
中国水稻科学 ›› 2017, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (4): 335-344.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2017.7007 335
• • 下一篇
徐婷婷1, 余宁1, 张迎信1, 毕真真1, 吴玮勋1, 曹永润1,2, 王备芳1, 张越1, 轩丹丹1, 陈代波1, 占小登1, 程式华1,*, 曹立勇1,2,*
收稿日期:2016-01-13
修回日期:2017-02-23
出版日期:2017-07-25
发布日期:2017-07-10
通讯作者:
程式华,曹立勇
基金资助:Tingting XU1, Ning YU1, Yingxin ZHANG1, Zhenzhen BI1, Weixun WU1, Yongrun CAO1, Beifang WANG1, Yue ZHANG1, Dandan XUAN1, Daibo CHEN1, Xiaodeng ZHAN1, Shihua CHENG1,*, Liyong CAO1,2,*
Received:2016-01-13
Revised:2017-02-23
Online:2017-07-25
Published:2017-07-10
Contact:
Shihua CHENG, Liyong CAO
摘要: 绝大多数水稻类病斑突变体中免疫系统被激活可以有效提升其对稻瘟病的抗性,为进一步解析类病斑突变体抗病的分子机制,对类病斑突变体lmm326进行了研究。 lmm326是粳稻中花11通过EMS辐射诱变,经多代自交和回交获得的一个类病斑突变体,并将突变体分别与中花11和Dular杂交获得的F2群体用于遗传分析,采用图位克隆的方法对目的基因进行精细定位。 5叶期时,该突变体下部叶片表面开始出现类病斑表型;与野生型相比,突变体叶片光合色素含量、净光合速率、株高、结实率、单株有效分蘖数、千粒重等显著下降;突变体带病斑叶片中死亡细胞数量及过氧化氢的积累量明显多于野生型;突变体相较于野生型对4个已鉴定的稻瘟病生理小种的抗性明显提高。遗传分析表明该性状由一对单隐性核基因控制。采用图位克隆方法将该基因定位在第1染色体长臂端38 kb的区间内,其中包含6个开放阅读框。测序发现基因Os01g0919900第2外显子上对应CDS的第433位碱基由C突变成T,最终导致其编码蛋白的第145个氨基酸由苯丙氨酸(F)变为亮氨酸(L)。qRT-PCR结果显示,与野生型相比,lmm326中参与水杨酸信号通路的防卫基因显著上调表达。 LMM326与OsSSI2互为等位基因,该基因可能参与负调控水杨酸信号转导途径,其突变激活了水稻体内的防卫反应。
徐婷婷, 余宁, 张迎信, 毕真真, 吴玮勋, 曹永润, 王备芳, 张越, 轩丹丹, 陈代波, 占小登, 程式华, 曹立勇. 水稻抗稻瘟病突变体lmm326的鉴定与调控通路初步分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(4): 335-344.
Tingting XU, Ning YU, Yingxin ZHANG, Zhenzhen BI, Weixun WU, Yongrun CAO, Beifang WANG, Yue ZHANG, Dandan XUAN, Daibo CHEN, Xiaodeng ZHAN, Shihua CHENG, Liyong CAO. Identification of Rice Blast Resistance Mutant lmm326 and Preliminary Analysis of Its Regulatory Pathway[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2017, 31(4): 335-344.
| 标记 | 前引物 | 后引物 |
|---|---|---|
| Marker | Forward primer | Reverse primer |
| RD0115 | GTTGTAGATGTGATTGGAGAA | GACTATGTATGGCACTGTTGA |
| RM5310 | TAGACAAAGCAACGGGTTCC | CGGAAGCAGGAGAATCGTAG |
| RM3362 | AAGTTGAAGCAGTCGCCAAC | GAATTGCGTGGGATATGGAC |
| ZH4 ZH7 | TCCACGAACAAAGACGAG GACTCCGAGCCAGCAAAA | ACGGCACATTATCAACAACA GTCTCCGTGCCCTTGTGC |
| ZH8 | ATGGAGTCGCCTTGTTGA | AAATGTGGCTGGCTGATC |
| ZH11 | TTCGTCTCATTAGCAGCAT | CATTTATTCACTTGCCACAT |
| Qpr10 | GTCCGGGCACCATCTACACC | CAAGCTTCGTCTCCGTCGAGT |
| Qpal1 | TTCAACGCCGACACCT | GTAGAGCGGATACGACCTG |
| Qaos2 | AAGCTGCTGCAATACGTGTACTGG | CGACGAGCAACAGCCTTCCG |
| WRKY45 | GCCGACGACCAGCACGATCACC | ACGAGCCGACGCCGCCCTC |
| PR1a | CGTGTCGGCGTGGGTGT | GGCGAGTAGTTGCAGGTGATG |
| PR1b Actin | TACGCCAGCCAGAGGAGC CAGGCCGTCCTCTCTCTGTA | GCCGAACCCCAGAAGAGG AAGGATAGCATGGGGGAGAG |
表1 定位LMM326基因及qRT-PCR所用的引物序列
Table 1 Sequence of primers used for fine mapping and qRT-PCR.
| 标记 | 前引物 | 后引物 |
|---|---|---|
| Marker | Forward primer | Reverse primer |
| RD0115 | GTTGTAGATGTGATTGGAGAA | GACTATGTATGGCACTGTTGA |
| RM5310 | TAGACAAAGCAACGGGTTCC | CGGAAGCAGGAGAATCGTAG |
| RM3362 | AAGTTGAAGCAGTCGCCAAC | GAATTGCGTGGGATATGGAC |
| ZH4 ZH7 | TCCACGAACAAAGACGAG GACTCCGAGCCAGCAAAA | ACGGCACATTATCAACAACA GTCTCCGTGCCCTTGTGC |
| ZH8 | ATGGAGTCGCCTTGTTGA | AAATGTGGCTGGCTGATC |
| ZH11 | TTCGTCTCATTAGCAGCAT | CATTTATTCACTTGCCACAT |
| Qpr10 | GTCCGGGCACCATCTACACC | CAAGCTTCGTCTCCGTCGAGT |
| Qpal1 | TTCAACGCCGACACCT | GTAGAGCGGATACGACCTG |
| Qaos2 | AAGCTGCTGCAATACGTGTACTGG | CGACGAGCAACAGCCTTCCG |
| WRKY45 | GCCGACGACCAGCACGATCACC | ACGAGCCGACGCCGCCCTC |
| PR1a | CGTGTCGGCGTGGGTGT | GGCGAGTAGTTGCAGGTGATG |
| PR1b Actin | TACGCCAGCCAGAGGAGC CAGGCCGTCCTCTCTCTGTA | GCCGAACCCCAGAAGAGG AAGGATAGCATGGGGGAGAG |
| 性状 Trait | 野生型 Wild type | 突变体 lmm326 |
|---|---|---|
| 株高Plant height/cm | 101.6±1.8 | 63.1±4.0** |
| 每株有效分蘖数No. of productive panicles per plant | 11.7±2.4 | 3.1±0.4** |
| 每穗总粒数No. of spikelets per panicle | 147.1±17.0 | 46.9±9.1** |
| 结实率Seed-setting rate/% | 85.5±0.0 | 77.4±0.0* |
| 千粒重1000-grain weight/g | 23.7±0.9 | 18.7±0.7** |
表2 野生型中花11和突变体lmm326的主要农艺性状比较(均值±标准差,n=10)
Table 2 Comparison of agronomic traits between wild type Zhonghua 11 and the mutant lmm326(mean ±SD, n=10).
| 性状 Trait | 野生型 Wild type | 突变体 lmm326 |
|---|---|---|
| 株高Plant height/cm | 101.6±1.8 | 63.1±4.0** |
| 每株有效分蘖数No. of productive panicles per plant | 11.7±2.4 | 3.1±0.4** |
| 每穗总粒数No. of spikelets per panicle | 147.1±17.0 | 46.9±9.1** |
| 结实率Seed-setting rate/% | 85.5±0.0 | 77.4±0.0* |
| 千粒重1000-grain weight/g | 23.7±0.9 | 18.7±0.7** |
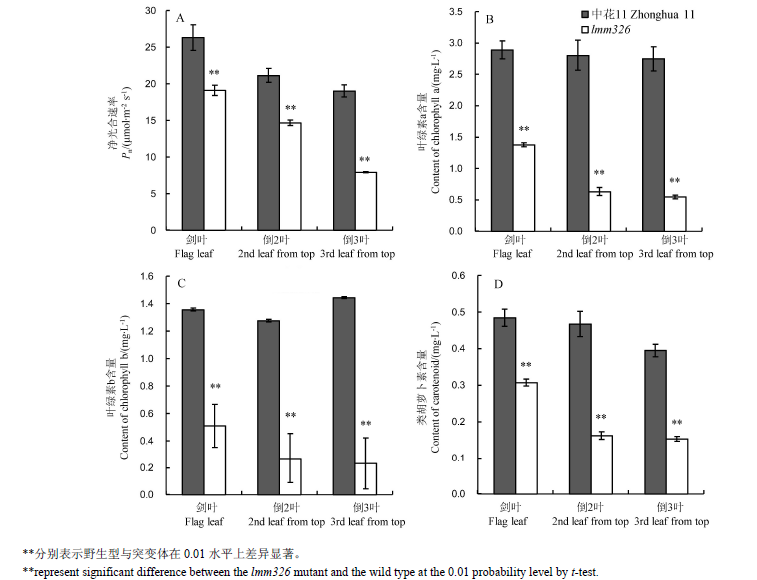
图3 野生型中花11和突变体lmm326抽穗期叶片的净光合速率和光合色素含量(均值±标准差,n=3)
Fig. 3. Net photosynthetic rate(Pn) and photosynthetic pigment contents of the wild type Zhonghua 11 and lmm326 mutant at
| 编号 Code | 野生型 Wild type | 突变体 Mutant |
|---|---|---|
| 12-26-49-2 | 4.26±0.08 | 0.79±0.07** |
| 12-128-12-1 | 3.89±0.05 | 0.82±0.08** |
| 12-901-48-1 | 4.45±0.14 | 0.83±0.08** |
| 13-600-33-2 | 4.56±0.08 | 0.81±0.03** |
表3 突变体lmm326稻瘟病抗性鉴定(均值±标准差,n=3)
Table 3 Resistance identification of lmm326 and Zhonghua 11 to rice blast(mean±SD, n=3). cm
| 编号 Code | 野生型 Wild type | 突变体 Mutant |
|---|---|---|
| 12-26-49-2 | 4.26±0.08 | 0.79±0.07** |
| 12-128-12-1 | 3.89±0.05 | 0.82±0.08** |
| 12-901-48-1 | 4.45±0.14 | 0.83±0.08** |
| 13-600-33-2 | 4.56±0.08 | 0.81±0.03** |
| 杂交组合 Hybrid combination | F2 | χ2(3∶1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 正常表型植株数 | 突变表型植株数 | ||||
| No. of normal plants | No. of mutant plants | ||||
| 中花11/lmm326 ZH11/lmm326 | 1761 | 629 | 2.21 | ||
| Dular/lmm326 | 1936 | 674 | 0.94 | ||
表4 突变体lmm326的遗传分析
Table 4 Genetic analysis of mutant lmm326.
| 杂交组合 Hybrid combination | F2 | χ2(3∶1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 正常表型植株数 | 突变表型植株数 | ||||
| No. of normal plants | No. of mutant plants | ||||
| 中花11/lmm326 ZH11/lmm326 | 1761 | 629 | 2.21 | ||
| Dular/lmm326 | 1936 | 674 | 0.94 | ||
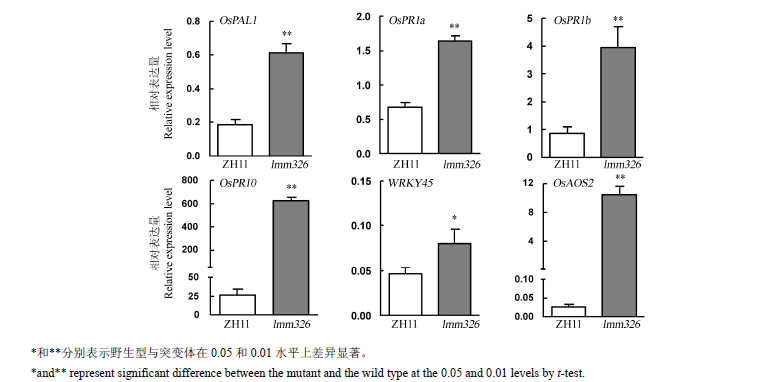
图6 实时定量PCR分析野生型(ZH11)和突变体lmm326中防卫反应相关基因表达(均值±标准差,n=3)
Fig. 6. Real-time PCR analysis of relative expression level of genes associated with defense response in the wild type(ZH11) and lmm326 mutant(mean±SD, n=3).
| [1] | Heath M C.Hypersensitive response-related death.Plant Mol Biol, 2000, 44: 321-334. |
| [2] | Wang S H, Lim J H, Kim S S, Cho S H, Yoo S C, Koh H J, Sakuraba Y, Paek N C.Mutation of SPOTTEDLEAF3 (SPL3) impairs abscisic acid-responsive signaling and delays leaf senescence in rice, J Exp Bot, 2015, 66(22): 7045-7059. |
| [3] | Gray J, Close P S, Briggs S P, Johal G S.A novel suppressor of cell death in plants encoded by the lls1 gene of maize. Cell, 1997, 89: 25-31. |
| [4] | Dietrich R A, Richberg M H, Schmidt R, Dean C, Dangl J L.A novel zinc finger protein is encoded by the Arabidopsis LSD1 gene and functions as a negative regulator of plant cell death. Cell, 1997, 88: 685-694. |
| [5] | Buschges R, Hollricher K, Panstruga R, Simons G, Wolter M,Frijters A, van Daelen R, van der Lee T, Diergaarde P, Groenendijk J, Töpsch S, Vos P, Salamini F, Schulze-Lefert P. The barley mol gene: A novel control element of plant pathogen resistance.Cell, 1997, 88: 695-705. |
| [6] | Brodersen P, Petersen M, Pike H M, Olszak B, Skov S, Odum N, Jørgensen L B, Brown R E, Mundy J.Knockout of Arabidopsis accelerated-cell-death11 encoding a sphingosine transfer protein causes activation of programmed cell death and defense. Genes Dev, 2002, 16: 490-502. |
| [7] | Wu C J, Bordeos A, Madamba M R, Baraoidan M, Ramos M, Wang G L, Leach J E, Leung H.Rice lesion mimic mutants with enhanced resistance to diseases.Mol Genet Genom, 2008, 279: 605-619. |
| [8] | Dangl J L, Dietrich R A, Richberg M H.Death don’t have no mercy: Cell death programs in plant-microbe interactions.Plant cell, 1996, 8(10):1793. |
| [9] | Neuffer M G, Calvert O H.Dominant disease lesion mimics in maize.J Hered, 1975, 6(5): 265-270. |
| [10] | Shirasu K, Chuize-Lefert P.Regulators of cell death in disease resistance. Plant Mol Biol, 2000, 44(3): 371-385. |
| [11] | Li Z, Zhang Y X, Liu L, Liu Q E, Bi Z Z, Yu N, Cheng S H, Cao L Y.Fine mapping of the lesion mimic and early senescence 1(lmes1) in rice(Oryza sativa). Plant Physiol Biochem, 2014, 80: 300-307. |
| [12] | Thomma B P, Penninckx I A, Broekaert W F, Cammue B P.The complexity of disease signaling in Arabidopsis. Curr Opin Immunol, 2001, 13(1): 63-68. |
| [13] | Yoshioka K, Kachroo P, Tsui F, Sharma S B, Shah J, Klessig D F.Environmentally sensitive, SA-dependent defense responses in the cpr22 mutant of Arabidopsis. Plant J, 2001, 26(4): 447-459. |
| [14] | Weymann K, Hunt M, Uknes S, Neuenschwander U, Lawton K, Steiner H Y, Ryals J.Suppression and restoration of lesion formation in Arabidopsis Isd mutants. Plant Cell, 1995, 7(12): 2013-2022. |
| [15] | Lu H, Salimian S, Gamelin E, Wang G Y, Fedorowski J, LaCourse W, Greenberg J T. Genetic analysis of acd6-1 reveals complex defense networks and leads to identification of novel defense genes inArabidopsis. Plant J, 2009, 58(3): 401-412. |
| [16] | Chong J L, Pierrel M A, Atanassova R, Werck-Reichhart D, Fritig B, Saindrenan P.Free and conjugated benzoic acid in tobacco plants and cell cultures. Induced accumulation upon elicitation of defense responses and role as salicylic acid precursors. Plant Physiol, 2001, 125: 318-328. |
| [17] | Lu H, Rate D N, Song J T, Greenberg J T.ACD6, a novel ankyrin protein, is a regulator and an effector of salicylic acid signaling in the Arabidopsis defense response. Plant Cell, 2003, 15(10): 2408-2420. |
| [18] | Yu D Q, Chen C H, Chen Z X.Evidence for an important role of WRKY DNA binding proteins in the regulation of NPR1 gene expression. Plant Cell, 2001, 13(7): 1527-1540. |
| [19] | Despré s C, De Long C, Glaze S, Liu E W, Fobert P R. The Arabidopsis NPR1 NIM1 protein enhances the DNA binding activity of a subgroup of the TGA family of bZIP transcription factors. Plant Cell, 2000, 12: 279-290. |
| [20] | Chen X F, Hao L, Pan J W, Zheng X X, Jiang G H, Jin Y, Gu Z M, Qian Q, Zhai W X, Ma B J.SPL5, a cell death and defense related gene, encodes a putative splicing factor 3b subunit 3(SF3b3) in rice. Mol Breeding, 2012, 30(2): 939-949. |
| [21] | Yamanouchi U, Yano M, Lin H, Ashikari M, Yamada K.A rice spotted leaf gene,SPL7, encodes a heat stress transcription factor protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci, 2002, 99: 7530-7535. |
| [22] | Zeng L R, Qu S H, Bordeos A, Yang C, Baraoidan M, Yan H, Xie Q, Nahm B H, Leung H, Wang G L.Spotted leaf 11, a negative regulator of plant cell death and defense, encodes a ubox/armadillo repeat protein endowed with E3 ubiquitinligase activity. Plant Cell, 2004, 16: 2795-2808. |
| [23] | Mori M, Tomita C, Sugimoto K, Hasegawa M, Hayashi N, Dubouzet J G, Ochiai H, Sekimoto H, Hirochika H, Kikuchi S.Isolation and molecular characterization of aSpotted leaf 18 mutant by modified activation-tagging in rice. Plant Mol Biol, 2007, 63: 847-860. |
| [24] | Qiao Y L, Jiang W Z, Lee J, Park B, Choi M S, Piao R H, Woo M O, Roh J H, Han L Z, Paek N C, Seo H S, Koh H J.SPL28 encodes a clathrin-associated adaptor protein complex 1, medium subunitu1(AP1M1) and early senescence in rice(Oryza sativa). New Phytol, 2010, 185(1): 258-274. |
| [25] | Fekih R, Tamiru M, Kanzaki H, Abe A, Yoshida K, Kanzaki E, Saitoh H, Takagi H, Natsume S, Undan J R, Undan J, Terauchi R.The rice(Oryza sativa L.) LESION MIMIC RESEMBLING, which encodes an AAA-type ATPase, is implicated in defense response. Mol Genet Genom, 2015, 290: 611-622 . |
| [26] | Yin Z C, Chen J, Zeng L R, Goh M, Leung H, Khush G S, Wang G L.Characterizing rice lesion mimic mutants and identifying a mutant with broad-spectrum resistance to rice blast and bacterial blight.Mol Plant Microbe Interact, 2000, 13(8): 869-876. |
| [27] | Wang L J, Pei Z Y, Tian Y C, He C Z.OsLSD1, a rice zinc finger protein, regulates programmed cell death and callus differentiation. Mol Plant Microb Interact, 2005, 18: 375-384. |
| [28] | Sun C H, Liu L C, Tang J Y, Lin A H, Zhang F T, Fang J, Zhang G F, Chu C C.RLIN1,encoding a putative coproporphyrinogen III oxidase, is involved in lesion initiation in rice. J Genet Genomics, 2011, 38: 29-37. |
| [29] | Sakuraba Y, Rahman M L, Cho S H, Kim Y S, Koh H J, Yoo S C, Paek N C.The rice faded green leaf locus encodes protochlorophyllide oxidoreductase B and is essential for chlorophyll synthesis under high light conditions.Plant J, 2013, 74: 122-133. |
| [30] | Thordal-Christansen H, Zhang Z G, Wei Y D.Subcellular localization of H2O2 in plants: H2O2 accumulation in papillae and hypersensitive response during the barley powdery mildew interaction. Plant J, 1997, 11: 1187-1194. |
| [31] | Kong X P, Li D Q.Hydrogen peroxide is not involved in HrpN from Erwinia amylovora-induced hypersensitive cell death in maize leaves. Plant Cell Rep, 2011, 30: 1273-1279. |
| [32] | Wellbuin A R.The spectral determination of chlorophyll a and b, as well as total carotenoids, using various solvents with spectrophotometer of different resolution.J Plant Physiol, 1994, 144: 307-313. |
| [33] | Rogers S O, Bendich A J.Extraction of DNA from milligram amounts of fresh, herbarium and mummified plant tissues. Plant Mol Biol, 1985, 5: 69-76. |
| [34] | 陈析丰, 金杨, 马伯军. 水稻类病变突变体及抗病性的研究进展. 植物病理学报, 2011, 41(1): 1-9. |
| Chen X F, Jin Y, Ma B J.Progress on the studies of rice lesion mimics and their resistant mechanism to the pathogens.Acta Phytopathol Sin, 2011, 41(1): 1-9. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [35] | Jiao B B, Wang J J, Zhu X D, Zeng L J, Li Q, He Z H.A novel protein RLS1 with NB-ARM domains is involved in chloroplast degradation during leaf senescence in rice.Mol Plant, 2012, 5(1): 205-217. |
| [36] | Takahashi A, Agrawal G K, Yamazaki M, Onosato K, Miyao A, Kawasaki T, Shimamoto K, Hirochika H.RicePti1a negatively regulates RAR1-dependent defense responses. Plant Cell, 2007, 19: 2940-2951. |
| [37] | Feng B H, Yang Y, Shi Y F, Shen H C, Wang H M, Huang Q N, Xu X, Lü X G, Wu J L.Characterization and genetic analysis of a novel rice spotted-leaf mutantHM47 with broad-spectrum resistance to Xanthomnas oryzae pv. oryzae. J Integr Plant Biol, 2013, 55(5): 473-483. |
| [38] | Liu X Q, Li F, Tang J Y, Wang W H, Zhang F X, Wang G D, Chu J F, Yan C Y, Wang T Q, Chu C C, Li C Y.Activation of the jasmonic acid pathway by depletion of the hydroxide lyaseOsHPL3 reveals crosstalk between the HPL and AOS branches of the oxylipin pathway in rice. Plos One, 2012, 7: e50089. |
| [39] | Jiang C J, Shimono M, Maeda S, Inoue H, Mori M, Hasegawa M, Sugano S, Takatsuji H.Suppression of the rice fatty-acid desaturase geneosssi2 enhances resistance to blast and leaf blight diseases in rice. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact, 2009, 22: 820-829. |
| [40] | Yang W, Dong R, Liu L, Hu Z B, Li J, Wang Y, Ding X H, Chu Z H.A novel mutant allele ofSSI2 confers a better balance between disease resistance and plant growth inhibition on Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol, 2016, 16: 208. |
| [41] | Song N, Hu Z R, Li Y H, Li C, Peng F X, Yao Y Y, Peng H R, Ni Z F, Xie C J, Sun Q X.Overexpression of a wheat stearoyl-ACP desaturase(SACPD) geneTaSSI2 in Arabidopsis ssi2 mutant compromise its resistance to powdery mildew. Gene, 2013, 524: 220-227. |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [6] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [7] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [8] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [9] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [10] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [11] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [12] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [13] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| [14] | 许用强, 姜宁, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 水稻开花期高温热害响应机理及其调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 111-126. |
| [15] | 吕海涛, 李建忠, 鲁艳辉, 徐红星, 郑许松, 吕仲贤. 稻田福寿螺的发生、危害及其防控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 127-139. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||