
中国水稻科学 ›› 2017, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (5): 489-499.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2017.7043 489
涂政军1, 邹国兴2, 黄李超1, 陈龙1, 代丽萍1, 高易宏1, 冷语佳1, 朱丽1, 张光恒1, 胡江1, 任德勇1, 高振宇1, 董国军1, 陈光1, 郭龙彪1, 钱前1,*( ), 曾大力1,*(
), 曾大力1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2017-04-11
修回日期:2017-05-12
出版日期:2017-10-10
发布日期:2017-09-10
通讯作者:
钱前,曾大力
基金资助:
Zhengjun TU1, Guoxing ZOU2, Lichao HUANG1, Long CHEN1, Liping DAI1, Yihong GAO1, Yujia LENG1, Li ZHU1, Guangheng ZHANG1, Jiang HU1, Deyong REN1, Zhenyu GAO1, Guojun DONG1, Guang CHEN1, Longbiao GUO1, Qian QIAN1,*( ), Dali ZENG1,*(
), Dali ZENG1,*( )
)
Received:2017-04-11
Revised:2017-05-12
Online:2017-10-10
Published:2017-09-10
Contact:
Qian QIAN, Dali ZENG
摘要:
目的 叶片是水稻进行光合作用的主要场所,叶片颜色的变化与水稻的生长发育直接相关。发掘水稻叶色突变体,是水稻功能基因组学研究的重要遗传基础。方法 利用EMS诱变日本晴获得一个能稳定遗传的淡绿叶突变体,暂命名为pgl11(pale green leaf 11)。在不同生育期测定野生型与突变体的叶绿素含量。在苗期,取野生型与突变体叶片进行叶绿体结构的透射电镜观察。在分蘖期,测定野生型与突变体的光合参数并观察气孔结构。在成熟期,测定野生型和pgl11的主要农艺性状。以pgl11为母本,南京6号为父本构建相应的F2群体,采用图位克隆的方法,对该基因进行定位。结果 从苗期开始,突变体pgl11的每一片新叶均表现为淡绿色,叶绿素含量显著降低,叶绿体发育异常。随着叶片的生长,叶色由淡绿逐渐转绿,至抽穗期时叶绿素含量亦无明显差异。pgl11还表现光合速率、气孔导度明显下降,胞间CO2浓度上升。扫描电镜观察发现,突变体pgl11的气孔发育异常。与野生型相比,突变体的农艺性状如株高、剑叶宽、二次枝梗数、每穗粒数、粒长、粒宽、千粒重以及结实率等均显著降低。对叶绿素合成、光合作用以及质体发育相关基因的表达量测定表明,突变体pgl11中参与叶绿体转录和翻译相关基因的表达量显著升高,而叶绿素合成和光合作用相关基因的表达量显著下降。遗传分析表明,该突变表型受一对隐性核基因控制。通过图位克隆的方法将该基因定位于第1染色体上的C6和C8标记之间,物理距离约为110 kb。结论 该定位区间内未见有叶色相关基因报道,推测PGL11基因可能是一个新的水稻叶色基因。
中图分类号:
涂政军, 邹国兴, 黄李超, 陈龙, 代丽萍, 高易宏, 冷语佳, 朱丽, 张光恒, 胡江, 任德勇, 高振宇, 董国军, 陈光, 郭龙彪, 钱前, 曾大力. 水稻淡绿叶基因PGL11的鉴定与精细定位[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(5): 489-499.
Zhengjun TU, Guoxing ZOU, Lichao HUANG, Long CHEN, Liping DAI, Yihong GAO, Yujia LENG, Li ZHU, Guangheng ZHANG, Jiang HU, Deyong REN, Zhenyu GAO, Guojun DONG, Guang CHEN, Longbiao GUO, Qian QIAN, Dali ZENG. Identification and Fine Mapping of Pale Green Leaf PGL11 in Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2017, 31(5): 489-499.
| 标记 Marker | 正向引物序列 Forward primer (5′-3′) | 反向引物序列 Reverse primer (5′-3′) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ubq | ACCCTGGCTGACTACAACATC | AGTTGACAGCCCTAGGGTG | |
| CAO1 | GATCCATACCCGATCGACAT | CGAGAGACATCCGGTAGAGC | |
| CHLH | AACTGGATGAGCCAGAAGAGA | AAATGCAAAAGACTTGCGACT | |
| LhcP2 | GAAGAAGATCAAGAACGGCC | TTGCCGGGGACGAAGTTGGT | |
| HEMA | CGCTATTTCTGATGCTATGGGT | TCTTGGGTGATGATTGTTTGG | |
| Lhcb1 | CCATGTTCTCCATGTTCGGCTTCT | TAGGCCCAGGCGTTGTTGTTGA | |
| Lhcb4 | TACCTGCAGTTCGAGCTGGAC | AGGCCGAACACCTCGGTGTA | |
| PORA | ATGGCTCTCCAAGTTCAG | TGGCTCACGCTAAGGAAC | |
| PORB | CCGCAAGGAGGGAGCGGTG | CCCTCTTGGTGCTAAGGCCG | |
| PsaA | CACGGTGTCTAAGGACACGA | GACAGCGCCCATAAAGGTCTC | |
| PsbA | AGAGACGCGAAAGTACAAGC | AAGTTGCGGTCAATAAGGTA | |
| Rps15 | AGATACGGAGACTTGCTTCA | GCTCCCTAATATCCAACTGACT | |
| OsSig2A | AGTCTTATGGCATCTTGAGTG | GACCGCTTCTTCTTTGAGG | |
表1 实时定量PCR引物
Table 1 Primers used in real-time PCR.
| 标记 Marker | 正向引物序列 Forward primer (5′-3′) | 反向引物序列 Reverse primer (5′-3′) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ubq | ACCCTGGCTGACTACAACATC | AGTTGACAGCCCTAGGGTG | |
| CAO1 | GATCCATACCCGATCGACAT | CGAGAGACATCCGGTAGAGC | |
| CHLH | AACTGGATGAGCCAGAAGAGA | AAATGCAAAAGACTTGCGACT | |
| LhcP2 | GAAGAAGATCAAGAACGGCC | TTGCCGGGGACGAAGTTGGT | |
| HEMA | CGCTATTTCTGATGCTATGGGT | TCTTGGGTGATGATTGTTTGG | |
| Lhcb1 | CCATGTTCTCCATGTTCGGCTTCT | TAGGCCCAGGCGTTGTTGTTGA | |
| Lhcb4 | TACCTGCAGTTCGAGCTGGAC | AGGCCGAACACCTCGGTGTA | |
| PORA | ATGGCTCTCCAAGTTCAG | TGGCTCACGCTAAGGAAC | |
| PORB | CCGCAAGGAGGGAGCGGTG | CCCTCTTGGTGCTAAGGCCG | |
| PsaA | CACGGTGTCTAAGGACACGA | GACAGCGCCCATAAAGGTCTC | |
| PsbA | AGAGACGCGAAAGTACAAGC | AAGTTGCGGTCAATAAGGTA | |
| Rps15 | AGATACGGAGACTTGCTTCA | GCTCCCTAATATCCAACTGACT | |
| OsSig2A | AGTCTTATGGCATCTTGAGTG | GACCGCTTCTTCTTTGAGG | |
| 农艺性状 Agronomic trait | 野生型 Wild type | 突变体 Mutant | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 株高 Plant height /cm | 84.2 | ±1.33 | 73.7 | ±2.65* * |
| 抽穗期Heading date/d | 106.3 | ±0.6 | 113.3 | ±1.2* * |
| 分蘖数Tillering number | 16.0 | ±1.0 | 15.0 | ±0.7 |
| 剑叶长Length of flag leaf /cm | 35.50 | ±2.12 | 33.30 | ±3.25 |
| 剑叶宽Width of flag leaf/cm | 1.54 | ±0.06 | 1.18 | ±0.03** |
| 穗长Panicle length /cm | 19.77 | ±1.26 | 19.29 | ±0.86 |
| 一次枝梗数No. of primary rachis branches | 8.7 | ±1.3 | 9.1 | ±0.7 |
| 二次枝梗数No. of secondary rachis branches | 16.4 | ±2.4 | 11.0 | ±1.5* * |
| 每穗粒数No. of grains per panicle | 97.3 | ±8.7 | 71.4 | ±2.4* * |
| 粒长Grain length/cm | 7.26 | ±0.01 | 7.47 | ±0.05* * |
| 粒宽Grain width/cm | 3.28 | ±0.01 | 2.95 | ±0.03* * |
| 千粒重1000-grain weight/g | 25.91 | ±0.25 | 21.11 | ±0.08* * |
| 结实率Seed-setting rate /% | 81.34 | ±6.40 | 63.91 | ±6.62* * |
表2 野生型WT和突变体pgl11的基本农艺性状(平均数±标准差, n=3)
Table 2 .Agronomic traits of the wild type(WT) and pgl11 mutant(Mean±SD, n=3).
| 农艺性状 Agronomic trait | 野生型 Wild type | 突变体 Mutant | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 株高 Plant height /cm | 84.2 | ±1.33 | 73.7 | ±2.65* * |
| 抽穗期Heading date/d | 106.3 | ±0.6 | 113.3 | ±1.2* * |
| 分蘖数Tillering number | 16.0 | ±1.0 | 15.0 | ±0.7 |
| 剑叶长Length of flag leaf /cm | 35.50 | ±2.12 | 33.30 | ±3.25 |
| 剑叶宽Width of flag leaf/cm | 1.54 | ±0.06 | 1.18 | ±0.03** |
| 穗长Panicle length /cm | 19.77 | ±1.26 | 19.29 | ±0.86 |
| 一次枝梗数No. of primary rachis branches | 8.7 | ±1.3 | 9.1 | ±0.7 |
| 二次枝梗数No. of secondary rachis branches | 16.4 | ±2.4 | 11.0 | ±1.5* * |
| 每穗粒数No. of grains per panicle | 97.3 | ±8.7 | 71.4 | ±2.4* * |
| 粒长Grain length/cm | 7.26 | ±0.01 | 7.47 | ±0.05* * |
| 粒宽Grain width/cm | 3.28 | ±0.01 | 2.95 | ±0.03* * |
| 千粒重1000-grain weight/g | 25.91 | ±0.25 | 21.11 | ±0.08* * |
| 结实率Seed-setting rate /% | 81.34 | ±6.40 | 63.91 | ±6.62* * |
| 材料 Material | 光合作用速率 Pn /(µmol·m-2 s-1) | 气孔导度 Gs /(mol·m-2 s-1) | 胞间CO2浓度 Ci /(µmol·mol-1) | 蒸腾速率 Tr /(mol·m-2 s-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 野生型WT | 25.20±0.23 | 0.32±0.01 | 169.56±3.68 | 12.07±0.26 |
| pgl11 | 17.06±1.82** | 0.25±0.01** | 203.90±15.22** | 7.93±0.29** |
表3 分蘖盛期野生型和突变体pgl11的剑叶光合参数(平均数±标准差, n=5)
Table 3 .Photosynthetic parameters of flag leaf of wild type(WT) and pgl111 mutant at the tillering stage(Mean±SD, n=5).
| 材料 Material | 光合作用速率 Pn /(µmol·m-2 s-1) | 气孔导度 Gs /(mol·m-2 s-1) | 胞间CO2浓度 Ci /(µmol·mol-1) | 蒸腾速率 Tr /(mol·m-2 s-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 野生型WT | 25.20±0.23 | 0.32±0.01 | 169.56±3.68 | 12.07±0.26 |
| pgl11 | 17.06±1.82** | 0.25±0.01** | 203.90±15.22** | 7.93±0.29** |
| 分离群体 Segregation population (F2) | 野生型 Wild type | 突变表型 Mutant | 总计 Total | χ2(3:1) | P值 P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pgl11/培矮64S pgl11/Peiai 64S | 413 | 141 | 554 | 0.0602 | 0.8062 |
| pgl11/南京6号 pgl11/Nanjing 6 | 504 | 167 | 671 | 0.0045 | 0.9467 |
表4 突变体基因PGL11的遗传分析
Table 4 .Genetic analysis of PGL11.
| 分离群体 Segregation population (F2) | 野生型 Wild type | 突变表型 Mutant | 总计 Total | χ2(3:1) | P值 P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pgl11/培矮64S pgl11/Peiai 64S | 413 | 141 | 554 | 0.0602 | 0.8062 |
| pgl11/南京6号 pgl11/Nanjing 6 | 504 | 167 | 671 | 0.0045 | 0.9467 |
| 标记 Marker | 正向引物序列 Forward primer (5′-3′) | 反向引物序列 Reverse primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| M1 | CTTGTCAACTTGGGCTGCAT | ATGAACCCTGAAGCTTTCGC |
| M2 | CCCTTCCTCCGTTGCCTATT | TGACGTCAGCAAAAGGGAGA |
| C1 | AGGCCTAGATGCACAAAGGT | AGTTCTTCCTCGGCCTTCAA |
| C2 | TTGTTTCACTTCCATCGCCG | GAACGGAAGCTCAGGACCT |
| C3 | GGGGTTATTACGGCAGCTCA | TTGTCCTCCCCTTAGCCAAG |
| C4 | ATCATACCATCGCCATGCCT | ACTAACCTTGCCTCCGACAC |
| C5 | GCTCATCAAGGTTGGGTAAGT | TGATCATGGAGCAGCTAGGG |
| C6 | AGCGACACCTGAACAGTACA | GCAAACGATGGAAGAAGTGGT |
| C7 | TCAGGTTCGTTCGAATAGGGT | CACAATCGCTAGAATACGAGGT |
| C8 | GCTGACCTGCATGCTAGTTT | TTGGAAGCAGCACTCTAGGG |
表5 本研究中精细定位所用引物
Table 5 .Primers used for fine mapping in the study.
| 标记 Marker | 正向引物序列 Forward primer (5′-3′) | 反向引物序列 Reverse primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| M1 | CTTGTCAACTTGGGCTGCAT | ATGAACCCTGAAGCTTTCGC |
| M2 | CCCTTCCTCCGTTGCCTATT | TGACGTCAGCAAAAGGGAGA |
| C1 | AGGCCTAGATGCACAAAGGT | AGTTCTTCCTCGGCCTTCAA |
| C2 | TTGTTTCACTTCCATCGCCG | GAACGGAAGCTCAGGACCT |
| C3 | GGGGTTATTACGGCAGCTCA | TTGTCCTCCCCTTAGCCAAG |
| C4 | ATCATACCATCGCCATGCCT | ACTAACCTTGCCTCCGACAC |
| C5 | GCTCATCAAGGTTGGGTAAGT | TGATCATGGAGCAGCTAGGG |
| C6 | AGCGACACCTGAACAGTACA | GCAAACGATGGAAGAAGTGGT |
| C7 | TCAGGTTCGTTCGAATAGGGT | CACAATCGCTAGAATACGAGGT |
| C8 | GCTGACCTGCATGCTAGTTT | TTGGAAGCAGCACTCTAGGG |
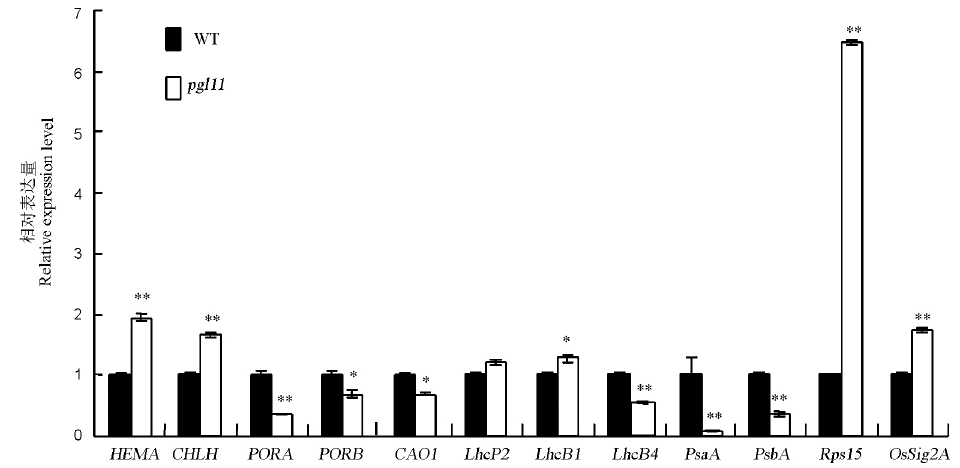
图6 野生型(WT)与突变体pgl11中叶绿素合成、光合作用及叶绿体发育相关基因的表达
Fig. 6. Expression analysis of genes associated with chlorophyll biosynthesis, photosynthesis and chloroplast development in the wild type(WT) and pgl11 mutant.
| [1] | Zhen X H, Xu J G, Shen W J, Zhang X J, Zhang Q J, Lu C G, Chen G X, Gao Z P.Photosynthetic characteristics of flag leaves in rice white stripe mutant 6001 during senescence process.Rice Sci, 2014, 21(6): 335-342. |
| [2] | Tanaka A, Tanaka R.Chlorophyll metabolism.Curr Opin Plant Biol, 2006, 9(3): 248-255. |
| [3] | Fromme P, Melkozernov A, Jordan P, Krauss N.Structure and function of photosystem: Ⅰ. Interaction with its soluble electron carriers and external antenna systems.FEBS Lett, 2003, 555: 40-44. |
| [4] | Huang J L, Qin F, Zang G C, Kang Z H, Zou H Y, Hu F, Yue C L, Li X Y, Wang G X.Mutation of OsDET1 increases chlorophyll content in rice.Plant Sci, 2013, 210: 241-249. |
| [5] | Bansal U, Saini R, Kaur A.Genetic variability in leaf area and chlorophyll content of aromatic rice.Int Rice Res Notes, 1999, 24: 21. |
| [6] | Mitchell P L, Sheehy J E.Supercharging rice photosynthesis to increase yield.New Phytol, 2006, 171: 688-693. |
| [7] | Gustafsson Å.The plastid development in various types of chlorophyll mutations.Hereditas, 2010, 28(3-4): 483-492. |
| [8] | Kusumi K, Mizutani A, Nishimura M, Iba K.A virescent gene V1 determines the expression timing of plastid genes for transcription/translation apparatus during early leaf development in rice.Plant J, 1997, 12(6): 1241-1250. |
| [9] | Sugimoto H, Kusumi K, Tozawa Y, Yazaki J, Kishimoto N, Kikuchi S, Iba K.The virescent-2 mutation inhibits translation of plastid transcripts for the plastid genetic system at an early stage of chloroplast differentiation.Plant Cell Physiol, 2004, 45(8): 985-996. |
| [10] | Nakanishi H, Nozue H, Suzuki K, Kaneko Y, Taguchi G, Hayashida N.Characterization of the Arabidopsis thaliana mutant pcb2 which accumulates divinyl chlorophylls.Plant Cell Physiol, 2005, 46(3): 467-473. |
| [11] | Roussell D L, Thompson D L, Pallardy S G, Miles D, Newton K J.Chloroplast structure and function is altered in the NCS2 maize mitochondrial mutant. Plant Physiol, 1991, 96: 232-238. |
| [12] | Alberte R S, Hesketh J D, Hofstea G, Thornber J P, Naylor A W, Bernard R L, Brim C, Endrizzi J, Kohel R J.Composition and activity ot the photosynthetic apparatus in temperature-sensitive mutants of higher plants.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1974, 71(6): 2414-2418. |
| [13] | Guardi M T, Kucera T, Briantais J M, Hodges M.Decreased photosystemⅡ core phosphorylation in a yellow-green mutant of wheat showing monophasic fluorescence induction curve.Plant Physiol, 1995, 109: 1059-1068. |
| [14] | 肖华贵, 杨焕文, 饶勇, 杨斌, 朱英, 张文龙. 甘蓝型油菜黄化突变体的叶绿体超微结构、气孔特征参数及光合特性. 中国农业科学, 2013, 46(4): 715-727. |
| Xiao H G, Yang H W, Rao Y, Yang B, Zhu Y, Zhang W L.Analysis of chloroplast ultrastructure, stomatal characteristic parameters and photosynthetic characteristics of chlorophyll-reduced mutant in Brassica napus L.Sci Agric Sin, 2013, 4: 715-727. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | Pérezruiz J M, Spínola M C, Kirchsteiger K, Moreno J, Sahrawy M, Cejudo F J.Rice NTRC is a high-efficiency redox system for chloroplast protection against oxidative damage.Plant Cell, 2006, 18(9): 2356-2368. |
| [16] | Tsugane K, Maekawa M, Takagi K, Takahara H, Qian Q, Eun C H, Iida S.An active DNA transposon nDart causing leaf variegation and mutable dwarfism and its related elements in rice.Plant J, 2006, 45(1): 46-57. |
| [17] | Jiang H W, Li M R, Liang N T, Yan H B, Wei Y B, Xu X L, Liu J, Xu Z F, Chen F, Wu G J.Molecular cloning and function analysis of the stay green gene in rice.Plant J, 2007, 52(2): 197-209. |
| [18] | Wang P R, Gao J X, Wan C M, Zhang F T, Xu Z J, Huang X Q, Sun X Q, Deng X J.Divinyl chlorophyll(ide) a can be converted to monovinyl chlorophyll(ide) a by a divinyl reductase in rice.Plant Physiol, 2010, 153(3): 994-1003. |
| [19] | Goh C H, Satoh K, Kikuchi S, Kim S C,Ko S M, Kang H G, Jeon J S, Kim C S, Park Y.Mitochondrial activity in illuminated leaves of chlorophyll-deficient mutant rice (OsCHLH) seedlings.Plant Biotechnol Rep, 2010, 4(4): 281-291. |
| [20] | Zhang H T, Li J J, Yoo J H, Yoo S C, Cho S H, Koh H J, Seo H S, Paek N C.Rice Chlorina-1 and Chlorina-9 encode ChlD and ChlI subunits of Mg-chelatase, a key enzyme for chlorophyll synthesis and chloroplast development.Plant Mol Biol, 2006, 62(3): 325-337. |
| [21] | Wu Z M, Zhang X, He B, Diao L P, Sheng S L, Wang J L, Guo X P, Su N, Wang L F, Jiang L, Wang C M, Zhai H Q, Wan J M.A Chlorophyll-deficient rice mutant with impaired chlorophyllide esterification in chlorophyll biosynthesis.Plant Physiol, 2007, 145(1): 29-40. |
| [22] | Lee S, Kim J H, Yoo E S, Lee C H, Hirochika H, An G.Differential regulation of chlorophyll a oxygenase genes in rice.Plant Mol Biol, 2005, 57(6): 805-818. |
| [23] | Yang Y L, Xu J, Huang L C, Leng Y J, Dai L P, Rao Y C, Chen L, Wang Y Q, Tu Z J, Hu J, Ren D Y, Zhang G H, Zhu L, Guo L B, Qian Q, Zeng D L.PGL, encoding chlorophyllide a oxygenase 1, impacts leaf senescence and indirectly affects grain yield and quality in rice.J Exp Bot, 2016, 67(5): 1297-1310. |
| [24] | Su N, Hu M L, Wu D X, Wu F Q, Fei G L, Lan Y, Chen X L, Shu X L, Zhang X, Guo X P, Cheng Z J, Lei C L, Qi C K, Jiang L, Wang H Y, Wan J M.Disruption of a rice pentatricopeptide repeat protein causes a seedling- specific albino phenotype and its utilization to enhance seed purity in hybrid rice production.Plant Physiol, 2012, 159(1): 227-238. |
| [25] | Kusumi K, Yara A, Mitsui N, Tozawa Y, Iba K.Characterization of a rice nuclear-encoded plastid RNA polymerase gene OsRpoTp.Plant Cell Physiol, 2004, 45: 1194-1201. |
| [26] | Zhao C F, Xu J M, Chen Y, Mao C Z, Zhang S L, Bai Y H, Jiang D A, Wu P.Molecular cloning and characterization of OsCHR4, a rice chromatin- remodeling factor required for early chloroplast development in adaxial mesophyll.Planta, 2012, 236(4): 1165-1176. |
| [27] | Kodiveri M G, Kim E S, Cho H, Chung Y Y, Kodiveri M G.OsPPR1, a pentatricopeptide repeat protein of rice is essential for the chloroplast biogenesis.Plant Mol Biol, 2005, 58(3): 421-433. |
| [28] | Fang J, Chai C L, Qian Q, Li C L, Tang J Y, Sun L, Huang Z J, Guo X L, Sun C H, Liu M, Zhang Y, Lu Q T, Wang Y Q, Lu C M, Han B, Chen F, Cheng Z K, Chu C C.Mutations of genes in synthesis of the carotenoid precursors of ABA lead to pre-harvest sprouting and photo-oxidation in rice.Plant J, 2008, 54(2): 177-189. |
| [29] | 钱前, 朱旭东, 曾大力, 张小惠, 严学强, 熊振民. 细胞质基因控制的新特异材料白绿苗的研究. 作物品种资源, 1996(4): 11-12. |
| Qian Q, Zhu X D, Zeng D L, Zhang X H, Yan X Q, Xiong Z M.Study on the new special material white-green seedlings controlled by cytoplasmic gene.China Seeds, 1996(4): 11-12. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | Wang F H, Wang G X, Li X Y, Huang J, Zheng J.Geredity, physiology and mapping of a chlorophyll content gene of rice(Oryza sativa L.).Plant Physiol, 2008, 165: 324-330. |
| [31] | 谢戎, 朱发云, 何光华, 邓锡洪, 左永树, 杨正林, 吴丽君. 水稻两用系温敏叶绿素自然突变体的初步研究. 西南农业学报, 1995, 8: 124-128. |
| Xie R, Zhu F Y, Deng X H, Zuo Y S, Yang Z L, Wu L J.A preliminary study on the temperature sensitive chlorophyll natural mutant in dual-purpose genic male sterile rice.Southwest China J Agric Sci, 1995, 8: 124-128. | |
| [32] | Huq E, Al-Sady B, Hudson M, Kim C, Apel K, Quail P H.Phytochrome-interacting factor 1 is a critical bHLH regulator of chlorophyll biosynthesis.Science, 2004, 305: 1937-1941. |
| [33] | Terry M J, Kendrick R E.Feedback inhibition of chlorophyll synthesis in the phytochrome chromophore- deficient aurea and yellow-green-2 mutants of tomato.Plant Physiol, 1999, 119: 143-152. |
| [34] | Beale S I.Green genes gleaned.Trends Plant Sci, 2005, 10: 309-312. |
| [35] | Nagata N, Tanaka R, Satoh S, Tanaka A.Identification of a vinyl reductase gene for chlorophyll synthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana and implications for the evolution of Prochlorococcus species.Plant Cell, 2005, 17(1): 233-240. |
| [36] | Sakuraba Y, Rahman M L, Cho S H, Kim Y S, Koh H J, Yoo S C, Paek N C.The rice faded green leaf locus encodes protochlorophyllide oxidoreductase B and is essential for chlorophyll synthesis under high light conditions.Plant J, 2013, 74(1): 122-133. |
| [37] | Yang Q S, He H, Li H Y, Tian H, Zhang J J, Zhai L G, Chen J D, Wu H, Yi G J, He Z H, Peng X X.NOA1 functions in a temperature-dependent manner to regulate chlorophyll biosynthesis and rubisco formation in rice.PLoS ONE, 2011, 6(5): e20015. |
| [38] | Sugimoto H, Kusumi K, Noguchi K, Yano M, Yoshimura A, Iba K.The rice nuclear gene, VIRESCENT 2, is essential for chloroplast development and encodes a novel type of guanylate kinase targeted to plastids and mitochondria.Plant J, 2007, 52(3): 512-527. |
| [39] | Yoo S C, Cho S H, Sugimoto H, Li J J, Kusumi K, Koh H J, Iba K, Paek N C.Rice virescent 3 and stripe 1 encoding the large and small subunits of ribonucleotide reductase are required for chloroplast biogenesis during early leaf development.Plant Physiol, 2009, 150(1): 388-401. |
| [40] | 苏正淑, 张宪政. 几种测定植物叶绿素含量的方法比较. 植物生理学通讯, 1989(5): 77-78. |
| Su Z S, Zhang X Z.Comparison of several methods for determining chlorophyll content of plants.Plant Physiol Commun, 1989(5): 77-78. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [41] | Lichtenthaler H K.Chlorophylls and caroteniods: Pigments of photosynthetic biomembranes.Method Enzymol, 1987, 148: 350-382. |
| [42] | 李超, 林冬枝, 董彦君, 叶胜海, 张小明. 一个水稻苗期温敏感白色条斑叶突变体的遗传分析及基因定位. 中国水稻科学, 2010, 24(3): 223-227. |
| Li C, Lin D Z, Dong Y J, Ye S H, Zhang X M.Genetic analysis and mapping of a thermo-sensitive white stripe leaf mutant at the seedling stage in rice(Oryza sativa).Chin J Rice Sci, 2010, 24(3): 223-227. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [43] | Livak K J, Schmittgen T D.Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method.Methods, 2001, 25: 402-408. |
| [44] | Gong X D, Su Q Q, Lin D Z, Jiang Q, Xu J L, Zhang J H, Teng S, Dong Y J.The rice OsV4 encoding a novel pentatricopeptide repeat protein is required for chloroplast development during the early leaf stage under cold stress.J Integr Plant Biol, 2014, 56(4): 400-410. |
| [45] | Kusaba M, Ito H, Morita R, Iida S, Sato Y, Fujimoto M, Kawasaki S, Tanaka R, Hirochika H, Nishimura M, Tanaka A.Rice NON-YELLOW COLORING1 is involved in light-harvesting complex II and grana degradation during leaf senescence.Plant Cell, 2007, 19(4): 1362-1375. |
| [46] | Song J, Wei X J, Shao G N, Sheng Z H, Chen D B, Liu C L, Jiao G A, Xie L H, Tang S Q, Hu P S.The rice nuclear gene WLP1 encoding a chloroplast ribosome L13 protein is needed for chloroplast development in rice grown under low temperature conditions.Plant Mol Biol, 2014, 84(3): 301-314. |
| [47] | Kong W Y, Yu X W, Chen H Y, Liu L L, Xiao Y J, Wang Y L, Wang C L, Lin Y, Yu Y, Wang C M, Jiang L, Zhai H Q, Zhao Z G, Wan J M.The catalytic subunit of magnesium-protoporphyrin IX monomethyl ester cyclase forms a chloroplast complex to regulate chlorophyll biosynthesis in rice.Plant Mol Biol, 2016, 92(1): 177-191. |
| [48] | Miyoshi K, Ito Y, Serizawa A, Kurata N.OsHAP3 genes regulate chloroplast biogenesis in rice.Plant J, 2003, 36(4): 532-540. |
| [49] | Zhu X L, Liang W Q, Cui X, Chen M J, Yin C S, Luo Z J, Zhu J Y, Lucas W J, Wang Z Y, Zhang D B.Brassinosteroids promote development of rice pollen grains and seeds by triggering expression of carbon starved anther, a MYB domain protein.Plant J, 2015, 82(4): 570-581 |
| [50] | 武立权, 尤翠翠, 柯建, 何清华. 叶色白化水稻突变体转绿中若干生理与叶绿体发育特型的研究. 热带作物学报, 2013, 34(6): 1115-1120. |
| Wu L Q, You C C, Ke J, He Q H.Chloroplast development and physiological characteristics of green-revertible albino leaf color mutants in rice.Chin J Trop Crops, 2013, 34(6): 1115-1120. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [6] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [7] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [8] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [9] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [10] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [11] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [12] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [13] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| [14] | 许用强, 姜宁, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 水稻开花期高温热害响应机理及其调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 111-126. |
| [15] | 吕海涛, 李建忠, 鲁艳辉, 徐红星, 郑许松, 吕仲贤. 稻田福寿螺的发生、危害及其防控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 127-139. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||