
中国水稻科学 ›› 2017, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (4): 379-390.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2017.7006 379
卞金龙1, 蒋玉兰1, 刘艳阳1, 冯咏芳2, 刘贺1, 夏仕明1, 刘立军1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2017-01-10
修回日期:2017-03-29
出版日期:2017-07-25
发布日期:2017-07-10
通讯作者:
刘立军
基金资助:
Jinlong BIAN1, Yulan JIANG1, Yanyang LIU1, Yongfang FENG2, He LIU1, Shiming XIA1, Lijun LIU1,*( )
)
Received:2017-01-10
Revised:2017-03-29
Online:2017-07-25
Published:2017-07-10
Contact:
Lijun LIU
摘要:
目的旨在阐明全生育期干湿交替灌溉对抗旱性不同水稻品种产量的影响。方法以抗旱性差异显著的4个水稻品种(籼稻扬稻6号和两优培九,粳稻旱优8号和镇稻88)为材料,以常规水层灌溉(CI)为对照,在盆栽条件下研究了轻干湿交替灌溉(WMD)和重干湿交替灌溉(WSD)对水稻产量、根系、叶片及籽粒部分生理特性的影响。结果与CI相比,WMD处理下抗旱性较强品种扬稻6号和旱优8号产量分别提高6.90%和7.45%,抗旱性较弱品种两优培九和镇稻88产量分别降低7.28%和8.10%。WSD处理下,4个水稻品种的产量均显著下降,抗旱性较弱的品种产量降幅远高于抗旱性较强的水稻品种。WMD处理下,扬稻6号和旱优8号复水后根系氧化力、根系与叶片细胞分裂素(玉米素+玉米素核苷)含量、叶片光合速率和籽粒中蔗糖-淀粉代谢途径关键酶的活性均较CI有不同程度提高,而两优培九和镇稻88上述指标则与CI持平或有不同程度降低。WSD处理下,4个品种上述指标均较CI不同程度降低。结论轻干湿交替灌溉条件下,根系活性强、叶片细胞分裂素含量和光合速率高、籽粒中蔗糖-淀粉代谢途径关键酶活性强是抗旱性较强水稻品种的基本生理特征。
卞金龙, 蒋玉兰, 刘艳阳, 冯咏芳, 刘贺, 夏仕明, 刘立军. 干湿交替灌溉对抗旱性不同水稻品种产量的影响及其生理原因分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(4): 379-390.
Jinlong BIAN, Yulan JIANG, Yanyang LIU, Yongfang FENG, He LIU, Shiming XIA, Lijun LIU. Effects of Alternate Wetting and Drying Irrigation on Grain Yield in Rice Cultivars with Different Drought Resistance and Its Physiological Mechanism[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2017, 31(4): 379-390.
| 品种 Cultivar | 处理 Treatment | 每盒穗数 Panicle number per pot | 每穗实粒数 Filled grain number per panicle | 结实率 Seed setting rate/% | 千粒重 1000-grain weigh/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 扬稻6号 | CI | 23±2 a | 168±5 b | 86.6±0.9 b | 28.1±0.4 b |
| Yangdao 6 | WMD | 21±1 ab | 181±4 a | 92.7±0.7 a | 28.8±0.3 ab |
| WSD | 18±2 b | 179±5 a | 88.2±0.8 b | 29.1±0.2 a | |
| 两优培九 | CI | 25±2 a | 185±4 b | 85.1±0.6 b | 26.4±0.3 c |
| Liangyoupeijiu | WMD | 21±1 b | 206±5 a | 87.2±0.9 a | 27.1±0.2 b |
| WSD | 18±1 c | 207±3 a | 83.8±0.6 c | 27.7±0.2 a | |
| 旱优8号 | CI | 25±1 a | 164±6 b | 88.5±0.7 a | 25.8±0.6 c |
| Hanyou 8 | WMD | 25±2 ab | 173±2 a | 88.5±0.8 a | 26.8±0.3 a |
| WSD | 22±1 b | 177±4 a | 87.8±0.8 a | 26.9±0.4 a | |
| 镇稻88 | CI | 28±2 a | 142±4 b | 93.5±0.9 a | 27.2±0.5 b |
| Zhendao 88 | WMD | 24±1 b | 155±6 a | 89.9±0.7 b | 28.3±0.4 a |
| WSD | 21±1 c | 158±3 a | 85.8±0.8 c | 27.1±0.4 b |
表1 干湿交替灌溉对抗旱性不同水稻品种产量构成因素的影响
Table 1 Effect of alternate wetting and drying irrigation on yield components of rice cultivars with different drought resistance
| 品种 Cultivar | 处理 Treatment | 每盒穗数 Panicle number per pot | 每穗实粒数 Filled grain number per panicle | 结实率 Seed setting rate/% | 千粒重 1000-grain weigh/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 扬稻6号 | CI | 23±2 a | 168±5 b | 86.6±0.9 b | 28.1±0.4 b |
| Yangdao 6 | WMD | 21±1 ab | 181±4 a | 92.7±0.7 a | 28.8±0.3 ab |
| WSD | 18±2 b | 179±5 a | 88.2±0.8 b | 29.1±0.2 a | |
| 两优培九 | CI | 25±2 a | 185±4 b | 85.1±0.6 b | 26.4±0.3 c |
| Liangyoupeijiu | WMD | 21±1 b | 206±5 a | 87.2±0.9 a | 27.1±0.2 b |
| WSD | 18±1 c | 207±3 a | 83.8±0.6 c | 27.7±0.2 a | |
| 旱优8号 | CI | 25±1 a | 164±6 b | 88.5±0.7 a | 25.8±0.6 c |
| Hanyou 8 | WMD | 25±2 ab | 173±2 a | 88.5±0.8 a | 26.8±0.3 a |
| WSD | 22±1 b | 177±4 a | 87.8±0.8 a | 26.9±0.4 a | |
| 镇稻88 | CI | 28±2 a | 142±4 b | 93.5±0.9 a | 27.2±0.5 b |
| Zhendao 88 | WMD | 24±1 b | 155±6 a | 89.9±0.7 b | 28.3±0.4 a |
| WSD | 21±1 c | 158±3 a | 85.8±0.8 c | 27.1±0.4 b |
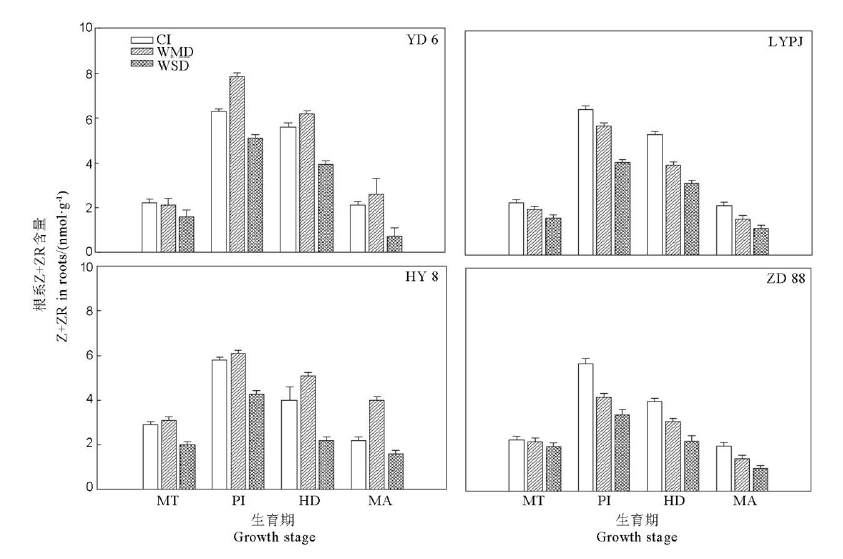
图3 干湿交替灌溉下不同水稻品种根系玉米素+玉米素核苷(Z+ZR)含量的变化(复水后测定结果)
Fig. 3. Effects of alternate wetting and drying irrigation on zeatin (Z) + zeatin riboside (ZR) content in roots
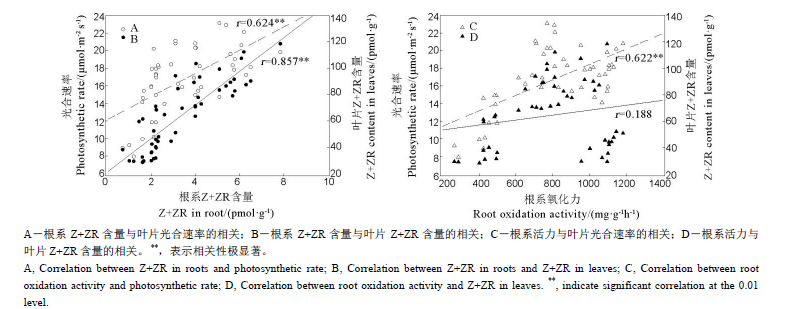
图5 根系Z+ZR含量与根系氧化力和叶片光合速率、Z+ZR含量的相关(n=48)
Fig. 5. Correlation coefficients of Z+ZR in roots and root oxidation activity with Z+ZR in leaves and photosynthetic rate.
| 品种 Cultivar | 处理 Treatment | 分蘖中期 Mid-tillering stage | 穗分化期 Panicle initiation | 抽穗期 Heading | 灌浆中期 Mid-filling stage | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W1 | W2 | W1 | W2 | W1 | W2 | W1 | W2 | |||||
| 扬稻6号 | CI | 17.1±0.9 a | 17.3±0.8 b | 16.9±0.8 a | 17.2±0.9 b | 19.1±0.9 a | 19.6±0.8 b | 10.3±0.6 a | 10.1±0.9 b | |||
| Yangdao 6 | WMD | 16.9±0.8 a | 20.2±0.8 a | 15.9±1.1 a | 19.8±1.2 a | 18.6±1.1 a | 22.1±1.1 a | 9.6±0.8 a | 13.9±0.7 a | |||
| WSD | 10.1±1.3 c | 14.1±1.2 c | 10.9±1.3 c | 14.7±1.3 c | 12.9±0.9 c | 16.9±0.8 c | 5.9±0.4 c | 8.9±0.6 c | ||||
| 两优培九 | CI | 17.8±1.2 a | 18.1±0.4 a | 17.7±0.4 a | 18.1±0.4 a | 22.1±1.1 a | 22.9±1.3 a | 14.3±0.7 a | 14.9±0.5 a | |||
| Liangyoupeiju | WMD | 15.2±0.9 b | 17.9±0.6 a | 17.1±0.7 a | 17.8±0.5 a | 19.6±0.7 b | 20.3±1.1 b | 12.0±0.9 b | 14.6±0.8 a | |||
| WSD | 12.5±0.6 c | 15.4±0.3 b | 12.9±0.5 c | 15.4±0.4 b | 13.4±0.4 c | 16.2±0.9 c | 5.6±0.3 c | 7.9±0.3 b | ||||
| 旱优8号 | CI | 18.1±0.9 a | 18.4±0.8 b | 18.0±0.7 a | 19.0±0.5 b | 19.2±0.5 a | 20.8±0.9 b | 11.7±0.3 a | 11.8±0.5 b | |||
| Hanyou 8 | WMD | 16.9±0.9 a | 20.8±1.1 a | 17.2±0.8 a | 20.6±0.6 a | 19.1±0.5 a | 23.1±1.1 a | 11.4±0.4 a | 14.9±0.5 a | |||
| WSD | 11.4±0.4 c | 15.9±0.6 c | 11.9±0.4 c | 15.8±0.5 c | 12.7±0.6 b | 17.2±0.6 c | 6.2±0.2 c | 9.9±0.3 c | ||||
| 镇稻88 | CI | 18.1±0.7 a | 18.3±0.7 a | 17.9±0.6 a | 18.3±0.7 a | 19.9±0.7 a | 20.3±0.9 a | 11.7±0.6 a | 11.8±0.5 a | |||
| Zhendao 88 | WMD | 15.9±0.6 b | 17.9±0.6 a | 16.2±0.4 b | 18.2±0.6 a | 19.2±0.8 a | 21.1±0.8 a | 10.4±0.6 b | 11.9±0.5 a | |||
| WSD | 11.4±0.4 c | 15.8±0.4 b | 11.8±0.5 c | 15.8±0.4 b | 12.2±0.5 b | 16.9±0.6 b | 6.4±0.3 c | 9.2±0.4 b | ||||
表2 干湿交替灌溉下抗旱性不同水稻品种光合速率的变化
Table 2 Effects of alternate wetting and drying irrigation on photosynthetic rate. µmol/(m2·s)
| 品种 Cultivar | 处理 Treatment | 分蘖中期 Mid-tillering stage | 穗分化期 Panicle initiation | 抽穗期 Heading | 灌浆中期 Mid-filling stage | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W1 | W2 | W1 | W2 | W1 | W2 | W1 | W2 | |||||
| 扬稻6号 | CI | 17.1±0.9 a | 17.3±0.8 b | 16.9±0.8 a | 17.2±0.9 b | 19.1±0.9 a | 19.6±0.8 b | 10.3±0.6 a | 10.1±0.9 b | |||
| Yangdao 6 | WMD | 16.9±0.8 a | 20.2±0.8 a | 15.9±1.1 a | 19.8±1.2 a | 18.6±1.1 a | 22.1±1.1 a | 9.6±0.8 a | 13.9±0.7 a | |||
| WSD | 10.1±1.3 c | 14.1±1.2 c | 10.9±1.3 c | 14.7±1.3 c | 12.9±0.9 c | 16.9±0.8 c | 5.9±0.4 c | 8.9±0.6 c | ||||
| 两优培九 | CI | 17.8±1.2 a | 18.1±0.4 a | 17.7±0.4 a | 18.1±0.4 a | 22.1±1.1 a | 22.9±1.3 a | 14.3±0.7 a | 14.9±0.5 a | |||
| Liangyoupeiju | WMD | 15.2±0.9 b | 17.9±0.6 a | 17.1±0.7 a | 17.8±0.5 a | 19.6±0.7 b | 20.3±1.1 b | 12.0±0.9 b | 14.6±0.8 a | |||
| WSD | 12.5±0.6 c | 15.4±0.3 b | 12.9±0.5 c | 15.4±0.4 b | 13.4±0.4 c | 16.2±0.9 c | 5.6±0.3 c | 7.9±0.3 b | ||||
| 旱优8号 | CI | 18.1±0.9 a | 18.4±0.8 b | 18.0±0.7 a | 19.0±0.5 b | 19.2±0.5 a | 20.8±0.9 b | 11.7±0.3 a | 11.8±0.5 b | |||
| Hanyou 8 | WMD | 16.9±0.9 a | 20.8±1.1 a | 17.2±0.8 a | 20.6±0.6 a | 19.1±0.5 a | 23.1±1.1 a | 11.4±0.4 a | 14.9±0.5 a | |||
| WSD | 11.4±0.4 c | 15.9±0.6 c | 11.9±0.4 c | 15.8±0.5 c | 12.7±0.6 b | 17.2±0.6 c | 6.2±0.2 c | 9.9±0.3 c | ||||
| 镇稻88 | CI | 18.1±0.7 a | 18.3±0.7 a | 17.9±0.6 a | 18.3±0.7 a | 19.9±0.7 a | 20.3±0.9 a | 11.7±0.6 a | 11.8±0.5 a | |||
| Zhendao 88 | WMD | 15.9±0.6 b | 17.9±0.6 a | 16.2±0.4 b | 18.2±0.6 a | 19.2±0.8 a | 21.1±0.8 a | 10.4±0.6 b | 11.9±0.5 a | |||
| WSD | 11.4±0.4 c | 15.8±0.4 b | 11.8±0.5 c | 15.8±0.4 b | 12.2±0.5 b | 16.9±0.6 b | 6.4±0.3 c | 9.2±0.4 b | ||||
| 品种 Cultivar | 处理 Treatment | 分蘖中期 Mid-tillering | 穗分化期 Panicle initiation | 抽穗期 Heading | 灌浆中期 Mid-filling stage | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W1 | W2 | W1 | W2 | W1 | W2 | W1 | W2 | |||||
| 扬稻6号 | CI | 43.2±2.3 a | 45.6±2.9 b | 89.0±3.1 b | 87.3±4.4 b | 83.0±3.2 b | 89.1±2.9 b | 28.6±1.9 b | 31.1±1.9 b | |||
| Yangdao 6 | WMD | 29.1±2.5 b | 52.1±3.2 a | 103.3±4.2 a | 118.4±4.2 a | 97.4±3.3 a | 112.2±3.6 a | 51.3±2.6 a | 64.5±2.2 a | |||
| WSD | 21.3±2.8 c | 32.3±2.4 c | 70.3±5.2 c | 83.2±4.3 c | 81.3±3.1 c | 89.0±3.1 b | 18.2±1.9 c | 37.9±2.1 c | ||||
| 两优培九 | CI | 45.0±3.1 a | 47.7±3.3 a | 88.9±4.2 a | 90.1±3.8 a | 83.6±2.9 b | 86.3±3.3 b | 27.2±1.8 b | 31.5±2.1 b | |||
| Liangyoupeijiu | WMD | 31.6±2.2 b | 42.1±2.9 b | 81.1±4.9 b | 91.4±3.7 a | 91.3±3.3 a | 103.3±3.9 a | 47.1±2.1 a | 61.2±1.9 a | |||
| WSD | 22.7±2.5 c | 29.3±2.8 c | 67.2±3.7 c | 77.6±3.6 c | 75.5±3.6 c | 84.3±2.8 c | 19.3±1.6 c | 29.1±2.3 b | ||||
| 旱优8号 | CI | 41.1±3.2 a | 44.3±2.9 b | 75.1±3.5 b | 82.5±3.3 b | 67.2±3.7 b | 70.4±3.1 b | 36.1±2.1 b | 40.1±2.2 b | |||
| Hanyou 8 | WMD | 30.0±2.7 b | 50.8±2.2 a | 95.7±3.7 a | 107.3±4.1 a | 90.4±4.5 a | 99.1±4.2 a | 52.5±2.7 a | 63.3±1.8 a | |||
| WSD | 20.5±3.2 c | 35.6±3.1 c | 61.8±3.4 c | 72.6±2.4 c | 50.3±3.6 c | 70.8±3.2 b | 20.4±2.6 c | 28.3±1.3 c | ||||
| 镇稻88 | CI | 41.4±2.7 a | 44.2±2.8 a | 76.3±3.1 b | 78.8±2.7 b | 70.3±3.8 b | 71.3±3.5 b | 34.7±2.2 b | 36.1±1.5 b | |||
| Zhendao 88 | WMD | 29.3±3.5 b | 39.3±3.2 b | 80.4±3.7 a | 93.1±4.1 a | 86.4±3.8 a | 94.0±2.9 a | 53.1±3.2 a | 59.3±1.6 a | |||
| WSD | 21.2±2.9 c | 29.5±1.9 c | 56.2±3.7 c | 69.4±3.9 c | 51.7±3.9 c | 68.2±2.9 c | 19.6±1.9 c | 29.4±1.1 c | ||||
表3 干湿交替灌溉下不同水稻品种叶片Z+ZR含量的变化
Table 3 Effects of alternate wetting and drying irrigation on Z+ZR in leaves. pmol/g
| 品种 Cultivar | 处理 Treatment | 分蘖中期 Mid-tillering | 穗分化期 Panicle initiation | 抽穗期 Heading | 灌浆中期 Mid-filling stage | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W1 | W2 | W1 | W2 | W1 | W2 | W1 | W2 | |||||
| 扬稻6号 | CI | 43.2±2.3 a | 45.6±2.9 b | 89.0±3.1 b | 87.3±4.4 b | 83.0±3.2 b | 89.1±2.9 b | 28.6±1.9 b | 31.1±1.9 b | |||
| Yangdao 6 | WMD | 29.1±2.5 b | 52.1±3.2 a | 103.3±4.2 a | 118.4±4.2 a | 97.4±3.3 a | 112.2±3.6 a | 51.3±2.6 a | 64.5±2.2 a | |||
| WSD | 21.3±2.8 c | 32.3±2.4 c | 70.3±5.2 c | 83.2±4.3 c | 81.3±3.1 c | 89.0±3.1 b | 18.2±1.9 c | 37.9±2.1 c | ||||
| 两优培九 | CI | 45.0±3.1 a | 47.7±3.3 a | 88.9±4.2 a | 90.1±3.8 a | 83.6±2.9 b | 86.3±3.3 b | 27.2±1.8 b | 31.5±2.1 b | |||
| Liangyoupeijiu | WMD | 31.6±2.2 b | 42.1±2.9 b | 81.1±4.9 b | 91.4±3.7 a | 91.3±3.3 a | 103.3±3.9 a | 47.1±2.1 a | 61.2±1.9 a | |||
| WSD | 22.7±2.5 c | 29.3±2.8 c | 67.2±3.7 c | 77.6±3.6 c | 75.5±3.6 c | 84.3±2.8 c | 19.3±1.6 c | 29.1±2.3 b | ||||
| 旱优8号 | CI | 41.1±3.2 a | 44.3±2.9 b | 75.1±3.5 b | 82.5±3.3 b | 67.2±3.7 b | 70.4±3.1 b | 36.1±2.1 b | 40.1±2.2 b | |||
| Hanyou 8 | WMD | 30.0±2.7 b | 50.8±2.2 a | 95.7±3.7 a | 107.3±4.1 a | 90.4±4.5 a | 99.1±4.2 a | 52.5±2.7 a | 63.3±1.8 a | |||
| WSD | 20.5±3.2 c | 35.6±3.1 c | 61.8±3.4 c | 72.6±2.4 c | 50.3±3.6 c | 70.8±3.2 b | 20.4±2.6 c | 28.3±1.3 c | ||||
| 镇稻88 | CI | 41.4±2.7 a | 44.2±2.8 a | 76.3±3.1 b | 78.8±2.7 b | 70.3±3.8 b | 71.3±3.5 b | 34.7±2.2 b | 36.1±1.5 b | |||
| Zhendao 88 | WMD | 29.3±3.5 b | 39.3±3.2 b | 80.4±3.7 a | 93.1±4.1 a | 86.4±3.8 a | 94.0±2.9 a | 53.1±3.2 a | 59.3±1.6 a | |||
| WSD | 21.2±2.9 c | 29.5±1.9 c | 56.2±3.7 c | 69.4±3.9 c | 51.7±3.9 c | 68.2±2.9 c | 19.6±1.9 c | 29.4±1.1 c | ||||
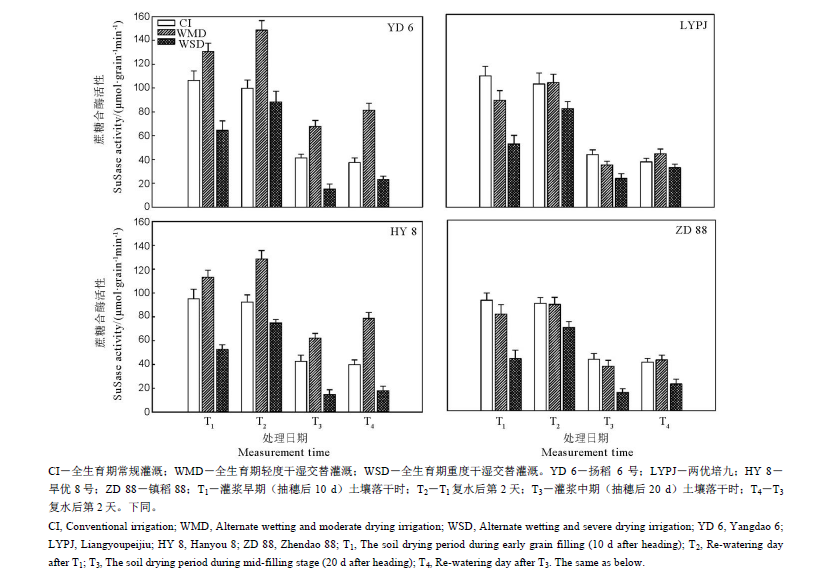
图6 干湿交替灌溉对不同水稻品种籽粒中蔗糖合酶(SuSase)活性的影响
Fig. 6. Effects of alternate wetting and drying irrigation on the activities of sucrose synthase (SuSase) in grains.
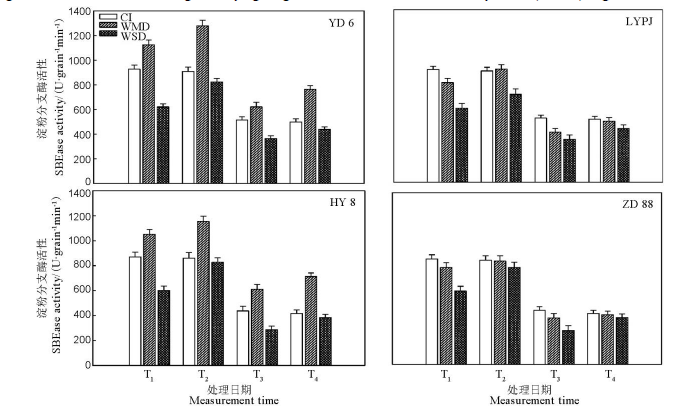
图7 干湿交替灌溉对不同水稻品种籽粒中淀粉分支酶(SBEase)活性的影响
Fig. 7. Effects of alternate wetting and drying irrigation on the activities of starch branching enzyme (SBEase) in grains.
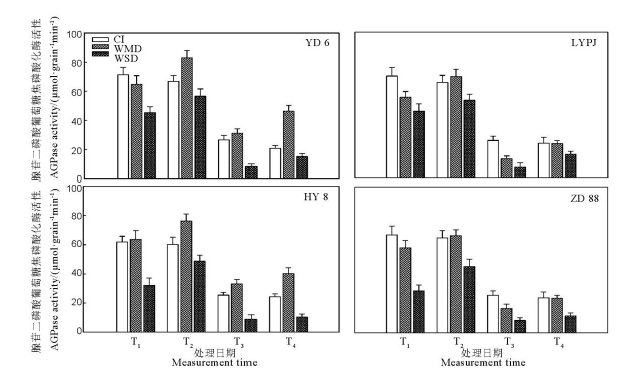
图8 干湿交替灌溉对不同水稻品种籽粒中腺苷二磷酸葡萄糖焦磷酸化酶(AGPase)活性的影响
Fig. 8. Effects of alternate wetting and drying irrigation on the activities of adenosine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase (AGPase) in grains.
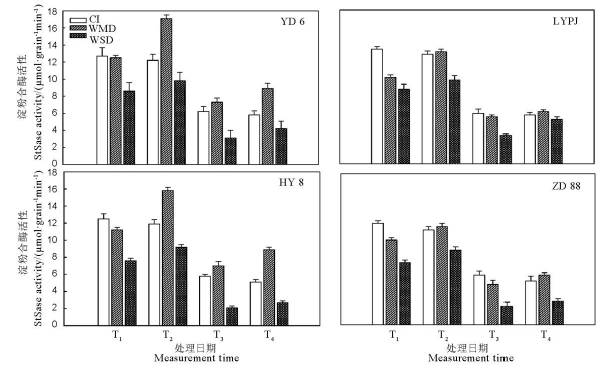
图9 干湿交替灌溉对不同水稻品种籽粒中淀粉合酶(StSase)活性的影响
Fig. 9. Effects of alternate wetting and drying irrigation on the activities of Starch synthase (StSase) in grains.
| [1] | 杨文钰, 屠乃美.作物栽培学各论. 北京:中国农业出版社, 2003, 2: 5-8. |
| Yang W Y, Tu N M. Crop Cultivation Theory.Beijing: China Agricultural Publishing House, 2003, 2: 5-8. | |
| [2] | 中华人民共和国水利部.2006年中国水资源公报. 北京:中国水利水电出版社, 2007. |
| The Ministry of Water Resources. China Water Resources Bulletin. Beijing: China Water Conservancy and Hydropower Press, 2007. | |
| [3] | 张伟义. 大力推广“薄、浅、湿润、晒”灌溉新技术促使农业再上新台阶.上海水利, 1998, s2: 37-39. |
| Zhang W Y.Vigorously promote the “thin、shallow、moist、sun” irrigation technology to promote agriculture to a new level.Shanghai Water, 1998, s2: 37-39. | |
| [4] | 吴端普, 吴天恩, 吴亚雄. 水稻需水规律与灌溉技术试验研究.农田水利与小水电, 1995, 11: 11-13. |
| Wu D P, Wu T E, Wu Y X.Study on rice water requirement and irrigation technique.China Rural Water Hydrop, 1995, 11: 11-13. | |
| [5] | 李远华, 张祖莲, 赵长友,薛继亮,余峰,赛力克·加甫. 水稻间歇灌溉的节水增产机理研究. 中国农村水利水电, 1998, 11:12-15. |
| Li Y H, Zhang Z L, Zhao C Y, Xue J L, Yu F, Sailike J.Study on water saving and yield increasing mechanism of rice intermittent irrigation.China Rural Water Hydrop, 1998, 11: 12-15. | |
| [6] | 张恩江, 韩雪冰, 刘春河. 寒区水稻节水控制灌溉技术应用研究. 黑龙江水专学报, 2007, 34(2): 11-13. |
| Zhang E J, Han X B, Liu C H.Water saving control irrigation technique of rice in cold regions of Heilongjiang province.J Heilongjiang Hydraul Engin Coll, 2007, 34(2): 11-13. | |
| [7] | 周立奎, 焦艳. 对水稻控制灌溉技术应用的研究. 中国科技信息, 2007, 12: 63-64. |
| Zhou L K, Jiao Y.Study on application of controlled irrigation technique of rice.China Sci Technol Infor, 2007, 12: 63-64. | |
| [8] | Toung TP, Bouman BAM, Mortimer M.More rice, less water-integrated approaches for increasing water productivity in irrigated rice-based systems in Asia.Plant Prod Sci, 2005, 8: 231-241. |
| [9] | Won J G, Choi J S, Lee S P, Son S H, Chung S O.Water saving by shallow intermittent irrigation and growth of rice.Plant Prod Sci, 2005, 8: 487-492. |
| [10] | Yang C, Yang L, Yang Y, Ouyang Z.Rice root growth and nutrient uptake as influenced by organic manure in continuously and alternately flooded paddy soils.Agric Water Manag, 2004, 70: 67-81. |
| [11] | Kukal S S, Aggarwal G C.Pudding depth and intensity effects in rice-wheat system on a sandy loam soil, II Water use and crop performance.Soil Till Res, 2003, 74: 37-45. |
| [12] | Bouman BAM, Fen Lg, Tuong TP, Lu L, Wang H, Feng Y.Exploring options to grow rice using less water in nitrogen China using a modeling approach: II. Quantifying yield, water balance components, and water productivity.Agric Water Manag, 2007, 88: 23-33. |
| [13] | Mishra H S, Rathore T R, Pant R C.Effect of intermittent irrigation on groundwater table contribution, irrigation requirement and yield of rice in Mullions of Tarai region.Agric Water Manag,1990, 18: 231-241. |
| [14] | Tabbal D F,Bouman B A M, Bhuiyan S I, Sibayan E B, Sattar MA. On-farm strategies for reducing water input in irrigated rice: case studies in the Philippines.Agric Water Manag, 2002,56: 93-112. |
| [15] | 陈新红, 徐国伟, 孙华山,王志琴,杨建昌. 结实期土壤水分与氮素营养对水稻产量与品质的影响. 扬州大学学报:农业与生命科学版, 2003, 24(3): 37-41. |
| Chen X H, Xu G W, Sun H S, Wang Z Q, Yang J C.Effects of soil moisture and nitrogen nutrition during grain filling on the grain yield and quality of rice. J Yangzhou Univ: Agric Life Sci Ed, 2003, 24(3): 37-41. | |
| [16] | 胡继超, 姜东, 曹卫星,罗卫红. 短期干旱对水稻叶水势、光合作用及干物质分配的影响. 应用生态学报, 2004, 15(1): 63-67. |
| Hu J C, Jiang D, Cao W X, Luo W H.Effect of short-term drought on leaf water potential photosynthesis and dry matter partitioning in paddy rice.Chin J Appl Ecol, 2004, 15(1): 63-67. | |
| [17] | 章骏德, 刘国屏, 施永宁. 植物生理实验法. 南昌:江西人民出版社, 1982, 52-57. |
| Zhang J D, Liu G P, Shi Y N.Experimental plant physiology. Nanchang: Jiangxi People’s Publishing House, 1981, 153: 561-571 | |
| [18] | 陈远平, 杨文钰. 卵叶韭休眠芽中GA3、IAA、ABA和ZT的高效液相色谱法测定. 四川农业大学学报, 2005, 23(4): 60-68. |
| Chen Y P, Yang W Y.Determination of GA3, IAA, ABA, and ZT in dormant buds of allium ovalifolium by HPLC.J Sichuan Agric Univ, 2005, 23(4): 60-68. | |
| [19] | Weiler E W, Jordan P S, Conrad W.Levels of indole-3-acetic acid in intact and decapitated as determined by a specific and highly sensitive solid-phase enzyme immay.Planta, 1981, 153: 561-571. |
| [20] | Yang J C, Zhang J H, Wang Z Q, Zhu Q S, Liu L J.Activities of enzymes involved in sucrose-to-starch metabolism in rice grains subjected to water stress during filling.Field Crops Res, 2003, 81: 69-81. |
| [21] | Yang J C, Zhang J H, Liu L J, Wang Z Q, Zhu Q S.Carbon remobilization and grain filling in japonica/indica hybrid rice subjected to postanthesis water deficits.Agron J, 2002, 94: 102-109. |
| [22] | Yang J C, Zhang J H, Wang Z Q, Liu L J, Zhu Q S.Postanthesis water deficits enhance grain filling in two-line hybrid rice.Crop Sci, 2003, 43(6): 2099-2108. |
| [23] | Belder P, Bouman B A M,Cabangon R, Guoan L, Quilang E J P,Li Y, Spiertz J H J, Tuong T P.Effect of water-saving irrigation on rice yield and water use in typical lowland conditions in Asia.Agric Water Manag, 2004, 65: 193-210. |
| [24] | Ramasamy S, Berge H, Purushothaman S.Yield formation in rice in response to drainage and nitrogen application.Field Crops Res, 1997, 51: 65-82. |
| [25] | Chu G, Chen T, Wang Z, Yang,J,Zhang J. Morphological and physiological traits of roots and their relationships with water productivity in water-saving and drought-resistant rice.Field Crops Res, 2014, 162: 108-119. |
| [26] | Li H, Liu L, Wang Z, Yang J, Zhang J.Agronomic and physiological performance of high-yielding wheat and rice in the lower reaches of Yangtze River of China.Field Crops Res, 2012, 133: 119-129. |
| [27] | Yao F, Huang J, Cui K, Nie L, Xiang J, Liu X, Wu W, Chen M, Peng S.Agronomic performance of high-yielding rice variety grown under alternate wetting an drying irrigation.Field Crops Res, 2012, 126: 16-22. |
| [28] | Stoop W A, Uphoff N, Kassam A.A review of agricultural research issues raised by the system of rice intensification (SRI) from Madagascar: opportunities for improving farming system for resource-poor farmers.Agric Sys, 2002, 71: 249-274. |
| [29] | Yang J, Zhang J, Wang Z, Zhu Q, Wang W.Hormonal changes in the grains of rice subjected to water stress during grain filling.Plant Physiol, 2001, 127: 315-323. |
| [30] | Wopereis M C S, Kropff M J, Maligaya A R, Tuong T P. Drought-stress responses of two lowland rice cultivars to soil water status.Field Crops Res, 1996, 46: 21-39. |
| [31] | Lu J, Ookawa T, Hirasawa T.The effects of irrigation regimes on the water use, dry matter production and physiological responses of paddy rice.Plant Soil, 2000, 223: 207-216. |
| [32] | Cheng C Y,Lur H S.Ethylene may be involved in abortion of the maize caryopsis.Physiol Plant, 1996, 98: 245-252. |
| [33] | Apelbaum A, Yang SF.Biosynthesis of stress-ethylene induced by water deficit.Plant Physiol, 1981, 68: 594-596. |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 吕宙, 易秉怀, 陈平平, 周文新, 唐文帮, 易镇邪. 施氮量与移栽密度对小粒型杂交水稻产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| [6] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [7] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [8] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [9] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [10] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [11] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [12] | 赵艺婷, 谢可冉, 高逖, 崔克辉. 水稻分蘖期干旱锻炼对幼穗分化期高温下穗发育和产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 277-289. |
| [13] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [14] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [15] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||