 朝鲜 North Korea | 0.698 | 22 |
| OB13 | 水原55 Suwon 55 | 韩国 Korea | 0.642 | 34 | OB45 | Hrborio Cyauco | 南斯拉夫 Yugoslavia | 0.851 | 3 |
| OB14 | 秋铃 Qiuling | 安徽 Anhui | 0.546 | 48 | OB46 | 新竹8号 Xinzhu 8 | 台湾 Taiwan | 0.684 | 24 |
| OB15 | 宁粳16 Ningjing 16 | 宁夏 Ningxia | 0.211 | 64 | OB47 | 镇稻2号 Zhendao 2 | 江苏 Jiangsu | 0.701 | 21 |
| OB16 | 嘉南8号 Jianan 8 | 台湾 Taiwan | 0.607 | 43 | OB48 | 嘉农485 Jianong 485 | 上海 Shanghai | 0.299 | 62 |
| OB17 | Balilla | 意大利 Italy | 0.610 | 42 | OB49 | YR251 | 澳大利亚 Australia | 0.795 | 9 |
| OB18 | 荒木 Araki | 日本 Japan | 0.502 | 55 | OB50 | Calrose | 美国 America | 0.675 | 26 |
| OB19 | 加合1号 Jiahe 1 | 浙江 Zhejiang | 0.428 | 58 | OB51 | 山福利亚 Shanfuliya | 西非几内亚 Guinea | 0.705 | 19 |
| OB20 | 嘉湖3号 Jiahu 3 | 浙江 Zhejiang | 0.636 | 37 | OB52 | 日本晴 Nipponbare | 日本 Japan | 0.651 | 31 |
| OB21 | Cristal | 法国 France | 0.633 | 38 | OB53 | 中花17 Zhonghua 17 | 北京 Peking | 0.623 | 40 |
| OB22 | 漾濞光壳陆稻Yangbiguangkeludao | 云南 Yunnan | 0.814 | 7 | OB54 | 早生光头 Zaoshengguangtou | 东北 Northeast of China | 0.603 | 44 |
| OB23 | Bertone | 葡萄牙 Portugal | 0.716 | 14 | OB55 | 小白芒 Xiaobaimang | 浙江 Zhejiang | 0.709 | 17 |
| OB24 | Farry | 法国 France | 0.528 | 52 | OB56 | 法国稻 Faguodao | 法国 France | 0.637 | 36 |
| OB25 | 中花9号 Zhonghua 9 | 北京 Beijing | 0.525 | 53 | OB57 | 陆羽132 Luyu 132 | 日本 Japan | 0.681 | 25 |
| OB26 | Amepukahmib | 意大利 Italy | 0.669 | 28 | OB58 | 芦苇稻 Luweidao | 东北 Northeast of China | 0.745 | 11 |
| OB27 | Kele (34978) | 孟加拉 Bengal | 0.484 | 57 | OB59 | 红尖 Hongjian | 浙江 Zhejiang | 0.648 | 32 |
| OB28 | Galhardo | 葡萄牙 Portugal | 0.706 | 18 | OB60 | 早糯稻 Zaonuodao | 山东 Shandong | 0.702 | 20 |
| OB29 | Kele (34979) | 孟加拉 Bengal | 0.629 | 39 | OB61 | 露水稻 Lushuidao | 河南 Henan | 0.570 | 46 |
| OB30 | 辽丰8号 Liaofeng 8 | 辽宁 Liaoning | 0.361 | 60 | OB62 | 永德3号 Yongde 3 | 韩国 Korea | 0.611 | 41 |
| OB31 | 千重浪 Qianchonglang | 日本 Japan | 0.394 | 59 | OB63 | 新竹4号 Xinzhu 4 | 台湾 Taiwan | 0.685 | 23 |
| OB32 | 圭陆1号 Guilu 1 | 云南 Yunnan | 0.660 | 30 | OB64 | ARC7042 | 印度 India | 0.313 | 61 |
| NaCl 浓度 NaCl Concentration /(mmol·L-1) | 芽期耐盐性 Salt tolerance | 相对发芽势 Relative germination potential/% | 相对盐害率 Relative salt damage rate /% | 相对芽长 Relative shoot length/% | 相对根长 Relative root length/% | 发芽指数 Germination index | 活力指数 Vigor index | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 d | 10 d | 5 d | 10 d | 5 d | 10 d | 5 d | 10 d | 10 d | 10 d | ||||||
| 0 | 耐盐 ST | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 14.5±0.1 A | 423.9±8.9 A | ||||
| 盐敏感 SS | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 14.8±0.3 A | 396.8±39.2 A | |||||
| 50 | 耐盐 ST | 96.6±2.7 A | 97.8±2.3 A | 3.4±2.7 A | 2.2±2.3 A | 63.7±2.4 A | 68.5±3.6 A | 69.1±1.1 A | 38.0±2.9 A | 14.4±0.4 A | 160.2±19.6 A | ||||
| 盐敏感 SS | 97.7±2.4 A | 98.2±1.9 A | 2.3±2.4 A | 1.8±1.9 A | 61.3±6.8 A | 62.6±7.8 A | 53.4±11.0 A | 35.5±3.3 A | 14.5±0.5 A | 137.9±11.5 A | |||||
| 100 | 耐盐 ST | 89.7±3.3 A | 94.8±2.8 A | 10.3±3.3 A | 5.2±2.8 A | 46.9±7.7 A | 24.5±1.1 A | 20.2±1.4 A | 13.0±3.1 A | 13.5±0.2 A | 51.5±12.2 A | ||||
| 盐敏感 SS | 85.6±5.6 A | 96.4±3.3 A | 14.4±5.6 A | 3.6±3.3 A | 38.4±2.7 A | 23.6±4.3 A | 16.1±2.7 A | 7.8±1.7 B | 13.2±0.4 A | 27.4±4.6 B | |||||
| 125 | 耐盐 ST | 84.6±4.9 A | 89.3±3.8 A | 15.4±4.9 A | 10.7±3.8 A | 48.5±2.5 A | 27.8±0.4 A | 25.8±1.8 A | 9.9±1.6 A | 13.1±0.4 A | 38.1±6.6 A | ||||
| 盐敏感 SS | 46.4±10.2 B | 64.2±4.9 B | 53.6±10.2 B | 35.8±5.0 B | 37.3±1.2 B | 20.7±0.6 B | 13.5±1.5 B | 6.4±0.3 B | 8.4±0.8 B | 14.2±0.7 B | |||||
| 150 | 耐盐 ST | 62.3±4.9 A | 73.4±5.5 A | 37.7±4.9 A | 26.6±5.5 A | 41.3±2.0 A | 27.4±3.3 A | 16.2±1.8 A | 11.0±0.9 A | 9.2±0.1 A | 29.5±1.6 A | ||||
| 盐敏感 SS | 48.5±9.4 B | 62.0±4.8 B | 51.5±9.4 B | 38.0±4.8 B | 38.0±1.8 A | 22.0±1.9 A | 12.3±0.8 B | 7.2±0.7 B | 7.9±0.5 B | 15.1±1.4 B | |||||
| 175 | 耐盐 ST | 34.2±4.9 A | 59.6±3.8 A | 65.8±4.9 A | 40.4±3.8 A | 28.7±2.2 A | 21.0±1.8 A | 7.6±2.3 A | 5.3±1.7 A | 6.3±0.7 A | 9.7±2.2 A | ||||
| 盐敏感 SS | 29.5±4.6 A | 51.4±9.9 A | 70.5±4.6 A | 48.6±9.9 A | 28.4±0.7 A | 18.5±1.7 A | 7.5±1.6 A | 4.7±0.7 A | 5.5±0.6 A | 7.0±2.5 A | |||||
| 200 | 耐盐 ST | 12.2±2.6 A | 47.4±4.5 A | 87.8±2.6 A | 52.6±4.5 A | 27.2±0.9 A | 20.4±0.6 A | 6.6±1.7 A | 5.2±0.7 A | 3.3±0.1 A | 5.1±0.5 A | ||||
| 盐敏感 SS | 9.2±3.9 A | 43.8±4.2 A | 90.8±3.9 A | 56.2±4.2 A | 28.1±0.5 A | 17.1±1.4 A | 6.4±0.2 A | 4.5±0.6 A | 3.1±0.2 A | 3.2±1.0 A | |||||
表2 典型耐盐和盐敏感粳稻种质资源在不同浓度NaCl胁迫条件下芽期各评价指标表现
Table 2 Phenotypic values of typical salt-tolerant and sensitive rice germplasm accessions under different NaCl concentrations at seed germination stage.
| NaCl 浓度 NaCl Concentration /(mmol·L-1) | 芽期耐盐性 Salt tolerance | 相对发芽势 Relative germination potential/% | 相对盐害率 Relative salt damage rate /% | 相对芽长 Relative shoot length/% | 相对根长 Relative root length/% | 发芽指数 Germination index | 活力指数 Vigor index | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 d | 10 d | 5 d | 10 d | 5 d | 10 d | 5 d | 10 d | 10 d | 10 d | ||||||
| 0 | 耐盐 ST | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 14.5±0.1 A | 423.9±8.9 A | ||||
| 盐敏感 SS | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 14.8±0.3 A | 396.8±39.2 A | |||||
| 50 | 耐盐 ST | 96.6±2.7 A | 97.8±2.3 A | 3.4±2.7 A | 2.2±2.3 A | 63.7±2.4 A | 68.5±3.6 A | 69.1±1.1 A | 38.0±2.9 A | 14.4±0.4 A | 160.2±19.6 A | ||||
| 盐敏感 SS | 97.7±2.4 A | 98.2±1.9 A | 2.3±2.4 A | 1.8±1.9 A | 61.3±6.8 A | 62.6±7.8 A | 53.4±11.0 A | 35.5±3.3 A | 14.5±0.5 A | 137.9±11.5 A | |||||
| 100 | 耐盐 ST | 89.7±3.3 A | 94.8±2.8 A | 10.3±3.3 A | 5.2±2.8 A | 46.9±7.7 A | 24.5±1.1 A | 20.2±1.4 A | 13.0±3.1 A | 13.5±0.2 A | 51.5±12.2 A | ||||
| 盐敏感 SS | 85.6±5.6 A | 96.4±3.3 A | 14.4±5.6 A | 3.6±3.3 A | 38.4±2.7 A | 23.6±4.3 A | 16.1±2.7 A | 7.8±1.7 B | 13.2±0.4 A | 27.4±4.6 B | |||||
| 125 | 耐盐 ST | 84.6±4.9 A | 89.3±3.8 A | 15.4±4.9 A | 10.7±3.8 A | 48.5±2.5 A | 27.8±0.4 A | 25.8±1.8 A | 9.9±1.6 A | 13.1±0.4 A | 38.1±6.6 A | ||||
| 盐敏感 SS | 46.4±10.2 B | 64.2±4.9 B | 53.6±10.2 B | 35.8±5.0 B | 37.3±1.2 B | 20.7±0.6 B | 13.5±1.5 B | 6.4±0.3 B | 8.4±0.8 B | 14.2±0.7 B | |||||
| 150 | 耐盐 ST | 62.3±4.9 A | 73.4±5.5 A | 37.7±4.9 A | 26.6±5.5 A | 41.3±2.0 A | 27.4±3.3 A | 16.2±1.8 A | 11.0±0.9 A | 9.2±0.1 A | 29.5±1.6 A | ||||
| 盐敏感 SS | 48.5±9.4 B | 62.0±4.8 B | 51.5±9.4 B | 38.0±4.8 B | 38.0±1.8 A | 22.0±1.9 A | 12.3±0.8 B | 7.2±0.7 B | 7.9±0.5 B | 15.1±1.4 B | |||||
| 175 | 耐盐 ST | 34.2±4.9 A | 59.6±3.8 A | 65.8±4.9 A | 40.4±3.8 A | 28.7±2.2 A | 21.0±1.8 A | 7.6±2.3 A | 5.3±1.7 A | 6.3±0.7 A | 9.7±2.2 A | ||||
| 盐敏感 SS | 29.5±4.6 A | 51.4±9.9 A | 70.5±4.6 A | 48.6±9.9 A | 28.4±0.7 A | 18.5±1.7 A | 7.5±1.6 A | 4.7±0.7 A | 5.5±0.6 A | 7.0±2.5 A | |||||
| 200 | 耐盐 ST | 12.2±2.6 A | 47.4±4.5 A | 87.8±2.6 A | 52.6±4.5 A | 27.2±0.9 A | 20.4±0.6 A | 6.6±1.7 A | 5.2±0.7 A | 3.3±0.1 A | 5.1±0.5 A | ||||
| 盐敏感 SS | 9.2±3.9 A | 43.8±4.2 A | 90.8±3.9 A | 56.2±4.2 A | 28.1±0.5 A | 17.1±1.4 A | 6.4±0.2 A | 4.5±0.6 A | 3.1±0.2 A | 3.2±1.0 A | |||||
| 发芽时间Germination time/d | 性状 Trait | 分布范围 Range | 均值±标准差 Mean±SD | F值 F-value | t值 t-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 相对芽长 Relative shoot length/% | 0.0~76.1 | 31.4±13.1 | 38.867 | 11.874** |
| 相对根长 Relative root length/% | 0.0~23.1 | 4.6±4.1 | 134.862 | 18.869** | |
| 相对发芽势 Relative germination potential/% | 0.8~100.0 | 81.0±25.8 | 49.951 | 5.225** | |
| 相对盐害率 Relative salt damage rate/% | 0.0~99.2 | 19.0±9.4 | – | – | |
| 10 | 相对芽长 Relative shoot length/% | 7.3~40.7 | 18.1±5.6 | 48.184 | 22.891** |
| 相对根长 Relative root length/% | 0.6~13.4 | 4.7±2.5 | 77.975 | 30.868** | |
| 相对发芽率 Relative germination rate/% | 58.9~100.0 | 94.9±7.4 | 21.272 | 4.238** | |
| 发芽指数 Germination index | 2.1~14.9 | 12.7±3.0 | 39.713 | 5.096** | |
| 活力指数 Vigor index | 1.7~67.7 | 27.5±15.4 | 73.327 | 30.660** | |
| 相对盐害率 Relative salt damage rate/% | 0.0~41.1 | 5.1±7.4 | – | – |
表3 粳稻种质资源盐胁迫条件下芽期各评价指标均值及分布范围
Table 3 Performance of salt tolerance-related traits of 64 rice germplasm accessions at seed germination stage
| 发芽时间Germination time/d | 性状 Trait | 分布范围 Range | 均值±标准差 Mean±SD | F值 F-value | t值 t-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 相对芽长 Relative shoot length/% | 0.0~76.1 | 31.4±13.1 | 38.867 | 11.874** |
| 相对根长 Relative root length/% | 0.0~23.1 | 4.6±4.1 | 134.862 | 18.869** | |
| 相对发芽势 Relative germination potential/% | 0.8~100.0 | 81.0±25.8 | 49.951 | 5.225** | |
| 相对盐害率 Relative salt damage rate/% | 0.0~99.2 | 19.0±9.4 | – | – | |
| 10 | 相对芽长 Relative shoot length/% | 7.3~40.7 | 18.1±5.6 | 48.184 | 22.891** |
| 相对根长 Relative root length/% | 0.6~13.4 | 4.7±2.5 | 77.975 | 30.868** | |
| 相对发芽率 Relative germination rate/% | 58.9~100.0 | 94.9±7.4 | 21.272 | 4.238** | |
| 发芽指数 Germination index | 2.1~14.9 | 12.7±3.0 | 39.713 | 5.096** | |
| 活力指数 Vigor index | 1.7~67.7 | 27.5±15.4 | 73.327 | 30.660** | |
| 相对盐害率 Relative salt damage rate/% | 0.0~41.1 | 5.1±7.4 | – | – |
| 指标 Index | X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | 1.000 | |||||||
| X2 | 0.180 | 1.000 | ||||||
| X3 | 0.010 | 0.524** | 1.000 | |||||
| X4 | –0.125 | 0.394** | 0.734** | 1.000 | ||||
| X5 | –0.011 | 0.510** | 0.978** | 0.816** | 1.000 | |||
| X6 | 0.071 | 0.877** | 0.654** | 0.537** | 0.658** | 1.000 | ||
| X7 | –0.035 | –0.404** | –0.767** | –0.780** | –0.860** | –0.510** | 1.000 | |
| X8 | 0.289* | 0.269* | 0.300* | 0.143 | 0.282* | 0.424** | –0.143 | 1.000 |
表4 盐胁迫处理下水稻芽期各单项指标与苗期耐盐级别的相关系数矩阵
Table 4 Correlation matrix of each single index of rice seed germination and salt tolerance score under salt stress.
| 指标 Index | X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | 1.000 | |||||||
| X2 | 0.180 | 1.000 | ||||||
| X3 | 0.010 | 0.524** | 1.000 | |||||
| X4 | –0.125 | 0.394** | 0.734** | 1.000 | ||||
| X5 | –0.011 | 0.510** | 0.978** | 0.816** | 1.000 | |||
| X6 | 0.071 | 0.877** | 0.654** | 0.537** | 0.658** | 1.000 | ||
| X7 | –0.035 | –0.404** | –0.767** | –0.780** | –0.860** | –0.510** | 1.000 | |
| X8 | 0.289* | 0.269* | 0.300* | 0.143 | 0.282* | 0.424** | –0.143 | 1.000 |
| 主成分 Principal component | 特征值 Eigen value | 贡献率 Contribution/% | 累计贡献率 Cumulative contribution/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| CI1 | 4.37 | 62.45 | 62.45 |
| CI2 | 1.20 | 17.14 | 79.60 |
| CI3 | 0.84 | 11.95 | 91.55 |
| CI4 | 0.29 | 4.13 | 95.68 |
| CI5 | 0.20 | 2.82 | 98.50 |
| CI6 | 0.10 | 1.42 | 99.92 |
| CI7 | 0.01 | 0.08 | 100.00 |
表5 各综合指标的特征值及贡献率
Table 5 Eigen values and proportion of comprehensive indexes [Clx].
| 主成分 Principal component | 特征值 Eigen value | 贡献率 Contribution/% | 累计贡献率 Cumulative contribution/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| CI1 | 4.37 | 62.45 | 62.45 |
| CI2 | 1.20 | 17.14 | 79.60 |
| CI3 | 0.84 | 11.95 | 91.55 |
| CI4 | 0.29 | 4.13 | 95.68 |
| CI5 | 0.20 | 2.82 | 98.50 |
| CI6 | 0.10 | 1.42 | 99.92 |
| CI7 | 0.01 | 0.08 | 100.00 |
| X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CI1 | 0.015 | 0.337 | 0.442 | 0.403 | 0.457 | 0.389 | –0.410 |
| CI2 | 0.707 | 0.490 | –0.009 | –0.288 | –0.152 | 0.331 | 0.185 |
| CI3 | –0.685 | 0.442 | –0.125 | –0.109 | –0.161 | 0.425 | 0.318 |
表6 各因子载荷矩阵
Table 6 Loading matrix of each component.
| X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CI1 | 0.015 | 0.337 | 0.442 | 0.403 | 0.457 | 0.389 | –0.410 |
| CI2 | 0.707 | 0.490 | –0.009 | –0.288 | –0.152 | 0.331 | 0.185 |
| CI3 | –0.685 | 0.442 | –0.125 | –0.109 | –0.161 | 0.425 | 0.318 |
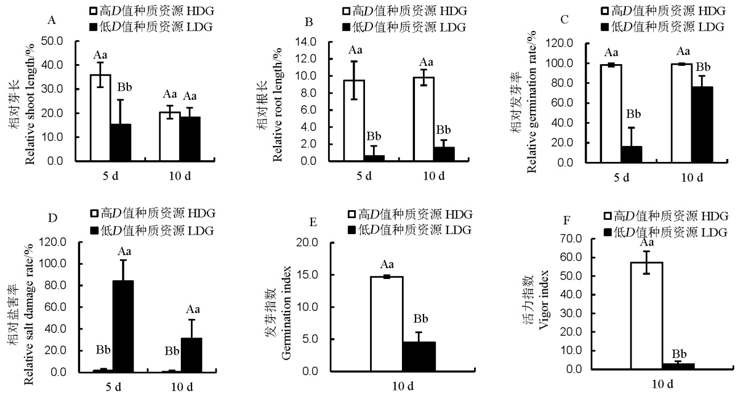
图2 125 mmol/L NaCl 胁迫下典型耐(敏)盐粳稻种质资源芽期形态指标表现柱上不同小写和大写字母分别表示差异显著和极显著(LSD, n=30)。
Fig. 2. Morphology indexes of typical salt tolerant and sensitive japonica rice germplasm at germination stage under salt stress. HDG, High D value germplasm; LDG, Low D value germplasm different lowercase and uppercase letters above the bars indicate significant difference at P≤0.01 and P≤0.05, respectively by the LSD test(n=30).
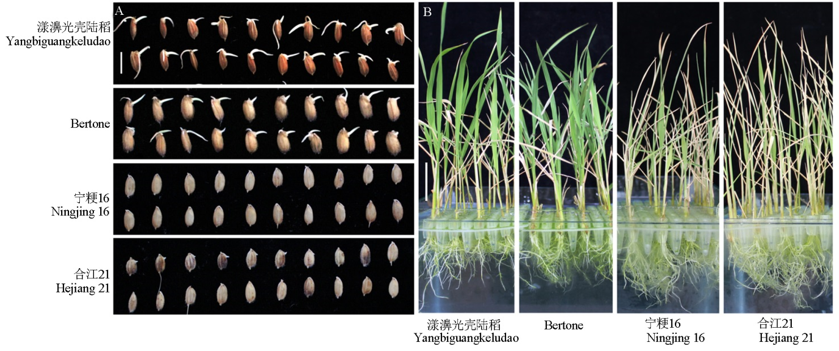
图3 125 mmol/L NaCl胁迫条件下典型耐盐和盐敏感水稻种质资源的表现型 A–125 mmol/L NaCl胁迫下发芽5 d; B–125 mmol/L NaCl胁迫6 d的秧苗;标尺=0.8 cm (A)、2.5 cm (B)。
Fig. 3. Phenotypes of two salt tolerant rice germplasm accessions and two salt sensitive rice germplasm accessions under 125 mmol/L NaCl for five and six days, respectively in germination and seedling stages. A, Seeds of four japonica rice germplasm accessions germinated in the 125 mmol/L NaCl solution for five days; B, Seedlings of four japonica rice germplasm accessions treated with 125 mmol/L NaCl for six days; Scale bar, 0.8 cm (A) and 2.5 cm (B).
| [1] | 张翼夫, 李洪文, 胡红, 陈婉芝, 王宪良, 牛琪. 盐碱地后悬挂随动式打孔通气机的设计与试验. 农业工程学报, 2016, 32(18): 42-49. |
| Zhang Y F, Li H W, Hu H, Chen W Z, Wang X L, Niu Q.Design and experiment on rear suspended passive aerator in saline-alkali land.Trans Chin Soc Agric Eng, 2016, 32(18): 42-49. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | Wang X, Wang J G, Liu H L, Zou D T, Zhao H W.Influence of natural saline-alkali stress on chlorophyll content and chloroplast ultrastructure of two contrasting rice (Oryza sativa L. japonica) cultivars. Aust J Crop Sci, 2013, 7(2): 289-292. |
| [3] | 王善仙, 刘宛, 李培军, 吴海燕. 盐碱土植物改良研究进展. 中国农学通报, 2011, 27(24): 1-7. |
| Wang S X, Liu W, Li P J, Wu H Y.Advances of researches in plant-improvement of saline-alkaline soil.Chin Agric Sci Bull, 2011, 27(24): 1-7. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | Yu J B, Wang Z C, Meixner F X, Yang F, Wu H F, Chen X B.Biogeochemical characterizations and reclamation strategies of saline sodic soil in northeastern China.Clean-Soil, Air, Water, 2010, 38(11): 1010-1016. |
| [5] | Tian L, Tan L B, Liu F X, Cai H W, Sun C Q.Identification of quantitative trait loci associated with salt tolerance at seedling stage fromOryza rufipogon. J Genet Genom, 2011, 38(12): 593-601. |
| [6] | 曾玲玲, 季生栋, 王俊强, 张成亮, 赵刚. 植物耐盐机理的研究进展. 黑龙江农业科学, 2009(3): 156-159. |
| Zeng L L, Ji S D,Wang J Q, Zhang C L, Zhao G.Advances on the mechanism of plant salt tolerance.Heilongjiang Agric Sci, 2009(3): 156-159. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | Wang Z F, Cheng J P, Chen Z W, Huang J, Bao Y M, Wang J F, Zhang H S.Identification of QTLs with main, epistatic and QTL×environment interaction effects for salt tolerance in rice seedlings under different salinity conditions.Theor Appl Genet, 2012, 125(4): 807-815. |
| [8] | Ghaffaria A, Gharechahib J, Nakhodaa B, Salekdeh G H.Physiology and proteome responses of two contrasting rice mutants and their wild type parent under salt stress conditions at the vegetative stage. J Plant Physiol, 2014, 171(1): 31-44. |
| [9] | Wang Z F, Wang J F, Bao Y M, Wu Y Y, Zhang H S.Quantitative trait loci controlling rice seed germination under salt stress.Euphytica, 2011, 178(3): 297-307. |
| [10] | 肖文斐, 马华升, 陈文岳, 裘劼人, 童建新, 郑桂珍, 忻雅, 王淑珍, 方献平, 阮松林. 籼稻耐盐性与稻米品质性状的关联分析. 核农学报, 2013, 27(12): 1938-1947. |
| Xiao W F, Ma H S, Chen W Y, Qiu J R, Tong J X, Zheng G Z, Xin Y, Wang S Z, Fang X P, Ruan S L.Correlation analysis of salt tolerance and grain quality traits inIndica rice(Oryza sativa L.). Acta Agric Nucl Sin, 2013, 27(12): 1938-1947. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 郭望模, 傅亚萍, 孙宗修, 郑镇一. 盐胁迫下不同水稻种质形态指标与耐盐性的相关分析. 植物遗传资源学报, 2003, 4(3): 245-251. |
| Guo W M, Fu Y P, Sun Z X, Zheng Z Y.The Correlation analysis between the morphological indices and salt tolerance in different rice germplasm under the salt stress.J Plant Genet Resour, 2003, 4(3): 245-251. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 贾宝艳, 周婵婵, 孙晓雪, 董立强, 黄元财, 王岩, 王术. 辽宁省水稻种质资源的耐盐性鉴定评价. 作物杂志, 2013, 4: 57-62. |
| Jia B Y, Zhou C C, Sun X X, Dong L Q, Hang Y C, Wang Y, Wang S.The evaluation of salt tolerance ability of rice varieties in Liaoning Province.Crops, 2013, 4: 57-62. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | Wang Z F, Wang J F, Bao Y M, Wu Y Y, Su X, Zang H S.Inheritance of rice seed germination ability under salt stress.Rice Sci, 2010, 17(2): 105-110. |
| [14] | Chen D F, Li Y L, Fang T, Shi X L, Chen X W.Specific roles of tocopherols and tocotrienols in seed longevity and germination tolerance to abiotic stress in transgenic rice.Plant Sci, 2016, 244: 31-39. |
| [15] | Hasthanasombut S, Supaibulwatana K, Mii M, Nakamura I.Genetic manipulation of japonica rice using theOsBADH1 gene from Indica rice to improve salinity tolerance. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult, 2011, 104(1): 79-89. |
| [16] | 冯钟慧, 刘晓龙, 姜昌杰, 梁正伟. 吉林省粳稻种质萌发期耐碱性和耐盐性综合评价. 土壤与作物, 2016, 5(2): 120-127. |
| Feng Z H, Liu X L, Jiang C J, Liang Z W.Comprehensive evaluation of rice(Oryza sativa japonica) germplasm for alkaline /saline tolerance at germination stage from Jilin province, China. Soil Crop, 2016, 5(2): 120-127. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | 朱丽伟, 曹栋栋, 付玉营, 胡琦娟, 利站, 关亚静, 胡伟民, 胡晋. 可溶性寡糖和小分子的热激蛋白与杂交水稻种子成熟过程中发芽能力及种子活力相关. 作物学报, 2016, 42(5): 714-724. |
| Zhu L W, Cao D D, Fu Y Y, Hu Q J, Li Z, Guan Y J, Hu W M, Hu J.Soluble oligosaccharide and small heat shock protein correlated with seed germination and vigor during hybrid rice seed maturation.Acta Agron Sin, 2016, 42(5): 714-724. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | 鱼小军, 肖红, 徐长林, 景媛媛, 柴成燕. 扁蓿豆和苜蓿种子萌发期抗旱性和耐盐性比较. 植物遗传资源学报, 2015, 16(2): 405-410. |
| Yu X J, Xiao H, Xu C L, Jing Y Y, Chai C Y.Comparative study on drought resistance and salt tolerance ofMedicago ruthenica and Medicago varia at seed germination period. J Plant Genet Resour, 2015, 16(2): 405-410. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | 李振, 廖同庆, 冯青春, 张东彦, 王强, 王晓楠, 张琳洁, 王秀. 基于图像处理技术的黄瓜种子活力指数检测系统设计. 种子, 2015, 34(6): 111-115. |
| Li Z, Liao T Q, Feng Q C, Zhang D Y, Wang Q, Wang X N, Zhang L J, Wang X.A system design on cucumber seed vigor index detection on based on image processing.Seed, 2015, 34(6): 111-115. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | 戴海芳, 武辉, 阿曼古丽.买买提阿力, 王立红, 麦麦提.阿皮孜, 张巨松. 不同基因型棉花苗期耐盐性分析及其鉴定指标筛选. 中国农业科学, 2014, 47(7): 1290-1300. |
| Dai H F, Wu H, Amanguli M A, Wang L H, Maimaiti A, Zhang J S.Analysis of salt-tolerance and determination of salt-tolerant evaluation indicators in cotton seedlings of different genotypes.Sci Agric Sin, 2014, 47(7): 1290-1300. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | 齐国昌, 余春磊, 张鹍飞, 罗小娇, 冯宗云. 青稞苗期耐盐性鉴定及评价. 麦类作物学报, 2014, 37(7): 950-956. |
| Qi G C, Yu C L, Zhang K F, Luo X J, Feng Z Y.Identification and assessment on salt resistance of hulless barley at seedling stage.J Triticeae Crops, 2014, 37(7): 950-956. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | 管志勇, 陈发棣, 滕年军, 陈素梅, 刘浦生. 5种菊花近缘种属植物的耐盐性比较. 中国农业科学, 2010,43(4): 784-787. |
| Guan Z Y, Chen F D, Teng N J, Chen S M, Liu P S.Study on the NaCl tolerance in five plant species fromDendranthema and its relatives. Sci Agric Sin, 2010,43(4): 784-787. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 田蕾, 王娜, 张雪艳, 杨斌林, 孙佳莹, 李敏, 李培富. 盐胁迫下不同粳稻品种的形态和生理特性. 广东农业科学, 2014, 41(23): 1-6. |
| Tian L, Wang N, Zhang X Y, Yang B L, Sun J Y, Li M, Li P F.Morphological and physiological characteristics of differentjaponica rice varieties under salt stress. Guangdong Agric Sci, 2014, 41(23): 1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | 王娜, 陈亚萍, 田蕾, 张得雯, 王瑞智, 杨苗, 李培富. 粳稻种质资源苗期根系形态特征与耐盐性相关分析. 广东农业科学, 2015, 42(10): 1-10. |
| Wang N, Chen Y P, Tian L, Zhang D W, Wang R Z, Yang M, Li P F.Correlation between root morphological characteristics ofjaponica rice germplasm and salt tolerance at seedling stage. Guangdong Agric Sci, 2015, 42(10): 1-10. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | Averinaa N G, Gritskevicha E R, Vershilovskayaa I V, Usatov A V, Yaronskaya E B.Mechanisms of salt stress tolerance development in barley plants under the Influence of 5-aminolevulinic acid.Russ J Plant Physiol-Engl Tr, 2010, 57(6): 792-798. |
| [26] | 崔江慧, 谢登磊, 常金华. 高粱材料耐盐性综合评价方法的初步建立与验证. 植物遗传资源学报, 2012, 13(1): 35-41. |
| Cui J H, Xie D L, Chang J H.Establishment and verification of comprehensive evaluation method for salt tolerance of sorghum materials.J Plant Genet Resour, 2012, 13(1): 35-41. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | 李培英, 孙宗玖. 33 份偃麦草种质芽期耐盐性评价. 草业科学, 2015, 32(4): 593-600. |
| Li P Y,Sun Z J.Evaluation on the salt resistance of germplasm resources of 33Elytrigria repens during seed germination period. Pratac Sci, 2015, 32(4): 593-600. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | 何晓兰, 徐照龙, 张大勇, 黄益洪, 彭陈, 邵宏波, 王为, 郭士伟. 65个高粱种质萌芽期的耐盐指标比较及其耐盐性综合评价. 植物资源与环境学报, 2015, 24(4): 52-60. |
| He X L, Xu Z L, Zhang D Y, Huang Y H, Peng C, Shao H B, Wang W, Guo S W.Comparison on salt tolerance indexes of 65 germplasms of Sorghum bicolor at germination stage and comprehensive evaluation on their salt tolerance. J Plant Resour Environ, 2015, 24(4): 52-60. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | 王萌萌, 姜奇彦, 胡正, 张辉, 樊守金, 冯沥, 张海玲. 小麦品种资源耐盐性鉴定. 植物遗传资源学报, 2012, 13(2): 189-194. |
| Wang M M, Jiang Q Y, Hu Z, Zhang H, Fan S J, Feng L, Zhang H L.Evaluation for salt tolerance of wheat cultivars.J Plant Genet Resour, 2012, 13(2): 189-194. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | 吴家富, 杨博文, 向珣朝, 许亮, 颜李梅. 不同水稻种质在不同生育期耐盐鉴定的差异. 植物学报, 2017, 52(1): 77-88. |
| Wu J F, Yang B W, Xiang X C, Xu L, Yan L M.Identification of salt tolerance in different rice germplasm at different growth stages.Chin Bull Bot, 2017, 52(1): 77-88. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | 张银平, 杜瑞成, 刁培松, 杨善东. 山东省水稻免耕旱直播试验及可行性分析. 农业工程学报, 2016, 32(12): 24-30. |
| Zhang Y P, Du R C, Diao P S, Yang S D.Experiment of no-tillage and drought direct sowing rice and feasibility analysis in Shandong Province. Trans Chin Soc Agric Eng, 2016, 32(12): 24-30. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [32] | Li Z K, Fu B Y, Gao Y M, Xu J L, Ali J, Lafitte H R, Jiang Y Z, Rey J D, Vijayakumar C H M, Maghirang R, Zheng T Q, Zhu L H. Genome-wide introgression lines and their use in genetic and molecular dissection of complex phenotypes in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Mol Biol, 2005, 59(1): 33-52. |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [6] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [7] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [8] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [9] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [10] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [11] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [12] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [13] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| [14] | 许用强, 姜宁, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 水稻开花期高温热害响应机理及其调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 111-126. |
| [15] | 吕海涛, 李建忠, 鲁艳辉, 徐红星, 郑许松, 吕仲贤. 稻田福寿螺的发生、危害及其防控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 127-139. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||