
中国水稻科学 ›› 2016, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (3): 291-303.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2016.5063
刘霞, 唐设, 窦志, 李刚华, 刘正辉, 王绍华, 丁承强, 丁艳锋*( )
)
收稿日期:2015-04-08
修回日期:2015-10-28
出版日期:2016-05-10
发布日期:2016-05-10
通讯作者:
丁艳锋
作者简介:# 共同第一作者;
基金资助:
Xia LIU, She TANG, Zhi DOU, Gang-hua LI, Zheng-hui LIU, Shao-hua WANG, Cheng-qiang DING, Yan-feng DING*( )
)
Received:2015-04-08
Revised:2015-10-28
Online:2016-05-10
Published:2016-05-10
Contact:
Yan-feng DING
About author:# These authors contributed equally to this work;
摘要:
以武运粳24和宁粳3号两个常规粳稻品种为材料,采用桶栽方式,研究高温条件下外源茉莉酸甲酯(MeJA)在灌浆早期对水稻生理特性及产量的影响。结果显示,喷施外源MeJA可以提高植株体内可溶性糖的积累量,维持膜的渗透平衡;外源MeJA通过增加叶片的气孔导度(Gs)和蒸腾速率(Tr),降低水稻的叶温及穗温;MeJA通过减轻高温对光合系统的损害,进而提高PSⅡ的最大光量子产量(Fv/Fm)、实际光化学效率(ΦPSⅡ)、光合电子传递速率(ETR)及分配给光化学反应的光能(Pr)比例,并最终提高净光合速率(Pn)。高温条件下,武运粳24中超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、过氧化物酶(POD)的活性降低,而宁粳3号中的SOD、POD酶活性在高温后期则高于常温处理,而喷施MeJA能提高两品种SOD和POD两种酶在高温处理后期的活性,并降低丙二醛(MDA)的后期积累量,维持膜稳定性。综上所述, 在高温条件下,MeJA可以有效降低水稻植株温度,有效缓解高温胁迫对植株生理生化过程的伤害,并通过提高千粒重和结实率减轻高温导致的产量损失。
中图分类号:
刘霞, 唐设, 窦志, 李刚华, 刘正辉, 王绍华, 丁承强, 丁艳锋. 茉莉酸甲酯对武运粳24和宁粳3号灌浆早期高温胁迫生理特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2016, 30(3): 291-303.
Xia LIU, She TANG, Zhi DOU, Gang-hua LI, Zheng-hui LIU, Shao-hua WANG, Cheng-qiang DING, Yan-feng DING. Effects of MeJA on the Physiological Characteristics of japonica Rice Wuyunjing 24 and Ningjing 3 During Early Grain Filling Stage Under Heat Stress[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2016, 30(3): 291-303.
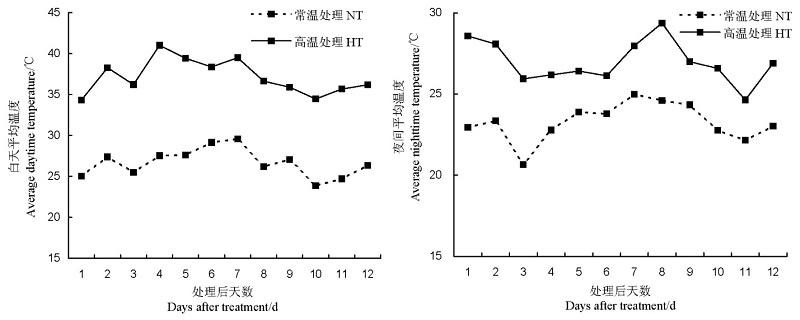
图1 高温处理期间的白天平均温度和夜间平均温度
Fig. 1. Average daytime and nighttime temperature during high temperature treatment. NT, Natural temperature; HT,High temperature.
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatments | 每桶穗数 No.of panicales per pot | 每穗粒数 No. of grains per panicale | 结实率 Seed setting rate/% | 千粒重 1000-grain weight/g | 每桶产量 Grain yield per pot/(g·pot-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 武运粳24 Wuyunjing 24 | CK | 28.0±0.6 a | 160.8±5.5 a | 36.7±0.02 c | 26.21±0.31 b | 43.68±3.15 b |
| MeJA+HT | 27.3±0.5 a | 160.3±4.6 a | 43.3±0.03 b | 26.47±0.32 b | 50.40±1.25 b | |
| NT | 27.4±0.3 a | 158.2±8.4 a | 97.9±0.00 a | 27.68±0.39 a | 115.52±6.22 a | |
| 宁粳3号Ningjing 3 | CK | 32.1±0.4 a | 148.4±2.4 a | 40.8±0.01 c | 23.36±0.15 c | 46.01±2.14 c |
| MeJA+HT | 32.0±0.5 a | 150.9±3.3 a | 43.7±0.05 b | 23.69±0.10 b | 51.18±2.23 b | |
| NT | 32.6±0.5 a | 151.0±3.9 a | 99.0±0.00 a | 25.29±0.06 a | 118.98±2.50 a |
表1 MeJA对高温胁迫水稻产量及产量构成的影响
Table 1 Effect of MeJA on yield components of rice under heat stress at early grain filling stage.
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatments | 每桶穗数 No.of panicales per pot | 每穗粒数 No. of grains per panicale | 结实率 Seed setting rate/% | 千粒重 1000-grain weight/g | 每桶产量 Grain yield per pot/(g·pot-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 武运粳24 Wuyunjing 24 | CK | 28.0±0.6 a | 160.8±5.5 a | 36.7±0.02 c | 26.21±0.31 b | 43.68±3.15 b |
| MeJA+HT | 27.3±0.5 a | 160.3±4.6 a | 43.3±0.03 b | 26.47±0.32 b | 50.40±1.25 b | |
| NT | 27.4±0.3 a | 158.2±8.4 a | 97.9±0.00 a | 27.68±0.39 a | 115.52±6.22 a | |
| 宁粳3号Ningjing 3 | CK | 32.1±0.4 a | 148.4±2.4 a | 40.8±0.01 c | 23.36±0.15 c | 46.01±2.14 c |
| MeJA+HT | 32.0±0.5 a | 150.9±3.3 a | 43.7±0.05 b | 23.69±0.10 b | 51.18±2.23 b | |
| NT | 32.6±0.5 a | 151.0±3.9 a | 99.0±0.00 a | 25.29±0.06 a | 118.98±2.50 a |
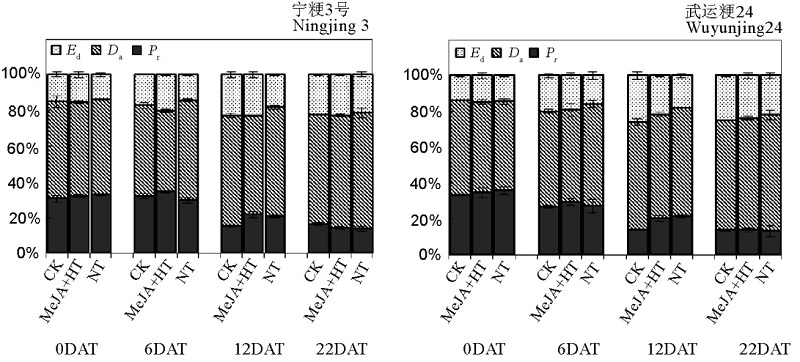
图6 MeJA对灌浆早期高温胁迫水稻的叶片捕获光能分配的影响 DAT-处理后天数。
Fig. 6. Effect of MeJA on allocations of absorbed-light energy by rice leaf under heat stress at early grain filling stage. DAT,Days after teatment.
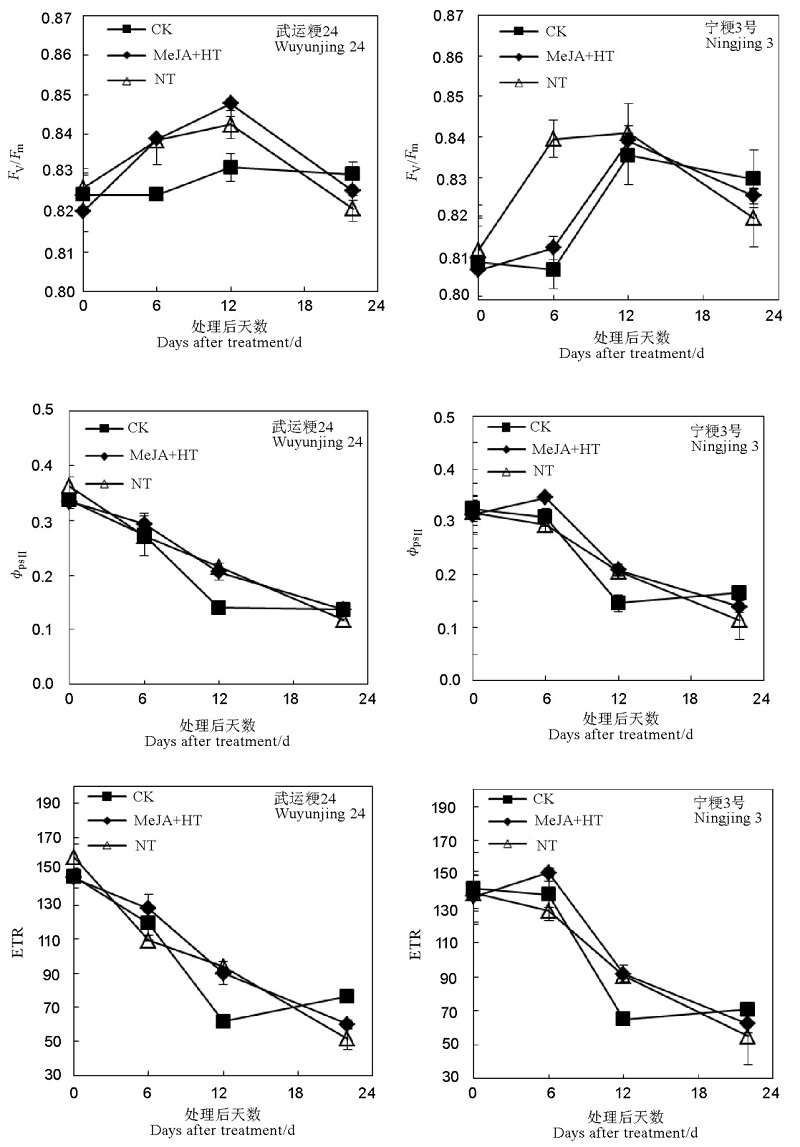
图7 MeJA对灌浆早期高温胁迫水稻叶片PSⅡ的最大光量子产量(Fv/Fm)、实际光化学效率(ΦPSⅡ)以及光合电子传递速率(ETR)的影响
Fig. 7. Effect of MeJA on Fv/Fm,ΦPSⅡ and electron transport rate(ETR) of rice leaf under heat stress at early grain filling stage.
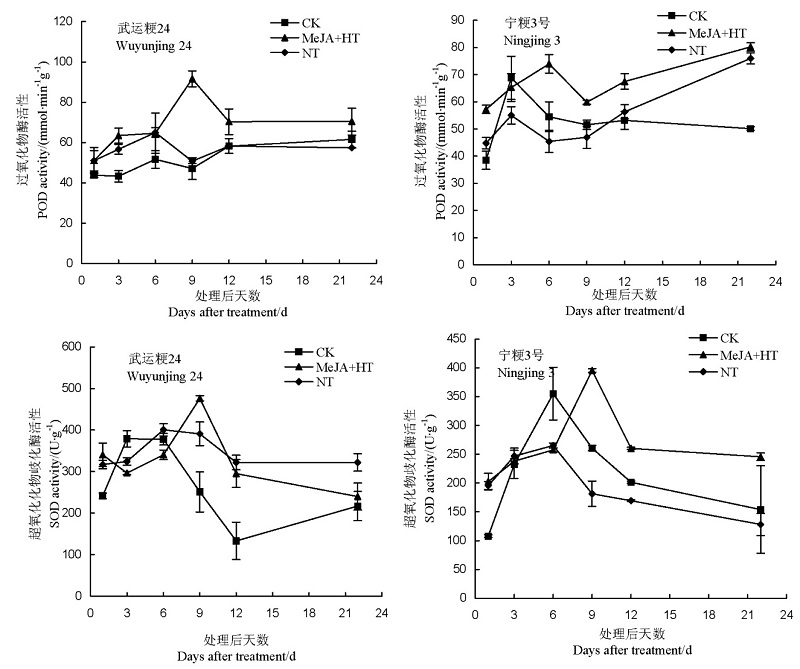
图9 MeJA对灌浆早期高温胁迫水稻叶片SOD和POD活性的影响
Fig. 9. Effect of MeJA on activities of superoxide dismutase(SOD) and peroxidase(POD) in rice leaf under heat stress at early grain filling stage.
| [1] | Barker T, Davidson O, Davidson W,et al. Climate change 2007: Synthesis report.Valencia; IPPC, 2007,(4):8-12;5-100. |
| [2] | Maclean J L, Dawe D C, Hardy B, Hettel G P. Rice. Almanac.Philippines: International Rice Research Institute, 2002. |
| [3] | Mohammed A, Tarpley L.High nighttime temperatures affect rice productivity through altered pollen germination and spikelet fertility.Agric Forest Meteorol, 2009,149(6):999-1008. |
| [4] | Das S, Krishnan P, Nayak M, et al.High temperature stress effects on pollens of rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes.Environ Exp Bot, 2014, 101: 36-46. |
| [5] | Shi W, Muthurajan R, Rahman H, et al.Source-sink dynamics and proteomic reprogramming under elevated night temperature and their impact on rice yield and grain quality.New Phytol, 2013, 197(3): 825-837. |
| [6] | Folsom J J, Begcy K, Hao X, et al.Rice fertilization-independent endosperm1 regulates seed size under heat stress by controlling early endosperm development.Plant Physiol, 2014, 165(1): 238-248. |
| [7] | 戴云云, 丁艳锋, 刘正辉, 等. 花后水稻穗部夜间远红外增温处理对稻米品质的影响. 中国水稻科学, 2009, 23(4): 414-420. |
| Dai Y Y, Ding Y F, Liu Z H, et al.Effects of elevated night temperature by far-infrared radiation at grain filling on grain quality of rice.Chin J Rice Sci, 2009, 23(4): 414-420.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | 段骅, 傅亮, 剧成欣, 等. 氮素穗肥对高温胁迫下水稻结实和稻米品质的影响. 中国水稻科学, 2013, 27(6): 591-602. |
| Duan H, Fu L, Ju L X, et al.Effects of application of nitrogen as panicle-promoting fertilizer on seed setting and grain quality of rice under high temperature stress.Chin J Rice Sci, 2013, 27(6): 591-602. (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [9] | Hossain M A, Munemasa S, Uraji M, et al.Involvement of endogenous abscisic acid in methyl jasmonate-induced stomatal closure inArabidopsis. Plant Physiol, 2011, 156(1): 430-438. |
| [10] | Zhu Z, An F, Feng Y, et al.Derepression of ethylene-stabilized transcription factors (EIN3/EIL1) mediates jasmonate and ethylene signaling synergy in Arabidopsis. PNAS, 2011, 108(30): 12539-12544. |
| [11] | Ma C, Wang Z Q, Zhang L T, et al.Photosynthetic responses of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) to combined effects of drought and exogenous methyl jasmonate.Photosynthetica, 2014, 52(3): 377-385. |
| [12] | 董桃杏, 蔡昆争, 张景欣, 等. 茉莉酸甲酯对水稻幼苗的抗旱生理效应. 生态环境, 2007, 16(4): 1261-1265. |
| Dong T, Cai K, Zhang J, et al.The physiological roles of methyl jasmonate (MeJA) in drought resistance of rice seedlings.Ecol Environ,2007,16(4):1261-1265. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | Lee T M, Lur H S, Lin Y H, et al.Physiological and biochemical changes related to methyl jasmonate-induced chilling tolerance of rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedling. Plant,Cell Environ, 1996, 19(1): 65-74. |
| [14] | 向妙莲, 何永明, 付永琦, 等. 茉莉酸甲酯对水稻白叶枯病的诱导抗性及相关防御酶活性的影响. 植物保护学报, 2013, 40(2): 97-101. |
| Xiang M L, He Y M,Fu Y Q, et al.Effect of methyl jasmonate on induced resistance of rice seedlings against bacterial leaf blight and activities of related defense enzymes.Acta Phytophyl Sin, 2013, 40(2): 97-101. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 张智慧, 聂燕芳, 何磊, 等. 外源茉莉酸甲酯诱导水稻抗瘟性相关防御酶和内源水杨酸的变化. 植物病理学报, 2010 (4): 395-403. |
| Zhang Z H, Nie H Y, He L,et al.Resistance-related defense enzymes and endogenous salicylic acid induced by exogenous methyl jasmonate in rice against blast disease.Acta Phytopathol Sin, 2010 (4): 395-403. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | Chuan Y, Ding Y F, Liu Z H, et al.Temperature difference between the air and organs of rice plant and its relation to spikelet fertility.Agric Sci China, 2008, 7(6): 678-685. |
| [17] | Demmig-Adams B, Adams III W W, Barker D H, Logan B A. Using chlorophyll fluorescence to assess the fraction of absorbed light allocated to thermal dissipation of excess excitation.Physiol Plant, 1996, 98: 253-264. |
| [18] | 李合生. 植物生理生化实验原理和技术.北京: 高等教育出版社, 2000: 184-185. |
| Li H S.Plant Physiology and Biochemistry Test Principles and Techniques.Beijing: High Education Press, 2000: 184-185. (in Chinese). | |
| [19] | 张宪政. 作物生理研究法. 北京: 农业出版社, 1992: 197-212. |
| Zhang X Z.Crop Physiology Research Methods. Beijing: Agricultural Press, 1992: 197-212 (in Chinese). | |
| [20] | Peng S B, Huang J L, Sheehy J E, et al.Rice yields decline with higher night temperature from global warming.PNAS, 2004, 101(27): 9971-9975. |
| [21] | Madan P, Jagadish S V K, Craufurd P Q, et al. Effect of elevated CO2 and high temperature on seed-set and grain quality of rice.J Experi Bot, 2012, 63(10): 3843-3852. |
| [22] | Yamakawa H, Hirose T, Kuroda M, et al.Comprehensive expression profiling of rice grain filling-related genes under high temperature using DNA microarray.Plant Physiol, 2007, 144(1): 258-277. |
| [23] | 张文忠, 韩亚东, 杜宏绢, 等. 水稻开花期冠层温度与土壤水分及产量结构的关系. 中国水稻科学, 2007, 21(1): 99-102. |
| Zhang W Z, Han Y D, Du H J, et al.Relationship between canopy temperature and soil water content, yield components at flowering stage in rice.Chin J Rice Sci, 2007, 21(1): 99-102 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [24] | Araus J L, Reynolds M P, Acevedo E.Leaf posture, grain yield, growth, leaf structure, and carbon isotope discrimination in wheat.Crop Sci, 1993, 33(6): 1273-1279. |
| [25] | Mackill D J, Coffman W R.Inheritance of high temperature tolerance and pollen shedding in a rice cross.J Plant Breeding, 1983, 91(1): 61-69. |
| [26] | 冯佰利, 高小丽, 赵琳, 等. 干旱条件下小麦冠层温度及其性状的关联研究. 生态学杂志, 2005, 24(5): 508-512. |
| Feng B L, Gao X L, Zhao L, et al.Relationship between canopy temperature and biological characters of wheat under drought stress.Chin J Ecol, 2005, 24(5): 508-512 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [27] | Salvucci M E, Crafts-Brandner S J. Inhibition of photosynthesis by heat stress: The activation state of Rubisco as a limiting factor in photosynthesis.Physiol Plant, 2004, 120(2): 179-186. |
| [28] | Sharkey T D.Effects of moderate heat stress on photosynthesis: importance of thylakoid reactions, rubisco deactivation, reactive oxygen species, and thermotolerance provided by isoprene. Plant,Cell Environ, 2005, 28(3): 269-277. |
| [29] | 滕中华,智丽,宗学凤,等.高温胁迫对水稻灌浆结实期叶绿素荧光、抗活性氧活力和稻米品质的影响.作物学报, 2008, 34(9): 1662-1666. |
| Teng Z H, Zhi L, Zong X F, et al.Effects of high temperature on chlorophyll fluorescence, active oxygen resistance activity, and grain quality in grain-filling periods in rice plants.Acta Agron Sin,2008, 34(9): 1662-1666 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [30] | Song L, Yue L, Zhao H, et al.Protection effect of nitric oxide on photosynthesis in rice under heat stress.Acta Physiol Plant, 2013, 35(12): 3323-3333. |
| [31] | 汤日圣, 郑建初, 陈留根, 等. 高温对杂交水稻籽粒灌浆和剑叶某些生理特性的影响. 植物生理与分子生物学学报, 2006, 31(6): 657-662. |
| Tang R S, Zheng J C, Chen L G, et al.Effects of high temperature on grain filling and some physiological characteristic in flag leaves of hybrid rice.J Plant Physiol Mol Biol, 2005, 31(6): 657-662 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [32] | 杨华庚, 颜速亮, 陈慧娟,等. 高温胁迫下外源茉莉酸甲酯、钙和水杨酸对蝴蝶兰幼苗耐热性的影响. 中国农学通报, 201 , 27(28): 150-157. |
| Yang H G, Yan S L, Chen H J, et al.Effect of exogenous methyl jasmonate, calcium and salicylic acid on the heat tolerance in phalaenopsis seedlings under high temperature stress.Chin Agric Sci Bull, 2011, 27(28): 150-157 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [33] | Liu X, Huang B.Heat stress injury in relation to membrane lipid peroxidation in creeping bentgrass.Crop Sci, 2000, 40(2): 503-510. |
| [34] | Mostofa M G, Yoshida N, Fujita M.Spermidine pretreatment enhances heat tolerance in rice seedlings through modulating antioxidative and glyoxalase systems.Plant Growth Reg, 2014, 73(1): 31-44. |
| [35] | 曹冬梅, 王云山, 康黎芳, 等. 高温对红掌幼苗叶片茉莉酸浓度及抗氧化系统的影响. 中国生态农业学报, 2007, 15(5): 102-104. |
| Cao D M, Wang Y S, Kang L F, et al.Effect of high temperature on jasmonic acid (JA) concentration and antioxidation of Anthurium andraeanum seedling leaf.Chin J Eco-Agric, 2007, 15(5): 102-104(in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [36] | 吕俊, 张蕊, 宗学凤, 等. 水杨酸对高温胁迫下水稻幼苗抗热性的影响. 中国生态农业学报, 2009, 17(6): 1168-1171. |
| LV J, Zhang R, Zong X F, et al.Effect of salicylic acid on heat resistance of rice seedling under heat stress.Chin J Eco-Agric, 2009, 17(6): 1168-1171 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [37] | Mohammed A R, Cothren J T, Chen M H, et al.1-Methylcyclopropene (1-MCP)-induced alteration in leaf photosynthetic rate, chlorophyll fluorescence, respiration and membrane damage in rice (Oryza sativa L.) under high night temperature.J Agron Crop Sci, 2014,201(2015): 105-116. |
| [38] | 程方民, 钟连进, 孙宗修. 灌浆结实期温度对早籼水稻籽粒淀粉合成代谢的影响. 中国农业科学,2003, 36(5) : 492-501. |
| Cheng F M, Zhong L J, Sun Z X.Effect of temperature at grain-filling stage on starch biosynthetic metabolism in developing rice grains of early-indica.Sci Agric Sin, 2003, 36(5) : 492-501. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [6] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [7] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [8] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [9] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [10] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [11] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [12] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [13] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| [14] | 许用强, 姜宁, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 水稻开花期高温热害响应机理及其调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 111-126. |
| [15] | 吕海涛, 李建忠, 鲁艳辉, 徐红星, 郑许松, 吕仲贤. 稻田福寿螺的发生、危害及其防控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 127-139. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||